Notice (8): Undefined variable: solution_of_interest [APP/View/Products/view.ctp, line 755]Code Context<!-- BEGIN: REQUEST_FORM MODAL -->
<div id="request_formModal" class="reveal-modal medium" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<?= $this->element('Forms/simple_form', array('solution_of_interest' => $solution_of_interest, 'header' => $header, 'message' => $message, 'campaign_id' => $campaign_id)) ?>
$viewFile = '/home/website-server/www/app/View/Products/view.ctp'
$dataForView = array(
'language' => 'en',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'product' => array(
'Product' => array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
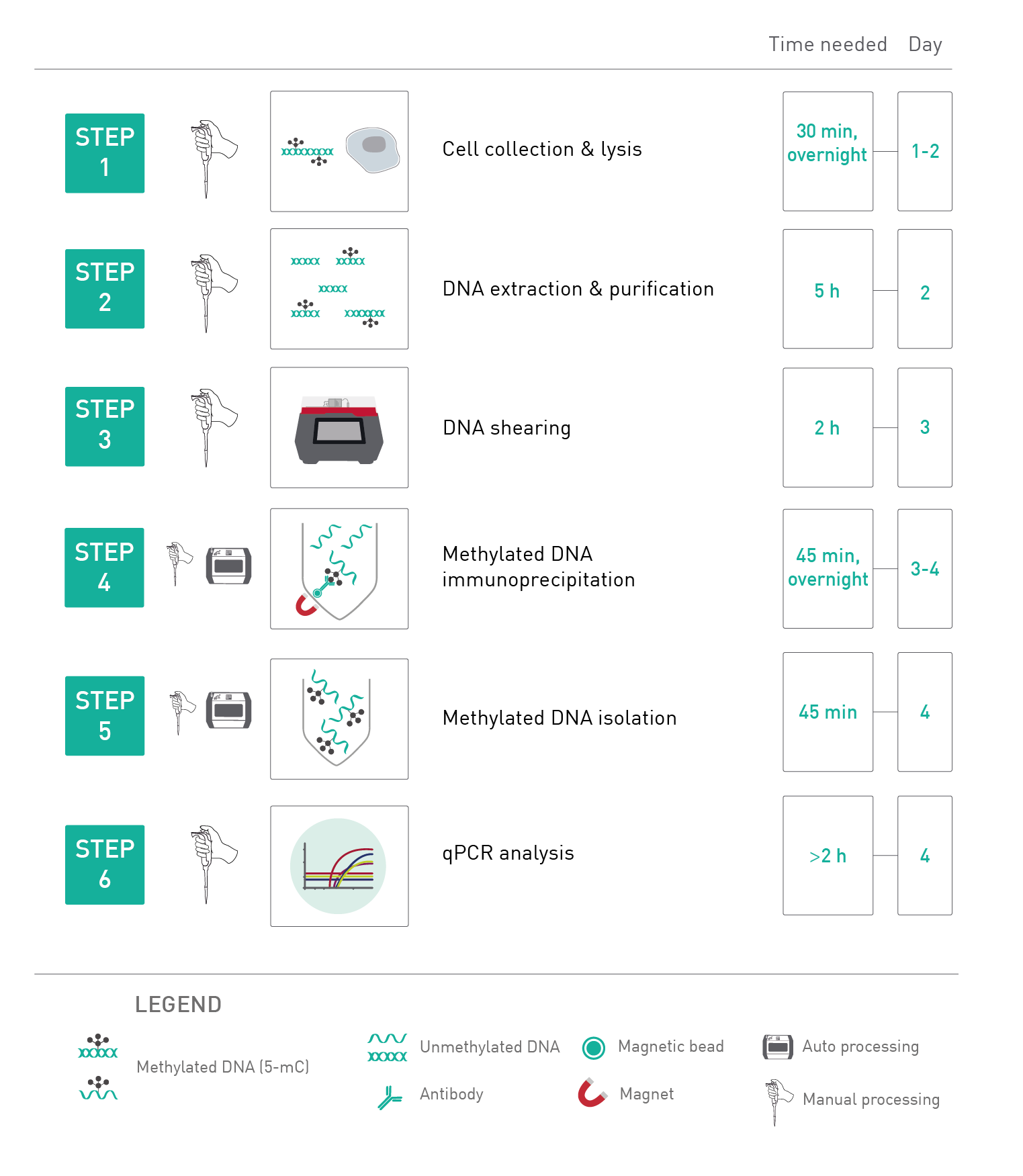
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
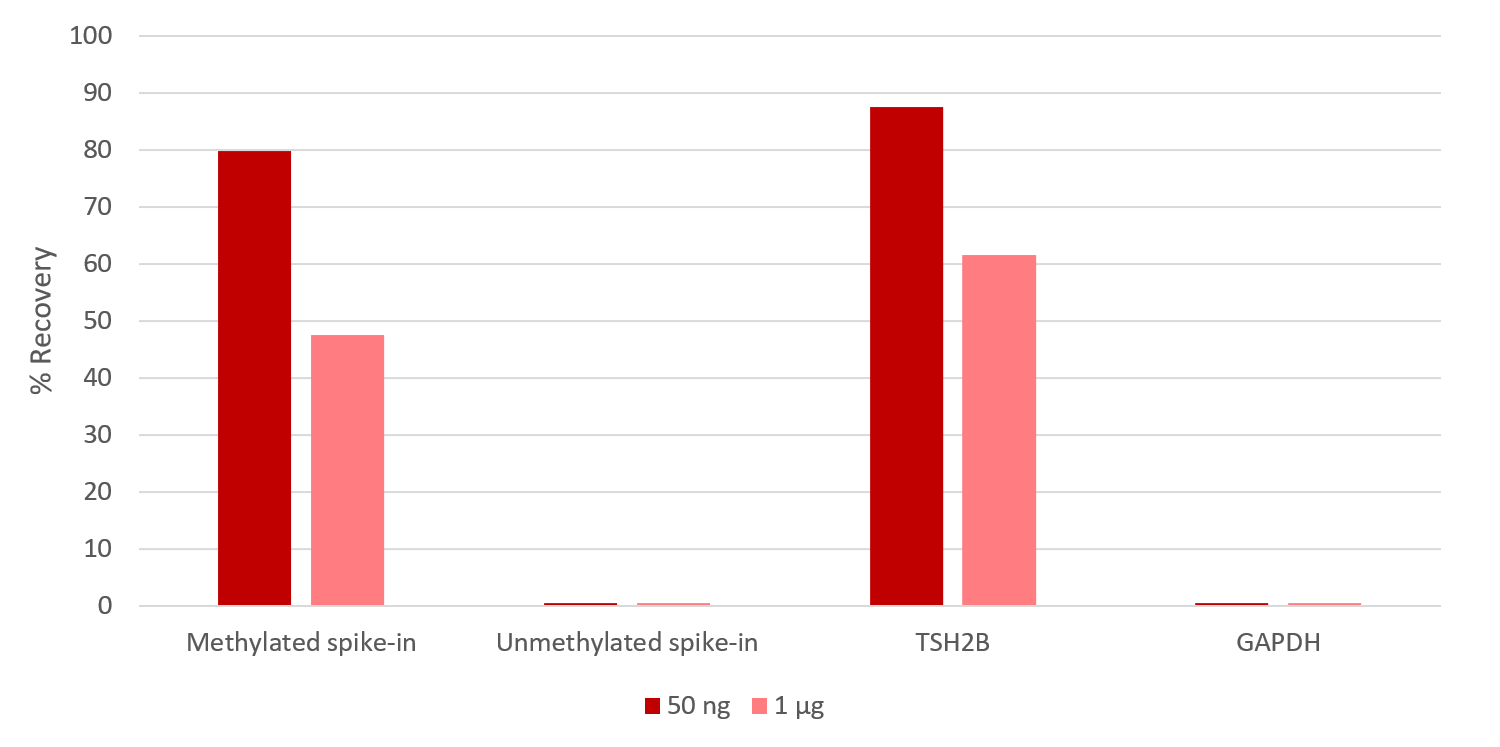
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
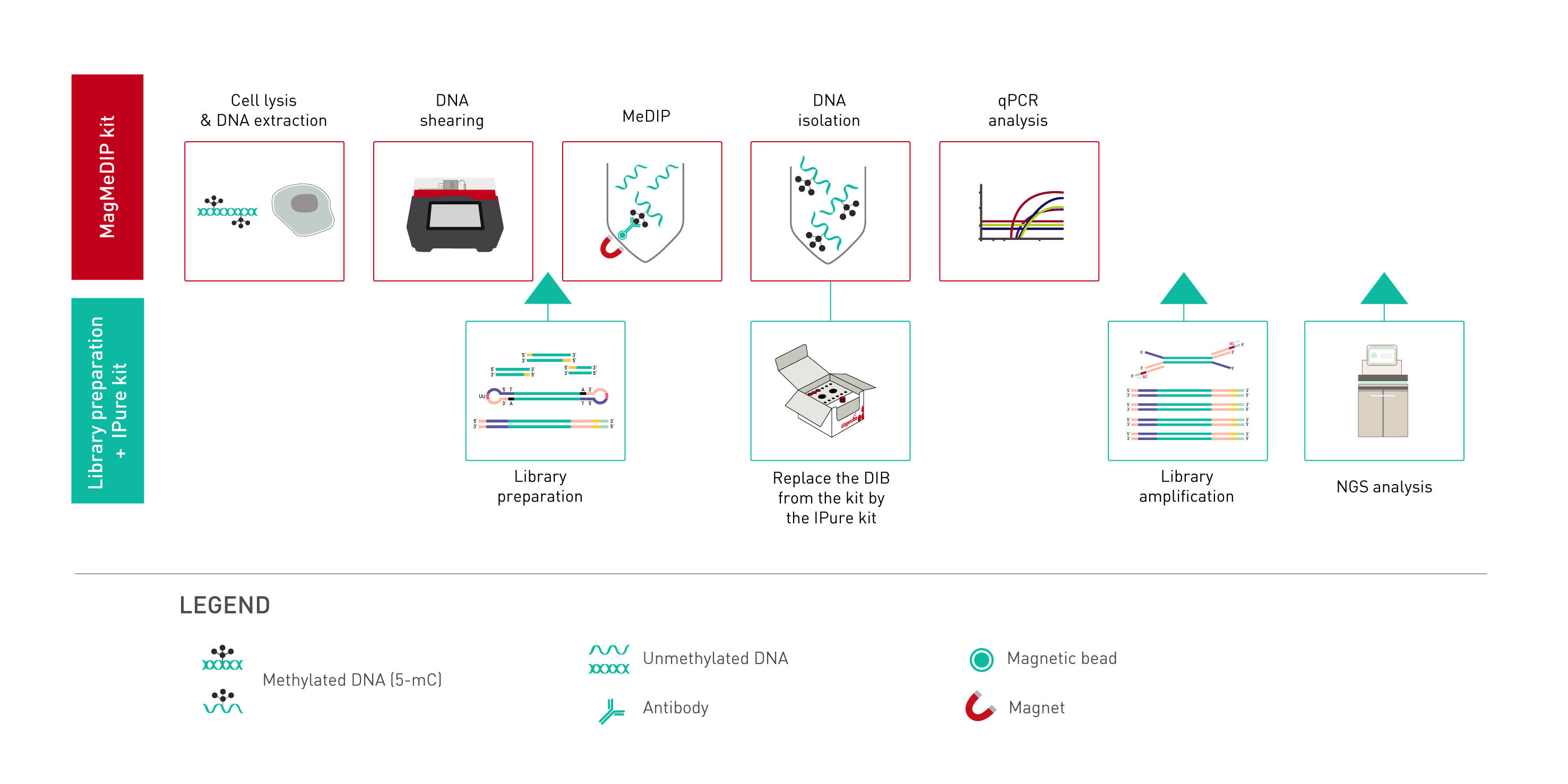
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
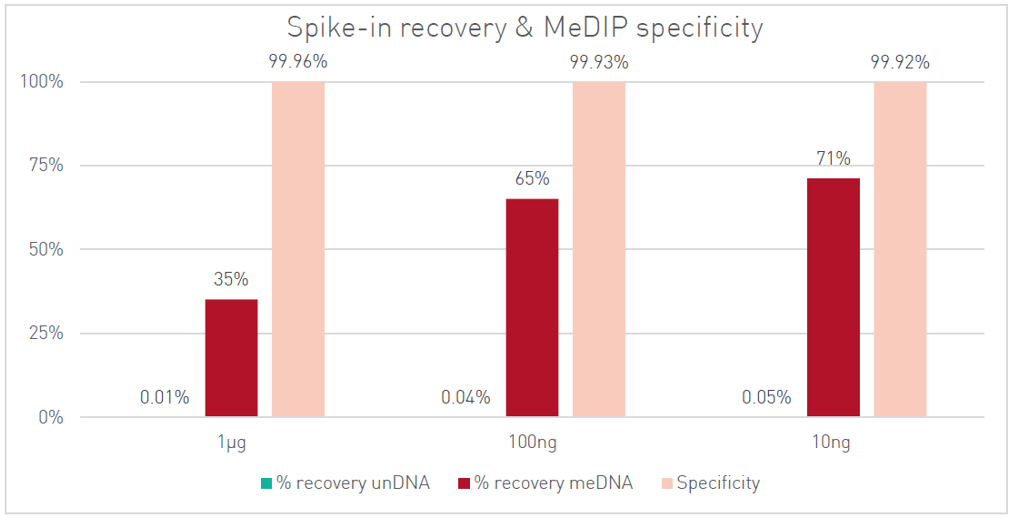
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
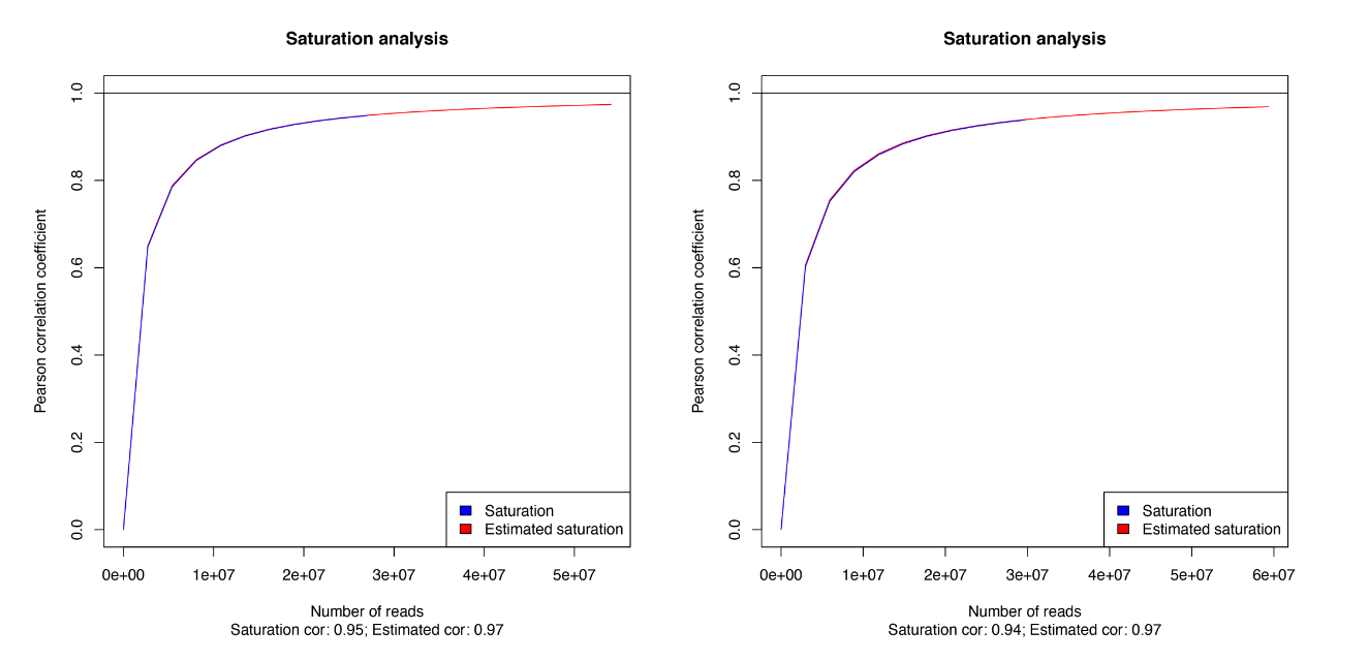
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
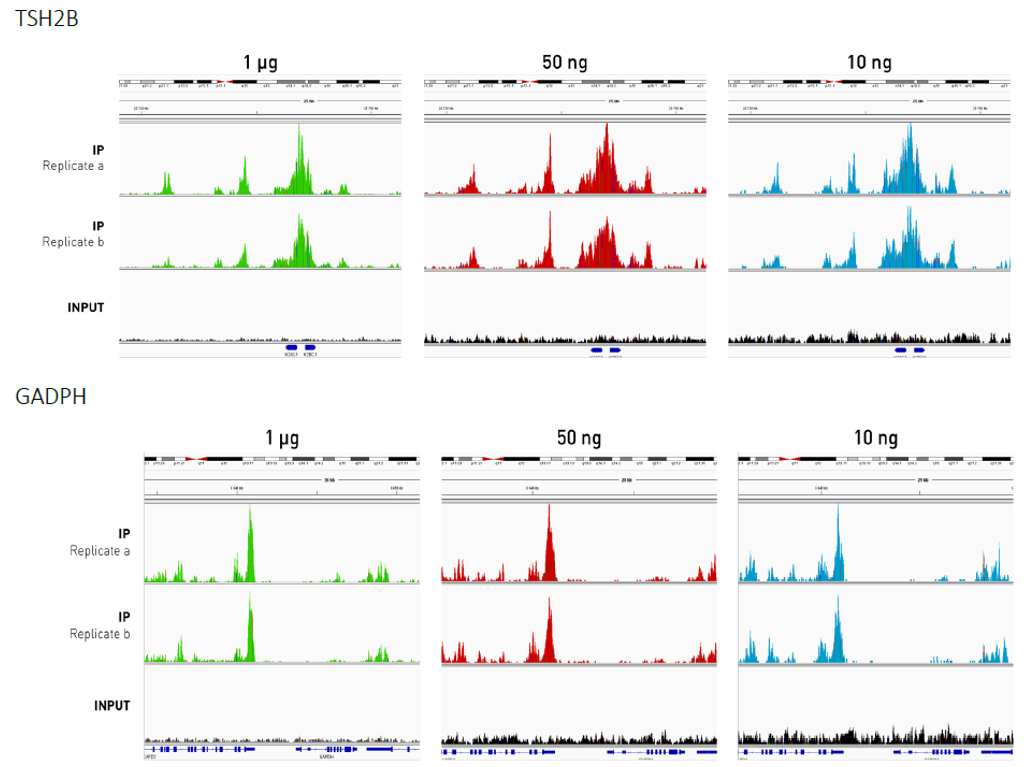
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'locale' => 'eng'
),
'Antibody' => array(
'host' => '*****',
'id' => null,
'name' => null,
'description' => null,
'clonality' => null,
'isotype' => null,
'lot' => null,
'concentration' => null,
'reactivity' => null,
'type' => null,
'purity' => null,
'classification' => null,
'application_table' => null,
'storage_conditions' => null,
'storage_buffer' => null,
'precautions' => null,
'uniprot_acc' => null,
'slug' => null,
'meta_keywords' => null,
'meta_description' => null,
'modified' => null,
'created' => null,
'select_label' => null
),
'Slave' => array(),
'Group' => array(
'Group' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Master' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Product' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Related' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Application' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Category' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Document' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Feature' => array(),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Promotion' => array(),
'Protocol' => array(),
'Publication' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 7 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 8 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 9 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 10 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 11 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 12 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 13 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 14 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 15 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 16 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 17 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 18 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 19 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 20 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 21 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 22 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 23 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 24 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 25 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 26 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 27 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 28 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 29 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 30 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 31 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 32 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 33 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 34 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 35 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 36 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 37 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 38 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 39 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 40 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 41 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 42 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 43 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 44 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 45 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 46 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 47 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 48 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 49 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 50 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 51 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 52 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 53 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 54 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 55 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 56 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 57 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 58 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 59 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 60 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 61 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 62 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 63 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 64 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 65 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 66 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 67 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 68 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 69 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 70 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 71 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 72 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 73 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 74 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 75 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 76 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 77 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 78 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 79 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 80 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 81 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 82 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 83 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 84 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 85 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 86 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 87 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 88 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 89 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 90 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 91 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 92 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 93 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 94 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 95 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 96 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 97 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 98 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 99 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 100 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 101 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 102 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 103 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 104 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 105 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Testimonial' => array(),
'Area' => array(),
'SafetySheet' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 7 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'meta_canonical' => 'https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns'
)
$language = 'en'
$meta_keywords = ''
$meta_description = 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.'
$meta_title = 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA'
$product = array(
'Product' => array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'locale' => 'eng'
),
'Antibody' => array(
'host' => '*****',
'id' => null,
'name' => null,
'description' => null,
'clonality' => null,
'isotype' => null,
'lot' => null,
'concentration' => null,
'reactivity' => null,
'type' => null,
'purity' => null,
'classification' => null,
'application_table' => null,
'storage_conditions' => null,
'storage_buffer' => null,
'precautions' => null,
'uniprot_acc' => null,
'slug' => null,
'meta_keywords' => null,
'meta_description' => null,
'modified' => null,
'created' => null,
'select_label' => null
),
'Slave' => array(),
'Group' => array(
'Group' => array(
'id' => '7',
'name' => 'C02010021',
'product_id' => '1880',
'modified' => '2016-02-18 17:02:55',
'created' => '2016-02-18 17:02:55'
),
'Master' => array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
),
'Product' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Related' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1819',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'description' => '<p>The DiaMag02 is a powerful magnet which has been designed for controlled and rapid isolation of your DNA bound to magnetic beads. It allows for processing 16 samples at a time.</p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B04000001',
'old_catalog_number' => 'kch-816-001',
'sf_code' => 'B04000001-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '250',
'price_USD' => '240',
'price_GBP' => '220',
'price_JPY' => '40960',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '600',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit',
'meta_title' => 'DiaMag02 - magnetic rack',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'DiaMag02 - magnetic rack',
'modified' => '2019-06-11 16:27:35',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '2597',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1043-050, -500 is specific to a CpG region of the TSH2B gene from rat. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17031043-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1043-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17031043-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:06:44',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '2599',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1046-050, -500 is specific to a promoter region of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from rat. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17031046-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1046-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17031046-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:05:49',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '2593',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1042-050, -500 is specific to a CpG region of the TSH2B gene from mouse. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17021042-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1042-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17021042-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:10:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '2595',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair Cat. No. C17021045 is specific to a promoter region of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from mouse. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17021045-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1045-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17021045-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '01-Accessory',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'modified' => '2021-01-18 10:00:33',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '2945',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit - ordering reference: C02010021',
'description' => '<p><span></span>The reference C02010014 has been replaced by <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns">C02010021</a><span>. </span> </p>
<p><span>Perform </span><strong>MeDIP</strong><span><span> </span>(Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation) <span>on the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/sx-8g-ip-star-compact-automated-system-1-unit" target="_blank">SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System</a> </span>followed by<span> </span></span><strong>qPCR</strong><span><span> </span>to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using </span><span>5-methylcytosine</span><span><span> </span>antibody. Our kit contains high quality reagents to get the h</span><span>ighest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</span></p>
<p>Diagenode’s Auto MagMeDIP qPCR is available in two formats (10 and 48 IPs) and has been optimized on the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/sx-8g-ip-star-compact-automated-system-1-unit" target="_blank">SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System</a> enabling highly reproducible results and allowing for high throughput assays.</p>
<h3><span>Characteristics</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Generate highly consistent results with internal controls in 24h</li>
<li>Minimize error with many reagents in 1 tube</li>
<li>Optimized purification (DIB - DNA isolation buffer)</li>
<li>Allows direct correlation between IP’d material & methylation status</li>
</ul>
<p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/magmedip-kit-validated-using-bioruptor.jpg" alt="MagMeDIP kit validated using Bioruptor" /></p>
<p><strong><em>Figure 1.</em></strong><em><span> </span><strong>IP results obtained with Diagenode Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit.</strong><span> </span>MeDIP assays were performed manually using DNA from blood, Gm12878, Hela and U20S cells and the Auto MagMeDIP qPCR kit (Diagenode). The DNA was prepared with the XL GenDNA Extraction Module included. The IP was performed including the kit meDNA and unDNA spike-in controls, together with the human DNA sample controls. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs also included in this kit.</em></p>
<p style="text-align: center;"><em><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/AutomatedMeDIP_9h.png" alt="" width="678" height="365" /></em></p>
<p style="text-align: justify;"><em><strong>Figure<span> </span>2. Automated MeDIP (9h). </strong>IP reaction was performed on the SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System with the anti-5-mC antibody. Methylated and unmethylated DNA were used as internal controls. Unmethylated DNA region of GADPH and a methylated DNA region of AlphaX1 were used to test DNA sample-IP efficiency. DNA has been isolated by using DNA Isolation Buffer (DIB).</em></p>
<p></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '48 rxns',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010014',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'C02010014-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '',
'price_USD' => '',
'price_GBP' => '',
'price_JPY' => '',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'Japan',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => true,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'auto-magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x48',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x48',
'modified' => '2023-03-20 12:50:08',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '3046',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://go.diagenode.com/bioruptor-upgrade"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-br-trade.png" /></a></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p><span>The Bioruptor® Pico is the latest innovation in shearing and represents a new breakthrough as an all-in-one shearing system capable of shearing samples from 150 bp to 1 kb. </span>Since 2004, Diagenode has accumulated <strong>shearing expertise</strong> to design the Bioruptor® Pico and guarantee the best experience with the <strong>sample preparation</strong> for <strong>number of applications -- in various fields of studies</strong> including environmental research, toxicology, genomics and epigenomics, cancer research, stem cells and development, neuroscience, clinical applications, agriculture, and many more.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
</div>
<p>The Bioruptor Pico shearing accessories and consumables have been developed to allow <strong>flexibility in sample volumes</strong> (20 µl - 2 ml) and a <strong>fast parallel processing of samples</strong> (up to 16 samples simultaneously). <span>The built-in cooling system (Bioruptor® Cooler) ensures high precision <strong>temperature control</strong>. The <strong>user-friendly interface</strong> has been designed for any researcher, providing an easy and advanced modes that give both beginners and experienced users the right level of control. </span></p>
<p>In addition, Diagenode provides fully-validated tubes that remain <strong>budget-friendly with low operating cost</strong> (< 1€/$/DNA sample) and shearing kits for best sample quality. <span></span></p>
<p><strong>Application versatility</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>DNA shearing for Next-Generation-Sequencing</li>
<li>Chromatin shearing</li>
<li>RNA shearing</li>
<li>Protein extraction from tissues and cells (also for mass spectrometry)</li>
<li>FFPE DNA extraction</li>
<li>Protein aggregation studies</li>
<li>CUT&RUN - shearing of input DNA for NGS</li>
</ul>
<div style="background-color: #f1f3f4; margin: 10px; padding: 50px;">
<p><strong>Bioruptor Pico: Recommended for CUT&RUN sequencing for input DNA</strong><br /><br /> By combining antibody-targeted controlled cleavage by MNase and NGS, <strong>CUT&RUN sequencing</strong> can be used to identify protein-DNA binding sites genome-wide. CUT&RUN works by using the DNA cleaving activity of a Protein A-fused MNase to isolate DNA that is bound by a protein of interest. This targeted digestion is controlled by the addition of calcium, which MNase requires for its nuclease activity. After MNase digestion, short DNA fragments are released and can then be purified for subsequent library preparation and high-throughput sequencing. While CUT&RUN does not require mechanical shearing chromatin given the enzymatic approach, sonication is highly recommended for the fragmentation of the input DNA (used to compare the enriched sample) in order to be compatible with downstream NGS. The Bioruptor Pico is the ideal instrument of choice for generating optimal DNA fragments with a tight distribution, assuring excellent library prep and excellent sequencing results for your CUT&RUN assay.<br /><br /> <strong>Explore the Bioruptor Pico now.</strong></p>
</div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for Chromatin shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-reproducibility-is-priority.jpg" /></center></div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/pages/form-demo"> <img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for RNA shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-request-demo.jpg" /></a></center></div>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label1' => 'Specifications',
'info1' => '<center><img alt="Ultrasonic Sonicator" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-table.jpg" /></center>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label2' => 'View accessories & consumables for Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico',
'info2' => '<h3>Shearing Accessories</h3>
<table style="width: 641px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Catalog number</td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Throughput</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-2-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.2 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201144</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">16 samples</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.65 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201143</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">12 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 1.5 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201140</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-sonication-accessories-for-bioruptor-standard-plus-pico-1-pack">15 ml sonication accessories</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01200016</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Shearing Consumables</h3>
<table style="width: 646px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;">Catalog Number</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/02ml-microtubes-for-bioruptor-pico">0.2 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010020</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-500-tubes">0.65 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010011</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-with-caps-300-tubes">1.5 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010016</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-50-pc">15 ml Pico Tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010017</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-sonication-beads-50-rxns">15 ml Pico Tubes & sonication beads</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C01020031</span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/shearing_technology/bioruptor_accessories/TDS-BioruptorTubes.pdf">Find datasheet for Diagenode tubes here</a></p>
<p><a href="../documents/bioruptor-organigram-tubes">Which tubes for which Bioruptor®?</a></p>',
'label3' => 'Available shearing Kits',
'info3' => '<p>Diagenode has optimized a range of solutions for <strong>successful chromatin preparation</strong>. Chromatin EasyShear Kits together with the Pico ultrasonicator combine the benefits of efficient cell lysis and chromatin shearing, while keeping epitopes accessible to the antibody, critical for efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation. Each Chromatin EasyShear Kit provides optimized reagents and a thoroughly validated protocol according to your specific experimental needs. SDS concentration is adapted to each workflow taking into account target-specific requirements.</p>
<p>For best results, choose your desired ChIP kit followed by the corresponding Chromatin EasyShear Kit (to optimize chromatin shearing ). The Chromatin EasyShear Kits can be used independently of Diagenode’s ChIP kits for chromatin preparation prior to any chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol. Choose an appropriate kit for your specific experimental needs.</p>
<h2>Kit choice guide</h2>
<table style="border: 0;" valign="center">
<tbody>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<th class="text-center"></th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE TYPE</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE INPUT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">KIT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SDS<br /> CONCENTRATION</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">NUCLEI<br /> ISOLATION</th>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="5"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-histones.png" /></td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">< 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-optimization-kit-high-sds-100-million-cells">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />High SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">1%</td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/cross-unvalid-green.jpg" width="18" height="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">> 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">PLANT TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-plant-chip-seq-kit">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />for Plant</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.5%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="6"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-tf.png" /></td>
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="extra-spaced">
<h3>Guide for optimal chromatin preparation using Chromatin EasyShear Kits <i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/pages/chromatin-prep-easyshear-kit-guide">Read more</a></h3>
</div>
<p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B01080010',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'B01080010-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '00-Machine',
'price_EUR' => '27600',
'price_USD' => '31000',
'price_GBP' => '24000',
'price_JPY' => '4522260',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '77500',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => true,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '',
'slug' => 'bioruptorpico2',
'meta_title' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'modified' => '2024-12-19 15:08:43',
'created' => '2020-01-09 16:27:17',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Application' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '7',
'position' => '10',
'parent_id' => '1',
'name' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'description' => '<div class="row extra-spaced">
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3>Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns"><span>The Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation is based on the affinity purification of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA using, respectively, an antibody directed against 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in the case of MeDIP or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in the case of hMeDIP.</span><br />
<h2></h2>
<h2>How it works</h2>
<p>In brief, Methyl DNA IP is performed as follows: Genomic DNA from cultured cells or tissues is prepared, sheared, and then denatured. Then, immunoselection and immunoprecipitation can take place using the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads. After isolation and purification is performed, the IP’d methylated DNA is ready for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<h2>Applications</h2>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> qPCR analysis</a></div>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-seq-package-V2-x10" class="center alert radius button"> NGS analysis </a></div>
<h2>Advantages</h2>
<ul style="font-size: 19px;" class="nobullet">
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Unaffected</strong> DNA</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>High enrichment</strong> yield</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Robust</strong> & <strong>reproducible</strong> techniques</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>NGS</strong> compatible</li>
</ul>
<h2></h2>
</div>
</div>
<div id="gtx-trans" style="position: absolute; left: 17px; top: 652.938px;">
<div class="gtx-trans-icon"></div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'slug' => 'methylated-dna-immunoprecipitation',
'meta_keywords' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation,Epigenetic,DNA Methylation,qPCR,5 methylcytosine (5-mC)',
'meta_description' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation method is based on the affinity purification of methylated DNA using an antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine (5-mC). ',
'meta_title' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation(MeDIP) - Dna methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2021-08-19 12:08:03',
'created' => '2014-09-14 05:33:34',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '1',
'position' => '9',
'parent_id' => null,
'name' => 'DNA Methylation',
'description' => '<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns">
<div style="text-align: justify;" class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h2>Complete solutions for DNA methylation studies</h2>
<p>Whether you are experienced or new to the field of DNA methylation, Diagenode has everything you need to make your assay as easy and convenient as possible while ensuring consistent data between samples and experiments. Diagenode offers sonication instruments, reagent kits, high quality antibodies, and high-throughput automation capability to address all of your specific DNA methylation analysis requirements.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns text-center"><a href="../landing-pages/dna-methylation-grant-applications"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-dna-grant.png" alt="" /></a></div>
<div style="text-align: justify;" class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark and is the most widely studied topic in epigenetics. <em>In vivo</em>, DNA is methylated following DNA replication and is involved in a number of biological processes including the regulation of imprinted genes, X chromosome inactivation. and tumor suppressor gene silencing in cancer cells. Methylation often occurs in cytosine-guanine rich regions of DNA (CpG islands), which are commonly upstream of promoter regions.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns"><br /><br />
<ul class="accordion" data-accordion="">
<li class="accordion-navigation"><a href="#dnamethyl"><i class="fa fa-caret-right"></i> Learn more</a>
<div id="dnamethyl" class="content">5-methylcytosine (5-mC) has been known for a long time as the only modification of DNA for epigenetic regulation. In 2009, however, Kriaucionis discovered a second methylated cytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC). The so-called 6th base, is generated by enzymatic conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine by the TET family of oxygenases. Early reports suggested that 5-hmC may represent an intermediate of active demethylation in a new pathway which demethylates DNA, converting 5-mC to cytosine. Recent evidence fuel this hypothesis suggesting that further oxidation of the hydroxymethyl group leads to a formyl or carboxyl group followed by either deformylation or decarboxylation. The formyl and carboxyl groups of 5-formylcytosine (5-fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5-caC) could be enzymatically removed without excision of the base.
<p class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/categories/kits_dna/dna_methylation_variants.jpg" /></p>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
<br />
<h2>Main DNA methylation technologies</h2>
<p style="text-align: justify;">Overview of the <span style="font-weight: 400;">three main approaches for studying DNA methylation.</span></p>
<div class="row">
<ol>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Chemical modification with bisulfite – Bisulfite conversion</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Enrichment of methylated DNA (including MeDIP and MBD)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Treatment with methylation-sensitive or dependent restriction enzymes</span></li>
</ol>
<p><span style="font-weight: 400;"> </span></p>
<div class="row">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>Description</th>
<th width="350">Features</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><strong>Bisulfite conversion</strong></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">Chemical conversion of unmethylated cytosine to uracil. Methylated cytosines are protected from this conversion allowing to determine DNA methylation at single nucleotide resolution.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Single nucleotide resolution</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Quantitative analysis - methylation rate (%)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Gold standard and well studied</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Compatible with automation</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><b>Methylated DNA enrichment</b></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">(Hydroxy-)Methylated DNA is enriched by using specific antibodies (hMeDIP or MeDIP) or proteins (MBD) that specifically bind methylated CpG sites in fragmented genomic DNA.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Resolution depends on the fragment size of the enriched methylated DNA (300 bp)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Qualitative analysis</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Compatible with automation</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><strong>Restriction enzyme-based digestion</strong></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">Use of (hydroxy)methylation-sensitive or (hydroxy)methylation-dependent restriction enzymes for DNA methylation analysis at specific sites.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Determination of methylation status is limited by the enzyme recognition site</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Easy to use</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="large-12 columns"></div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => true,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'slug' => 'epigenetics-dna-methylation',
'meta_keywords' => 'Epigenetics, DNA Methylation,5-hmC monoclonal antibody,hMeDIP,Bisulfite conversion,Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'meta_description' => 'Complete, optimized solutions for analyzing DNA methylation manually or on our automated system.',
'meta_title' => 'DNA Methylation - Bisulfite sequencing - Epigenetics | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2019-03-25 10:07:27',
'created' => '2015-05-03 13:47:53',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '6',
'position' => '10',
'parent_id' => '1',
'name' => 'メチル化DNA結合タンパク質',
'description' => '<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns">MBD方法は、メチル化DNAに対するH6-GST-MBD融合タンパク質の非常に高い親和性に基づいています。 このタンパク質は、N末端His6タグを含むグルタチオン-S-トランスフェラーゼ(GST)とのC末端融合物として、ヒトMeCP2のメチル結合ドメイン(MBD)を含有します。 このH6-GST-MBD融合タンパク質を用いて、メチル化CpGを含むDNAを特異的に単離する事が可能です。<br /><br />DiagenodeのMethylCap®キットは、二本鎖DNAの高濃縮と、メチル化CpG密度の関数における微分分画を可能にします。 分画はサンプルの複雑さを軽減し、次世代のシーケンシングを容易にします。 MethylCapアッセイに先立ち、DNAを最初に抽出し、Picoruptorソニケーターを用いて断片化します。<br />
<h3>概要</h3>
<p class="text-center"><br /><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/applications/methyl_binding_domain_overview.jpg" /></p>
</div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => false,
'slug' => 'methylbinding-domain-protein',
'meta_keywords' => 'Epigenetic,Methylbinding Domain Protein,MBD,DNA methylation,DNA replication,MethylCap,MethylCap assay,',
'meta_description' => 'Methylbinding Domain Protein(MBD) approach is based on the very high affinity of a H6-GST-MBD fusion protein for methylated DNA. This protein consists of the methyl binding domain (MBD) of human MeCP2, as a C-terminal fusion with Glutathione-S-transferase',
'meta_title' => 'Epigenetic Methylbinding Domain Protein(MBD) - DNA methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2019-03-22 12:32:12',
'created' => '2015-06-02 17:05:42',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Category' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '52',
'position' => '2',
'parent_id' => '12',
'name' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-seq-package-V2-x10"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/b-email-magmedip.png" /></a></p>
<p>The Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation is based on the affinity purification of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA using, respectively, an antibody directed against 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in the case of MeDIP or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in the case of hMeDIP.</p>
<h2>How it works</h2>
<p>In brief, Methyl DNA IP is performed as follows: Genomic DNA from cultured cells or tissues is prepared, sheared, and then denatured. Then, immunoselection and immunoprecipitation can take place using the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads. After isolation and purification is performed, the IP’d methylated DNA is ready for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<h2>Applications</h2>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> qPCR analysis</a></div>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> NGS analysis </a></div>
<h2>Advantages</h2>
<ul style="font-size: 19px;" class="nobullet">
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Unaffected</strong> DNA</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>High enrichment</strong> yield</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Robust</strong> & <strong>reproducible</strong> techniques</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>NGS</strong> compatible</li>
</ul>
<h2></h2>',
'no_promo' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'hide' => false,
'all_format' => false,
'is_antibody' => false,
'slug' => 'methylated-dna-immunoprecipitation',
'cookies_tag_id' => null,
'meta_keywords' => 'Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation,DNA methylation',
'meta_description' => 'Diagenode provides Antibody-based isolation of methylated DNA for DNA immunoprecipitation ',
'meta_title' => 'Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation for DNA Methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2022-11-25 10:46:50',
'created' => '2015-07-08 09:30:57',
'ProductsCategory' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'CookiesTag' => array([maximum depth reached])
)
),
'Document' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1166',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit ',
'description' => '',
'image_id' => null,
'type' => 'Manual',
'url' => 'files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-manual-c02010020-21',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => '',
'modified' => '2022-11-22 15:50:08',
'created' => '2022-11-22 15:41:49',
'ProductsDocument' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Feature' => array(),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1796',
'name' => 'https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/C02010020-magmedip-qpcr.jpg',
'alt' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10',
'modified' => '2019-04-24 17:06:59',
'created' => '2019-04-24 17:04:52',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Promotion' => array(),
'Protocol' => array(),
'Publication' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '4989',
'name' => 'Differential methylation of circulating free DNA assessed through cfMeDiP as a new tool for breast cancer diagnosis and detection of BRCA1/2 mutation',
'authors' => 'Piera Grisolia et al.',
'description' => '<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Background</h3>
<p>Recent studies have highlighted the importance of the cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation profile in detecting breast cancer (BC) and its different subtypes. We investigated whether plasma cfDNA methylation, using cell-free Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation and High-Throughput Sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq), may be informative in characterizing breast cancer in patients with BRCA1/2 germline mutations for early cancer detection and response to therapy.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Methods</h3>
<p>We enrolled 23 BC patients with germline mutation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, 19 healthy controls without BRCA1/2 mutation, and two healthy individuals who carried BRCA1/2 mutations. Blood samples were collected for all study subjects at the diagnosis, and plasma was isolated by centrifugation. Cell-free DNA was extracted from 1 mL of plasma, and cfMeDIP-seq was performed for each sample. Shallow whole genome sequencing was performed on the immuno-precipitated samples. Then, the differentially methylated 300-bp regions (DMRs) between 25 BRCA germline mutation carriers and 19 non-carriers were identified. DMRs were compared with tumor-specific regions from public datasets to perform an unbiased analysis. Finally, two statistical classifiers were trained based on the GLMnet and random forest model to evaluate if the identified DMRs could discriminate BRCA-positive from healthy samples.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Results</h3>
<p>We identified 7,095 hypermethylated and 212 hypomethylated regions in 25 BRCA germline mutation carriers compared to 19 controls. These regions discriminate tumors from healthy samples with high accuracy and sensitivity. We show that the circulating tumor DNA of BRCA1/2 mutant breast cancers is characterized by the hypomethylation of genes involved in DNA repair and cell cycle. We uncovered the TFs associated with these DRMs and identified that proteins of the Erythroblast Transformation Specific (ETS) family are particularly active in the hypermethylated regions. Finally, we assessed that these regions could discriminate between BRCA positives from healthy samples with an AUC of 0.95, a sensitivity of 88%, and a specificity of 94.74%.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p>Our study emphasizes the importance of tumor cell-derived DNA methylation in BC, reporting a different methylation profile between patients carrying mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, and wild-type controls. Our minimally invasive approach could allow early cancer diagnosis, assessment of minimal residual disease, and monitoring of response to therapy.</p>',
'date' => '2024-10-15',
'pmid' => 'https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-024-05734-2',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-05734-2',
'modified' => '2024-10-18 11:43:43',
'created' => '2024-10-18 11:43:43',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '4981',
'name' => 'Prediction of brain metastasis development with DNA methylation signatures',
'authors' => 'Jeffrey A. Zuccato et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Brain metastases (BMs) are the most common and among the deadliest brain tumors. Currently, there are no reliable predictors of BM development from primary cancer, which limits early intervention. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common BM source and here we obtained 402 tumor and plasma samples from a large cohort of patients with LUAD with or without BM (</span><i>n</i><span> = 346). LUAD DNA methylation signatures were evaluated to build and validate an accurate model predicting BM development from LUAD, which was integrated with clinical factors to provide comprehensive patient-specific BM risk probabilities in a nomogram. Additionally, immune and cell interaction gene sets were differentially methylated at promoters in BM versus paired primary LUAD and had aligning dysregulation in the proteome. Immune cells were differentially abundant in BM versus LUAD. Finally, liquid biomarkers identified from methylated cell-free DNA sequenced in plasma were used to generate and validate accurate classifiers for early BM detection. Overall, LUAD methylomes can be leveraged to predict and noninvasively identify BM, moving toward improved patient outcomes with personalized treatment.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-10-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03286-y',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03286-y',
'modified' => '2024-10-11 09:58:45',
'created' => '2024-10-11 09:58:45',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '4957',
'name' => 'Association between TNF-α, cortisol levels, and exposure to PM10 and PM2.5: a pilot study',
'authors' => 'Dolcini J. et al.',
'description' => '<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Purpose</h3>
<p>The most harmful atmospheric pollutant for human health is particulate matter (PM). We analyzed the correlation between short-term lag exposure to PM10 and PM2.5, salivary cortisol and TNF-α level, and methylation levels of the TNF-α promoter.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Methods</h3>
<p>A pilot study including 20 subjects. Eight salivary samples for each subject at various times of the day were collected for comparing cortisol levels and TNFα detection. TNFα promoter methylation levels on salivary DNA were analyzed. Regression analyses were performed using generalized linear mixed models between the different outcomes and 4, 3, 2 and 1 day’s lag values of PM10/PM2.5.Generalized additive mixed model (GAMM) was used to evaluate any potential deviation from linearity.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Results</h3>
<p>Area under the curve with respect to the ground (AUCg) showed a statistically positive association with 4-, 3-, 2-, and 1-day lag of exposure to PM10. Area under the curve with respect to the increase (AUCi) showed a statistically negative association with 4-, 3- and 1-day lag of exposure to PM10. TNFα showed statistically significant association with both exposures, PM10 and PM2.5, at 4-, 3-, 2-, and 1-day lag.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p>Regarding cortisol levels there is an increase of overall hormone levels but a less dynamism of the system to answer to external stressors. Increase of TNF-α may reflect increased levels of oxidative stress and inflammation due to pollution exposure.</p>',
'date' => '2024-08-07',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12302-024-00961-2',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-024-00961-2',
'modified' => '2024-09-02 10:01:14',
'created' => '2024-09-02 10:00:08',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '4942',
'name' => 'Epigenomic signatures of sarcomatoid differentiation to guide the treatment of renal cell carcinoma',
'authors' => 'Talal El Zarif et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (sRCC) is associated with poor survival and a heightened response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Two major barriers to improving outcomes for sRCC are the limited understanding of its gene regulatory programs and the low diagnostic yield of tumor biopsies due to spatial heterogeneity. Herein, we characterized the epigenomic landscape of sRCC by profiling 107 epigenomic libraries from tissue and plasma samples from 50 patients with RCC and healthy volunteers. By profiling histone modifications and DNA methylation, we identified highly recurrent epigenomic reprogramming enriched in sRCC. Furthermore, CRISPRa experiments implicated the transcription factor FOSL1 in activating sRCC-associated gene regulatory programs, and </span><em>FOSL1</em><span><span> </span>expression was associated with the response to ICIs in RCC in two randomized clinical trials. Finally, we established a blood-based diagnostic approach using detectable sRCC epigenomic signatures in patient plasma, providing a framework for discovering epigenomic correlates of tumor histology via liquid biopsy.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-25',
'pmid' => 'https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)00678-8',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114350',
'modified' => '2024-06-24 10:33:29',
'created' => '2024-06-24 10:33:29',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '4947',
'name' => 'Detecting small cell transformation in patients with advanced EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma through epigenomic cfDNA profiling',
'authors' => 'Talal El Zarif et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Purpose: Histologic transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a mechanism of treatment resistance in patients with advanced oncogene-driven lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) that currently requires histologic review for diagnosis. Herein, we sought to develop an epigenomic cell-free (cf)DNA-based approach to non-invasively detect small cell transformation in patients with EGFR mutant (EGFRm) LUAD. Experimental Design: To characterize the epigenomic landscape of transformed (t)SCLC relative to LUAD and de novo SCLC, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) to profile the histone modifications H3K27ac, H3K4me3, and H3K27me3, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq), assay for transposase-accessible chromatin sequencing (ATAC-seq), and RNA sequencing on 26 lung cancer patient-derived xenograft (PDX) tumors. We then generated and analyzed H3K27ac ChIP-seq, MeDIP-seq, and whole genome sequencing cfDNA data from 1 ml aliquots of plasma from patients with EGFRm LUAD with or without tSCLC. Results: Analysis of 126 epigenomic libraries from the lung cancer PDXs revealed widespread epigenomic reprogramming between LUAD and tSCLC, with a large number of differential H3K27ac (n=24,424), DNA methylation (n=3,298), and chromatin accessibility (n=16,352) sites between the two histologies. Tumor-informed analysis of each of these three epigenomic features in cfDNA resulted in accurate non-invasive discrimination between patients with EGFRm LUAD versus tSCLC (AUROC=0.82-0.87). A multi-analyte cfDNA-based classifier integrating these three epigenomic features discriminated between EGFRm LUAD versus tSCLC with an AUROC of 0.94. Conclusions: These data demonstrate the feasibility of detecting small cell transformation in patients with EGFRm LUAD through epigenomic cfDNA profiling of 1 ml of patient plasma.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-24',
'pmid' => 'https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article/doi/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0466/746147/Detecting-small-cell-transformation-in-patients',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0466',
'modified' => '2024-07-04 14:50:38',
'created' => '2024-07-04 14:50:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '4949',
'name' => 'Prostate cancer detection through unbiased capture of methylated cell-free DNA',
'authors' => 'Ermira Lleshi et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Prostate cancer screening using prostate-specific antigen (PSA) has been shown to reduce mortality but with substantial overdiagnosis, leading to unnecessary biopsies. The identification of a highly specific biomarker using liquid biopsies, represents an unmet need in the diagnostic pathway for prostate cancer. In this study, we employed a method that enriches for methylated cell-free DNA fragments coupled with a machine learning algorithm which enabled the detection of metastatic and localised cancers with AUCs of 0.96 and 0.74, respectively. The model also detected 51.8% (14/27) of localised and 88.7% (79/89) of metastatic cancer patients in an external dataset. Furthermore, we show that the differentially methylated regions reflect epigenetic and transcriptomic changes at the tissue level. Notably, these regions are significantly enriched for biologically relevant pathways associated with the regulation of cellular proliferation and TGF-beta signalling. This demonstrates the potential of circulating tumour DNA methylation for prostate cancer detection and prognostication.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-20',
'pmid' => 'https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004224015554',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110330',
'modified' => '2024-07-04 15:29:13',
'created' => '2024-07-04 15:29:13',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '4921',
'name' => 'A Pre-Leukemic DNA Methylation Signature in Healthy Individuals at Higher Risk for Developing Myeloid Malignancy',
'authors' => 'Zhentang Lao et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Purpose: DNA methylation alterations are widespread in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), some of which appear to have evolved independently of somatic mutations in epigenetic regulators. While the presence of somatic mutations in peripheral blood can predict the risk of development of AML and MDS, its accuracy remains unsatisfactory. Experimental Design: We performed global DNA methylation profiling in a case-control study nested within Singapore Chinese Health Study to evaluate if DNA methylation alterations were associated with AML/MDS development. Targeted deep sequencing and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) were performed on peripheral blood collected a median of 9.9 years prior to diagnosis of AML or MDS, together with age-matched still healthy individuals as controls. Results: Sixty-six individuals who developed AML or MDS displayed significant DNA methylation changes in the peripheral blood compared with 167 age- and gender-matched controls who did not develop AML/MDS during the follow up period. Alterations in methylation in the differentially methylation regions (DMRs) were associated with increased odds of developing AML/MDS. Conclusions: The epigenetic changes may be acquired independently and prior to somatic mutations that relevant for AML/MDS development. The association between methylation changes and the risk of pre-AML/MDS in these individuals was considerably stronger than somatic mutations, suggesting that methylation changes could be used as biomarkers for pre- AML/MDS screening.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-03-04',
'pmid' => 'https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article-abstract/doi/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3804/735044/A-Pre-Leukemic-DNA-Methylation-Signature-in?redirectedFrom=fulltext',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3804',
'modified' => '2024-03-12 16:50:46',
'created' => '2024-03-12 16:50:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 7 => array(
'id' => '4912',
'name' => 'Neurofibromin 1 controls metabolic balance and Notch-dependent quiescence of murine juvenile myogenic progenitors',
'authors' => 'Wei X. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Patients affected by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) frequently show muscle weakness with unknown etiology. Here we show that, in mice, Neurofibromin 1 (</span><i>Nf1</i><span>) is not required in muscle fibers, but specifically in early postnatal myogenic progenitors (MPs), where<span> </span></span><i>Nf1</i><span><span> </span>loss led to cell cycle exit and differentiation blockade, depleting the MP pool resulting in reduced myonuclear accretion as well as reduced muscle stem cell numbers. This was caused by precocious induction of stem cell quiescence coupled to metabolic reprogramming of MPs impinging on glycolytic shutdown, which was conserved in muscle fibers. We show that a Mek/Erk/NOS pathway hypersensitizes<span> </span></span><i>Nf1</i><span>-deficient MPs to Notch signaling, consequently, early postnatal Notch pathway inhibition ameliorated premature quiescence, metabolic reprogramming and muscle growth. This reveals an unexpected role of Ras/Mek/Erk signaling supporting postnatal MP quiescence in concert with Notch signaling, which is controlled by Nf1 safeguarding coordinated muscle growth and muscle stem cell pool establishment. Furthermore, our data suggest transmission of metabolic reprogramming across cellular differentiation, affecting fiber metabolism and function in NF1.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-02-15',
'pmid' => 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-45618-z',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45618-z',
'modified' => '2024-02-22 12:22:26',
'created' => '2024-02-22 12:22:26',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 8 => array(
'id' => '4892',
'name' => 'Promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions are associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival',
'authors' => 'Rivera‑Peña B. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) can be used as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets in precision medicine workflows. DNA from 21 HNSCC and 10 healthy oral tissue samples was hybridized to a genome‑wide tiling array to identify DMRs in a discovery cohort. Downstream analyses identified differences in promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival. Genome‑wide DMR analysis showed 2,565 DMRs common to the three subsites. A total of 738 DMRs were unique to laryngeal cancer (n=7), 889 DMRs were unique to oral cavity cancer (n=10) and 363 DMRs were unique to pharyngeal cancer (n=6). Based on the genome‑wide analysis and a Gene Ontology analysis, 10 candidate genes were selected to test for prognostic value and association with clinicopathological features. </span><em>TIMP3</em><span><span> </span>was associated with tumor differentiation in oral cavity cancer (P=0.039),<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span><span> </span>was associated with nodal involvement in pharyngeal cancer (P=0.017) and<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span><span> </span>was associated with tumor differentiation in laryngeal cancer (P=0.040). A total of five candidate genes were selected,<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>CDH1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>CALCA</em><span><span> </span>and<span> </span></span><em>TIMP3</em><span>, for a prevalence study in a larger validation cohort: Oral cavity cancer samples (n=42), pharyngeal cancer tissues (n=25) and laryngeal cancer samples (n=52).<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span><span> </span>hypermethylation differed across HNSCC anatomic subsites (P=0.029), and was predominantly detected in laryngeal cancer. Kaplan‑Meier survival analysis (P=0.043) and Cox regression analysis of overall survival (P=0.001) showed that<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span><span> </span>methylation is associated with better prognosis in HNSCC. The findings of the present study showed that the HNSCC subsites oral cavity, pharynx and larynx display substantial differences in aberrant DNA methylation patterns, which may serve as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-01-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/ol.2024.14223/abstract',
'doi' => ' https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2024.14223',
'modified' => '2024-01-11 08:48:03',
'created' => '2024-01-11 08:48:03',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 9 => array(
'id' => '4732',
'name' => 'Cerebrospinal fluid methylome-based liquid biopsies for accuratemalignant brain neoplasm classification.',
'authors' => 'Zuccato Jeffrey A et al.',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Resolving the differential diagnosis between brain metastases (BM), glioblastomas (GBM), and central nervous system lymphomas (CNSL) is an important dilemma for the clinical management of the main three intra-axial brain tumor types. Currently, treatment decisions require invasive diagnostic surgical biopsies that carry risks and morbidity. This study aimed to utilize methylomes from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a biofluid proximal to brain tumors, for reliable non-invasive classification that addresses limitations associated with low target abundance in existing approaches. METHODS: Binomial GLMnet classifiers of tumor type were built, in fifty iterations of 80\% discovery sets, using CSF methylomes obtained from 57 BM, GBM, CNSL, and non-neoplastic control patients. Publicly-available tissue methylation profiles (N=197) on these entities and normal brain parenchyma were used for validation and model optimization. RESULTS: Models reliably distinguished between BM (area under receiver operating characteristic curve [AUROC]=0.93, 95\% confidence interval [CI]: 0.71-1.0), GBM (AUROC=0.83, 95\% CI: 0.63-1.0), and CNSL (AUROC=0.91, 95\% CI: 0.66-1.0) in independent 20\% validation sets. For validation, CSF-based methylome signatures reliably distinguished between tumor types within external tissue samples and tumors from non-neoplastic controls in CSF and tissue. CSF methylome signals were observed to align closely with tissue signatures for each entity. An additional set of optimized CSF-based models, built using tumor-specific features present in tissue data, showed enhanced classification accuracy. CONCLUSIONS: CSF methylomes are reliable for liquid biopsy-based classification of the major three malignant brain tumor types. We discuss how liquid biopsies may impact brain cancer management in the future by avoiding surgical risks, classifying unbiopsiable tumors, and guiding surgical planning when resection is indicated.</p>',
'date' => '2023-08-03',
'pmid' => 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36455236/',
'doi' => '10.1093/neuonc/noac264',
'modified' => '2023-10-13 08:50:06',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 10 => array(
'id' => '4803',
'name' => 'Transgenerational endocrine disruptor effects of cadmium in zebrafish andcontribution of standing epigenetic variation to adaptation.',
'authors' => 'Pierron F. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Evidence has emerged that environmentally-induced epigenetic changes can have long-lasting effects on gene transcription across generations. These recent findings highlight the need to investigate the transgenerational impacts of pollutants to assess their long term effects on populations. In this study, we investigated the transgenerational effect of cadmium on zebrafish across 4 generations. A first whole methylome approach carried out on fish of the first two generations led us to focus our investigations on the estradiol receptor alpha gene (esr1). We observed a sex-dependent transgenerational inheritance of Cd-induced DNA methylation changes up to the last generation. These changes were associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that were themselves at the origin of the creation or deletion of methylation sites. Thus, Cd-induced genetic selection gave rise to DNA methylation changes. We also analyzed the transcription level of various sections of esr1 as well as estrogen responsive genes. While Cd triggered transgenerational disorders, Cd-induced epigenetic changes in esr1 contributed to the rapid transgenerational adaptation of fish to Cd. Our results provide insight into the processes underpinning rapid adaptation and highlight the need to maintain genetic diversity within natural populations to bolster the resilience of species faced with the global environmental changes.</span></p>',
'date' => '2023-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37163897',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131579',
'modified' => '2023-06-15 08:44:52',
'created' => '2023-06-13 21:11:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 11 => array(
'id' => '4843',
'name' => 'Differentiation block in acute myeloid leukemia regulated by intronicsequences of FTO',
'authors' => 'Camera F. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Iroquois transcription factor gene IRX3 is highly expressed in 20–30\% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and contributes to the pathognomonic differentiation block. Intron 8 FTO sequences ∼220kB downstream of IRX3 exhibit histone acetylation, DNA methylation, and contacts with the IRX3 promoter, which correlate with IRX3 expression. Deletion of these intronic elements confirms a role in positively regulating IRX3. RNAseq revealed long non-coding (lnc) transcripts arising from this locus. FTO-lncAML knockdown (KD) induced differentiation of AML cells, loss of clonogenic activity, and reduced FTO intron 8:IRX3 promoter contacts. While both FTO-lncAML KD and IRX3 KD induced differentiation, FTO-lncAML but not IRX3 KD led to HOXA downregulation suggesting transcript activity in trans. FTO-lncAMLhigh AML samples expressed higher levels of HOXA and lower levels of differentiation genes. Thus, a regulatory module in FTO intron 8 consisting of clustered enhancer elements and a long non-coding RNA is active in human AML, impeding myeloid differentiation.</p>',
'date' => '2023-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004223013962',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.isci.2023.107319',
'modified' => '2023-08-01 14:14:01',
'created' => '2023-08-01 15:59:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 12 => array(
'id' => '4777',
'name' => 'Epigenetic modifier alpha-ketoglutarate modulates aberrant gene bodymethylation and hydroxymethylation marks in diabetic heart.',
'authors' => 'Dhat R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Hyperglycemic myocardial microenvironment significantly alters chromatin architecture and the transcriptome, resulting in aberrant activation of signaling pathways in a diabetic heart. Epigenetic marks play vital roles in transcriptional reprogramming during the development of DCM. The current study is aimed to profile genome-wide DNA (hydroxy)methylation patterns in the hearts of control and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats and decipher the effect of modulation of DNA methylation by alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), a TET enzyme cofactor, on the progression of DCM. METHODS: Diabetes was induced in male adult Wistar rats with an intraperitoneal injection of STZ. Diabetic and vehicle control animals were randomly divided into groups with/without AKG treatment. Cardiac function was monitored by performing cardiac catheterization. Global methylation (5mC) and hydroxymethylation (5hmC) patterns were mapped in the Left ventricular tissue of control and diabetic rats with the help of an enrichment-based (h)MEDIP-sequencing technique by using antibodies specific for 5mC and 5hmC. Sequencing data were validated by performing (h)MEDIP-qPCR analysis at the gene-specific level, and gene expression was analyzed by qPCR. The mRNA and protein expression of enzymes involved in the DNA methylation and demethylation cycle were analyzed by qPCR and western blotting. Global 5mC and 5hmC levels were also assessed in high glucose-treated DNMT3B knockdown H9c2 cells. RESULTS: We found the increased expression of DNMT3B, MBD2, and MeCP2 with a concomitant accumulation of 5mC and 5hmC, specifically in gene body regions of diabetic rat hearts compared to the control. Calcium signaling was the most significantly affected pathway by cytosine modifications in the diabetic heart. Additionally, hypermethylated gene body regions were associated with Rap1, apelin, and phosphatidyl inositol signaling, while metabolic pathways were most affected by hyperhydroxymethylation. AKG supplementation in diabetic rats reversed aberrant methylation patterns and restored cardiac function. Hyperglycemia also increased 5mC and 5hmC levels in H9c2 cells, which was normalized by DNMT3B knockdown or AKG supplementation. CONCLUSION: This study demonstrates that reverting hyperglycemic damage to cardiac tissue might be possible by erasing adverse epigenetic signatures by supplementing epigenetic modulators such as AKG along with an existing antidiabetic treatment regimen.</p>',
'date' => '2023-04-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37101286',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13072-023-00489-4',
'modified' => '2023-06-12 09:20:54',
'created' => '2023-05-05 12:34:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 13 => array(
'id' => '4611',
'name' => 'Pre-diagnosis plasma cell-free DNA methylome profiling up to sevenyears prior to clinical detection reveals early signatures of breast cancer',
'authors' => 'Cheng N. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Profiling of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has been well demonstrated to be a potential non-invasive screening tool for early cancer detection. However, limited studies have investigated the detectability of cfDNA methylation markers that are predictive of cancers in asymptomatic individuals. We performed cfDNA methylation profiling using cell-free DNA methylation immunoprecipitation sequencing (cfMeDIP-Seq) in blood collected from individuals up to seven years before a breast cancer diagnosis in addition to matched cancer-free controls. We identified differentially methylated cfDNA signatures that discriminated cancer-free controls from pre-diagnosis breast cancer cases in a discovery cohort that is used to build a classification model. We show that predictive models built from pre-diagnosis cfDNA hypermethylated regions can accurately predict early breast cancers in an independent test set (AUC=0.930) and are generalizable to late-stage breast cancers cases at the time of diagnosis (AUC=0.912). Characterizing the top hypermethylated cfDNA regions revealed significant enrichment for hypermethylation in external bulk breast cancer tissues compared to peripheral blood leukocytes and breast normal tissues. Our findings demonstrate that cfDNA methylation markers predictive of breast cancers can be detected in blood among asymptomatic individuals up to six years prior to clinical detection.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2023.01.30.23285027',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.01.30.23285027',
'modified' => '2023-04-04 08:34:20',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 14 => array(
'id' => '4612',
'name' => 'Cell-free multi-omics analysis reveals tumor status-informativesignatures in gastrointestinal cancer patients’ plasma',
'authors' => 'Tao Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>During cancer development, host’s tumorigenesis and immune signals are released to and informed by circulating molecules, like cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and RNA (cfRNA) in blood. However, these two kinds of molecules are still not systematically compared in gastrointestinal cancer. Here, we profiled 4 types of cell-free omics data from colorectal and stomach cancer patients, and assayed 15 types of genomic, epi-genomic, and transcriptomic variations. First, we demonstrated that the multi-omics data were more capable of detecting cancer genes than the single-omics data, where cfRNAs were more sensitive and informative than cfDNAs in terms of detection ratio, variation type, altered number, and enriched functional pathway. Moreover, we revealed several peripheral immune signatures that were suppressed in cancer patients and originated from specific circulating and tumor-microenvironment cells. Particularly, we defined a γδ-T-cell score and a cancer-associated-fibroblast (CAF) score using the cfRNA-seq data of 143 cancer patients. They were informative of clinical status like cancer stage, tumor size, and survival. In summary, our work reveals the cell-free multi-molecular landscape of colorectal and stomach cancer, and provides a potential monitoring utility in blood for the personalized cancer treatment.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2023.01.31.526431',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.01.31.526431',
'modified' => '2023-04-04 08:36:37',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 15 => array(
'id' => '4674',
'name' => 'Methylation and expression of glucocorticoid receptor exon-1 variants andFKBP5 in teenage suicide-completers.',
'authors' => 'Rizavi H. et al.',
'description' => '<p>A dysregulated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis has repeatedly been demonstrated to play a fundamental role in psychiatric disorders and suicide, yet the mechanisms underlying this dysregulation are not clear. Decreased expression of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene, which is also susceptible to epigenetic modulation, is a strong indicator of impaired HPA axis control. In the context of teenage suicide-completers, we have systematically analyzed the 5'UTR of the GR gene to determine the expression levels of all GR exon-1 transcript variants and their epigenetic state. We also measured the expression and the epigenetic state of the FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP5/FKBP51), an important modulator of GR activity. Furthermore, steady-state DNA methylation levels depend upon the interplay between enzymes that promote DNA methylation and demethylation activities, thus we analyzed DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), ten-eleven translocation enzymes (TETs), and growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins (GADD45). Focusing on both the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus, our results show decreased expression in specific GR exon-1 variants and a strong correlation of DNA methylation changes with gene expression in the PFC. FKBP5 expression is also increased in both areas suggesting a decreased GR sensitivity to cortisol binding. We also identified aberrant expression of DNA methylating and demethylating enzymes in both brain regions. These findings enhance our understanding of the complex transcriptional regulation of GR, providing evidence of epigenetically mediated reprogramming of the GR gene, which could lead to possible epigenetic influences that result in lasting modifications underlying an individual's overall HPA axis response and resilience to stress.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36781843',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41398-023-02345-1',
'modified' => '2023-04-14 09:26:37',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 16 => array(
'id' => '4675',
'name' => 'Bridging biological cfDNA features and machine learning approaches.',
'authors' => 'Moser T. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Liquid biopsies (LBs), particularly using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), are expected to revolutionize precision oncology and blood-based cancer screening. Recent technological improvements, in combination with the ever-growing understanding of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) biology, are enabling the detection of tumor-specific changes with extremely high resolution and new analysis concepts beyond genetic alterations, including methylomics, fragmentomics, and nucleosomics. The interrogation of a large number of markers and the high complexity of data render traditional correlation methods insufficient. In this regard, machine learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly being used to decipher disease- and tissue-specific signals from cfDNA. Here, we review recent insights into biological ctDNA features and how these are incorporated into sophisticated ML applications.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36792446',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.tig.2023.01.004',
'modified' => '2023-04-14 09:28:00',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 17 => array(
'id' => '4823',
'name' => 'Gene body DNA hydroxymethylation restricts the magnitude oftranscriptional changes during aging.',
'authors' => 'Occean J. R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC) is the most abundant oxidative derivative of DNA methylation (5mC) and is typically enriched at enhancers and gene bodies of transcriptionally active and tissue-specific genes. Although aberrant genomic 5hmC has been implicated in many age-related diseases, the functional role of the modification in aging remains largely unknown. Here, we report that 5hmC is stably enriched in multiple aged organs. Using the liver and cerebellum as model organs, we show that 5hmC accumulates in gene bodies associated with tissue-specific function and thereby restricts the magnitude of gene expression changes during aging. Mechanistically, we found that 5hmC decreases binding affinity of splicing factors compared to unmodified cytosine and 5mC, and is correlated with age-related alternative splicing events, suggesting RNA splicing as a potential mediator of 5hmC’s transcriptionally restrictive function. Furthermore, we show that various age-related contexts, such as prolonged quiescence and senescence, are partially responsible for driving the accumulation of 5hmC with age. We provide evidence that this age-related function is conserved in mouse and human tissues, and further show that the modification is altered by regimens known to modulate lifespan. Our findings reveal that 5hmC is a regulator of tissue-specific function and may play a role in regulating longevity.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36824863',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.02.15.528714',
'modified' => '2023-06-14 08:39:26',
'created' => '2023-06-13 22:16:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 18 => array(
'id' => '4711',
'name' => 'Neonatal inflammation increases hippocampal KCC2 expression throughmethylation-mediated TGF-β1 downregulation leading to impairedhippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity in adult mice.',
'authors' => 'Rong J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The mechanisms by which neonatal inflammation leads to cognitive deficits in adulthood remain poorly understood. Inhibitory GABAergic synaptic transmission plays a vital role in controlling learning, memory and synaptic plasticity. Since early-life inflammation has been reported to adversely affect the GABAergic synaptic transmission, the aim of this study was to investigate whether and how neonatal inflammation affects GABAergic synaptic transmission resulting in cognitive impairment. Neonatal mice received a daily subcutaneous injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 50 μg/kg) or saline on postnatal days 3-5. It was found that blocking GABAergic synaptic transmission reversed the deficit in hippocampus-dependent memory or the induction failure of long-term potentiation in the dorsal CA1 in adult LPS mice. An increase of mIPSCs amplitude was further detected in adult LPS mice indicative of postsynaptic potentiation of GABAergic transmission. Additionally, neonatal LPS resulted in the increased expression and function of K-Cl-cotransporter 2 (KCC2) and the decreased expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) in the dorsal CA1 during adulthood. The local TGF-β1 overexpression improved KCC2 expression and function, synaptic plasticity and memory of adult LPS mice. Adult LPS mice show hypermethylation of TGFb1 promoter and negatively correlate with reduced TGF-β1 transcripts. 5-Aza-deoxycytidine restored the changes in TGFb1 promoter methylation and TGF-β1 expression. Altogether, the results suggest that hypermethylation-induced reduction of TGF-β1 leads to enhanced GABAergic synaptic inhibition through increased KCC2 expression, which is a underlying mechanism of neonatal inflammation-induced hippocampus-dependent memory impairment in adult mice.</p>',
'date' => '2023-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36691035',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12974-023-02697-x',
'modified' => '2023-04-05 08:42:07',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 19 => array(
'id' => '4589',
'name' => 'Impact of FecB Mutation on Ovarian DNA Methylome inSmall-Tail Han Sheep.',
'authors' => 'Xie L. et al.',
'description' => '<p>UNLABELLED: Booroola fecundity (FecB) gene, a mutant of bone morphogenetic protein 1B (BMPR-1B) that was discovered in Booroola Merino, was the first prolificacy gene identified in sheep related to increased ovulation rate and litter size. The mechanism of FecB impact on reproduction is unclear. METHODS: In this study, adult Han ewes with homozygous FecB(B)/FecB(B) mutations (Han BB group) and ewes with FecB(+)/FecB(+) wildtype (Han ++ group) were selected. Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) was used to identify differences in methylated genes in ovary tissue. RESULTS: We examined differences in DNA methylation patterns between HanBB and Han ++ sheep. In both sheep, methylated reads were mainly distributed at the gene body regions, CpG islands and introns. The differentially methylated genes were enriched in neurotrophy in signaling pathway, Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) signaling pathway, Wnt signaling pathway, oocyte meiosis, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway, etc. Differentially-methylated genes were co-analyzed with differentially-expressed mRNAs. Several genes which could be associated with female reproduction were identified, such as FOXP3 (forkhead box P3), TMEFF2 (Transmembrane Protein with EGF Like and Two Follistatin Like Domains 2) and ADAT2 (Adenosine Deaminase TRNA Specific 2). CONCLUSIONS: We constructed a MeDIP-seq based methylomic study to investigate the ovarian DNA methylation differences between Small-Tail Han sheep with homozygous FecB mutant and wildtype, and successfully identified FecB gene-associated differentially-methylated genes. This study has provided information with which to understand the mechanisms of FecB gene-induced hyperprolificacy in sheep.</p>',
'date' => '2023-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36672944',
'doi' => '10.3390/genes14010203',
'modified' => '2023-04-11 10:04:29',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 20 => array(
'id' => '4631',
'name' => 'Consistent DNA Hypomethylations in Prostate Cancer.',
'authors' => 'Araúzo-Bravo M.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>With approximately 1.4 million men annually diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa) worldwide, PCa remains a dreaded threat to life and source of devastating morbidity. In recent decades, a significant decrease in age-specific PCa mortality has been achieved by increasing prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening and improving treatments. Nevertheless, upcoming, augmented recommendations against PSA screening underline an escalating disproportion between the benefit and harm of current diagnosis/prognosis and application of radical treatment standards. Undoubtedly, new potent diagnostic and prognostic tools are urgently needed to alleviate this tensed situation. They should allow a more reliable early assessment of the upcoming threat, in order to enable applying timely adjusted and personalized therapy and monitoring. Here, we present a basic study on an epigenetic screening approach by Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP). We identified genes associated with hypomethylated CpG islands in three PCa sample cohorts. By adjusting our computational biology analyses to focus on single CpG-enriched 60-nucleotide-long DNA probes, we revealed numerous consistently differential methylated DNA segments in PCa. They were associated among other genes with and . These can be used for early discrimination, and might contribute to a new epigenetic tumor classification system of PCa. Our analysis shows that we can dissect short, differential methylated CpG-rich DNA fragments and combinations of them that are consistently present in all tumors. We name them tumor cell-specific differential methylated CpG dinucleotide signatures (TUMS).</p>',
'date' => '2022-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36613831',
'doi' => '10.3390/ijms24010386',
'modified' => '2023-03-28 09:03:47',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 21 => array(
'id' => '4488',
'name' => 'Cell-free DNA methylation-defined prognostic subgroups in small celllung cancer identified by leukocyte methylation subtraction',
'authors' => 'Ul Haq Sami et al.',
'description' => '<p>Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) methylome is understudied. Here, we comprehensively profile SCLC using cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from plasma of 74 SCLC patients pre-treatment and from 20 non-cancer participants, genomic DNA (gDNA) from peripheral blood leukocytes from the same 74 patients and 7 accompanying circulating-tumour-cell patient-derived xenografts (CDX) underwent cfMeDIP-seq. PeRIpheral blood leukocyte MEthylation (PRIME) subtraction to improve tumour specificity. SCLC cfDNA methylation is distinct from non-cancer but correlates with CDX tumor methylation. PRIME and k-means consensus identified two methylome clusters with prognostic associations that related to axon guidance, neuroactive ligand−receptor interaction, pluripotency of stem cells, and differentially methylated at long noncoding RNA and other repeats features. We comprehensively profiled the SCLC methylome in a large patient cohort and identified methylome clusters with prognostic associations. Our work demonstrates the potential of liquid biopsies in examining SCLC biology encoded in the methylome.</p>',
'date' => '2022-11-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.isci.2022.105487',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.isci.2022.105487',
'modified' => '2022-11-18 12:35:39',
'created' => '2022-11-15 09:26:20',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 22 => array(
'id' => '4547',
'name' => 'The cell-free DNA methylome captures distinctions between localized andmetastatic prostate tumors.',
'authors' => 'Chen Sujun et al.',
'description' => '<p>Metastatic prostate cancer remains a major clinical challenge and metastatic lesions are highly heterogeneous and difficult to biopsy. Liquid biopsy provides opportunities to gain insights into the underlying biology. Here, using the highly sensitive enrichment-based sequencing technology, we provide analysis of 60 and 175 plasma DNA methylomes from patients with localized and metastatic prostate cancer, respectively. We show that the cell-free DNA methylome can capture variations beyond the tumor. A global hypermethylation in metastatic samples is observed, coupled with hypomethylation in the pericentromeric regions. Hypermethylation at the promoter of a glucocorticoid receptor gene NR3C1 is associated with a decreased immune signature. The cell-free DNA methylome is reflective of clinical outcomes and can distinguish different disease types with 0.989 prediction accuracy. Finally, we show the ability of predicting copy number alterations from the data, providing opportunities for joint genetic and epigenetic analysis on limited biological samples.</p>',
'date' => '2022-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36309516',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41467-022-34012-2',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:30:03',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 23 => array(
'id' => '4550',
'name' => 'A SOX2-engineered epigenetic silencer factor represses the glioblastomagenetic program and restrains tumor development.',
'authors' => 'Benedetti V. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Current therapies remain unsatisfactory in preventing the recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), which leads to poor patient survival. By rational engineering of the transcription factor SOX2, a key promoter of GBM malignancy, together with the Kruppel-associated box and DNA methyltransferase3A/L catalytic domains, we generated a synthetic repressor named SOX2 epigenetic silencer (SES), which induces the transcriptional silencing of its original targets. By doing so, SES kills both glioma cell lines and patient-derived cancer stem cells in vitro and in vivo. SES expression, through local viral delivery in mouse xenografts, induces strong regression of human tumors and survival rescue. Conversely, SES is not harmful to neurons and glia, also thanks to a minimal promoter that restricts its expression in mitotically active cells, rarely present in the brain parenchyma. Collectively, SES produces a significant silencing of a large fraction of the SOX2 transcriptional network, achieving high levels of efficacy in repressing aggressive brain tumors.</p>',
'date' => '2022-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35921410/',
'doi' => '10.1126/sciadv.abn3986',
'modified' => '2023-09-28 11:26:02',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 24 => array(
'id' => '4551',
'name' => 'mTORC1 is required for epigenetic silencing during β-cell functionalmaturation.',
'authors' => 'Ni Qicheng et al.',
'description' => '<p>OBJECTIVE: The mechanistic target of rapamycin comple×1 (mTORC1) is a key molecule that links nutrients, hormones, and growth factors to cell growth/function. Our previous studies have shown that mTORC1 is required for β-cell functional maturation and identity maintenance; however, the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. This work aimed to understand the underlying epigenetic mechanisms of mTORC1 in regulating β-cell functional maturation. METHODS: We performed Microarray, MeDIP-seq and ATAC-seq analysis to explore the abnormal epigenetic regulation in 8-week-old immature βRapKO islets. Moreover, DNMT3A was overexpressed in βRapKO islets by lentivirus, and the transcriptome changes and GSIS function were analyzed. RESULTS: We identified two major epigenetic silencing mechanisms, DNMT3A-dependent DNA methylation and PRC2-dependent H3K27me3 modification, which are responsible for functional immaturity of Raptor-deficient β-cell. Overexpression of DNMT3A partially reversed the immature transcriptome pattern and restored the impaired GSIS in Raptor-deficient β-cells. Moreover, we found that Raptor directly regulated PRC2/EED2 and H3K27me3 expression levels, as well as a group of immature genes marked with H3K27me3. Combined with ATAC-seq, MeDIP-seq and ChIP-seq, we identified β-cell immature genes with either DNA methylation and/or H3K27me3 modification. CONCLUSION: The present study advances our understanding of the nutrient sensor mTORC1, by integrating environmental nutrient supply and epigenetic modification, i.e., DNMT3A-mediated DNA methylation and PRC2-mediated histone methylation in regulating β-cell identity and functional maturation, and therefore may impact the disease risk of type 2 diabetes.</p>',
'date' => '2022-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35940555',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101559',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:09:58',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 25 => array(
'id' => '4391',
'name' => 'Detection of ovarian cancer using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Lu Huaiwu et al. ',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a highly lethal gynecologic cancer, and it is hard to diagnose at an early stage. Clinically, there are no ovarian cancer-specific markers for early detection. Here, we demonstrate the use of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylomes to detect ovarian cancer, especially the early-stage OC. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Plasma from 74 epithelial ovarian cancer patients, 86 healthy volunteers, and 20 patients with benign pelvic masses was collected. The cfDNA methylomes of these samples were generated by cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). The differentially methylated regions (DMRs) were identified by the contrasts between tumor and non-tumor groups, and the discrimination performance was evaluated with the iterative training and testing method. RESULTS: The DMRs identified for cfDNA methylomes can well discriminate tumor groups and non-tumor groups (ROC values from 0.86 to 0.98). The late-stage top 300 DMRs are more late-stage-specific and failed to detect early-stage OC. However, the early-stage markers have the potential to discriminate all-stage OCs from non-tumor samples. CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrates that cfDNA methylomes generated with cfMeDIP-seq could be used to identify OC-specific biomarkers for OC, especially early OC detection. To detect early-stage OC, the biomarkers should be directly identified from early OC plasma samples rather than mix-stage ones. Further exploration of DMRs from a k larger early-stage OC cohort is warranted.</p>',
'date' => '2022-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35681212',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13148-022-01285-9',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:19:10',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 26 => array(
'id' => '4438',
'name' => 'A genome-wide screen reveals new regulators of the 2-cell-like cell state',
'authors' => 'Defossez Pierre-Antoine et al.',
'description' => '<p>In mammals, only the zygote and blastomeres of the early embryo are fully totipotent. This totipotency is mirrored in vitro by mouse "2-cell-like cells" (2CLCs), which appear at low frequency in cultures of Embryonic Stem cells (ESCs). Because totipotency is incompletely understood, we carried out a genomewide CRISPR KO screen in mouse ESCs, searching for mutants that reactivate the expression of Dazl, a robust 2-cell-like marker. Using secondary screens, we identify four mutants that reactivate not just Dazl, but also a broader 2-cell-like signature: the E3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor SPOP, the Zinc Finger transcription factor ZBTB14, MCM3AP, a component of the RNA processing complex TREX-2, and the lysine demethylase KDM5C. Functional experiments show how these factors link to known players of the 2 celllike state. These results extend our knowledge of totipotency, a key phase of organismal life.</p>',
'date' => '2022-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.21203%2Frs.3.rs-1561018%2Fv1',
'doi' => '10.21203/rs.3.rs-1561018/v1',
'modified' => '2022-09-28 09:23:42',
'created' => '2022-09-08 16:32:20',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 27 => array(
'id' => '4394',
'name' => 'Heat stress during grain filling regulates seed germination throughalterations of DNA methylation in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).',
'authors' => 'Sakai Yuki et al.',
'description' => '<p>KEY MESSAGE: Alterations in DNA methylation levels of ROS, GA and ABA related gene promoters cause transcriptional changes upon imbibition to induce seed germination in barley seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling. Environmental changes, especially changes in temperature, during seed development affect germination in several plant species. We have previously shown that heat stress during rice grain filling alters DNA methylation, an epigenetic mark important for gene silencing, regulates transcript levels of phytohormone metabolism genes, and delays seed germination. However, whether this phenomenon is present in other plant species remained to be elucidated. In this study, we compared seeds germination of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) plants grown at 15 °C (control) or 25 °C (heat stress) during grain filling. Heat stress during grain filling significantly promoted seed germination in comparison with the control. The phytohormone gibberellic acid (GA) and reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidases promote seed germination, whereas phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) suppresses seed germination. We found that in heat-stressed seeds, genes related to ABA biosynthesis (HvNCED1 and 2) were significantly suppressed, whereas genes related to ABA catabolism (HvABA8'OH) and GA biosynthesis (HvHA20ox, HvGA3ox), and NADPH oxidase (HvRboh) genes were significantly upregulated after imbibition. Using MeDIP-qPCR, we showed that the promoters of HvNCED were hyper-methylated, and those of HvABA8'OH1, HvABA8'OH3, HvGA3ox2, and HvRbohF2 were hypo-methylated in heat treated seeds. Taken together, our data suggest that heat stress during grain filling affects DNA methylation of germination-related genes and promotes seed germination in barley.</p>',
'date' => '2022-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35581415',
'doi' => '10.1007/s11103-022-01278-5',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:24:13',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 28 => array(
'id' => '4398',
'name' => 'Hexokinase 2 is a transcriptional target and a positive modulator ofAHR signalling.',
'authors' => 'Watzky M. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) regulates the expression of numerous genes in response to activation by agonists including xenobiotics. Although it is well appreciated that environmental signals and cell intrinsic features may modulate this transcriptional response, how it is mechanistically achieved remains poorly understood. We show that hexokinase 2 (HK2) a metabolic enzyme fuelling cancer cell growth, is a transcriptional target of AHR as well as a modulator of its activity. Expression of HK2 is positively regulated by AHR upon exposure to agonists both in human cells and in mice lung tissues. Conversely, over-expression of HK2 regulates the abundance of many proteins involved in the regulation of AHR signalling and these changes are linked with altered AHR expression levels and transcriptional activity. HK2 expression also shows a negative correlation with AHR promoter methylation in tumours, and these tumours with high HK2 expression and low AHR methylation are associated with a worse overall survival in patients. In sum, our study provides novel insights into how AHR signalling is regulated which may help our understanding of the context-specific effects of this pathway and may have implications in cancer.</p>',
'date' => '2022-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1093%2Fnar%2Fgkac360',
'doi' => '10.1093/nar/gkac360',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:32:40',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 29 => array(
'id' => '4561',
'name' => 'Corticosterone induces discrete epigenetic signatures in the dorsal andventral hippocampus that depend upon sex and genotype: focus on methylatedNr3c1 gene.',
'authors' => 'Caradonna S. G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The genomic effects of circulating glucocorticoids are particularly relevant in cortico-limbic structures, which express a high concentration of steroid hormone receptors. To date, no studies have investigated genomic differences in hippocampal subregions, namely the dorsal (dHPC) and ventral (vHPC) hippocampus, in preclinical models treated with exogenous glucocorticoids. Chronic oral corticosterone (CORT) in mouse is a pharmacological approach that disrupts the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, increases affective behavior, and induces genomic changes after stress in the HPC of wildtype (WT) mice and mice heterozygous for the gene coding for brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met (hMet), a variant associated with genetic susceptibility to stress. Using RNA-sequencing, we investigated the genomic signatures of oral CORT in the dHPC and vHPC of WT and hMet male and female mice, and examined sex and genotype differences in response to oral CORT. Males under CORT showed lower glycemia and increased anxiety- and depression-like behavior compared to females that showed instead opposite affective behavior in response to CORT. Rank-rank-hypergeometric overlap (RRHO) was used to identify genes from a continuous gradient of significancy that were concordant across groups. RRHO showed that CORT-induced differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in WT mice and hMet mice converged in the dHPC of males and females, while in the vHPC, DEGs converged in males and diverged in females. The vHPC showed a higher number of DEGs compared to the dHPC and exhibited sex differences related to glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-binding genes and epigenetic modifiers. Methyl-DNA-immunoprecipitation in the vHPC revealed differential methylation of the exons 1 and 1 of the GR gene (Nr3c1) in hMet females. Together, we report behavioral and endocrinological sex differences in response to CORT, as well as epigenetic signatures that i) differ in the dHPC and vHPC,ii) are distinct in males and females, and iii) implicate differential methylation of Nr3c1 selectively in hMet females.</p>',
'date' => '2022-03-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35296634',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41398-022-01864-7',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:03:20',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 30 => array(
'id' => '4364',
'name' => 'Methionine Metabolism Controls the B-cell EBV Epigenome andViral Latency',
'authors' => 'Guo R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) subverts host epigenetic pathways to switch between viral latency programs, colonize the B-cell compartment and reactivate. Within memory B-cells, the reservoir for lifelong infection, EBV genomic DNA and histone methylation marks restrict gene expression. But, this epigenetic strategy also enables EBV-infected tumors, including Burkitt lymphomas to evade immune detection. Little is known about host cell metabolic pathways that support EBV epigenome landscapes. We therefore used amino acid restriction, metabolomic and CRISPR approaches to identify that an abundant methionine supply, and interconnecting methionine and folate cycles, maintain Burkitt EBV gene silencing. Methionine restriction, or methionine cycle perturbation, hypomethylated EBV genomes, de-repressed latent membrane protein and lytic gene expression. Methionine metabolism also shaped EBV latency gene regulation required for B-cell immortalization. Dietary methionine restriction altered murine Burkitt xenograft metabolomes and de-repressed EBV immunogens in vivo. These results highlight epigenetic/immunometabolism crosstalk supporting the EBV B-cell lifecycle and suggest therapeutic approaches.</p>',
'date' => '2022-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2022.02.24.481783',
'doi' => '10.1101/2022.02.24.481783',
'modified' => '2022-08-04 15:50:37',
'created' => '2022-08-04 14:55:36',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 31 => array(
'id' => '4281',
'name' => 'Integrating SNPs-based genetic risk factor with blood epigenomicresponse of differentially arsenic-exposed rural subjects revealsdisease-associated signaling pathways.',
'authors' => 'Rehman Muhammad Yasir Abdur et al.',
'description' => '<p>Arsenic (As) contamination in groundwater is responsible for numerous adverse health outcomes among millions of people. Epigenetic alterations are among the most widely studied mechanisms of As toxicity. To understand how As exposure alters gene expression through epigenetic modifications, a systematic genome-wide study was designed to address the impact of multiple important single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to As exposure on the methylome of drinking water As-exposed rural subjects from Pakistan. Urinary As levels were used to stratify subjects into low, medium and high exposure groups. Genome-wide DNA methylation was investigated using MeDIP in combination with NimbleGen 2.1 M Deluxe Promotor arrays. Transcriptome levels were measured using Agilent 8 × 60 K expression arrays. Genotyping of selected SNPs (As3MT, DNMT1a, ERCC2, EGFR and MTHFR) was measured and an integrated genetic risk factor for each respondent was calculated by assigning a specific value to the measured genotypes based on known risk allele numbers. To select a representative model related to As exposure we compared 9 linear mixed models comprising of model 1 (including the genetic risk factor), model 2 (without the genetic risk factor) and models with individual SNPs incorporated into the methylome data. Pathway analysis was performed using ConsensusPathDB. Model 1 comprising the integrated genetic risk factor disclosed biochemical pathways including muscle contraction, cardio-vascular diseases, ATR signaling, GPCR signaling, methionine metabolism and chromatin modification in association with hypo- and hyper-methylated gene targets. A unique pathway (direct P53 effector) was found associated with the individual DNMT1a polymorphism due to hyper-methylation of CSE1L and TRRAP. Most importantly, we provide here the first evidence of As-associated DNA methylation in relation with gene expression of ATR, ATF7IP, TPM3, UBE2J2. We report the first evidence that integrating SNPs data with methylome data generates a more representative epigenome profile and discloses a better insight in disease risks of As-exposed individuals.</p>',
'date' => '2022-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.envpol.2021.118279',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118279',
'modified' => '2022-05-23 10:04:20',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 32 => array(
'id' => '4404',
'name' => 'Stella regulates the Development of Female Germline Stem Cells byModulating Chromatin Structure and DNA Methylation.',
'authors' => 'Hou Changliang et al.',
'description' => '<p>Female germline stem cells (FGSCs) have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into oocytes. , encoded by a maternal effect gene, plays an important role in oogenesis and early embryonic development. However, its function in FGSCs remains unclear. In this study, we showed that CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of promoted FGSC proliferation and reduced the level of genome-wide DNA methylation of FGSCs. Conversely, overexpression led to the opposite results, and enhanced FGSC differentiation. We also performed an integrative analysis of chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq), high-throughput genome-wide chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C), and use of our published epigenetic data. Results indicated that the binding sites of STELLA and active histones H3K4me3 and H3K27ac were enriched near the TAD boundaries. Hi-C analysis showed that overexpression attenuated the interaction within TADs, and interestingly enhanced the TAD boundary strength in STELLA-associated regions. Taking these findings together, our study not only reveals the role of in regulating DNA methylation and chromatin structure, but also provides a better understanding of FGSC development.</p>',
'date' => '2022-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9066111/',
'doi' => '10.7150/ijbs.69240',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:54:29',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 33 => array(
'id' => '4302',
'name' => 'Examining age-dependent DNA methylation patterns and gene expression inthe male and female mouse hippocampus.',
'authors' => 'Chinn Carlene A et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a well-characterized epigenetic modification involved in numerous molecular and cellular functions. Methylation patterns have also been associated with aging mechanisms. However, how DNA methylation patterns change within key brain regions involved in memory formation in an age- and sex-specific manner remains unclear. Here, we performed reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) from mouse dorsal hippocampus - which is necessary for the formation and consolidation of specific types of memories - in young and aging mice of both sexes. Overall, our findings demonstrate that methylation levels within the dorsal hippocampus are divergent between sexes during aging in genomic features correlating to mRNA functionality, transcription factor binding sites, and gene regulatory elements. These results define age-related changes in the methylome across genomic features and build a foundation for investigating potential target genes regulated by DNA methylation in an age- and sex-specific manner.</p>',
'date' => '2021-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.neurobiolaging.2021.08.006',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.08.006',
'modified' => '2022-05-30 09:54:05',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 34 => array(
'id' => '4100',
'name' => 'Therapy-induced DNA methylation inactivates MCT1 and renders tumor cells vulnerable to MCT4 inhibition',
'authors' => 'Catherine Vander Linden, Cyril Corbet, Estelle Bastien, Ruben Martherus, Céline Guilbaud, Laurenne Petit, Loris Wauthier, Axelle Loriot, Charles De Smet, Olivier Feron',
'description' => '<p><span>Metabolic plasticity in cancer cells makes use of metabolism-targeting agents very challenging. Drug-induced metabolic rewiring may, however, uncover vulnerabilities that can be exploited. We report that resistance to glycolysis inhibitor 3-bromopyruvate (3-BrPA) arises from DNA methylation in treated cancer cells and subsequent silencing of the monocarboxylate transporter MCT1. We observe that, unexpectedly, 3-BrPA-resistant cancer cells mostly rely on glycolysis to sustain their growth, with MCT4 as an essential player to support lactate flux. This shift makes cancer cells particularly suited to adapt to hypoxic conditions and resist OXPHOS inhibitors and anti-proliferative chemotherapy. In contrast, blockade of MCT4 activity in 3-BrPA-exposed cancer cells with diclofenac or genetic knockout, inhibits growth of derived spheroids and tumors in mice. This study supports a potential mode of collateral lethality according to which metabolic adaptation of tumor cells to a first-line therapy makes them more responsive to a second-line treatment.</span></p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)00551-9#%20',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109202',
'modified' => '2021-06-03 16:04:34',
'created' => '2021-06-03 14:16:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 35 => array(
'id' => '4330',
'name' => 'Epigenetic Plasticity Enables CNS-Trafficking of EBV-infectedB Lymphocytes',
'authors' => 'Soldan S. S. et al. ',
'description' => '<p>Subpopulations of B-lymphocytes traffic to different sites and organs to provide diverse and tissue-specific functions. Here, we provide evidence that epigenetic differences confer a neuroinvasive phenotype. An EBV+ B cell lymphoma cell line (M14) with low frequency trafficking to the CNS was neuroadapted to generate a highly neuroinvasive B-cell population (MUN14). MUN14 B cells efficiently infiltrated the CNS within one week and produced neurological pathologies. We compared the gene expression profiles of viral and cellular genes using RNA-Seq and identified one viral (EBNA1) and several cellular gene candidates, including secreted phosphoprotein 1/osteopontin (SPP1/OPN), neuron navigator 3 (NAV3), CXCR4, and germinal center-associated signaling and motility protein (GCSAM) that were selectively upregulated in MUN14. ATAC-Seq and ChIP-qPCR revealed that these gene expression changes correlated with epigenetic changes at gene regulatory elements. The neuroinvasive phenotype could be attenuated with a neutralizing antibody to OPN, confirming the functional role of this protein in trafficking EBV+ B cells to the CNS. These studies indicate that B-cell trafficking to the CNS can be acquired by epigenetic adaptations and provide a new model to study B-cell neuroinvasion associated CNS lymphoma and autoimmune disease of the CNS, including multiple sclerosis (MS).</p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34106998',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.ppat.1009618',
'modified' => '2022-08-03 16:11:53',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 36 => array(
'id' => '4354',
'name' => 'Dnmt1 has de novo activity targeted to transposable elements',
'authors' => 'Haggerty C. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation plays a critical role during development, particularly in repressing retrotransposons. The mammalian methylation landscape is dependent on the combined activities of the canonical maintenance enzyme Dnmt1 and the de novo Dnmts, 3a and 3b. Here, we demonstrate that Dnmt1 displays de novo methylation activity in vitro and in vivo with specific retrotransposon targeting. We used whole-genome bisulfite and long-read Nanopore sequencing in genetically engineered methylation-depleted mouse embryonic stem cells to provide an in-depth assessment and quantification of this activity. Utilizing additional knockout lines and molecular characterization, we show that the de novo methylation activity of Dnmt1 depends on Uhrf1, and its genomic recruitment overlaps with regions that enrich for Uhrf1, Trim28 and H3K9 trimethylation. Our data demonstrate that Dnmt1 can catalyze DNA methylation in both a de novo and maintenance context, especially at retrotransposons, where this mechanism may provide additional stability for long-term repression and epigenetic propagation throughout development.</p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34140676',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41594-021-00603-8',
'modified' => '2022-08-03 16:55:11',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 37 => array(
'id' => '4135',
'name' => 'Alterations of DNA Methylation Caused by Cold Plasma Treatment Restore Delayed Germination of Heat-Stressed Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seeds',
'authors' => 'Suriyasak, C. et al. ',
'description' => '<p>In rice (Oryza sativa L.), seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling exhibit delayed germination because of DNA methylation levels at promoters of abscisic acid (ABA, a germination-inhibiting hormone) catabolism genes and α-amylase (starchhydrolyzing enzyme) genes, affecting their expression levels. Cold atmospheric plasma is known as an innovative and sustainable energy that has positive effects on the growth and development of many plant species. We, therefore, treated seeds that matured under heat stress with cold plasma and found that subsequent germination was significantly restored; genes involved in ABA biosynthesis (OsNCED2 and OsNCED5) were downregulated, whereas genes involved in ABA catabolism (OsABA8′OH1 and OsABA8′OH3) and α-amylase genes (OsAmy1A, OsAmy1C, OsAmy3B, and OsAmy3E) were upregulated. Cold plasma treatment caused significant hypermethylation of the OsNCED5 promoter and hypomethylation of OsAmy1C and OsAmy3E promoters, which matched their expression patterns. We suggest that cold plasma treatment can significantly improve the germination of rice seeds affected by heat stress by affecting epigenetic regulation.</p>',
'date' => '2021-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1021%2Facsagscitech.0c00070',
'doi' => '10.1021/acsagscitech.0c00070',
'modified' => '2021-12-10 17:15:10',
'created' => '2021-12-06 15:53:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 38 => array(
'id' => '4057',
'name' => 'Prenatal Stress Leads to the Altered Maturation of Corticostriatal SynapticPlasticity and Related Behavioral Impairments Through EpigeneticModifications of Dopamine D2 Receptor in Mice.',
'authors' => 'Li, Yingchun and Rong, Jing and Zhong, Haiquan and Liang, Min and Zhu,Chunting and Chang, Fei and Zhou, Rong',
'description' => '<p>Prenatal stress (PRS) had a long-term adverse effect on motor behaviors. Corticostriatal synaptic plasticity, a cellular basis for motor controlling, has been proven to participate in the pathogenesis of many behavior disorders. Based on the reports about the involvement of epigenetic DNA alterations in PRS-induced long-term effects, this research investigated the influence of PRS on the development and maturation of corticostriatal synaptic plasticity and related behaviors and explored the underlying epigenetic mechanism. Subjects were male offspring of dams that were exposed to stress three times per day from the 10th day of pregnancy until delivery. The development and maturation of plasticity at corticostriatal synapses, dopamine signaling, behavioral habituation, and DNA methylation were examined and analyzed. Control mice expressed long-term potentiation (LTP) at corticostriatal synapses during postnatal days (PD) 12-14 and produced long-term depression (LTD) during PD 20-60. However, PRS mice exhibited sustained LTP during PD 12-60. The treatment with dopamine 2 receptor (D2R) agonist quinpirole recovered striatal LTD and improved the impaired behavioral habituation in PD 45 adult PRS mice. Additionally, adult PRS mice showed reduced D2R, excess DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), increased binding of DNMT1 to D2R promoter, and hypermethylation at D2R promoter in the striatum. The DNMT1 inhibitor 5-aza-deoxycytidine restored striatal synaptic plasticity and improved behavioral habituation in adult PRS mice via D2R-mediated dopamine signaling. DNMT1-associated D2R hypermethylation is responsible for altering the maturation of plasticity at corticostriatal synapses and impairing the behavioral habituation in PRS mice.</p>',
'date' => '2021-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32935231',
'doi' => '10.1007/s12035-020-02127-6',
'modified' => '2021-02-19 17:23:03',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 39 => array(
'id' => '4200',
'name' => 'Comparative genome-wide methylation analysis of longissimus dorsi musclesin Yorkshire and Wannanhua pigs.',
'authors' => 'Li, X-J et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation was one of the earliest discovered epigenetic modifications in vertebrates, and is an important epigenetic mechanism involved in the expression of genes in many biological processes, including muscle growth and development. Its effects on economically important traits are evidenced in reported differences in meat quality traits between Chinese indigenous pig breeds (Wannanhua pig) and Western commercial pig breeds (Yorkshire pig), and this presents a unique model for analyzing the effects of DNA methylation on these traits. In the present study, a whole genome DNA methylation analysis was performed on the two breeds using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation. GO functional enrichment and pathway enrichment analyses identified differentially methylated genes primarily associated with fatty acid metabolism, biological processes of muscle development and signaling pathways related to muscle development and pork quality. Differentially methylated genes were verified by sodium pyrosequencing, and the results were consistent with the sequencing results. The results of the integrative analysis between DNA methylation and gene expression revealed that the DNA methylation levels showed a significantly negative correlation with gene expression levels around the transcription start site of genes. In total, 41 genes were both differentially expressed and methylated; these genes were related to fat metabolism, lipid metabolism and skeletal muscle development. This study could help further explore the molecular mechanisms and phenotypic differences in pig growth and development among different breeds.</p>',
'date' => '2020-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33301219',
'doi' => '10.1111/age.13029',
'modified' => '2022-01-06 14:43:32',
'created' => '2021-12-06 15:53:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 40 => array(
'id' => '4041',
'name' => 'Mechanism of delayed seed germination caused by high temperature duringgrain filling in rice (Oryza sativa L.).',
'authors' => 'Suriyasak, Chetphilin and Oyama, Yui and Ishida, Toshiaki and Mashiguchi,Kiyoshi and Yamaguchi, Shinjiro and Hamaoka, Norimitsu and Iwaya-Inoue,Mari and Ishibashi, Yushi',
'description' => '<p>High temperature during grain filling considerably reduces yield and quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.); however, how high temperature affects seed germination of the next generation is not yet well understood. Here, we report that seeds from plants exposed to high temperature during the grain filling stage germinated significantly later than seeds from unstressed plants. This delay remained even after dormancy release treatments, suggesting that it was not due to primary seed dormancy determined during grain filling. In imbibed embryos of heat-stressed seeds, expression of abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis genes (OsNCEDs) was higher than in those of control seeds, whereas that of ABA catabolism genes (OsABA8'OHs) was lower. In the aleurone layer, despite no change in GA signaling as evidenced by no effect of heat stress on OsGAMYB gene expression, the transcripts of α-amylase genes OsAmy1C, OsAmy3B, and OsAmy3E were significantly down-regulated in heat-stressed seeds in comparison with controls. Changes in promoter methylation levels were consistent with transcriptional changes of ABA catabolism-related and α-amylase genes. These data suggest that high temperature during grain filling results in DNA methylation of ABA catabolism-related and α-amylase gene promoters, delaying germination of heat-stressed seeds.</p>',
'date' => '2020-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33060675',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-020-74281-9',
'modified' => '2021-02-19 12:09:29',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 41 => array(
'id' => '4094',
'name' => 'Network integration and modelling of dynamic drug responses at multi-omicslevels.',
'authors' => 'Selevsek, Nathalie and Caiment, Florian and Nudischer, Ramona and Gmuender,Hans and Agarkova, Irina and Atkinson, Francis L and Bachmann, Ivo andBaier, Vanessa and Barel, Gal and Bauer, Chris and Boerno, Stefan and Bosc,Nicolas and Clayton, Olivia and ',
'description' => '<p>Uncovering cellular responses from heterogeneous genomic data is crucial for molecular medicine in particular for drug safety. This can be realized by integrating the molecular activities in networks of interacting proteins. As proof-of-concept we challenge network modeling with time-resolved proteome, transcriptome and methylome measurements in iPSC-derived human 3D cardiac microtissues to elucidate adverse mechanisms of anthracycline cardiotoxicity measured with four different drugs (doxorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin and daunorubicin). Dynamic molecular analysis at in vivo drug exposure levels reveal a network of 175 disease-associated proteins and identify common modules of anthracycline cardiotoxicity in vitro, related to mitochondrial and sarcomere function as well as remodeling of extracellular matrix. These in vitro-identified modules are transferable and are evaluated with biopsies of cardiomyopathy patients. This to our knowledge most comprehensive study on anthracycline cardiotoxicity demonstrates a reproducible workflow for molecular medicine and serves as a template for detecting adverse drug responses from complex omics data.</p>',
'date' => '2020-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33060801',
'doi' => '10.1038/s42003-020-01302-8',
'modified' => '2021-03-17 17:16:56',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 42 => array(
'id' => '4009',
'name' => 'Frataxin gene editing rescues Friedreich's ataxia pathology in dorsal rootganglia organoid-derived sensory neurons.',
'authors' => 'Mazzara, PG and Muggeo, S and Luoni, M and Massimino, L and Zaghi, M andValverde, PT and Brusco, S and Marzi, MJ and Palma, C and Colasante, Gand Iannielli, A and Paulis, M and Cordiglieri, C and Giannelli, SG andPodini, P and Gellera, C and Ta',
'description' => '<p>Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal-recessive neurodegenerative and cardiac disorder which occurs when transcription of the FXN gene is silenced due to an excessive expansion of GAA repeats into its first intron. Herein, we generate dorsal root ganglia organoids (DRG organoids) by in vitro differentiation of human iPSCs. Bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing show that DRG organoids present a transcriptional signature similar to native DRGs and display the main peripheral sensory neuronal and glial cell subtypes. Furthermore, when co-cultured with human intrafusal muscle fibers, DRG organoid sensory neurons contact their peripheral targets and reconstitute the muscle spindle proprioceptive receptors. FRDA DRG organoids model some molecular and cellular deficits of the disease that are rescued when the entire FXN intron 1 is removed, and not with the excision of the expanded GAA tract. These results strongly suggest that removal of the repressed chromatin flanking the GAA tract might contribute to rescue FXN total expression and fully revert the pathological hallmarks of FRDA DRG neurons.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-21',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32826895',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41467-020-17954-3',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:12:57',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 43 => array(
'id' => '4017',
'name' => 'Integrated analysis of DNA methylation profile of HLA-G gene andimaging in coronary heart disease: Pilot study.',
'authors' => 'Schiano, C and Benincasa, G and Infante, T and Franzese, M and Castaldo, Rand Fiorito, C and Mansueto, G and Grimaldi, V and Della, Valle G andFatone, G and Soricelli, A and Nicoletti, GF and Ruocco, A and Mauro, Cand Salvatore, M and Napoli, C',
'description' => '<p>AIMS: Immune endothelial inflammation, underlying coronary heart disease (CHD) related phenotypes, could provide new insight into the pathobiology of the disease. We investigated DNA methylation level of the unique CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients and evaluated the correlation with cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) features. METHODS: Thirty-two patients that underwent CCTA for suspected CHD were enrolled for this study. Obstructive CHD group included fourteen patients, in which there was a stenosis greater than or equal to 50\% in one or more of the major coronary arteries detected; whereas subjects with Calcium (Ca) Score = 0, uninjured coronaries and with no obstructive CHD (no critical stenosis, NCS) were considered as control subjects (n = 18). For both groups, DNA methylation profile of the whole 5'UTR-CpG island of HLA-G was measured. The plasma soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) levels were detected in all subjects by specific ELISA assay. Statistical analysis was performed using R software. RESULTS: For the first time, our study reported that 1) a significant hypomethylation characterized three specific fragments (B, C and F) of the 5'UTR-CpG island (p = 0.05) of HLA-G gene in CHD patients compared to control group; 2) the hypomethylation level of one specific fragment of 161bp (+616/+777) positively correlated with coronary Ca score, a relevant parameter of CCTA (p<0.05) between two groups evaluated and was predictive for disease severity. CONCLUSIONS: Reduced levels of circulating HLA-G molecules could derive from epigenetic marks. Epigenetics phenomena induce hypomethylation of specific regions into 5'UTR-CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients with obstructive non critical stenosis vs coronary stenosis individuals.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-13',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32790754',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0236951',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:37:03',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 44 => array(
'id' => '4021',
'name' => 'Comparative DNA methylome analysis of estrus ewes reveals the complexregulatory pathways of sheep fecundity.',
'authors' => 'Miao, X and Luo, Q and Xie, L and Zhao, H and Qin, X',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND/AIMS: Sheep are important livestock with variant ovulation rate and fertility. Dorset sheep is a typical breed with low prolificacy, whereas Small Tail Han sheep with FecB mutation (HanBB) have hyperprolificacy. Our previous studies have revealed the gene expression difference between the ovaries from Dorset and HanBB sheep contributes to the difference of fecundity, however, what leads to these gene expression difference remains unclear. DNA methylation, an important epigenetic process, plays a crucial role in gene expression regulation. METHODS: In the present study, we constructed a methylated DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) strategy to investigate the differentially methylated genes between the Dorset and HanBB ovaries. RESULTS: Our findings suggest the genes involved in immune response, branched-chain amino acid metabolism, cell growth and cell junction were differentially methylated in or around the gene body regions. CONCLUSIONS: These findings provide prospective insights on the epigenetic basis of sheep fecundity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32753034',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12958-020-00633-9',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:45:28',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 45 => array(
'id' => '4028',
'name' => 'Methylation in pericytes after acute injury promotes chronic kidneydisease.',
'authors' => 'Chou, YH and Pan, SY and Shao, YH and Shih, HM and Wei, SY andLai, CF and Chiang, WC and Schrimpf, C and Yang, KC and Lai, LC andChen, YM and Chu, TS and Lin, SL',
'description' => '<p>The origin and fate of renal myofibroblasts is not clear after acute kidney injury (AKI). Here, we demonstrate that myofibroblasts were activated from quiescent pericytes (qPericytes) and the cell numbers increased after ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced AKI (IRI-AKI). Myofibroblasts underwent apoptosis during renal recovery but one-fifth of them survived in the recovered kidneys on day 28 after IRI-AKI and their cell numbers increased again after day 56. Microarray data showed the distinctive gene expression patterns of qPericytes, activated pericytes (aPericytes, myofibroblasts), and inactivated pericytes (iPericytes) isolated from kidneys before, on day 7, and on day 28 after IRI-AKI. Hypermethylation of the Acta2 repressor Ybx2 during IRI-AKI resulted in epigenetic modification of iPericytes to promote the transition to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and aggravated fibrogenesis induced by a second AKI induced by adenine. Mechanistically, transforming growth factor-β1 decreased the binding of YBX2 to the promoter of Acta2 and induced Ybx2 hypermethylation, thereby increasing α-smooth muscle actin expression in aPericytes. Demethylation by 5-azacytidine recovered the microvascular stabilizing function of aPericytes, reversed the profibrotic property of iPericytes, prevented AKI-CKD transition, and attenuated fibrogenesis induced by a second adenine-AKI. In conclusion, intervention to erase hypermethylation of pericytes after AKI provides a strategy to stop the transition to CKD.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32749240',
'doi' => '10.1172/JCI135773.',
'modified' => '2020-12-18 13:25:55',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 46 => array(
'id' => '3998',
'name' => 'Integrated epigenetic biomarkers in circulating cell-free DNA as a robust classifier for pancreatic cancer.',
'authors' => 'Cao F, Wei A, Hu X, He Y, Zhang J, Xia L, Tu K, Yuan J, Guo Z, Liu H, Xie D, Li A',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: The high lethal rate of pancreatic cancer is partly due to a lack of efficient biomarkers for screening and early diagnosis. We attempted to develop effective and noninvasive methods using 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) markers from circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for the detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). RESULTS: A 24-feature 5mC model that can accurately discriminate PDAC from healthy controls (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.977, sensitivity = 0.824, specificity = 1) and a 5hmC prediction model with 27 features demonstrated excellent detection power in two distinct validation sets (AUC = 0.992 and 0.960, sensitivity = 0.786 and 0.857, specificity = 1 and 0.993). The 51-feature model combining 5mC and 5hmC markers outperformed both of the individual models, with an AUC of 0.997 (sensitivity = 0.938, specificity = 0.955) and particularly an improvement in the prediction sensitivity of PDAC. In addition, the weighted diagnosis score (wd-score) calculated with the 5hmC model can distinguish stage I patients from stage II-IV patients. CONCLUSIONS: Both 5mC and 5hmC biomarkers in cfDNA are effective in PDAC detection, and the 5mC-5hmC integrated model significantly improve the detection sensitivity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-07-23',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32703318',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13148-020-00898-2',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 14:43:06',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 47 => array(
'id' => '3985',
'name' => 'Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Nuzzo PV, Berchuck JE, Korthauer K, Spisak S, Nassar AH, Abou Alaiwi S, Chakravarthy A, Shen SY, Bakouny Z, Boccardo F, Steinharter J, Bouchard G, Curran CR, Pan W, Baca SC, Seo JH, Lee GM, Michaelson MD, Chang SL, Waikar SS, Sonpavde G, Irizarry RA, Pome',
'description' => '<p>Improving early cancer detection has the potential to substantially reduce cancer-related mortality. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) is a highly sensitive assay capable of detecting early-stage tumors. We report accurate classification of patients across all stages of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in plasma (area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.99) and demonstrate the validity of this assay to identify patients with RCC using urine cell-free DNA (cfDNA; AUROC of 0.86).</p>',
'date' => '2020-06-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32572266',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41591-020-0933-1',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 15:13:49',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 48 => array(
'id' => '3984',
'name' => 'Detection and discrimination of intracranial tumors using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Nassiri F, Chakravarthy A, Feng S, Shen SY, Nejad R, Zuccato JA, Voisin MR, Patil V, Horbinski C, Aldape K, Zadeh G, De Carvalho DD',
'description' => '<p>Definitive diagnosis of intracranial tumors relies on tissue specimens obtained by invasive surgery. Noninvasive diagnostic approaches provide an opportunity to avoid surgery and mitigate unnecessary risk to patients. In the present study, we show that DNA-methylation profiles from plasma reveal highly specific signatures to detect and accurately discriminate common primary intracranial tumors that share cell-of-origin lineages and can be challenging to distinguish using standard-of-care imaging.</p>',
'date' => '2020-06-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32572265',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41591-020-0932-2',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 15:14:45',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 49 => array(
'id' => '3942',
'name' => 'DNA methylation enzymes and PRC1 restrict B-cell Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein expression.',
'authors' => 'Guo R, Zhang Y, Teng M, Jiang C, Schineller M, Zhao B, Doench JG, O'Reilly RJ, Cesarman E, Giulino-Roth L, Gewurz BE',
'description' => '<p>To accomplish the remarkable task of lifelong infection, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) switches between four viral genome latency and lytic programmes to navigate the B-cell compartment and evade immune responses. The transforming programme, consisting of highly immunogenic EBV nuclear antigen (EBNA) and latent membrane proteins (LMPs), is expressed in newly infected B lymphocytes and in post-transplant lymphomas. On memory cell differentiation and in most EBV-associated Burkitt's lymphomas, all but one viral antigen are repressed for immunoevasion. To gain insights into the epigenetic mechanisms that restrict immunogenic oncoprotein expression, a genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screen was performed in EBV and Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Here, we show that the ubiquitin ligase ubiquitin-like PHD and RING finger domain-containing protein 1 (UHRF1) and its DNA methyltransferase partner DNA methyltransferase I (DNMT1) are critical for the restriction of EBNA and LMP expression. All UHRF1 reader and writer domains were necessary for silencing and DNMT3B was identified as an upstream viral genome CpG methylation initiator. Polycomb repressive complex I exerted a further layer of control over LMP expression, suggesting a second mechanism for latency programme switching. UHRF1, DNMT1 and DNMT3B are upregulated in germinal centre B cells, the Burkitt's lymphoma cell of origin, providing a molecular link between B-cell state and the EBV latency programme. These results suggest rational therapeutic targets to manipulate EBV oncoprotein expression.</p>',
'date' => '2020-05-18',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32424339',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41564-020-0724-y',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:24:57',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 50 => array(
'id' => '3926',
'name' => 'TET-Mediated Hypermethylation Primes SDH-Deficient Cells for HIF2α-Driven Mesenchymal Transition.',
'authors' => 'Morin A, Goncalves J, Moog S, Castro-Vega LJ, Job S, Buffet A, Fontenille MJ, Woszczyk J, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Letouzé E, Favier J',
'description' => '<p>Loss-of-function mutations in the SDHB subunit of succinate dehydrogenase predispose patients to aggressive tumors characterized by pseudohypoxic and hypermethylator phenotypes. The mechanisms leading to DNA hypermethylation and its contribution to SDH-deficient cancers remain undemonstrated. We examine the genome-wide distribution of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and their correlation with RNA expression in SDHB-deficient tumors and murine Sdhb cells. We report that DNA hypermethylation results from TET inhibition. Although it preferentially affects PRC2 targets and known developmental genes, PRC2 activity does not contribute to the DNA hypermethylator phenotype. We also prove, in vitro and in vivo, that TET silencing, although recapitulating the methylation profile of Sdhb cells, is not sufficient to drive their EMT-like phenotype, which requires additional HIF2α activation. Altogether, our findings reveal synergistic roles of TET repression and pseudohypoxia in the acquisition of metastatic traits, providing a rationale for targeting HIF2α and DNA methylation in SDH-associated malignancies.</p>',
'date' => '2020-03-31',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32234487',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.022',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:50:11',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 51 => array(
'id' => '3920',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Mantle Edge and Mantle Central from Pearl Oyster Pinctada fucata martensii.',
'authors' => 'Zhang J, Luo S, Gu Z, Deng Y, Jiao Y',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a type of epigenetic modification that alters gene expression without changing the DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. In this study, we identified six DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) genes and two methyl-CpG binding domain protein2 (MBD2) gene from Pinctada fucata martensii. We also analyzed the genome-wide DNA methylation levels of mantle edge (ME) and mantle central (MC) from P. f. martensii via methylated immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-Seq). Results revealed that both ME and MC had 122 million reads, and had 58,702 and 55,721 peaks, respectively. The obtained methylation patterns of gene elements and repeats showed that the methylation of the protein-coding genes, particularly intron and coding exons (CDSs), was more frequent than that of other genomic elements in the pearl oyster genome. We combined the methylation data with the RNA-seq data of the ME and MC of P. f. martensii and found that promoter, CDS, and intron methylation levels were positively correlated with gene expression levels except the highest gene expression level. We also identified 313 differential methylation genes (DMGs) and annotated 212 of them. These DMGs were significantly enriched in 30 pathways, such as amino acid and protein metabolism, energy metabolism, terpenoid synthesis, and immune-related pathways. This study comprehensively analyzed the methylomes of biomineralization-related tissues and helped enhance our understanding of the regulatory mechanism underlying shell formation.</p>',
'date' => '2020-03-06',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32140888',
'doi' => '10.1007/s10126-020-09957-4',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:58:42',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 52 => array(
'id' => '3859',
'name' => 'Preterm birth is associated with epigenetic programming of transgenerational hypertension in mice.',
'authors' => 'Dumeige L, Nehlich M, Viengchareun S, Perrot J, Pussard E, Lombès M, Martinerie L',
'description' => '<p>Renal and cardiovascular complications of prematurity are well established, notably the development of hypertension in adulthood. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Our objective was to investigate the impact of prematurity on the ontogenesis of renal corticosteroid pathways, to evaluate its implication in perinatal renal complications and in the emergence of hypertension in adulthood. Swiss CD1 pregnant mice were injected with lipopolysaccharides at 18 days of gestation (E18) to induce prematurity at E18.5. Pups were sacrificed at birth, 7 days and 6 months of life. Second (F2) and third (F3) generations, established by mating prematurely born adult females with wild-type males, were also analyzed. Former preterm males developed hypertension at M6 (P < 0.0001). We found robust activation of renal corticosteroid target gene transcription at birth in preterm mice (αENaC (+45%), Gilz (+85%)), independent of any change in mineralocorticoid or glucocorticoid receptor expression. The offspring of the preterm group displayed increased blood pressure in F2 and F3, associated with increased renal Gilz mRNA expression, despite similar MR or GR expression and plasma corticosteroid levels measured by LC-MS/MS. Gilz promoter methylation measured by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR was reduced with a negative correlation between methylation and expression (P = 0.0106). Our study demonstrates prematurity-related alterations in renal corticosteroid signaling pathways, with transgenerational inheritance of blood pressure dysregulation and epigenetic Gilz regulation up to the third generation. This study provides a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in essential hypertension, which could partly be due to perinatal epigenetic programming from previous generations.</p>',
'date' => '2020-01-24',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31974504',
'doi' => '10.1038/s12276-020-0373-5',
'modified' => '2020-03-20 17:55:50',
'created' => '2020-03-13 13:45:54',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 53 => array(
'id' => '3855',
'name' => 'Alteration in global DNA methylation status following preconditioning injury influences axon growth competence of the sensory neurons.',
'authors' => 'Shin HY, Kim K, Kwon MJ, Oh YJ, Kim EH, Kim HS, Hong CP, Lee JH, Lee K, Kim BG',
'description' => '<p>Preconditioning peripheral nerve injury primes the sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) to acquire axon regeneration competence. Transcription of a large set of regeneration-associated-genes (RAGs) contributes to the enhanced intrinsic axonal regeneration capacity. However, the mechanism underlying the coordinated upregulation of RAGs orchestrated by preconditioning injury is unclear. We sought to determine potential influence of DNA methylation change on transcriptional activation of RAGs in the L4-L6 DRGs following sciatic nerve injury. Genome-wide sequencing revealed that about 20% of the methylated DNA fragments were differentially methylated, and >3000 genes contained differentially methylated regions. Not only demethylation but also increased methylation was observed to a similar extent. The change in the global DNA methylation did not correlate with the gene expression level of most genes, including the well-documented RAGs. However, pharmacological inhibition or activation of DNA methylation markedly attenuated the axon growth capacity of the preconditioned DRG neurons. Pharmacological perturbation of DNA methylation resulted in simultaneous downregulation of many highly overlapping non-transcription factor RAGs, which was accompanied by a concurrent, robust upregulation of SOCS3 and Serpine1. Overexpression of SOCS3 and Serpine1 in the DRG neurons overrode injury-induced axon growth competence, corroborating their roles as the negative regulators of axon regeneration. We conclude that the injury-induced global alteration of DNA methylome strongly influences the axon growth competence in preconditioned DRG neurons. Our results also suggest a possibility that perturbing DNA methylome changes might lead to the upregulation of negative regulator RAGs thereby attenuating axon growth capacity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-01-08',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31926166',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113177',
'modified' => '2020-03-20 17:59:09',
'created' => '2020-03-13 13:45:54',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 54 => array(
'id' => '3814',
'name' => 'Lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced changes in rodent neural progenitors and rescues cognition.',
'authors' => 'Zanni G, Goto S, Fragopoulou AF, Gaudenzi G, Naidoo V, Di Martino E, Levy G, Dominguez CA, Dethlefsen O, Cedazo-Minguez A, Merino-Serrais P, Stamatakis A, Hermanson O, Blomgren K',
'description' => '<p>Cranial radiotherapy in children has detrimental effects on cognition, mood, and social competence in young cancer survivors. Treatments harnessing hippocampal neurogenesis are currently of great relevance in this context. Lithium, a well-known mood stabilizer, has both neuroprotective, pro-neurogenic as well as antitumor effects, and in the current study we introduced lithium treatment 4 weeks after irradiation. Female mice received a single 4 Gy whole-brain radiation dose on postnatal day (PND) 21 and were randomized to 0.24% Li2CO chow or normal chow from PND 49 to 77. Hippocampal neurogenesis was assessed on PND 77, 91, and 105. We found that lithium treatment had a pro-proliferative effect on neural progenitors, but neuronal integration occurred only after it was discontinued. Also, the treatment ameliorated deficits in spatial learning and memory retention observed in irradiated mice. Gene expression profiling and DNA methylation analysis identified two novel factors related to the observed effects, Tppp, associated with microtubule stabilization, and GAD2/65, associated with neuronal signaling. Our results show that lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced loss of hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive impairment even when introduced long after the injury. We propose that lithium treatment should be intermittent in order to first make neural progenitors proliferate and then, upon discontinuation, allow them to differentiate. Our findings suggest that pharmacological treatment of cognitive so-called late effects in childhood cancer survivors is possible.</p>',
'date' => '2019-11-14',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31723242',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41380-019-0584-0',
'modified' => '2019-12-05 10:58:44',
'created' => '2019-12-02 15:25:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 55 => array(
'id' => '3773',
'name' => 'Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA.',
'authors' => 'Shen SY, Burgener JM, Bratman SV, De Carvalho DD',
'description' => '<p>Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) comprises small DNA fragments derived from normal and tumor tissue that are released into the bloodstream. Recently, methylation profiling of cfDNA as a liquid biopsy tool has been gaining prominence due to the presence of tissue-specific markers in cfDNA. We have previously reported cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) as a sensitive, low-input, cost-efficient and bisulfite-free approach to profiling DNA methylomes of plasma cfDNA. cfMeDIP-seq is an extension of a previously published MeDIP-seq protocol and is adapted to allow for methylome profiling of samples with low input (ranging from 1 to 10 ng) of DNA, which is enabled by the addition of 'filler DNA' before immunoprecipitation. This protocol is not limited to plasma cfDNA; it can also be applied to other samples that are naturally sheared and at low availability (e.g., urinary cfDNA and cerebrospinal fluid cfDNA), and is potentially applicable to other applications beyond cancer detection, including prenatal diagnostics, cardiology and monitoring of immune response. The protocol presented here should enable any standard molecular laboratory to generate cfMeDIP-seq libraries from plasma cfDNA in ~3-4 d.</p>',
'date' => '2019-08-30',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31471598',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41596-019-0202-2',
'modified' => '2019-10-02 17:07:45',
'created' => '2019-10-02 16:16:55',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 56 => array(
'id' => '3761',
'name' => 'Single-base methylome profiling of the giant kelp Saccharina japonica reveals significant differences in DNA methylation to microalgae and plants.',
'authors' => 'Fan X, Han W, Teng L, Jiang P, Zhang X, Xu D, Li C, Pellegrini M, Wu C, Wang Y, Kaczurowski MJS, Lin X, Tirichine L, Mock T, Ye N',
'description' => '<p>Brown algae have convergently evolved plant-like body plans and reproductive cycles, which in plants are controlled by differential DNA methylation. Here we provide the first single-base methylome profiles of haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes of a multicellular alga. Although only c. 1.4% of cytosines in Saccharina japonica were methylated mainly at CHH sites and characterised by 5-methylcytosine (5mC), there were significant differences between life-cycle stages. DNA methyltransferase 2 (DNMT2), known to efficiently catalyze tRNA methylation, is assumed to methylate the genome of S. japonica in the structural context of tRNAs as the genome does not encode any other DNA methyltransferases. Circular and long non-coding RNA genes were the most strongly methylated regulatory elements in S. japonica. Differential expression of genes was negatively correlated with DNA methylation with the highest methylation levels measured in both haploid gametophytes. Hypomethylated and highly expressed genes in diploid sporophytes included genes involved in morphogenesis and halogen metabolism. Our data give evidence that cytosine methylation, although occurring at a low level, is significantly contributing to the formation of different life-cycle stages, tissue differentiation, and metabolism in brown algae.</p>',
'date' => '2019-08-16',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31419316',
'doi' => '10.1111/nph.16125',
'modified' => '2019-10-03 10:04:08',
'created' => '2019-10-02 16:16:55',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 57 => array(
'id' => '3720',
'name' => 'Genome-wide methylation in alcohol use disorder subjects: implications for an epigenetic regulation of the cortico-limbic glucocorticoid receptors (NR3C1).',
'authors' => 'Gatta E, Grayson DR, Auta J, Saudagar V, Dong E, Chen Y, Krishnan HR, Drnevich J, Pandey SC, Guidotti A',
'description' => '<p>Environmental factors, including substance abuse and stress, cause long-lasting changes in the regulation of gene expression in the brain via epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation. We examined genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the prefrontal cortex (PFC, BA10) of 25 pairs of control and individuals with alcohol use disorder (AUD), using the Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip. We identified 5254 differentially methylated CpGs (p < 0.005). Bioinformatic analyses highlighted biological processes containing genes related to stress adaptation, including the glucocorticoid receptor (encoded by NR3C1). Considering that alcohol is a stressor, we focused our attention on differentially methylated regions of the NR3C1 gene and validated the differential methylation of several genes in the NR3C1 network. Chronic alcohol drinking results in a significant increased methylation of the NR3C1 exon variant 1, with a particular increase in the levels of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine over 5-methylcytosine. These changes in DNA methylation were associated with reduced NR3C1 mRNA and protein expression levels in PFC, as well as other cortico-limbic regions of AUD subjects when compared with controls. Furthermore, we show that the expression of several stress-responsive genes (e.g., CRF, POMC, and FKBP5) is altered in the PFC of AUD subjects. These stress-response genes were also changed in the hippocampus, a region that is highly susceptible to stress. These data suggest that alcohol-dependent aberrant DNA methylation of NR3C1 and consequent changes in other stress-related genes might be fundamental in the pathophysiology of AUD and lay the groundwork for treatments targeting the epigenetic mechanisms regulating NR3C1 in AUD.</p>',
'date' => '2019-06-25',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31239533',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41380-019-0449-6',
'modified' => '2019-07-04 18:07:16',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 58 => array(
'id' => '3604',
'name' => 'DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene in a CUMS model of depression.',
'authors' => 'Xiang D, Xiao J, Fu L, Yao L, Wan Q, Xiao L, Zhu F, Wang G, Liu Z',
'description' => '<p>Tacr2, the gene encoding the NK2 receptor, belongs to G protein-coupled receptors. Accumulating evidence has indicated that the tachykinin receptors may contribute to the pathophysiology of depression. During the last decade, some studies have shown that Tacr2 activation is involved in the modulation of emotional processes. However, the extent, to which stress impacts Tacr2 expression remains unclear. The molecular mechanisms underlying depression also remain poorly understood. In this study, we subjected adult male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) to induce a depression-like phenotype. We then measured the body weight and performed the sucrose preference test, forced swimming test (FST) and open field test to detect the effects of stress on anhedonia and activity. Western blotting and real-time PCR were used to study the protein and mRNA expression levels of Tacr2, respectively, in the hypothalamus. To explore DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene, we used methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Additionally, we used the bisulfite sequencing PCR (BSP) to further verify the DNA methylation levels of the Tacr2 receptor gene in rats. We found that the CUMS-sensitive rats exhibited a decrease in body weight and sucrose preference, a decrease in the distance traveled, rearing frequency and velocity in the open field test, and an increase in immobility time in the FST. Compared with the expression in the control rats, Tacr2 protein and mRNA expression in the hypothalamus significantly increased in the CUMS-sensitive rats; however, the DNA methylation levels of the Tacr2 gene were significantly lower than in the control rats. In summary, according to our findings, the stress-induced increase in Tacr2 expression in the hypothalamus correlated with a specific decrease in DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene. These results may enrich the understanding of the pathological processes of depression and provide insights into therapeutic approaches for its treatment.</p>',
'date' => '2019-06-03',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30711443',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.bbr.2019.01.059',
'modified' => '2019-04-16 13:54:40',
'created' => '2019-04-16 12:25:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 59 => array(
'id' => '3666',
'name' => 'Epigenetic Alterations in Juvenile Spondyloarthritis Patients: a Preliminary Study of Selected Genes Promoter Methylation and Silencing',
'authors' => 'Lamot Lovro, Blažeković Antonela, Jerčić Kristina Gotovac, Ivković Tina Catela, Vidović Mandica, Lamot Mirta, Kapitanović Sanja, Borovečki Fran, Harjaček Miroslav',
'description' => '<p>Juvenile spondyloarthritis (jSpA) is a complex disease with both genetic and environmental factors contributing to etiology. Multiple studies have shown that epigenetic mechanisms could link the environment and gene expression and thus provide a potential explanation for external contribution in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, including rheumatic. Previously obtained gene signatures in jSpA patients revealed distinctive expression of important immune-related genes, though the mechanism(s) responsible for those alterations remained unknown. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the methylation levels of the TLR4, CXCR4, NLRP3, and PTPN12 gene promoter, along with the expression of several non-coding microRNAs (miR-150, miR-146a, miR-181a, and miR-223) in jSpA patients. Peripheral blood samples were obtained from 19 patients newly diagnosed with jSpA according to ILAR classification criteria for enthesitis-related arthritis (ErA) and seven gender- and age-matched subjects without any symptoms or signs of inflammatory disease. The expression of specific microRNAs was analyzed using qRT-PCR with predeveloped microRNA assays. DNA promoter region methylation status of selected genes was assessed by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) analysis. Fold enrichment of immunoprecipitated DNA differed significantly for NLRP3 promoter site, while the expression analysis of selected microRNAs showed no significant difference in fold change between jSpA patients and healthy controls. The results indicated that epigenetic modifications in the initial phase of the disease could be responsible for some of the expression alterations in jSpA patients. Since NLRP3 has a crucial role in inflammasome assembly and inflammasomes have been shown to shape microbiota, it is tempting to assume that dysbiosis in jSpA patients can at least partially be explained by reduced NLRP3 expression due to hypermethylation, stressing for the first time the epigenetic contribution to jSpA pathophysiology</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-09',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42399-019-00070-9',
'doi' => '10.1007/s42399-019-00070-9',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:53:06',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 60 => array(
'id' => '3846',
'name' => 'The methylation pattern of DNA and complex correlations with gene expressions during TuMV infection in Chinese cabbage',
'authors' => 'J. YU , L.-W. GAO , Y. YANG , C. LIU , R.-J. ZHANG , F.-F. SUN , L.-X. SONG , D. XIAO , T.-K. LIU , X.-L. HOU , and C.-W. ZHANG',
'description' => '<p>Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) is one of the most important economic crops. However, its yield and quality can be severely threatened by Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV). Emerging evidence indicates that epigenetic mechanisms, especially DNA methylation, play an important role in regulating gene expression. Therefore, identification of resistance genes modified by DNA methylation during the virus infection would provide a critical clue for improving disease resistance breeding programs. Here, we present detailed analysis for the correlation of DNA methylation and gene expression involved in several anti-pathogen pathways. We also found that different methylation patterns exist in different methylation sites (CG, CHG, and CHH, where H represents A, G, or T) and genomic regions. Furthermore, we identified disease-resistant genes related to the nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeats family, auxin, salicylic acid signaling transduction, cell wall biosynthesis, and protein degradation among the different methylated genes (DMGs) suggesting that these genes may be modified by DNA methylation and work together to activate an immune response. The identified DMGs are a valuable resource for discovering resistance genes. Our study not only provides valuable data for future biotechnology research and epigenetic studies, but also helps to explore how the epigenetic mechanisms modify antiviral pathways.</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-09',
'pmid' => 'https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337128882_The_methylation_pattern_of_DNA_and_complex_correlations_with_gene_expressions_during_TuMV_infection_in_Chinese_cabbage',
'doi' => '10.32615/bp.2019.073',
'modified' => '2020-02-20 11:12:23',
'created' => '2020-02-13 10:02:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 61 => array(
'id' => '3716',
'name' => 'Epigenetic control of the angiotensin-converting enzyme in endothelial cells during inflammation.',
'authors' => 'Mudersbach T, Siuda D, Kohlstedt K, Fleming I',
'description' => '<p>The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) plays a central role in the renin-angiotensin system, which is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. Alterations in ACE expression or activity are associated with various pathological phenotypes, particularly cardiovascular diseases. In human endothelial cells, ACE was shown to be negatively regulated by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α. To examine, whether or not, epigenetic factors were involved in ACE expression regulation, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and RNA interference experiments directed against regulators of DNA methylation homeostasis i.e., DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenases (TETs), were performed. TNFα stimulation enhanced DNA methylation in two distinct regions within the ACE promoter via a mechanism linked to DNMT3a and DNMT3b, but not to DNMT1. At the same time, TET1 protein expression was downregulated. In addition, DNA methylation decreased the binding affinity of the transcription factor MYC associated factor X to the ACE promoter. In conclusion, DNA methylation determines the TNFα-dependent regulation of ACE gene transcription and thus protein expression in human endothelial cells.</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31042763',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0216218',
'modified' => '2019-07-05 13:14:33',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 62 => array(
'id' => '3698',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in Tibetan and Yorkshire pigs under high-altitude hypoxia.',
'authors' => 'Zhang B, Ban D, Gou X, Zhang Y, Yang L, Chamba Y, Zhang H',
'description' => '<p>Background: Tibetan pigs, which inhabit the Tibetan Plateau, exhibit distinct phenotypic and physiological characteristics from those of lowland pigs and have adapted well to the extreme conditions at high altitude. However, the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of hypoxic adaptation in animals remain unclear. Methods: Whole-genome DNA methylation data were generated for heart tissues of Tibetan pigs grown in the highland (TH,  = 4) and lowland (TL,  = 4), as well as Yorkshire pigs grown in the highland (YH,  = 4) and lowland (YL,  = 4), using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing. Results: We obtained 480 million reads and detected 280679, 287224, 259066, and 332078 methylation enrichment peaks in TH, YH, TL, and YL, respectively. Pairwise TH vs. YH, TL vs. YL, TH vs. TL, and YH vs. YL comparisons revealed 6829, 11997, 2828, and 1286 differentially methylated regions (DMRs), respectively. These DMRs contained 384, 619, 192, and 92 differentially methylated genes (DMGs), respectively. DMGs that were enriched in the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signaling pathway and pathways involved in cancer and hypoxia-related processes were considered to be important candidate genes for high-altitude adaptation in Tibetan pigs. Conclusions: This study elucidates the molecular and epigenetic mechanisms involved in hypoxic adaptation in pigs and may help further understand human hypoxia-related diseases.</p>',
'date' => '2019-04-28',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30867905',
'doi' => '10.1186/s40104-019-0316-y',
'modified' => '2019-07-05 14:47:45',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 63 => array(
'id' => '3648',
'name' => 'Assessment and site-specific manipulation of DNA (hydroxy-)methylation during mouse corticogenesis.',
'authors' => 'Noack F, Pataskar A, Schneider M, Buchholz F, Tiwari VK, Calegari F',
'description' => '<p>Dynamic changes in DNA (hydroxy-)methylation are fundamental for stem cell differentiation. However, the signature of these epigenetic marks in specific cell types during corticogenesis is unknown. Moreover, site-specific manipulation of cytosine modifications is needed to reveal the significance and function of these changes. Here, we report the first assessment of (hydroxy-)methylation in neural stem cells, neurogenic progenitors, and newborn neurons during mammalian corticogenesis. We found that gain in hydroxymethylation and loss in methylation occur sequentially at specific cellular transitions during neurogenic commitment. We also found that these changes predominantly occur within enhancers of neurogenic genes up-regulated during neurogenesis and target of pioneer transcription factors. We further optimized the use of dCas9-Tet1 manipulation of (hydroxy-)methylation, locus-specifically, in vivo, showing the biological relevance of our observations for , a regulator of corticogenesis involved in developmental malformations and cognitive impairment. Together, our data reveal the dynamics of cytosine modifications in lineage-related cell types, whereby methylation is reduced and hydroxymethylation gained during the neurogenic lineage concurrently with up-regulation of pioneer transcription factors and activation of enhancers for neurogenic genes.</p>',
'date' => '2019-04-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30814272',
'doi' => '10.1038/nrg.2017.57',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:13:14',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 64 => array(
'id' => '3647',
'name' => 'DMSO induces drastic changes in human cellular processes and epigenetic landscape in vitro.',
'authors' => 'Verheijen M, Lienhard M, Schrooders Y, Clayton O, Nudischer R, Boerno S, Timmermann B, Selevsek N, Schlapbach R, Gmuender H, Gotta S, Geraedts J, Herwig R, Kleinjans J, Caiment F',
'description' => '<p>Though clinical trials for medical applications of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) reported toxicity in the 1960s, later, the FDA classified DMSO in the safest solvent category. DMSO became widely used in many biomedical fields and biological effects were overlooked. Meanwhile, biomedical science has evolved towards sensitive high-throughput techniques and new research areas, including epigenomics and microRNAs. Considering its wide use, especially for cryopreservation and in vitro assays, we evaluated biological effect of DMSO using these technological innovations. We exposed 3D cardiac and hepatic microtissues to medium with or without 0.1% DMSO and analyzed the transcriptome, proteome and DNA methylation profiles. In both tissue types, transcriptome analysis detected >2000 differentially expressed genes affecting similar biological processes, thereby indicating consistent cross-organ actions of DMSO. Furthermore, microRNA analysis revealed large-scale deregulations of cardiac microRNAs and smaller, though still massive, effects in hepatic microtissues. Genome-wide methylation patterns also revealed tissue-specificity. While hepatic microtissues demonstrated non-significant changes, findings from cardiac microtissues suggested disruption of DNA methylation mechanisms leading to genome-wide changes. The extreme changes in microRNAs and alterations in the epigenetic landscape indicate that DMSO is not inert. Its use should be reconsidered, especially for cryopreservation of embryos and oocytes, since it may impact embryonic development.</p>',
'date' => '2019-03-15',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30874586',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-019-40660-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:14:07',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 65 => array(
'id' => '3673',
'name' => 'Evidence of association of circulating epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers with suspected coronary heart disease evaluated by Cardiac Computed Tomography.',
'authors' => 'Infante T, Forte E, Schiano C, Punzo B, Cademartiri F, Cavaliere C, Salvatore M, Napoli C',
'description' => '<p>Circulating biomarkers available in clinical practice do not allow to stratify patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) prior the onset of a clinically relevant event. We evaluated the methylation status of specific genomic segments and gene expression in peripheral blood of patients undergoing Cardiac Computed Tomography (CCT) for CHD (n = 95). We choose to investigate cholesterol metabolism. Methylation and gene expression of low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), sterol regulatory element-binding factor 2 (SREBF2) and ATP-binding cassette transporter 1 (ABCA1) were evaluated by qRT-PCR. Calcium score (CACS), stenosis degree, total plaque volume (TPV), calcified plaque volume (CPV), non-calcified plaque volume (NCPV) and plaque burden (PB) were assessed in all CHD patients (n = 65). The percentage of methylation at the specific analyzed segment of LDLR promoter was higher in CHD patients vs healthy subjects (HS) (n = 30) (p = 0.001). LDLR, SREBF2 and ABCA1 mRNAs were up-regulated in CHD patients vs HS (p = 0.02; p = 0.019; p = 0.008). SREBF2 was overexpressed in patients with coronary stenosis ≥50% vs subjects with stenosis <50% (p = 0.036). After adjustment for risk factors and clinical features, ABCA1 (p = 0.005) and SREBF2 (p = 0.010) gene expression were identified as independent predictors of CHD and severity. ROC curve analysis revealed a good performance of ABCA1 on predicting CHD (AUC = 0.768; p<0.001) and of SREBF2 for the prediction of disease severity (AUC = 0.815; p<0.001). Moreover, adjusted multivariate analysis demonstrated SREBF2 as independent predictor of CPV, NCPV and TPV (p = 0.022; p = 0.002 and p = 0.006) and ABCA1 as independent predictor of NCPV and TPV (p = 0.002 and p = 0.013). CHD presence and characteristics are related to selected circulating transcriptional and epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers linked to cholesterol pathway. More extensive analysis of CHD phenotypes and circulating biomarkers might improve and personalize cardiovascular risk stratification in the clinical settings.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-23',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30673762',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0210909',
'modified' => '2019-07-01 11:27:58',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 66 => array(
'id' => '3655',
'name' => 'LncRNA Dnmt3aos regulates Dnmt3a expression leading to aberrant DNA methylation in macrophage polarization',
'authors' => 'Xueqin Li, Yingying Zhang, Mengying Zhang, Xiang Kong, Hui Yang, Min Zhong, Weiya Pei, Yang Xu, Xiaolong Zhu, Tianbing Chen, Jingjing Ye, and Kun ',
'description' => '<p>Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play key roles in various biological processes. However, the roles of lncRNAs in macrophage polarization remain largely unexplored. In this study, thousands of lncRNAs were identified that are differentially expressed in distinct polarized bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Among them, Dnmt3aos (DNA methyltransferase 3A, opposite strand), as a known lncRNA, locates on the antisense strand of Dnmt3a. Functional experiments further confirmed that Dnmt3aos were highly expressed in M(IL-4) macrophages and participated in the regulation of Dnmt3a expression, and played a key role in macrophage polarization. The DNA methylation profiles between the Dnmt3aos knockdown group and the control group in M(IL-4) macrophages were determined by MeDIP-seq technique for the first time, and the Dnmt3aos-Dnmt3a axis-mediated DNA methylation modification-regulated macrophage polarization related gene IFN-γ was identified. Our study will help to enrich our knowledge of the mechanism of macrophage polarization and will provide new insights for immunotherapy in macrophage-associated diseases.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-07',
'pmid' => 'https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/514307v1',
'doi' => '/',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:39:53',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 67 => array(
'id' => '3660',
'name' => 'Global distribution of DNA hydroxymethylation and DNA methylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.',
'authors' => 'Wernig-Zorc S, Yadav MP, Kopparapu PK, Bemark M, Kristjansdottir HL, Andersson PO, Kanduri C, Kanduri M',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has been a good model system to understand the functional role of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in cancer progression. More recently, an oxidized form of 5-mC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has gained lot of attention as a regulatory epigenetic modification with prognostic and diagnostic implications for several cancers. However, there is no global study exploring the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) levels in CLL. Herein, using mass spectrometry and hMeDIP-sequencing, we analysed the dynamics of 5-hmC during B cell maturation and CLL pathogenesis. RESULTS: We show that naïve B-cells had higher levels of 5-hmC and 5-mC compared to non-class switched and class-switched memory B-cells. We found a significant decrease in global 5-mC levels in CLL patients (n = 15) compared to naïve and memory B cells, with no changes detected between the CLL prognostic groups. On the other hand, global 5-hmC levels of CLL patients were similar to memory B cells and reduced compared to naïve B cells. Interestingly, 5-hmC levels were increased at regulatory regions such as gene-body, CpG island shores and shelves and 5-hmC distribution over the gene-body positively correlated with degree of transcriptional activity. Importantly, CLL samples showed aberrant 5-hmC and 5-mC pattern over gene-body compared to well-defined patterns in normal B-cells. Integrated analysis of 5-hmC and RNA-sequencing from CLL datasets identified three novel oncogenic drivers that could have potential roles in CLL development and progression. CONCLUSIONS: Thus, our study suggests that the global loss of 5-hmC, accompanied by its significant increase at the gene regulatory regions, constitute a novel hallmark of CLL pathogenesis. Our combined analysis of 5-mC and 5-hmC sequencing provided insights into the potential role of 5-hmC in modulating gene expression changes during CLL pathogenesis.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30616658',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13072‑018‑0252‑7',
'modified' => '2019-07-01 11:46:16',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 68 => array(
'id' => '3430',
'name' => 'Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Shen SY, Singhania R, Fehringer G, Chakravarthy A, Roehrl MHA, Chadwick D, Zuzarte PC, Borgida A, Wang TT, Li T, Kis O, Zhao Z, Spreafico A, Medina TDS, Wang Y, Roulois D, Ettayebi I, Chen Z, Chow S, Murphy T, Arruda A, O'Kane GM, Liu J, Mansour M, McPher',
'description' => '<p>The use of liquid biopsies for cancer detection and management is rapidly gaining prominence. Current methods for the detection of circulating tumour DNA involve sequencing somatic mutations using cell-free DNA, but the sensitivity of these methods may be low among patients with early-stage cancer given the limited number of recurrent mutations. By contrast, large-scale epigenetic alterations-which are tissue- and cancer-type specific-are not similarly constrained and therefore potentially have greater ability to detect and classify cancers in patients with early-stage disease. Here we develop a sensitive, immunoprecipitation-based protocol to analyse the methylome of small quantities of circulating cell-free DNA, and demonstrate the ability to detect large-scale DNA methylation changes that are enriched for tumour-specific patterns. We also demonstrate robust performance in cancer detection and classification across an extensive collection of plasma samples from several tumour types. This work sets the stage to establish biomarkers for the minimally invasive detection, interception and classification of early-stage cancers based on plasma cell-free DNA methylation patterns.</p>',
'date' => '2018-11-14',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30429608',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41586-018-0703-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-11 16:22:54',
'created' => '2018-12-04 09:51:07',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 69 => array(
'id' => '3511',
'name' => 'Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation to identify genes and pathways associated with male sterility in soybean',
'authors' => 'Han Shaohuai, Li Yanwei, Li Jiajia, Zhang Hao, Ding Xianlong, He Tingting, Gai Junyi, Yang Shouping',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification, which is important for gene expression regulation. Although genome-wide DNA methylation studies have been reported in several plant species, the difference in the methylation pattern between the cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) line and its maintainer in soybean remains unclear. We compared genome-wide DNA methylation between the soybean CMS line NJCMS1A and its maintainer NJCMS1B using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) technology. The results showed that the methylation level was higher in transposable elements (TEs) than promoter and intron; however, the methylation levels varied among different types of TEs with the highest level for long terminal repeats (LTRs) and the lowest for transcription start sites (TSS) and transcription termination sites (TTS). We observed 178 differentially methylated genes (DMGs) between NJCMS1A and NJCMS1B, including 156 hypomethylated and 22 hyper-methylated genes in NJCMS1A compared to NJCMS1B. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis showed that 114 DMGs were annotated to one or more GO categories, among which four GO terms were significantly enriched. KEGG pathway analysis showed that 18 DMGs were significantly enriched in 10 metabolism pathways, including homologous recombination, purine metabolism, proteasome, non-homologous end-joining, and pyrimidine</p>',
'date' => '2018-09-16',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11032-018-0875-1',
'doi' => '10.1007/s11032-018-0875-1',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:44:53',
'created' => '2019-02-27 12:54:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 70 => array(
'id' => '3585',
'name' => 'Folic acid supplementation alters the DNA methylation profile and improves insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed mice.',
'authors' => 'Li W, Tang R, Ma F, Ouyang S, Liu Z, Wu J',
'description' => '<p>Folic acid (FA) supplementation may protect from obesity and insulin resistance, the effects and mechanism of FA on chronic high-fat-diet-induced obesity-related metabolic disorders are not well elucidated. We adopted a genome-wide approach to directly examine whether FA supplementation affects the DNA methylation profile of mouse adipose tissue and identify the functional consequences of these changes. Mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), normal diet (ND) or an HFD supplemented with folic acid (20 μg/ml in drinking water) for 10 weeks, epididymal fat was harvested, and genome-wide DNA methylation analyses were performed using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Mice exposed to the HFD expanded their adipose mass, which was accompanied by a significant increase in circulating glucose and insulin levels. FA supplementation reduced the fat mass and serum glucose levels and improved insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. MeDIP-seq revealed distribution of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) throughout the adipocyte genome, with more hypermethylated regions in HFD mice. Methylome profiling identified DMRs associated with 3787 annotated genes from HFD mice in response to FA supplementation. Pathway analyses showed novel DNA methylation changes in adipose genes associated with insulin secretion, pancreatic secretion and type 2 diabetes. The differential DNA methylation corresponded to changes in the adipose tissue gene expression of Adcy3 and Rapgef4 in mice exposed to a diet containing FA. FA supplementation improved insulin resistance, decreased the fat mass, and induced DNA methylation and gene expression changes in genes associated with obesity and insulin secretion in obese mice fed a HFD.</p>',
'date' => '2018-09-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29986310',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.05.010',
'modified' => '2019-04-17 15:33:46',
'created' => '2019-04-16 12:25:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 71 => array(
'id' => '3633',
'name' => 'Embryonic germ cell extracts erase imprinted genes and improve the efficiency of induced pluripotent stem cells.',
'authors' => 'Hu J, Zhao Q, Feng Y, Li N, Gu Y, Sun R, Duan L, Wu Y, Shan Z, Lei L',
'description' => '<p>Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have the potential to be useful in the treatment of human diseases. While prior studies have reported multiple methods to generate iPSCs, DNA methylation continues to limit the totipotency and reprogramming efficiency of iPSCs. Here, we first show the competency of embryonic germ cells (EGCs) as a reprogramming catalyst capable of effectively promoting reprogramming induced by four defined factors, including Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc. Combining EGC extracts with these four factors resulted in formation of more embryonic stem cell-like colonies than did factors alone. Notably, expression of imprinted genes was higher with combined induction than with factors alone. Moreover, iPSCs derived from the combined inductors tended to have more global hypomethylation. Our research not only provides evidence that EGC extracts could activate DNA demethylation and reprogram imprinted genes, but also establishes a new way to enhance reprogramming of iPSCs, which remains a critical safety concern for potential use of iPSCs in regenerative medicine.</p>',
'date' => '2018-07-19',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30026469',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-018-29339-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:30:27',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 72 => array(
'id' => '3393',
'name' => 'Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos.',
'authors' => 'Sussarellu R, Lebreton M, Rouxel J, Akcha F, Rivière G',
'description' => '<p>Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better understand whether the embryotoxic effects of copper in Crassostrea gigas could be mediated by alterations in gene expression, and the putative role of DNA methylation, which is known to contribute to gene regulation in early embryo development. For that purpose, oyster embryos were exposed to 4 nominal copper concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 μg L Cu) during early development assays. Embryotoxicity was monitored through the oyster embryo-larval bioassay at the D-larva stage 24 h post fertilization (hpf) and genotoxicity at gastrulation 7 hpf. In parallel, the relative expression of 15 genes encoding putative homeotic, biomineralization and DNA methylation proteins was measured at three developmental stages (3 hpf morula stage, 7 hpf gastrula stage, 24 hpf D-larvae stage) using RT-qPCR. Global DNA content in methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine were measured by HPLC and gene-specific DNA methylation levels were monitored using MeDIP-qPCR. A significant increase in larval abnormalities was observed from copper concentrations of 10 μg L, while significant genotoxic effects were detected at 1 μg L and above. All the selected genes presented a stage-dependent expression pattern, which was impaired for some homeobox and DNA methylation genes (Notochord, HOXA1, HOX2, Lox5, DNMT3b and CXXC-1) after copper exposure. While global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) at gastrula stage didn't show significant changes between experimental conditions, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its degradation product, decreased upon copper treatment. The DNA methylation of exons and the transcript levels were correlated in control samples for HOXA1 but such a correlation was diminished following copper exposure. The methylation level of some specific gene regions (HoxA1, Hox2, Engrailed2 and Notochord) displayed changes upon copper exposure. Such changes were gene and exon-specific and no obvious global trends could be identified. Our study suggests that the embryotoxic effects of copper in oysters could involve homeotic gene expression impairment possibly by changing DNA methylation levels.</p>',
'date' => '2018-03-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29353135',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.001',
'modified' => '2018-11-09 12:21:38',
'created' => '2018-11-08 12:59:45',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 73 => array(
'id' => '3448',
'name' => 'Aberrant methylated key genes of methyl group metabolism within the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinogenesis.',
'authors' => 'Erichsen L, Ghanjati F, Beermann A, Poyet C, Hermanns T, Schulz WA, Seifert HH, Wild PJ, Buser L, Kröning A, Braunstein S, Anlauf M, Jankowiak S, Hassan M, Bendhack ML, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Santourlidis S',
'description' => '<p>Urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common cancer of the urinary bladder causes severe morbidity and mortality, e.g. about 40.000 deaths in the EU annually, and incurs considerable costs for the health system due to the need for prolonged treatments and long-term monitoring. Extensive aberrant DNA methylation is described to prevail in urothelial carcinoma and is thought to contribute to genetic instability, altered gene expression and tumor progression. However, it is unknown how this epigenetic alteration arises during carcinogenesis. Intact methyl group metabolism is required to ensure maintenance of cell-type specific methylomes and thereby genetic integrity and proper cellular function. Here, using two independent techniques for detecting DNA methylation, we observed DNA hypermethylation of the 5'-regulatory regions of the key methyl group metabolism genes ODC1, AHCY and MTHFR in early urothelial carcinoma. These hypermethylation events are associated with genome-wide DNA hypomethylation which is commonly associated with genetic instability. We therefore infer that hypermethylation of methyl group metabolism genes acts in a feed-forward cycle to promote additional DNA methylation changes and suggest a new hypothesis on the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinoma.</p>',
'date' => '2018-02-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29472622',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-018-21932-7',
'modified' => '2019-02-15 21:31:04',
'created' => '2019-02-14 15:01:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 74 => array(
'id' => '3325',
'name' => 'Integrative omics data analyses of repeated dose toxicity of valproic acid in vitro reveal new mechanisms of steatosis induction',
'authors' => 'van Breda S.G.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is a very potent anti-cancer and neuro-protective drug probably by its HDAC inhibiting properties, which may cause steatosis in the liver. The present study investigates the effect of repetitive VPA treatment of primary human hepatocytes (PHH) on whole genome gene expression-, DNA methylation-, and miRNA changes, using microarrays and integrated data analyses. PHH were exposed to a non-cytotoxic dose of VPA for 5days daily which induced lipid accumulation. Part of the PHH was left untreated for 3days for studying the persistence of 'omics' changes. VPA treatment appeared to inhibit the expression of the transcription factors HNF1A and ONECUT1. HNF1A interacted with 41 differentially expressed genes of which 12 were also differentially methylated. None of the genes present in this network were regulated by a DE-miR. The subnetwork of ONECUT1 consisted of 44 differentially expressed genes of which 15 were differentially methylated, and 3 were regulated by a DE-miR. A number of genes in the networks are involved in fatty acid metabolism, and may contribute to the development of steatosis by increasing oxidative stress thereby causing mitochondrial dysfunction, and by shifting metabolism of VPA towards β-oxidation due to reduced glucuronidation. Part of the changes remained persistent after washing out of VPA, like PMAIP1 which is associated with cellular stress in liver of patients with NASH. The MMP2 gene showed the highest number of interactions with other persistently expressed genes, among which LCN2 which is a key modulator of lipid homeostasis. Furthermore, VPA modulated the expression and DNA methylation level of nuclear receptors and their target genes involved in the adverse outcome pathway of steatosis, thereby expanding our current knowledge of the pathway. In particular, VPA modulated PPARγ, and PPARα, AHR and CD36 on both the gene expression and the DNA methylation level, thereby inhibiting β-oxidation and increasing uptake of fatty acid into the hepatocytes, respectively. Overall, our integrative data analyses identified novel genes modulated by VPA, which provide more insight into the mechanisms of repeated dose toxicity of VPA, leading to steatosis.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-15',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29154799',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-02-06 09:28:05',
'created' => '2018-02-06 09:28:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 75 => array(
'id' => '3316',
'name' => 'Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos',
'authors' => 'Rossana Sussarellu, Morgane Lebreton, Julien Rouxel, Farida Akcha, Guillaume Rivière ',
'description' => '<p id="spar0045">Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better understand whether the embryotoxic effects of copper in <em>Crassostrea gigas</em> could be mediated by alterations in gene expression, and the putative role of DNA methylation, which is known to contribute to gene regulation in early embryo development.</p>
<p id="spar0050">For that purpose, oyster embryos were exposed to 4 nominal copper concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 μg L<sup>−1</sup> Cu<sup>2+</sup>) during early development assays. Embryotoxicity was monitored through the oyster embryo-larval bioassay at the D-larva stage 24 h post fertilization (hpf) and genotoxicity at gastrulation 7 hpf. In parallel, the relative expression of 15 genes encoding putative homeotic, biomineralization and DNA methylation proteins was measured at three developmental stages (3 hpf morula stage, 7 hpf gastrula stage, 24 hpf D-larvae stage) using RT-qPCR. Global DNA content in methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine were measured by HPLC and gene-specific DNA methylation levels were monitored using MeDIP-qPCR.</p>
<p id="spar0055">A significant increase in larval abnormalities was observed from copper concentrations of 10 μg L<sup>−1</sup>, while significant genotoxic effects were detected at 1 μg L<sup>−1</sup> and above. All the selected genes presented a stage-dependent expression pattern, which was impaired for some homeobox and DNA methylation genes (<em>Notochord, HOXA1, HOX2, Lox5, DNMT3b and CXXC-1</em>) after copper exposure. While global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) at gastrula stage didn’t show significant changes between experimental conditions, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its degradation product, decreased upon copper treatment. The DNA methylation of exons and the transcript levels were correlated in control samples for <em>HOXA1</em> but such a correlation was diminished following copper exposure. The methylation level of some specific gene regions (<em>HoxA1, Hox2, Engrailed2</em> and <em>Notochord</em>) displayed changes upon copper exposure. Such changes were gene and exon-specific and no obvious global trends could be identified. Our study suggests that the embryotoxic effects of copper in oysters could involve homeotic gene expression impairment possibly by changing DNA methylation levels.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-03',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166445X18300018?via%3Dihub',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.001',
'modified' => '2018-01-14 01:21:09',
'created' => '2018-01-14 01:21:09',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 76 => array(
'id' => '3383',
'name' => 'Genome-wide analysis of day/night DNA methylation differences in Populus nigra.',
'authors' => 'Ding C.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is an important mechanism of epigenetic modification. Methylation changes during stress responses and developmental processes have been well studied; however, their role in plant adaptation to the day/night cycle is poorly understood. In this study, we detected global methylation patterns in leaves of the black poplar Populus nigra 'N46' at 8:00 and 24:00 by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). We found 10,027 and 10,242 genes to be methylated in the 8:00 and 24:00 samples, respectively. The methylated genes appeared to be involved in multiple biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components, suggesting important roles for DNA methylation in poplar cells. Comparing the 8:00 and 24:00 samples, only 440 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) overlapped with genic regions, including 193 hyper- and 247 hypo-methylated DMRs, and may influence the expression of 137 downstream genes. Most hyper-methylated genes were associated with transferase activity, kinase activity, and phosphotransferase activity, whereas most hypo-methylated genes were associated with protein binding, ATP binding, and adenyl ribonucleotide binding, suggesting that different biological processes were activated during the day and night. Our results indicated that methylated genes were prevalent in the poplar genome, but that only a few of these participated in diurnal gene expression regulation.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-02',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29293569',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-08-07 09:45:38',
'created' => '2018-08-07 09:45:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 77 => array(
'id' => '3384',
'name' => 'Obligatory and facilitative allelic variation in the DNA methylome within common disease-associated loci',
'authors' => 'Bell C.G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Integrating epigenetic data with genome-wide association study (GWAS) results can reveal disease mechanisms. The genome sequence itself also shapes the epigenome, with CpG density and transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) strongly encoding the DNA methylome. Therefore, genetic polymorphism impacts on the observed epigenome. Furthermore, large genetic variants alter epigenetic signal dosage. Here, we identify DNA methylation variability between GWAS-SNP risk and non-risk haplotypes. In three subsets comprising 3128 MeDIP-seq peripheral-blood DNA methylomes, we find 7173 consistent and functionally enriched Differentially Methylated Regions. 36.8% can be attributed to common non-SNP genetic variants. CpG-SNPs, as well as facilitative TFBS-motifs, are also enriched. Highlighting their functional potential, CpG-SNPs strongly associate with allele-specific DNase-I hypersensitivity sites. Our results demonstrate strong DNA methylation allelic differences driven by obligatory or facilitative genetic effects, with potential direct or regional disease-related repercussions. These allelic variations require disentangling from pure tissue-specific modifications, may influence array studies, and imply underestimated population variability in current reference epigenomes.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-02',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29295990',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-08-07 10:13:12',
'created' => '2018-08-07 10:13:12',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 78 => array(
'id' => '3449',
'name' => 'Epigenetic alterations in TRAMP mice: epigenome DNA methylation profiling using MeDIP-seq.',
'authors' => 'Li W, Huang Y, Sargsyan D, Khor TO, Guo Y, Shu L, Yang AY, Zhang C, Paredes-Gonzalez X, Verzi M, Hart RP, Kong AN',
'description' => '<p>Purpose: We investigated the genomic DNA methylation profile of prostate cancer in transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) cancer model and to analyze the crosstalk among targeted genes and the related functional pathways. Methods: Prostate DNA samples from 24-week-old TRAMP and C57BL/6 male mice were isolated. The DNA methylation profiles were analyzed by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) followed by next-generation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Canonical pathways, diseases and function and network analyses of the different samples were then performed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software. Some target genes with significant difference in methylation were selected for validation using methylation specific primers (MSP) and qPCR. Results: TRAMP mice undergo extensive aberrant CpG hyper- and hypo-methylation. There were 2147 genes with a significant (log2-change ≥ 2) change in CpG methylation between the two groups, as mapped by the IPA software. Among these genes, the methylation of 1105 and 1042 genes was significantly decreased and increased, respectively, in TRAMP prostate tumors. The top associated disease identified by IPA was adenocarcinoma; however, the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-, histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2)-, glutathione S-transferase pi (GSTP1)- and polyubiquitin-C (UBC)-related pathways showed significantly altered methylation profiles based on the canonical pathway and network analyses. MSP and qPCR results of genes of interests corroborated with MeDIP-seq findings. Conclusions: This is the first MeDIP-seq with IPA analysis of the TRAMP model to provide novel insight into the genome-wide methylation profile of prostate cancer. Studies on epigenetics, such as DNA methylation, will potentially provide novel avenues and strategies for further development of biomarkers targeted for treatment and prevention approaches for prostate cancer.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29344347',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13578-018-0201-y',
'modified' => '2019-02-15 21:41:39',
'created' => '2019-02-14 15:01:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 79 => array(
'id' => '3508',
'name' => 'Analysis of DNA methylome and transcriptome profiling following Gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application in Nicotiana tabacum L.',
'authors' => 'Manoharlal Raman, Saiprasad G. V. S., Kaikala Vinay, Suresh Kumar R., Kovařík Ales',
'description' => '<p>The present work investigated a comprehensive genome-wide landscape of DNA methylome and its relationship with transcriptome upon gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application under practical field conditions in solanaceae model, Nicotiana tabacum L. Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation-Sequencing (MeDIP-Seq) analysis uncovered over 82% (18,456) of differential methylated regions (DMRs) in intergenic-region. Within protein-coding region, 2339 and 1685 of identified DMRs were observed in genebody- and promoter-region, respectively. Microarray study revealed 7032 differential expressed genes (DEGs) with 3507 and 3525 genes displaying upand down-regulation, respectively. Integration analysis revealed 520 unique non-redundant annotated DMRs overlapping with DEGs. Our results indicated that GA3 induced DNA hypo- as well as hyper-methylation were associated with both gene-silencing and -activation. No complete biasness or correlation was observed in either of the promoter- or genebody-regions, which otherwise showed an overall trend towards GA3 induced global DNA hypo-methylation. Taken together, our results suggested that differential DNA methylation mediated by GA3 may only play a permissive role in regulating the gene expression.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40502-018-0393-5',
'doi' => '10.1007/s40502-018-0393-5',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:43:47',
'created' => '2019-02-27 12:54:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 80 => array(
'id' => '3334',
'name' => 'Data on novel DNA methylation changes induced by valproic acid in human hepatocytes',
'authors' => 'Wolters J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is a widely prescribed antiepileptic drug in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis. However the exact mechanism of the steatosis formation is unknown. The data presented in this DIB publication is used to further investigate the VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in patterns of methylation. Therefore, primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were exposed to VPA at a concentration which was shown to cause steatosis without inducing overt cytotoxicity. VPA was administered for 5 days daily to PHHs. Furthermore, after 5 days VPA-treatment parts of the PHHs were followed for a 3 days washout. Differentially methylated DNA regions (DMRs) were identified by using the 'Methylated DNA Immuno-Precipitation - sequencing' (MeDIP-seq) method. The data presented in this DIB demonstrate induced steatosis pathways by all DMRs during VPA-treatment, covering interesting drug-induced steatosis genes (persistent DMRs upon terminating VPA treatment and the <i>EP300</i> network). This was illustrated in our associated article (Wolters et al., 2017) [1]. MeDIP-seq raw data are available on ArrayExpress (accession number: E-MTAB-4437).</p>',
'date' => '2017-11-10',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29201983',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-02-08 17:16:22',
'created' => '2018-02-08 17:16:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 81 => array(
'id' => '3283',
'name' => 'Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Methylation Patterns Induced by Valproic Acid in Human Hepatocytes',
'authors' => 'Wolters J.E.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is one of the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis through mitochondrial dysfunction. The aim of this study is to further investigate VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in patterns of methylation in nuclear DNA (nDNA) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Therefore, primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were exposed to an incubation concentration of VPA that was shown to cause steatosis without inducing overt cytotoxicity. VPA was administered daily for 5 days, and this was followed by a 3 day washout (WO). Methylated DNA regions (DMRs) were identified by using the methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-sequencing (MeDIP-seq) method. The nDNA DMRs after VPA treatment could indeed be classified into oxidative stress- and steatosis-related pathways. In particular, networks of the steatosis-related gene EP300 provided novel insight into the mechanisms of toxicity induced by VPA treatment. Furthermore, we suggest that VPA induces a crosstalk between nDNA hypermethylation and mtDNA hypomethylation that plays a role in oxidative stress and steatosis development. Although most VPA-induced methylation patterns appeared reversible upon terminating VPA treatment, 31 nDNA DMRs (including 5 zinc finger protein genes) remained persistent after the WO period. Overall, we have shown that MeDIP-seq analysis is highly informative in disclosing novel mechanisms of VPA-induced toxicity in PHHs. Our results thus provide a prototype for the novel generation of interesting methylation biomarkers for repeated dose liver toxicity in vitro.</p>',
'date' => '2017-10-16',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28853863',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-24 09:33:19',
'created' => '2017-10-24 09:33:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 82 => array(
'id' => '3271',
'name' => ' Genome methylation and regulatory functions for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chicken embryos',
'authors' => 'Zhang Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Tibetan chickens have unique adaptations to the extreme high-altitude environment that they inhabit. Epigenetic DNA methylation affects many biological processes, including hypoxic adaptation; however, the regulatory genes for DNA methylation in hypoxic adaptation remain unknown. In this study, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation with high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) was used to provide an atlas of the DNA methylomes of the heart tissue of hypoxic highland Tibetan and lowland Chahua chicken embryos. A total of 31.2 gigabases of sequence data were generated from six MeDIP-seq libraries. We identified 1,049 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and 695 related differentially methylated genes (DMGs) between the two chicken breeds. The DMGs are involved in vascular smooth muscle contraction, VEGF signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, and other hypoxia-related pathways. Five candidate genes that had low methylation (<i>EDNRA</i>, <i>EDNRB2</i>,<i> BMPR1B</i>,<i> BMPRII</i>, and <i>ITGA2</i>) might play key regulatory roles in the adaptation to hypoxia in Tibetan chicken embryos. Our study provides significant explanations for the functions of genes and their epigenetic regulation for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chickens.</p>',
'date' => '2017-10-06',
'pmid' => 'https://peerj.com/articles/3891/',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-13 17:02:21',
'created' => '2017-10-13 17:02:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 83 => array(
'id' => '3265',
'name' => 'Emerging Role of One-Carbon Metabolism and DNA Methylation Enrichment on δ-Containing GABAA Receptor Expression in the Cerebellum of Subjects with Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD',
'authors' => 'Gatta E. et al.',
'description' => '<section class="abstract">
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Background</div>
<p>Cerebellum is an area of the brain particularly sensitive to the effects of acute and chronic alcohol consumption. Alcohol exposure decreases cerebellar Purkinje cell output by increasing GABA release from Golgi cells onto extrasynaptic α<sub>6</sub>/δ-containing GABA<sub>A</sub> receptors located on glutamatergic granule cells. Here, we studied whether chronic alcohol consumption induces changes in GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor subunit expression and whether these changes are associated with alterations in epigenetic mechanisms via DNA methylation.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Methods</div>
<p>We used a cohort of postmortem cerebellum from control and chronic alcoholics, here defined as alcohol use disorders subjects (n=25/group). <em>S</em>-adenosyl-methionine/<em>S</em>-adenosyl-homocysteine were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. mRNA levels of various genes were assessed by reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Promoter methylation enrichment was assessed using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and hydroxy-methylated DNA immunoprecipitation assays.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Results</div>
<p>mRNAs encoding key enzymes of 1-carbon metabolism that determine the <em>S</em>-adenosyl-methionine/<em>S</em>-adenosyl-homocysteine ratio were increased, indicating higher “methylation index” in alcohol use disorder subjects. We found that increased methylation of the promoter of the δ subunit GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor was associated with reduced mRNA and protein levels in the cerebellum of alcohol use disorder subjects. No changes were observed in α<sub>1</sub>- or α<sub>6</sub>-containing GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor subunits. The expression of DNA-methyltransferases (1, 3A, and 3B) was unaltered, whereas the mRNA level of TET1, which participates in the DNA demethylation pathway, was decreased. Hence, increased methylation of the δ subunit GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor promoter may result from alcohol-induced reduction of DNA demethylation.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Conclusion</div>
<p>Together, these results support the hypothesis that aberrant DNA methylation pathways may be involved in cerebellar pathophysiology of alcoholism. Furthermore, this work provides novel evidence for a central role of DNA methylation mechanisms in the alcohol-induced neuroadaptive changes of human cerebellar GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor function.</p>
</section>
</section>',
'date' => '2017-08-19',
'pmid' => 'https://academic.oup.com/ijnp/article/doi/10.1093/ijnp/pyx075/4085582/Emerging-role-of-one-carbon-metabolism-and-DNA',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-09 16:11:05',
'created' => '2017-10-09 16:11:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 84 => array(
'id' => '3251',
'name' => 'Coordinate Regulation of TET2 and EBNA2 Control DNA Methylation State of Latent Epstein-Barr Virus',
'authors' => 'Lu F. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and its associated carcinogenesis are regulated by dynamic changes in DNA methylation of both virus and host genomes. We show here that the Ten-Eleven Translocation 2 (TET2) gene, implicated in hydroxymethylation and active DNA demethylation, is a key regulator of EBV latency type DNA methylation patterning. EBV latency types are defined by DNA methylation patterns that restrict expression of viral latency genes. We show that TET2 mRNA and protein expression correlate with the highly demethylated EBV type III latency program permissive for expression of EBNA2, EBNA3s, and LMP transcripts. We show that shRNA depletion of TET2 results in a decrease in latency gene expression, but can also trigger a switch to lytic gene expression. TET2 depletion results in the loss of hydroxymethylated cytosine, and corresponding increase in cytosine methylation at key regulatory regions on the viral and host genomes. This also corresponded to a loss of RBP-jκ binding, and decreased histone H3K4 trimethylation at these sites. Furthermore, we show that the TET2 gene, itself, is regulated similar to the EBV genome. ChIP-Seq revealed that TET2 gene contains EBNA2-dependent RBP-jκ and EBF1 binding sites, and is subject to DNA methylation associated transcriptional silencing similar to EBV latency type III genomes. Finally, we provide evidence that TET2 colocalizes with EBNA2-EBF1-RBP-jκ binding sites, and can interact with EBNA2 by co-immunoprecipitation. Taken together, these findings indicate that TET2 gene transcripts are regulated similarly to EBV type III latency genes, and that TET2 protein is a cofactor of EBNA2 and co-regulator of the EBV type III latency program and DNA methylation state..<b>IMPORTANCE</b> Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and carcinogenesis involves the selective epigenetic modification of viral and cellular genes. Here, we show that TET2, a cellular tumor suppressor involved in active DNA demethylation, plays a central role in regulating DNA methylation state during EBV latency. TET2 is coordinately regulated and functionally interacts with the viral oncogene EBNA2. TET2 and EBNA2 function cooperatively to demethylate genes important for EBV-driven B cells growth transformation.</p>',
'date' => '2017-08-07',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28794029',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-09-26 09:54:39',
'created' => '2017-09-26 09:54:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 85 => array(
'id' => '3237',
'name' => 'Intracellular adenosine regulates epigenetic programming in endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis',
'authors' => 'Xu Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The nucleoside adenosine is a potent regulator of vascular homeostasis, but it remains unclear how expression or function of the adenosine-metabolizing enzyme adenosine kinase (ADK) and the intracellular adenosine levels influence angiogenesis. We show here that hypoxia lowered the expression of ADK and increased the levels of intracellular adenosine in human endothelial cells. Knockdown (KD) of ADK elevated intracellular adenosine, promoted proliferation, migration, and angiogenic sprouting in human endothelial cells. Additionally, mice deficient in endothelial ADK displayed increased angiogenesis as evidenced by the rapid development of the retinal and hindbrain vasculature, increased healing of skin wounds, and prompt recovery of arterial blood flow in the ischemic hindlimb. Mechanistically, hypomethylation of the promoters of a series of pro-angiogenic genes, especially for VEGFR2 in ADK KD cells, was demonstrated by the Infinium methylation assay. Methylation-specific PCR, bisulfite sequencing, and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation further confirmed hypomethylation in the promoter region of VEGFR2 in ADK-deficient endothelial cells. Accordingly, loss or inactivation of ADK increased VEGFR2 expression and signaling in endothelial cells. Based on these findings, we propose that ADK downregulation-induced elevation of intracellular adenosine levels in endothelial cells in the setting of hypoxia is one of the crucial intrinsic mechanisms that promote angiogenesis.</p>',
'date' => '2017-07-17',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28751580',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-08-29 09:15:21',
'created' => '2017-08-29 09:15:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 86 => array(
'id' => '3216',
'name' => 'Vitamin C induces specific demethylation of H3K9me2 in mouse embryonic stem cells via Kdm3a/b',
'authors' => 'Kevin T. Ebata, Kathryn Mesh, Shichong Liu, Misha Bilenky, Alexander Fekete, Michael G. Acker, Martin Hirst, Benjamin A. Garcia and Miguel Ramalho-Santos',
'description' => '<section xmlns="" xmlns:fn="http://www.w3.org/2005/xpath-functions" xmlns:meta="http://www.springer.com/app/meta" class="Abstract" id="Abs1" lang="en">
<div class="js-CollapseSection">
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec1">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Background</h3>
<p id="Par1" class="Para">Histone methylation patterns regulate gene expression and are highly dynamic during development. The erasure of histone methylation is carried out by histone demethylase enzymes. We had previously shown that vitamin C enhances the activity of Tet enzymes in embryonic stem (ES) cells, leading to DNA demethylation and activation of germline genes.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec2">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Results</h3>
<p id="Par2" class="Para">We report here that vitamin C induces a remarkably specific demethylation of histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) in naïve ES cells. Vitamin C treatment reduces global levels of H3K9me2, but not other histone methylation marks analyzed, as measured by western blot, immunofluorescence and mass spectrometry. Vitamin C leads to widespread loss of H3K9me2 at large chromosomal domains as well as gene promoters and repeat elements. Vitamin C-induced loss of H3K9me2 occurs rapidly within 24 h and is reversible. Importantly, we found that the histone demethylases Kdm3a and Kdm3b are required for vitamin C-induced demethylation of H3K9me2. Moreover, we show that vitamin C-induced Kdm3a/b-mediated H3K9me2 demethylation and Tet-mediated DNA demethylation are independent processes at specific loci. Lastly, we document Kdm3a/b are partially required for the upregulation of germline genes by vitamin C.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec3">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p id="Par3" class="Para">These results reveal a specific role for vitamin C in histone demethylation in ES cells and document that DNA methylation and H3K9me2 cooperate to silence germline genes in pluripotent cells.</p>
</div>
</div>
</section>',
'date' => '2017-07-12',
'pmid' => 'https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-017-0143-3',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-017-0143-3',
'modified' => '2017-08-23 14:47:51',
'created' => '2017-07-29 08:04:03',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 87 => array(
'id' => '3205',
'name' => 'Dynamics of DNA methylomes underlie oyster development',
'authors' => 'Riviere G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a critical epigenetic regulator of development in mammals and social insects, but its significance in development outside these groups is not understood. Here we investigated the genome-wide dynamics of DNA methylation in a mollusc model, the oyster Crassostrea gigas, from the egg to the completion of organogenesis. Large-scale methylation maps reveal that the oyster genome displays a succession of methylated and non methylated regions, which persist throughout development. Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) are strongly regulated during cleavage and metamorphosis. The distribution and levels of methylated DNA within genomic features (exons, introns, promoters, repeats and transposons) show different developmental lansdscapes marked by a strong increase in the methylation of exons against introns after metamorphosis. Kinetics of methylation in gene-bodies correlate to their transcription regulation and to distinct functional gene clusters, and DMRs at cleavage and metamorphosis bear the genes functionally related to these steps, respectively. This study shows that DNA methylome dynamics underlie development through transcription regulation in the oyster, a lophotrochozoan species. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of such epigenetic regulation outside vertebrates and ecdysozoan models, bringing new insights into the evolution and the epigenetic regulation of developmental processes.</p>',
'date' => '2017-06-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28594821',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-07-03 10:24:12',
'created' => '2017-07-03 10:24:12',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 88 => array(
'id' => '3186',
'name' => 'MeDIP-seq and nCpG analyses illuminate sexually dimorphic methylation of gonadal development genes with high historic methylation in turtle hatchlings with temperature-dependent sex determination',
'authors' => 'Radhakrishnan S. et al.',
'description' => '<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec1">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Background</h3>
<p id="Par1" class="Para">DNA methylation alters gene expression but not DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. Temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) epitomizes phenotypic plasticity where environmental temperature drives embryonic sexual fate, as occurs commonly in turtles. Importantly, the temperature-specific transcription of two genes underlying gonadal differentiation is known to be induced by differential methylation in TSD fish, turtle and alligator. Yet, how extensive is the link between DNA methylation and TSD remains unclear. Here we test for broad differences in genome-wide DNA methylation between male and female hatchling gonads of the TSD painted turtle <em xmlns="" class="EmphasisTypeItalic">Chrysemys picta</em> using methyl DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing, to identify differentially methylated candidates for future study. We also examine the genome-wide nCpG distribution (which affects DNA methylation) in painted turtles and test for historic methylation in genes regulating vertebrate gonadogenesis.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec2">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Results</h3>
<p id="Par2" class="Para">Turtle global methylation was consistent with other vertebrates (57% of the genome, 78% of all CpG dinucleotides). Numerous genes predicted to regulate turtle gonadogenesis exhibited sex-specific methylation and were proximal to methylated repeats. nCpG distribution predicted actual turtle DNA methylation and was bimodal in gene promoters (as other vertebrates) and introns (unlike other vertebrates). Differentially methylated genes, including regulators of sexual development, had lower nCpG content indicative of higher historic methylation.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec3">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p id="Par3" class="Para">Ours is the first evidence suggesting that sexually dimorphic DNA methylation is pervasive in turtle gonads (perhaps mediated by repeat methylation) and that it targets numerous regulators of gonadal development, consistent with the hypothesis that it may regulate thermosensitive transcription in TSD vertebrates. However, further research during embryogenesis will help test this hypothesis and the alternative that instead, most differential methylation observed in hatchlings is the by-product of sexual differentiation and not its cause.</p>
</div>',
'date' => '2017-05-19',
'pmid' => 'https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-017-0136-2',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-05-22 10:21:02',
'created' => '2017-05-22 10:21:02',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 89 => array(
'id' => '3210',
'name' => 'Protective vaccination and blood-stage malaria modify DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver of Balb/c mice.',
'authors' => 'Al-Quraishy S. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation are increasingly recognized to be critical for vaccination efficacy and outcome of different infectious diseases, but corresponding information is scarcely available for host defense against malaria. In the experimental blood-stage malaria Plasmodium chabaudi, we investigate the possible effects of a blood-stage vaccine on DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver, known as effector against blood-stage malaria, using DNA methylation microarrays. Naturally susceptible Balb/c mice acquire, by protective vaccination, the potency to survive P. chabaudi malaria and, concomitantly, modifications of constitutive DNA methylation of promoters of numerous genes in the liver; specifically, promoters of 256 genes are hyper(=up)- and 345 genes are hypo(=down)-methylated (p < 0.05). Protective vaccination also leads to changes in promoter DNA methylation upon challenge with P. chabaudi at peak parasitemia on day 8 post infection (p.i.), when 571 and 1013 gene promoters are up- and down-methylated, respectively, in relation to constitutive DNA methylation (p < 0.05). Gene set enrichment analyses reveal that both vaccination and P. chabaudi infections mainly modify promoters of those genes which are most statistically enriched with functions relating to regulation of transcription. Genes with down-methylated promoters encompass those encoding CX3CL1, GP130, and GATA2, known to be involved in monocyte recruitment, IL-6 trans-signaling, and onset of erythropoiesis, respectively. Our data suggest that vaccination may epigenetically improve parts of several effector functions of the liver against blood-stage malaria, as, e.g., recruitment of monocyte/macrophage to the liver accelerated liver regeneration and extramedullary hepatic erythropoiesis, thus leading to self-healing of otherwise lethal P. chabaudi blood-stage malaria.</p>',
'date' => '2017-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28315013',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-07-07 16:36:58',
'created' => '2017-07-07 16:36:58',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 90 => array(
'id' => '3184',
'name' => 'Comparative analysis of MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq and estimation of gene expression changes in a rodent model of schizophrenia',
'authors' => 'Neary J.L. et al.',
'description' => '<p>We conducted a comparative study of multiplexed affinity enrichment sequence methodologies (MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq) in a rodent model of schizophrenia, induced by in utero methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) exposure. We also examined related gene expression changes using a pooled sample approach. MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq identified 769 and 1771 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) between F2 offspring of MAM-exposed rats and saline control rats, respectively. The assays showed good concordance, with ~ 56% of MBD-seq-detected DMRs being identified by or proximal to MeDIP-seq DMRs. There was no significant overlap between DMRs and differentially expressed genes, suggesting that DNA methylation regulatory effects may act upon more distal genes, or are too subtle to detect using our approach. Methylation and gene expression gene ontology enrichment analyses identified biological processes important to schizophrenia pathophysiology, including neuron differentiation, prepulse inhibition, amphetamine response, and glutamatergic synaptic transmission regulation, reinforcing the utility of the MAM rodent model for schizophrenia research.</p>',
'date' => '2017-03-29',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S088875431730023X',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-05-22 09:53:51',
'created' => '2017-05-22 09:53:51',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 91 => array(
'id' => '3148',
'name' => 'Overexpression of LINE-1 Retrotransposons in Autism Brain',
'authors' => 'Shpyleva S. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Long interspersed nuclear elements-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are mobile DNA sequences that are capable of duplication and insertion (retrotransposition) within the genome. Recently, retrotransposition of L1 was shown to occur within human brain leading to somatic mosaicism in hippocampus and cerebellum. Because unregulated L1 activity can promote genomic instability and mutagenesis, multiple mechanisms including epigenetic chromatin condensation have evolved to effectively repress L1 expression. Nonetheless, L1 expression has been shown to be increased in patients with Rett syndrome and schizophrenia. Based on this evidence and our reports of oxidative stress and epigenetic dysregulation in autism cerebellum, we sought to determine whether L1 expression was increased in autism brain. The results indicated that L1 expression was significantly elevated in the autism cerebellum but not in BA9, BA22, or BA24. The binding of repressive MeCP2 and histone H3K9me3 to L1 sequences was significantly lower in autism cerebellum suggesting that relaxation of epigenetic repression may have contributed to increased expression. Further, the increase in L1 expression was inversely correlated with glutathione redox status consistent with reports indicating that L1 expression is increased under pro-oxidant conditions. Finally, the expression of transcription factor FOXO3, sensor of oxidative stress, was significantly increased and positively associated with L1 expression and negatively associated with glutathione redox status. While these novel results are an important first step, future understanding of the contribution of elevated L1 expression to neuronal CNVs and genomic instability in autism will depend on emerging cell-specific genomic technologies, a challenge that warrants future investigation.</p>',
'date' => '2017-02-20',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28220356',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-03-24 17:12:49',
'created' => '2017-03-24 17:12:49',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 92 => array(
'id' => '3092',
'name' => 'Integrative "-Omics" Analysis in Primary Human Hepatocytes Unravels Persistent Mechanisms of Cyclosporine A-Induced Cholestasis',
'authors' => 'Wolters J.E. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Cyclosporine A (CsA) is an undecapeptide with strong immunosuppressant activities and is used a lot after organ transplantation. Furthermore, it may induce cholestasis in the liver. In general, the drug-induced cholestasis (DIC) pathway includes genes involved in the uptake, synthesis, conjugation, and secretion of bile acids. However, whether CsA-induced changes in the cholestasis pathway in vitro are persistent for repeated dose toxicity has not yet been investigated. To explore this, primary human hepatocytes (PHH) were exposed to a subcytotoxic dose of 30 μM CsA daily for 3 and 5 days. To investigate the persistence of induced changes upon terminating CsA exposure after 5 days, a subset of PHH was subjected to a washout period (WO-period) of 3 days. Multiple -omics analyses, comprising whole genome analysis of DNA methylation, gene expression, and microRNA expression, were performed. The CsA-treatment resulted after 3 and 5 days, respectively, in 476 and 20 differentially methylated genes (DMGs), 1353 and 1481 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and in 22 and 29 differentially expressed microRNAs (DE-miRs). Cholestasis-related pathways appeared induced during CsA-treatment. Interestingly, 828 persistent DEGs and 6 persistent DE-miRs but no persistent DMGs were found after the WO-period. These persistent DEGs and DE-miRs showed concordance for 22 genes. Furthermore, 29 persistent DEGs changed into the same direction as observed in livers from cholestasis patients. None of those 29 DEGs which among others relate to oxidative stress and lipid metabolism are yet present in the DIC pathway or cholestasis adverse outcome pathway (AOP) thus presenting novel findings. In summary, we have demonstrated for the first time a persistent impact of repeated dose administration of CsA on genes and microRNAs related to DIC in the gold standard human liver in vitro model with PHH.</p>',
'date' => '2016-12-19',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27989131',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-01-03 10:33:43',
'created' => '2017-01-03 10:33:43',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 93 => array(
'id' => '3086',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA promoter methylation and transcriptome analysis in human adipose tissue unravels novel candidate genes for obesity',
'authors' => 'Keller M. et al.',
'description' => '<h4 id="absSec_1">Objective/methods</h4>
<p id="abspara0010">DNA methylation plays an important role in obesity and related metabolic complications. We examined genome-wide DNA promoter methylation along with mRNA profiles in paired samples of human subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) and omental visceral adipose tissue (OVAT) from non-obese <em>vs.</em> obese individuals.</p>
<h4 id="absSec_2">Results</h4>
<p id="abspara0015">We identified negatively correlated methylation and expression of several obesity-associated genes in our discovery dataset and <em>in silico</em> replicated <em>ETV6</em> in two independent cohorts. Further, we identified six adipose tissue depot-specific genes (<em>HAND2</em>, <em>HOXC6</em>, <em>PPARG</em>, <em>SORBS2</em>, <em>CD36</em>, and <em>CLDN1</em>). The effects were further supported in additional independent cohorts. Our top hits might play a role in adipogenesis and differentiation, obesity, lipid metabolism, and adipose tissue expandability. Finally, we show that <em>in vitro</em> methylation of <em>SORBS2</em> directly represses gene expression.</p>
<h4 id="absSec_3">Conclusions</h4>
<p id="abspara0020">Taken together, our data show distinct tissue specific epigenetic alterations which associate with obesity.</p>',
'date' => '2016-11-16',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212877816302757',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-12-21 10:36:19',
'created' => '2016-12-21 10:36:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 94 => array(
'id' => '3061',
'name' => 'Novel regional age-associated DNA methylation changes within human common disease-associated loci',
'authors' => 'Bell CG et al.',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Advancing age progressively impacts on risk and severity of chronic disease. It also modifies the epigenome, with changes in DNA methylation, due to both random drift and variation within specific functional loci.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">In a discovery set of 2238 peripheral-blood genome-wide DNA methylomes aged 19-82 years, we identify 71 age-associated differentially methylated regions within the linkage disequilibrium blocks of the single nucleotide polymorphisms from the NIH genome-wide association study catalogue. This included 52 novel regions, 29 within loci not covered by 450 k or 27 k Illumina array, and with enrichment for DNase-I Hypersensitivity sites across the full range of tissues. These age-associated differentially methylated regions also show marked enrichment for enhancers and poised promoters across multiple cell types. In a replication set of 2084 DNA methylomes, 95.7 % of the age-associated differentially methylated regions showed the same direction of ageing effect, with 80.3 % and 53.5 % replicated to p < 0.05 and p < 1.85 × 10<sup>-8</sup>, respectively.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">By analysing the functionally enriched disease and trait-associated regions of the human genome, we identify novel epigenetic ageing changes, which could be useful biomarkers or provide mechanistic insights into age-related common diseases.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2016-09-26',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27663977',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-11-04 10:56:10',
'created' => '2016-11-02 09:54:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 95 => array(
'id' => '3058',
'name' => 'Inheritable Silencing of Endogenous Genes by Hit-and-Run Targeted Epigenetic Editing',
'authors' => 'Amabile A. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Gene silencing is instrumental to interrogate gene function and holds promise for therapeutic applications. Here, we repurpose the endogenous retroviruses' silencing machinery of embryonic stem cells to stably silence three highly expressed genes in somatic cells by epigenetics. This was achieved by transiently expressing combinations of engineered transcriptional repressors that bind to and synergize at the target locus to instruct repressive histone marks and de novo DNA methylation, thus ensuring long-term memory of the repressive epigenetic state. Silencing was highly specific, as shown by genome-wide analyses, sharply confined to the targeted locus without spreading to nearby genes, resistant to activation induced by cytokine stimulation, and relieved only by targeted DNA demethylation. We demonstrate the portability of this technology by multiplex gene silencing, adopting different DNA binding platforms and interrogating thousands of genomic loci in different cell types, including primary T lymphocytes. Targeted epigenome editing might have broad application in research and medicine.</p>',
'date' => '2016-09-22',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27662090',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-10-27 15:48:08',
'created' => '2016-10-27 15:48:08',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 96 => array(
'id' => '3047',
'name' => 'Trichloroethylene-Induced DNA Methylation Changes in Male F344 Rat Liver',
'authors' => 'Jiang Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Trichloroethylene (TCE), a common environmental contaminant, causes hepatocellular carcinoma in mice but not in rats. To understand the mechanisms of the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE, we examined the methylation status of DNA in the liver of rats exposed to TCE at 0 or 1000 mg/kg b.w. for 5 days using MeDIP-chip, bisulfite sequencing, COBRA, and LC-MS/MS. The related mRNA expression levels were measured by qPCR. Although no global DNA methylation change was detected, 806 genes were hypermethylated and 186 genes were hypomethylated. The genes with hypermethylated DNA were enriched in endocytosis, MAPK, and cAMP signaling pathways. We further confirmed the hypermethylation of Uhrf2 DNA and the hypomethylation of Hadhb DNA, which were negatively correlated with their mRNA expression levels. The transcriptional levels of Jun, Ihh, and Tet2 were significantly downregulated, whereas Cdkn1a was overexpressed. No mRNA expression change was found for Mki67, Myc, Uhrf1, and Dnmt1. In conclusion, TCE-induced DNA methylation changes in rats appear to suppress instead of promote hepatocarcinogenesis, which might play a role in the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE.</p>',
'date' => '2016-09-21',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27618143',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-10-10 11:10:05',
'created' => '2016-10-10 11:10:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 97 => array(
'id' => '3001',
'name' => 'Dynamic Interplay between the Transcriptome and Methylome in Response to Oxidative and Alkylating Stress',
'authors' => 'Deferme L et al.',
'description' => '<p>In recent years, it has been shown that free radicals not only react directly with DNA but also regulate epigenetic processes such as DNA methylation, which may be relevant within the context of, for example, tumorigenesis. However, how these free radicals impact the epigenome remains unclear. We therefore investigated whether methyl and hydroxyl radicals, formed by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBH), change temporal DNA methylation patterns and how this interferes with genome-wide gene expression. At three time points, TBH-induced radicals in HepG2 cells were identified by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Total 5-methylcytosine (5mC) levels were determined by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry and genome-wide changes in 5mC and gene expression by microarrays. Induced methylome changes rather represent an adaptive response to the oxidative stress-related reactions observed in the transcriptome. More specifically, we found that methyl radicals did not induce DNA methylation directly. An initial oxidative and alkylating stress-related response of the transcriptome during the early phase of TBH treatment was followed by an epigenetic response associated with cell survival signaling. Also, we identified genes of which the expression seems directly regulated by DNA methylation. This work suggests an important role of the methylome in counter-regulating primary oxidative and alkylating stress responses in the transcriptome to restore normal cell function. Altogether, the methylome may play an important role in counter-regulating primary oxidative and alkylating stress responses in the transcriptome presumably to restore normal cell function.</p>',
'date' => '2016-08-24',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27509014',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-08-25 17:17:48',
'created' => '2016-08-25 17:17:48',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 98 => array(
'id' => '2984',
'name' => 'Efficiency of methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing for whole-genome DNA methylation analysis',
'authors' => 'Jeong HM et al.',
'description' => '<p><abstracttext label="AIMS" nlmcategory="OBJECTIVE">We compared four common methods for measuring DNA methylation levels and recommended the most efficient method in terms of cost and coverage.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>MATERIALS & METHODS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="MATERIALS & METHODS" nlmcategory="METHODS">The DNA methylation status of liver and stomach tissues was profiled using four different methods, whole-genome bisulphite sequencing (WG-BS), targeted bisulphite sequencing (Targeted-BS), methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing (MeDIP-BS). We calculated DNA methylation levels using each method and compared the results.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">MeDIP-BS yielded the most similar DNA methylation profile to WG-BS, with 20 times less data, suggesting remarkable cost savings and coverage efficiency compared with the other methods.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">MeDIP-BS is a practical cost-effective method for analyzing whole-genome DNA methylation that is highly accurate at base-pair resolution.</abstracttext></p>',
'date' => '2016-06-08',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27266718',
'doi' => ' 10.2217/epi-2016-0038',
'modified' => '2016-07-26 09:17:24',
'created' => '2016-07-26 09:17:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 99 => array(
'id' => '2904',
'name' => 'Aflatoxin B1 induces persistent epigenomic effects in primary human hepatocytes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma',
'authors' => 'Linda Rieswijka, Sandra M.H. Claessena, Otto Bekersc, Marcel van Herwijnena, Daniël H.J. Theunissena, Danyel G.J. Jennena, Theo M.C.M. de Koka, Jos C.S. Kleinjansa,Simone G.J. van Bredaa',
'description' => '<p><span>Chronic exposure to aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) has, in certain regions in the world, been strongly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. AFB1 is a very potent hepatotoxic and carcinogenic mycotoxin which is frequently reported as a food contaminant. Epigenetic modifications provoked by environmental exposures, such as AFB1, may create a persistent epigenetic footprint. Deregulation of epigenetic mechanisms has actually been reported in HCC patients following AFB1 exposure; however, no attempts have yet been made to investigate early effects on the epigenome level which may be persistent on longer term, thereby possibly initiating carcinogenic events. In this study, we aim to identify methyl DNA-mRNA-interactions representative for a persistent epigenetic footprint associated with the early onset of AFB1-induced HCC. For this, primary human hepatocytes were exposed to 0.3 μM of AFB1 for 5 days. Persistent epigenetic effects were measured 3 days after terminating the carcinogenic exposure. Whole genome DNA methylation changes and whole genome transcriptomic analysis were analyzed applying microarray technologies, and cross-omics interactions were evaluated. Upon combining transcriptomics data with results on DNA methylation, a range of persistent hyper- and hypo-methylated genes was identified which also appeared affected on the transcriptome level. For six of the hypo-methylated and up-regulated genes, namely TXNRD1, PCNA, CCNK, DIAPH3, RAB27A and HIST1H2BF, a clear role in carcinogenic events could be identified. This study is the first to report on a carcinogen-induced persistent impact on the epigenetic footprint in relation with the transcriptome which could be indicative for the early onset of AFB1-related development of HCC.</span></p>',
'date' => '2016-05-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0300483X16300427',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.tox.2016.05.002',
'modified' => '2016-05-13 14:13:03',
'created' => '2016-05-08 07:29:28',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 100 => array(
'id' => '2855',
'name' => 'Paternal B Vitamin Intake Is a Determinant of Growth, Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Tumor Volume in Female Apc1638N Mouse Offspring',
'authors' => 'Sabet JA, Park LK, Iyer LK, Tai AK, Koh GY, Pfalzer AC, Parnell LD, Mason JB, Liu Z, Byun AJ, Crott JW',
'description' => '<h3>Background</h3>
<p>The importance of maternal nutrition to offspring health and risk of disease is well established. Emerging evidence suggests paternal diet may affect offspring health as well.</p>
<h3>Objective</h3>
<p>In the current study we sought to determine whether modulating pre-conception paternal B vitamin intake alters intestinal tumor formation in offspring. Additionally, we sought to identify potential mechanisms for the observed weight differential among offspring by profiling hepatic gene expression and lipid content.</p>
<h3>Methods</h3>
<p>Male Apc<sup>1638N</sup> mice (prone to intestinal tumor formation) were fed diets containing replete (control, CTRL), mildly deficient (DEF), or supplemental (SUPP) quantities of vitamins B<sub>2</sub>, B<sub>6</sub>, B<sub>12</sub>, and folate for 8 weeks before mating with control-fed wild type females. Wild type offspring were euthanized at weaning and hepatic gene expression profiled. Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring were fed a replete diet and euthanized at 28 weeks of age to assess tumor burden.</p>
<h3>Results</h3>
<p>No differences in intestinal tumor incidence or burden were found between male Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring of different paternal diet groups. Although in female Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring there were no differences in tumor incidence or multiplicity, a stepwise increase in tumor volume with increasing paternal B vitamin intake was observed. Interestingly, female offspring of SUPP and DEF fathers had a significantly lower body weight than those of CTRL fed fathers. Moreover, hepatic trigylcerides and cholesterol were elevated 3-fold in adult female offspring of SUPP fathers. Weanling offspring of the same fathers displayed altered expression of several key lipid-metabolism genes. Hundreds of differentially methylated regions were identified in the paternal sperm in response to DEF and SUPP diets. Aside from a few genes including Igf2, there was a striking lack of overlap between these genes differentially methylated in sperm and differentially expressed in offspring.</p>
<h3>Conclusions</h3>
<p>In this animal model, modulation of paternal B vitamin intake prior to mating alters offspring weight gain, lipid metabolism and tumor growth in a sex-specific fashion. These results highlight the need to better define how paternal nutrition affects the health of offspring.</p>',
'date' => '2016-03-11',
'pmid' => 'http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0151579#abstract0',
'doi' => ' 10.1371/journal.pone.0151579',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 10:26:38',
'created' => '2016-03-15 10:26:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 101 => array(
'id' => '2977',
'name' => 'Regulation of miR-200c/141 expression by intergenic DNA-looping and transcriptional read-through',
'authors' => 'Batista L et al.',
'description' => '<p>The miR-200 family members have been implicated in stress responses and ovarian tumorigenesis. Here, we find that miR-200c/141 transcription is intimately linked to the transcription of the proximal upstream gene PTPN6 (SHP1) in all physiological conditions tested. PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 are transcriptionally co-regulated by two complementary mechanisms. First, a bypass of the regular PTPN6 polyadenylation signal allows the transcription of the downstream miR-200c/141. Second, the promoters of the PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 transcription units physically interact through a 3-dimensional DNA loop and exhibit similar epigenetic regulation. Our findings highlight that transcription of intergenic miRNAs is a novel outcome of transcriptional read-through and reveal a yet unexplored type of DNA loop associating two closely located promoters. These mechanisms have significant relevance in ovarian cancers and stress response, pathophysiological conditions in which miR-200c/141 exert key functions.</p>',
'date' => '2016-01-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26725650',
'doi' => '10.1038/ncomms9959',
'modified' => '2016-07-07 10:27:25',
'created' => '2016-07-07 10:27:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 102 => array(
'id' => '2951',
'name' => 'Maternal immune activation induces GAD1 and GAD2 promoter remodeling in the offspring prefrontal cortex',
'authors' => 'Labouesse MA et al.',
'description' => '<p>Maternal infection during pregnancy increases the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in the offspring. In addition to its influence on other neuronal systems, this early-life environmental adversity has been shown to negatively affect cortical γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) functions in adult life, including impaired prefrontal expression of enzymes required for GABA synthesis. The underlying molecular processes, however, remain largely unknown. In the present study, we explored whether epigenetic modifications represent a mechanism whereby maternal infection during pregnancy can induce such GABAergic impairments in the offspring. We used an established mouse model of prenatal immune challenge that is based on maternal treatment with the viral mimetic poly(I:C). We found that prenatal immune activation increased prefrontal levels of 5-methylated cytosines (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylated cytosines (5hmC) in the promoter region of GAD1, which encodes the 67-kDa isoform of the GABA-synthesising enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67). The early-life challenge also increased 5mC levels at the promoter region of GAD2, which encodes the 65-kDa GAD isoform (GAD65). These effects were accompanied by elevated GAD1 and GAD2 promoter binding of methyl CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) and by reduced GAD67 and GAD65 mRNA expression. Moreover, the epigenetic modifications at the GAD1 promoter correlated with prenatal infection-induced impairments in working memory and social interaction. Our study thus highlights that hypermethylation of GAD1 and GAD2 promoters may be an important molecular mechanism linking prenatal infection to presynaptic GABAergic impairments and associated behavioral and cognitive abnormalities in the offspring.</p>',
'date' => '2015-12-02',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26575259',
'doi' => ' 10.1080/15592294.2015.1114202',
'modified' => '2016-06-10 16:32:32',
'created' => '2016-06-10 16:32:32',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 103 => array(
'id' => '2860',
'name' => 'DNA methylation profiling: comparison of genome-wide sequencing methods and the Infinium Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip',
'authors' => 'Walker DL, Bhagwate AV, Baheti S, Smalley RL, Hilker CA, Sun Z, Cunningham JM',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>AIMS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="AIMS" nlmcategory="OBJECTIVE">To compare the performance of four sequence-based and one microarray methods for DNA methylation profiling.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>METHODS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="METHODS" nlmcategory="METHODS">DNA from two cell lines were profiled by reduced representation bisulfite sequencing, methyl capture sequencing (SS-Meth Seq), NimbleGen SeqCapEpi CpGiant(Nimblegen MethSeq), methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) and the Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip (Meth450K).</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS & CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS & CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">Despite differences in genome-wide coverage, high correlation and concordance were observed between different methods. Significant overlap of differentially methylated regions was identified between sequenced-based platforms. MeDIP provided the best coverage for the whole genome and gene body regions, while RRBS and Nimblegen MethSeq were superior for CpGs in CpG islands and promoters. Methylation analyses can be achieved by any of the five methods but understanding their differences may better address the research question being posed.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-12-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26192535',
'doi' => '10.2217/EPI.15.64',
'modified' => '2016-03-16 11:06:05',
'created' => '2016-03-16 11:06:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 104 => array(
'id' => '2892',
'name' => 'High cortisol in 5-year-old children causes loss of DNA methylation in SINE retrotransposons: a possible role for ZNF263 in stress-related diseases',
'authors' => 'Nätt D, Johansson I, Faresjö T, Ludvigsson J, Thorsell A',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Childhood stress leads to increased risk of many adult diseases, such as major depression and cardiovascular disease. Studies show that adults with experienced childhood stress have specific epigenetic changes, but to understand the pathways that lead to disease, we also need to study the epigenetic link prospectively in children.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Here, we studied a homogenous group of 48 5-year-old children. By combining hair cortisol measurements (a well-documented biomarker for chronic stress), with whole-genome DNA-methylation sequencing, we show that high cortisol associates with a genome-wide decrease in DNA methylation and targets short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs; a type of retrotransposon) and genes important for calcium transport: phenomena commonly affected in stress-related diseases and in biological aging. More importantly, we identify a zinc-finger transcription factor, ZNF263, whose binding sites where highly overrepresented in regions experiencing methylation loss. This type of zinc-finger protein has previously shown to be involved in the defense against retrotransposons.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">Our results show that stress in preschool children leads to changes in DNA methylation similar to those seen in biological aging. We suggest that this may affect future disease susceptibility by alterations in the epigenetic mechanisms that keep retrotransposons dormant. Future treatments for stress- and age-related diseases may therefore seek to target zinc-finger proteins that epigenetically control retrotransposon reactivation, such as ZNF263.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-09-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26339299',
'doi' => ' 10.1186/s13148-015-0123-z',
'modified' => '2016-04-14 10:03:28',
'created' => '2016-04-14 10:03:28',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 105 => array(
'id' => '2857',
'name' => 'Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo',
'authors' => 'Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associated with disturbed blood flow. DNA methylation is a powerful epigenetic regulator of endothelial transcription recently associated with flow characteristics. We investigated differential DNA methylation in flow region-specific aortic endothelial cells in vivo in adult domestic male and female swine.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Genome-wide DNA methylation was profiled in endothelial cells (EC) isolated from two robust locations of differing patho-susceptibility:--an athero-susceptible site located at the inner curvature of the aortic arch (AA) and an athero-protected region in the descending thoracic (DT) aorta. Complete methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) identified over 5500 endothelial differentially methylated regions (DMRs). DMR density was significantly enriched in exons and 5'UTR sequences of annotated genes, 60 of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. The set of DMR-associated genes was enriched in transcriptional regulation, pattern specification HOX loci, oxidative stress and the ER stress adaptive pathway, all categories linked to athero-susceptible endothelium. Examination of the relationship between DMR and mRNA in HOXA genes demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between CpG island promoter methylation and gene expression. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) confirmed differential CpG methylation of HOXA genes, the ER stress gene ATF4, inflammatory regulator microRNA-10a and ARHGAP25 that encodes a negative regulator of Rho GTPases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Gender-specific DMRs associated with ciliogenesis that may be linked to defects in cilia development were also identified in AA DMRs.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">An endothelial methylome analysis identifies epigenetic DMR characteristics associated with transcriptional regulation in regions of atherosusceptibility in swine aorta in vivo. The data represent the first methylome blueprint for spatio-temporal analyses of lesion susceptibility predisposing to endothelial dysfunction in complex flow environments in vivo.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-07-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12864-015-1656-4',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'created' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Testimonial' => array(),
'Area' => array(),
'SafetySheet' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '656',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS US en',
'language' => 'en',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-US-en-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'US',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:56:19',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:56:19',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '654',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS GB en',
'language' => 'en',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-GB-en-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'GB',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:28',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:28',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '649',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE fr',
'language' => 'fr',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-fr-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:52:41',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:52:41',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '653',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS FR fr',
'language' => 'fr',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-FR-fr-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'FR',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:02',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:02',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '652',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS ES es',
'language' => 'es',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-ES-es-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'ES',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:54:39',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:54:39',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '651',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS DE de',
'language' => 'de',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-DE-de-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'DE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:54:02',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:54:02',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '655',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS JP ja',
'language' => 'ja',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-JP-ja-1_1.pdf',
'countries' => 'JP',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:55',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:55',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 7 => array(
'id' => '650',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE nl',
'language' => 'nl',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-nl-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
)
)
$meta_canonical = 'https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns'
$country = 'US'
$countries_allowed = array(
(int) 0 => 'CA',
(int) 1 => 'US',
(int) 2 => 'IE',
(int) 3 => 'GB',
(int) 4 => 'DK',
(int) 5 => 'NO',
(int) 6 => 'SE',
(int) 7 => 'FI',
(int) 8 => 'NL',
(int) 9 => 'BE',
(int) 10 => 'LU',
(int) 11 => 'FR',
(int) 12 => 'DE',
(int) 13 => 'CH',
(int) 14 => 'AT',
(int) 15 => 'ES',
(int) 16 => 'IT',
(int) 17 => 'PT'
)
$outsource = false
$other_formats = array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
)
)
$pro = array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsGroup' => array(
'id' => '10',
'product_id' => '1879',
'group_id' => '7'
)
)
$edit = ''
$testimonials = ''
$featured_testimonials = ''
$related_products = '<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit"><img src="/img/product/reagents/diamag02.png" alt="some alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">B04000001</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-1819" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/1819" id="CartAdd/1819Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="1819" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'B04000001',
'240',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'B04000001',
'240',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit" data-reveal-id="cartModal-1819" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17031043-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2597" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2597" id="CartAdd/2597Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2597" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17031043-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17031043-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2597" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17031046-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2599" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2599" id="CartAdd/2599Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2599" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'C17031046-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'C17031046-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2599" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17021042-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2593" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2593" id="CartAdd/2593Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2593" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17021042-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17021042-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2593" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17021045-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2595" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2595" id="CartAdd/2595Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2595" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'C17021045-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'C17021045-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2595" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/auto-magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns"><img src="/img/product/kits/methyl-kit-icon.png" alt="Methylation kit icon" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C02010014</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit - ordering reference: C0...</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/bioruptorpico2"><img src="/img/product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-1.jpg" alt="Bioruptor Pico" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">B01080010</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: QUOTE MODAL --><div id="quoteModal-3046" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<h3>Get a quote</h3><p class="lead">You are about to request a quote for <strong>Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device</strong>. Fill out the form below and we will be in touch with you very soon.</p><p><small>All <span style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</span> fields are mandatory</small></p>
</div>
</div>
<form action="/en/quotes/quote?id=3046" id="Quote-3046" class="quote" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][product_id]" value="3046" id="QuoteProductId"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][formLoaded6tY4bPYk]" value="c0sveHAvS0dieWhxT3RCV3dlb3pnUT09" id="QuoteFormLoaded6tY4bPYk"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][product_rfq_tag]" value="bioruptorpico2" id="QuoteProductRfqTag"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][source_quote]" value="modal quote" id="QuoteSourceQuote"/>
<div class="row collapse">
<h2>Contact Information</h2>
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">First name <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][first_name]" placeholder="john" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteFirstName" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Last name <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][last_name]" placeholder="doe" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteLastName" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Company <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][company]" placeholder="Organisation / Institute" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteCompany" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Phone number</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][phone_number]" placeholder="+1 862 209-4680" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuotePhoneNumber"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">City</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][city]" placeholder="Denville" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteCity"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Country <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<select name="data[Quote][country]" required="required" class="triggers" id="country_selector_quote-3046">
<option value="">-- select a country --</option>
<option value="AF">Afghanistan</option>
<option value="AX">Åland Islands</option>
<option value="AL">Albania</option>
<option value="DZ">Algeria</option>
<option value="AS">American Samoa</option>
<option value="AD">Andorra</option>
<option value="AO">Angola</option>
<option value="AI">Anguilla</option>
<option value="AQ">Antarctica</option>
<option value="AG">Antigua and Barbuda</option>
<option value="AR">Argentina</option>
<option value="AM">Armenia</option>
<option value="AW">Aruba</option>
<option value="AU">Australia</option>
<option value="AT">Austria</option>
<option value="AZ">Azerbaijan</option>
<option value="BS">Bahamas</option>
<option value="BH">Bahrain</option>
<option value="BD">Bangladesh</option>
<option value="BB">Barbados</option>
<option value="BY">Belarus</option>
<option value="BE">Belgium</option>
<option value="BZ">Belize</option>
<option value="BJ">Benin</option>
<option value="BM">Bermuda</option>
<option value="BT">Bhutan</option>
<option value="BO">Bolivia</option>
<option value="BQ">Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba</option>
<option value="BA">Bosnia and Herzegovina</option>
<option value="BW">Botswana</option>
<option value="BV">Bouvet Island</option>
<option value="BR">Brazil</option>
<option value="IO">British Indian Ocean Territory</option>
<option value="BN">Brunei Darussalam</option>
<option value="BG">Bulgaria</option>
<option value="BF">Burkina Faso</option>
<option value="BI">Burundi</option>
<option value="KH">Cambodia</option>
<option value="CM">Cameroon</option>
<option value="CA">Canada</option>
<option value="CV">Cape Verde</option>
<option value="KY">Cayman Islands</option>
<option value="CF">Central African Republic</option>
<option value="TD">Chad</option>
<option value="CL">Chile</option>
<option value="CN">China</option>
<option value="CX">Christmas Island</option>
<option value="CC">Cocos (Keeling) Islands</option>
<option value="CO">Colombia</option>
<option value="KM">Comoros</option>
<option value="CG">Congo</option>
<option value="CD">Congo, The Democratic Republic of the</option>
<option value="CK">Cook Islands</option>
<option value="CR">Costa Rica</option>
<option value="CI">Côte d'Ivoire</option>
<option value="HR">Croatia</option>
<option value="CU">Cuba</option>
<option value="CW">Curaçao</option>
<option value="CY">Cyprus</option>
<option value="CZ">Czech Republic</option>
<option value="DK">Denmark</option>
<option value="DJ">Djibouti</option>
<option value="DM">Dominica</option>
<option value="DO">Dominican Republic</option>
<option value="EC">Ecuador</option>
<option value="EG">Egypt</option>
<option value="SV">El Salvador</option>
<option value="GQ">Equatorial Guinea</option>
<option value="ER">Eritrea</option>
<option value="EE">Estonia</option>
<option value="ET">Ethiopia</option>
<option value="FK">Falkland Islands (Malvinas)</option>
<option value="FO">Faroe Islands</option>
<option value="FJ">Fiji</option>
<option value="FI">Finland</option>
<option value="FR">France</option>
<option value="GF">French Guiana</option>
<option value="PF">French Polynesia</option>
<option value="TF">French Southern Territories</option>
<option value="GA">Gabon</option>
<option value="GM">Gambia</option>
<option value="GE">Georgia</option>
<option value="DE">Germany</option>
<option value="GH">Ghana</option>
<option value="GI">Gibraltar</option>
<option value="GR">Greece</option>
<option value="GL">Greenland</option>
<option value="GD">Grenada</option>
<option value="GP">Guadeloupe</option>
<option value="GU">Guam</option>
<option value="GT">Guatemala</option>
<option value="GG">Guernsey</option>
<option value="GN">Guinea</option>
<option value="GW">Guinea-Bissau</option>
<option value="GY">Guyana</option>
<option value="HT">Haiti</option>
<option value="HM">Heard Island and McDonald Islands</option>
<option value="VA">Holy See (Vatican City State)</option>
<option value="HN">Honduras</option>
<option value="HK">Hong Kong</option>
<option value="HU">Hungary</option>
<option value="IS">Iceland</option>
<option value="IN">India</option>
<option value="ID">Indonesia</option>
<option value="IR">Iran, Islamic Republic of</option>
<option value="IQ">Iraq</option>
<option value="IE">Ireland</option>
<option value="IM">Isle of Man</option>
<option value="IL">Israel</option>
<option value="IT">Italy</option>
<option value="JM">Jamaica</option>
<option value="JP">Japan</option>
<option value="JE">Jersey</option>
<option value="JO">Jordan</option>
<option value="KZ">Kazakhstan</option>
<option value="KE">Kenya</option>
<option value="KI">Kiribati</option>
<option value="KP">Korea, Democratic People's Republic of</option>
<option value="KR">Korea, Republic of</option>
<option value="KW">Kuwait</option>
<option value="KG">Kyrgyzstan</option>
<option value="LA">Lao People's Democratic Republic</option>
<option value="LV">Latvia</option>
<option value="LB">Lebanon</option>
<option value="LS">Lesotho</option>
<option value="LR">Liberia</option>
<option value="LY">Libya</option>
<option value="LI">Liechtenstein</option>
<option value="LT">Lithuania</option>
<option value="LU">Luxembourg</option>
<option value="MO">Macao</option>
<option value="MK">Macedonia, Republic of</option>
<option value="MG">Madagascar</option>
<option value="MW">Malawi</option>
<option value="MY">Malaysia</option>
<option value="MV">Maldives</option>
<option value="ML">Mali</option>
<option value="MT">Malta</option>
<option value="MH">Marshall Islands</option>
<option value="MQ">Martinique</option>
<option value="MR">Mauritania</option>
<option value="MU">Mauritius</option>
<option value="YT">Mayotte</option>
<option value="MX">Mexico</option>
<option value="FM">Micronesia, Federated States of</option>
<option value="MD">Moldova</option>
<option value="MC">Monaco</option>
<option value="MN">Mongolia</option>
<option value="ME">Montenegro</option>
<option value="MS">Montserrat</option>
<option value="MA">Morocco</option>
<option value="MZ">Mozambique</option>
<option value="MM">Myanmar</option>
<option value="NA">Namibia</option>
<option value="NR">Nauru</option>
<option value="NP">Nepal</option>
<option value="NL">Netherlands</option>
<option value="NC">New Caledonia</option>
<option value="NZ">New Zealand</option>
<option value="NI">Nicaragua</option>
<option value="NE">Niger</option>
<option value="NG">Nigeria</option>
<option value="NU">Niue</option>
<option value="NF">Norfolk Island</option>
<option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands</option>
<option value="NO">Norway</option>
<option value="OM">Oman</option>
<option value="PK">Pakistan</option>
<option value="PW">Palau</option>
<option value="PS">Palestine, State of</option>
<option value="PA">Panama</option>
<option value="PG">Papua New Guinea</option>
<option value="PY">Paraguay</option>
<option value="PE">Peru</option>
<option value="PH">Philippines</option>
<option value="PN">Pitcairn</option>
<option value="PL">Poland</option>
<option value="PT">Portugal</option>
<option value="PR">Puerto Rico</option>
<option value="QA">Qatar</option>
<option value="RE">Réunion</option>
<option value="RO">Romania</option>
<option value="RU">Russian Federation</option>
<option value="RW">Rwanda</option>
<option value="BL">Saint Barthélemy</option>
<option value="SH">Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha</option>
<option value="KN">Saint Kitts and Nevis</option>
<option value="LC">Saint Lucia</option>
<option value="MF">Saint Martin (French part)</option>
<option value="PM">Saint Pierre and Miquelon</option>
<option value="VC">Saint Vincent and the Grenadines</option>
<option value="WS">Samoa</option>
<option value="SM">San Marino</option>
<option value="ST">Sao Tome and Principe</option>
<option value="SA">Saudi Arabia</option>
<option value="SN">Senegal</option>
<option value="RS">Serbia</option>
<option value="SC">Seychelles</option>
<option value="SL">Sierra Leone</option>
<option value="SG">Singapore</option>
<option value="SX">Sint Maarten (Dutch part)</option>
<option value="SK">Slovakia</option>
<option value="SI">Slovenia</option>
<option value="SB">Solomon Islands</option>
<option value="SO">Somalia</option>
<option value="ZA">South Africa</option>
<option value="GS">South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands</option>
<option value="ES">Spain</option>
<option value="LK">Sri Lanka</option>
<option value="SD">Sudan</option>
<option value="SR">Suriname</option>
<option value="SS">South Sudan</option>
<option value="SJ">Svalbard and Jan Mayen</option>
<option value="SZ">Swaziland</option>
<option value="SE">Sweden</option>
<option value="CH">Switzerland</option>
<option value="SY">Syrian Arab Republic</option>
<option value="TW">Taiwan</option>
<option value="TJ">Tajikistan</option>
<option value="TZ">Tanzania</option>
<option value="TH">Thailand</option>
<option value="TL">Timor-Leste</option>
<option value="TG">Togo</option>
<option value="TK">Tokelau</option>
<option value="TO">Tonga</option>
<option value="TT">Trinidad and Tobago</option>
<option value="TN">Tunisia</option>
<option value="TR">Turkey</option>
<option value="TM">Turkmenistan</option>
<option value="TC">Turks and Caicos Islands</option>
<option value="TV">Tuvalu</option>
<option value="UG">Uganda</option>
<option value="UA">Ukraine</option>
<option value="AE">United Arab Emirates</option>
<option value="GB">United Kingdom</option>
<option value="US" selected="selected">United States</option>
<option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands</option>
<option value="UY">Uruguay</option>
<option value="UZ">Uzbekistan</option>
<option value="VU">Vanuatu</option>
<option value="VE">Venezuela</option>
<option value="VN">Viet Nam</option>
<option value="VG">Virgin Islands, British</option>
<option value="VI">Virgin Islands, U.S.</option>
<option value="WF">Wallis and Futuna</option>
<option value="EH">Western Sahara</option>
<option value="YE">Yemen</option>
<option value="ZM">Zambia</option>
<option value="ZW">Zimbabwe</option>
</select><script>
$('#country_selector_quote-3046').selectize();
</script><br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">State</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" maxlength="3" type="text"/><br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Email <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][email]" placeholder="email@address.com" maxlength="255" type="email" id="QuoteEmail" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse" id="email_v">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Email verification<sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][email_v]" autocomplete="nope" type="text" id="QuoteEmailV"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Comment</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<textarea name="data[Quote][comment]" placeholder="Additional comments" cols="30" rows="6" id="QuoteComment"></textarea> </div>
</div>
<!------------SERVICES PARTICULAR FORM START---------------->
<!------------DATA TO POPULATE REGARDING SPECIFIC SERVICES----->
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<div class="recaptcha"><div id="recaptcha6776db64c3be6"></div></div> </div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<button id="submit_btn-3046" class="alert button expand" form="Quote-3046" type="submit">Contact me</button> </div>
</div>
</form><script>
var pardotFormHandlerURL = 'https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2022-10-10/36b1c';
function postToPardot(formAction, id) {
$('#pardot-form-handler').load(function(){
$('#Quote-' + id).attr('action', formAction);
$('#Quote-' + id).submit();
});
$('#pardot-form-handler').attr('src', pardotFormHandlerURL + '?' + $('#Quote-' + id).serialize());
}
$(document).ready(function() {
$('body').append('<iframe id="pardot-form-handler" height="0" width="0" style="position:absolute; left:-100000px; top:-100000px" src="javascript:false;"></iframe>');
$('#Quote-3046').attr('action','javascript:postToPardot(\'' + $('#Quote-3046').attr('action') + '\', 3046)');
});
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").click(function (e) {
if($(this).closest('form')[0].checkValidity()){
e.preventDefault();
//disable the submit button
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").attr("disabled", true);
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").html("Processing...");
//submit the form
$("#Quote-3046").submit();
}
})
</script>
<script>
if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'US') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AL">Alabama (AL)</option><option value="AK">Alaska (AK)</option><option value="AZ">Arizona (AZ)</option><option value="AR">Arkansas (AR)</option><option value="CA">California (CA)</option><option value="CO">Colorado (CO)</option><option value="CT">Connecticut (CT)</option><option value="DE">Delaware (DE)</option><option value="FL">Florida (FL)</option><option value="GA">Georgia (GA)</option><option value="HI">Hawaii (HI)</option><option value="ID">Idaho (ID)</option><option value="IL">Illinois (IL)</option><option value="IN">Indiana (IN)</option><option value="IA">Iowa (IA)</option><option value="KS">Kansas (KS)</option><option value="KY">Kentucky (KY)</option><option value="LA">Louisiana (LA)</option><option value="ME">Maine (ME)</option><option value="MD">Maryland (MD)</option><option value="MA">Massachusetts (MA)</option><option value="MI">Michigan (MI)</option><option value="MN">Minnesota (MN)</option><option value="MS">Mississippi (MS)</option><option value="MO">Missouri (MO)</option><option value="MT">Montana (MT)</option><option value="NE">Nebraska (NE)</option><option value="NV">Nevada (NV)</option><option value="NH">New Hampshire (NH)</option><option value="NJ">New Jersey (NJ)</option><option value="NM">New Mexico (NM)</option><option value="NY">New York (NY)</option><option value="NC">North Carolina (NC)</option><option value="ND">North Dakota (ND)</option><option value="OH">Ohio (OH)</option><option value="OK">Oklahoma (OK)</option><option value="OR">Oregon (OR)</option><option value="PA">Pennsylvania (PA)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="RI">Rhode Island (RI)</option><option value="SC">South Carolina (SC)</option><option value="SD">South Dakota (SD)</option><option value="TN">Tennessee (TN)</option><option value="TX">Texas (TX)</option><option value="UT">Utah (UT)</option><option value="VT">Vermont (VT)</option><option value="VA">Virginia (VA)</option><option value="WA">Washington (WA)</option><option value="WV">West Virginia (WV)</option><option value="WI">Wisconsin (WI)</option><option value="WY">Wyoming (WY)</option><option value="DC">District of Columbia (DC)</option><option value="AS">American Samoa (AS)</option><option value="GU">Guam (GU)</option><option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands (MP)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands (UM)</option><option value="VI">Virgin Islands (VI)</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'CA') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AB">Alberta (AB)</option><option value="BC">British Columbia (BC)</option><option value="MB">Manitoba (MB)</option><option value="NB">New Brunswick (NB)</option><option value="NL">Newfoundland and Labrador (NL)</option><option value="NS">Nova Scotia (NS)</option><option value="ON">Ontario (ON)</option><option value="PE">Prince Edward Island (PE)</option><option value="QC">Quebec (QC)</option><option value="SK">Saskatchewan (SK)</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'DE') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="BW">Baden-Württemberg (BW)</option><option value="BY">Bayern (BY)</option><option value="BE">Berlin (BE)</option><option value="BB">Brandeburg (BB)</option><option value="HB">Bremen (HB)</option><option value="HH">Hamburg (HH)</option><option value="HE">Hessen (HE)</option><option value="MV">Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV)</option><option value="NI">Niedersachsen (NI)</option><option value="NW">Nordrhein-Westfalen (NW)</option><option value="RP">Rheinland-Pfalz (RP)</option><option value="SL">Saarland (SL)</option><option value="SN">Sachsen (SN)</option><option value ="SA">Sachsen-Anhalt (SA)</option><option value="SH">Schleswig-Holstein (SH)</option><option value="TH">Thüringen</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().hide();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<input name="data[Quote][state]" maxlength="255" type="text" id="state-3046" value="">');
}
$("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").change(function() {
if (this.value == 'US') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AL">Alabama (AL)</option><option value="AK">Alaska (AK)</option><option value="AZ">Arizona (AZ)</option><option value="AR">Arkansas (AR)</option><option value="CA">California (CA)</option><option value="CO">Colorado (CO)</option><option value="CT">Connecticut (CT)</option><option value="DE">Delaware (DE)</option><option value="FL">Florida (FL)</option><option value="GA">Georgia (GA)</option><option value="HI">Hawaii (HI)</option><option value="ID">Idaho (ID)</option><option value="IL">Illinois (IL)</option><option value="IN">Indiana (IN)</option><option value="IA">Iowa (IA)</option><option value="KS">Kansas (KS)</option><option value="KY">Kentucky (KY)</option><option value="LA">Louisiana (LA)</option><option value="ME">Maine (ME)</option><option value="MD">Maryland (MD)</option><option value="MA">Massachusetts (MA)</option><option value="MI">Michigan (MI)</option><option value="MN">Minnesota (MN)</option><option value="MS">Mississippi (MS)</option><option value="MO">Missouri (MO)</option><option value="MT">Montana (MT)</option><option value="NE">Nebraska (NE)</option><option value="NV">Nevada (NV)</option><option value="NH">New Hampshire (NH)</option><option value="NJ">New Jersey (NJ)</option><option value="NM">New Mexico (NM)</option><option value="NY">New York (NY)</option><option value="NC">North Carolina (NC)</option><option value="ND">North Dakota (ND)</option><option value="OH">Ohio (OH)</option><option value="OK">Oklahoma (OK)</option><option value="OR">Oregon (OR)</option><option value="PA">Pennsylvania (PA)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="RI">Rhode Island (RI)</option><option value="SC">South Carolina (SC)</option><option value="SD">South Dakota (SD)</option><option value="TN">Tennessee (TN)</option><option value="TX">Texas (TX)</option><option value="UT">Utah (UT)</option><option value="VT">Vermont (VT)</option><option value="VA">Virginia (VA)</option><option value="WA">Washington (WA)</option><option value="WV">West Virginia (WV)</option><option value="WI">Wisconsin (WI)</option><option value="WY">Wyoming (WY)</option><option value="DC">District of Columbia (DC)</option><option value="AS">American Samoa (AS)</option><option value="GU">Guam (GU)</option><option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands (MP)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands (UM)</option><option value="VI">Virgin Islands (VI)</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if (this.value == 'CA') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AB">Alberta (AB)</option><option value="BC">British Columbia (BC)</option><option value="MB">Manitoba (MB)</option><option value="NB">New Brunswick (NB)</option><option value="NL">Newfoundland and Labrador (NL)</option><option value="NS">Nova Scotia (NS)</option><option value="ON">Ontario (ON)</option><option value="PE">Prince Edward Island (PE)</option><option value="QC">Quebec (QC)</option><option value="SK">Saskatchewan (SK)</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if (this.value == 'DE') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="BW">Baden-Württemberg (BW)</option><option value="BY">Bayern (BY)</option><option value="BE">Berlin (BE)</option><option value="BB">Brandeburg (BB)</option><option value="HB">Bremen (HB)</option><option value="HH">Hamburg (HH)</option><option value="HE">Hessen (HE)</option><option value="MV">Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV)</option><option value="NI">Niedersachsen (NI)</option><option value="NW">Nordrhein-Westfalen (NW)</option><option value="RP">Rheinland-Pfalz (RP)</option><option value="SL">Saarland (SL)</option><option value="SN">Sachsen (SN)</option><option value ="SA">Sachsen-Anhalt (SA)</option><option value="SH">Schleswig-Holstein (SH)</option><option value="TH">Thüringen</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().hide();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<input name="data[Quote][state]" maxlength="255" type="text" id="state-3046" value="">');
}
});
</script>
<a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: QUOTE MODAL --><a href="#" id="bioruptorpico2" data-reveal-id="quoteModal-3046" class="quote_btn" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Bioruptor® Pico sonication device</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
'
$related = array(
'id' => '3046',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://go.diagenode.com/bioruptor-upgrade"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-br-trade.png" /></a></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p><span>The Bioruptor® Pico is the latest innovation in shearing and represents a new breakthrough as an all-in-one shearing system capable of shearing samples from 150 bp to 1 kb. </span>Since 2004, Diagenode has accumulated <strong>shearing expertise</strong> to design the Bioruptor® Pico and guarantee the best experience with the <strong>sample preparation</strong> for <strong>number of applications -- in various fields of studies</strong> including environmental research, toxicology, genomics and epigenomics, cancer research, stem cells and development, neuroscience, clinical applications, agriculture, and many more.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
</div>
<p>The Bioruptor Pico shearing accessories and consumables have been developed to allow <strong>flexibility in sample volumes</strong> (20 µl - 2 ml) and a <strong>fast parallel processing of samples</strong> (up to 16 samples simultaneously). <span>The built-in cooling system (Bioruptor® Cooler) ensures high precision <strong>temperature control</strong>. The <strong>user-friendly interface</strong> has been designed for any researcher, providing an easy and advanced modes that give both beginners and experienced users the right level of control. </span></p>
<p>In addition, Diagenode provides fully-validated tubes that remain <strong>budget-friendly with low operating cost</strong> (< 1€/$/DNA sample) and shearing kits for best sample quality. <span></span></p>
<p><strong>Application versatility</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>DNA shearing for Next-Generation-Sequencing</li>
<li>Chromatin shearing</li>
<li>RNA shearing</li>
<li>Protein extraction from tissues and cells (also for mass spectrometry)</li>
<li>FFPE DNA extraction</li>
<li>Protein aggregation studies</li>
<li>CUT&RUN - shearing of input DNA for NGS</li>
</ul>
<div style="background-color: #f1f3f4; margin: 10px; padding: 50px;">
<p><strong>Bioruptor Pico: Recommended for CUT&RUN sequencing for input DNA</strong><br /><br /> By combining antibody-targeted controlled cleavage by MNase and NGS, <strong>CUT&RUN sequencing</strong> can be used to identify protein-DNA binding sites genome-wide. CUT&RUN works by using the DNA cleaving activity of a Protein A-fused MNase to isolate DNA that is bound by a protein of interest. This targeted digestion is controlled by the addition of calcium, which MNase requires for its nuclease activity. After MNase digestion, short DNA fragments are released and can then be purified for subsequent library preparation and high-throughput sequencing. While CUT&RUN does not require mechanical shearing chromatin given the enzymatic approach, sonication is highly recommended for the fragmentation of the input DNA (used to compare the enriched sample) in order to be compatible with downstream NGS. The Bioruptor Pico is the ideal instrument of choice for generating optimal DNA fragments with a tight distribution, assuring excellent library prep and excellent sequencing results for your CUT&RUN assay.<br /><br /> <strong>Explore the Bioruptor Pico now.</strong></p>
</div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for Chromatin shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-reproducibility-is-priority.jpg" /></center></div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/pages/form-demo"> <img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for RNA shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-request-demo.jpg" /></a></center></div>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label1' => 'Specifications',
'info1' => '<center><img alt="Ultrasonic Sonicator" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-table.jpg" /></center>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label2' => 'View accessories & consumables for Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico',
'info2' => '<h3>Shearing Accessories</h3>
<table style="width: 641px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Catalog number</td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Throughput</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-2-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.2 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201144</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">16 samples</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.65 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201143</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">12 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 1.5 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201140</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-sonication-accessories-for-bioruptor-standard-plus-pico-1-pack">15 ml sonication accessories</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01200016</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Shearing Consumables</h3>
<table style="width: 646px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;">Catalog Number</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/02ml-microtubes-for-bioruptor-pico">0.2 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010020</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-500-tubes">0.65 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010011</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-with-caps-300-tubes">1.5 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010016</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-50-pc">15 ml Pico Tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010017</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-sonication-beads-50-rxns">15 ml Pico Tubes & sonication beads</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C01020031</span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/shearing_technology/bioruptor_accessories/TDS-BioruptorTubes.pdf">Find datasheet for Diagenode tubes here</a></p>
<p><a href="../documents/bioruptor-organigram-tubes">Which tubes for which Bioruptor®?</a></p>',
'label3' => 'Available shearing Kits',
'info3' => '<p>Diagenode has optimized a range of solutions for <strong>successful chromatin preparation</strong>. Chromatin EasyShear Kits together with the Pico ultrasonicator combine the benefits of efficient cell lysis and chromatin shearing, while keeping epitopes accessible to the antibody, critical for efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation. Each Chromatin EasyShear Kit provides optimized reagents and a thoroughly validated protocol according to your specific experimental needs. SDS concentration is adapted to each workflow taking into account target-specific requirements.</p>
<p>For best results, choose your desired ChIP kit followed by the corresponding Chromatin EasyShear Kit (to optimize chromatin shearing ). The Chromatin EasyShear Kits can be used independently of Diagenode’s ChIP kits for chromatin preparation prior to any chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol. Choose an appropriate kit for your specific experimental needs.</p>
<h2>Kit choice guide</h2>
<table style="border: 0;" valign="center">
<tbody>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<th class="text-center"></th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE TYPE</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE INPUT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">KIT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SDS<br /> CONCENTRATION</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">NUCLEI<br /> ISOLATION</th>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="5"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-histones.png" /></td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">< 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-optimization-kit-high-sds-100-million-cells">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />High SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">1%</td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/cross-unvalid-green.jpg" width="18" height="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">> 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">PLANT TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-plant-chip-seq-kit">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />for Plant</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.5%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="6"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-tf.png" /></td>
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="extra-spaced">
<h3>Guide for optimal chromatin preparation using Chromatin EasyShear Kits <i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/pages/chromatin-prep-easyshear-kit-guide">Read more</a></h3>
</div>
<p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B01080010',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'B01080010-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '00-Machine',
'price_EUR' => '27600',
'price_USD' => '31000',
'price_GBP' => '24000',
'price_JPY' => '4522260',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '77500',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => true,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '',
'slug' => 'bioruptorpico2',
'meta_title' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'modified' => '2024-12-19 15:08:43',
'created' => '2020-01-09 16:27:17',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
'id' => '4858',
'product_id' => '1879',
'related_id' => '3046'
),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1803',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-1.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:55:07',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:52:54',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '1804',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-2.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:08',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:08',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '1805',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-3.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:46',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:46',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '1806',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-4.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:56',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:56',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '1807',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-5.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:54:06',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:54:06',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '1772',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B010600010.jpg',
'alt' => 'B010600010',
'modified' => '2018-02-14 15:41:46',
'created' => '2018-02-14 15:41:46',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
)
)
$rrbs_service = array(
(int) 0 => (int) 1894,
(int) 1 => (int) 1895
)
$chipseq_service = array(
(int) 0 => (int) 2683,
(int) 1 => (int) 1835,
(int) 2 => (int) 1836,
(int) 3 => (int) 2684,
(int) 4 => (int) 1838,
(int) 5 => (int) 1839,
(int) 6 => (int) 1856
)
$labelize = object(Closure) {
}
$old_catalog_number = ' <span style="color:#CCC">(mc-magme-048)</span>'
$country_code = 'US'
$other_format = array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
)
$label = '<img src="/img/banners/banner-customizer-back.png" alt=""/>'
$document = array(
'id' => '1166',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit ',
'description' => '',
'image_id' => null,
'type' => 'Manual',
'url' => 'files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-manual-c02010020-21',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => '',
'modified' => '2022-11-22 15:50:08',
'created' => '2022-11-22 15:41:49',
'ProductsDocument' => array(
'id' => '3257',
'product_id' => '1879',
'document_id' => '1166'
)
)
$sds = array(
'id' => '650',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE nl',
'language' => 'nl',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-nl-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
'id' => '1194',
'product_id' => '1879',
'safety_sheet_id' => '650'
)
)
$publication = array(
'id' => '2857',
'name' => 'Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo',
'authors' => 'Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associated with disturbed blood flow. DNA methylation is a powerful epigenetic regulator of endothelial transcription recently associated with flow characteristics. We investigated differential DNA methylation in flow region-specific aortic endothelial cells in vivo in adult domestic male and female swine.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Genome-wide DNA methylation was profiled in endothelial cells (EC) isolated from two robust locations of differing patho-susceptibility:--an athero-susceptible site located at the inner curvature of the aortic arch (AA) and an athero-protected region in the descending thoracic (DT) aorta. Complete methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) identified over 5500 endothelial differentially methylated regions (DMRs). DMR density was significantly enriched in exons and 5'UTR sequences of annotated genes, 60 of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. The set of DMR-associated genes was enriched in transcriptional regulation, pattern specification HOX loci, oxidative stress and the ER stress adaptive pathway, all categories linked to athero-susceptible endothelium. Examination of the relationship between DMR and mRNA in HOXA genes demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between CpG island promoter methylation and gene expression. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) confirmed differential CpG methylation of HOXA genes, the ER stress gene ATF4, inflammatory regulator microRNA-10a and ARHGAP25 that encodes a negative regulator of Rho GTPases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Gender-specific DMRs associated with ciliogenesis that may be linked to defects in cilia development were also identified in AA DMRs.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">An endothelial methylome analysis identifies epigenetic DMR characteristics associated with transcriptional regulation in regions of atherosusceptibility in swine aorta in vivo. The data represent the first methylome blueprint for spatio-temporal analyses of lesion susceptibility predisposing to endothelial dysfunction in complex flow environments in vivo.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-07-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12864-015-1656-4',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'created' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
'id' => '550',
'product_id' => '1879',
'publication_id' => '2857'
)
)
$externalLink = ' <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682" target="_blank"><i class="fa fa-external-link"></i></a>'include - APP/View/Products/view.ctp, line 755
View::_evaluate() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 971
View::_render() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 933
View::render() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 473
Controller::render() - CORE/Cake/Controller/Controller.php, line 963
ProductsController::slug() - APP/Controller/ProductsController.php, line 1052
ReflectionMethod::invokeArgs() - [internal], line ??
Controller::invokeAction() - CORE/Cake/Controller/Controller.php, line 491
Dispatcher::_invoke() - CORE/Cake/Routing/Dispatcher.php, line 193
Dispatcher::dispatch() - CORE/Cake/Routing/Dispatcher.php, line 167
[main] - APP/webroot/index.php, line 118
Notice (8): Undefined variable: header [APP/View/Products/view.ctp, line 755]Code Context<!-- BEGIN: REQUEST_FORM MODAL -->
<div id="request_formModal" class="reveal-modal medium" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<?= $this->element('Forms/simple_form', array('solution_of_interest' => $solution_of_interest, 'header' => $header, 'message' => $message, 'campaign_id' => $campaign_id)) ?>
$viewFile = '/home/website-server/www/app/View/Products/view.ctp'
$dataForView = array(
'language' => 'en',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'product' => array(
'Product' => array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'locale' => 'eng'
),
'Antibody' => array(
'host' => '*****',
'id' => null,
'name' => null,
'description' => null,
'clonality' => null,
'isotype' => null,
'lot' => null,
'concentration' => null,
'reactivity' => null,
'type' => null,
'purity' => null,
'classification' => null,
'application_table' => null,
'storage_conditions' => null,
'storage_buffer' => null,
'precautions' => null,
'uniprot_acc' => null,
'slug' => null,
'meta_keywords' => null,
'meta_description' => null,
'modified' => null,
'created' => null,
'select_label' => null
),
'Slave' => array(),
'Group' => array(
'Group' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Master' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Product' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Related' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Application' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Category' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Document' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Feature' => array(),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Promotion' => array(),
'Protocol' => array(),
'Publication' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 7 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 8 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 9 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 10 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 11 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 12 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 13 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 14 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 15 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 16 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 17 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 18 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 19 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 20 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 21 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 22 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 23 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 24 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 25 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 26 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 27 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 28 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 29 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 30 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 31 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 32 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 33 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 34 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 35 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 36 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 37 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 38 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 39 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 40 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 41 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 42 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 43 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 44 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 45 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 46 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 47 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 48 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 49 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 50 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 51 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 52 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 53 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 54 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 55 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 56 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 57 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 58 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 59 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 60 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 61 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 62 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 63 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 64 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 65 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 66 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 67 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 68 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 69 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 70 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 71 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 72 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 73 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 74 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 75 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 76 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 77 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 78 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 79 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 80 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 81 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 82 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 83 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 84 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 85 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 86 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 87 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 88 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 89 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 90 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 91 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 92 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 93 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 94 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 95 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 96 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 97 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 98 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 99 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 100 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 101 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 102 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 103 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 104 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 105 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Testimonial' => array(),
'Area' => array(),
'SafetySheet' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 7 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'meta_canonical' => 'https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns'
)
$language = 'en'
$meta_keywords = ''
$meta_description = 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.'
$meta_title = 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA'
$product = array(
'Product' => array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'locale' => 'eng'
),
'Antibody' => array(
'host' => '*****',
'id' => null,
'name' => null,
'description' => null,
'clonality' => null,
'isotype' => null,
'lot' => null,
'concentration' => null,
'reactivity' => null,
'type' => null,
'purity' => null,
'classification' => null,
'application_table' => null,
'storage_conditions' => null,
'storage_buffer' => null,
'precautions' => null,
'uniprot_acc' => null,
'slug' => null,
'meta_keywords' => null,
'meta_description' => null,
'modified' => null,
'created' => null,
'select_label' => null
),
'Slave' => array(),
'Group' => array(
'Group' => array(
'id' => '7',
'name' => 'C02010021',
'product_id' => '1880',
'modified' => '2016-02-18 17:02:55',
'created' => '2016-02-18 17:02:55'
),
'Master' => array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
),
'Product' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Related' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1819',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'description' => '<p>The DiaMag02 is a powerful magnet which has been designed for controlled and rapid isolation of your DNA bound to magnetic beads. It allows for processing 16 samples at a time.</p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B04000001',
'old_catalog_number' => 'kch-816-001',
'sf_code' => 'B04000001-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '250',
'price_USD' => '240',
'price_GBP' => '220',
'price_JPY' => '40960',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '600',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit',
'meta_title' => 'DiaMag02 - magnetic rack',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'DiaMag02 - magnetic rack',
'modified' => '2019-06-11 16:27:35',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '2597',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1043-050, -500 is specific to a CpG region of the TSH2B gene from rat. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17031043-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1043-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17031043-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:06:44',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '2599',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1046-050, -500 is specific to a promoter region of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from rat. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17031046-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1046-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17031046-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:05:49',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '2593',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1042-050, -500 is specific to a CpG region of the TSH2B gene from mouse. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17021042-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1042-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17021042-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:10:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '2595',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair Cat. No. C17021045 is specific to a promoter region of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from mouse. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17021045-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1045-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17021045-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '01-Accessory',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'modified' => '2021-01-18 10:00:33',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '2945',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit - ordering reference: C02010021',
'description' => '<p><span></span>The reference C02010014 has been replaced by <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns">C02010021</a><span>. </span> </p>
<p><span>Perform </span><strong>MeDIP</strong><span><span> </span>(Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation) <span>on the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/sx-8g-ip-star-compact-automated-system-1-unit" target="_blank">SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System</a> </span>followed by<span> </span></span><strong>qPCR</strong><span><span> </span>to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using </span><span>5-methylcytosine</span><span><span> </span>antibody. Our kit contains high quality reagents to get the h</span><span>ighest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</span></p>
<p>Diagenode’s Auto MagMeDIP qPCR is available in two formats (10 and 48 IPs) and has been optimized on the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/sx-8g-ip-star-compact-automated-system-1-unit" target="_blank">SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System</a> enabling highly reproducible results and allowing for high throughput assays.</p>
<h3><span>Characteristics</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Generate highly consistent results with internal controls in 24h</li>
<li>Minimize error with many reagents in 1 tube</li>
<li>Optimized purification (DIB - DNA isolation buffer)</li>
<li>Allows direct correlation between IP’d material & methylation status</li>
</ul>
<p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/magmedip-kit-validated-using-bioruptor.jpg" alt="MagMeDIP kit validated using Bioruptor" /></p>
<p><strong><em>Figure 1.</em></strong><em><span> </span><strong>IP results obtained with Diagenode Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit.</strong><span> </span>MeDIP assays were performed manually using DNA from blood, Gm12878, Hela and U20S cells and the Auto MagMeDIP qPCR kit (Diagenode). The DNA was prepared with the XL GenDNA Extraction Module included. The IP was performed including the kit meDNA and unDNA spike-in controls, together with the human DNA sample controls. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs also included in this kit.</em></p>
<p style="text-align: center;"><em><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/AutomatedMeDIP_9h.png" alt="" width="678" height="365" /></em></p>
<p style="text-align: justify;"><em><strong>Figure<span> </span>2. Automated MeDIP (9h). </strong>IP reaction was performed on the SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System with the anti-5-mC antibody. Methylated and unmethylated DNA were used as internal controls. Unmethylated DNA region of GADPH and a methylated DNA region of AlphaX1 were used to test DNA sample-IP efficiency. DNA has been isolated by using DNA Isolation Buffer (DIB).</em></p>
<p></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '48 rxns',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010014',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'C02010014-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '',
'price_USD' => '',
'price_GBP' => '',
'price_JPY' => '',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'Japan',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => true,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'auto-magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x48',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x48',
'modified' => '2023-03-20 12:50:08',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '3046',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://go.diagenode.com/bioruptor-upgrade"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-br-trade.png" /></a></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p><span>The Bioruptor® Pico is the latest innovation in shearing and represents a new breakthrough as an all-in-one shearing system capable of shearing samples from 150 bp to 1 kb. </span>Since 2004, Diagenode has accumulated <strong>shearing expertise</strong> to design the Bioruptor® Pico and guarantee the best experience with the <strong>sample preparation</strong> for <strong>number of applications -- in various fields of studies</strong> including environmental research, toxicology, genomics and epigenomics, cancer research, stem cells and development, neuroscience, clinical applications, agriculture, and many more.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
</div>
<p>The Bioruptor Pico shearing accessories and consumables have been developed to allow <strong>flexibility in sample volumes</strong> (20 µl - 2 ml) and a <strong>fast parallel processing of samples</strong> (up to 16 samples simultaneously). <span>The built-in cooling system (Bioruptor® Cooler) ensures high precision <strong>temperature control</strong>. The <strong>user-friendly interface</strong> has been designed for any researcher, providing an easy and advanced modes that give both beginners and experienced users the right level of control. </span></p>
<p>In addition, Diagenode provides fully-validated tubes that remain <strong>budget-friendly with low operating cost</strong> (< 1€/$/DNA sample) and shearing kits for best sample quality. <span></span></p>
<p><strong>Application versatility</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>DNA shearing for Next-Generation-Sequencing</li>
<li>Chromatin shearing</li>
<li>RNA shearing</li>
<li>Protein extraction from tissues and cells (also for mass spectrometry)</li>
<li>FFPE DNA extraction</li>
<li>Protein aggregation studies</li>
<li>CUT&RUN - shearing of input DNA for NGS</li>
</ul>
<div style="background-color: #f1f3f4; margin: 10px; padding: 50px;">
<p><strong>Bioruptor Pico: Recommended for CUT&RUN sequencing for input DNA</strong><br /><br /> By combining antibody-targeted controlled cleavage by MNase and NGS, <strong>CUT&RUN sequencing</strong> can be used to identify protein-DNA binding sites genome-wide. CUT&RUN works by using the DNA cleaving activity of a Protein A-fused MNase to isolate DNA that is bound by a protein of interest. This targeted digestion is controlled by the addition of calcium, which MNase requires for its nuclease activity. After MNase digestion, short DNA fragments are released and can then be purified for subsequent library preparation and high-throughput sequencing. While CUT&RUN does not require mechanical shearing chromatin given the enzymatic approach, sonication is highly recommended for the fragmentation of the input DNA (used to compare the enriched sample) in order to be compatible with downstream NGS. The Bioruptor Pico is the ideal instrument of choice for generating optimal DNA fragments with a tight distribution, assuring excellent library prep and excellent sequencing results for your CUT&RUN assay.<br /><br /> <strong>Explore the Bioruptor Pico now.</strong></p>
</div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for Chromatin shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-reproducibility-is-priority.jpg" /></center></div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/pages/form-demo"> <img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for RNA shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-request-demo.jpg" /></a></center></div>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label1' => 'Specifications',
'info1' => '<center><img alt="Ultrasonic Sonicator" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-table.jpg" /></center>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label2' => 'View accessories & consumables for Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico',
'info2' => '<h3>Shearing Accessories</h3>
<table style="width: 641px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Catalog number</td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Throughput</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-2-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.2 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201144</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">16 samples</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.65 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201143</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">12 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 1.5 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201140</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-sonication-accessories-for-bioruptor-standard-plus-pico-1-pack">15 ml sonication accessories</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01200016</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Shearing Consumables</h3>
<table style="width: 646px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;">Catalog Number</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/02ml-microtubes-for-bioruptor-pico">0.2 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010020</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-500-tubes">0.65 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010011</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-with-caps-300-tubes">1.5 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010016</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-50-pc">15 ml Pico Tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010017</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-sonication-beads-50-rxns">15 ml Pico Tubes & sonication beads</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C01020031</span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/shearing_technology/bioruptor_accessories/TDS-BioruptorTubes.pdf">Find datasheet for Diagenode tubes here</a></p>
<p><a href="../documents/bioruptor-organigram-tubes">Which tubes for which Bioruptor®?</a></p>',
'label3' => 'Available shearing Kits',
'info3' => '<p>Diagenode has optimized a range of solutions for <strong>successful chromatin preparation</strong>. Chromatin EasyShear Kits together with the Pico ultrasonicator combine the benefits of efficient cell lysis and chromatin shearing, while keeping epitopes accessible to the antibody, critical for efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation. Each Chromatin EasyShear Kit provides optimized reagents and a thoroughly validated protocol according to your specific experimental needs. SDS concentration is adapted to each workflow taking into account target-specific requirements.</p>
<p>For best results, choose your desired ChIP kit followed by the corresponding Chromatin EasyShear Kit (to optimize chromatin shearing ). The Chromatin EasyShear Kits can be used independently of Diagenode’s ChIP kits for chromatin preparation prior to any chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol. Choose an appropriate kit for your specific experimental needs.</p>
<h2>Kit choice guide</h2>
<table style="border: 0;" valign="center">
<tbody>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<th class="text-center"></th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE TYPE</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE INPUT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">KIT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SDS<br /> CONCENTRATION</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">NUCLEI<br /> ISOLATION</th>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="5"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-histones.png" /></td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">< 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-optimization-kit-high-sds-100-million-cells">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />High SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">1%</td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/cross-unvalid-green.jpg" width="18" height="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">> 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">PLANT TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-plant-chip-seq-kit">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />for Plant</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.5%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="6"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-tf.png" /></td>
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="extra-spaced">
<h3>Guide for optimal chromatin preparation using Chromatin EasyShear Kits <i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/pages/chromatin-prep-easyshear-kit-guide">Read more</a></h3>
</div>
<p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B01080010',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'B01080010-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '00-Machine',
'price_EUR' => '27600',
'price_USD' => '31000',
'price_GBP' => '24000',
'price_JPY' => '4522260',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '77500',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => true,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '',
'slug' => 'bioruptorpico2',
'meta_title' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'modified' => '2024-12-19 15:08:43',
'created' => '2020-01-09 16:27:17',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Application' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '7',
'position' => '10',
'parent_id' => '1',
'name' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'description' => '<div class="row extra-spaced">
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3>Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns"><span>The Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation is based on the affinity purification of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA using, respectively, an antibody directed against 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in the case of MeDIP or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in the case of hMeDIP.</span><br />
<h2></h2>
<h2>How it works</h2>
<p>In brief, Methyl DNA IP is performed as follows: Genomic DNA from cultured cells or tissues is prepared, sheared, and then denatured. Then, immunoselection and immunoprecipitation can take place using the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads. After isolation and purification is performed, the IP’d methylated DNA is ready for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<h2>Applications</h2>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> qPCR analysis</a></div>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-seq-package-V2-x10" class="center alert radius button"> NGS analysis </a></div>
<h2>Advantages</h2>
<ul style="font-size: 19px;" class="nobullet">
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Unaffected</strong> DNA</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>High enrichment</strong> yield</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Robust</strong> & <strong>reproducible</strong> techniques</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>NGS</strong> compatible</li>
</ul>
<h2></h2>
</div>
</div>
<div id="gtx-trans" style="position: absolute; left: 17px; top: 652.938px;">
<div class="gtx-trans-icon"></div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'slug' => 'methylated-dna-immunoprecipitation',
'meta_keywords' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation,Epigenetic,DNA Methylation,qPCR,5 methylcytosine (5-mC)',
'meta_description' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation method is based on the affinity purification of methylated DNA using an antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine (5-mC). ',
'meta_title' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation(MeDIP) - Dna methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2021-08-19 12:08:03',
'created' => '2014-09-14 05:33:34',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '1',
'position' => '9',
'parent_id' => null,
'name' => 'DNA Methylation',
'description' => '<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns">
<div style="text-align: justify;" class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h2>Complete solutions for DNA methylation studies</h2>
<p>Whether you are experienced or new to the field of DNA methylation, Diagenode has everything you need to make your assay as easy and convenient as possible while ensuring consistent data between samples and experiments. Diagenode offers sonication instruments, reagent kits, high quality antibodies, and high-throughput automation capability to address all of your specific DNA methylation analysis requirements.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns text-center"><a href="../landing-pages/dna-methylation-grant-applications"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-dna-grant.png" alt="" /></a></div>
<div style="text-align: justify;" class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark and is the most widely studied topic in epigenetics. <em>In vivo</em>, DNA is methylated following DNA replication and is involved in a number of biological processes including the regulation of imprinted genes, X chromosome inactivation. and tumor suppressor gene silencing in cancer cells. Methylation often occurs in cytosine-guanine rich regions of DNA (CpG islands), which are commonly upstream of promoter regions.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns"><br /><br />
<ul class="accordion" data-accordion="">
<li class="accordion-navigation"><a href="#dnamethyl"><i class="fa fa-caret-right"></i> Learn more</a>
<div id="dnamethyl" class="content">5-methylcytosine (5-mC) has been known for a long time as the only modification of DNA for epigenetic regulation. In 2009, however, Kriaucionis discovered a second methylated cytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC). The so-called 6th base, is generated by enzymatic conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine by the TET family of oxygenases. Early reports suggested that 5-hmC may represent an intermediate of active demethylation in a new pathway which demethylates DNA, converting 5-mC to cytosine. Recent evidence fuel this hypothesis suggesting that further oxidation of the hydroxymethyl group leads to a formyl or carboxyl group followed by either deformylation or decarboxylation. The formyl and carboxyl groups of 5-formylcytosine (5-fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5-caC) could be enzymatically removed without excision of the base.
<p class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/categories/kits_dna/dna_methylation_variants.jpg" /></p>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
<br />
<h2>Main DNA methylation technologies</h2>
<p style="text-align: justify;">Overview of the <span style="font-weight: 400;">three main approaches for studying DNA methylation.</span></p>
<div class="row">
<ol>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Chemical modification with bisulfite – Bisulfite conversion</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Enrichment of methylated DNA (including MeDIP and MBD)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Treatment with methylation-sensitive or dependent restriction enzymes</span></li>
</ol>
<p><span style="font-weight: 400;"> </span></p>
<div class="row">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>Description</th>
<th width="350">Features</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><strong>Bisulfite conversion</strong></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">Chemical conversion of unmethylated cytosine to uracil. Methylated cytosines are protected from this conversion allowing to determine DNA methylation at single nucleotide resolution.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Single nucleotide resolution</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Quantitative analysis - methylation rate (%)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Gold standard and well studied</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Compatible with automation</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><b>Methylated DNA enrichment</b></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">(Hydroxy-)Methylated DNA is enriched by using specific antibodies (hMeDIP or MeDIP) or proteins (MBD) that specifically bind methylated CpG sites in fragmented genomic DNA.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Resolution depends on the fragment size of the enriched methylated DNA (300 bp)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Qualitative analysis</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Compatible with automation</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><strong>Restriction enzyme-based digestion</strong></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">Use of (hydroxy)methylation-sensitive or (hydroxy)methylation-dependent restriction enzymes for DNA methylation analysis at specific sites.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Determination of methylation status is limited by the enzyme recognition site</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Easy to use</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="large-12 columns"></div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => true,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'slug' => 'epigenetics-dna-methylation',
'meta_keywords' => 'Epigenetics, DNA Methylation,5-hmC monoclonal antibody,hMeDIP,Bisulfite conversion,Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'meta_description' => 'Complete, optimized solutions for analyzing DNA methylation manually or on our automated system.',
'meta_title' => 'DNA Methylation - Bisulfite sequencing - Epigenetics | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2019-03-25 10:07:27',
'created' => '2015-05-03 13:47:53',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '6',
'position' => '10',
'parent_id' => '1',
'name' => 'メチル化DNA結合タンパク質',
'description' => '<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns">MBD方法は、メチル化DNAに対するH6-GST-MBD融合タンパク質の非常に高い親和性に基づいています。 このタンパク質は、N末端His6タグを含むグルタチオン-S-トランスフェラーゼ(GST)とのC末端融合物として、ヒトMeCP2のメチル結合ドメイン(MBD)を含有します。 このH6-GST-MBD融合タンパク質を用いて、メチル化CpGを含むDNAを特異的に単離する事が可能です。<br /><br />DiagenodeのMethylCap®キットは、二本鎖DNAの高濃縮と、メチル化CpG密度の関数における微分分画を可能にします。 分画はサンプルの複雑さを軽減し、次世代のシーケンシングを容易にします。 MethylCapアッセイに先立ち、DNAを最初に抽出し、Picoruptorソニケーターを用いて断片化します。<br />
<h3>概要</h3>
<p class="text-center"><br /><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/applications/methyl_binding_domain_overview.jpg" /></p>
</div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => false,
'slug' => 'methylbinding-domain-protein',
'meta_keywords' => 'Epigenetic,Methylbinding Domain Protein,MBD,DNA methylation,DNA replication,MethylCap,MethylCap assay,',
'meta_description' => 'Methylbinding Domain Protein(MBD) approach is based on the very high affinity of a H6-GST-MBD fusion protein for methylated DNA. This protein consists of the methyl binding domain (MBD) of human MeCP2, as a C-terminal fusion with Glutathione-S-transferase',
'meta_title' => 'Epigenetic Methylbinding Domain Protein(MBD) - DNA methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2019-03-22 12:32:12',
'created' => '2015-06-02 17:05:42',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Category' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '52',
'position' => '2',
'parent_id' => '12',
'name' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-seq-package-V2-x10"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/b-email-magmedip.png" /></a></p>
<p>The Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation is based on the affinity purification of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA using, respectively, an antibody directed against 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in the case of MeDIP or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in the case of hMeDIP.</p>
<h2>How it works</h2>
<p>In brief, Methyl DNA IP is performed as follows: Genomic DNA from cultured cells or tissues is prepared, sheared, and then denatured. Then, immunoselection and immunoprecipitation can take place using the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads. After isolation and purification is performed, the IP’d methylated DNA is ready for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<h2>Applications</h2>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> qPCR analysis</a></div>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> NGS analysis </a></div>
<h2>Advantages</h2>
<ul style="font-size: 19px;" class="nobullet">
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Unaffected</strong> DNA</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>High enrichment</strong> yield</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Robust</strong> & <strong>reproducible</strong> techniques</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>NGS</strong> compatible</li>
</ul>
<h2></h2>',
'no_promo' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'hide' => false,
'all_format' => false,
'is_antibody' => false,
'slug' => 'methylated-dna-immunoprecipitation',
'cookies_tag_id' => null,
'meta_keywords' => 'Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation,DNA methylation',
'meta_description' => 'Diagenode provides Antibody-based isolation of methylated DNA for DNA immunoprecipitation ',
'meta_title' => 'Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation for DNA Methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2022-11-25 10:46:50',
'created' => '2015-07-08 09:30:57',
'ProductsCategory' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'CookiesTag' => array([maximum depth reached])
)
),
'Document' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1166',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit ',
'description' => '',
'image_id' => null,
'type' => 'Manual',
'url' => 'files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-manual-c02010020-21',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => '',
'modified' => '2022-11-22 15:50:08',
'created' => '2022-11-22 15:41:49',
'ProductsDocument' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Feature' => array(),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1796',
'name' => 'https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/C02010020-magmedip-qpcr.jpg',
'alt' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10',
'modified' => '2019-04-24 17:06:59',
'created' => '2019-04-24 17:04:52',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Promotion' => array(),
'Protocol' => array(),
'Publication' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '4989',
'name' => 'Differential methylation of circulating free DNA assessed through cfMeDiP as a new tool for breast cancer diagnosis and detection of BRCA1/2 mutation',
'authors' => 'Piera Grisolia et al.',
'description' => '<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Background</h3>
<p>Recent studies have highlighted the importance of the cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation profile in detecting breast cancer (BC) and its different subtypes. We investigated whether plasma cfDNA methylation, using cell-free Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation and High-Throughput Sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq), may be informative in characterizing breast cancer in patients with BRCA1/2 germline mutations for early cancer detection and response to therapy.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Methods</h3>
<p>We enrolled 23 BC patients with germline mutation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, 19 healthy controls without BRCA1/2 mutation, and two healthy individuals who carried BRCA1/2 mutations. Blood samples were collected for all study subjects at the diagnosis, and plasma was isolated by centrifugation. Cell-free DNA was extracted from 1 mL of plasma, and cfMeDIP-seq was performed for each sample. Shallow whole genome sequencing was performed on the immuno-precipitated samples. Then, the differentially methylated 300-bp regions (DMRs) between 25 BRCA germline mutation carriers and 19 non-carriers were identified. DMRs were compared with tumor-specific regions from public datasets to perform an unbiased analysis. Finally, two statistical classifiers were trained based on the GLMnet and random forest model to evaluate if the identified DMRs could discriminate BRCA-positive from healthy samples.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Results</h3>
<p>We identified 7,095 hypermethylated and 212 hypomethylated regions in 25 BRCA germline mutation carriers compared to 19 controls. These regions discriminate tumors from healthy samples with high accuracy and sensitivity. We show that the circulating tumor DNA of BRCA1/2 mutant breast cancers is characterized by the hypomethylation of genes involved in DNA repair and cell cycle. We uncovered the TFs associated with these DRMs and identified that proteins of the Erythroblast Transformation Specific (ETS) family are particularly active in the hypermethylated regions. Finally, we assessed that these regions could discriminate between BRCA positives from healthy samples with an AUC of 0.95, a sensitivity of 88%, and a specificity of 94.74%.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p>Our study emphasizes the importance of tumor cell-derived DNA methylation in BC, reporting a different methylation profile between patients carrying mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, and wild-type controls. Our minimally invasive approach could allow early cancer diagnosis, assessment of minimal residual disease, and monitoring of response to therapy.</p>',
'date' => '2024-10-15',
'pmid' => 'https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-024-05734-2',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-05734-2',
'modified' => '2024-10-18 11:43:43',
'created' => '2024-10-18 11:43:43',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '4981',
'name' => 'Prediction of brain metastasis development with DNA methylation signatures',
'authors' => 'Jeffrey A. Zuccato et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Brain metastases (BMs) are the most common and among the deadliest brain tumors. Currently, there are no reliable predictors of BM development from primary cancer, which limits early intervention. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common BM source and here we obtained 402 tumor and plasma samples from a large cohort of patients with LUAD with or without BM (</span><i>n</i><span> = 346). LUAD DNA methylation signatures were evaluated to build and validate an accurate model predicting BM development from LUAD, which was integrated with clinical factors to provide comprehensive patient-specific BM risk probabilities in a nomogram. Additionally, immune and cell interaction gene sets were differentially methylated at promoters in BM versus paired primary LUAD and had aligning dysregulation in the proteome. Immune cells were differentially abundant in BM versus LUAD. Finally, liquid biomarkers identified from methylated cell-free DNA sequenced in plasma were used to generate and validate accurate classifiers for early BM detection. Overall, LUAD methylomes can be leveraged to predict and noninvasively identify BM, moving toward improved patient outcomes with personalized treatment.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-10-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03286-y',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03286-y',
'modified' => '2024-10-11 09:58:45',
'created' => '2024-10-11 09:58:45',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '4957',
'name' => 'Association between TNF-α, cortisol levels, and exposure to PM10 and PM2.5: a pilot study',
'authors' => 'Dolcini J. et al.',
'description' => '<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Purpose</h3>
<p>The most harmful atmospheric pollutant for human health is particulate matter (PM). We analyzed the correlation between short-term lag exposure to PM10 and PM2.5, salivary cortisol and TNF-α level, and methylation levels of the TNF-α promoter.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Methods</h3>
<p>A pilot study including 20 subjects. Eight salivary samples for each subject at various times of the day were collected for comparing cortisol levels and TNFα detection. TNFα promoter methylation levels on salivary DNA were analyzed. Regression analyses were performed using generalized linear mixed models between the different outcomes and 4, 3, 2 and 1 day’s lag values of PM10/PM2.5.Generalized additive mixed model (GAMM) was used to evaluate any potential deviation from linearity.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Results</h3>
<p>Area under the curve with respect to the ground (AUCg) showed a statistically positive association with 4-, 3-, 2-, and 1-day lag of exposure to PM10. Area under the curve with respect to the increase (AUCi) showed a statistically negative association with 4-, 3- and 1-day lag of exposure to PM10. TNFα showed statistically significant association with both exposures, PM10 and PM2.5, at 4-, 3-, 2-, and 1-day lag.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p>Regarding cortisol levels there is an increase of overall hormone levels but a less dynamism of the system to answer to external stressors. Increase of TNF-α may reflect increased levels of oxidative stress and inflammation due to pollution exposure.</p>',
'date' => '2024-08-07',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12302-024-00961-2',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-024-00961-2',
'modified' => '2024-09-02 10:01:14',
'created' => '2024-09-02 10:00:08',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '4942',
'name' => 'Epigenomic signatures of sarcomatoid differentiation to guide the treatment of renal cell carcinoma',
'authors' => 'Talal El Zarif et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (sRCC) is associated with poor survival and a heightened response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Two major barriers to improving outcomes for sRCC are the limited understanding of its gene regulatory programs and the low diagnostic yield of tumor biopsies due to spatial heterogeneity. Herein, we characterized the epigenomic landscape of sRCC by profiling 107 epigenomic libraries from tissue and plasma samples from 50 patients with RCC and healthy volunteers. By profiling histone modifications and DNA methylation, we identified highly recurrent epigenomic reprogramming enriched in sRCC. Furthermore, CRISPRa experiments implicated the transcription factor FOSL1 in activating sRCC-associated gene regulatory programs, and </span><em>FOSL1</em><span><span> </span>expression was associated with the response to ICIs in RCC in two randomized clinical trials. Finally, we established a blood-based diagnostic approach using detectable sRCC epigenomic signatures in patient plasma, providing a framework for discovering epigenomic correlates of tumor histology via liquid biopsy.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-25',
'pmid' => 'https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)00678-8',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114350',
'modified' => '2024-06-24 10:33:29',
'created' => '2024-06-24 10:33:29',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '4947',
'name' => 'Detecting small cell transformation in patients with advanced EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma through epigenomic cfDNA profiling',
'authors' => 'Talal El Zarif et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Purpose: Histologic transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a mechanism of treatment resistance in patients with advanced oncogene-driven lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) that currently requires histologic review for diagnosis. Herein, we sought to develop an epigenomic cell-free (cf)DNA-based approach to non-invasively detect small cell transformation in patients with EGFR mutant (EGFRm) LUAD. Experimental Design: To characterize the epigenomic landscape of transformed (t)SCLC relative to LUAD and de novo SCLC, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) to profile the histone modifications H3K27ac, H3K4me3, and H3K27me3, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq), assay for transposase-accessible chromatin sequencing (ATAC-seq), and RNA sequencing on 26 lung cancer patient-derived xenograft (PDX) tumors. We then generated and analyzed H3K27ac ChIP-seq, MeDIP-seq, and whole genome sequencing cfDNA data from 1 ml aliquots of plasma from patients with EGFRm LUAD with or without tSCLC. Results: Analysis of 126 epigenomic libraries from the lung cancer PDXs revealed widespread epigenomic reprogramming between LUAD and tSCLC, with a large number of differential H3K27ac (n=24,424), DNA methylation (n=3,298), and chromatin accessibility (n=16,352) sites between the two histologies. Tumor-informed analysis of each of these three epigenomic features in cfDNA resulted in accurate non-invasive discrimination between patients with EGFRm LUAD versus tSCLC (AUROC=0.82-0.87). A multi-analyte cfDNA-based classifier integrating these three epigenomic features discriminated between EGFRm LUAD versus tSCLC with an AUROC of 0.94. Conclusions: These data demonstrate the feasibility of detecting small cell transformation in patients with EGFRm LUAD through epigenomic cfDNA profiling of 1 ml of patient plasma.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-24',
'pmid' => 'https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article/doi/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0466/746147/Detecting-small-cell-transformation-in-patients',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0466',
'modified' => '2024-07-04 14:50:38',
'created' => '2024-07-04 14:50:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '4949',
'name' => 'Prostate cancer detection through unbiased capture of methylated cell-free DNA',
'authors' => 'Ermira Lleshi et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Prostate cancer screening using prostate-specific antigen (PSA) has been shown to reduce mortality but with substantial overdiagnosis, leading to unnecessary biopsies. The identification of a highly specific biomarker using liquid biopsies, represents an unmet need in the diagnostic pathway for prostate cancer. In this study, we employed a method that enriches for methylated cell-free DNA fragments coupled with a machine learning algorithm which enabled the detection of metastatic and localised cancers with AUCs of 0.96 and 0.74, respectively. The model also detected 51.8% (14/27) of localised and 88.7% (79/89) of metastatic cancer patients in an external dataset. Furthermore, we show that the differentially methylated regions reflect epigenetic and transcriptomic changes at the tissue level. Notably, these regions are significantly enriched for biologically relevant pathways associated with the regulation of cellular proliferation and TGF-beta signalling. This demonstrates the potential of circulating tumour DNA methylation for prostate cancer detection and prognostication.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-20',
'pmid' => 'https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004224015554',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110330',
'modified' => '2024-07-04 15:29:13',
'created' => '2024-07-04 15:29:13',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '4921',
'name' => 'A Pre-Leukemic DNA Methylation Signature in Healthy Individuals at Higher Risk for Developing Myeloid Malignancy',
'authors' => 'Zhentang Lao et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Purpose: DNA methylation alterations are widespread in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), some of which appear to have evolved independently of somatic mutations in epigenetic regulators. While the presence of somatic mutations in peripheral blood can predict the risk of development of AML and MDS, its accuracy remains unsatisfactory. Experimental Design: We performed global DNA methylation profiling in a case-control study nested within Singapore Chinese Health Study to evaluate if DNA methylation alterations were associated with AML/MDS development. Targeted deep sequencing and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) were performed on peripheral blood collected a median of 9.9 years prior to diagnosis of AML or MDS, together with age-matched still healthy individuals as controls. Results: Sixty-six individuals who developed AML or MDS displayed significant DNA methylation changes in the peripheral blood compared with 167 age- and gender-matched controls who did not develop AML/MDS during the follow up period. Alterations in methylation in the differentially methylation regions (DMRs) were associated with increased odds of developing AML/MDS. Conclusions: The epigenetic changes may be acquired independently and prior to somatic mutations that relevant for AML/MDS development. The association between methylation changes and the risk of pre-AML/MDS in these individuals was considerably stronger than somatic mutations, suggesting that methylation changes could be used as biomarkers for pre- AML/MDS screening.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-03-04',
'pmid' => 'https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article-abstract/doi/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3804/735044/A-Pre-Leukemic-DNA-Methylation-Signature-in?redirectedFrom=fulltext',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3804',
'modified' => '2024-03-12 16:50:46',
'created' => '2024-03-12 16:50:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 7 => array(
'id' => '4912',
'name' => 'Neurofibromin 1 controls metabolic balance and Notch-dependent quiescence of murine juvenile myogenic progenitors',
'authors' => 'Wei X. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Patients affected by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) frequently show muscle weakness with unknown etiology. Here we show that, in mice, Neurofibromin 1 (</span><i>Nf1</i><span>) is not required in muscle fibers, but specifically in early postnatal myogenic progenitors (MPs), where<span> </span></span><i>Nf1</i><span><span> </span>loss led to cell cycle exit and differentiation blockade, depleting the MP pool resulting in reduced myonuclear accretion as well as reduced muscle stem cell numbers. This was caused by precocious induction of stem cell quiescence coupled to metabolic reprogramming of MPs impinging on glycolytic shutdown, which was conserved in muscle fibers. We show that a Mek/Erk/NOS pathway hypersensitizes<span> </span></span><i>Nf1</i><span>-deficient MPs to Notch signaling, consequently, early postnatal Notch pathway inhibition ameliorated premature quiescence, metabolic reprogramming and muscle growth. This reveals an unexpected role of Ras/Mek/Erk signaling supporting postnatal MP quiescence in concert with Notch signaling, which is controlled by Nf1 safeguarding coordinated muscle growth and muscle stem cell pool establishment. Furthermore, our data suggest transmission of metabolic reprogramming across cellular differentiation, affecting fiber metabolism and function in NF1.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-02-15',
'pmid' => 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-45618-z',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45618-z',
'modified' => '2024-02-22 12:22:26',
'created' => '2024-02-22 12:22:26',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 8 => array(
'id' => '4892',
'name' => 'Promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions are associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival',
'authors' => 'Rivera‑Peña B. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) can be used as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets in precision medicine workflows. DNA from 21 HNSCC and 10 healthy oral tissue samples was hybridized to a genome‑wide tiling array to identify DMRs in a discovery cohort. Downstream analyses identified differences in promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival. Genome‑wide DMR analysis showed 2,565 DMRs common to the three subsites. A total of 738 DMRs were unique to laryngeal cancer (n=7), 889 DMRs were unique to oral cavity cancer (n=10) and 363 DMRs were unique to pharyngeal cancer (n=6). Based on the genome‑wide analysis and a Gene Ontology analysis, 10 candidate genes were selected to test for prognostic value and association with clinicopathological features. </span><em>TIMP3</em><span><span> </span>was associated with tumor differentiation in oral cavity cancer (P=0.039),<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span><span> </span>was associated with nodal involvement in pharyngeal cancer (P=0.017) and<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span><span> </span>was associated with tumor differentiation in laryngeal cancer (P=0.040). A total of five candidate genes were selected,<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>CDH1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>CALCA</em><span><span> </span>and<span> </span></span><em>TIMP3</em><span>, for a prevalence study in a larger validation cohort: Oral cavity cancer samples (n=42), pharyngeal cancer tissues (n=25) and laryngeal cancer samples (n=52).<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span><span> </span>hypermethylation differed across HNSCC anatomic subsites (P=0.029), and was predominantly detected in laryngeal cancer. Kaplan‑Meier survival analysis (P=0.043) and Cox regression analysis of overall survival (P=0.001) showed that<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span><span> </span>methylation is associated with better prognosis in HNSCC. The findings of the present study showed that the HNSCC subsites oral cavity, pharynx and larynx display substantial differences in aberrant DNA methylation patterns, which may serve as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-01-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/ol.2024.14223/abstract',
'doi' => ' https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2024.14223',
'modified' => '2024-01-11 08:48:03',
'created' => '2024-01-11 08:48:03',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 9 => array(
'id' => '4732',
'name' => 'Cerebrospinal fluid methylome-based liquid biopsies for accuratemalignant brain neoplasm classification.',
'authors' => 'Zuccato Jeffrey A et al.',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Resolving the differential diagnosis between brain metastases (BM), glioblastomas (GBM), and central nervous system lymphomas (CNSL) is an important dilemma for the clinical management of the main three intra-axial brain tumor types. Currently, treatment decisions require invasive diagnostic surgical biopsies that carry risks and morbidity. This study aimed to utilize methylomes from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a biofluid proximal to brain tumors, for reliable non-invasive classification that addresses limitations associated with low target abundance in existing approaches. METHODS: Binomial GLMnet classifiers of tumor type were built, in fifty iterations of 80\% discovery sets, using CSF methylomes obtained from 57 BM, GBM, CNSL, and non-neoplastic control patients. Publicly-available tissue methylation profiles (N=197) on these entities and normal brain parenchyma were used for validation and model optimization. RESULTS: Models reliably distinguished between BM (area under receiver operating characteristic curve [AUROC]=0.93, 95\% confidence interval [CI]: 0.71-1.0), GBM (AUROC=0.83, 95\% CI: 0.63-1.0), and CNSL (AUROC=0.91, 95\% CI: 0.66-1.0) in independent 20\% validation sets. For validation, CSF-based methylome signatures reliably distinguished between tumor types within external tissue samples and tumors from non-neoplastic controls in CSF and tissue. CSF methylome signals were observed to align closely with tissue signatures for each entity. An additional set of optimized CSF-based models, built using tumor-specific features present in tissue data, showed enhanced classification accuracy. CONCLUSIONS: CSF methylomes are reliable for liquid biopsy-based classification of the major three malignant brain tumor types. We discuss how liquid biopsies may impact brain cancer management in the future by avoiding surgical risks, classifying unbiopsiable tumors, and guiding surgical planning when resection is indicated.</p>',
'date' => '2023-08-03',
'pmid' => 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36455236/',
'doi' => '10.1093/neuonc/noac264',
'modified' => '2023-10-13 08:50:06',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 10 => array(
'id' => '4803',
'name' => 'Transgenerational endocrine disruptor effects of cadmium in zebrafish andcontribution of standing epigenetic variation to adaptation.',
'authors' => 'Pierron F. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Evidence has emerged that environmentally-induced epigenetic changes can have long-lasting effects on gene transcription across generations. These recent findings highlight the need to investigate the transgenerational impacts of pollutants to assess their long term effects on populations. In this study, we investigated the transgenerational effect of cadmium on zebrafish across 4 generations. A first whole methylome approach carried out on fish of the first two generations led us to focus our investigations on the estradiol receptor alpha gene (esr1). We observed a sex-dependent transgenerational inheritance of Cd-induced DNA methylation changes up to the last generation. These changes were associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that were themselves at the origin of the creation or deletion of methylation sites. Thus, Cd-induced genetic selection gave rise to DNA methylation changes. We also analyzed the transcription level of various sections of esr1 as well as estrogen responsive genes. While Cd triggered transgenerational disorders, Cd-induced epigenetic changes in esr1 contributed to the rapid transgenerational adaptation of fish to Cd. Our results provide insight into the processes underpinning rapid adaptation and highlight the need to maintain genetic diversity within natural populations to bolster the resilience of species faced with the global environmental changes.</span></p>',
'date' => '2023-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37163897',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131579',
'modified' => '2023-06-15 08:44:52',
'created' => '2023-06-13 21:11:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 11 => array(
'id' => '4843',
'name' => 'Differentiation block in acute myeloid leukemia regulated by intronicsequences of FTO',
'authors' => 'Camera F. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Iroquois transcription factor gene IRX3 is highly expressed in 20–30\% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and contributes to the pathognomonic differentiation block. Intron 8 FTO sequences ∼220kB downstream of IRX3 exhibit histone acetylation, DNA methylation, and contacts with the IRX3 promoter, which correlate with IRX3 expression. Deletion of these intronic elements confirms a role in positively regulating IRX3. RNAseq revealed long non-coding (lnc) transcripts arising from this locus. FTO-lncAML knockdown (KD) induced differentiation of AML cells, loss of clonogenic activity, and reduced FTO intron 8:IRX3 promoter contacts. While both FTO-lncAML KD and IRX3 KD induced differentiation, FTO-lncAML but not IRX3 KD led to HOXA downregulation suggesting transcript activity in trans. FTO-lncAMLhigh AML samples expressed higher levels of HOXA and lower levels of differentiation genes. Thus, a regulatory module in FTO intron 8 consisting of clustered enhancer elements and a long non-coding RNA is active in human AML, impeding myeloid differentiation.</p>',
'date' => '2023-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004223013962',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.isci.2023.107319',
'modified' => '2023-08-01 14:14:01',
'created' => '2023-08-01 15:59:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 12 => array(
'id' => '4777',
'name' => 'Epigenetic modifier alpha-ketoglutarate modulates aberrant gene bodymethylation and hydroxymethylation marks in diabetic heart.',
'authors' => 'Dhat R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Hyperglycemic myocardial microenvironment significantly alters chromatin architecture and the transcriptome, resulting in aberrant activation of signaling pathways in a diabetic heart. Epigenetic marks play vital roles in transcriptional reprogramming during the development of DCM. The current study is aimed to profile genome-wide DNA (hydroxy)methylation patterns in the hearts of control and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats and decipher the effect of modulation of DNA methylation by alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), a TET enzyme cofactor, on the progression of DCM. METHODS: Diabetes was induced in male adult Wistar rats with an intraperitoneal injection of STZ. Diabetic and vehicle control animals were randomly divided into groups with/without AKG treatment. Cardiac function was monitored by performing cardiac catheterization. Global methylation (5mC) and hydroxymethylation (5hmC) patterns were mapped in the Left ventricular tissue of control and diabetic rats with the help of an enrichment-based (h)MEDIP-sequencing technique by using antibodies specific for 5mC and 5hmC. Sequencing data were validated by performing (h)MEDIP-qPCR analysis at the gene-specific level, and gene expression was analyzed by qPCR. The mRNA and protein expression of enzymes involved in the DNA methylation and demethylation cycle were analyzed by qPCR and western blotting. Global 5mC and 5hmC levels were also assessed in high glucose-treated DNMT3B knockdown H9c2 cells. RESULTS: We found the increased expression of DNMT3B, MBD2, and MeCP2 with a concomitant accumulation of 5mC and 5hmC, specifically in gene body regions of diabetic rat hearts compared to the control. Calcium signaling was the most significantly affected pathway by cytosine modifications in the diabetic heart. Additionally, hypermethylated gene body regions were associated with Rap1, apelin, and phosphatidyl inositol signaling, while metabolic pathways were most affected by hyperhydroxymethylation. AKG supplementation in diabetic rats reversed aberrant methylation patterns and restored cardiac function. Hyperglycemia also increased 5mC and 5hmC levels in H9c2 cells, which was normalized by DNMT3B knockdown or AKG supplementation. CONCLUSION: This study demonstrates that reverting hyperglycemic damage to cardiac tissue might be possible by erasing adverse epigenetic signatures by supplementing epigenetic modulators such as AKG along with an existing antidiabetic treatment regimen.</p>',
'date' => '2023-04-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37101286',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13072-023-00489-4',
'modified' => '2023-06-12 09:20:54',
'created' => '2023-05-05 12:34:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 13 => array(
'id' => '4611',
'name' => 'Pre-diagnosis plasma cell-free DNA methylome profiling up to sevenyears prior to clinical detection reveals early signatures of breast cancer',
'authors' => 'Cheng N. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Profiling of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has been well demonstrated to be a potential non-invasive screening tool for early cancer detection. However, limited studies have investigated the detectability of cfDNA methylation markers that are predictive of cancers in asymptomatic individuals. We performed cfDNA methylation profiling using cell-free DNA methylation immunoprecipitation sequencing (cfMeDIP-Seq) in blood collected from individuals up to seven years before a breast cancer diagnosis in addition to matched cancer-free controls. We identified differentially methylated cfDNA signatures that discriminated cancer-free controls from pre-diagnosis breast cancer cases in a discovery cohort that is used to build a classification model. We show that predictive models built from pre-diagnosis cfDNA hypermethylated regions can accurately predict early breast cancers in an independent test set (AUC=0.930) and are generalizable to late-stage breast cancers cases at the time of diagnosis (AUC=0.912). Characterizing the top hypermethylated cfDNA regions revealed significant enrichment for hypermethylation in external bulk breast cancer tissues compared to peripheral blood leukocytes and breast normal tissues. Our findings demonstrate that cfDNA methylation markers predictive of breast cancers can be detected in blood among asymptomatic individuals up to six years prior to clinical detection.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2023.01.30.23285027',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.01.30.23285027',
'modified' => '2023-04-04 08:34:20',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 14 => array(
'id' => '4612',
'name' => 'Cell-free multi-omics analysis reveals tumor status-informativesignatures in gastrointestinal cancer patients’ plasma',
'authors' => 'Tao Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>During cancer development, host’s tumorigenesis and immune signals are released to and informed by circulating molecules, like cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and RNA (cfRNA) in blood. However, these two kinds of molecules are still not systematically compared in gastrointestinal cancer. Here, we profiled 4 types of cell-free omics data from colorectal and stomach cancer patients, and assayed 15 types of genomic, epi-genomic, and transcriptomic variations. First, we demonstrated that the multi-omics data were more capable of detecting cancer genes than the single-omics data, where cfRNAs were more sensitive and informative than cfDNAs in terms of detection ratio, variation type, altered number, and enriched functional pathway. Moreover, we revealed several peripheral immune signatures that were suppressed in cancer patients and originated from specific circulating and tumor-microenvironment cells. Particularly, we defined a γδ-T-cell score and a cancer-associated-fibroblast (CAF) score using the cfRNA-seq data of 143 cancer patients. They were informative of clinical status like cancer stage, tumor size, and survival. In summary, our work reveals the cell-free multi-molecular landscape of colorectal and stomach cancer, and provides a potential monitoring utility in blood for the personalized cancer treatment.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2023.01.31.526431',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.01.31.526431',
'modified' => '2023-04-04 08:36:37',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 15 => array(
'id' => '4674',
'name' => 'Methylation and expression of glucocorticoid receptor exon-1 variants andFKBP5 in teenage suicide-completers.',
'authors' => 'Rizavi H. et al.',
'description' => '<p>A dysregulated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis has repeatedly been demonstrated to play a fundamental role in psychiatric disorders and suicide, yet the mechanisms underlying this dysregulation are not clear. Decreased expression of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene, which is also susceptible to epigenetic modulation, is a strong indicator of impaired HPA axis control. In the context of teenage suicide-completers, we have systematically analyzed the 5'UTR of the GR gene to determine the expression levels of all GR exon-1 transcript variants and their epigenetic state. We also measured the expression and the epigenetic state of the FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP5/FKBP51), an important modulator of GR activity. Furthermore, steady-state DNA methylation levels depend upon the interplay between enzymes that promote DNA methylation and demethylation activities, thus we analyzed DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), ten-eleven translocation enzymes (TETs), and growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins (GADD45). Focusing on both the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus, our results show decreased expression in specific GR exon-1 variants and a strong correlation of DNA methylation changes with gene expression in the PFC. FKBP5 expression is also increased in both areas suggesting a decreased GR sensitivity to cortisol binding. We also identified aberrant expression of DNA methylating and demethylating enzymes in both brain regions. These findings enhance our understanding of the complex transcriptional regulation of GR, providing evidence of epigenetically mediated reprogramming of the GR gene, which could lead to possible epigenetic influences that result in lasting modifications underlying an individual's overall HPA axis response and resilience to stress.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36781843',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41398-023-02345-1',
'modified' => '2023-04-14 09:26:37',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 16 => array(
'id' => '4675',
'name' => 'Bridging biological cfDNA features and machine learning approaches.',
'authors' => 'Moser T. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Liquid biopsies (LBs), particularly using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), are expected to revolutionize precision oncology and blood-based cancer screening. Recent technological improvements, in combination with the ever-growing understanding of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) biology, are enabling the detection of tumor-specific changes with extremely high resolution and new analysis concepts beyond genetic alterations, including methylomics, fragmentomics, and nucleosomics. The interrogation of a large number of markers and the high complexity of data render traditional correlation methods insufficient. In this regard, machine learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly being used to decipher disease- and tissue-specific signals from cfDNA. Here, we review recent insights into biological ctDNA features and how these are incorporated into sophisticated ML applications.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36792446',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.tig.2023.01.004',
'modified' => '2023-04-14 09:28:00',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 17 => array(
'id' => '4823',
'name' => 'Gene body DNA hydroxymethylation restricts the magnitude oftranscriptional changes during aging.',
'authors' => 'Occean J. R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC) is the most abundant oxidative derivative of DNA methylation (5mC) and is typically enriched at enhancers and gene bodies of transcriptionally active and tissue-specific genes. Although aberrant genomic 5hmC has been implicated in many age-related diseases, the functional role of the modification in aging remains largely unknown. Here, we report that 5hmC is stably enriched in multiple aged organs. Using the liver and cerebellum as model organs, we show that 5hmC accumulates in gene bodies associated with tissue-specific function and thereby restricts the magnitude of gene expression changes during aging. Mechanistically, we found that 5hmC decreases binding affinity of splicing factors compared to unmodified cytosine and 5mC, and is correlated with age-related alternative splicing events, suggesting RNA splicing as a potential mediator of 5hmC’s transcriptionally restrictive function. Furthermore, we show that various age-related contexts, such as prolonged quiescence and senescence, are partially responsible for driving the accumulation of 5hmC with age. We provide evidence that this age-related function is conserved in mouse and human tissues, and further show that the modification is altered by regimens known to modulate lifespan. Our findings reveal that 5hmC is a regulator of tissue-specific function and may play a role in regulating longevity.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36824863',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.02.15.528714',
'modified' => '2023-06-14 08:39:26',
'created' => '2023-06-13 22:16:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 18 => array(
'id' => '4711',
'name' => 'Neonatal inflammation increases hippocampal KCC2 expression throughmethylation-mediated TGF-β1 downregulation leading to impairedhippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity in adult mice.',
'authors' => 'Rong J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The mechanisms by which neonatal inflammation leads to cognitive deficits in adulthood remain poorly understood. Inhibitory GABAergic synaptic transmission plays a vital role in controlling learning, memory and synaptic plasticity. Since early-life inflammation has been reported to adversely affect the GABAergic synaptic transmission, the aim of this study was to investigate whether and how neonatal inflammation affects GABAergic synaptic transmission resulting in cognitive impairment. Neonatal mice received a daily subcutaneous injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 50 μg/kg) or saline on postnatal days 3-5. It was found that blocking GABAergic synaptic transmission reversed the deficit in hippocampus-dependent memory or the induction failure of long-term potentiation in the dorsal CA1 in adult LPS mice. An increase of mIPSCs amplitude was further detected in adult LPS mice indicative of postsynaptic potentiation of GABAergic transmission. Additionally, neonatal LPS resulted in the increased expression and function of K-Cl-cotransporter 2 (KCC2) and the decreased expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) in the dorsal CA1 during adulthood. The local TGF-β1 overexpression improved KCC2 expression and function, synaptic plasticity and memory of adult LPS mice. Adult LPS mice show hypermethylation of TGFb1 promoter and negatively correlate with reduced TGF-β1 transcripts. 5-Aza-deoxycytidine restored the changes in TGFb1 promoter methylation and TGF-β1 expression. Altogether, the results suggest that hypermethylation-induced reduction of TGF-β1 leads to enhanced GABAergic synaptic inhibition through increased KCC2 expression, which is a underlying mechanism of neonatal inflammation-induced hippocampus-dependent memory impairment in adult mice.</p>',
'date' => '2023-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36691035',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12974-023-02697-x',
'modified' => '2023-04-05 08:42:07',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 19 => array(
'id' => '4589',
'name' => 'Impact of FecB Mutation on Ovarian DNA Methylome inSmall-Tail Han Sheep.',
'authors' => 'Xie L. et al.',
'description' => '<p>UNLABELLED: Booroola fecundity (FecB) gene, a mutant of bone morphogenetic protein 1B (BMPR-1B) that was discovered in Booroola Merino, was the first prolificacy gene identified in sheep related to increased ovulation rate and litter size. The mechanism of FecB impact on reproduction is unclear. METHODS: In this study, adult Han ewes with homozygous FecB(B)/FecB(B) mutations (Han BB group) and ewes with FecB(+)/FecB(+) wildtype (Han ++ group) were selected. Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) was used to identify differences in methylated genes in ovary tissue. RESULTS: We examined differences in DNA methylation patterns between HanBB and Han ++ sheep. In both sheep, methylated reads were mainly distributed at the gene body regions, CpG islands and introns. The differentially methylated genes were enriched in neurotrophy in signaling pathway, Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) signaling pathway, Wnt signaling pathway, oocyte meiosis, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway, etc. Differentially-methylated genes were co-analyzed with differentially-expressed mRNAs. Several genes which could be associated with female reproduction were identified, such as FOXP3 (forkhead box P3), TMEFF2 (Transmembrane Protein with EGF Like and Two Follistatin Like Domains 2) and ADAT2 (Adenosine Deaminase TRNA Specific 2). CONCLUSIONS: We constructed a MeDIP-seq based methylomic study to investigate the ovarian DNA methylation differences between Small-Tail Han sheep with homozygous FecB mutant and wildtype, and successfully identified FecB gene-associated differentially-methylated genes. This study has provided information with which to understand the mechanisms of FecB gene-induced hyperprolificacy in sheep.</p>',
'date' => '2023-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36672944',
'doi' => '10.3390/genes14010203',
'modified' => '2023-04-11 10:04:29',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 20 => array(
'id' => '4631',
'name' => 'Consistent DNA Hypomethylations in Prostate Cancer.',
'authors' => 'Araúzo-Bravo M.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>With approximately 1.4 million men annually diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa) worldwide, PCa remains a dreaded threat to life and source of devastating morbidity. In recent decades, a significant decrease in age-specific PCa mortality has been achieved by increasing prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening and improving treatments. Nevertheless, upcoming, augmented recommendations against PSA screening underline an escalating disproportion between the benefit and harm of current diagnosis/prognosis and application of radical treatment standards. Undoubtedly, new potent diagnostic and prognostic tools are urgently needed to alleviate this tensed situation. They should allow a more reliable early assessment of the upcoming threat, in order to enable applying timely adjusted and personalized therapy and monitoring. Here, we present a basic study on an epigenetic screening approach by Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP). We identified genes associated with hypomethylated CpG islands in three PCa sample cohorts. By adjusting our computational biology analyses to focus on single CpG-enriched 60-nucleotide-long DNA probes, we revealed numerous consistently differential methylated DNA segments in PCa. They were associated among other genes with and . These can be used for early discrimination, and might contribute to a new epigenetic tumor classification system of PCa. Our analysis shows that we can dissect short, differential methylated CpG-rich DNA fragments and combinations of them that are consistently present in all tumors. We name them tumor cell-specific differential methylated CpG dinucleotide signatures (TUMS).</p>',
'date' => '2022-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36613831',
'doi' => '10.3390/ijms24010386',
'modified' => '2023-03-28 09:03:47',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 21 => array(
'id' => '4488',
'name' => 'Cell-free DNA methylation-defined prognostic subgroups in small celllung cancer identified by leukocyte methylation subtraction',
'authors' => 'Ul Haq Sami et al.',
'description' => '<p>Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) methylome is understudied. Here, we comprehensively profile SCLC using cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from plasma of 74 SCLC patients pre-treatment and from 20 non-cancer participants, genomic DNA (gDNA) from peripheral blood leukocytes from the same 74 patients and 7 accompanying circulating-tumour-cell patient-derived xenografts (CDX) underwent cfMeDIP-seq. PeRIpheral blood leukocyte MEthylation (PRIME) subtraction to improve tumour specificity. SCLC cfDNA methylation is distinct from non-cancer but correlates with CDX tumor methylation. PRIME and k-means consensus identified two methylome clusters with prognostic associations that related to axon guidance, neuroactive ligand−receptor interaction, pluripotency of stem cells, and differentially methylated at long noncoding RNA and other repeats features. We comprehensively profiled the SCLC methylome in a large patient cohort and identified methylome clusters with prognostic associations. Our work demonstrates the potential of liquid biopsies in examining SCLC biology encoded in the methylome.</p>',
'date' => '2022-11-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.isci.2022.105487',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.isci.2022.105487',
'modified' => '2022-11-18 12:35:39',
'created' => '2022-11-15 09:26:20',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 22 => array(
'id' => '4547',
'name' => 'The cell-free DNA methylome captures distinctions between localized andmetastatic prostate tumors.',
'authors' => 'Chen Sujun et al.',
'description' => '<p>Metastatic prostate cancer remains a major clinical challenge and metastatic lesions are highly heterogeneous and difficult to biopsy. Liquid biopsy provides opportunities to gain insights into the underlying biology. Here, using the highly sensitive enrichment-based sequencing technology, we provide analysis of 60 and 175 plasma DNA methylomes from patients with localized and metastatic prostate cancer, respectively. We show that the cell-free DNA methylome can capture variations beyond the tumor. A global hypermethylation in metastatic samples is observed, coupled with hypomethylation in the pericentromeric regions. Hypermethylation at the promoter of a glucocorticoid receptor gene NR3C1 is associated with a decreased immune signature. The cell-free DNA methylome is reflective of clinical outcomes and can distinguish different disease types with 0.989 prediction accuracy. Finally, we show the ability of predicting copy number alterations from the data, providing opportunities for joint genetic and epigenetic analysis on limited biological samples.</p>',
'date' => '2022-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36309516',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41467-022-34012-2',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:30:03',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 23 => array(
'id' => '4550',
'name' => 'A SOX2-engineered epigenetic silencer factor represses the glioblastomagenetic program and restrains tumor development.',
'authors' => 'Benedetti V. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Current therapies remain unsatisfactory in preventing the recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), which leads to poor patient survival. By rational engineering of the transcription factor SOX2, a key promoter of GBM malignancy, together with the Kruppel-associated box and DNA methyltransferase3A/L catalytic domains, we generated a synthetic repressor named SOX2 epigenetic silencer (SES), which induces the transcriptional silencing of its original targets. By doing so, SES kills both glioma cell lines and patient-derived cancer stem cells in vitro and in vivo. SES expression, through local viral delivery in mouse xenografts, induces strong regression of human tumors and survival rescue. Conversely, SES is not harmful to neurons and glia, also thanks to a minimal promoter that restricts its expression in mitotically active cells, rarely present in the brain parenchyma. Collectively, SES produces a significant silencing of a large fraction of the SOX2 transcriptional network, achieving high levels of efficacy in repressing aggressive brain tumors.</p>',
'date' => '2022-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35921410/',
'doi' => '10.1126/sciadv.abn3986',
'modified' => '2023-09-28 11:26:02',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 24 => array(
'id' => '4551',
'name' => 'mTORC1 is required for epigenetic silencing during β-cell functionalmaturation.',
'authors' => 'Ni Qicheng et al.',
'description' => '<p>OBJECTIVE: The mechanistic target of rapamycin comple×1 (mTORC1) is a key molecule that links nutrients, hormones, and growth factors to cell growth/function. Our previous studies have shown that mTORC1 is required for β-cell functional maturation and identity maintenance; however, the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. This work aimed to understand the underlying epigenetic mechanisms of mTORC1 in regulating β-cell functional maturation. METHODS: We performed Microarray, MeDIP-seq and ATAC-seq analysis to explore the abnormal epigenetic regulation in 8-week-old immature βRapKO islets. Moreover, DNMT3A was overexpressed in βRapKO islets by lentivirus, and the transcriptome changes and GSIS function were analyzed. RESULTS: We identified two major epigenetic silencing mechanisms, DNMT3A-dependent DNA methylation and PRC2-dependent H3K27me3 modification, which are responsible for functional immaturity of Raptor-deficient β-cell. Overexpression of DNMT3A partially reversed the immature transcriptome pattern and restored the impaired GSIS in Raptor-deficient β-cells. Moreover, we found that Raptor directly regulated PRC2/EED2 and H3K27me3 expression levels, as well as a group of immature genes marked with H3K27me3. Combined with ATAC-seq, MeDIP-seq and ChIP-seq, we identified β-cell immature genes with either DNA methylation and/or H3K27me3 modification. CONCLUSION: The present study advances our understanding of the nutrient sensor mTORC1, by integrating environmental nutrient supply and epigenetic modification, i.e., DNMT3A-mediated DNA methylation and PRC2-mediated histone methylation in regulating β-cell identity and functional maturation, and therefore may impact the disease risk of type 2 diabetes.</p>',
'date' => '2022-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35940555',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101559',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:09:58',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 25 => array(
'id' => '4391',
'name' => 'Detection of ovarian cancer using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Lu Huaiwu et al. ',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a highly lethal gynecologic cancer, and it is hard to diagnose at an early stage. Clinically, there are no ovarian cancer-specific markers for early detection. Here, we demonstrate the use of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylomes to detect ovarian cancer, especially the early-stage OC. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Plasma from 74 epithelial ovarian cancer patients, 86 healthy volunteers, and 20 patients with benign pelvic masses was collected. The cfDNA methylomes of these samples were generated by cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). The differentially methylated regions (DMRs) were identified by the contrasts between tumor and non-tumor groups, and the discrimination performance was evaluated with the iterative training and testing method. RESULTS: The DMRs identified for cfDNA methylomes can well discriminate tumor groups and non-tumor groups (ROC values from 0.86 to 0.98). The late-stage top 300 DMRs are more late-stage-specific and failed to detect early-stage OC. However, the early-stage markers have the potential to discriminate all-stage OCs from non-tumor samples. CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrates that cfDNA methylomes generated with cfMeDIP-seq could be used to identify OC-specific biomarkers for OC, especially early OC detection. To detect early-stage OC, the biomarkers should be directly identified from early OC plasma samples rather than mix-stage ones. Further exploration of DMRs from a k larger early-stage OC cohort is warranted.</p>',
'date' => '2022-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35681212',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13148-022-01285-9',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:19:10',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 26 => array(
'id' => '4438',
'name' => 'A genome-wide screen reveals new regulators of the 2-cell-like cell state',
'authors' => 'Defossez Pierre-Antoine et al.',
'description' => '<p>In mammals, only the zygote and blastomeres of the early embryo are fully totipotent. This totipotency is mirrored in vitro by mouse "2-cell-like cells" (2CLCs), which appear at low frequency in cultures of Embryonic Stem cells (ESCs). Because totipotency is incompletely understood, we carried out a genomewide CRISPR KO screen in mouse ESCs, searching for mutants that reactivate the expression of Dazl, a robust 2-cell-like marker. Using secondary screens, we identify four mutants that reactivate not just Dazl, but also a broader 2-cell-like signature: the E3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor SPOP, the Zinc Finger transcription factor ZBTB14, MCM3AP, a component of the RNA processing complex TREX-2, and the lysine demethylase KDM5C. Functional experiments show how these factors link to known players of the 2 celllike state. These results extend our knowledge of totipotency, a key phase of organismal life.</p>',
'date' => '2022-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.21203%2Frs.3.rs-1561018%2Fv1',
'doi' => '10.21203/rs.3.rs-1561018/v1',
'modified' => '2022-09-28 09:23:42',
'created' => '2022-09-08 16:32:20',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 27 => array(
'id' => '4394',
'name' => 'Heat stress during grain filling regulates seed germination throughalterations of DNA methylation in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).',
'authors' => 'Sakai Yuki et al.',
'description' => '<p>KEY MESSAGE: Alterations in DNA methylation levels of ROS, GA and ABA related gene promoters cause transcriptional changes upon imbibition to induce seed germination in barley seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling. Environmental changes, especially changes in temperature, during seed development affect germination in several plant species. We have previously shown that heat stress during rice grain filling alters DNA methylation, an epigenetic mark important for gene silencing, regulates transcript levels of phytohormone metabolism genes, and delays seed germination. However, whether this phenomenon is present in other plant species remained to be elucidated. In this study, we compared seeds germination of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) plants grown at 15 °C (control) or 25 °C (heat stress) during grain filling. Heat stress during grain filling significantly promoted seed germination in comparison with the control. The phytohormone gibberellic acid (GA) and reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidases promote seed germination, whereas phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) suppresses seed germination. We found that in heat-stressed seeds, genes related to ABA biosynthesis (HvNCED1 and 2) were significantly suppressed, whereas genes related to ABA catabolism (HvABA8'OH) and GA biosynthesis (HvHA20ox, HvGA3ox), and NADPH oxidase (HvRboh) genes were significantly upregulated after imbibition. Using MeDIP-qPCR, we showed that the promoters of HvNCED were hyper-methylated, and those of HvABA8'OH1, HvABA8'OH3, HvGA3ox2, and HvRbohF2 were hypo-methylated in heat treated seeds. Taken together, our data suggest that heat stress during grain filling affects DNA methylation of germination-related genes and promotes seed germination in barley.</p>',
'date' => '2022-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35581415',
'doi' => '10.1007/s11103-022-01278-5',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:24:13',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 28 => array(
'id' => '4398',
'name' => 'Hexokinase 2 is a transcriptional target and a positive modulator ofAHR signalling.',
'authors' => 'Watzky M. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) regulates the expression of numerous genes in response to activation by agonists including xenobiotics. Although it is well appreciated that environmental signals and cell intrinsic features may modulate this transcriptional response, how it is mechanistically achieved remains poorly understood. We show that hexokinase 2 (HK2) a metabolic enzyme fuelling cancer cell growth, is a transcriptional target of AHR as well as a modulator of its activity. Expression of HK2 is positively regulated by AHR upon exposure to agonists both in human cells and in mice lung tissues. Conversely, over-expression of HK2 regulates the abundance of many proteins involved in the regulation of AHR signalling and these changes are linked with altered AHR expression levels and transcriptional activity. HK2 expression also shows a negative correlation with AHR promoter methylation in tumours, and these tumours with high HK2 expression and low AHR methylation are associated with a worse overall survival in patients. In sum, our study provides novel insights into how AHR signalling is regulated which may help our understanding of the context-specific effects of this pathway and may have implications in cancer.</p>',
'date' => '2022-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1093%2Fnar%2Fgkac360',
'doi' => '10.1093/nar/gkac360',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:32:40',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 29 => array(
'id' => '4561',
'name' => 'Corticosterone induces discrete epigenetic signatures in the dorsal andventral hippocampus that depend upon sex and genotype: focus on methylatedNr3c1 gene.',
'authors' => 'Caradonna S. G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The genomic effects of circulating glucocorticoids are particularly relevant in cortico-limbic structures, which express a high concentration of steroid hormone receptors. To date, no studies have investigated genomic differences in hippocampal subregions, namely the dorsal (dHPC) and ventral (vHPC) hippocampus, in preclinical models treated with exogenous glucocorticoids. Chronic oral corticosterone (CORT) in mouse is a pharmacological approach that disrupts the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, increases affective behavior, and induces genomic changes after stress in the HPC of wildtype (WT) mice and mice heterozygous for the gene coding for brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met (hMet), a variant associated with genetic susceptibility to stress. Using RNA-sequencing, we investigated the genomic signatures of oral CORT in the dHPC and vHPC of WT and hMet male and female mice, and examined sex and genotype differences in response to oral CORT. Males under CORT showed lower glycemia and increased anxiety- and depression-like behavior compared to females that showed instead opposite affective behavior in response to CORT. Rank-rank-hypergeometric overlap (RRHO) was used to identify genes from a continuous gradient of significancy that were concordant across groups. RRHO showed that CORT-induced differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in WT mice and hMet mice converged in the dHPC of males and females, while in the vHPC, DEGs converged in males and diverged in females. The vHPC showed a higher number of DEGs compared to the dHPC and exhibited sex differences related to glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-binding genes and epigenetic modifiers. Methyl-DNA-immunoprecipitation in the vHPC revealed differential methylation of the exons 1 and 1 of the GR gene (Nr3c1) in hMet females. Together, we report behavioral and endocrinological sex differences in response to CORT, as well as epigenetic signatures that i) differ in the dHPC and vHPC,ii) are distinct in males and females, and iii) implicate differential methylation of Nr3c1 selectively in hMet females.</p>',
'date' => '2022-03-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35296634',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41398-022-01864-7',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:03:20',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 30 => array(
'id' => '4364',
'name' => 'Methionine Metabolism Controls the B-cell EBV Epigenome andViral Latency',
'authors' => 'Guo R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) subverts host epigenetic pathways to switch between viral latency programs, colonize the B-cell compartment and reactivate. Within memory B-cells, the reservoir for lifelong infection, EBV genomic DNA and histone methylation marks restrict gene expression. But, this epigenetic strategy also enables EBV-infected tumors, including Burkitt lymphomas to evade immune detection. Little is known about host cell metabolic pathways that support EBV epigenome landscapes. We therefore used amino acid restriction, metabolomic and CRISPR approaches to identify that an abundant methionine supply, and interconnecting methionine and folate cycles, maintain Burkitt EBV gene silencing. Methionine restriction, or methionine cycle perturbation, hypomethylated EBV genomes, de-repressed latent membrane protein and lytic gene expression. Methionine metabolism also shaped EBV latency gene regulation required for B-cell immortalization. Dietary methionine restriction altered murine Burkitt xenograft metabolomes and de-repressed EBV immunogens in vivo. These results highlight epigenetic/immunometabolism crosstalk supporting the EBV B-cell lifecycle and suggest therapeutic approaches.</p>',
'date' => '2022-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2022.02.24.481783',
'doi' => '10.1101/2022.02.24.481783',
'modified' => '2022-08-04 15:50:37',
'created' => '2022-08-04 14:55:36',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 31 => array(
'id' => '4281',
'name' => 'Integrating SNPs-based genetic risk factor with blood epigenomicresponse of differentially arsenic-exposed rural subjects revealsdisease-associated signaling pathways.',
'authors' => 'Rehman Muhammad Yasir Abdur et al.',
'description' => '<p>Arsenic (As) contamination in groundwater is responsible for numerous adverse health outcomes among millions of people. Epigenetic alterations are among the most widely studied mechanisms of As toxicity. To understand how As exposure alters gene expression through epigenetic modifications, a systematic genome-wide study was designed to address the impact of multiple important single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to As exposure on the methylome of drinking water As-exposed rural subjects from Pakistan. Urinary As levels were used to stratify subjects into low, medium and high exposure groups. Genome-wide DNA methylation was investigated using MeDIP in combination with NimbleGen 2.1 M Deluxe Promotor arrays. Transcriptome levels were measured using Agilent 8 × 60 K expression arrays. Genotyping of selected SNPs (As3MT, DNMT1a, ERCC2, EGFR and MTHFR) was measured and an integrated genetic risk factor for each respondent was calculated by assigning a specific value to the measured genotypes based on known risk allele numbers. To select a representative model related to As exposure we compared 9 linear mixed models comprising of model 1 (including the genetic risk factor), model 2 (without the genetic risk factor) and models with individual SNPs incorporated into the methylome data. Pathway analysis was performed using ConsensusPathDB. Model 1 comprising the integrated genetic risk factor disclosed biochemical pathways including muscle contraction, cardio-vascular diseases, ATR signaling, GPCR signaling, methionine metabolism and chromatin modification in association with hypo- and hyper-methylated gene targets. A unique pathway (direct P53 effector) was found associated with the individual DNMT1a polymorphism due to hyper-methylation of CSE1L and TRRAP. Most importantly, we provide here the first evidence of As-associated DNA methylation in relation with gene expression of ATR, ATF7IP, TPM3, UBE2J2. We report the first evidence that integrating SNPs data with methylome data generates a more representative epigenome profile and discloses a better insight in disease risks of As-exposed individuals.</p>',
'date' => '2022-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.envpol.2021.118279',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118279',
'modified' => '2022-05-23 10:04:20',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 32 => array(
'id' => '4404',
'name' => 'Stella regulates the Development of Female Germline Stem Cells byModulating Chromatin Structure and DNA Methylation.',
'authors' => 'Hou Changliang et al.',
'description' => '<p>Female germline stem cells (FGSCs) have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into oocytes. , encoded by a maternal effect gene, plays an important role in oogenesis and early embryonic development. However, its function in FGSCs remains unclear. In this study, we showed that CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of promoted FGSC proliferation and reduced the level of genome-wide DNA methylation of FGSCs. Conversely, overexpression led to the opposite results, and enhanced FGSC differentiation. We also performed an integrative analysis of chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq), high-throughput genome-wide chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C), and use of our published epigenetic data. Results indicated that the binding sites of STELLA and active histones H3K4me3 and H3K27ac were enriched near the TAD boundaries. Hi-C analysis showed that overexpression attenuated the interaction within TADs, and interestingly enhanced the TAD boundary strength in STELLA-associated regions. Taking these findings together, our study not only reveals the role of in regulating DNA methylation and chromatin structure, but also provides a better understanding of FGSC development.</p>',
'date' => '2022-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9066111/',
'doi' => '10.7150/ijbs.69240',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:54:29',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 33 => array(
'id' => '4302',
'name' => 'Examining age-dependent DNA methylation patterns and gene expression inthe male and female mouse hippocampus.',
'authors' => 'Chinn Carlene A et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a well-characterized epigenetic modification involved in numerous molecular and cellular functions. Methylation patterns have also been associated with aging mechanisms. However, how DNA methylation patterns change within key brain regions involved in memory formation in an age- and sex-specific manner remains unclear. Here, we performed reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) from mouse dorsal hippocampus - which is necessary for the formation and consolidation of specific types of memories - in young and aging mice of both sexes. Overall, our findings demonstrate that methylation levels within the dorsal hippocampus are divergent between sexes during aging in genomic features correlating to mRNA functionality, transcription factor binding sites, and gene regulatory elements. These results define age-related changes in the methylome across genomic features and build a foundation for investigating potential target genes regulated by DNA methylation in an age- and sex-specific manner.</p>',
'date' => '2021-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.neurobiolaging.2021.08.006',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.08.006',
'modified' => '2022-05-30 09:54:05',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 34 => array(
'id' => '4100',
'name' => 'Therapy-induced DNA methylation inactivates MCT1 and renders tumor cells vulnerable to MCT4 inhibition',
'authors' => 'Catherine Vander Linden, Cyril Corbet, Estelle Bastien, Ruben Martherus, Céline Guilbaud, Laurenne Petit, Loris Wauthier, Axelle Loriot, Charles De Smet, Olivier Feron',
'description' => '<p><span>Metabolic plasticity in cancer cells makes use of metabolism-targeting agents very challenging. Drug-induced metabolic rewiring may, however, uncover vulnerabilities that can be exploited. We report that resistance to glycolysis inhibitor 3-bromopyruvate (3-BrPA) arises from DNA methylation in treated cancer cells and subsequent silencing of the monocarboxylate transporter MCT1. We observe that, unexpectedly, 3-BrPA-resistant cancer cells mostly rely on glycolysis to sustain their growth, with MCT4 as an essential player to support lactate flux. This shift makes cancer cells particularly suited to adapt to hypoxic conditions and resist OXPHOS inhibitors and anti-proliferative chemotherapy. In contrast, blockade of MCT4 activity in 3-BrPA-exposed cancer cells with diclofenac or genetic knockout, inhibits growth of derived spheroids and tumors in mice. This study supports a potential mode of collateral lethality according to which metabolic adaptation of tumor cells to a first-line therapy makes them more responsive to a second-line treatment.</span></p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)00551-9#%20',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109202',
'modified' => '2021-06-03 16:04:34',
'created' => '2021-06-03 14:16:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 35 => array(
'id' => '4330',
'name' => 'Epigenetic Plasticity Enables CNS-Trafficking of EBV-infectedB Lymphocytes',
'authors' => 'Soldan S. S. et al. ',
'description' => '<p>Subpopulations of B-lymphocytes traffic to different sites and organs to provide diverse and tissue-specific functions. Here, we provide evidence that epigenetic differences confer a neuroinvasive phenotype. An EBV+ B cell lymphoma cell line (M14) with low frequency trafficking to the CNS was neuroadapted to generate a highly neuroinvasive B-cell population (MUN14). MUN14 B cells efficiently infiltrated the CNS within one week and produced neurological pathologies. We compared the gene expression profiles of viral and cellular genes using RNA-Seq and identified one viral (EBNA1) and several cellular gene candidates, including secreted phosphoprotein 1/osteopontin (SPP1/OPN), neuron navigator 3 (NAV3), CXCR4, and germinal center-associated signaling and motility protein (GCSAM) that were selectively upregulated in MUN14. ATAC-Seq and ChIP-qPCR revealed that these gene expression changes correlated with epigenetic changes at gene regulatory elements. The neuroinvasive phenotype could be attenuated with a neutralizing antibody to OPN, confirming the functional role of this protein in trafficking EBV+ B cells to the CNS. These studies indicate that B-cell trafficking to the CNS can be acquired by epigenetic adaptations and provide a new model to study B-cell neuroinvasion associated CNS lymphoma and autoimmune disease of the CNS, including multiple sclerosis (MS).</p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34106998',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.ppat.1009618',
'modified' => '2022-08-03 16:11:53',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 36 => array(
'id' => '4354',
'name' => 'Dnmt1 has de novo activity targeted to transposable elements',
'authors' => 'Haggerty C. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation plays a critical role during development, particularly in repressing retrotransposons. The mammalian methylation landscape is dependent on the combined activities of the canonical maintenance enzyme Dnmt1 and the de novo Dnmts, 3a and 3b. Here, we demonstrate that Dnmt1 displays de novo methylation activity in vitro and in vivo with specific retrotransposon targeting. We used whole-genome bisulfite and long-read Nanopore sequencing in genetically engineered methylation-depleted mouse embryonic stem cells to provide an in-depth assessment and quantification of this activity. Utilizing additional knockout lines and molecular characterization, we show that the de novo methylation activity of Dnmt1 depends on Uhrf1, and its genomic recruitment overlaps with regions that enrich for Uhrf1, Trim28 and H3K9 trimethylation. Our data demonstrate that Dnmt1 can catalyze DNA methylation in both a de novo and maintenance context, especially at retrotransposons, where this mechanism may provide additional stability for long-term repression and epigenetic propagation throughout development.</p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34140676',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41594-021-00603-8',
'modified' => '2022-08-03 16:55:11',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 37 => array(
'id' => '4135',
'name' => 'Alterations of DNA Methylation Caused by Cold Plasma Treatment Restore Delayed Germination of Heat-Stressed Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seeds',
'authors' => 'Suriyasak, C. et al. ',
'description' => '<p>In rice (Oryza sativa L.), seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling exhibit delayed germination because of DNA methylation levels at promoters of abscisic acid (ABA, a germination-inhibiting hormone) catabolism genes and α-amylase (starchhydrolyzing enzyme) genes, affecting their expression levels. Cold atmospheric plasma is known as an innovative and sustainable energy that has positive effects on the growth and development of many plant species. We, therefore, treated seeds that matured under heat stress with cold plasma and found that subsequent germination was significantly restored; genes involved in ABA biosynthesis (OsNCED2 and OsNCED5) were downregulated, whereas genes involved in ABA catabolism (OsABA8′OH1 and OsABA8′OH3) and α-amylase genes (OsAmy1A, OsAmy1C, OsAmy3B, and OsAmy3E) were upregulated. Cold plasma treatment caused significant hypermethylation of the OsNCED5 promoter and hypomethylation of OsAmy1C and OsAmy3E promoters, which matched their expression patterns. We suggest that cold plasma treatment can significantly improve the germination of rice seeds affected by heat stress by affecting epigenetic regulation.</p>',
'date' => '2021-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1021%2Facsagscitech.0c00070',
'doi' => '10.1021/acsagscitech.0c00070',
'modified' => '2021-12-10 17:15:10',
'created' => '2021-12-06 15:53:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 38 => array(
'id' => '4057',
'name' => 'Prenatal Stress Leads to the Altered Maturation of Corticostriatal SynapticPlasticity and Related Behavioral Impairments Through EpigeneticModifications of Dopamine D2 Receptor in Mice.',
'authors' => 'Li, Yingchun and Rong, Jing and Zhong, Haiquan and Liang, Min and Zhu,Chunting and Chang, Fei and Zhou, Rong',
'description' => '<p>Prenatal stress (PRS) had a long-term adverse effect on motor behaviors. Corticostriatal synaptic plasticity, a cellular basis for motor controlling, has been proven to participate in the pathogenesis of many behavior disorders. Based on the reports about the involvement of epigenetic DNA alterations in PRS-induced long-term effects, this research investigated the influence of PRS on the development and maturation of corticostriatal synaptic plasticity and related behaviors and explored the underlying epigenetic mechanism. Subjects were male offspring of dams that were exposed to stress three times per day from the 10th day of pregnancy until delivery. The development and maturation of plasticity at corticostriatal synapses, dopamine signaling, behavioral habituation, and DNA methylation were examined and analyzed. Control mice expressed long-term potentiation (LTP) at corticostriatal synapses during postnatal days (PD) 12-14 and produced long-term depression (LTD) during PD 20-60. However, PRS mice exhibited sustained LTP during PD 12-60. The treatment with dopamine 2 receptor (D2R) agonist quinpirole recovered striatal LTD and improved the impaired behavioral habituation in PD 45 adult PRS mice. Additionally, adult PRS mice showed reduced D2R, excess DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), increased binding of DNMT1 to D2R promoter, and hypermethylation at D2R promoter in the striatum. The DNMT1 inhibitor 5-aza-deoxycytidine restored striatal synaptic plasticity and improved behavioral habituation in adult PRS mice via D2R-mediated dopamine signaling. DNMT1-associated D2R hypermethylation is responsible for altering the maturation of plasticity at corticostriatal synapses and impairing the behavioral habituation in PRS mice.</p>',
'date' => '2021-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32935231',
'doi' => '10.1007/s12035-020-02127-6',
'modified' => '2021-02-19 17:23:03',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 39 => array(
'id' => '4200',
'name' => 'Comparative genome-wide methylation analysis of longissimus dorsi musclesin Yorkshire and Wannanhua pigs.',
'authors' => 'Li, X-J et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation was one of the earliest discovered epigenetic modifications in vertebrates, and is an important epigenetic mechanism involved in the expression of genes in many biological processes, including muscle growth and development. Its effects on economically important traits are evidenced in reported differences in meat quality traits between Chinese indigenous pig breeds (Wannanhua pig) and Western commercial pig breeds (Yorkshire pig), and this presents a unique model for analyzing the effects of DNA methylation on these traits. In the present study, a whole genome DNA methylation analysis was performed on the two breeds using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation. GO functional enrichment and pathway enrichment analyses identified differentially methylated genes primarily associated with fatty acid metabolism, biological processes of muscle development and signaling pathways related to muscle development and pork quality. Differentially methylated genes were verified by sodium pyrosequencing, and the results were consistent with the sequencing results. The results of the integrative analysis between DNA methylation and gene expression revealed that the DNA methylation levels showed a significantly negative correlation with gene expression levels around the transcription start site of genes. In total, 41 genes were both differentially expressed and methylated; these genes were related to fat metabolism, lipid metabolism and skeletal muscle development. This study could help further explore the molecular mechanisms and phenotypic differences in pig growth and development among different breeds.</p>',
'date' => '2020-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33301219',
'doi' => '10.1111/age.13029',
'modified' => '2022-01-06 14:43:32',
'created' => '2021-12-06 15:53:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 40 => array(
'id' => '4041',
'name' => 'Mechanism of delayed seed germination caused by high temperature duringgrain filling in rice (Oryza sativa L.).',
'authors' => 'Suriyasak, Chetphilin and Oyama, Yui and Ishida, Toshiaki and Mashiguchi,Kiyoshi and Yamaguchi, Shinjiro and Hamaoka, Norimitsu and Iwaya-Inoue,Mari and Ishibashi, Yushi',
'description' => '<p>High temperature during grain filling considerably reduces yield and quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.); however, how high temperature affects seed germination of the next generation is not yet well understood. Here, we report that seeds from plants exposed to high temperature during the grain filling stage germinated significantly later than seeds from unstressed plants. This delay remained even after dormancy release treatments, suggesting that it was not due to primary seed dormancy determined during grain filling. In imbibed embryos of heat-stressed seeds, expression of abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis genes (OsNCEDs) was higher than in those of control seeds, whereas that of ABA catabolism genes (OsABA8'OHs) was lower. In the aleurone layer, despite no change in GA signaling as evidenced by no effect of heat stress on OsGAMYB gene expression, the transcripts of α-amylase genes OsAmy1C, OsAmy3B, and OsAmy3E were significantly down-regulated in heat-stressed seeds in comparison with controls. Changes in promoter methylation levels were consistent with transcriptional changes of ABA catabolism-related and α-amylase genes. These data suggest that high temperature during grain filling results in DNA methylation of ABA catabolism-related and α-amylase gene promoters, delaying germination of heat-stressed seeds.</p>',
'date' => '2020-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33060675',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-020-74281-9',
'modified' => '2021-02-19 12:09:29',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 41 => array(
'id' => '4094',
'name' => 'Network integration and modelling of dynamic drug responses at multi-omicslevels.',
'authors' => 'Selevsek, Nathalie and Caiment, Florian and Nudischer, Ramona and Gmuender,Hans and Agarkova, Irina and Atkinson, Francis L and Bachmann, Ivo andBaier, Vanessa and Barel, Gal and Bauer, Chris and Boerno, Stefan and Bosc,Nicolas and Clayton, Olivia and ',
'description' => '<p>Uncovering cellular responses from heterogeneous genomic data is crucial for molecular medicine in particular for drug safety. This can be realized by integrating the molecular activities in networks of interacting proteins. As proof-of-concept we challenge network modeling with time-resolved proteome, transcriptome and methylome measurements in iPSC-derived human 3D cardiac microtissues to elucidate adverse mechanisms of anthracycline cardiotoxicity measured with four different drugs (doxorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin and daunorubicin). Dynamic molecular analysis at in vivo drug exposure levels reveal a network of 175 disease-associated proteins and identify common modules of anthracycline cardiotoxicity in vitro, related to mitochondrial and sarcomere function as well as remodeling of extracellular matrix. These in vitro-identified modules are transferable and are evaluated with biopsies of cardiomyopathy patients. This to our knowledge most comprehensive study on anthracycline cardiotoxicity demonstrates a reproducible workflow for molecular medicine and serves as a template for detecting adverse drug responses from complex omics data.</p>',
'date' => '2020-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33060801',
'doi' => '10.1038/s42003-020-01302-8',
'modified' => '2021-03-17 17:16:56',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 42 => array(
'id' => '4009',
'name' => 'Frataxin gene editing rescues Friedreich's ataxia pathology in dorsal rootganglia organoid-derived sensory neurons.',
'authors' => 'Mazzara, PG and Muggeo, S and Luoni, M and Massimino, L and Zaghi, M andValverde, PT and Brusco, S and Marzi, MJ and Palma, C and Colasante, Gand Iannielli, A and Paulis, M and Cordiglieri, C and Giannelli, SG andPodini, P and Gellera, C and Ta',
'description' => '<p>Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal-recessive neurodegenerative and cardiac disorder which occurs when transcription of the FXN gene is silenced due to an excessive expansion of GAA repeats into its first intron. Herein, we generate dorsal root ganglia organoids (DRG organoids) by in vitro differentiation of human iPSCs. Bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing show that DRG organoids present a transcriptional signature similar to native DRGs and display the main peripheral sensory neuronal and glial cell subtypes. Furthermore, when co-cultured with human intrafusal muscle fibers, DRG organoid sensory neurons contact their peripheral targets and reconstitute the muscle spindle proprioceptive receptors. FRDA DRG organoids model some molecular and cellular deficits of the disease that are rescued when the entire FXN intron 1 is removed, and not with the excision of the expanded GAA tract. These results strongly suggest that removal of the repressed chromatin flanking the GAA tract might contribute to rescue FXN total expression and fully revert the pathological hallmarks of FRDA DRG neurons.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-21',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32826895',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41467-020-17954-3',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:12:57',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 43 => array(
'id' => '4017',
'name' => 'Integrated analysis of DNA methylation profile of HLA-G gene andimaging in coronary heart disease: Pilot study.',
'authors' => 'Schiano, C and Benincasa, G and Infante, T and Franzese, M and Castaldo, Rand Fiorito, C and Mansueto, G and Grimaldi, V and Della, Valle G andFatone, G and Soricelli, A and Nicoletti, GF and Ruocco, A and Mauro, Cand Salvatore, M and Napoli, C',
'description' => '<p>AIMS: Immune endothelial inflammation, underlying coronary heart disease (CHD) related phenotypes, could provide new insight into the pathobiology of the disease. We investigated DNA methylation level of the unique CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients and evaluated the correlation with cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) features. METHODS: Thirty-two patients that underwent CCTA for suspected CHD were enrolled for this study. Obstructive CHD group included fourteen patients, in which there was a stenosis greater than or equal to 50\% in one or more of the major coronary arteries detected; whereas subjects with Calcium (Ca) Score = 0, uninjured coronaries and with no obstructive CHD (no critical stenosis, NCS) were considered as control subjects (n = 18). For both groups, DNA methylation profile of the whole 5'UTR-CpG island of HLA-G was measured. The plasma soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) levels were detected in all subjects by specific ELISA assay. Statistical analysis was performed using R software. RESULTS: For the first time, our study reported that 1) a significant hypomethylation characterized three specific fragments (B, C and F) of the 5'UTR-CpG island (p = 0.05) of HLA-G gene in CHD patients compared to control group; 2) the hypomethylation level of one specific fragment of 161bp (+616/+777) positively correlated with coronary Ca score, a relevant parameter of CCTA (p<0.05) between two groups evaluated and was predictive for disease severity. CONCLUSIONS: Reduced levels of circulating HLA-G molecules could derive from epigenetic marks. Epigenetics phenomena induce hypomethylation of specific regions into 5'UTR-CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients with obstructive non critical stenosis vs coronary stenosis individuals.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-13',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32790754',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0236951',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:37:03',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 44 => array(
'id' => '4021',
'name' => 'Comparative DNA methylome analysis of estrus ewes reveals the complexregulatory pathways of sheep fecundity.',
'authors' => 'Miao, X and Luo, Q and Xie, L and Zhao, H and Qin, X',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND/AIMS: Sheep are important livestock with variant ovulation rate and fertility. Dorset sheep is a typical breed with low prolificacy, whereas Small Tail Han sheep with FecB mutation (HanBB) have hyperprolificacy. Our previous studies have revealed the gene expression difference between the ovaries from Dorset and HanBB sheep contributes to the difference of fecundity, however, what leads to these gene expression difference remains unclear. DNA methylation, an important epigenetic process, plays a crucial role in gene expression regulation. METHODS: In the present study, we constructed a methylated DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) strategy to investigate the differentially methylated genes between the Dorset and HanBB ovaries. RESULTS: Our findings suggest the genes involved in immune response, branched-chain amino acid metabolism, cell growth and cell junction were differentially methylated in or around the gene body regions. CONCLUSIONS: These findings provide prospective insights on the epigenetic basis of sheep fecundity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32753034',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12958-020-00633-9',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:45:28',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 45 => array(
'id' => '4028',
'name' => 'Methylation in pericytes after acute injury promotes chronic kidneydisease.',
'authors' => 'Chou, YH and Pan, SY and Shao, YH and Shih, HM and Wei, SY andLai, CF and Chiang, WC and Schrimpf, C and Yang, KC and Lai, LC andChen, YM and Chu, TS and Lin, SL',
'description' => '<p>The origin and fate of renal myofibroblasts is not clear after acute kidney injury (AKI). Here, we demonstrate that myofibroblasts were activated from quiescent pericytes (qPericytes) and the cell numbers increased after ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced AKI (IRI-AKI). Myofibroblasts underwent apoptosis during renal recovery but one-fifth of them survived in the recovered kidneys on day 28 after IRI-AKI and their cell numbers increased again after day 56. Microarray data showed the distinctive gene expression patterns of qPericytes, activated pericytes (aPericytes, myofibroblasts), and inactivated pericytes (iPericytes) isolated from kidneys before, on day 7, and on day 28 after IRI-AKI. Hypermethylation of the Acta2 repressor Ybx2 during IRI-AKI resulted in epigenetic modification of iPericytes to promote the transition to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and aggravated fibrogenesis induced by a second AKI induced by adenine. Mechanistically, transforming growth factor-β1 decreased the binding of YBX2 to the promoter of Acta2 and induced Ybx2 hypermethylation, thereby increasing α-smooth muscle actin expression in aPericytes. Demethylation by 5-azacytidine recovered the microvascular stabilizing function of aPericytes, reversed the profibrotic property of iPericytes, prevented AKI-CKD transition, and attenuated fibrogenesis induced by a second adenine-AKI. In conclusion, intervention to erase hypermethylation of pericytes after AKI provides a strategy to stop the transition to CKD.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32749240',
'doi' => '10.1172/JCI135773.',
'modified' => '2020-12-18 13:25:55',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 46 => array(
'id' => '3998',
'name' => 'Integrated epigenetic biomarkers in circulating cell-free DNA as a robust classifier for pancreatic cancer.',
'authors' => 'Cao F, Wei A, Hu X, He Y, Zhang J, Xia L, Tu K, Yuan J, Guo Z, Liu H, Xie D, Li A',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: The high lethal rate of pancreatic cancer is partly due to a lack of efficient biomarkers for screening and early diagnosis. We attempted to develop effective and noninvasive methods using 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) markers from circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for the detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). RESULTS: A 24-feature 5mC model that can accurately discriminate PDAC from healthy controls (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.977, sensitivity = 0.824, specificity = 1) and a 5hmC prediction model with 27 features demonstrated excellent detection power in two distinct validation sets (AUC = 0.992 and 0.960, sensitivity = 0.786 and 0.857, specificity = 1 and 0.993). The 51-feature model combining 5mC and 5hmC markers outperformed both of the individual models, with an AUC of 0.997 (sensitivity = 0.938, specificity = 0.955) and particularly an improvement in the prediction sensitivity of PDAC. In addition, the weighted diagnosis score (wd-score) calculated with the 5hmC model can distinguish stage I patients from stage II-IV patients. CONCLUSIONS: Both 5mC and 5hmC biomarkers in cfDNA are effective in PDAC detection, and the 5mC-5hmC integrated model significantly improve the detection sensitivity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-07-23',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32703318',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13148-020-00898-2',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 14:43:06',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 47 => array(
'id' => '3985',
'name' => 'Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Nuzzo PV, Berchuck JE, Korthauer K, Spisak S, Nassar AH, Abou Alaiwi S, Chakravarthy A, Shen SY, Bakouny Z, Boccardo F, Steinharter J, Bouchard G, Curran CR, Pan W, Baca SC, Seo JH, Lee GM, Michaelson MD, Chang SL, Waikar SS, Sonpavde G, Irizarry RA, Pome',
'description' => '<p>Improving early cancer detection has the potential to substantially reduce cancer-related mortality. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) is a highly sensitive assay capable of detecting early-stage tumors. We report accurate classification of patients across all stages of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in plasma (area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.99) and demonstrate the validity of this assay to identify patients with RCC using urine cell-free DNA (cfDNA; AUROC of 0.86).</p>',
'date' => '2020-06-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32572266',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41591-020-0933-1',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 15:13:49',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 48 => array(
'id' => '3984',
'name' => 'Detection and discrimination of intracranial tumors using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Nassiri F, Chakravarthy A, Feng S, Shen SY, Nejad R, Zuccato JA, Voisin MR, Patil V, Horbinski C, Aldape K, Zadeh G, De Carvalho DD',
'description' => '<p>Definitive diagnosis of intracranial tumors relies on tissue specimens obtained by invasive surgery. Noninvasive diagnostic approaches provide an opportunity to avoid surgery and mitigate unnecessary risk to patients. In the present study, we show that DNA-methylation profiles from plasma reveal highly specific signatures to detect and accurately discriminate common primary intracranial tumors that share cell-of-origin lineages and can be challenging to distinguish using standard-of-care imaging.</p>',
'date' => '2020-06-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32572265',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41591-020-0932-2',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 15:14:45',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 49 => array(
'id' => '3942',
'name' => 'DNA methylation enzymes and PRC1 restrict B-cell Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein expression.',
'authors' => 'Guo R, Zhang Y, Teng M, Jiang C, Schineller M, Zhao B, Doench JG, O'Reilly RJ, Cesarman E, Giulino-Roth L, Gewurz BE',
'description' => '<p>To accomplish the remarkable task of lifelong infection, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) switches between four viral genome latency and lytic programmes to navigate the B-cell compartment and evade immune responses. The transforming programme, consisting of highly immunogenic EBV nuclear antigen (EBNA) and latent membrane proteins (LMPs), is expressed in newly infected B lymphocytes and in post-transplant lymphomas. On memory cell differentiation and in most EBV-associated Burkitt's lymphomas, all but one viral antigen are repressed for immunoevasion. To gain insights into the epigenetic mechanisms that restrict immunogenic oncoprotein expression, a genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screen was performed in EBV and Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Here, we show that the ubiquitin ligase ubiquitin-like PHD and RING finger domain-containing protein 1 (UHRF1) and its DNA methyltransferase partner DNA methyltransferase I (DNMT1) are critical for the restriction of EBNA and LMP expression. All UHRF1 reader and writer domains were necessary for silencing and DNMT3B was identified as an upstream viral genome CpG methylation initiator. Polycomb repressive complex I exerted a further layer of control over LMP expression, suggesting a second mechanism for latency programme switching. UHRF1, DNMT1 and DNMT3B are upregulated in germinal centre B cells, the Burkitt's lymphoma cell of origin, providing a molecular link between B-cell state and the EBV latency programme. These results suggest rational therapeutic targets to manipulate EBV oncoprotein expression.</p>',
'date' => '2020-05-18',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32424339',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41564-020-0724-y',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:24:57',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 50 => array(
'id' => '3926',
'name' => 'TET-Mediated Hypermethylation Primes SDH-Deficient Cells for HIF2α-Driven Mesenchymal Transition.',
'authors' => 'Morin A, Goncalves J, Moog S, Castro-Vega LJ, Job S, Buffet A, Fontenille MJ, Woszczyk J, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Letouzé E, Favier J',
'description' => '<p>Loss-of-function mutations in the SDHB subunit of succinate dehydrogenase predispose patients to aggressive tumors characterized by pseudohypoxic and hypermethylator phenotypes. The mechanisms leading to DNA hypermethylation and its contribution to SDH-deficient cancers remain undemonstrated. We examine the genome-wide distribution of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and their correlation with RNA expression in SDHB-deficient tumors and murine Sdhb cells. We report that DNA hypermethylation results from TET inhibition. Although it preferentially affects PRC2 targets and known developmental genes, PRC2 activity does not contribute to the DNA hypermethylator phenotype. We also prove, in vitro and in vivo, that TET silencing, although recapitulating the methylation profile of Sdhb cells, is not sufficient to drive their EMT-like phenotype, which requires additional HIF2α activation. Altogether, our findings reveal synergistic roles of TET repression and pseudohypoxia in the acquisition of metastatic traits, providing a rationale for targeting HIF2α and DNA methylation in SDH-associated malignancies.</p>',
'date' => '2020-03-31',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32234487',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.022',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:50:11',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 51 => array(
'id' => '3920',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Mantle Edge and Mantle Central from Pearl Oyster Pinctada fucata martensii.',
'authors' => 'Zhang J, Luo S, Gu Z, Deng Y, Jiao Y',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a type of epigenetic modification that alters gene expression without changing the DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. In this study, we identified six DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) genes and two methyl-CpG binding domain protein2 (MBD2) gene from Pinctada fucata martensii. We also analyzed the genome-wide DNA methylation levels of mantle edge (ME) and mantle central (MC) from P. f. martensii via methylated immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-Seq). Results revealed that both ME and MC had 122 million reads, and had 58,702 and 55,721 peaks, respectively. The obtained methylation patterns of gene elements and repeats showed that the methylation of the protein-coding genes, particularly intron and coding exons (CDSs), was more frequent than that of other genomic elements in the pearl oyster genome. We combined the methylation data with the RNA-seq data of the ME and MC of P. f. martensii and found that promoter, CDS, and intron methylation levels were positively correlated with gene expression levels except the highest gene expression level. We also identified 313 differential methylation genes (DMGs) and annotated 212 of them. These DMGs were significantly enriched in 30 pathways, such as amino acid and protein metabolism, energy metabolism, terpenoid synthesis, and immune-related pathways. This study comprehensively analyzed the methylomes of biomineralization-related tissues and helped enhance our understanding of the regulatory mechanism underlying shell formation.</p>',
'date' => '2020-03-06',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32140888',
'doi' => '10.1007/s10126-020-09957-4',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:58:42',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 52 => array(
'id' => '3859',
'name' => 'Preterm birth is associated with epigenetic programming of transgenerational hypertension in mice.',
'authors' => 'Dumeige L, Nehlich M, Viengchareun S, Perrot J, Pussard E, Lombès M, Martinerie L',
'description' => '<p>Renal and cardiovascular complications of prematurity are well established, notably the development of hypertension in adulthood. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Our objective was to investigate the impact of prematurity on the ontogenesis of renal corticosteroid pathways, to evaluate its implication in perinatal renal complications and in the emergence of hypertension in adulthood. Swiss CD1 pregnant mice were injected with lipopolysaccharides at 18 days of gestation (E18) to induce prematurity at E18.5. Pups were sacrificed at birth, 7 days and 6 months of life. Second (F2) and third (F3) generations, established by mating prematurely born adult females with wild-type males, were also analyzed. Former preterm males developed hypertension at M6 (P < 0.0001). We found robust activation of renal corticosteroid target gene transcription at birth in preterm mice (αENaC (+45%), Gilz (+85%)), independent of any change in mineralocorticoid or glucocorticoid receptor expression. The offspring of the preterm group displayed increased blood pressure in F2 and F3, associated with increased renal Gilz mRNA expression, despite similar MR or GR expression and plasma corticosteroid levels measured by LC-MS/MS. Gilz promoter methylation measured by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR was reduced with a negative correlation between methylation and expression (P = 0.0106). Our study demonstrates prematurity-related alterations in renal corticosteroid signaling pathways, with transgenerational inheritance of blood pressure dysregulation and epigenetic Gilz regulation up to the third generation. This study provides a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in essential hypertension, which could partly be due to perinatal epigenetic programming from previous generations.</p>',
'date' => '2020-01-24',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31974504',
'doi' => '10.1038/s12276-020-0373-5',
'modified' => '2020-03-20 17:55:50',
'created' => '2020-03-13 13:45:54',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 53 => array(
'id' => '3855',
'name' => 'Alteration in global DNA methylation status following preconditioning injury influences axon growth competence of the sensory neurons.',
'authors' => 'Shin HY, Kim K, Kwon MJ, Oh YJ, Kim EH, Kim HS, Hong CP, Lee JH, Lee K, Kim BG',
'description' => '<p>Preconditioning peripheral nerve injury primes the sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) to acquire axon regeneration competence. Transcription of a large set of regeneration-associated-genes (RAGs) contributes to the enhanced intrinsic axonal regeneration capacity. However, the mechanism underlying the coordinated upregulation of RAGs orchestrated by preconditioning injury is unclear. We sought to determine potential influence of DNA methylation change on transcriptional activation of RAGs in the L4-L6 DRGs following sciatic nerve injury. Genome-wide sequencing revealed that about 20% of the methylated DNA fragments were differentially methylated, and >3000 genes contained differentially methylated regions. Not only demethylation but also increased methylation was observed to a similar extent. The change in the global DNA methylation did not correlate with the gene expression level of most genes, including the well-documented RAGs. However, pharmacological inhibition or activation of DNA methylation markedly attenuated the axon growth capacity of the preconditioned DRG neurons. Pharmacological perturbation of DNA methylation resulted in simultaneous downregulation of many highly overlapping non-transcription factor RAGs, which was accompanied by a concurrent, robust upregulation of SOCS3 and Serpine1. Overexpression of SOCS3 and Serpine1 in the DRG neurons overrode injury-induced axon growth competence, corroborating their roles as the negative regulators of axon regeneration. We conclude that the injury-induced global alteration of DNA methylome strongly influences the axon growth competence in preconditioned DRG neurons. Our results also suggest a possibility that perturbing DNA methylome changes might lead to the upregulation of negative regulator RAGs thereby attenuating axon growth capacity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-01-08',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31926166',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113177',
'modified' => '2020-03-20 17:59:09',
'created' => '2020-03-13 13:45:54',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 54 => array(
'id' => '3814',
'name' => 'Lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced changes in rodent neural progenitors and rescues cognition.',
'authors' => 'Zanni G, Goto S, Fragopoulou AF, Gaudenzi G, Naidoo V, Di Martino E, Levy G, Dominguez CA, Dethlefsen O, Cedazo-Minguez A, Merino-Serrais P, Stamatakis A, Hermanson O, Blomgren K',
'description' => '<p>Cranial radiotherapy in children has detrimental effects on cognition, mood, and social competence in young cancer survivors. Treatments harnessing hippocampal neurogenesis are currently of great relevance in this context. Lithium, a well-known mood stabilizer, has both neuroprotective, pro-neurogenic as well as antitumor effects, and in the current study we introduced lithium treatment 4 weeks after irradiation. Female mice received a single 4 Gy whole-brain radiation dose on postnatal day (PND) 21 and were randomized to 0.24% Li2CO chow or normal chow from PND 49 to 77. Hippocampal neurogenesis was assessed on PND 77, 91, and 105. We found that lithium treatment had a pro-proliferative effect on neural progenitors, but neuronal integration occurred only after it was discontinued. Also, the treatment ameliorated deficits in spatial learning and memory retention observed in irradiated mice. Gene expression profiling and DNA methylation analysis identified two novel factors related to the observed effects, Tppp, associated with microtubule stabilization, and GAD2/65, associated with neuronal signaling. Our results show that lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced loss of hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive impairment even when introduced long after the injury. We propose that lithium treatment should be intermittent in order to first make neural progenitors proliferate and then, upon discontinuation, allow them to differentiate. Our findings suggest that pharmacological treatment of cognitive so-called late effects in childhood cancer survivors is possible.</p>',
'date' => '2019-11-14',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31723242',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41380-019-0584-0',
'modified' => '2019-12-05 10:58:44',
'created' => '2019-12-02 15:25:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 55 => array(
'id' => '3773',
'name' => 'Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA.',
'authors' => 'Shen SY, Burgener JM, Bratman SV, De Carvalho DD',
'description' => '<p>Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) comprises small DNA fragments derived from normal and tumor tissue that are released into the bloodstream. Recently, methylation profiling of cfDNA as a liquid biopsy tool has been gaining prominence due to the presence of tissue-specific markers in cfDNA. We have previously reported cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) as a sensitive, low-input, cost-efficient and bisulfite-free approach to profiling DNA methylomes of plasma cfDNA. cfMeDIP-seq is an extension of a previously published MeDIP-seq protocol and is adapted to allow for methylome profiling of samples with low input (ranging from 1 to 10 ng) of DNA, which is enabled by the addition of 'filler DNA' before immunoprecipitation. This protocol is not limited to plasma cfDNA; it can also be applied to other samples that are naturally sheared and at low availability (e.g., urinary cfDNA and cerebrospinal fluid cfDNA), and is potentially applicable to other applications beyond cancer detection, including prenatal diagnostics, cardiology and monitoring of immune response. The protocol presented here should enable any standard molecular laboratory to generate cfMeDIP-seq libraries from plasma cfDNA in ~3-4 d.</p>',
'date' => '2019-08-30',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31471598',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41596-019-0202-2',
'modified' => '2019-10-02 17:07:45',
'created' => '2019-10-02 16:16:55',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 56 => array(
'id' => '3761',
'name' => 'Single-base methylome profiling of the giant kelp Saccharina japonica reveals significant differences in DNA methylation to microalgae and plants.',
'authors' => 'Fan X, Han W, Teng L, Jiang P, Zhang X, Xu D, Li C, Pellegrini M, Wu C, Wang Y, Kaczurowski MJS, Lin X, Tirichine L, Mock T, Ye N',
'description' => '<p>Brown algae have convergently evolved plant-like body plans and reproductive cycles, which in plants are controlled by differential DNA methylation. Here we provide the first single-base methylome profiles of haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes of a multicellular alga. Although only c. 1.4% of cytosines in Saccharina japonica were methylated mainly at CHH sites and characterised by 5-methylcytosine (5mC), there were significant differences between life-cycle stages. DNA methyltransferase 2 (DNMT2), known to efficiently catalyze tRNA methylation, is assumed to methylate the genome of S. japonica in the structural context of tRNAs as the genome does not encode any other DNA methyltransferases. Circular and long non-coding RNA genes were the most strongly methylated regulatory elements in S. japonica. Differential expression of genes was negatively correlated with DNA methylation with the highest methylation levels measured in both haploid gametophytes. Hypomethylated and highly expressed genes in diploid sporophytes included genes involved in morphogenesis and halogen metabolism. Our data give evidence that cytosine methylation, although occurring at a low level, is significantly contributing to the formation of different life-cycle stages, tissue differentiation, and metabolism in brown algae.</p>',
'date' => '2019-08-16',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31419316',
'doi' => '10.1111/nph.16125',
'modified' => '2019-10-03 10:04:08',
'created' => '2019-10-02 16:16:55',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 57 => array(
'id' => '3720',
'name' => 'Genome-wide methylation in alcohol use disorder subjects: implications for an epigenetic regulation of the cortico-limbic glucocorticoid receptors (NR3C1).',
'authors' => 'Gatta E, Grayson DR, Auta J, Saudagar V, Dong E, Chen Y, Krishnan HR, Drnevich J, Pandey SC, Guidotti A',
'description' => '<p>Environmental factors, including substance abuse and stress, cause long-lasting changes in the regulation of gene expression in the brain via epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation. We examined genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the prefrontal cortex (PFC, BA10) of 25 pairs of control and individuals with alcohol use disorder (AUD), using the Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip. We identified 5254 differentially methylated CpGs (p < 0.005). Bioinformatic analyses highlighted biological processes containing genes related to stress adaptation, including the glucocorticoid receptor (encoded by NR3C1). Considering that alcohol is a stressor, we focused our attention on differentially methylated regions of the NR3C1 gene and validated the differential methylation of several genes in the NR3C1 network. Chronic alcohol drinking results in a significant increased methylation of the NR3C1 exon variant 1, with a particular increase in the levels of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine over 5-methylcytosine. These changes in DNA methylation were associated with reduced NR3C1 mRNA and protein expression levels in PFC, as well as other cortico-limbic regions of AUD subjects when compared with controls. Furthermore, we show that the expression of several stress-responsive genes (e.g., CRF, POMC, and FKBP5) is altered in the PFC of AUD subjects. These stress-response genes were also changed in the hippocampus, a region that is highly susceptible to stress. These data suggest that alcohol-dependent aberrant DNA methylation of NR3C1 and consequent changes in other stress-related genes might be fundamental in the pathophysiology of AUD and lay the groundwork for treatments targeting the epigenetic mechanisms regulating NR3C1 in AUD.</p>',
'date' => '2019-06-25',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31239533',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41380-019-0449-6',
'modified' => '2019-07-04 18:07:16',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 58 => array(
'id' => '3604',
'name' => 'DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene in a CUMS model of depression.',
'authors' => 'Xiang D, Xiao J, Fu L, Yao L, Wan Q, Xiao L, Zhu F, Wang G, Liu Z',
'description' => '<p>Tacr2, the gene encoding the NK2 receptor, belongs to G protein-coupled receptors. Accumulating evidence has indicated that the tachykinin receptors may contribute to the pathophysiology of depression. During the last decade, some studies have shown that Tacr2 activation is involved in the modulation of emotional processes. However, the extent, to which stress impacts Tacr2 expression remains unclear. The molecular mechanisms underlying depression also remain poorly understood. In this study, we subjected adult male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) to induce a depression-like phenotype. We then measured the body weight and performed the sucrose preference test, forced swimming test (FST) and open field test to detect the effects of stress on anhedonia and activity. Western blotting and real-time PCR were used to study the protein and mRNA expression levels of Tacr2, respectively, in the hypothalamus. To explore DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene, we used methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Additionally, we used the bisulfite sequencing PCR (BSP) to further verify the DNA methylation levels of the Tacr2 receptor gene in rats. We found that the CUMS-sensitive rats exhibited a decrease in body weight and sucrose preference, a decrease in the distance traveled, rearing frequency and velocity in the open field test, and an increase in immobility time in the FST. Compared with the expression in the control rats, Tacr2 protein and mRNA expression in the hypothalamus significantly increased in the CUMS-sensitive rats; however, the DNA methylation levels of the Tacr2 gene were significantly lower than in the control rats. In summary, according to our findings, the stress-induced increase in Tacr2 expression in the hypothalamus correlated with a specific decrease in DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene. These results may enrich the understanding of the pathological processes of depression and provide insights into therapeutic approaches for its treatment.</p>',
'date' => '2019-06-03',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30711443',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.bbr.2019.01.059',
'modified' => '2019-04-16 13:54:40',
'created' => '2019-04-16 12:25:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 59 => array(
'id' => '3666',
'name' => 'Epigenetic Alterations in Juvenile Spondyloarthritis Patients: a Preliminary Study of Selected Genes Promoter Methylation and Silencing',
'authors' => 'Lamot Lovro, Blažeković Antonela, Jerčić Kristina Gotovac, Ivković Tina Catela, Vidović Mandica, Lamot Mirta, Kapitanović Sanja, Borovečki Fran, Harjaček Miroslav',
'description' => '<p>Juvenile spondyloarthritis (jSpA) is a complex disease with both genetic and environmental factors contributing to etiology. Multiple studies have shown that epigenetic mechanisms could link the environment and gene expression and thus provide a potential explanation for external contribution in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, including rheumatic. Previously obtained gene signatures in jSpA patients revealed distinctive expression of important immune-related genes, though the mechanism(s) responsible for those alterations remained unknown. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the methylation levels of the TLR4, CXCR4, NLRP3, and PTPN12 gene promoter, along with the expression of several non-coding microRNAs (miR-150, miR-146a, miR-181a, and miR-223) in jSpA patients. Peripheral blood samples were obtained from 19 patients newly diagnosed with jSpA according to ILAR classification criteria for enthesitis-related arthritis (ErA) and seven gender- and age-matched subjects without any symptoms or signs of inflammatory disease. The expression of specific microRNAs was analyzed using qRT-PCR with predeveloped microRNA assays. DNA promoter region methylation status of selected genes was assessed by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) analysis. Fold enrichment of immunoprecipitated DNA differed significantly for NLRP3 promoter site, while the expression analysis of selected microRNAs showed no significant difference in fold change between jSpA patients and healthy controls. The results indicated that epigenetic modifications in the initial phase of the disease could be responsible for some of the expression alterations in jSpA patients. Since NLRP3 has a crucial role in inflammasome assembly and inflammasomes have been shown to shape microbiota, it is tempting to assume that dysbiosis in jSpA patients can at least partially be explained by reduced NLRP3 expression due to hypermethylation, stressing for the first time the epigenetic contribution to jSpA pathophysiology</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-09',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42399-019-00070-9',
'doi' => '10.1007/s42399-019-00070-9',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:53:06',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 60 => array(
'id' => '3846',
'name' => 'The methylation pattern of DNA and complex correlations with gene expressions during TuMV infection in Chinese cabbage',
'authors' => 'J. YU , L.-W. GAO , Y. YANG , C. LIU , R.-J. ZHANG , F.-F. SUN , L.-X. SONG , D. XIAO , T.-K. LIU , X.-L. HOU , and C.-W. ZHANG',
'description' => '<p>Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) is one of the most important economic crops. However, its yield and quality can be severely threatened by Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV). Emerging evidence indicates that epigenetic mechanisms, especially DNA methylation, play an important role in regulating gene expression. Therefore, identification of resistance genes modified by DNA methylation during the virus infection would provide a critical clue for improving disease resistance breeding programs. Here, we present detailed analysis for the correlation of DNA methylation and gene expression involved in several anti-pathogen pathways. We also found that different methylation patterns exist in different methylation sites (CG, CHG, and CHH, where H represents A, G, or T) and genomic regions. Furthermore, we identified disease-resistant genes related to the nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeats family, auxin, salicylic acid signaling transduction, cell wall biosynthesis, and protein degradation among the different methylated genes (DMGs) suggesting that these genes may be modified by DNA methylation and work together to activate an immune response. The identified DMGs are a valuable resource for discovering resistance genes. Our study not only provides valuable data for future biotechnology research and epigenetic studies, but also helps to explore how the epigenetic mechanisms modify antiviral pathways.</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-09',
'pmid' => 'https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337128882_The_methylation_pattern_of_DNA_and_complex_correlations_with_gene_expressions_during_TuMV_infection_in_Chinese_cabbage',
'doi' => '10.32615/bp.2019.073',
'modified' => '2020-02-20 11:12:23',
'created' => '2020-02-13 10:02:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 61 => array(
'id' => '3716',
'name' => 'Epigenetic control of the angiotensin-converting enzyme in endothelial cells during inflammation.',
'authors' => 'Mudersbach T, Siuda D, Kohlstedt K, Fleming I',
'description' => '<p>The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) plays a central role in the renin-angiotensin system, which is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. Alterations in ACE expression or activity are associated with various pathological phenotypes, particularly cardiovascular diseases. In human endothelial cells, ACE was shown to be negatively regulated by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α. To examine, whether or not, epigenetic factors were involved in ACE expression regulation, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and RNA interference experiments directed against regulators of DNA methylation homeostasis i.e., DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenases (TETs), were performed. TNFα stimulation enhanced DNA methylation in two distinct regions within the ACE promoter via a mechanism linked to DNMT3a and DNMT3b, but not to DNMT1. At the same time, TET1 protein expression was downregulated. In addition, DNA methylation decreased the binding affinity of the transcription factor MYC associated factor X to the ACE promoter. In conclusion, DNA methylation determines the TNFα-dependent regulation of ACE gene transcription and thus protein expression in human endothelial cells.</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31042763',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0216218',
'modified' => '2019-07-05 13:14:33',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 62 => array(
'id' => '3698',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in Tibetan and Yorkshire pigs under high-altitude hypoxia.',
'authors' => 'Zhang B, Ban D, Gou X, Zhang Y, Yang L, Chamba Y, Zhang H',
'description' => '<p>Background: Tibetan pigs, which inhabit the Tibetan Plateau, exhibit distinct phenotypic and physiological characteristics from those of lowland pigs and have adapted well to the extreme conditions at high altitude. However, the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of hypoxic adaptation in animals remain unclear. Methods: Whole-genome DNA methylation data were generated for heart tissues of Tibetan pigs grown in the highland (TH,  = 4) and lowland (TL,  = 4), as well as Yorkshire pigs grown in the highland (YH,  = 4) and lowland (YL,  = 4), using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing. Results: We obtained 480 million reads and detected 280679, 287224, 259066, and 332078 methylation enrichment peaks in TH, YH, TL, and YL, respectively. Pairwise TH vs. YH, TL vs. YL, TH vs. TL, and YH vs. YL comparisons revealed 6829, 11997, 2828, and 1286 differentially methylated regions (DMRs), respectively. These DMRs contained 384, 619, 192, and 92 differentially methylated genes (DMGs), respectively. DMGs that were enriched in the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signaling pathway and pathways involved in cancer and hypoxia-related processes were considered to be important candidate genes for high-altitude adaptation in Tibetan pigs. Conclusions: This study elucidates the molecular and epigenetic mechanisms involved in hypoxic adaptation in pigs and may help further understand human hypoxia-related diseases.</p>',
'date' => '2019-04-28',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30867905',
'doi' => '10.1186/s40104-019-0316-y',
'modified' => '2019-07-05 14:47:45',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 63 => array(
'id' => '3648',
'name' => 'Assessment and site-specific manipulation of DNA (hydroxy-)methylation during mouse corticogenesis.',
'authors' => 'Noack F, Pataskar A, Schneider M, Buchholz F, Tiwari VK, Calegari F',
'description' => '<p>Dynamic changes in DNA (hydroxy-)methylation are fundamental for stem cell differentiation. However, the signature of these epigenetic marks in specific cell types during corticogenesis is unknown. Moreover, site-specific manipulation of cytosine modifications is needed to reveal the significance and function of these changes. Here, we report the first assessment of (hydroxy-)methylation in neural stem cells, neurogenic progenitors, and newborn neurons during mammalian corticogenesis. We found that gain in hydroxymethylation and loss in methylation occur sequentially at specific cellular transitions during neurogenic commitment. We also found that these changes predominantly occur within enhancers of neurogenic genes up-regulated during neurogenesis and target of pioneer transcription factors. We further optimized the use of dCas9-Tet1 manipulation of (hydroxy-)methylation, locus-specifically, in vivo, showing the biological relevance of our observations for , a regulator of corticogenesis involved in developmental malformations and cognitive impairment. Together, our data reveal the dynamics of cytosine modifications in lineage-related cell types, whereby methylation is reduced and hydroxymethylation gained during the neurogenic lineage concurrently with up-regulation of pioneer transcription factors and activation of enhancers for neurogenic genes.</p>',
'date' => '2019-04-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30814272',
'doi' => '10.1038/nrg.2017.57',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:13:14',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 64 => array(
'id' => '3647',
'name' => 'DMSO induces drastic changes in human cellular processes and epigenetic landscape in vitro.',
'authors' => 'Verheijen M, Lienhard M, Schrooders Y, Clayton O, Nudischer R, Boerno S, Timmermann B, Selevsek N, Schlapbach R, Gmuender H, Gotta S, Geraedts J, Herwig R, Kleinjans J, Caiment F',
'description' => '<p>Though clinical trials for medical applications of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) reported toxicity in the 1960s, later, the FDA classified DMSO in the safest solvent category. DMSO became widely used in many biomedical fields and biological effects were overlooked. Meanwhile, biomedical science has evolved towards sensitive high-throughput techniques and new research areas, including epigenomics and microRNAs. Considering its wide use, especially for cryopreservation and in vitro assays, we evaluated biological effect of DMSO using these technological innovations. We exposed 3D cardiac and hepatic microtissues to medium with or without 0.1% DMSO and analyzed the transcriptome, proteome and DNA methylation profiles. In both tissue types, transcriptome analysis detected >2000 differentially expressed genes affecting similar biological processes, thereby indicating consistent cross-organ actions of DMSO. Furthermore, microRNA analysis revealed large-scale deregulations of cardiac microRNAs and smaller, though still massive, effects in hepatic microtissues. Genome-wide methylation patterns also revealed tissue-specificity. While hepatic microtissues demonstrated non-significant changes, findings from cardiac microtissues suggested disruption of DNA methylation mechanisms leading to genome-wide changes. The extreme changes in microRNAs and alterations in the epigenetic landscape indicate that DMSO is not inert. Its use should be reconsidered, especially for cryopreservation of embryos and oocytes, since it may impact embryonic development.</p>',
'date' => '2019-03-15',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30874586',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-019-40660-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:14:07',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 65 => array(
'id' => '3673',
'name' => 'Evidence of association of circulating epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers with suspected coronary heart disease evaluated by Cardiac Computed Tomography.',
'authors' => 'Infante T, Forte E, Schiano C, Punzo B, Cademartiri F, Cavaliere C, Salvatore M, Napoli C',
'description' => '<p>Circulating biomarkers available in clinical practice do not allow to stratify patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) prior the onset of a clinically relevant event. We evaluated the methylation status of specific genomic segments and gene expression in peripheral blood of patients undergoing Cardiac Computed Tomography (CCT) for CHD (n = 95). We choose to investigate cholesterol metabolism. Methylation and gene expression of low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), sterol regulatory element-binding factor 2 (SREBF2) and ATP-binding cassette transporter 1 (ABCA1) were evaluated by qRT-PCR. Calcium score (CACS), stenosis degree, total plaque volume (TPV), calcified plaque volume (CPV), non-calcified plaque volume (NCPV) and plaque burden (PB) were assessed in all CHD patients (n = 65). The percentage of methylation at the specific analyzed segment of LDLR promoter was higher in CHD patients vs healthy subjects (HS) (n = 30) (p = 0.001). LDLR, SREBF2 and ABCA1 mRNAs were up-regulated in CHD patients vs HS (p = 0.02; p = 0.019; p = 0.008). SREBF2 was overexpressed in patients with coronary stenosis ≥50% vs subjects with stenosis <50% (p = 0.036). After adjustment for risk factors and clinical features, ABCA1 (p = 0.005) and SREBF2 (p = 0.010) gene expression were identified as independent predictors of CHD and severity. ROC curve analysis revealed a good performance of ABCA1 on predicting CHD (AUC = 0.768; p<0.001) and of SREBF2 for the prediction of disease severity (AUC = 0.815; p<0.001). Moreover, adjusted multivariate analysis demonstrated SREBF2 as independent predictor of CPV, NCPV and TPV (p = 0.022; p = 0.002 and p = 0.006) and ABCA1 as independent predictor of NCPV and TPV (p = 0.002 and p = 0.013). CHD presence and characteristics are related to selected circulating transcriptional and epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers linked to cholesterol pathway. More extensive analysis of CHD phenotypes and circulating biomarkers might improve and personalize cardiovascular risk stratification in the clinical settings.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-23',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30673762',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0210909',
'modified' => '2019-07-01 11:27:58',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 66 => array(
'id' => '3655',
'name' => 'LncRNA Dnmt3aos regulates Dnmt3a expression leading to aberrant DNA methylation in macrophage polarization',
'authors' => 'Xueqin Li, Yingying Zhang, Mengying Zhang, Xiang Kong, Hui Yang, Min Zhong, Weiya Pei, Yang Xu, Xiaolong Zhu, Tianbing Chen, Jingjing Ye, and Kun ',
'description' => '<p>Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play key roles in various biological processes. However, the roles of lncRNAs in macrophage polarization remain largely unexplored. In this study, thousands of lncRNAs were identified that are differentially expressed in distinct polarized bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Among them, Dnmt3aos (DNA methyltransferase 3A, opposite strand), as a known lncRNA, locates on the antisense strand of Dnmt3a. Functional experiments further confirmed that Dnmt3aos were highly expressed in M(IL-4) macrophages and participated in the regulation of Dnmt3a expression, and played a key role in macrophage polarization. The DNA methylation profiles between the Dnmt3aos knockdown group and the control group in M(IL-4) macrophages were determined by MeDIP-seq technique for the first time, and the Dnmt3aos-Dnmt3a axis-mediated DNA methylation modification-regulated macrophage polarization related gene IFN-γ was identified. Our study will help to enrich our knowledge of the mechanism of macrophage polarization and will provide new insights for immunotherapy in macrophage-associated diseases.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-07',
'pmid' => 'https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/514307v1',
'doi' => '/',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:39:53',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 67 => array(
'id' => '3660',
'name' => 'Global distribution of DNA hydroxymethylation and DNA methylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.',
'authors' => 'Wernig-Zorc S, Yadav MP, Kopparapu PK, Bemark M, Kristjansdottir HL, Andersson PO, Kanduri C, Kanduri M',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has been a good model system to understand the functional role of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in cancer progression. More recently, an oxidized form of 5-mC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has gained lot of attention as a regulatory epigenetic modification with prognostic and diagnostic implications for several cancers. However, there is no global study exploring the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) levels in CLL. Herein, using mass spectrometry and hMeDIP-sequencing, we analysed the dynamics of 5-hmC during B cell maturation and CLL pathogenesis. RESULTS: We show that naïve B-cells had higher levels of 5-hmC and 5-mC compared to non-class switched and class-switched memory B-cells. We found a significant decrease in global 5-mC levels in CLL patients (n = 15) compared to naïve and memory B cells, with no changes detected between the CLL prognostic groups. On the other hand, global 5-hmC levels of CLL patients were similar to memory B cells and reduced compared to naïve B cells. Interestingly, 5-hmC levels were increased at regulatory regions such as gene-body, CpG island shores and shelves and 5-hmC distribution over the gene-body positively correlated with degree of transcriptional activity. Importantly, CLL samples showed aberrant 5-hmC and 5-mC pattern over gene-body compared to well-defined patterns in normal B-cells. Integrated analysis of 5-hmC and RNA-sequencing from CLL datasets identified three novel oncogenic drivers that could have potential roles in CLL development and progression. CONCLUSIONS: Thus, our study suggests that the global loss of 5-hmC, accompanied by its significant increase at the gene regulatory regions, constitute a novel hallmark of CLL pathogenesis. Our combined analysis of 5-mC and 5-hmC sequencing provided insights into the potential role of 5-hmC in modulating gene expression changes during CLL pathogenesis.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30616658',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13072‑018‑0252‑7',
'modified' => '2019-07-01 11:46:16',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 68 => array(
'id' => '3430',
'name' => 'Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Shen SY, Singhania R, Fehringer G, Chakravarthy A, Roehrl MHA, Chadwick D, Zuzarte PC, Borgida A, Wang TT, Li T, Kis O, Zhao Z, Spreafico A, Medina TDS, Wang Y, Roulois D, Ettayebi I, Chen Z, Chow S, Murphy T, Arruda A, O'Kane GM, Liu J, Mansour M, McPher',
'description' => '<p>The use of liquid biopsies for cancer detection and management is rapidly gaining prominence. Current methods for the detection of circulating tumour DNA involve sequencing somatic mutations using cell-free DNA, but the sensitivity of these methods may be low among patients with early-stage cancer given the limited number of recurrent mutations. By contrast, large-scale epigenetic alterations-which are tissue- and cancer-type specific-are not similarly constrained and therefore potentially have greater ability to detect and classify cancers in patients with early-stage disease. Here we develop a sensitive, immunoprecipitation-based protocol to analyse the methylome of small quantities of circulating cell-free DNA, and demonstrate the ability to detect large-scale DNA methylation changes that are enriched for tumour-specific patterns. We also demonstrate robust performance in cancer detection and classification across an extensive collection of plasma samples from several tumour types. This work sets the stage to establish biomarkers for the minimally invasive detection, interception and classification of early-stage cancers based on plasma cell-free DNA methylation patterns.</p>',
'date' => '2018-11-14',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30429608',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41586-018-0703-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-11 16:22:54',
'created' => '2018-12-04 09:51:07',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 69 => array(
'id' => '3511',
'name' => 'Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation to identify genes and pathways associated with male sterility in soybean',
'authors' => 'Han Shaohuai, Li Yanwei, Li Jiajia, Zhang Hao, Ding Xianlong, He Tingting, Gai Junyi, Yang Shouping',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification, which is important for gene expression regulation. Although genome-wide DNA methylation studies have been reported in several plant species, the difference in the methylation pattern between the cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) line and its maintainer in soybean remains unclear. We compared genome-wide DNA methylation between the soybean CMS line NJCMS1A and its maintainer NJCMS1B using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) technology. The results showed that the methylation level was higher in transposable elements (TEs) than promoter and intron; however, the methylation levels varied among different types of TEs with the highest level for long terminal repeats (LTRs) and the lowest for transcription start sites (TSS) and transcription termination sites (TTS). We observed 178 differentially methylated genes (DMGs) between NJCMS1A and NJCMS1B, including 156 hypomethylated and 22 hyper-methylated genes in NJCMS1A compared to NJCMS1B. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis showed that 114 DMGs were annotated to one or more GO categories, among which four GO terms were significantly enriched. KEGG pathway analysis showed that 18 DMGs were significantly enriched in 10 metabolism pathways, including homologous recombination, purine metabolism, proteasome, non-homologous end-joining, and pyrimidine</p>',
'date' => '2018-09-16',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11032-018-0875-1',
'doi' => '10.1007/s11032-018-0875-1',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:44:53',
'created' => '2019-02-27 12:54:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 70 => array(
'id' => '3585',
'name' => 'Folic acid supplementation alters the DNA methylation profile and improves insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed mice.',
'authors' => 'Li W, Tang R, Ma F, Ouyang S, Liu Z, Wu J',
'description' => '<p>Folic acid (FA) supplementation may protect from obesity and insulin resistance, the effects and mechanism of FA on chronic high-fat-diet-induced obesity-related metabolic disorders are not well elucidated. We adopted a genome-wide approach to directly examine whether FA supplementation affects the DNA methylation profile of mouse adipose tissue and identify the functional consequences of these changes. Mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), normal diet (ND) or an HFD supplemented with folic acid (20 μg/ml in drinking water) for 10 weeks, epididymal fat was harvested, and genome-wide DNA methylation analyses were performed using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Mice exposed to the HFD expanded their adipose mass, which was accompanied by a significant increase in circulating glucose and insulin levels. FA supplementation reduced the fat mass and serum glucose levels and improved insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. MeDIP-seq revealed distribution of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) throughout the adipocyte genome, with more hypermethylated regions in HFD mice. Methylome profiling identified DMRs associated with 3787 annotated genes from HFD mice in response to FA supplementation. Pathway analyses showed novel DNA methylation changes in adipose genes associated with insulin secretion, pancreatic secretion and type 2 diabetes. The differential DNA methylation corresponded to changes in the adipose tissue gene expression of Adcy3 and Rapgef4 in mice exposed to a diet containing FA. FA supplementation improved insulin resistance, decreased the fat mass, and induced DNA methylation and gene expression changes in genes associated with obesity and insulin secretion in obese mice fed a HFD.</p>',
'date' => '2018-09-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29986310',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.05.010',
'modified' => '2019-04-17 15:33:46',
'created' => '2019-04-16 12:25:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 71 => array(
'id' => '3633',
'name' => 'Embryonic germ cell extracts erase imprinted genes and improve the efficiency of induced pluripotent stem cells.',
'authors' => 'Hu J, Zhao Q, Feng Y, Li N, Gu Y, Sun R, Duan L, Wu Y, Shan Z, Lei L',
'description' => '<p>Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have the potential to be useful in the treatment of human diseases. While prior studies have reported multiple methods to generate iPSCs, DNA methylation continues to limit the totipotency and reprogramming efficiency of iPSCs. Here, we first show the competency of embryonic germ cells (EGCs) as a reprogramming catalyst capable of effectively promoting reprogramming induced by four defined factors, including Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc. Combining EGC extracts with these four factors resulted in formation of more embryonic stem cell-like colonies than did factors alone. Notably, expression of imprinted genes was higher with combined induction than with factors alone. Moreover, iPSCs derived from the combined inductors tended to have more global hypomethylation. Our research not only provides evidence that EGC extracts could activate DNA demethylation and reprogram imprinted genes, but also establishes a new way to enhance reprogramming of iPSCs, which remains a critical safety concern for potential use of iPSCs in regenerative medicine.</p>',
'date' => '2018-07-19',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30026469',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-018-29339-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:30:27',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 72 => array(
'id' => '3393',
'name' => 'Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos.',
'authors' => 'Sussarellu R, Lebreton M, Rouxel J, Akcha F, Rivière G',
'description' => '<p>Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better understand whether the embryotoxic effects of copper in Crassostrea gigas could be mediated by alterations in gene expression, and the putative role of DNA methylation, which is known to contribute to gene regulation in early embryo development. For that purpose, oyster embryos were exposed to 4 nominal copper concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 μg L Cu) during early development assays. Embryotoxicity was monitored through the oyster embryo-larval bioassay at the D-larva stage 24 h post fertilization (hpf) and genotoxicity at gastrulation 7 hpf. In parallel, the relative expression of 15 genes encoding putative homeotic, biomineralization and DNA methylation proteins was measured at three developmental stages (3 hpf morula stage, 7 hpf gastrula stage, 24 hpf D-larvae stage) using RT-qPCR. Global DNA content in methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine were measured by HPLC and gene-specific DNA methylation levels were monitored using MeDIP-qPCR. A significant increase in larval abnormalities was observed from copper concentrations of 10 μg L, while significant genotoxic effects were detected at 1 μg L and above. All the selected genes presented a stage-dependent expression pattern, which was impaired for some homeobox and DNA methylation genes (Notochord, HOXA1, HOX2, Lox5, DNMT3b and CXXC-1) after copper exposure. While global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) at gastrula stage didn't show significant changes between experimental conditions, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its degradation product, decreased upon copper treatment. The DNA methylation of exons and the transcript levels were correlated in control samples for HOXA1 but such a correlation was diminished following copper exposure. The methylation level of some specific gene regions (HoxA1, Hox2, Engrailed2 and Notochord) displayed changes upon copper exposure. Such changes were gene and exon-specific and no obvious global trends could be identified. Our study suggests that the embryotoxic effects of copper in oysters could involve homeotic gene expression impairment possibly by changing DNA methylation levels.</p>',
'date' => '2018-03-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29353135',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.001',
'modified' => '2018-11-09 12:21:38',
'created' => '2018-11-08 12:59:45',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 73 => array(
'id' => '3448',
'name' => 'Aberrant methylated key genes of methyl group metabolism within the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinogenesis.',
'authors' => 'Erichsen L, Ghanjati F, Beermann A, Poyet C, Hermanns T, Schulz WA, Seifert HH, Wild PJ, Buser L, Kröning A, Braunstein S, Anlauf M, Jankowiak S, Hassan M, Bendhack ML, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Santourlidis S',
'description' => '<p>Urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common cancer of the urinary bladder causes severe morbidity and mortality, e.g. about 40.000 deaths in the EU annually, and incurs considerable costs for the health system due to the need for prolonged treatments and long-term monitoring. Extensive aberrant DNA methylation is described to prevail in urothelial carcinoma and is thought to contribute to genetic instability, altered gene expression and tumor progression. However, it is unknown how this epigenetic alteration arises during carcinogenesis. Intact methyl group metabolism is required to ensure maintenance of cell-type specific methylomes and thereby genetic integrity and proper cellular function. Here, using two independent techniques for detecting DNA methylation, we observed DNA hypermethylation of the 5'-regulatory regions of the key methyl group metabolism genes ODC1, AHCY and MTHFR in early urothelial carcinoma. These hypermethylation events are associated with genome-wide DNA hypomethylation which is commonly associated with genetic instability. We therefore infer that hypermethylation of methyl group metabolism genes acts in a feed-forward cycle to promote additional DNA methylation changes and suggest a new hypothesis on the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinoma.</p>',
'date' => '2018-02-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29472622',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-018-21932-7',
'modified' => '2019-02-15 21:31:04',
'created' => '2019-02-14 15:01:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 74 => array(
'id' => '3325',
'name' => 'Integrative omics data analyses of repeated dose toxicity of valproic acid in vitro reveal new mechanisms of steatosis induction',
'authors' => 'van Breda S.G.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is a very potent anti-cancer and neuro-protective drug probably by its HDAC inhibiting properties, which may cause steatosis in the liver. The present study investigates the effect of repetitive VPA treatment of primary human hepatocytes (PHH) on whole genome gene expression-, DNA methylation-, and miRNA changes, using microarrays and integrated data analyses. PHH were exposed to a non-cytotoxic dose of VPA for 5days daily which induced lipid accumulation. Part of the PHH was left untreated for 3days for studying the persistence of 'omics' changes. VPA treatment appeared to inhibit the expression of the transcription factors HNF1A and ONECUT1. HNF1A interacted with 41 differentially expressed genes of which 12 were also differentially methylated. None of the genes present in this network were regulated by a DE-miR. The subnetwork of ONECUT1 consisted of 44 differentially expressed genes of which 15 were differentially methylated, and 3 were regulated by a DE-miR. A number of genes in the networks are involved in fatty acid metabolism, and may contribute to the development of steatosis by increasing oxidative stress thereby causing mitochondrial dysfunction, and by shifting metabolism of VPA towards β-oxidation due to reduced glucuronidation. Part of the changes remained persistent after washing out of VPA, like PMAIP1 which is associated with cellular stress in liver of patients with NASH. The MMP2 gene showed the highest number of interactions with other persistently expressed genes, among which LCN2 which is a key modulator of lipid homeostasis. Furthermore, VPA modulated the expression and DNA methylation level of nuclear receptors and their target genes involved in the adverse outcome pathway of steatosis, thereby expanding our current knowledge of the pathway. In particular, VPA modulated PPARγ, and PPARα, AHR and CD36 on both the gene expression and the DNA methylation level, thereby inhibiting β-oxidation and increasing uptake of fatty acid into the hepatocytes, respectively. Overall, our integrative data analyses identified novel genes modulated by VPA, which provide more insight into the mechanisms of repeated dose toxicity of VPA, leading to steatosis.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-15',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29154799',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-02-06 09:28:05',
'created' => '2018-02-06 09:28:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 75 => array(
'id' => '3316',
'name' => 'Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos',
'authors' => 'Rossana Sussarellu, Morgane Lebreton, Julien Rouxel, Farida Akcha, Guillaume Rivière ',
'description' => '<p id="spar0045">Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better understand whether the embryotoxic effects of copper in <em>Crassostrea gigas</em> could be mediated by alterations in gene expression, and the putative role of DNA methylation, which is known to contribute to gene regulation in early embryo development.</p>
<p id="spar0050">For that purpose, oyster embryos were exposed to 4 nominal copper concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 μg L<sup>−1</sup> Cu<sup>2+</sup>) during early development assays. Embryotoxicity was monitored through the oyster embryo-larval bioassay at the D-larva stage 24 h post fertilization (hpf) and genotoxicity at gastrulation 7 hpf. In parallel, the relative expression of 15 genes encoding putative homeotic, biomineralization and DNA methylation proteins was measured at three developmental stages (3 hpf morula stage, 7 hpf gastrula stage, 24 hpf D-larvae stage) using RT-qPCR. Global DNA content in methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine were measured by HPLC and gene-specific DNA methylation levels were monitored using MeDIP-qPCR.</p>
<p id="spar0055">A significant increase in larval abnormalities was observed from copper concentrations of 10 μg L<sup>−1</sup>, while significant genotoxic effects were detected at 1 μg L<sup>−1</sup> and above. All the selected genes presented a stage-dependent expression pattern, which was impaired for some homeobox and DNA methylation genes (<em>Notochord, HOXA1, HOX2, Lox5, DNMT3b and CXXC-1</em>) after copper exposure. While global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) at gastrula stage didn’t show significant changes between experimental conditions, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its degradation product, decreased upon copper treatment. The DNA methylation of exons and the transcript levels were correlated in control samples for <em>HOXA1</em> but such a correlation was diminished following copper exposure. The methylation level of some specific gene regions (<em>HoxA1, Hox2, Engrailed2</em> and <em>Notochord</em>) displayed changes upon copper exposure. Such changes were gene and exon-specific and no obvious global trends could be identified. Our study suggests that the embryotoxic effects of copper in oysters could involve homeotic gene expression impairment possibly by changing DNA methylation levels.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-03',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166445X18300018?via%3Dihub',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.001',
'modified' => '2018-01-14 01:21:09',
'created' => '2018-01-14 01:21:09',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 76 => array(
'id' => '3383',
'name' => 'Genome-wide analysis of day/night DNA methylation differences in Populus nigra.',
'authors' => 'Ding C.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is an important mechanism of epigenetic modification. Methylation changes during stress responses and developmental processes have been well studied; however, their role in plant adaptation to the day/night cycle is poorly understood. In this study, we detected global methylation patterns in leaves of the black poplar Populus nigra 'N46' at 8:00 and 24:00 by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). We found 10,027 and 10,242 genes to be methylated in the 8:00 and 24:00 samples, respectively. The methylated genes appeared to be involved in multiple biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components, suggesting important roles for DNA methylation in poplar cells. Comparing the 8:00 and 24:00 samples, only 440 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) overlapped with genic regions, including 193 hyper- and 247 hypo-methylated DMRs, and may influence the expression of 137 downstream genes. Most hyper-methylated genes were associated with transferase activity, kinase activity, and phosphotransferase activity, whereas most hypo-methylated genes were associated with protein binding, ATP binding, and adenyl ribonucleotide binding, suggesting that different biological processes were activated during the day and night. Our results indicated that methylated genes were prevalent in the poplar genome, but that only a few of these participated in diurnal gene expression regulation.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-02',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29293569',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-08-07 09:45:38',
'created' => '2018-08-07 09:45:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 77 => array(
'id' => '3384',
'name' => 'Obligatory and facilitative allelic variation in the DNA methylome within common disease-associated loci',
'authors' => 'Bell C.G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Integrating epigenetic data with genome-wide association study (GWAS) results can reveal disease mechanisms. The genome sequence itself also shapes the epigenome, with CpG density and transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) strongly encoding the DNA methylome. Therefore, genetic polymorphism impacts on the observed epigenome. Furthermore, large genetic variants alter epigenetic signal dosage. Here, we identify DNA methylation variability between GWAS-SNP risk and non-risk haplotypes. In three subsets comprising 3128 MeDIP-seq peripheral-blood DNA methylomes, we find 7173 consistent and functionally enriched Differentially Methylated Regions. 36.8% can be attributed to common non-SNP genetic variants. CpG-SNPs, as well as facilitative TFBS-motifs, are also enriched. Highlighting their functional potential, CpG-SNPs strongly associate with allele-specific DNase-I hypersensitivity sites. Our results demonstrate strong DNA methylation allelic differences driven by obligatory or facilitative genetic effects, with potential direct or regional disease-related repercussions. These allelic variations require disentangling from pure tissue-specific modifications, may influence array studies, and imply underestimated population variability in current reference epigenomes.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-02',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29295990',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-08-07 10:13:12',
'created' => '2018-08-07 10:13:12',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 78 => array(
'id' => '3449',
'name' => 'Epigenetic alterations in TRAMP mice: epigenome DNA methylation profiling using MeDIP-seq.',
'authors' => 'Li W, Huang Y, Sargsyan D, Khor TO, Guo Y, Shu L, Yang AY, Zhang C, Paredes-Gonzalez X, Verzi M, Hart RP, Kong AN',
'description' => '<p>Purpose: We investigated the genomic DNA methylation profile of prostate cancer in transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) cancer model and to analyze the crosstalk among targeted genes and the related functional pathways. Methods: Prostate DNA samples from 24-week-old TRAMP and C57BL/6 male mice were isolated. The DNA methylation profiles were analyzed by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) followed by next-generation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Canonical pathways, diseases and function and network analyses of the different samples were then performed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software. Some target genes with significant difference in methylation were selected for validation using methylation specific primers (MSP) and qPCR. Results: TRAMP mice undergo extensive aberrant CpG hyper- and hypo-methylation. There were 2147 genes with a significant (log2-change ≥ 2) change in CpG methylation between the two groups, as mapped by the IPA software. Among these genes, the methylation of 1105 and 1042 genes was significantly decreased and increased, respectively, in TRAMP prostate tumors. The top associated disease identified by IPA was adenocarcinoma; however, the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-, histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2)-, glutathione S-transferase pi (GSTP1)- and polyubiquitin-C (UBC)-related pathways showed significantly altered methylation profiles based on the canonical pathway and network analyses. MSP and qPCR results of genes of interests corroborated with MeDIP-seq findings. Conclusions: This is the first MeDIP-seq with IPA analysis of the TRAMP model to provide novel insight into the genome-wide methylation profile of prostate cancer. Studies on epigenetics, such as DNA methylation, will potentially provide novel avenues and strategies for further development of biomarkers targeted for treatment and prevention approaches for prostate cancer.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29344347',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13578-018-0201-y',
'modified' => '2019-02-15 21:41:39',
'created' => '2019-02-14 15:01:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 79 => array(
'id' => '3508',
'name' => 'Analysis of DNA methylome and transcriptome profiling following Gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application in Nicotiana tabacum L.',
'authors' => 'Manoharlal Raman, Saiprasad G. V. S., Kaikala Vinay, Suresh Kumar R., Kovařík Ales',
'description' => '<p>The present work investigated a comprehensive genome-wide landscape of DNA methylome and its relationship with transcriptome upon gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application under practical field conditions in solanaceae model, Nicotiana tabacum L. Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation-Sequencing (MeDIP-Seq) analysis uncovered over 82% (18,456) of differential methylated regions (DMRs) in intergenic-region. Within protein-coding region, 2339 and 1685 of identified DMRs were observed in genebody- and promoter-region, respectively. Microarray study revealed 7032 differential expressed genes (DEGs) with 3507 and 3525 genes displaying upand down-regulation, respectively. Integration analysis revealed 520 unique non-redundant annotated DMRs overlapping with DEGs. Our results indicated that GA3 induced DNA hypo- as well as hyper-methylation were associated with both gene-silencing and -activation. No complete biasness or correlation was observed in either of the promoter- or genebody-regions, which otherwise showed an overall trend towards GA3 induced global DNA hypo-methylation. Taken together, our results suggested that differential DNA methylation mediated by GA3 may only play a permissive role in regulating the gene expression.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40502-018-0393-5',
'doi' => '10.1007/s40502-018-0393-5',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:43:47',
'created' => '2019-02-27 12:54:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 80 => array(
'id' => '3334',
'name' => 'Data on novel DNA methylation changes induced by valproic acid in human hepatocytes',
'authors' => 'Wolters J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is a widely prescribed antiepileptic drug in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis. However the exact mechanism of the steatosis formation is unknown. The data presented in this DIB publication is used to further investigate the VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in patterns of methylation. Therefore, primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were exposed to VPA at a concentration which was shown to cause steatosis without inducing overt cytotoxicity. VPA was administered for 5 days daily to PHHs. Furthermore, after 5 days VPA-treatment parts of the PHHs were followed for a 3 days washout. Differentially methylated DNA regions (DMRs) were identified by using the 'Methylated DNA Immuno-Precipitation - sequencing' (MeDIP-seq) method. The data presented in this DIB demonstrate induced steatosis pathways by all DMRs during VPA-treatment, covering interesting drug-induced steatosis genes (persistent DMRs upon terminating VPA treatment and the <i>EP300</i> network). This was illustrated in our associated article (Wolters et al., 2017) [1]. MeDIP-seq raw data are available on ArrayExpress (accession number: E-MTAB-4437).</p>',
'date' => '2017-11-10',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29201983',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-02-08 17:16:22',
'created' => '2018-02-08 17:16:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 81 => array(
'id' => '3283',
'name' => 'Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Methylation Patterns Induced by Valproic Acid in Human Hepatocytes',
'authors' => 'Wolters J.E.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is one of the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis through mitochondrial dysfunction. The aim of this study is to further investigate VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in patterns of methylation in nuclear DNA (nDNA) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Therefore, primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were exposed to an incubation concentration of VPA that was shown to cause steatosis without inducing overt cytotoxicity. VPA was administered daily for 5 days, and this was followed by a 3 day washout (WO). Methylated DNA regions (DMRs) were identified by using the methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-sequencing (MeDIP-seq) method. The nDNA DMRs after VPA treatment could indeed be classified into oxidative stress- and steatosis-related pathways. In particular, networks of the steatosis-related gene EP300 provided novel insight into the mechanisms of toxicity induced by VPA treatment. Furthermore, we suggest that VPA induces a crosstalk between nDNA hypermethylation and mtDNA hypomethylation that plays a role in oxidative stress and steatosis development. Although most VPA-induced methylation patterns appeared reversible upon terminating VPA treatment, 31 nDNA DMRs (including 5 zinc finger protein genes) remained persistent after the WO period. Overall, we have shown that MeDIP-seq analysis is highly informative in disclosing novel mechanisms of VPA-induced toxicity in PHHs. Our results thus provide a prototype for the novel generation of interesting methylation biomarkers for repeated dose liver toxicity in vitro.</p>',
'date' => '2017-10-16',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28853863',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-24 09:33:19',
'created' => '2017-10-24 09:33:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 82 => array(
'id' => '3271',
'name' => ' Genome methylation and regulatory functions for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chicken embryos',
'authors' => 'Zhang Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Tibetan chickens have unique adaptations to the extreme high-altitude environment that they inhabit. Epigenetic DNA methylation affects many biological processes, including hypoxic adaptation; however, the regulatory genes for DNA methylation in hypoxic adaptation remain unknown. In this study, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation with high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) was used to provide an atlas of the DNA methylomes of the heart tissue of hypoxic highland Tibetan and lowland Chahua chicken embryos. A total of 31.2 gigabases of sequence data were generated from six MeDIP-seq libraries. We identified 1,049 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and 695 related differentially methylated genes (DMGs) between the two chicken breeds. The DMGs are involved in vascular smooth muscle contraction, VEGF signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, and other hypoxia-related pathways. Five candidate genes that had low methylation (<i>EDNRA</i>, <i>EDNRB2</i>,<i> BMPR1B</i>,<i> BMPRII</i>, and <i>ITGA2</i>) might play key regulatory roles in the adaptation to hypoxia in Tibetan chicken embryos. Our study provides significant explanations for the functions of genes and their epigenetic regulation for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chickens.</p>',
'date' => '2017-10-06',
'pmid' => 'https://peerj.com/articles/3891/',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-13 17:02:21',
'created' => '2017-10-13 17:02:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 83 => array(
'id' => '3265',
'name' => 'Emerging Role of One-Carbon Metabolism and DNA Methylation Enrichment on δ-Containing GABAA Receptor Expression in the Cerebellum of Subjects with Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD',
'authors' => 'Gatta E. et al.',
'description' => '<section class="abstract">
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Background</div>
<p>Cerebellum is an area of the brain particularly sensitive to the effects of acute and chronic alcohol consumption. Alcohol exposure decreases cerebellar Purkinje cell output by increasing GABA release from Golgi cells onto extrasynaptic α<sub>6</sub>/δ-containing GABA<sub>A</sub> receptors located on glutamatergic granule cells. Here, we studied whether chronic alcohol consumption induces changes in GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor subunit expression and whether these changes are associated with alterations in epigenetic mechanisms via DNA methylation.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Methods</div>
<p>We used a cohort of postmortem cerebellum from control and chronic alcoholics, here defined as alcohol use disorders subjects (n=25/group). <em>S</em>-adenosyl-methionine/<em>S</em>-adenosyl-homocysteine were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. mRNA levels of various genes were assessed by reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Promoter methylation enrichment was assessed using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and hydroxy-methylated DNA immunoprecipitation assays.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Results</div>
<p>mRNAs encoding key enzymes of 1-carbon metabolism that determine the <em>S</em>-adenosyl-methionine/<em>S</em>-adenosyl-homocysteine ratio were increased, indicating higher “methylation index” in alcohol use disorder subjects. We found that increased methylation of the promoter of the δ subunit GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor was associated with reduced mRNA and protein levels in the cerebellum of alcohol use disorder subjects. No changes were observed in α<sub>1</sub>- or α<sub>6</sub>-containing GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor subunits. The expression of DNA-methyltransferases (1, 3A, and 3B) was unaltered, whereas the mRNA level of TET1, which participates in the DNA demethylation pathway, was decreased. Hence, increased methylation of the δ subunit GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor promoter may result from alcohol-induced reduction of DNA demethylation.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Conclusion</div>
<p>Together, these results support the hypothesis that aberrant DNA methylation pathways may be involved in cerebellar pathophysiology of alcoholism. Furthermore, this work provides novel evidence for a central role of DNA methylation mechanisms in the alcohol-induced neuroadaptive changes of human cerebellar GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor function.</p>
</section>
</section>',
'date' => '2017-08-19',
'pmid' => 'https://academic.oup.com/ijnp/article/doi/10.1093/ijnp/pyx075/4085582/Emerging-role-of-one-carbon-metabolism-and-DNA',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-09 16:11:05',
'created' => '2017-10-09 16:11:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 84 => array(
'id' => '3251',
'name' => 'Coordinate Regulation of TET2 and EBNA2 Control DNA Methylation State of Latent Epstein-Barr Virus',
'authors' => 'Lu F. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and its associated carcinogenesis are regulated by dynamic changes in DNA methylation of both virus and host genomes. We show here that the Ten-Eleven Translocation 2 (TET2) gene, implicated in hydroxymethylation and active DNA demethylation, is a key regulator of EBV latency type DNA methylation patterning. EBV latency types are defined by DNA methylation patterns that restrict expression of viral latency genes. We show that TET2 mRNA and protein expression correlate with the highly demethylated EBV type III latency program permissive for expression of EBNA2, EBNA3s, and LMP transcripts. We show that shRNA depletion of TET2 results in a decrease in latency gene expression, but can also trigger a switch to lytic gene expression. TET2 depletion results in the loss of hydroxymethylated cytosine, and corresponding increase in cytosine methylation at key regulatory regions on the viral and host genomes. This also corresponded to a loss of RBP-jκ binding, and decreased histone H3K4 trimethylation at these sites. Furthermore, we show that the TET2 gene, itself, is regulated similar to the EBV genome. ChIP-Seq revealed that TET2 gene contains EBNA2-dependent RBP-jκ and EBF1 binding sites, and is subject to DNA methylation associated transcriptional silencing similar to EBV latency type III genomes. Finally, we provide evidence that TET2 colocalizes with EBNA2-EBF1-RBP-jκ binding sites, and can interact with EBNA2 by co-immunoprecipitation. Taken together, these findings indicate that TET2 gene transcripts are regulated similarly to EBV type III latency genes, and that TET2 protein is a cofactor of EBNA2 and co-regulator of the EBV type III latency program and DNA methylation state..<b>IMPORTANCE</b> Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and carcinogenesis involves the selective epigenetic modification of viral and cellular genes. Here, we show that TET2, a cellular tumor suppressor involved in active DNA demethylation, plays a central role in regulating DNA methylation state during EBV latency. TET2 is coordinately regulated and functionally interacts with the viral oncogene EBNA2. TET2 and EBNA2 function cooperatively to demethylate genes important for EBV-driven B cells growth transformation.</p>',
'date' => '2017-08-07',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28794029',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-09-26 09:54:39',
'created' => '2017-09-26 09:54:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 85 => array(
'id' => '3237',
'name' => 'Intracellular adenosine regulates epigenetic programming in endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis',
'authors' => 'Xu Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The nucleoside adenosine is a potent regulator of vascular homeostasis, but it remains unclear how expression or function of the adenosine-metabolizing enzyme adenosine kinase (ADK) and the intracellular adenosine levels influence angiogenesis. We show here that hypoxia lowered the expression of ADK and increased the levels of intracellular adenosine in human endothelial cells. Knockdown (KD) of ADK elevated intracellular adenosine, promoted proliferation, migration, and angiogenic sprouting in human endothelial cells. Additionally, mice deficient in endothelial ADK displayed increased angiogenesis as evidenced by the rapid development of the retinal and hindbrain vasculature, increased healing of skin wounds, and prompt recovery of arterial blood flow in the ischemic hindlimb. Mechanistically, hypomethylation of the promoters of a series of pro-angiogenic genes, especially for VEGFR2 in ADK KD cells, was demonstrated by the Infinium methylation assay. Methylation-specific PCR, bisulfite sequencing, and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation further confirmed hypomethylation in the promoter region of VEGFR2 in ADK-deficient endothelial cells. Accordingly, loss or inactivation of ADK increased VEGFR2 expression and signaling in endothelial cells. Based on these findings, we propose that ADK downregulation-induced elevation of intracellular adenosine levels in endothelial cells in the setting of hypoxia is one of the crucial intrinsic mechanisms that promote angiogenesis.</p>',
'date' => '2017-07-17',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28751580',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-08-29 09:15:21',
'created' => '2017-08-29 09:15:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 86 => array(
'id' => '3216',
'name' => 'Vitamin C induces specific demethylation of H3K9me2 in mouse embryonic stem cells via Kdm3a/b',
'authors' => 'Kevin T. Ebata, Kathryn Mesh, Shichong Liu, Misha Bilenky, Alexander Fekete, Michael G. Acker, Martin Hirst, Benjamin A. Garcia and Miguel Ramalho-Santos',
'description' => '<section xmlns="" xmlns:fn="http://www.w3.org/2005/xpath-functions" xmlns:meta="http://www.springer.com/app/meta" class="Abstract" id="Abs1" lang="en">
<div class="js-CollapseSection">
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec1">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Background</h3>
<p id="Par1" class="Para">Histone methylation patterns regulate gene expression and are highly dynamic during development. The erasure of histone methylation is carried out by histone demethylase enzymes. We had previously shown that vitamin C enhances the activity of Tet enzymes in embryonic stem (ES) cells, leading to DNA demethylation and activation of germline genes.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec2">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Results</h3>
<p id="Par2" class="Para">We report here that vitamin C induces a remarkably specific demethylation of histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) in naïve ES cells. Vitamin C treatment reduces global levels of H3K9me2, but not other histone methylation marks analyzed, as measured by western blot, immunofluorescence and mass spectrometry. Vitamin C leads to widespread loss of H3K9me2 at large chromosomal domains as well as gene promoters and repeat elements. Vitamin C-induced loss of H3K9me2 occurs rapidly within 24 h and is reversible. Importantly, we found that the histone demethylases Kdm3a and Kdm3b are required for vitamin C-induced demethylation of H3K9me2. Moreover, we show that vitamin C-induced Kdm3a/b-mediated H3K9me2 demethylation and Tet-mediated DNA demethylation are independent processes at specific loci. Lastly, we document Kdm3a/b are partially required for the upregulation of germline genes by vitamin C.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec3">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p id="Par3" class="Para">These results reveal a specific role for vitamin C in histone demethylation in ES cells and document that DNA methylation and H3K9me2 cooperate to silence germline genes in pluripotent cells.</p>
</div>
</div>
</section>',
'date' => '2017-07-12',
'pmid' => 'https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-017-0143-3',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-017-0143-3',
'modified' => '2017-08-23 14:47:51',
'created' => '2017-07-29 08:04:03',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 87 => array(
'id' => '3205',
'name' => 'Dynamics of DNA methylomes underlie oyster development',
'authors' => 'Riviere G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a critical epigenetic regulator of development in mammals and social insects, but its significance in development outside these groups is not understood. Here we investigated the genome-wide dynamics of DNA methylation in a mollusc model, the oyster Crassostrea gigas, from the egg to the completion of organogenesis. Large-scale methylation maps reveal that the oyster genome displays a succession of methylated and non methylated regions, which persist throughout development. Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) are strongly regulated during cleavage and metamorphosis. The distribution and levels of methylated DNA within genomic features (exons, introns, promoters, repeats and transposons) show different developmental lansdscapes marked by a strong increase in the methylation of exons against introns after metamorphosis. Kinetics of methylation in gene-bodies correlate to their transcription regulation and to distinct functional gene clusters, and DMRs at cleavage and metamorphosis bear the genes functionally related to these steps, respectively. This study shows that DNA methylome dynamics underlie development through transcription regulation in the oyster, a lophotrochozoan species. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of such epigenetic regulation outside vertebrates and ecdysozoan models, bringing new insights into the evolution and the epigenetic regulation of developmental processes.</p>',
'date' => '2017-06-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28594821',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-07-03 10:24:12',
'created' => '2017-07-03 10:24:12',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 88 => array(
'id' => '3186',
'name' => 'MeDIP-seq and nCpG analyses illuminate sexually dimorphic methylation of gonadal development genes with high historic methylation in turtle hatchlings with temperature-dependent sex determination',
'authors' => 'Radhakrishnan S. et al.',
'description' => '<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec1">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Background</h3>
<p id="Par1" class="Para">DNA methylation alters gene expression but not DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. Temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) epitomizes phenotypic plasticity where environmental temperature drives embryonic sexual fate, as occurs commonly in turtles. Importantly, the temperature-specific transcription of two genes underlying gonadal differentiation is known to be induced by differential methylation in TSD fish, turtle and alligator. Yet, how extensive is the link between DNA methylation and TSD remains unclear. Here we test for broad differences in genome-wide DNA methylation between male and female hatchling gonads of the TSD painted turtle <em xmlns="" class="EmphasisTypeItalic">Chrysemys picta</em> using methyl DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing, to identify differentially methylated candidates for future study. We also examine the genome-wide nCpG distribution (which affects DNA methylation) in painted turtles and test for historic methylation in genes regulating vertebrate gonadogenesis.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec2">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Results</h3>
<p id="Par2" class="Para">Turtle global methylation was consistent with other vertebrates (57% of the genome, 78% of all CpG dinucleotides). Numerous genes predicted to regulate turtle gonadogenesis exhibited sex-specific methylation and were proximal to methylated repeats. nCpG distribution predicted actual turtle DNA methylation and was bimodal in gene promoters (as other vertebrates) and introns (unlike other vertebrates). Differentially methylated genes, including regulators of sexual development, had lower nCpG content indicative of higher historic methylation.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec3">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p id="Par3" class="Para">Ours is the first evidence suggesting that sexually dimorphic DNA methylation is pervasive in turtle gonads (perhaps mediated by repeat methylation) and that it targets numerous regulators of gonadal development, consistent with the hypothesis that it may regulate thermosensitive transcription in TSD vertebrates. However, further research during embryogenesis will help test this hypothesis and the alternative that instead, most differential methylation observed in hatchlings is the by-product of sexual differentiation and not its cause.</p>
</div>',
'date' => '2017-05-19',
'pmid' => 'https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-017-0136-2',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-05-22 10:21:02',
'created' => '2017-05-22 10:21:02',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 89 => array(
'id' => '3210',
'name' => 'Protective vaccination and blood-stage malaria modify DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver of Balb/c mice.',
'authors' => 'Al-Quraishy S. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation are increasingly recognized to be critical for vaccination efficacy and outcome of different infectious diseases, but corresponding information is scarcely available for host defense against malaria. In the experimental blood-stage malaria Plasmodium chabaudi, we investigate the possible effects of a blood-stage vaccine on DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver, known as effector against blood-stage malaria, using DNA methylation microarrays. Naturally susceptible Balb/c mice acquire, by protective vaccination, the potency to survive P. chabaudi malaria and, concomitantly, modifications of constitutive DNA methylation of promoters of numerous genes in the liver; specifically, promoters of 256 genes are hyper(=up)- and 345 genes are hypo(=down)-methylated (p < 0.05). Protective vaccination also leads to changes in promoter DNA methylation upon challenge with P. chabaudi at peak parasitemia on day 8 post infection (p.i.), when 571 and 1013 gene promoters are up- and down-methylated, respectively, in relation to constitutive DNA methylation (p < 0.05). Gene set enrichment analyses reveal that both vaccination and P. chabaudi infections mainly modify promoters of those genes which are most statistically enriched with functions relating to regulation of transcription. Genes with down-methylated promoters encompass those encoding CX3CL1, GP130, and GATA2, known to be involved in monocyte recruitment, IL-6 trans-signaling, and onset of erythropoiesis, respectively. Our data suggest that vaccination may epigenetically improve parts of several effector functions of the liver against blood-stage malaria, as, e.g., recruitment of monocyte/macrophage to the liver accelerated liver regeneration and extramedullary hepatic erythropoiesis, thus leading to self-healing of otherwise lethal P. chabaudi blood-stage malaria.</p>',
'date' => '2017-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28315013',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-07-07 16:36:58',
'created' => '2017-07-07 16:36:58',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 90 => array(
'id' => '3184',
'name' => 'Comparative analysis of MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq and estimation of gene expression changes in a rodent model of schizophrenia',
'authors' => 'Neary J.L. et al.',
'description' => '<p>We conducted a comparative study of multiplexed affinity enrichment sequence methodologies (MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq) in a rodent model of schizophrenia, induced by in utero methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) exposure. We also examined related gene expression changes using a pooled sample approach. MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq identified 769 and 1771 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) between F2 offspring of MAM-exposed rats and saline control rats, respectively. The assays showed good concordance, with ~ 56% of MBD-seq-detected DMRs being identified by or proximal to MeDIP-seq DMRs. There was no significant overlap between DMRs and differentially expressed genes, suggesting that DNA methylation regulatory effects may act upon more distal genes, or are too subtle to detect using our approach. Methylation and gene expression gene ontology enrichment analyses identified biological processes important to schizophrenia pathophysiology, including neuron differentiation, prepulse inhibition, amphetamine response, and glutamatergic synaptic transmission regulation, reinforcing the utility of the MAM rodent model for schizophrenia research.</p>',
'date' => '2017-03-29',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S088875431730023X',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-05-22 09:53:51',
'created' => '2017-05-22 09:53:51',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 91 => array(
'id' => '3148',
'name' => 'Overexpression of LINE-1 Retrotransposons in Autism Brain',
'authors' => 'Shpyleva S. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Long interspersed nuclear elements-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are mobile DNA sequences that are capable of duplication and insertion (retrotransposition) within the genome. Recently, retrotransposition of L1 was shown to occur within human brain leading to somatic mosaicism in hippocampus and cerebellum. Because unregulated L1 activity can promote genomic instability and mutagenesis, multiple mechanisms including epigenetic chromatin condensation have evolved to effectively repress L1 expression. Nonetheless, L1 expression has been shown to be increased in patients with Rett syndrome and schizophrenia. Based on this evidence and our reports of oxidative stress and epigenetic dysregulation in autism cerebellum, we sought to determine whether L1 expression was increased in autism brain. The results indicated that L1 expression was significantly elevated in the autism cerebellum but not in BA9, BA22, or BA24. The binding of repressive MeCP2 and histone H3K9me3 to L1 sequences was significantly lower in autism cerebellum suggesting that relaxation of epigenetic repression may have contributed to increased expression. Further, the increase in L1 expression was inversely correlated with glutathione redox status consistent with reports indicating that L1 expression is increased under pro-oxidant conditions. Finally, the expression of transcription factor FOXO3, sensor of oxidative stress, was significantly increased and positively associated with L1 expression and negatively associated with glutathione redox status. While these novel results are an important first step, future understanding of the contribution of elevated L1 expression to neuronal CNVs and genomic instability in autism will depend on emerging cell-specific genomic technologies, a challenge that warrants future investigation.</p>',
'date' => '2017-02-20',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28220356',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-03-24 17:12:49',
'created' => '2017-03-24 17:12:49',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 92 => array(
'id' => '3092',
'name' => 'Integrative "-Omics" Analysis in Primary Human Hepatocytes Unravels Persistent Mechanisms of Cyclosporine A-Induced Cholestasis',
'authors' => 'Wolters J.E. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Cyclosporine A (CsA) is an undecapeptide with strong immunosuppressant activities and is used a lot after organ transplantation. Furthermore, it may induce cholestasis in the liver. In general, the drug-induced cholestasis (DIC) pathway includes genes involved in the uptake, synthesis, conjugation, and secretion of bile acids. However, whether CsA-induced changes in the cholestasis pathway in vitro are persistent for repeated dose toxicity has not yet been investigated. To explore this, primary human hepatocytes (PHH) were exposed to a subcytotoxic dose of 30 μM CsA daily for 3 and 5 days. To investigate the persistence of induced changes upon terminating CsA exposure after 5 days, a subset of PHH was subjected to a washout period (WO-period) of 3 days. Multiple -omics analyses, comprising whole genome analysis of DNA methylation, gene expression, and microRNA expression, were performed. The CsA-treatment resulted after 3 and 5 days, respectively, in 476 and 20 differentially methylated genes (DMGs), 1353 and 1481 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and in 22 and 29 differentially expressed microRNAs (DE-miRs). Cholestasis-related pathways appeared induced during CsA-treatment. Interestingly, 828 persistent DEGs and 6 persistent DE-miRs but no persistent DMGs were found after the WO-period. These persistent DEGs and DE-miRs showed concordance for 22 genes. Furthermore, 29 persistent DEGs changed into the same direction as observed in livers from cholestasis patients. None of those 29 DEGs which among others relate to oxidative stress and lipid metabolism are yet present in the DIC pathway or cholestasis adverse outcome pathway (AOP) thus presenting novel findings. In summary, we have demonstrated for the first time a persistent impact of repeated dose administration of CsA on genes and microRNAs related to DIC in the gold standard human liver in vitro model with PHH.</p>',
'date' => '2016-12-19',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27989131',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-01-03 10:33:43',
'created' => '2017-01-03 10:33:43',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 93 => array(
'id' => '3086',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA promoter methylation and transcriptome analysis in human adipose tissue unravels novel candidate genes for obesity',
'authors' => 'Keller M. et al.',
'description' => '<h4 id="absSec_1">Objective/methods</h4>
<p id="abspara0010">DNA methylation plays an important role in obesity and related metabolic complications. We examined genome-wide DNA promoter methylation along with mRNA profiles in paired samples of human subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) and omental visceral adipose tissue (OVAT) from non-obese <em>vs.</em> obese individuals.</p>
<h4 id="absSec_2">Results</h4>
<p id="abspara0015">We identified negatively correlated methylation and expression of several obesity-associated genes in our discovery dataset and <em>in silico</em> replicated <em>ETV6</em> in two independent cohorts. Further, we identified six adipose tissue depot-specific genes (<em>HAND2</em>, <em>HOXC6</em>, <em>PPARG</em>, <em>SORBS2</em>, <em>CD36</em>, and <em>CLDN1</em>). The effects were further supported in additional independent cohorts. Our top hits might play a role in adipogenesis and differentiation, obesity, lipid metabolism, and adipose tissue expandability. Finally, we show that <em>in vitro</em> methylation of <em>SORBS2</em> directly represses gene expression.</p>
<h4 id="absSec_3">Conclusions</h4>
<p id="abspara0020">Taken together, our data show distinct tissue specific epigenetic alterations which associate with obesity.</p>',
'date' => '2016-11-16',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212877816302757',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-12-21 10:36:19',
'created' => '2016-12-21 10:36:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 94 => array(
'id' => '3061',
'name' => 'Novel regional age-associated DNA methylation changes within human common disease-associated loci',
'authors' => 'Bell CG et al.',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Advancing age progressively impacts on risk and severity of chronic disease. It also modifies the epigenome, with changes in DNA methylation, due to both random drift and variation within specific functional loci.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">In a discovery set of 2238 peripheral-blood genome-wide DNA methylomes aged 19-82 years, we identify 71 age-associated differentially methylated regions within the linkage disequilibrium blocks of the single nucleotide polymorphisms from the NIH genome-wide association study catalogue. This included 52 novel regions, 29 within loci not covered by 450 k or 27 k Illumina array, and with enrichment for DNase-I Hypersensitivity sites across the full range of tissues. These age-associated differentially methylated regions also show marked enrichment for enhancers and poised promoters across multiple cell types. In a replication set of 2084 DNA methylomes, 95.7 % of the age-associated differentially methylated regions showed the same direction of ageing effect, with 80.3 % and 53.5 % replicated to p < 0.05 and p < 1.85 × 10<sup>-8</sup>, respectively.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">By analysing the functionally enriched disease and trait-associated regions of the human genome, we identify novel epigenetic ageing changes, which could be useful biomarkers or provide mechanistic insights into age-related common diseases.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2016-09-26',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27663977',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-11-04 10:56:10',
'created' => '2016-11-02 09:54:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 95 => array(
'id' => '3058',
'name' => 'Inheritable Silencing of Endogenous Genes by Hit-and-Run Targeted Epigenetic Editing',
'authors' => 'Amabile A. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Gene silencing is instrumental to interrogate gene function and holds promise for therapeutic applications. Here, we repurpose the endogenous retroviruses' silencing machinery of embryonic stem cells to stably silence three highly expressed genes in somatic cells by epigenetics. This was achieved by transiently expressing combinations of engineered transcriptional repressors that bind to and synergize at the target locus to instruct repressive histone marks and de novo DNA methylation, thus ensuring long-term memory of the repressive epigenetic state. Silencing was highly specific, as shown by genome-wide analyses, sharply confined to the targeted locus without spreading to nearby genes, resistant to activation induced by cytokine stimulation, and relieved only by targeted DNA demethylation. We demonstrate the portability of this technology by multiplex gene silencing, adopting different DNA binding platforms and interrogating thousands of genomic loci in different cell types, including primary T lymphocytes. Targeted epigenome editing might have broad application in research and medicine.</p>',
'date' => '2016-09-22',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27662090',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-10-27 15:48:08',
'created' => '2016-10-27 15:48:08',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 96 => array(
'id' => '3047',
'name' => 'Trichloroethylene-Induced DNA Methylation Changes in Male F344 Rat Liver',
'authors' => 'Jiang Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Trichloroethylene (TCE), a common environmental contaminant, causes hepatocellular carcinoma in mice but not in rats. To understand the mechanisms of the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE, we examined the methylation status of DNA in the liver of rats exposed to TCE at 0 or 1000 mg/kg b.w. for 5 days using MeDIP-chip, bisulfite sequencing, COBRA, and LC-MS/MS. The related mRNA expression levels were measured by qPCR. Although no global DNA methylation change was detected, 806 genes were hypermethylated and 186 genes were hypomethylated. The genes with hypermethylated DNA were enriched in endocytosis, MAPK, and cAMP signaling pathways. We further confirmed the hypermethylation of Uhrf2 DNA and the hypomethylation of Hadhb DNA, which were negatively correlated with their mRNA expression levels. The transcriptional levels of Jun, Ihh, and Tet2 were significantly downregulated, whereas Cdkn1a was overexpressed. No mRNA expression change was found for Mki67, Myc, Uhrf1, and Dnmt1. In conclusion, TCE-induced DNA methylation changes in rats appear to suppress instead of promote hepatocarcinogenesis, which might play a role in the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE.</p>',
'date' => '2016-09-21',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27618143',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-10-10 11:10:05',
'created' => '2016-10-10 11:10:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 97 => array(
'id' => '3001',
'name' => 'Dynamic Interplay between the Transcriptome and Methylome in Response to Oxidative and Alkylating Stress',
'authors' => 'Deferme L et al.',
'description' => '<p>In recent years, it has been shown that free radicals not only react directly with DNA but also regulate epigenetic processes such as DNA methylation, which may be relevant within the context of, for example, tumorigenesis. However, how these free radicals impact the epigenome remains unclear. We therefore investigated whether methyl and hydroxyl radicals, formed by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBH), change temporal DNA methylation patterns and how this interferes with genome-wide gene expression. At three time points, TBH-induced radicals in HepG2 cells were identified by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Total 5-methylcytosine (5mC) levels were determined by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry and genome-wide changes in 5mC and gene expression by microarrays. Induced methylome changes rather represent an adaptive response to the oxidative stress-related reactions observed in the transcriptome. More specifically, we found that methyl radicals did not induce DNA methylation directly. An initial oxidative and alkylating stress-related response of the transcriptome during the early phase of TBH treatment was followed by an epigenetic response associated with cell survival signaling. Also, we identified genes of which the expression seems directly regulated by DNA methylation. This work suggests an important role of the methylome in counter-regulating primary oxidative and alkylating stress responses in the transcriptome to restore normal cell function. Altogether, the methylome may play an important role in counter-regulating primary oxidative and alkylating stress responses in the transcriptome presumably to restore normal cell function.</p>',
'date' => '2016-08-24',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27509014',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-08-25 17:17:48',
'created' => '2016-08-25 17:17:48',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 98 => array(
'id' => '2984',
'name' => 'Efficiency of methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing for whole-genome DNA methylation analysis',
'authors' => 'Jeong HM et al.',
'description' => '<p><abstracttext label="AIMS" nlmcategory="OBJECTIVE">We compared four common methods for measuring DNA methylation levels and recommended the most efficient method in terms of cost and coverage.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>MATERIALS & METHODS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="MATERIALS & METHODS" nlmcategory="METHODS">The DNA methylation status of liver and stomach tissues was profiled using four different methods, whole-genome bisulphite sequencing (WG-BS), targeted bisulphite sequencing (Targeted-BS), methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing (MeDIP-BS). We calculated DNA methylation levels using each method and compared the results.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">MeDIP-BS yielded the most similar DNA methylation profile to WG-BS, with 20 times less data, suggesting remarkable cost savings and coverage efficiency compared with the other methods.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">MeDIP-BS is a practical cost-effective method for analyzing whole-genome DNA methylation that is highly accurate at base-pair resolution.</abstracttext></p>',
'date' => '2016-06-08',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27266718',
'doi' => ' 10.2217/epi-2016-0038',
'modified' => '2016-07-26 09:17:24',
'created' => '2016-07-26 09:17:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 99 => array(
'id' => '2904',
'name' => 'Aflatoxin B1 induces persistent epigenomic effects in primary human hepatocytes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma',
'authors' => 'Linda Rieswijka, Sandra M.H. Claessena, Otto Bekersc, Marcel van Herwijnena, Daniël H.J. Theunissena, Danyel G.J. Jennena, Theo M.C.M. de Koka, Jos C.S. Kleinjansa,Simone G.J. van Bredaa',
'description' => '<p><span>Chronic exposure to aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) has, in certain regions in the world, been strongly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. AFB1 is a very potent hepatotoxic and carcinogenic mycotoxin which is frequently reported as a food contaminant. Epigenetic modifications provoked by environmental exposures, such as AFB1, may create a persistent epigenetic footprint. Deregulation of epigenetic mechanisms has actually been reported in HCC patients following AFB1 exposure; however, no attempts have yet been made to investigate early effects on the epigenome level which may be persistent on longer term, thereby possibly initiating carcinogenic events. In this study, we aim to identify methyl DNA-mRNA-interactions representative for a persistent epigenetic footprint associated with the early onset of AFB1-induced HCC. For this, primary human hepatocytes were exposed to 0.3 μM of AFB1 for 5 days. Persistent epigenetic effects were measured 3 days after terminating the carcinogenic exposure. Whole genome DNA methylation changes and whole genome transcriptomic analysis were analyzed applying microarray technologies, and cross-omics interactions were evaluated. Upon combining transcriptomics data with results on DNA methylation, a range of persistent hyper- and hypo-methylated genes was identified which also appeared affected on the transcriptome level. For six of the hypo-methylated and up-regulated genes, namely TXNRD1, PCNA, CCNK, DIAPH3, RAB27A and HIST1H2BF, a clear role in carcinogenic events could be identified. This study is the first to report on a carcinogen-induced persistent impact on the epigenetic footprint in relation with the transcriptome which could be indicative for the early onset of AFB1-related development of HCC.</span></p>',
'date' => '2016-05-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0300483X16300427',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.tox.2016.05.002',
'modified' => '2016-05-13 14:13:03',
'created' => '2016-05-08 07:29:28',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 100 => array(
'id' => '2855',
'name' => 'Paternal B Vitamin Intake Is a Determinant of Growth, Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Tumor Volume in Female Apc1638N Mouse Offspring',
'authors' => 'Sabet JA, Park LK, Iyer LK, Tai AK, Koh GY, Pfalzer AC, Parnell LD, Mason JB, Liu Z, Byun AJ, Crott JW',
'description' => '<h3>Background</h3>
<p>The importance of maternal nutrition to offspring health and risk of disease is well established. Emerging evidence suggests paternal diet may affect offspring health as well.</p>
<h3>Objective</h3>
<p>In the current study we sought to determine whether modulating pre-conception paternal B vitamin intake alters intestinal tumor formation in offspring. Additionally, we sought to identify potential mechanisms for the observed weight differential among offspring by profiling hepatic gene expression and lipid content.</p>
<h3>Methods</h3>
<p>Male Apc<sup>1638N</sup> mice (prone to intestinal tumor formation) were fed diets containing replete (control, CTRL), mildly deficient (DEF), or supplemental (SUPP) quantities of vitamins B<sub>2</sub>, B<sub>6</sub>, B<sub>12</sub>, and folate for 8 weeks before mating with control-fed wild type females. Wild type offspring were euthanized at weaning and hepatic gene expression profiled. Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring were fed a replete diet and euthanized at 28 weeks of age to assess tumor burden.</p>
<h3>Results</h3>
<p>No differences in intestinal tumor incidence or burden were found between male Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring of different paternal diet groups. Although in female Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring there were no differences in tumor incidence or multiplicity, a stepwise increase in tumor volume with increasing paternal B vitamin intake was observed. Interestingly, female offspring of SUPP and DEF fathers had a significantly lower body weight than those of CTRL fed fathers. Moreover, hepatic trigylcerides and cholesterol were elevated 3-fold in adult female offspring of SUPP fathers. Weanling offspring of the same fathers displayed altered expression of several key lipid-metabolism genes. Hundreds of differentially methylated regions were identified in the paternal sperm in response to DEF and SUPP diets. Aside from a few genes including Igf2, there was a striking lack of overlap between these genes differentially methylated in sperm and differentially expressed in offspring.</p>
<h3>Conclusions</h3>
<p>In this animal model, modulation of paternal B vitamin intake prior to mating alters offspring weight gain, lipid metabolism and tumor growth in a sex-specific fashion. These results highlight the need to better define how paternal nutrition affects the health of offspring.</p>',
'date' => '2016-03-11',
'pmid' => 'http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0151579#abstract0',
'doi' => ' 10.1371/journal.pone.0151579',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 10:26:38',
'created' => '2016-03-15 10:26:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 101 => array(
'id' => '2977',
'name' => 'Regulation of miR-200c/141 expression by intergenic DNA-looping and transcriptional read-through',
'authors' => 'Batista L et al.',
'description' => '<p>The miR-200 family members have been implicated in stress responses and ovarian tumorigenesis. Here, we find that miR-200c/141 transcription is intimately linked to the transcription of the proximal upstream gene PTPN6 (SHP1) in all physiological conditions tested. PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 are transcriptionally co-regulated by two complementary mechanisms. First, a bypass of the regular PTPN6 polyadenylation signal allows the transcription of the downstream miR-200c/141. Second, the promoters of the PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 transcription units physically interact through a 3-dimensional DNA loop and exhibit similar epigenetic regulation. Our findings highlight that transcription of intergenic miRNAs is a novel outcome of transcriptional read-through and reveal a yet unexplored type of DNA loop associating two closely located promoters. These mechanisms have significant relevance in ovarian cancers and stress response, pathophysiological conditions in which miR-200c/141 exert key functions.</p>',
'date' => '2016-01-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26725650',
'doi' => '10.1038/ncomms9959',
'modified' => '2016-07-07 10:27:25',
'created' => '2016-07-07 10:27:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 102 => array(
'id' => '2951',
'name' => 'Maternal immune activation induces GAD1 and GAD2 promoter remodeling in the offspring prefrontal cortex',
'authors' => 'Labouesse MA et al.',
'description' => '<p>Maternal infection during pregnancy increases the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in the offspring. In addition to its influence on other neuronal systems, this early-life environmental adversity has been shown to negatively affect cortical γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) functions in adult life, including impaired prefrontal expression of enzymes required for GABA synthesis. The underlying molecular processes, however, remain largely unknown. In the present study, we explored whether epigenetic modifications represent a mechanism whereby maternal infection during pregnancy can induce such GABAergic impairments in the offspring. We used an established mouse model of prenatal immune challenge that is based on maternal treatment with the viral mimetic poly(I:C). We found that prenatal immune activation increased prefrontal levels of 5-methylated cytosines (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylated cytosines (5hmC) in the promoter region of GAD1, which encodes the 67-kDa isoform of the GABA-synthesising enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67). The early-life challenge also increased 5mC levels at the promoter region of GAD2, which encodes the 65-kDa GAD isoform (GAD65). These effects were accompanied by elevated GAD1 and GAD2 promoter binding of methyl CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) and by reduced GAD67 and GAD65 mRNA expression. Moreover, the epigenetic modifications at the GAD1 promoter correlated with prenatal infection-induced impairments in working memory and social interaction. Our study thus highlights that hypermethylation of GAD1 and GAD2 promoters may be an important molecular mechanism linking prenatal infection to presynaptic GABAergic impairments and associated behavioral and cognitive abnormalities in the offspring.</p>',
'date' => '2015-12-02',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26575259',
'doi' => ' 10.1080/15592294.2015.1114202',
'modified' => '2016-06-10 16:32:32',
'created' => '2016-06-10 16:32:32',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 103 => array(
'id' => '2860',
'name' => 'DNA methylation profiling: comparison of genome-wide sequencing methods and the Infinium Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip',
'authors' => 'Walker DL, Bhagwate AV, Baheti S, Smalley RL, Hilker CA, Sun Z, Cunningham JM',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>AIMS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="AIMS" nlmcategory="OBJECTIVE">To compare the performance of four sequence-based and one microarray methods for DNA methylation profiling.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>METHODS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="METHODS" nlmcategory="METHODS">DNA from two cell lines were profiled by reduced representation bisulfite sequencing, methyl capture sequencing (SS-Meth Seq), NimbleGen SeqCapEpi CpGiant(Nimblegen MethSeq), methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) and the Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip (Meth450K).</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS & CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS & CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">Despite differences in genome-wide coverage, high correlation and concordance were observed between different methods. Significant overlap of differentially methylated regions was identified between sequenced-based platforms. MeDIP provided the best coverage for the whole genome and gene body regions, while RRBS and Nimblegen MethSeq were superior for CpGs in CpG islands and promoters. Methylation analyses can be achieved by any of the five methods but understanding their differences may better address the research question being posed.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-12-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26192535',
'doi' => '10.2217/EPI.15.64',
'modified' => '2016-03-16 11:06:05',
'created' => '2016-03-16 11:06:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 104 => array(
'id' => '2892',
'name' => 'High cortisol in 5-year-old children causes loss of DNA methylation in SINE retrotransposons: a possible role for ZNF263 in stress-related diseases',
'authors' => 'Nätt D, Johansson I, Faresjö T, Ludvigsson J, Thorsell A',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Childhood stress leads to increased risk of many adult diseases, such as major depression and cardiovascular disease. Studies show that adults with experienced childhood stress have specific epigenetic changes, but to understand the pathways that lead to disease, we also need to study the epigenetic link prospectively in children.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Here, we studied a homogenous group of 48 5-year-old children. By combining hair cortisol measurements (a well-documented biomarker for chronic stress), with whole-genome DNA-methylation sequencing, we show that high cortisol associates with a genome-wide decrease in DNA methylation and targets short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs; a type of retrotransposon) and genes important for calcium transport: phenomena commonly affected in stress-related diseases and in biological aging. More importantly, we identify a zinc-finger transcription factor, ZNF263, whose binding sites where highly overrepresented in regions experiencing methylation loss. This type of zinc-finger protein has previously shown to be involved in the defense against retrotransposons.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">Our results show that stress in preschool children leads to changes in DNA methylation similar to those seen in biological aging. We suggest that this may affect future disease susceptibility by alterations in the epigenetic mechanisms that keep retrotransposons dormant. Future treatments for stress- and age-related diseases may therefore seek to target zinc-finger proteins that epigenetically control retrotransposon reactivation, such as ZNF263.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-09-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26339299',
'doi' => ' 10.1186/s13148-015-0123-z',
'modified' => '2016-04-14 10:03:28',
'created' => '2016-04-14 10:03:28',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 105 => array(
'id' => '2857',
'name' => 'Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo',
'authors' => 'Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associated with disturbed blood flow. DNA methylation is a powerful epigenetic regulator of endothelial transcription recently associated with flow characteristics. We investigated differential DNA methylation in flow region-specific aortic endothelial cells in vivo in adult domestic male and female swine.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Genome-wide DNA methylation was profiled in endothelial cells (EC) isolated from two robust locations of differing patho-susceptibility:--an athero-susceptible site located at the inner curvature of the aortic arch (AA) and an athero-protected region in the descending thoracic (DT) aorta. Complete methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) identified over 5500 endothelial differentially methylated regions (DMRs). DMR density was significantly enriched in exons and 5'UTR sequences of annotated genes, 60 of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. The set of DMR-associated genes was enriched in transcriptional regulation, pattern specification HOX loci, oxidative stress and the ER stress adaptive pathway, all categories linked to athero-susceptible endothelium. Examination of the relationship between DMR and mRNA in HOXA genes demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between CpG island promoter methylation and gene expression. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) confirmed differential CpG methylation of HOXA genes, the ER stress gene ATF4, inflammatory regulator microRNA-10a and ARHGAP25 that encodes a negative regulator of Rho GTPases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Gender-specific DMRs associated with ciliogenesis that may be linked to defects in cilia development were also identified in AA DMRs.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">An endothelial methylome analysis identifies epigenetic DMR characteristics associated with transcriptional regulation in regions of atherosusceptibility in swine aorta in vivo. The data represent the first methylome blueprint for spatio-temporal analyses of lesion susceptibility predisposing to endothelial dysfunction in complex flow environments in vivo.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-07-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12864-015-1656-4',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'created' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Testimonial' => array(),
'Area' => array(),
'SafetySheet' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '656',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS US en',
'language' => 'en',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-US-en-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'US',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:56:19',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:56:19',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '654',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS GB en',
'language' => 'en',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-GB-en-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'GB',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:28',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:28',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '649',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE fr',
'language' => 'fr',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-fr-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:52:41',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:52:41',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '653',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS FR fr',
'language' => 'fr',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-FR-fr-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'FR',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:02',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:02',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '652',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS ES es',
'language' => 'es',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-ES-es-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'ES',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:54:39',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:54:39',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '651',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS DE de',
'language' => 'de',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-DE-de-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'DE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:54:02',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:54:02',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '655',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS JP ja',
'language' => 'ja',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-JP-ja-1_1.pdf',
'countries' => 'JP',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:55',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:55',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 7 => array(
'id' => '650',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE nl',
'language' => 'nl',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-nl-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
)
)
$meta_canonical = 'https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns'
$country = 'US'
$countries_allowed = array(
(int) 0 => 'CA',
(int) 1 => 'US',
(int) 2 => 'IE',
(int) 3 => 'GB',
(int) 4 => 'DK',
(int) 5 => 'NO',
(int) 6 => 'SE',
(int) 7 => 'FI',
(int) 8 => 'NL',
(int) 9 => 'BE',
(int) 10 => 'LU',
(int) 11 => 'FR',
(int) 12 => 'DE',
(int) 13 => 'CH',
(int) 14 => 'AT',
(int) 15 => 'ES',
(int) 16 => 'IT',
(int) 17 => 'PT'
)
$outsource = false
$other_formats = array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
)
)
$pro = array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsGroup' => array(
'id' => '10',
'product_id' => '1879',
'group_id' => '7'
)
)
$edit = ''
$testimonials = ''
$featured_testimonials = ''
$related_products = '<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit"><img src="/img/product/reagents/diamag02.png" alt="some alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">B04000001</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-1819" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/1819" id="CartAdd/1819Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="1819" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'B04000001',
'240',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'B04000001',
'240',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit" data-reveal-id="cartModal-1819" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17031043-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2597" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2597" id="CartAdd/2597Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2597" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17031043-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17031043-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2597" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17031046-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2599" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2599" id="CartAdd/2599Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2599" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'C17031046-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'C17031046-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2599" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17021042-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2593" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2593" id="CartAdd/2593Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2593" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17021042-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17021042-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2593" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17021045-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2595" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2595" id="CartAdd/2595Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2595" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'C17021045-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'C17021045-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2595" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/auto-magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns"><img src="/img/product/kits/methyl-kit-icon.png" alt="Methylation kit icon" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C02010014</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit - ordering reference: C0...</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/bioruptorpico2"><img src="/img/product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-1.jpg" alt="Bioruptor Pico" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">B01080010</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: QUOTE MODAL --><div id="quoteModal-3046" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<h3>Get a quote</h3><p class="lead">You are about to request a quote for <strong>Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device</strong>. Fill out the form below and we will be in touch with you very soon.</p><p><small>All <span style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</span> fields are mandatory</small></p>
</div>
</div>
<form action="/en/quotes/quote?id=3046" id="Quote-3046" class="quote" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][product_id]" value="3046" id="QuoteProductId"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][formLoaded6tY4bPYk]" value="c0sveHAvS0dieWhxT3RCV3dlb3pnUT09" id="QuoteFormLoaded6tY4bPYk"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][product_rfq_tag]" value="bioruptorpico2" id="QuoteProductRfqTag"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][source_quote]" value="modal quote" id="QuoteSourceQuote"/>
<div class="row collapse">
<h2>Contact Information</h2>
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">First name <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][first_name]" placeholder="john" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteFirstName" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Last name <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][last_name]" placeholder="doe" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteLastName" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Company <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][company]" placeholder="Organisation / Institute" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteCompany" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Phone number</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][phone_number]" placeholder="+1 862 209-4680" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuotePhoneNumber"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">City</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][city]" placeholder="Denville" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteCity"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Country <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<select name="data[Quote][country]" required="required" class="triggers" id="country_selector_quote-3046">
<option value="">-- select a country --</option>
<option value="AF">Afghanistan</option>
<option value="AX">Åland Islands</option>
<option value="AL">Albania</option>
<option value="DZ">Algeria</option>
<option value="AS">American Samoa</option>
<option value="AD">Andorra</option>
<option value="AO">Angola</option>
<option value="AI">Anguilla</option>
<option value="AQ">Antarctica</option>
<option value="AG">Antigua and Barbuda</option>
<option value="AR">Argentina</option>
<option value="AM">Armenia</option>
<option value="AW">Aruba</option>
<option value="AU">Australia</option>
<option value="AT">Austria</option>
<option value="AZ">Azerbaijan</option>
<option value="BS">Bahamas</option>
<option value="BH">Bahrain</option>
<option value="BD">Bangladesh</option>
<option value="BB">Barbados</option>
<option value="BY">Belarus</option>
<option value="BE">Belgium</option>
<option value="BZ">Belize</option>
<option value="BJ">Benin</option>
<option value="BM">Bermuda</option>
<option value="BT">Bhutan</option>
<option value="BO">Bolivia</option>
<option value="BQ">Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba</option>
<option value="BA">Bosnia and Herzegovina</option>
<option value="BW">Botswana</option>
<option value="BV">Bouvet Island</option>
<option value="BR">Brazil</option>
<option value="IO">British Indian Ocean Territory</option>
<option value="BN">Brunei Darussalam</option>
<option value="BG">Bulgaria</option>
<option value="BF">Burkina Faso</option>
<option value="BI">Burundi</option>
<option value="KH">Cambodia</option>
<option value="CM">Cameroon</option>
<option value="CA">Canada</option>
<option value="CV">Cape Verde</option>
<option value="KY">Cayman Islands</option>
<option value="CF">Central African Republic</option>
<option value="TD">Chad</option>
<option value="CL">Chile</option>
<option value="CN">China</option>
<option value="CX">Christmas Island</option>
<option value="CC">Cocos (Keeling) Islands</option>
<option value="CO">Colombia</option>
<option value="KM">Comoros</option>
<option value="CG">Congo</option>
<option value="CD">Congo, The Democratic Republic of the</option>
<option value="CK">Cook Islands</option>
<option value="CR">Costa Rica</option>
<option value="CI">Côte d'Ivoire</option>
<option value="HR">Croatia</option>
<option value="CU">Cuba</option>
<option value="CW">Curaçao</option>
<option value="CY">Cyprus</option>
<option value="CZ">Czech Republic</option>
<option value="DK">Denmark</option>
<option value="DJ">Djibouti</option>
<option value="DM">Dominica</option>
<option value="DO">Dominican Republic</option>
<option value="EC">Ecuador</option>
<option value="EG">Egypt</option>
<option value="SV">El Salvador</option>
<option value="GQ">Equatorial Guinea</option>
<option value="ER">Eritrea</option>
<option value="EE">Estonia</option>
<option value="ET">Ethiopia</option>
<option value="FK">Falkland Islands (Malvinas)</option>
<option value="FO">Faroe Islands</option>
<option value="FJ">Fiji</option>
<option value="FI">Finland</option>
<option value="FR">France</option>
<option value="GF">French Guiana</option>
<option value="PF">French Polynesia</option>
<option value="TF">French Southern Territories</option>
<option value="GA">Gabon</option>
<option value="GM">Gambia</option>
<option value="GE">Georgia</option>
<option value="DE">Germany</option>
<option value="GH">Ghana</option>
<option value="GI">Gibraltar</option>
<option value="GR">Greece</option>
<option value="GL">Greenland</option>
<option value="GD">Grenada</option>
<option value="GP">Guadeloupe</option>
<option value="GU">Guam</option>
<option value="GT">Guatemala</option>
<option value="GG">Guernsey</option>
<option value="GN">Guinea</option>
<option value="GW">Guinea-Bissau</option>
<option value="GY">Guyana</option>
<option value="HT">Haiti</option>
<option value="HM">Heard Island and McDonald Islands</option>
<option value="VA">Holy See (Vatican City State)</option>
<option value="HN">Honduras</option>
<option value="HK">Hong Kong</option>
<option value="HU">Hungary</option>
<option value="IS">Iceland</option>
<option value="IN">India</option>
<option value="ID">Indonesia</option>
<option value="IR">Iran, Islamic Republic of</option>
<option value="IQ">Iraq</option>
<option value="IE">Ireland</option>
<option value="IM">Isle of Man</option>
<option value="IL">Israel</option>
<option value="IT">Italy</option>
<option value="JM">Jamaica</option>
<option value="JP">Japan</option>
<option value="JE">Jersey</option>
<option value="JO">Jordan</option>
<option value="KZ">Kazakhstan</option>
<option value="KE">Kenya</option>
<option value="KI">Kiribati</option>
<option value="KP">Korea, Democratic People's Republic of</option>
<option value="KR">Korea, Republic of</option>
<option value="KW">Kuwait</option>
<option value="KG">Kyrgyzstan</option>
<option value="LA">Lao People's Democratic Republic</option>
<option value="LV">Latvia</option>
<option value="LB">Lebanon</option>
<option value="LS">Lesotho</option>
<option value="LR">Liberia</option>
<option value="LY">Libya</option>
<option value="LI">Liechtenstein</option>
<option value="LT">Lithuania</option>
<option value="LU">Luxembourg</option>
<option value="MO">Macao</option>
<option value="MK">Macedonia, Republic of</option>
<option value="MG">Madagascar</option>
<option value="MW">Malawi</option>
<option value="MY">Malaysia</option>
<option value="MV">Maldives</option>
<option value="ML">Mali</option>
<option value="MT">Malta</option>
<option value="MH">Marshall Islands</option>
<option value="MQ">Martinique</option>
<option value="MR">Mauritania</option>
<option value="MU">Mauritius</option>
<option value="YT">Mayotte</option>
<option value="MX">Mexico</option>
<option value="FM">Micronesia, Federated States of</option>
<option value="MD">Moldova</option>
<option value="MC">Monaco</option>
<option value="MN">Mongolia</option>
<option value="ME">Montenegro</option>
<option value="MS">Montserrat</option>
<option value="MA">Morocco</option>
<option value="MZ">Mozambique</option>
<option value="MM">Myanmar</option>
<option value="NA">Namibia</option>
<option value="NR">Nauru</option>
<option value="NP">Nepal</option>
<option value="NL">Netherlands</option>
<option value="NC">New Caledonia</option>
<option value="NZ">New Zealand</option>
<option value="NI">Nicaragua</option>
<option value="NE">Niger</option>
<option value="NG">Nigeria</option>
<option value="NU">Niue</option>
<option value="NF">Norfolk Island</option>
<option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands</option>
<option value="NO">Norway</option>
<option value="OM">Oman</option>
<option value="PK">Pakistan</option>
<option value="PW">Palau</option>
<option value="PS">Palestine, State of</option>
<option value="PA">Panama</option>
<option value="PG">Papua New Guinea</option>
<option value="PY">Paraguay</option>
<option value="PE">Peru</option>
<option value="PH">Philippines</option>
<option value="PN">Pitcairn</option>
<option value="PL">Poland</option>
<option value="PT">Portugal</option>
<option value="PR">Puerto Rico</option>
<option value="QA">Qatar</option>
<option value="RE">Réunion</option>
<option value="RO">Romania</option>
<option value="RU">Russian Federation</option>
<option value="RW">Rwanda</option>
<option value="BL">Saint Barthélemy</option>
<option value="SH">Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha</option>
<option value="KN">Saint Kitts and Nevis</option>
<option value="LC">Saint Lucia</option>
<option value="MF">Saint Martin (French part)</option>
<option value="PM">Saint Pierre and Miquelon</option>
<option value="VC">Saint Vincent and the Grenadines</option>
<option value="WS">Samoa</option>
<option value="SM">San Marino</option>
<option value="ST">Sao Tome and Principe</option>
<option value="SA">Saudi Arabia</option>
<option value="SN">Senegal</option>
<option value="RS">Serbia</option>
<option value="SC">Seychelles</option>
<option value="SL">Sierra Leone</option>
<option value="SG">Singapore</option>
<option value="SX">Sint Maarten (Dutch part)</option>
<option value="SK">Slovakia</option>
<option value="SI">Slovenia</option>
<option value="SB">Solomon Islands</option>
<option value="SO">Somalia</option>
<option value="ZA">South Africa</option>
<option value="GS">South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands</option>
<option value="ES">Spain</option>
<option value="LK">Sri Lanka</option>
<option value="SD">Sudan</option>
<option value="SR">Suriname</option>
<option value="SS">South Sudan</option>
<option value="SJ">Svalbard and Jan Mayen</option>
<option value="SZ">Swaziland</option>
<option value="SE">Sweden</option>
<option value="CH">Switzerland</option>
<option value="SY">Syrian Arab Republic</option>
<option value="TW">Taiwan</option>
<option value="TJ">Tajikistan</option>
<option value="TZ">Tanzania</option>
<option value="TH">Thailand</option>
<option value="TL">Timor-Leste</option>
<option value="TG">Togo</option>
<option value="TK">Tokelau</option>
<option value="TO">Tonga</option>
<option value="TT">Trinidad and Tobago</option>
<option value="TN">Tunisia</option>
<option value="TR">Turkey</option>
<option value="TM">Turkmenistan</option>
<option value="TC">Turks and Caicos Islands</option>
<option value="TV">Tuvalu</option>
<option value="UG">Uganda</option>
<option value="UA">Ukraine</option>
<option value="AE">United Arab Emirates</option>
<option value="GB">United Kingdom</option>
<option value="US" selected="selected">United States</option>
<option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands</option>
<option value="UY">Uruguay</option>
<option value="UZ">Uzbekistan</option>
<option value="VU">Vanuatu</option>
<option value="VE">Venezuela</option>
<option value="VN">Viet Nam</option>
<option value="VG">Virgin Islands, British</option>
<option value="VI">Virgin Islands, U.S.</option>
<option value="WF">Wallis and Futuna</option>
<option value="EH">Western Sahara</option>
<option value="YE">Yemen</option>
<option value="ZM">Zambia</option>
<option value="ZW">Zimbabwe</option>
</select><script>
$('#country_selector_quote-3046').selectize();
</script><br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">State</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" maxlength="3" type="text"/><br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Email <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][email]" placeholder="email@address.com" maxlength="255" type="email" id="QuoteEmail" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse" id="email_v">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Email verification<sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][email_v]" autocomplete="nope" type="text" id="QuoteEmailV"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Comment</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<textarea name="data[Quote][comment]" placeholder="Additional comments" cols="30" rows="6" id="QuoteComment"></textarea> </div>
</div>
<!------------SERVICES PARTICULAR FORM START---------------->
<!------------DATA TO POPULATE REGARDING SPECIFIC SERVICES----->
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<div class="recaptcha"><div id="recaptcha6776db64c3be6"></div></div> </div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<button id="submit_btn-3046" class="alert button expand" form="Quote-3046" type="submit">Contact me</button> </div>
</div>
</form><script>
var pardotFormHandlerURL = 'https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2022-10-10/36b1c';
function postToPardot(formAction, id) {
$('#pardot-form-handler').load(function(){
$('#Quote-' + id).attr('action', formAction);
$('#Quote-' + id).submit();
});
$('#pardot-form-handler').attr('src', pardotFormHandlerURL + '?' + $('#Quote-' + id).serialize());
}
$(document).ready(function() {
$('body').append('<iframe id="pardot-form-handler" height="0" width="0" style="position:absolute; left:-100000px; top:-100000px" src="javascript:false;"></iframe>');
$('#Quote-3046').attr('action','javascript:postToPardot(\'' + $('#Quote-3046').attr('action') + '\', 3046)');
});
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").click(function (e) {
if($(this).closest('form')[0].checkValidity()){
e.preventDefault();
//disable the submit button
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").attr("disabled", true);
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").html("Processing...");
//submit the form
$("#Quote-3046").submit();
}
})
</script>
<script>
if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'US') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AL">Alabama (AL)</option><option value="AK">Alaska (AK)</option><option value="AZ">Arizona (AZ)</option><option value="AR">Arkansas (AR)</option><option value="CA">California (CA)</option><option value="CO">Colorado (CO)</option><option value="CT">Connecticut (CT)</option><option value="DE">Delaware (DE)</option><option value="FL">Florida (FL)</option><option value="GA">Georgia (GA)</option><option value="HI">Hawaii (HI)</option><option value="ID">Idaho (ID)</option><option value="IL">Illinois (IL)</option><option value="IN">Indiana (IN)</option><option value="IA">Iowa (IA)</option><option value="KS">Kansas (KS)</option><option value="KY">Kentucky (KY)</option><option value="LA">Louisiana (LA)</option><option value="ME">Maine (ME)</option><option value="MD">Maryland (MD)</option><option value="MA">Massachusetts (MA)</option><option value="MI">Michigan (MI)</option><option value="MN">Minnesota (MN)</option><option value="MS">Mississippi (MS)</option><option value="MO">Missouri (MO)</option><option value="MT">Montana (MT)</option><option value="NE">Nebraska (NE)</option><option value="NV">Nevada (NV)</option><option value="NH">New Hampshire (NH)</option><option value="NJ">New Jersey (NJ)</option><option value="NM">New Mexico (NM)</option><option value="NY">New York (NY)</option><option value="NC">North Carolina (NC)</option><option value="ND">North Dakota (ND)</option><option value="OH">Ohio (OH)</option><option value="OK">Oklahoma (OK)</option><option value="OR">Oregon (OR)</option><option value="PA">Pennsylvania (PA)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="RI">Rhode Island (RI)</option><option value="SC">South Carolina (SC)</option><option value="SD">South Dakota (SD)</option><option value="TN">Tennessee (TN)</option><option value="TX">Texas (TX)</option><option value="UT">Utah (UT)</option><option value="VT">Vermont (VT)</option><option value="VA">Virginia (VA)</option><option value="WA">Washington (WA)</option><option value="WV">West Virginia (WV)</option><option value="WI">Wisconsin (WI)</option><option value="WY">Wyoming (WY)</option><option value="DC">District of Columbia (DC)</option><option value="AS">American Samoa (AS)</option><option value="GU">Guam (GU)</option><option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands (MP)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands (UM)</option><option value="VI">Virgin Islands (VI)</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'CA') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AB">Alberta (AB)</option><option value="BC">British Columbia (BC)</option><option value="MB">Manitoba (MB)</option><option value="NB">New Brunswick (NB)</option><option value="NL">Newfoundland and Labrador (NL)</option><option value="NS">Nova Scotia (NS)</option><option value="ON">Ontario (ON)</option><option value="PE">Prince Edward Island (PE)</option><option value="QC">Quebec (QC)</option><option value="SK">Saskatchewan (SK)</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'DE') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="BW">Baden-Württemberg (BW)</option><option value="BY">Bayern (BY)</option><option value="BE">Berlin (BE)</option><option value="BB">Brandeburg (BB)</option><option value="HB">Bremen (HB)</option><option value="HH">Hamburg (HH)</option><option value="HE">Hessen (HE)</option><option value="MV">Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV)</option><option value="NI">Niedersachsen (NI)</option><option value="NW">Nordrhein-Westfalen (NW)</option><option value="RP">Rheinland-Pfalz (RP)</option><option value="SL">Saarland (SL)</option><option value="SN">Sachsen (SN)</option><option value ="SA">Sachsen-Anhalt (SA)</option><option value="SH">Schleswig-Holstein (SH)</option><option value="TH">Thüringen</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().hide();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<input name="data[Quote][state]" maxlength="255" type="text" id="state-3046" value="">');
}
$("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").change(function() {
if (this.value == 'US') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AL">Alabama (AL)</option><option value="AK">Alaska (AK)</option><option value="AZ">Arizona (AZ)</option><option value="AR">Arkansas (AR)</option><option value="CA">California (CA)</option><option value="CO">Colorado (CO)</option><option value="CT">Connecticut (CT)</option><option value="DE">Delaware (DE)</option><option value="FL">Florida (FL)</option><option value="GA">Georgia (GA)</option><option value="HI">Hawaii (HI)</option><option value="ID">Idaho (ID)</option><option value="IL">Illinois (IL)</option><option value="IN">Indiana (IN)</option><option value="IA">Iowa (IA)</option><option value="KS">Kansas (KS)</option><option value="KY">Kentucky (KY)</option><option value="LA">Louisiana (LA)</option><option value="ME">Maine (ME)</option><option value="MD">Maryland (MD)</option><option value="MA">Massachusetts (MA)</option><option value="MI">Michigan (MI)</option><option value="MN">Minnesota (MN)</option><option value="MS">Mississippi (MS)</option><option value="MO">Missouri (MO)</option><option value="MT">Montana (MT)</option><option value="NE">Nebraska (NE)</option><option value="NV">Nevada (NV)</option><option value="NH">New Hampshire (NH)</option><option value="NJ">New Jersey (NJ)</option><option value="NM">New Mexico (NM)</option><option value="NY">New York (NY)</option><option value="NC">North Carolina (NC)</option><option value="ND">North Dakota (ND)</option><option value="OH">Ohio (OH)</option><option value="OK">Oklahoma (OK)</option><option value="OR">Oregon (OR)</option><option value="PA">Pennsylvania (PA)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="RI">Rhode Island (RI)</option><option value="SC">South Carolina (SC)</option><option value="SD">South Dakota (SD)</option><option value="TN">Tennessee (TN)</option><option value="TX">Texas (TX)</option><option value="UT">Utah (UT)</option><option value="VT">Vermont (VT)</option><option value="VA">Virginia (VA)</option><option value="WA">Washington (WA)</option><option value="WV">West Virginia (WV)</option><option value="WI">Wisconsin (WI)</option><option value="WY">Wyoming (WY)</option><option value="DC">District of Columbia (DC)</option><option value="AS">American Samoa (AS)</option><option value="GU">Guam (GU)</option><option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands (MP)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands (UM)</option><option value="VI">Virgin Islands (VI)</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if (this.value == 'CA') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AB">Alberta (AB)</option><option value="BC">British Columbia (BC)</option><option value="MB">Manitoba (MB)</option><option value="NB">New Brunswick (NB)</option><option value="NL">Newfoundland and Labrador (NL)</option><option value="NS">Nova Scotia (NS)</option><option value="ON">Ontario (ON)</option><option value="PE">Prince Edward Island (PE)</option><option value="QC">Quebec (QC)</option><option value="SK">Saskatchewan (SK)</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if (this.value == 'DE') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="BW">Baden-Württemberg (BW)</option><option value="BY">Bayern (BY)</option><option value="BE">Berlin (BE)</option><option value="BB">Brandeburg (BB)</option><option value="HB">Bremen (HB)</option><option value="HH">Hamburg (HH)</option><option value="HE">Hessen (HE)</option><option value="MV">Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV)</option><option value="NI">Niedersachsen (NI)</option><option value="NW">Nordrhein-Westfalen (NW)</option><option value="RP">Rheinland-Pfalz (RP)</option><option value="SL">Saarland (SL)</option><option value="SN">Sachsen (SN)</option><option value ="SA">Sachsen-Anhalt (SA)</option><option value="SH">Schleswig-Holstein (SH)</option><option value="TH">Thüringen</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().hide();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<input name="data[Quote][state]" maxlength="255" type="text" id="state-3046" value="">');
}
});
</script>
<a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: QUOTE MODAL --><a href="#" id="bioruptorpico2" data-reveal-id="quoteModal-3046" class="quote_btn" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Bioruptor® Pico sonication device</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
'
$related = array(
'id' => '3046',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://go.diagenode.com/bioruptor-upgrade"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-br-trade.png" /></a></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p><span>The Bioruptor® Pico is the latest innovation in shearing and represents a new breakthrough as an all-in-one shearing system capable of shearing samples from 150 bp to 1 kb. </span>Since 2004, Diagenode has accumulated <strong>shearing expertise</strong> to design the Bioruptor® Pico and guarantee the best experience with the <strong>sample preparation</strong> for <strong>number of applications -- in various fields of studies</strong> including environmental research, toxicology, genomics and epigenomics, cancer research, stem cells and development, neuroscience, clinical applications, agriculture, and many more.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
</div>
<p>The Bioruptor Pico shearing accessories and consumables have been developed to allow <strong>flexibility in sample volumes</strong> (20 µl - 2 ml) and a <strong>fast parallel processing of samples</strong> (up to 16 samples simultaneously). <span>The built-in cooling system (Bioruptor® Cooler) ensures high precision <strong>temperature control</strong>. The <strong>user-friendly interface</strong> has been designed for any researcher, providing an easy and advanced modes that give both beginners and experienced users the right level of control. </span></p>
<p>In addition, Diagenode provides fully-validated tubes that remain <strong>budget-friendly with low operating cost</strong> (< 1€/$/DNA sample) and shearing kits for best sample quality. <span></span></p>
<p><strong>Application versatility</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>DNA shearing for Next-Generation-Sequencing</li>
<li>Chromatin shearing</li>
<li>RNA shearing</li>
<li>Protein extraction from tissues and cells (also for mass spectrometry)</li>
<li>FFPE DNA extraction</li>
<li>Protein aggregation studies</li>
<li>CUT&RUN - shearing of input DNA for NGS</li>
</ul>
<div style="background-color: #f1f3f4; margin: 10px; padding: 50px;">
<p><strong>Bioruptor Pico: Recommended for CUT&RUN sequencing for input DNA</strong><br /><br /> By combining antibody-targeted controlled cleavage by MNase and NGS, <strong>CUT&RUN sequencing</strong> can be used to identify protein-DNA binding sites genome-wide. CUT&RUN works by using the DNA cleaving activity of a Protein A-fused MNase to isolate DNA that is bound by a protein of interest. This targeted digestion is controlled by the addition of calcium, which MNase requires for its nuclease activity. After MNase digestion, short DNA fragments are released and can then be purified for subsequent library preparation and high-throughput sequencing. While CUT&RUN does not require mechanical shearing chromatin given the enzymatic approach, sonication is highly recommended for the fragmentation of the input DNA (used to compare the enriched sample) in order to be compatible with downstream NGS. The Bioruptor Pico is the ideal instrument of choice for generating optimal DNA fragments with a tight distribution, assuring excellent library prep and excellent sequencing results for your CUT&RUN assay.<br /><br /> <strong>Explore the Bioruptor Pico now.</strong></p>
</div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for Chromatin shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-reproducibility-is-priority.jpg" /></center></div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/pages/form-demo"> <img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for RNA shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-request-demo.jpg" /></a></center></div>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label1' => 'Specifications',
'info1' => '<center><img alt="Ultrasonic Sonicator" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-table.jpg" /></center>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label2' => 'View accessories & consumables for Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico',
'info2' => '<h3>Shearing Accessories</h3>
<table style="width: 641px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Catalog number</td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Throughput</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-2-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.2 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201144</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">16 samples</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.65 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201143</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">12 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 1.5 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201140</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-sonication-accessories-for-bioruptor-standard-plus-pico-1-pack">15 ml sonication accessories</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01200016</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Shearing Consumables</h3>
<table style="width: 646px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;">Catalog Number</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/02ml-microtubes-for-bioruptor-pico">0.2 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010020</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-500-tubes">0.65 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010011</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-with-caps-300-tubes">1.5 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010016</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-50-pc">15 ml Pico Tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010017</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-sonication-beads-50-rxns">15 ml Pico Tubes & sonication beads</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C01020031</span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/shearing_technology/bioruptor_accessories/TDS-BioruptorTubes.pdf">Find datasheet for Diagenode tubes here</a></p>
<p><a href="../documents/bioruptor-organigram-tubes">Which tubes for which Bioruptor®?</a></p>',
'label3' => 'Available shearing Kits',
'info3' => '<p>Diagenode has optimized a range of solutions for <strong>successful chromatin preparation</strong>. Chromatin EasyShear Kits together with the Pico ultrasonicator combine the benefits of efficient cell lysis and chromatin shearing, while keeping epitopes accessible to the antibody, critical for efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation. Each Chromatin EasyShear Kit provides optimized reagents and a thoroughly validated protocol according to your specific experimental needs. SDS concentration is adapted to each workflow taking into account target-specific requirements.</p>
<p>For best results, choose your desired ChIP kit followed by the corresponding Chromatin EasyShear Kit (to optimize chromatin shearing ). The Chromatin EasyShear Kits can be used independently of Diagenode’s ChIP kits for chromatin preparation prior to any chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol. Choose an appropriate kit for your specific experimental needs.</p>
<h2>Kit choice guide</h2>
<table style="border: 0;" valign="center">
<tbody>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<th class="text-center"></th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE TYPE</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE INPUT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">KIT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SDS<br /> CONCENTRATION</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">NUCLEI<br /> ISOLATION</th>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="5"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-histones.png" /></td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">< 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-optimization-kit-high-sds-100-million-cells">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />High SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">1%</td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/cross-unvalid-green.jpg" width="18" height="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">> 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">PLANT TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-plant-chip-seq-kit">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />for Plant</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.5%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="6"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-tf.png" /></td>
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="extra-spaced">
<h3>Guide for optimal chromatin preparation using Chromatin EasyShear Kits <i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/pages/chromatin-prep-easyshear-kit-guide">Read more</a></h3>
</div>
<p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B01080010',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'B01080010-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '00-Machine',
'price_EUR' => '27600',
'price_USD' => '31000',
'price_GBP' => '24000',
'price_JPY' => '4522260',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '77500',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => true,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '',
'slug' => 'bioruptorpico2',
'meta_title' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'modified' => '2024-12-19 15:08:43',
'created' => '2020-01-09 16:27:17',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
'id' => '4858',
'product_id' => '1879',
'related_id' => '3046'
),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1803',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-1.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:55:07',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:52:54',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '1804',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-2.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:08',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:08',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '1805',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-3.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:46',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:46',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '1806',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-4.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:56',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:56',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '1807',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-5.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:54:06',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:54:06',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '1772',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B010600010.jpg',
'alt' => 'B010600010',
'modified' => '2018-02-14 15:41:46',
'created' => '2018-02-14 15:41:46',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
)
)
$rrbs_service = array(
(int) 0 => (int) 1894,
(int) 1 => (int) 1895
)
$chipseq_service = array(
(int) 0 => (int) 2683,
(int) 1 => (int) 1835,
(int) 2 => (int) 1836,
(int) 3 => (int) 2684,
(int) 4 => (int) 1838,
(int) 5 => (int) 1839,
(int) 6 => (int) 1856
)
$labelize = object(Closure) {
}
$old_catalog_number = ' <span style="color:#CCC">(mc-magme-048)</span>'
$country_code = 'US'
$other_format = array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
)
$label = '<img src="/img/banners/banner-customizer-back.png" alt=""/>'
$document = array(
'id' => '1166',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit ',
'description' => '',
'image_id' => null,
'type' => 'Manual',
'url' => 'files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-manual-c02010020-21',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => '',
'modified' => '2022-11-22 15:50:08',
'created' => '2022-11-22 15:41:49',
'ProductsDocument' => array(
'id' => '3257',
'product_id' => '1879',
'document_id' => '1166'
)
)
$sds = array(
'id' => '650',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE nl',
'language' => 'nl',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-nl-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
'id' => '1194',
'product_id' => '1879',
'safety_sheet_id' => '650'
)
)
$publication = array(
'id' => '2857',
'name' => 'Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo',
'authors' => 'Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associated with disturbed blood flow. DNA methylation is a powerful epigenetic regulator of endothelial transcription recently associated with flow characteristics. We investigated differential DNA methylation in flow region-specific aortic endothelial cells in vivo in adult domestic male and female swine.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Genome-wide DNA methylation was profiled in endothelial cells (EC) isolated from two robust locations of differing patho-susceptibility:--an athero-susceptible site located at the inner curvature of the aortic arch (AA) and an athero-protected region in the descending thoracic (DT) aorta. Complete methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) identified over 5500 endothelial differentially methylated regions (DMRs). DMR density was significantly enriched in exons and 5'UTR sequences of annotated genes, 60 of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. The set of DMR-associated genes was enriched in transcriptional regulation, pattern specification HOX loci, oxidative stress and the ER stress adaptive pathway, all categories linked to athero-susceptible endothelium. Examination of the relationship between DMR and mRNA in HOXA genes demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between CpG island promoter methylation and gene expression. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) confirmed differential CpG methylation of HOXA genes, the ER stress gene ATF4, inflammatory regulator microRNA-10a and ARHGAP25 that encodes a negative regulator of Rho GTPases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Gender-specific DMRs associated with ciliogenesis that may be linked to defects in cilia development were also identified in AA DMRs.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">An endothelial methylome analysis identifies epigenetic DMR characteristics associated with transcriptional regulation in regions of atherosusceptibility in swine aorta in vivo. The data represent the first methylome blueprint for spatio-temporal analyses of lesion susceptibility predisposing to endothelial dysfunction in complex flow environments in vivo.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-07-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12864-015-1656-4',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'created' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
'id' => '550',
'product_id' => '1879',
'publication_id' => '2857'
)
)
$externalLink = ' <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682" target="_blank"><i class="fa fa-external-link"></i></a>'include - APP/View/Products/view.ctp, line 755
View::_evaluate() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 971
View::_render() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 933
View::render() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 473
Controller::render() - CORE/Cake/Controller/Controller.php, line 963
ProductsController::slug() - APP/Controller/ProductsController.php, line 1052
ReflectionMethod::invokeArgs() - [internal], line ??
Controller::invokeAction() - CORE/Cake/Controller/Controller.php, line 491
Dispatcher::_invoke() - CORE/Cake/Routing/Dispatcher.php, line 193
Dispatcher::dispatch() - CORE/Cake/Routing/Dispatcher.php, line 167
[main] - APP/webroot/index.php, line 118
Notice (8): Undefined variable: message [APP/View/Products/view.ctp, line 755]Code Context<!-- BEGIN: REQUEST_FORM MODAL -->
<div id="request_formModal" class="reveal-modal medium" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<?= $this->element('Forms/simple_form', array('solution_of_interest' => $solution_of_interest, 'header' => $header, 'message' => $message, 'campaign_id' => $campaign_id)) ?>
$viewFile = '/home/website-server/www/app/View/Products/view.ctp'
$dataForView = array(
'language' => 'en',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'product' => array(
'Product' => array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'locale' => 'eng'
),
'Antibody' => array(
'host' => '*****',
'id' => null,
'name' => null,
'description' => null,
'clonality' => null,
'isotype' => null,
'lot' => null,
'concentration' => null,
'reactivity' => null,
'type' => null,
'purity' => null,
'classification' => null,
'application_table' => null,
'storage_conditions' => null,
'storage_buffer' => null,
'precautions' => null,
'uniprot_acc' => null,
'slug' => null,
'meta_keywords' => null,
'meta_description' => null,
'modified' => null,
'created' => null,
'select_label' => null
),
'Slave' => array(),
'Group' => array(
'Group' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Master' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Product' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Related' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Application' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Category' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Document' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Feature' => array(),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Promotion' => array(),
'Protocol' => array(),
'Publication' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 7 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 8 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 9 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 10 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 11 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 12 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 13 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 14 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 15 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 16 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 17 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 18 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 19 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 20 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 21 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 22 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 23 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 24 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 25 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 26 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 27 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 28 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 29 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 30 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 31 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 32 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 33 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 34 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 35 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 36 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 37 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 38 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 39 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 40 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 41 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 42 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 43 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 44 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 45 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 46 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 47 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 48 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 49 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 50 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 51 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 52 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 53 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 54 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 55 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 56 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 57 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 58 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 59 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 60 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 61 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 62 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 63 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 64 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 65 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 66 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 67 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 68 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 69 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 70 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 71 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 72 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 73 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 74 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 75 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 76 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 77 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 78 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 79 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 80 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 81 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 82 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 83 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 84 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 85 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 86 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 87 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 88 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 89 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 90 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 91 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 92 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 93 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 94 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 95 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 96 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 97 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 98 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 99 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 100 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 101 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 102 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 103 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 104 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 105 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Testimonial' => array(),
'Area' => array(),
'SafetySheet' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 7 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'meta_canonical' => 'https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns'
)
$language = 'en'
$meta_keywords = ''
$meta_description = 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.'
$meta_title = 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA'
$product = array(
'Product' => array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'locale' => 'eng'
),
'Antibody' => array(
'host' => '*****',
'id' => null,
'name' => null,
'description' => null,
'clonality' => null,
'isotype' => null,
'lot' => null,
'concentration' => null,
'reactivity' => null,
'type' => null,
'purity' => null,
'classification' => null,
'application_table' => null,
'storage_conditions' => null,
'storage_buffer' => null,
'precautions' => null,
'uniprot_acc' => null,
'slug' => null,
'meta_keywords' => null,
'meta_description' => null,
'modified' => null,
'created' => null,
'select_label' => null
),
'Slave' => array(),
'Group' => array(
'Group' => array(
'id' => '7',
'name' => 'C02010021',
'product_id' => '1880',
'modified' => '2016-02-18 17:02:55',
'created' => '2016-02-18 17:02:55'
),
'Master' => array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
),
'Product' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Related' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1819',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'description' => '<p>The DiaMag02 is a powerful magnet which has been designed for controlled and rapid isolation of your DNA bound to magnetic beads. It allows for processing 16 samples at a time.</p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B04000001',
'old_catalog_number' => 'kch-816-001',
'sf_code' => 'B04000001-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '250',
'price_USD' => '240',
'price_GBP' => '220',
'price_JPY' => '40960',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '600',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit',
'meta_title' => 'DiaMag02 - magnetic rack',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'DiaMag02 - magnetic rack',
'modified' => '2019-06-11 16:27:35',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '2597',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1043-050, -500 is specific to a CpG region of the TSH2B gene from rat. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17031043-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1043-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17031043-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:06:44',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '2599',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1046-050, -500 is specific to a promoter region of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from rat. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17031046-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1046-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17031046-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:05:49',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '2593',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1042-050, -500 is specific to a CpG region of the TSH2B gene from mouse. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17021042-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1042-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17021042-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:10:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '2595',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair Cat. No. C17021045 is specific to a promoter region of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from mouse. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17021045-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1045-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17021045-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '01-Accessory',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'modified' => '2021-01-18 10:00:33',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '2945',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit - ordering reference: C02010021',
'description' => '<p><span></span>The reference C02010014 has been replaced by <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns">C02010021</a><span>. </span> </p>
<p><span>Perform </span><strong>MeDIP</strong><span><span> </span>(Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation) <span>on the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/sx-8g-ip-star-compact-automated-system-1-unit" target="_blank">SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System</a> </span>followed by<span> </span></span><strong>qPCR</strong><span><span> </span>to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using </span><span>5-methylcytosine</span><span><span> </span>antibody. Our kit contains high quality reagents to get the h</span><span>ighest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</span></p>
<p>Diagenode’s Auto MagMeDIP qPCR is available in two formats (10 and 48 IPs) and has been optimized on the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/sx-8g-ip-star-compact-automated-system-1-unit" target="_blank">SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System</a> enabling highly reproducible results and allowing for high throughput assays.</p>
<h3><span>Characteristics</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Generate highly consistent results with internal controls in 24h</li>
<li>Minimize error with many reagents in 1 tube</li>
<li>Optimized purification (DIB - DNA isolation buffer)</li>
<li>Allows direct correlation between IP’d material & methylation status</li>
</ul>
<p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/magmedip-kit-validated-using-bioruptor.jpg" alt="MagMeDIP kit validated using Bioruptor" /></p>
<p><strong><em>Figure 1.</em></strong><em><span> </span><strong>IP results obtained with Diagenode Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit.</strong><span> </span>MeDIP assays were performed manually using DNA from blood, Gm12878, Hela and U20S cells and the Auto MagMeDIP qPCR kit (Diagenode). The DNA was prepared with the XL GenDNA Extraction Module included. The IP was performed including the kit meDNA and unDNA spike-in controls, together with the human DNA sample controls. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs also included in this kit.</em></p>
<p style="text-align: center;"><em><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/AutomatedMeDIP_9h.png" alt="" width="678" height="365" /></em></p>
<p style="text-align: justify;"><em><strong>Figure<span> </span>2. Automated MeDIP (9h). </strong>IP reaction was performed on the SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System with the anti-5-mC antibody. Methylated and unmethylated DNA were used as internal controls. Unmethylated DNA region of GADPH and a methylated DNA region of AlphaX1 were used to test DNA sample-IP efficiency. DNA has been isolated by using DNA Isolation Buffer (DIB).</em></p>
<p></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '48 rxns',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010014',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'C02010014-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '',
'price_USD' => '',
'price_GBP' => '',
'price_JPY' => '',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'Japan',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => true,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'auto-magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x48',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x48',
'modified' => '2023-03-20 12:50:08',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '3046',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://go.diagenode.com/bioruptor-upgrade"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-br-trade.png" /></a></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p><span>The Bioruptor® Pico is the latest innovation in shearing and represents a new breakthrough as an all-in-one shearing system capable of shearing samples from 150 bp to 1 kb. </span>Since 2004, Diagenode has accumulated <strong>shearing expertise</strong> to design the Bioruptor® Pico and guarantee the best experience with the <strong>sample preparation</strong> for <strong>number of applications -- in various fields of studies</strong> including environmental research, toxicology, genomics and epigenomics, cancer research, stem cells and development, neuroscience, clinical applications, agriculture, and many more.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
</div>
<p>The Bioruptor Pico shearing accessories and consumables have been developed to allow <strong>flexibility in sample volumes</strong> (20 µl - 2 ml) and a <strong>fast parallel processing of samples</strong> (up to 16 samples simultaneously). <span>The built-in cooling system (Bioruptor® Cooler) ensures high precision <strong>temperature control</strong>. The <strong>user-friendly interface</strong> has been designed for any researcher, providing an easy and advanced modes that give both beginners and experienced users the right level of control. </span></p>
<p>In addition, Diagenode provides fully-validated tubes that remain <strong>budget-friendly with low operating cost</strong> (< 1€/$/DNA sample) and shearing kits for best sample quality. <span></span></p>
<p><strong>Application versatility</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>DNA shearing for Next-Generation-Sequencing</li>
<li>Chromatin shearing</li>
<li>RNA shearing</li>
<li>Protein extraction from tissues and cells (also for mass spectrometry)</li>
<li>FFPE DNA extraction</li>
<li>Protein aggregation studies</li>
<li>CUT&RUN - shearing of input DNA for NGS</li>
</ul>
<div style="background-color: #f1f3f4; margin: 10px; padding: 50px;">
<p><strong>Bioruptor Pico: Recommended for CUT&RUN sequencing for input DNA</strong><br /><br /> By combining antibody-targeted controlled cleavage by MNase and NGS, <strong>CUT&RUN sequencing</strong> can be used to identify protein-DNA binding sites genome-wide. CUT&RUN works by using the DNA cleaving activity of a Protein A-fused MNase to isolate DNA that is bound by a protein of interest. This targeted digestion is controlled by the addition of calcium, which MNase requires for its nuclease activity. After MNase digestion, short DNA fragments are released and can then be purified for subsequent library preparation and high-throughput sequencing. While CUT&RUN does not require mechanical shearing chromatin given the enzymatic approach, sonication is highly recommended for the fragmentation of the input DNA (used to compare the enriched sample) in order to be compatible with downstream NGS. The Bioruptor Pico is the ideal instrument of choice for generating optimal DNA fragments with a tight distribution, assuring excellent library prep and excellent sequencing results for your CUT&RUN assay.<br /><br /> <strong>Explore the Bioruptor Pico now.</strong></p>
</div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for Chromatin shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-reproducibility-is-priority.jpg" /></center></div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/pages/form-demo"> <img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for RNA shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-request-demo.jpg" /></a></center></div>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label1' => 'Specifications',
'info1' => '<center><img alt="Ultrasonic Sonicator" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-table.jpg" /></center>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label2' => 'View accessories & consumables for Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico',
'info2' => '<h3>Shearing Accessories</h3>
<table style="width: 641px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Catalog number</td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Throughput</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-2-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.2 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201144</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">16 samples</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.65 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201143</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">12 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 1.5 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201140</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-sonication-accessories-for-bioruptor-standard-plus-pico-1-pack">15 ml sonication accessories</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01200016</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Shearing Consumables</h3>
<table style="width: 646px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;">Catalog Number</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/02ml-microtubes-for-bioruptor-pico">0.2 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010020</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-500-tubes">0.65 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010011</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-with-caps-300-tubes">1.5 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010016</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-50-pc">15 ml Pico Tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010017</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-sonication-beads-50-rxns">15 ml Pico Tubes & sonication beads</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C01020031</span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/shearing_technology/bioruptor_accessories/TDS-BioruptorTubes.pdf">Find datasheet for Diagenode tubes here</a></p>
<p><a href="../documents/bioruptor-organigram-tubes">Which tubes for which Bioruptor®?</a></p>',
'label3' => 'Available shearing Kits',
'info3' => '<p>Diagenode has optimized a range of solutions for <strong>successful chromatin preparation</strong>. Chromatin EasyShear Kits together with the Pico ultrasonicator combine the benefits of efficient cell lysis and chromatin shearing, while keeping epitopes accessible to the antibody, critical for efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation. Each Chromatin EasyShear Kit provides optimized reagents and a thoroughly validated protocol according to your specific experimental needs. SDS concentration is adapted to each workflow taking into account target-specific requirements.</p>
<p>For best results, choose your desired ChIP kit followed by the corresponding Chromatin EasyShear Kit (to optimize chromatin shearing ). The Chromatin EasyShear Kits can be used independently of Diagenode’s ChIP kits for chromatin preparation prior to any chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol. Choose an appropriate kit for your specific experimental needs.</p>
<h2>Kit choice guide</h2>
<table style="border: 0;" valign="center">
<tbody>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<th class="text-center"></th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE TYPE</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE INPUT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">KIT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SDS<br /> CONCENTRATION</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">NUCLEI<br /> ISOLATION</th>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="5"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-histones.png" /></td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">< 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-optimization-kit-high-sds-100-million-cells">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />High SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">1%</td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/cross-unvalid-green.jpg" width="18" height="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">> 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">PLANT TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-plant-chip-seq-kit">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />for Plant</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.5%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="6"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-tf.png" /></td>
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="extra-spaced">
<h3>Guide for optimal chromatin preparation using Chromatin EasyShear Kits <i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/pages/chromatin-prep-easyshear-kit-guide">Read more</a></h3>
</div>
<p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B01080010',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'B01080010-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '00-Machine',
'price_EUR' => '27600',
'price_USD' => '31000',
'price_GBP' => '24000',
'price_JPY' => '4522260',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '77500',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => true,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '',
'slug' => 'bioruptorpico2',
'meta_title' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'modified' => '2024-12-19 15:08:43',
'created' => '2020-01-09 16:27:17',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Application' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '7',
'position' => '10',
'parent_id' => '1',
'name' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'description' => '<div class="row extra-spaced">
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3>Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns"><span>The Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation is based on the affinity purification of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA using, respectively, an antibody directed against 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in the case of MeDIP or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in the case of hMeDIP.</span><br />
<h2></h2>
<h2>How it works</h2>
<p>In brief, Methyl DNA IP is performed as follows: Genomic DNA from cultured cells or tissues is prepared, sheared, and then denatured. Then, immunoselection and immunoprecipitation can take place using the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads. After isolation and purification is performed, the IP’d methylated DNA is ready for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<h2>Applications</h2>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> qPCR analysis</a></div>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-seq-package-V2-x10" class="center alert radius button"> NGS analysis </a></div>
<h2>Advantages</h2>
<ul style="font-size: 19px;" class="nobullet">
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Unaffected</strong> DNA</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>High enrichment</strong> yield</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Robust</strong> & <strong>reproducible</strong> techniques</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>NGS</strong> compatible</li>
</ul>
<h2></h2>
</div>
</div>
<div id="gtx-trans" style="position: absolute; left: 17px; top: 652.938px;">
<div class="gtx-trans-icon"></div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'slug' => 'methylated-dna-immunoprecipitation',
'meta_keywords' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation,Epigenetic,DNA Methylation,qPCR,5 methylcytosine (5-mC)',
'meta_description' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation method is based on the affinity purification of methylated DNA using an antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine (5-mC). ',
'meta_title' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation(MeDIP) - Dna methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2021-08-19 12:08:03',
'created' => '2014-09-14 05:33:34',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '1',
'position' => '9',
'parent_id' => null,
'name' => 'DNA Methylation',
'description' => '<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns">
<div style="text-align: justify;" class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h2>Complete solutions for DNA methylation studies</h2>
<p>Whether you are experienced or new to the field of DNA methylation, Diagenode has everything you need to make your assay as easy and convenient as possible while ensuring consistent data between samples and experiments. Diagenode offers sonication instruments, reagent kits, high quality antibodies, and high-throughput automation capability to address all of your specific DNA methylation analysis requirements.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns text-center"><a href="../landing-pages/dna-methylation-grant-applications"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-dna-grant.png" alt="" /></a></div>
<div style="text-align: justify;" class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark and is the most widely studied topic in epigenetics. <em>In vivo</em>, DNA is methylated following DNA replication and is involved in a number of biological processes including the regulation of imprinted genes, X chromosome inactivation. and tumor suppressor gene silencing in cancer cells. Methylation often occurs in cytosine-guanine rich regions of DNA (CpG islands), which are commonly upstream of promoter regions.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns"><br /><br />
<ul class="accordion" data-accordion="">
<li class="accordion-navigation"><a href="#dnamethyl"><i class="fa fa-caret-right"></i> Learn more</a>
<div id="dnamethyl" class="content">5-methylcytosine (5-mC) has been known for a long time as the only modification of DNA for epigenetic regulation. In 2009, however, Kriaucionis discovered a second methylated cytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC). The so-called 6th base, is generated by enzymatic conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine by the TET family of oxygenases. Early reports suggested that 5-hmC may represent an intermediate of active demethylation in a new pathway which demethylates DNA, converting 5-mC to cytosine. Recent evidence fuel this hypothesis suggesting that further oxidation of the hydroxymethyl group leads to a formyl or carboxyl group followed by either deformylation or decarboxylation. The formyl and carboxyl groups of 5-formylcytosine (5-fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5-caC) could be enzymatically removed without excision of the base.
<p class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/categories/kits_dna/dna_methylation_variants.jpg" /></p>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
<br />
<h2>Main DNA methylation technologies</h2>
<p style="text-align: justify;">Overview of the <span style="font-weight: 400;">three main approaches for studying DNA methylation.</span></p>
<div class="row">
<ol>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Chemical modification with bisulfite – Bisulfite conversion</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Enrichment of methylated DNA (including MeDIP and MBD)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Treatment with methylation-sensitive or dependent restriction enzymes</span></li>
</ol>
<p><span style="font-weight: 400;"> </span></p>
<div class="row">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>Description</th>
<th width="350">Features</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><strong>Bisulfite conversion</strong></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">Chemical conversion of unmethylated cytosine to uracil. Methylated cytosines are protected from this conversion allowing to determine DNA methylation at single nucleotide resolution.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Single nucleotide resolution</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Quantitative analysis - methylation rate (%)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Gold standard and well studied</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Compatible with automation</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><b>Methylated DNA enrichment</b></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">(Hydroxy-)Methylated DNA is enriched by using specific antibodies (hMeDIP or MeDIP) or proteins (MBD) that specifically bind methylated CpG sites in fragmented genomic DNA.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Resolution depends on the fragment size of the enriched methylated DNA (300 bp)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Qualitative analysis</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Compatible with automation</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><strong>Restriction enzyme-based digestion</strong></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">Use of (hydroxy)methylation-sensitive or (hydroxy)methylation-dependent restriction enzymes for DNA methylation analysis at specific sites.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Determination of methylation status is limited by the enzyme recognition site</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Easy to use</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="large-12 columns"></div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => true,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'slug' => 'epigenetics-dna-methylation',
'meta_keywords' => 'Epigenetics, DNA Methylation,5-hmC monoclonal antibody,hMeDIP,Bisulfite conversion,Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'meta_description' => 'Complete, optimized solutions for analyzing DNA methylation manually or on our automated system.',
'meta_title' => 'DNA Methylation - Bisulfite sequencing - Epigenetics | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2019-03-25 10:07:27',
'created' => '2015-05-03 13:47:53',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '6',
'position' => '10',
'parent_id' => '1',
'name' => 'メチル化DNA結合タンパク質',
'description' => '<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns">MBD方法は、メチル化DNAに対するH6-GST-MBD融合タンパク質の非常に高い親和性に基づいています。 このタンパク質は、N末端His6タグを含むグルタチオン-S-トランスフェラーゼ(GST)とのC末端融合物として、ヒトMeCP2のメチル結合ドメイン(MBD)を含有します。 このH6-GST-MBD融合タンパク質を用いて、メチル化CpGを含むDNAを特異的に単離する事が可能です。<br /><br />DiagenodeのMethylCap®キットは、二本鎖DNAの高濃縮と、メチル化CpG密度の関数における微分分画を可能にします。 分画はサンプルの複雑さを軽減し、次世代のシーケンシングを容易にします。 MethylCapアッセイに先立ち、DNAを最初に抽出し、Picoruptorソニケーターを用いて断片化します。<br />
<h3>概要</h3>
<p class="text-center"><br /><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/applications/methyl_binding_domain_overview.jpg" /></p>
</div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => false,
'slug' => 'methylbinding-domain-protein',
'meta_keywords' => 'Epigenetic,Methylbinding Domain Protein,MBD,DNA methylation,DNA replication,MethylCap,MethylCap assay,',
'meta_description' => 'Methylbinding Domain Protein(MBD) approach is based on the very high affinity of a H6-GST-MBD fusion protein for methylated DNA. This protein consists of the methyl binding domain (MBD) of human MeCP2, as a C-terminal fusion with Glutathione-S-transferase',
'meta_title' => 'Epigenetic Methylbinding Domain Protein(MBD) - DNA methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2019-03-22 12:32:12',
'created' => '2015-06-02 17:05:42',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Category' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '52',
'position' => '2',
'parent_id' => '12',
'name' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-seq-package-V2-x10"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/b-email-magmedip.png" /></a></p>
<p>The Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation is based on the affinity purification of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA using, respectively, an antibody directed against 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in the case of MeDIP or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in the case of hMeDIP.</p>
<h2>How it works</h2>
<p>In brief, Methyl DNA IP is performed as follows: Genomic DNA from cultured cells or tissues is prepared, sheared, and then denatured. Then, immunoselection and immunoprecipitation can take place using the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads. After isolation and purification is performed, the IP’d methylated DNA is ready for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<h2>Applications</h2>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> qPCR analysis</a></div>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> NGS analysis </a></div>
<h2>Advantages</h2>
<ul style="font-size: 19px;" class="nobullet">
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Unaffected</strong> DNA</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>High enrichment</strong> yield</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Robust</strong> & <strong>reproducible</strong> techniques</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>NGS</strong> compatible</li>
</ul>
<h2></h2>',
'no_promo' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'hide' => false,
'all_format' => false,
'is_antibody' => false,
'slug' => 'methylated-dna-immunoprecipitation',
'cookies_tag_id' => null,
'meta_keywords' => 'Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation,DNA methylation',
'meta_description' => 'Diagenode provides Antibody-based isolation of methylated DNA for DNA immunoprecipitation ',
'meta_title' => 'Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation for DNA Methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2022-11-25 10:46:50',
'created' => '2015-07-08 09:30:57',
'ProductsCategory' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'CookiesTag' => array([maximum depth reached])
)
),
'Document' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1166',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit ',
'description' => '',
'image_id' => null,
'type' => 'Manual',
'url' => 'files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-manual-c02010020-21',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => '',
'modified' => '2022-11-22 15:50:08',
'created' => '2022-11-22 15:41:49',
'ProductsDocument' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Feature' => array(),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1796',
'name' => 'https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/C02010020-magmedip-qpcr.jpg',
'alt' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10',
'modified' => '2019-04-24 17:06:59',
'created' => '2019-04-24 17:04:52',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Promotion' => array(),
'Protocol' => array(),
'Publication' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '4989',
'name' => 'Differential methylation of circulating free DNA assessed through cfMeDiP as a new tool for breast cancer diagnosis and detection of BRCA1/2 mutation',
'authors' => 'Piera Grisolia et al.',
'description' => '<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Background</h3>
<p>Recent studies have highlighted the importance of the cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation profile in detecting breast cancer (BC) and its different subtypes. We investigated whether plasma cfDNA methylation, using cell-free Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation and High-Throughput Sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq), may be informative in characterizing breast cancer in patients with BRCA1/2 germline mutations for early cancer detection and response to therapy.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Methods</h3>
<p>We enrolled 23 BC patients with germline mutation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, 19 healthy controls without BRCA1/2 mutation, and two healthy individuals who carried BRCA1/2 mutations. Blood samples were collected for all study subjects at the diagnosis, and plasma was isolated by centrifugation. Cell-free DNA was extracted from 1 mL of plasma, and cfMeDIP-seq was performed for each sample. Shallow whole genome sequencing was performed on the immuno-precipitated samples. Then, the differentially methylated 300-bp regions (DMRs) between 25 BRCA germline mutation carriers and 19 non-carriers were identified. DMRs were compared with tumor-specific regions from public datasets to perform an unbiased analysis. Finally, two statistical classifiers were trained based on the GLMnet and random forest model to evaluate if the identified DMRs could discriminate BRCA-positive from healthy samples.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Results</h3>
<p>We identified 7,095 hypermethylated and 212 hypomethylated regions in 25 BRCA germline mutation carriers compared to 19 controls. These regions discriminate tumors from healthy samples with high accuracy and sensitivity. We show that the circulating tumor DNA of BRCA1/2 mutant breast cancers is characterized by the hypomethylation of genes involved in DNA repair and cell cycle. We uncovered the TFs associated with these DRMs and identified that proteins of the Erythroblast Transformation Specific (ETS) family are particularly active in the hypermethylated regions. Finally, we assessed that these regions could discriminate between BRCA positives from healthy samples with an AUC of 0.95, a sensitivity of 88%, and a specificity of 94.74%.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p>Our study emphasizes the importance of tumor cell-derived DNA methylation in BC, reporting a different methylation profile between patients carrying mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, and wild-type controls. Our minimally invasive approach could allow early cancer diagnosis, assessment of minimal residual disease, and monitoring of response to therapy.</p>',
'date' => '2024-10-15',
'pmid' => 'https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-024-05734-2',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-05734-2',
'modified' => '2024-10-18 11:43:43',
'created' => '2024-10-18 11:43:43',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '4981',
'name' => 'Prediction of brain metastasis development with DNA methylation signatures',
'authors' => 'Jeffrey A. Zuccato et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Brain metastases (BMs) are the most common and among the deadliest brain tumors. Currently, there are no reliable predictors of BM development from primary cancer, which limits early intervention. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common BM source and here we obtained 402 tumor and plasma samples from a large cohort of patients with LUAD with or without BM (</span><i>n</i><span> = 346). LUAD DNA methylation signatures were evaluated to build and validate an accurate model predicting BM development from LUAD, which was integrated with clinical factors to provide comprehensive patient-specific BM risk probabilities in a nomogram. Additionally, immune and cell interaction gene sets were differentially methylated at promoters in BM versus paired primary LUAD and had aligning dysregulation in the proteome. Immune cells were differentially abundant in BM versus LUAD. Finally, liquid biomarkers identified from methylated cell-free DNA sequenced in plasma were used to generate and validate accurate classifiers for early BM detection. Overall, LUAD methylomes can be leveraged to predict and noninvasively identify BM, moving toward improved patient outcomes with personalized treatment.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-10-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03286-y',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03286-y',
'modified' => '2024-10-11 09:58:45',
'created' => '2024-10-11 09:58:45',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '4957',
'name' => 'Association between TNF-α, cortisol levels, and exposure to PM10 and PM2.5: a pilot study',
'authors' => 'Dolcini J. et al.',
'description' => '<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Purpose</h3>
<p>The most harmful atmospheric pollutant for human health is particulate matter (PM). We analyzed the correlation between short-term lag exposure to PM10 and PM2.5, salivary cortisol and TNF-α level, and methylation levels of the TNF-α promoter.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Methods</h3>
<p>A pilot study including 20 subjects. Eight salivary samples for each subject at various times of the day were collected for comparing cortisol levels and TNFα detection. TNFα promoter methylation levels on salivary DNA were analyzed. Regression analyses were performed using generalized linear mixed models between the different outcomes and 4, 3, 2 and 1 day’s lag values of PM10/PM2.5.Generalized additive mixed model (GAMM) was used to evaluate any potential deviation from linearity.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Results</h3>
<p>Area under the curve with respect to the ground (AUCg) showed a statistically positive association with 4-, 3-, 2-, and 1-day lag of exposure to PM10. Area under the curve with respect to the increase (AUCi) showed a statistically negative association with 4-, 3- and 1-day lag of exposure to PM10. TNFα showed statistically significant association with both exposures, PM10 and PM2.5, at 4-, 3-, 2-, and 1-day lag.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p>Regarding cortisol levels there is an increase of overall hormone levels but a less dynamism of the system to answer to external stressors. Increase of TNF-α may reflect increased levels of oxidative stress and inflammation due to pollution exposure.</p>',
'date' => '2024-08-07',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12302-024-00961-2',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-024-00961-2',
'modified' => '2024-09-02 10:01:14',
'created' => '2024-09-02 10:00:08',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '4942',
'name' => 'Epigenomic signatures of sarcomatoid differentiation to guide the treatment of renal cell carcinoma',
'authors' => 'Talal El Zarif et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (sRCC) is associated with poor survival and a heightened response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Two major barriers to improving outcomes for sRCC are the limited understanding of its gene regulatory programs and the low diagnostic yield of tumor biopsies due to spatial heterogeneity. Herein, we characterized the epigenomic landscape of sRCC by profiling 107 epigenomic libraries from tissue and plasma samples from 50 patients with RCC and healthy volunteers. By profiling histone modifications and DNA methylation, we identified highly recurrent epigenomic reprogramming enriched in sRCC. Furthermore, CRISPRa experiments implicated the transcription factor FOSL1 in activating sRCC-associated gene regulatory programs, and </span><em>FOSL1</em><span><span> </span>expression was associated with the response to ICIs in RCC in two randomized clinical trials. Finally, we established a blood-based diagnostic approach using detectable sRCC epigenomic signatures in patient plasma, providing a framework for discovering epigenomic correlates of tumor histology via liquid biopsy.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-25',
'pmid' => 'https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)00678-8',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114350',
'modified' => '2024-06-24 10:33:29',
'created' => '2024-06-24 10:33:29',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '4947',
'name' => 'Detecting small cell transformation in patients with advanced EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma through epigenomic cfDNA profiling',
'authors' => 'Talal El Zarif et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Purpose: Histologic transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a mechanism of treatment resistance in patients with advanced oncogene-driven lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) that currently requires histologic review for diagnosis. Herein, we sought to develop an epigenomic cell-free (cf)DNA-based approach to non-invasively detect small cell transformation in patients with EGFR mutant (EGFRm) LUAD. Experimental Design: To characterize the epigenomic landscape of transformed (t)SCLC relative to LUAD and de novo SCLC, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) to profile the histone modifications H3K27ac, H3K4me3, and H3K27me3, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq), assay for transposase-accessible chromatin sequencing (ATAC-seq), and RNA sequencing on 26 lung cancer patient-derived xenograft (PDX) tumors. We then generated and analyzed H3K27ac ChIP-seq, MeDIP-seq, and whole genome sequencing cfDNA data from 1 ml aliquots of plasma from patients with EGFRm LUAD with or without tSCLC. Results: Analysis of 126 epigenomic libraries from the lung cancer PDXs revealed widespread epigenomic reprogramming between LUAD and tSCLC, with a large number of differential H3K27ac (n=24,424), DNA methylation (n=3,298), and chromatin accessibility (n=16,352) sites between the two histologies. Tumor-informed analysis of each of these three epigenomic features in cfDNA resulted in accurate non-invasive discrimination between patients with EGFRm LUAD versus tSCLC (AUROC=0.82-0.87). A multi-analyte cfDNA-based classifier integrating these three epigenomic features discriminated between EGFRm LUAD versus tSCLC with an AUROC of 0.94. Conclusions: These data demonstrate the feasibility of detecting small cell transformation in patients with EGFRm LUAD through epigenomic cfDNA profiling of 1 ml of patient plasma.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-24',
'pmid' => 'https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article/doi/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0466/746147/Detecting-small-cell-transformation-in-patients',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0466',
'modified' => '2024-07-04 14:50:38',
'created' => '2024-07-04 14:50:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '4949',
'name' => 'Prostate cancer detection through unbiased capture of methylated cell-free DNA',
'authors' => 'Ermira Lleshi et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Prostate cancer screening using prostate-specific antigen (PSA) has been shown to reduce mortality but with substantial overdiagnosis, leading to unnecessary biopsies. The identification of a highly specific biomarker using liquid biopsies, represents an unmet need in the diagnostic pathway for prostate cancer. In this study, we employed a method that enriches for methylated cell-free DNA fragments coupled with a machine learning algorithm which enabled the detection of metastatic and localised cancers with AUCs of 0.96 and 0.74, respectively. The model also detected 51.8% (14/27) of localised and 88.7% (79/89) of metastatic cancer patients in an external dataset. Furthermore, we show that the differentially methylated regions reflect epigenetic and transcriptomic changes at the tissue level. Notably, these regions are significantly enriched for biologically relevant pathways associated with the regulation of cellular proliferation and TGF-beta signalling. This demonstrates the potential of circulating tumour DNA methylation for prostate cancer detection and prognostication.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-20',
'pmid' => 'https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004224015554',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110330',
'modified' => '2024-07-04 15:29:13',
'created' => '2024-07-04 15:29:13',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '4921',
'name' => 'A Pre-Leukemic DNA Methylation Signature in Healthy Individuals at Higher Risk for Developing Myeloid Malignancy',
'authors' => 'Zhentang Lao et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Purpose: DNA methylation alterations are widespread in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), some of which appear to have evolved independently of somatic mutations in epigenetic regulators. While the presence of somatic mutations in peripheral blood can predict the risk of development of AML and MDS, its accuracy remains unsatisfactory. Experimental Design: We performed global DNA methylation profiling in a case-control study nested within Singapore Chinese Health Study to evaluate if DNA methylation alterations were associated with AML/MDS development. Targeted deep sequencing and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) were performed on peripheral blood collected a median of 9.9 years prior to diagnosis of AML or MDS, together with age-matched still healthy individuals as controls. Results: Sixty-six individuals who developed AML or MDS displayed significant DNA methylation changes in the peripheral blood compared with 167 age- and gender-matched controls who did not develop AML/MDS during the follow up period. Alterations in methylation in the differentially methylation regions (DMRs) were associated with increased odds of developing AML/MDS. Conclusions: The epigenetic changes may be acquired independently and prior to somatic mutations that relevant for AML/MDS development. The association between methylation changes and the risk of pre-AML/MDS in these individuals was considerably stronger than somatic mutations, suggesting that methylation changes could be used as biomarkers for pre- AML/MDS screening.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-03-04',
'pmid' => 'https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article-abstract/doi/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3804/735044/A-Pre-Leukemic-DNA-Methylation-Signature-in?redirectedFrom=fulltext',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3804',
'modified' => '2024-03-12 16:50:46',
'created' => '2024-03-12 16:50:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 7 => array(
'id' => '4912',
'name' => 'Neurofibromin 1 controls metabolic balance and Notch-dependent quiescence of murine juvenile myogenic progenitors',
'authors' => 'Wei X. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Patients affected by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) frequently show muscle weakness with unknown etiology. Here we show that, in mice, Neurofibromin 1 (</span><i>Nf1</i><span>) is not required in muscle fibers, but specifically in early postnatal myogenic progenitors (MPs), where<span> </span></span><i>Nf1</i><span><span> </span>loss led to cell cycle exit and differentiation blockade, depleting the MP pool resulting in reduced myonuclear accretion as well as reduced muscle stem cell numbers. This was caused by precocious induction of stem cell quiescence coupled to metabolic reprogramming of MPs impinging on glycolytic shutdown, which was conserved in muscle fibers. We show that a Mek/Erk/NOS pathway hypersensitizes<span> </span></span><i>Nf1</i><span>-deficient MPs to Notch signaling, consequently, early postnatal Notch pathway inhibition ameliorated premature quiescence, metabolic reprogramming and muscle growth. This reveals an unexpected role of Ras/Mek/Erk signaling supporting postnatal MP quiescence in concert with Notch signaling, which is controlled by Nf1 safeguarding coordinated muscle growth and muscle stem cell pool establishment. Furthermore, our data suggest transmission of metabolic reprogramming across cellular differentiation, affecting fiber metabolism and function in NF1.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-02-15',
'pmid' => 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-45618-z',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45618-z',
'modified' => '2024-02-22 12:22:26',
'created' => '2024-02-22 12:22:26',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 8 => array(
'id' => '4892',
'name' => 'Promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions are associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival',
'authors' => 'Rivera‑Peña B. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) can be used as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets in precision medicine workflows. DNA from 21 HNSCC and 10 healthy oral tissue samples was hybridized to a genome‑wide tiling array to identify DMRs in a discovery cohort. Downstream analyses identified differences in promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival. Genome‑wide DMR analysis showed 2,565 DMRs common to the three subsites. A total of 738 DMRs were unique to laryngeal cancer (n=7), 889 DMRs were unique to oral cavity cancer (n=10) and 363 DMRs were unique to pharyngeal cancer (n=6). Based on the genome‑wide analysis and a Gene Ontology analysis, 10 candidate genes were selected to test for prognostic value and association with clinicopathological features. </span><em>TIMP3</em><span><span> </span>was associated with tumor differentiation in oral cavity cancer (P=0.039),<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span><span> </span>was associated with nodal involvement in pharyngeal cancer (P=0.017) and<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span><span> </span>was associated with tumor differentiation in laryngeal cancer (P=0.040). A total of five candidate genes were selected,<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>CDH1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>CALCA</em><span><span> </span>and<span> </span></span><em>TIMP3</em><span>, for a prevalence study in a larger validation cohort: Oral cavity cancer samples (n=42), pharyngeal cancer tissues (n=25) and laryngeal cancer samples (n=52).<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span><span> </span>hypermethylation differed across HNSCC anatomic subsites (P=0.029), and was predominantly detected in laryngeal cancer. Kaplan‑Meier survival analysis (P=0.043) and Cox regression analysis of overall survival (P=0.001) showed that<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span><span> </span>methylation is associated with better prognosis in HNSCC. The findings of the present study showed that the HNSCC subsites oral cavity, pharynx and larynx display substantial differences in aberrant DNA methylation patterns, which may serve as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-01-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/ol.2024.14223/abstract',
'doi' => ' https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2024.14223',
'modified' => '2024-01-11 08:48:03',
'created' => '2024-01-11 08:48:03',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 9 => array(
'id' => '4732',
'name' => 'Cerebrospinal fluid methylome-based liquid biopsies for accuratemalignant brain neoplasm classification.',
'authors' => 'Zuccato Jeffrey A et al.',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Resolving the differential diagnosis between brain metastases (BM), glioblastomas (GBM), and central nervous system lymphomas (CNSL) is an important dilemma for the clinical management of the main three intra-axial brain tumor types. Currently, treatment decisions require invasive diagnostic surgical biopsies that carry risks and morbidity. This study aimed to utilize methylomes from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a biofluid proximal to brain tumors, for reliable non-invasive classification that addresses limitations associated with low target abundance in existing approaches. METHODS: Binomial GLMnet classifiers of tumor type were built, in fifty iterations of 80\% discovery sets, using CSF methylomes obtained from 57 BM, GBM, CNSL, and non-neoplastic control patients. Publicly-available tissue methylation profiles (N=197) on these entities and normal brain parenchyma were used for validation and model optimization. RESULTS: Models reliably distinguished between BM (area under receiver operating characteristic curve [AUROC]=0.93, 95\% confidence interval [CI]: 0.71-1.0), GBM (AUROC=0.83, 95\% CI: 0.63-1.0), and CNSL (AUROC=0.91, 95\% CI: 0.66-1.0) in independent 20\% validation sets. For validation, CSF-based methylome signatures reliably distinguished between tumor types within external tissue samples and tumors from non-neoplastic controls in CSF and tissue. CSF methylome signals were observed to align closely with tissue signatures for each entity. An additional set of optimized CSF-based models, built using tumor-specific features present in tissue data, showed enhanced classification accuracy. CONCLUSIONS: CSF methylomes are reliable for liquid biopsy-based classification of the major three malignant brain tumor types. We discuss how liquid biopsies may impact brain cancer management in the future by avoiding surgical risks, classifying unbiopsiable tumors, and guiding surgical planning when resection is indicated.</p>',
'date' => '2023-08-03',
'pmid' => 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36455236/',
'doi' => '10.1093/neuonc/noac264',
'modified' => '2023-10-13 08:50:06',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 10 => array(
'id' => '4803',
'name' => 'Transgenerational endocrine disruptor effects of cadmium in zebrafish andcontribution of standing epigenetic variation to adaptation.',
'authors' => 'Pierron F. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Evidence has emerged that environmentally-induced epigenetic changes can have long-lasting effects on gene transcription across generations. These recent findings highlight the need to investigate the transgenerational impacts of pollutants to assess their long term effects on populations. In this study, we investigated the transgenerational effect of cadmium on zebrafish across 4 generations. A first whole methylome approach carried out on fish of the first two generations led us to focus our investigations on the estradiol receptor alpha gene (esr1). We observed a sex-dependent transgenerational inheritance of Cd-induced DNA methylation changes up to the last generation. These changes were associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that were themselves at the origin of the creation or deletion of methylation sites. Thus, Cd-induced genetic selection gave rise to DNA methylation changes. We also analyzed the transcription level of various sections of esr1 as well as estrogen responsive genes. While Cd triggered transgenerational disorders, Cd-induced epigenetic changes in esr1 contributed to the rapid transgenerational adaptation of fish to Cd. Our results provide insight into the processes underpinning rapid adaptation and highlight the need to maintain genetic diversity within natural populations to bolster the resilience of species faced with the global environmental changes.</span></p>',
'date' => '2023-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37163897',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131579',
'modified' => '2023-06-15 08:44:52',
'created' => '2023-06-13 21:11:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 11 => array(
'id' => '4843',
'name' => 'Differentiation block in acute myeloid leukemia regulated by intronicsequences of FTO',
'authors' => 'Camera F. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Iroquois transcription factor gene IRX3 is highly expressed in 20–30\% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and contributes to the pathognomonic differentiation block. Intron 8 FTO sequences ∼220kB downstream of IRX3 exhibit histone acetylation, DNA methylation, and contacts with the IRX3 promoter, which correlate with IRX3 expression. Deletion of these intronic elements confirms a role in positively regulating IRX3. RNAseq revealed long non-coding (lnc) transcripts arising from this locus. FTO-lncAML knockdown (KD) induced differentiation of AML cells, loss of clonogenic activity, and reduced FTO intron 8:IRX3 promoter contacts. While both FTO-lncAML KD and IRX3 KD induced differentiation, FTO-lncAML but not IRX3 KD led to HOXA downregulation suggesting transcript activity in trans. FTO-lncAMLhigh AML samples expressed higher levels of HOXA and lower levels of differentiation genes. Thus, a regulatory module in FTO intron 8 consisting of clustered enhancer elements and a long non-coding RNA is active in human AML, impeding myeloid differentiation.</p>',
'date' => '2023-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004223013962',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.isci.2023.107319',
'modified' => '2023-08-01 14:14:01',
'created' => '2023-08-01 15:59:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 12 => array(
'id' => '4777',
'name' => 'Epigenetic modifier alpha-ketoglutarate modulates aberrant gene bodymethylation and hydroxymethylation marks in diabetic heart.',
'authors' => 'Dhat R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Hyperglycemic myocardial microenvironment significantly alters chromatin architecture and the transcriptome, resulting in aberrant activation of signaling pathways in a diabetic heart. Epigenetic marks play vital roles in transcriptional reprogramming during the development of DCM. The current study is aimed to profile genome-wide DNA (hydroxy)methylation patterns in the hearts of control and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats and decipher the effect of modulation of DNA methylation by alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), a TET enzyme cofactor, on the progression of DCM. METHODS: Diabetes was induced in male adult Wistar rats with an intraperitoneal injection of STZ. Diabetic and vehicle control animals were randomly divided into groups with/without AKG treatment. Cardiac function was monitored by performing cardiac catheterization. Global methylation (5mC) and hydroxymethylation (5hmC) patterns were mapped in the Left ventricular tissue of control and diabetic rats with the help of an enrichment-based (h)MEDIP-sequencing technique by using antibodies specific for 5mC and 5hmC. Sequencing data were validated by performing (h)MEDIP-qPCR analysis at the gene-specific level, and gene expression was analyzed by qPCR. The mRNA and protein expression of enzymes involved in the DNA methylation and demethylation cycle were analyzed by qPCR and western blotting. Global 5mC and 5hmC levels were also assessed in high glucose-treated DNMT3B knockdown H9c2 cells. RESULTS: We found the increased expression of DNMT3B, MBD2, and MeCP2 with a concomitant accumulation of 5mC and 5hmC, specifically in gene body regions of diabetic rat hearts compared to the control. Calcium signaling was the most significantly affected pathway by cytosine modifications in the diabetic heart. Additionally, hypermethylated gene body regions were associated with Rap1, apelin, and phosphatidyl inositol signaling, while metabolic pathways were most affected by hyperhydroxymethylation. AKG supplementation in diabetic rats reversed aberrant methylation patterns and restored cardiac function. Hyperglycemia also increased 5mC and 5hmC levels in H9c2 cells, which was normalized by DNMT3B knockdown or AKG supplementation. CONCLUSION: This study demonstrates that reverting hyperglycemic damage to cardiac tissue might be possible by erasing adverse epigenetic signatures by supplementing epigenetic modulators such as AKG along with an existing antidiabetic treatment regimen.</p>',
'date' => '2023-04-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37101286',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13072-023-00489-4',
'modified' => '2023-06-12 09:20:54',
'created' => '2023-05-05 12:34:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 13 => array(
'id' => '4611',
'name' => 'Pre-diagnosis plasma cell-free DNA methylome profiling up to sevenyears prior to clinical detection reveals early signatures of breast cancer',
'authors' => 'Cheng N. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Profiling of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has been well demonstrated to be a potential non-invasive screening tool for early cancer detection. However, limited studies have investigated the detectability of cfDNA methylation markers that are predictive of cancers in asymptomatic individuals. We performed cfDNA methylation profiling using cell-free DNA methylation immunoprecipitation sequencing (cfMeDIP-Seq) in blood collected from individuals up to seven years before a breast cancer diagnosis in addition to matched cancer-free controls. We identified differentially methylated cfDNA signatures that discriminated cancer-free controls from pre-diagnosis breast cancer cases in a discovery cohort that is used to build a classification model. We show that predictive models built from pre-diagnosis cfDNA hypermethylated regions can accurately predict early breast cancers in an independent test set (AUC=0.930) and are generalizable to late-stage breast cancers cases at the time of diagnosis (AUC=0.912). Characterizing the top hypermethylated cfDNA regions revealed significant enrichment for hypermethylation in external bulk breast cancer tissues compared to peripheral blood leukocytes and breast normal tissues. Our findings demonstrate that cfDNA methylation markers predictive of breast cancers can be detected in blood among asymptomatic individuals up to six years prior to clinical detection.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2023.01.30.23285027',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.01.30.23285027',
'modified' => '2023-04-04 08:34:20',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 14 => array(
'id' => '4612',
'name' => 'Cell-free multi-omics analysis reveals tumor status-informativesignatures in gastrointestinal cancer patients’ plasma',
'authors' => 'Tao Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>During cancer development, host’s tumorigenesis and immune signals are released to and informed by circulating molecules, like cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and RNA (cfRNA) in blood. However, these two kinds of molecules are still not systematically compared in gastrointestinal cancer. Here, we profiled 4 types of cell-free omics data from colorectal and stomach cancer patients, and assayed 15 types of genomic, epi-genomic, and transcriptomic variations. First, we demonstrated that the multi-omics data were more capable of detecting cancer genes than the single-omics data, where cfRNAs were more sensitive and informative than cfDNAs in terms of detection ratio, variation type, altered number, and enriched functional pathway. Moreover, we revealed several peripheral immune signatures that were suppressed in cancer patients and originated from specific circulating and tumor-microenvironment cells. Particularly, we defined a γδ-T-cell score and a cancer-associated-fibroblast (CAF) score using the cfRNA-seq data of 143 cancer patients. They were informative of clinical status like cancer stage, tumor size, and survival. In summary, our work reveals the cell-free multi-molecular landscape of colorectal and stomach cancer, and provides a potential monitoring utility in blood for the personalized cancer treatment.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2023.01.31.526431',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.01.31.526431',
'modified' => '2023-04-04 08:36:37',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 15 => array(
'id' => '4674',
'name' => 'Methylation and expression of glucocorticoid receptor exon-1 variants andFKBP5 in teenage suicide-completers.',
'authors' => 'Rizavi H. et al.',
'description' => '<p>A dysregulated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis has repeatedly been demonstrated to play a fundamental role in psychiatric disorders and suicide, yet the mechanisms underlying this dysregulation are not clear. Decreased expression of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene, which is also susceptible to epigenetic modulation, is a strong indicator of impaired HPA axis control. In the context of teenage suicide-completers, we have systematically analyzed the 5'UTR of the GR gene to determine the expression levels of all GR exon-1 transcript variants and their epigenetic state. We also measured the expression and the epigenetic state of the FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP5/FKBP51), an important modulator of GR activity. Furthermore, steady-state DNA methylation levels depend upon the interplay between enzymes that promote DNA methylation and demethylation activities, thus we analyzed DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), ten-eleven translocation enzymes (TETs), and growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins (GADD45). Focusing on both the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus, our results show decreased expression in specific GR exon-1 variants and a strong correlation of DNA methylation changes with gene expression in the PFC. FKBP5 expression is also increased in both areas suggesting a decreased GR sensitivity to cortisol binding. We also identified aberrant expression of DNA methylating and demethylating enzymes in both brain regions. These findings enhance our understanding of the complex transcriptional regulation of GR, providing evidence of epigenetically mediated reprogramming of the GR gene, which could lead to possible epigenetic influences that result in lasting modifications underlying an individual's overall HPA axis response and resilience to stress.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36781843',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41398-023-02345-1',
'modified' => '2023-04-14 09:26:37',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 16 => array(
'id' => '4675',
'name' => 'Bridging biological cfDNA features and machine learning approaches.',
'authors' => 'Moser T. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Liquid biopsies (LBs), particularly using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), are expected to revolutionize precision oncology and blood-based cancer screening. Recent technological improvements, in combination with the ever-growing understanding of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) biology, are enabling the detection of tumor-specific changes with extremely high resolution and new analysis concepts beyond genetic alterations, including methylomics, fragmentomics, and nucleosomics. The interrogation of a large number of markers and the high complexity of data render traditional correlation methods insufficient. In this regard, machine learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly being used to decipher disease- and tissue-specific signals from cfDNA. Here, we review recent insights into biological ctDNA features and how these are incorporated into sophisticated ML applications.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36792446',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.tig.2023.01.004',
'modified' => '2023-04-14 09:28:00',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 17 => array(
'id' => '4823',
'name' => 'Gene body DNA hydroxymethylation restricts the magnitude oftranscriptional changes during aging.',
'authors' => 'Occean J. R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC) is the most abundant oxidative derivative of DNA methylation (5mC) and is typically enriched at enhancers and gene bodies of transcriptionally active and tissue-specific genes. Although aberrant genomic 5hmC has been implicated in many age-related diseases, the functional role of the modification in aging remains largely unknown. Here, we report that 5hmC is stably enriched in multiple aged organs. Using the liver and cerebellum as model organs, we show that 5hmC accumulates in gene bodies associated with tissue-specific function and thereby restricts the magnitude of gene expression changes during aging. Mechanistically, we found that 5hmC decreases binding affinity of splicing factors compared to unmodified cytosine and 5mC, and is correlated with age-related alternative splicing events, suggesting RNA splicing as a potential mediator of 5hmC’s transcriptionally restrictive function. Furthermore, we show that various age-related contexts, such as prolonged quiescence and senescence, are partially responsible for driving the accumulation of 5hmC with age. We provide evidence that this age-related function is conserved in mouse and human tissues, and further show that the modification is altered by regimens known to modulate lifespan. Our findings reveal that 5hmC is a regulator of tissue-specific function and may play a role in regulating longevity.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36824863',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.02.15.528714',
'modified' => '2023-06-14 08:39:26',
'created' => '2023-06-13 22:16:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 18 => array(
'id' => '4711',
'name' => 'Neonatal inflammation increases hippocampal KCC2 expression throughmethylation-mediated TGF-β1 downregulation leading to impairedhippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity in adult mice.',
'authors' => 'Rong J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The mechanisms by which neonatal inflammation leads to cognitive deficits in adulthood remain poorly understood. Inhibitory GABAergic synaptic transmission plays a vital role in controlling learning, memory and synaptic plasticity. Since early-life inflammation has been reported to adversely affect the GABAergic synaptic transmission, the aim of this study was to investigate whether and how neonatal inflammation affects GABAergic synaptic transmission resulting in cognitive impairment. Neonatal mice received a daily subcutaneous injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 50 μg/kg) or saline on postnatal days 3-5. It was found that blocking GABAergic synaptic transmission reversed the deficit in hippocampus-dependent memory or the induction failure of long-term potentiation in the dorsal CA1 in adult LPS mice. An increase of mIPSCs amplitude was further detected in adult LPS mice indicative of postsynaptic potentiation of GABAergic transmission. Additionally, neonatal LPS resulted in the increased expression and function of K-Cl-cotransporter 2 (KCC2) and the decreased expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) in the dorsal CA1 during adulthood. The local TGF-β1 overexpression improved KCC2 expression and function, synaptic plasticity and memory of adult LPS mice. Adult LPS mice show hypermethylation of TGFb1 promoter and negatively correlate with reduced TGF-β1 transcripts. 5-Aza-deoxycytidine restored the changes in TGFb1 promoter methylation and TGF-β1 expression. Altogether, the results suggest that hypermethylation-induced reduction of TGF-β1 leads to enhanced GABAergic synaptic inhibition through increased KCC2 expression, which is a underlying mechanism of neonatal inflammation-induced hippocampus-dependent memory impairment in adult mice.</p>',
'date' => '2023-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36691035',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12974-023-02697-x',
'modified' => '2023-04-05 08:42:07',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 19 => array(
'id' => '4589',
'name' => 'Impact of FecB Mutation on Ovarian DNA Methylome inSmall-Tail Han Sheep.',
'authors' => 'Xie L. et al.',
'description' => '<p>UNLABELLED: Booroola fecundity (FecB) gene, a mutant of bone morphogenetic protein 1B (BMPR-1B) that was discovered in Booroola Merino, was the first prolificacy gene identified in sheep related to increased ovulation rate and litter size. The mechanism of FecB impact on reproduction is unclear. METHODS: In this study, adult Han ewes with homozygous FecB(B)/FecB(B) mutations (Han BB group) and ewes with FecB(+)/FecB(+) wildtype (Han ++ group) were selected. Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) was used to identify differences in methylated genes in ovary tissue. RESULTS: We examined differences in DNA methylation patterns between HanBB and Han ++ sheep. In both sheep, methylated reads were mainly distributed at the gene body regions, CpG islands and introns. The differentially methylated genes were enriched in neurotrophy in signaling pathway, Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) signaling pathway, Wnt signaling pathway, oocyte meiosis, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway, etc. Differentially-methylated genes were co-analyzed with differentially-expressed mRNAs. Several genes which could be associated with female reproduction were identified, such as FOXP3 (forkhead box P3), TMEFF2 (Transmembrane Protein with EGF Like and Two Follistatin Like Domains 2) and ADAT2 (Adenosine Deaminase TRNA Specific 2). CONCLUSIONS: We constructed a MeDIP-seq based methylomic study to investigate the ovarian DNA methylation differences between Small-Tail Han sheep with homozygous FecB mutant and wildtype, and successfully identified FecB gene-associated differentially-methylated genes. This study has provided information with which to understand the mechanisms of FecB gene-induced hyperprolificacy in sheep.</p>',
'date' => '2023-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36672944',
'doi' => '10.3390/genes14010203',
'modified' => '2023-04-11 10:04:29',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 20 => array(
'id' => '4631',
'name' => 'Consistent DNA Hypomethylations in Prostate Cancer.',
'authors' => 'Araúzo-Bravo M.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>With approximately 1.4 million men annually diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa) worldwide, PCa remains a dreaded threat to life and source of devastating morbidity. In recent decades, a significant decrease in age-specific PCa mortality has been achieved by increasing prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening and improving treatments. Nevertheless, upcoming, augmented recommendations against PSA screening underline an escalating disproportion between the benefit and harm of current diagnosis/prognosis and application of radical treatment standards. Undoubtedly, new potent diagnostic and prognostic tools are urgently needed to alleviate this tensed situation. They should allow a more reliable early assessment of the upcoming threat, in order to enable applying timely adjusted and personalized therapy and monitoring. Here, we present a basic study on an epigenetic screening approach by Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP). We identified genes associated with hypomethylated CpG islands in three PCa sample cohorts. By adjusting our computational biology analyses to focus on single CpG-enriched 60-nucleotide-long DNA probes, we revealed numerous consistently differential methylated DNA segments in PCa. They were associated among other genes with and . These can be used for early discrimination, and might contribute to a new epigenetic tumor classification system of PCa. Our analysis shows that we can dissect short, differential methylated CpG-rich DNA fragments and combinations of them that are consistently present in all tumors. We name them tumor cell-specific differential methylated CpG dinucleotide signatures (TUMS).</p>',
'date' => '2022-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36613831',
'doi' => '10.3390/ijms24010386',
'modified' => '2023-03-28 09:03:47',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 21 => array(
'id' => '4488',
'name' => 'Cell-free DNA methylation-defined prognostic subgroups in small celllung cancer identified by leukocyte methylation subtraction',
'authors' => 'Ul Haq Sami et al.',
'description' => '<p>Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) methylome is understudied. Here, we comprehensively profile SCLC using cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from plasma of 74 SCLC patients pre-treatment and from 20 non-cancer participants, genomic DNA (gDNA) from peripheral blood leukocytes from the same 74 patients and 7 accompanying circulating-tumour-cell patient-derived xenografts (CDX) underwent cfMeDIP-seq. PeRIpheral blood leukocyte MEthylation (PRIME) subtraction to improve tumour specificity. SCLC cfDNA methylation is distinct from non-cancer but correlates with CDX tumor methylation. PRIME and k-means consensus identified two methylome clusters with prognostic associations that related to axon guidance, neuroactive ligand−receptor interaction, pluripotency of stem cells, and differentially methylated at long noncoding RNA and other repeats features. We comprehensively profiled the SCLC methylome in a large patient cohort and identified methylome clusters with prognostic associations. Our work demonstrates the potential of liquid biopsies in examining SCLC biology encoded in the methylome.</p>',
'date' => '2022-11-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.isci.2022.105487',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.isci.2022.105487',
'modified' => '2022-11-18 12:35:39',
'created' => '2022-11-15 09:26:20',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 22 => array(
'id' => '4547',
'name' => 'The cell-free DNA methylome captures distinctions between localized andmetastatic prostate tumors.',
'authors' => 'Chen Sujun et al.',
'description' => '<p>Metastatic prostate cancer remains a major clinical challenge and metastatic lesions are highly heterogeneous and difficult to biopsy. Liquid biopsy provides opportunities to gain insights into the underlying biology. Here, using the highly sensitive enrichment-based sequencing technology, we provide analysis of 60 and 175 plasma DNA methylomes from patients with localized and metastatic prostate cancer, respectively. We show that the cell-free DNA methylome can capture variations beyond the tumor. A global hypermethylation in metastatic samples is observed, coupled with hypomethylation in the pericentromeric regions. Hypermethylation at the promoter of a glucocorticoid receptor gene NR3C1 is associated with a decreased immune signature. The cell-free DNA methylome is reflective of clinical outcomes and can distinguish different disease types with 0.989 prediction accuracy. Finally, we show the ability of predicting copy number alterations from the data, providing opportunities for joint genetic and epigenetic analysis on limited biological samples.</p>',
'date' => '2022-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36309516',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41467-022-34012-2',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:30:03',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 23 => array(
'id' => '4550',
'name' => 'A SOX2-engineered epigenetic silencer factor represses the glioblastomagenetic program and restrains tumor development.',
'authors' => 'Benedetti V. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Current therapies remain unsatisfactory in preventing the recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), which leads to poor patient survival. By rational engineering of the transcription factor SOX2, a key promoter of GBM malignancy, together with the Kruppel-associated box and DNA methyltransferase3A/L catalytic domains, we generated a synthetic repressor named SOX2 epigenetic silencer (SES), which induces the transcriptional silencing of its original targets. By doing so, SES kills both glioma cell lines and patient-derived cancer stem cells in vitro and in vivo. SES expression, through local viral delivery in mouse xenografts, induces strong regression of human tumors and survival rescue. Conversely, SES is not harmful to neurons and glia, also thanks to a minimal promoter that restricts its expression in mitotically active cells, rarely present in the brain parenchyma. Collectively, SES produces a significant silencing of a large fraction of the SOX2 transcriptional network, achieving high levels of efficacy in repressing aggressive brain tumors.</p>',
'date' => '2022-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35921410/',
'doi' => '10.1126/sciadv.abn3986',
'modified' => '2023-09-28 11:26:02',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 24 => array(
'id' => '4551',
'name' => 'mTORC1 is required for epigenetic silencing during β-cell functionalmaturation.',
'authors' => 'Ni Qicheng et al.',
'description' => '<p>OBJECTIVE: The mechanistic target of rapamycin comple×1 (mTORC1) is a key molecule that links nutrients, hormones, and growth factors to cell growth/function. Our previous studies have shown that mTORC1 is required for β-cell functional maturation and identity maintenance; however, the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. This work aimed to understand the underlying epigenetic mechanisms of mTORC1 in regulating β-cell functional maturation. METHODS: We performed Microarray, MeDIP-seq and ATAC-seq analysis to explore the abnormal epigenetic regulation in 8-week-old immature βRapKO islets. Moreover, DNMT3A was overexpressed in βRapKO islets by lentivirus, and the transcriptome changes and GSIS function were analyzed. RESULTS: We identified two major epigenetic silencing mechanisms, DNMT3A-dependent DNA methylation and PRC2-dependent H3K27me3 modification, which are responsible for functional immaturity of Raptor-deficient β-cell. Overexpression of DNMT3A partially reversed the immature transcriptome pattern and restored the impaired GSIS in Raptor-deficient β-cells. Moreover, we found that Raptor directly regulated PRC2/EED2 and H3K27me3 expression levels, as well as a group of immature genes marked with H3K27me3. Combined with ATAC-seq, MeDIP-seq and ChIP-seq, we identified β-cell immature genes with either DNA methylation and/or H3K27me3 modification. CONCLUSION: The present study advances our understanding of the nutrient sensor mTORC1, by integrating environmental nutrient supply and epigenetic modification, i.e., DNMT3A-mediated DNA methylation and PRC2-mediated histone methylation in regulating β-cell identity and functional maturation, and therefore may impact the disease risk of type 2 diabetes.</p>',
'date' => '2022-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35940555',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101559',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:09:58',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 25 => array(
'id' => '4391',
'name' => 'Detection of ovarian cancer using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Lu Huaiwu et al. ',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a highly lethal gynecologic cancer, and it is hard to diagnose at an early stage. Clinically, there are no ovarian cancer-specific markers for early detection. Here, we demonstrate the use of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylomes to detect ovarian cancer, especially the early-stage OC. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Plasma from 74 epithelial ovarian cancer patients, 86 healthy volunteers, and 20 patients with benign pelvic masses was collected. The cfDNA methylomes of these samples were generated by cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). The differentially methylated regions (DMRs) were identified by the contrasts between tumor and non-tumor groups, and the discrimination performance was evaluated with the iterative training and testing method. RESULTS: The DMRs identified for cfDNA methylomes can well discriminate tumor groups and non-tumor groups (ROC values from 0.86 to 0.98). The late-stage top 300 DMRs are more late-stage-specific and failed to detect early-stage OC. However, the early-stage markers have the potential to discriminate all-stage OCs from non-tumor samples. CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrates that cfDNA methylomes generated with cfMeDIP-seq could be used to identify OC-specific biomarkers for OC, especially early OC detection. To detect early-stage OC, the biomarkers should be directly identified from early OC plasma samples rather than mix-stage ones. Further exploration of DMRs from a k larger early-stage OC cohort is warranted.</p>',
'date' => '2022-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35681212',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13148-022-01285-9',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:19:10',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 26 => array(
'id' => '4438',
'name' => 'A genome-wide screen reveals new regulators of the 2-cell-like cell state',
'authors' => 'Defossez Pierre-Antoine et al.',
'description' => '<p>In mammals, only the zygote and blastomeres of the early embryo are fully totipotent. This totipotency is mirrored in vitro by mouse "2-cell-like cells" (2CLCs), which appear at low frequency in cultures of Embryonic Stem cells (ESCs). Because totipotency is incompletely understood, we carried out a genomewide CRISPR KO screen in mouse ESCs, searching for mutants that reactivate the expression of Dazl, a robust 2-cell-like marker. Using secondary screens, we identify four mutants that reactivate not just Dazl, but also a broader 2-cell-like signature: the E3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor SPOP, the Zinc Finger transcription factor ZBTB14, MCM3AP, a component of the RNA processing complex TREX-2, and the lysine demethylase KDM5C. Functional experiments show how these factors link to known players of the 2 celllike state. These results extend our knowledge of totipotency, a key phase of organismal life.</p>',
'date' => '2022-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.21203%2Frs.3.rs-1561018%2Fv1',
'doi' => '10.21203/rs.3.rs-1561018/v1',
'modified' => '2022-09-28 09:23:42',
'created' => '2022-09-08 16:32:20',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 27 => array(
'id' => '4394',
'name' => 'Heat stress during grain filling regulates seed germination throughalterations of DNA methylation in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).',
'authors' => 'Sakai Yuki et al.',
'description' => '<p>KEY MESSAGE: Alterations in DNA methylation levels of ROS, GA and ABA related gene promoters cause transcriptional changes upon imbibition to induce seed germination in barley seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling. Environmental changes, especially changes in temperature, during seed development affect germination in several plant species. We have previously shown that heat stress during rice grain filling alters DNA methylation, an epigenetic mark important for gene silencing, regulates transcript levels of phytohormone metabolism genes, and delays seed germination. However, whether this phenomenon is present in other plant species remained to be elucidated. In this study, we compared seeds germination of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) plants grown at 15 °C (control) or 25 °C (heat stress) during grain filling. Heat stress during grain filling significantly promoted seed germination in comparison with the control. The phytohormone gibberellic acid (GA) and reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidases promote seed germination, whereas phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) suppresses seed germination. We found that in heat-stressed seeds, genes related to ABA biosynthesis (HvNCED1 and 2) were significantly suppressed, whereas genes related to ABA catabolism (HvABA8'OH) and GA biosynthesis (HvHA20ox, HvGA3ox), and NADPH oxidase (HvRboh) genes were significantly upregulated after imbibition. Using MeDIP-qPCR, we showed that the promoters of HvNCED were hyper-methylated, and those of HvABA8'OH1, HvABA8'OH3, HvGA3ox2, and HvRbohF2 were hypo-methylated in heat treated seeds. Taken together, our data suggest that heat stress during grain filling affects DNA methylation of germination-related genes and promotes seed germination in barley.</p>',
'date' => '2022-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35581415',
'doi' => '10.1007/s11103-022-01278-5',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:24:13',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 28 => array(
'id' => '4398',
'name' => 'Hexokinase 2 is a transcriptional target and a positive modulator ofAHR signalling.',
'authors' => 'Watzky M. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) regulates the expression of numerous genes in response to activation by agonists including xenobiotics. Although it is well appreciated that environmental signals and cell intrinsic features may modulate this transcriptional response, how it is mechanistically achieved remains poorly understood. We show that hexokinase 2 (HK2) a metabolic enzyme fuelling cancer cell growth, is a transcriptional target of AHR as well as a modulator of its activity. Expression of HK2 is positively regulated by AHR upon exposure to agonists both in human cells and in mice lung tissues. Conversely, over-expression of HK2 regulates the abundance of many proteins involved in the regulation of AHR signalling and these changes are linked with altered AHR expression levels and transcriptional activity. HK2 expression also shows a negative correlation with AHR promoter methylation in tumours, and these tumours with high HK2 expression and low AHR methylation are associated with a worse overall survival in patients. In sum, our study provides novel insights into how AHR signalling is regulated which may help our understanding of the context-specific effects of this pathway and may have implications in cancer.</p>',
'date' => '2022-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1093%2Fnar%2Fgkac360',
'doi' => '10.1093/nar/gkac360',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:32:40',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 29 => array(
'id' => '4561',
'name' => 'Corticosterone induces discrete epigenetic signatures in the dorsal andventral hippocampus that depend upon sex and genotype: focus on methylatedNr3c1 gene.',
'authors' => 'Caradonna S. G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The genomic effects of circulating glucocorticoids are particularly relevant in cortico-limbic structures, which express a high concentration of steroid hormone receptors. To date, no studies have investigated genomic differences in hippocampal subregions, namely the dorsal (dHPC) and ventral (vHPC) hippocampus, in preclinical models treated with exogenous glucocorticoids. Chronic oral corticosterone (CORT) in mouse is a pharmacological approach that disrupts the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, increases affective behavior, and induces genomic changes after stress in the HPC of wildtype (WT) mice and mice heterozygous for the gene coding for brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met (hMet), a variant associated with genetic susceptibility to stress. Using RNA-sequencing, we investigated the genomic signatures of oral CORT in the dHPC and vHPC of WT and hMet male and female mice, and examined sex and genotype differences in response to oral CORT. Males under CORT showed lower glycemia and increased anxiety- and depression-like behavior compared to females that showed instead opposite affective behavior in response to CORT. Rank-rank-hypergeometric overlap (RRHO) was used to identify genes from a continuous gradient of significancy that were concordant across groups. RRHO showed that CORT-induced differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in WT mice and hMet mice converged in the dHPC of males and females, while in the vHPC, DEGs converged in males and diverged in females. The vHPC showed a higher number of DEGs compared to the dHPC and exhibited sex differences related to glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-binding genes and epigenetic modifiers. Methyl-DNA-immunoprecipitation in the vHPC revealed differential methylation of the exons 1 and 1 of the GR gene (Nr3c1) in hMet females. Together, we report behavioral and endocrinological sex differences in response to CORT, as well as epigenetic signatures that i) differ in the dHPC and vHPC,ii) are distinct in males and females, and iii) implicate differential methylation of Nr3c1 selectively in hMet females.</p>',
'date' => '2022-03-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35296634',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41398-022-01864-7',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:03:20',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 30 => array(
'id' => '4364',
'name' => 'Methionine Metabolism Controls the B-cell EBV Epigenome andViral Latency',
'authors' => 'Guo R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) subverts host epigenetic pathways to switch between viral latency programs, colonize the B-cell compartment and reactivate. Within memory B-cells, the reservoir for lifelong infection, EBV genomic DNA and histone methylation marks restrict gene expression. But, this epigenetic strategy also enables EBV-infected tumors, including Burkitt lymphomas to evade immune detection. Little is known about host cell metabolic pathways that support EBV epigenome landscapes. We therefore used amino acid restriction, metabolomic and CRISPR approaches to identify that an abundant methionine supply, and interconnecting methionine and folate cycles, maintain Burkitt EBV gene silencing. Methionine restriction, or methionine cycle perturbation, hypomethylated EBV genomes, de-repressed latent membrane protein and lytic gene expression. Methionine metabolism also shaped EBV latency gene regulation required for B-cell immortalization. Dietary methionine restriction altered murine Burkitt xenograft metabolomes and de-repressed EBV immunogens in vivo. These results highlight epigenetic/immunometabolism crosstalk supporting the EBV B-cell lifecycle and suggest therapeutic approaches.</p>',
'date' => '2022-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2022.02.24.481783',
'doi' => '10.1101/2022.02.24.481783',
'modified' => '2022-08-04 15:50:37',
'created' => '2022-08-04 14:55:36',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 31 => array(
'id' => '4281',
'name' => 'Integrating SNPs-based genetic risk factor with blood epigenomicresponse of differentially arsenic-exposed rural subjects revealsdisease-associated signaling pathways.',
'authors' => 'Rehman Muhammad Yasir Abdur et al.',
'description' => '<p>Arsenic (As) contamination in groundwater is responsible for numerous adverse health outcomes among millions of people. Epigenetic alterations are among the most widely studied mechanisms of As toxicity. To understand how As exposure alters gene expression through epigenetic modifications, a systematic genome-wide study was designed to address the impact of multiple important single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to As exposure on the methylome of drinking water As-exposed rural subjects from Pakistan. Urinary As levels were used to stratify subjects into low, medium and high exposure groups. Genome-wide DNA methylation was investigated using MeDIP in combination with NimbleGen 2.1 M Deluxe Promotor arrays. Transcriptome levels were measured using Agilent 8 × 60 K expression arrays. Genotyping of selected SNPs (As3MT, DNMT1a, ERCC2, EGFR and MTHFR) was measured and an integrated genetic risk factor for each respondent was calculated by assigning a specific value to the measured genotypes based on known risk allele numbers. To select a representative model related to As exposure we compared 9 linear mixed models comprising of model 1 (including the genetic risk factor), model 2 (without the genetic risk factor) and models with individual SNPs incorporated into the methylome data. Pathway analysis was performed using ConsensusPathDB. Model 1 comprising the integrated genetic risk factor disclosed biochemical pathways including muscle contraction, cardio-vascular diseases, ATR signaling, GPCR signaling, methionine metabolism and chromatin modification in association with hypo- and hyper-methylated gene targets. A unique pathway (direct P53 effector) was found associated with the individual DNMT1a polymorphism due to hyper-methylation of CSE1L and TRRAP. Most importantly, we provide here the first evidence of As-associated DNA methylation in relation with gene expression of ATR, ATF7IP, TPM3, UBE2J2. We report the first evidence that integrating SNPs data with methylome data generates a more representative epigenome profile and discloses a better insight in disease risks of As-exposed individuals.</p>',
'date' => '2022-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.envpol.2021.118279',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118279',
'modified' => '2022-05-23 10:04:20',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 32 => array(
'id' => '4404',
'name' => 'Stella regulates the Development of Female Germline Stem Cells byModulating Chromatin Structure and DNA Methylation.',
'authors' => 'Hou Changliang et al.',
'description' => '<p>Female germline stem cells (FGSCs) have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into oocytes. , encoded by a maternal effect gene, plays an important role in oogenesis and early embryonic development. However, its function in FGSCs remains unclear. In this study, we showed that CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of promoted FGSC proliferation and reduced the level of genome-wide DNA methylation of FGSCs. Conversely, overexpression led to the opposite results, and enhanced FGSC differentiation. We also performed an integrative analysis of chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq), high-throughput genome-wide chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C), and use of our published epigenetic data. Results indicated that the binding sites of STELLA and active histones H3K4me3 and H3K27ac were enriched near the TAD boundaries. Hi-C analysis showed that overexpression attenuated the interaction within TADs, and interestingly enhanced the TAD boundary strength in STELLA-associated regions. Taking these findings together, our study not only reveals the role of in regulating DNA methylation and chromatin structure, but also provides a better understanding of FGSC development.</p>',
'date' => '2022-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9066111/',
'doi' => '10.7150/ijbs.69240',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:54:29',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 33 => array(
'id' => '4302',
'name' => 'Examining age-dependent DNA methylation patterns and gene expression inthe male and female mouse hippocampus.',
'authors' => 'Chinn Carlene A et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a well-characterized epigenetic modification involved in numerous molecular and cellular functions. Methylation patterns have also been associated with aging mechanisms. However, how DNA methylation patterns change within key brain regions involved in memory formation in an age- and sex-specific manner remains unclear. Here, we performed reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) from mouse dorsal hippocampus - which is necessary for the formation and consolidation of specific types of memories - in young and aging mice of both sexes. Overall, our findings demonstrate that methylation levels within the dorsal hippocampus are divergent between sexes during aging in genomic features correlating to mRNA functionality, transcription factor binding sites, and gene regulatory elements. These results define age-related changes in the methylome across genomic features and build a foundation for investigating potential target genes regulated by DNA methylation in an age- and sex-specific manner.</p>',
'date' => '2021-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.neurobiolaging.2021.08.006',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.08.006',
'modified' => '2022-05-30 09:54:05',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 34 => array(
'id' => '4100',
'name' => 'Therapy-induced DNA methylation inactivates MCT1 and renders tumor cells vulnerable to MCT4 inhibition',
'authors' => 'Catherine Vander Linden, Cyril Corbet, Estelle Bastien, Ruben Martherus, Céline Guilbaud, Laurenne Petit, Loris Wauthier, Axelle Loriot, Charles De Smet, Olivier Feron',
'description' => '<p><span>Metabolic plasticity in cancer cells makes use of metabolism-targeting agents very challenging. Drug-induced metabolic rewiring may, however, uncover vulnerabilities that can be exploited. We report that resistance to glycolysis inhibitor 3-bromopyruvate (3-BrPA) arises from DNA methylation in treated cancer cells and subsequent silencing of the monocarboxylate transporter MCT1. We observe that, unexpectedly, 3-BrPA-resistant cancer cells mostly rely on glycolysis to sustain their growth, with MCT4 as an essential player to support lactate flux. This shift makes cancer cells particularly suited to adapt to hypoxic conditions and resist OXPHOS inhibitors and anti-proliferative chemotherapy. In contrast, blockade of MCT4 activity in 3-BrPA-exposed cancer cells with diclofenac or genetic knockout, inhibits growth of derived spheroids and tumors in mice. This study supports a potential mode of collateral lethality according to which metabolic adaptation of tumor cells to a first-line therapy makes them more responsive to a second-line treatment.</span></p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)00551-9#%20',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109202',
'modified' => '2021-06-03 16:04:34',
'created' => '2021-06-03 14:16:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 35 => array(
'id' => '4330',
'name' => 'Epigenetic Plasticity Enables CNS-Trafficking of EBV-infectedB Lymphocytes',
'authors' => 'Soldan S. S. et al. ',
'description' => '<p>Subpopulations of B-lymphocytes traffic to different sites and organs to provide diverse and tissue-specific functions. Here, we provide evidence that epigenetic differences confer a neuroinvasive phenotype. An EBV+ B cell lymphoma cell line (M14) with low frequency trafficking to the CNS was neuroadapted to generate a highly neuroinvasive B-cell population (MUN14). MUN14 B cells efficiently infiltrated the CNS within one week and produced neurological pathologies. We compared the gene expression profiles of viral and cellular genes using RNA-Seq and identified one viral (EBNA1) and several cellular gene candidates, including secreted phosphoprotein 1/osteopontin (SPP1/OPN), neuron navigator 3 (NAV3), CXCR4, and germinal center-associated signaling and motility protein (GCSAM) that were selectively upregulated in MUN14. ATAC-Seq and ChIP-qPCR revealed that these gene expression changes correlated with epigenetic changes at gene regulatory elements. The neuroinvasive phenotype could be attenuated with a neutralizing antibody to OPN, confirming the functional role of this protein in trafficking EBV+ B cells to the CNS. These studies indicate that B-cell trafficking to the CNS can be acquired by epigenetic adaptations and provide a new model to study B-cell neuroinvasion associated CNS lymphoma and autoimmune disease of the CNS, including multiple sclerosis (MS).</p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34106998',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.ppat.1009618',
'modified' => '2022-08-03 16:11:53',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 36 => array(
'id' => '4354',
'name' => 'Dnmt1 has de novo activity targeted to transposable elements',
'authors' => 'Haggerty C. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation plays a critical role during development, particularly in repressing retrotransposons. The mammalian methylation landscape is dependent on the combined activities of the canonical maintenance enzyme Dnmt1 and the de novo Dnmts, 3a and 3b. Here, we demonstrate that Dnmt1 displays de novo methylation activity in vitro and in vivo with specific retrotransposon targeting. We used whole-genome bisulfite and long-read Nanopore sequencing in genetically engineered methylation-depleted mouse embryonic stem cells to provide an in-depth assessment and quantification of this activity. Utilizing additional knockout lines and molecular characterization, we show that the de novo methylation activity of Dnmt1 depends on Uhrf1, and its genomic recruitment overlaps with regions that enrich for Uhrf1, Trim28 and H3K9 trimethylation. Our data demonstrate that Dnmt1 can catalyze DNA methylation in both a de novo and maintenance context, especially at retrotransposons, where this mechanism may provide additional stability for long-term repression and epigenetic propagation throughout development.</p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34140676',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41594-021-00603-8',
'modified' => '2022-08-03 16:55:11',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 37 => array(
'id' => '4135',
'name' => 'Alterations of DNA Methylation Caused by Cold Plasma Treatment Restore Delayed Germination of Heat-Stressed Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seeds',
'authors' => 'Suriyasak, C. et al. ',
'description' => '<p>In rice (Oryza sativa L.), seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling exhibit delayed germination because of DNA methylation levels at promoters of abscisic acid (ABA, a germination-inhibiting hormone) catabolism genes and α-amylase (starchhydrolyzing enzyme) genes, affecting their expression levels. Cold atmospheric plasma is known as an innovative and sustainable energy that has positive effects on the growth and development of many plant species. We, therefore, treated seeds that matured under heat stress with cold plasma and found that subsequent germination was significantly restored; genes involved in ABA biosynthesis (OsNCED2 and OsNCED5) were downregulated, whereas genes involved in ABA catabolism (OsABA8′OH1 and OsABA8′OH3) and α-amylase genes (OsAmy1A, OsAmy1C, OsAmy3B, and OsAmy3E) were upregulated. Cold plasma treatment caused significant hypermethylation of the OsNCED5 promoter and hypomethylation of OsAmy1C and OsAmy3E promoters, which matched their expression patterns. We suggest that cold plasma treatment can significantly improve the germination of rice seeds affected by heat stress by affecting epigenetic regulation.</p>',
'date' => '2021-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1021%2Facsagscitech.0c00070',
'doi' => '10.1021/acsagscitech.0c00070',
'modified' => '2021-12-10 17:15:10',
'created' => '2021-12-06 15:53:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 38 => array(
'id' => '4057',
'name' => 'Prenatal Stress Leads to the Altered Maturation of Corticostriatal SynapticPlasticity and Related Behavioral Impairments Through EpigeneticModifications of Dopamine D2 Receptor in Mice.',
'authors' => 'Li, Yingchun and Rong, Jing and Zhong, Haiquan and Liang, Min and Zhu,Chunting and Chang, Fei and Zhou, Rong',
'description' => '<p>Prenatal stress (PRS) had a long-term adverse effect on motor behaviors. Corticostriatal synaptic plasticity, a cellular basis for motor controlling, has been proven to participate in the pathogenesis of many behavior disorders. Based on the reports about the involvement of epigenetic DNA alterations in PRS-induced long-term effects, this research investigated the influence of PRS on the development and maturation of corticostriatal synaptic plasticity and related behaviors and explored the underlying epigenetic mechanism. Subjects were male offspring of dams that were exposed to stress three times per day from the 10th day of pregnancy until delivery. The development and maturation of plasticity at corticostriatal synapses, dopamine signaling, behavioral habituation, and DNA methylation were examined and analyzed. Control mice expressed long-term potentiation (LTP) at corticostriatal synapses during postnatal days (PD) 12-14 and produced long-term depression (LTD) during PD 20-60. However, PRS mice exhibited sustained LTP during PD 12-60. The treatment with dopamine 2 receptor (D2R) agonist quinpirole recovered striatal LTD and improved the impaired behavioral habituation in PD 45 adult PRS mice. Additionally, adult PRS mice showed reduced D2R, excess DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), increased binding of DNMT1 to D2R promoter, and hypermethylation at D2R promoter in the striatum. The DNMT1 inhibitor 5-aza-deoxycytidine restored striatal synaptic plasticity and improved behavioral habituation in adult PRS mice via D2R-mediated dopamine signaling. DNMT1-associated D2R hypermethylation is responsible for altering the maturation of plasticity at corticostriatal synapses and impairing the behavioral habituation in PRS mice.</p>',
'date' => '2021-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32935231',
'doi' => '10.1007/s12035-020-02127-6',
'modified' => '2021-02-19 17:23:03',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 39 => array(
'id' => '4200',
'name' => 'Comparative genome-wide methylation analysis of longissimus dorsi musclesin Yorkshire and Wannanhua pigs.',
'authors' => 'Li, X-J et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation was one of the earliest discovered epigenetic modifications in vertebrates, and is an important epigenetic mechanism involved in the expression of genes in many biological processes, including muscle growth and development. Its effects on economically important traits are evidenced in reported differences in meat quality traits between Chinese indigenous pig breeds (Wannanhua pig) and Western commercial pig breeds (Yorkshire pig), and this presents a unique model for analyzing the effects of DNA methylation on these traits. In the present study, a whole genome DNA methylation analysis was performed on the two breeds using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation. GO functional enrichment and pathway enrichment analyses identified differentially methylated genes primarily associated with fatty acid metabolism, biological processes of muscle development and signaling pathways related to muscle development and pork quality. Differentially methylated genes were verified by sodium pyrosequencing, and the results were consistent with the sequencing results. The results of the integrative analysis between DNA methylation and gene expression revealed that the DNA methylation levels showed a significantly negative correlation with gene expression levels around the transcription start site of genes. In total, 41 genes were both differentially expressed and methylated; these genes were related to fat metabolism, lipid metabolism and skeletal muscle development. This study could help further explore the molecular mechanisms and phenotypic differences in pig growth and development among different breeds.</p>',
'date' => '2020-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33301219',
'doi' => '10.1111/age.13029',
'modified' => '2022-01-06 14:43:32',
'created' => '2021-12-06 15:53:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 40 => array(
'id' => '4041',
'name' => 'Mechanism of delayed seed germination caused by high temperature duringgrain filling in rice (Oryza sativa L.).',
'authors' => 'Suriyasak, Chetphilin and Oyama, Yui and Ishida, Toshiaki and Mashiguchi,Kiyoshi and Yamaguchi, Shinjiro and Hamaoka, Norimitsu and Iwaya-Inoue,Mari and Ishibashi, Yushi',
'description' => '<p>High temperature during grain filling considerably reduces yield and quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.); however, how high temperature affects seed germination of the next generation is not yet well understood. Here, we report that seeds from plants exposed to high temperature during the grain filling stage germinated significantly later than seeds from unstressed plants. This delay remained even after dormancy release treatments, suggesting that it was not due to primary seed dormancy determined during grain filling. In imbibed embryos of heat-stressed seeds, expression of abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis genes (OsNCEDs) was higher than in those of control seeds, whereas that of ABA catabolism genes (OsABA8'OHs) was lower. In the aleurone layer, despite no change in GA signaling as evidenced by no effect of heat stress on OsGAMYB gene expression, the transcripts of α-amylase genes OsAmy1C, OsAmy3B, and OsAmy3E were significantly down-regulated in heat-stressed seeds in comparison with controls. Changes in promoter methylation levels were consistent with transcriptional changes of ABA catabolism-related and α-amylase genes. These data suggest that high temperature during grain filling results in DNA methylation of ABA catabolism-related and α-amylase gene promoters, delaying germination of heat-stressed seeds.</p>',
'date' => '2020-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33060675',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-020-74281-9',
'modified' => '2021-02-19 12:09:29',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 41 => array(
'id' => '4094',
'name' => 'Network integration and modelling of dynamic drug responses at multi-omicslevels.',
'authors' => 'Selevsek, Nathalie and Caiment, Florian and Nudischer, Ramona and Gmuender,Hans and Agarkova, Irina and Atkinson, Francis L and Bachmann, Ivo andBaier, Vanessa and Barel, Gal and Bauer, Chris and Boerno, Stefan and Bosc,Nicolas and Clayton, Olivia and ',
'description' => '<p>Uncovering cellular responses from heterogeneous genomic data is crucial for molecular medicine in particular for drug safety. This can be realized by integrating the molecular activities in networks of interacting proteins. As proof-of-concept we challenge network modeling with time-resolved proteome, transcriptome and methylome measurements in iPSC-derived human 3D cardiac microtissues to elucidate adverse mechanisms of anthracycline cardiotoxicity measured with four different drugs (doxorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin and daunorubicin). Dynamic molecular analysis at in vivo drug exposure levels reveal a network of 175 disease-associated proteins and identify common modules of anthracycline cardiotoxicity in vitro, related to mitochondrial and sarcomere function as well as remodeling of extracellular matrix. These in vitro-identified modules are transferable and are evaluated with biopsies of cardiomyopathy patients. This to our knowledge most comprehensive study on anthracycline cardiotoxicity demonstrates a reproducible workflow for molecular medicine and serves as a template for detecting adverse drug responses from complex omics data.</p>',
'date' => '2020-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33060801',
'doi' => '10.1038/s42003-020-01302-8',
'modified' => '2021-03-17 17:16:56',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 42 => array(
'id' => '4009',
'name' => 'Frataxin gene editing rescues Friedreich's ataxia pathology in dorsal rootganglia organoid-derived sensory neurons.',
'authors' => 'Mazzara, PG and Muggeo, S and Luoni, M and Massimino, L and Zaghi, M andValverde, PT and Brusco, S and Marzi, MJ and Palma, C and Colasante, Gand Iannielli, A and Paulis, M and Cordiglieri, C and Giannelli, SG andPodini, P and Gellera, C and Ta',
'description' => '<p>Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal-recessive neurodegenerative and cardiac disorder which occurs when transcription of the FXN gene is silenced due to an excessive expansion of GAA repeats into its first intron. Herein, we generate dorsal root ganglia organoids (DRG organoids) by in vitro differentiation of human iPSCs. Bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing show that DRG organoids present a transcriptional signature similar to native DRGs and display the main peripheral sensory neuronal and glial cell subtypes. Furthermore, when co-cultured with human intrafusal muscle fibers, DRG organoid sensory neurons contact their peripheral targets and reconstitute the muscle spindle proprioceptive receptors. FRDA DRG organoids model some molecular and cellular deficits of the disease that are rescued when the entire FXN intron 1 is removed, and not with the excision of the expanded GAA tract. These results strongly suggest that removal of the repressed chromatin flanking the GAA tract might contribute to rescue FXN total expression and fully revert the pathological hallmarks of FRDA DRG neurons.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-21',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32826895',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41467-020-17954-3',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:12:57',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 43 => array(
'id' => '4017',
'name' => 'Integrated analysis of DNA methylation profile of HLA-G gene andimaging in coronary heart disease: Pilot study.',
'authors' => 'Schiano, C and Benincasa, G and Infante, T and Franzese, M and Castaldo, Rand Fiorito, C and Mansueto, G and Grimaldi, V and Della, Valle G andFatone, G and Soricelli, A and Nicoletti, GF and Ruocco, A and Mauro, Cand Salvatore, M and Napoli, C',
'description' => '<p>AIMS: Immune endothelial inflammation, underlying coronary heart disease (CHD) related phenotypes, could provide new insight into the pathobiology of the disease. We investigated DNA methylation level of the unique CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients and evaluated the correlation with cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) features. METHODS: Thirty-two patients that underwent CCTA for suspected CHD were enrolled for this study. Obstructive CHD group included fourteen patients, in which there was a stenosis greater than or equal to 50\% in one or more of the major coronary arteries detected; whereas subjects with Calcium (Ca) Score = 0, uninjured coronaries and with no obstructive CHD (no critical stenosis, NCS) were considered as control subjects (n = 18). For both groups, DNA methylation profile of the whole 5'UTR-CpG island of HLA-G was measured. The plasma soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) levels were detected in all subjects by specific ELISA assay. Statistical analysis was performed using R software. RESULTS: For the first time, our study reported that 1) a significant hypomethylation characterized three specific fragments (B, C and F) of the 5'UTR-CpG island (p = 0.05) of HLA-G gene in CHD patients compared to control group; 2) the hypomethylation level of one specific fragment of 161bp (+616/+777) positively correlated with coronary Ca score, a relevant parameter of CCTA (p<0.05) between two groups evaluated and was predictive for disease severity. CONCLUSIONS: Reduced levels of circulating HLA-G molecules could derive from epigenetic marks. Epigenetics phenomena induce hypomethylation of specific regions into 5'UTR-CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients with obstructive non critical stenosis vs coronary stenosis individuals.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-13',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32790754',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0236951',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:37:03',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 44 => array(
'id' => '4021',
'name' => 'Comparative DNA methylome analysis of estrus ewes reveals the complexregulatory pathways of sheep fecundity.',
'authors' => 'Miao, X and Luo, Q and Xie, L and Zhao, H and Qin, X',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND/AIMS: Sheep are important livestock with variant ovulation rate and fertility. Dorset sheep is a typical breed with low prolificacy, whereas Small Tail Han sheep with FecB mutation (HanBB) have hyperprolificacy. Our previous studies have revealed the gene expression difference between the ovaries from Dorset and HanBB sheep contributes to the difference of fecundity, however, what leads to these gene expression difference remains unclear. DNA methylation, an important epigenetic process, plays a crucial role in gene expression regulation. METHODS: In the present study, we constructed a methylated DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) strategy to investigate the differentially methylated genes between the Dorset and HanBB ovaries. RESULTS: Our findings suggest the genes involved in immune response, branched-chain amino acid metabolism, cell growth and cell junction were differentially methylated in or around the gene body regions. CONCLUSIONS: These findings provide prospective insights on the epigenetic basis of sheep fecundity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32753034',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12958-020-00633-9',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:45:28',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 45 => array(
'id' => '4028',
'name' => 'Methylation in pericytes after acute injury promotes chronic kidneydisease.',
'authors' => 'Chou, YH and Pan, SY and Shao, YH and Shih, HM and Wei, SY andLai, CF and Chiang, WC and Schrimpf, C and Yang, KC and Lai, LC andChen, YM and Chu, TS and Lin, SL',
'description' => '<p>The origin and fate of renal myofibroblasts is not clear after acute kidney injury (AKI). Here, we demonstrate that myofibroblasts were activated from quiescent pericytes (qPericytes) and the cell numbers increased after ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced AKI (IRI-AKI). Myofibroblasts underwent apoptosis during renal recovery but one-fifth of them survived in the recovered kidneys on day 28 after IRI-AKI and their cell numbers increased again after day 56. Microarray data showed the distinctive gene expression patterns of qPericytes, activated pericytes (aPericytes, myofibroblasts), and inactivated pericytes (iPericytes) isolated from kidneys before, on day 7, and on day 28 after IRI-AKI. Hypermethylation of the Acta2 repressor Ybx2 during IRI-AKI resulted in epigenetic modification of iPericytes to promote the transition to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and aggravated fibrogenesis induced by a second AKI induced by adenine. Mechanistically, transforming growth factor-β1 decreased the binding of YBX2 to the promoter of Acta2 and induced Ybx2 hypermethylation, thereby increasing α-smooth muscle actin expression in aPericytes. Demethylation by 5-azacytidine recovered the microvascular stabilizing function of aPericytes, reversed the profibrotic property of iPericytes, prevented AKI-CKD transition, and attenuated fibrogenesis induced by a second adenine-AKI. In conclusion, intervention to erase hypermethylation of pericytes after AKI provides a strategy to stop the transition to CKD.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32749240',
'doi' => '10.1172/JCI135773.',
'modified' => '2020-12-18 13:25:55',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 46 => array(
'id' => '3998',
'name' => 'Integrated epigenetic biomarkers in circulating cell-free DNA as a robust classifier for pancreatic cancer.',
'authors' => 'Cao F, Wei A, Hu X, He Y, Zhang J, Xia L, Tu K, Yuan J, Guo Z, Liu H, Xie D, Li A',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: The high lethal rate of pancreatic cancer is partly due to a lack of efficient biomarkers for screening and early diagnosis. We attempted to develop effective and noninvasive methods using 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) markers from circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for the detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). RESULTS: A 24-feature 5mC model that can accurately discriminate PDAC from healthy controls (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.977, sensitivity = 0.824, specificity = 1) and a 5hmC prediction model with 27 features demonstrated excellent detection power in two distinct validation sets (AUC = 0.992 and 0.960, sensitivity = 0.786 and 0.857, specificity = 1 and 0.993). The 51-feature model combining 5mC and 5hmC markers outperformed both of the individual models, with an AUC of 0.997 (sensitivity = 0.938, specificity = 0.955) and particularly an improvement in the prediction sensitivity of PDAC. In addition, the weighted diagnosis score (wd-score) calculated with the 5hmC model can distinguish stage I patients from stage II-IV patients. CONCLUSIONS: Both 5mC and 5hmC biomarkers in cfDNA are effective in PDAC detection, and the 5mC-5hmC integrated model significantly improve the detection sensitivity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-07-23',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32703318',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13148-020-00898-2',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 14:43:06',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 47 => array(
'id' => '3985',
'name' => 'Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Nuzzo PV, Berchuck JE, Korthauer K, Spisak S, Nassar AH, Abou Alaiwi S, Chakravarthy A, Shen SY, Bakouny Z, Boccardo F, Steinharter J, Bouchard G, Curran CR, Pan W, Baca SC, Seo JH, Lee GM, Michaelson MD, Chang SL, Waikar SS, Sonpavde G, Irizarry RA, Pome',
'description' => '<p>Improving early cancer detection has the potential to substantially reduce cancer-related mortality. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) is a highly sensitive assay capable of detecting early-stage tumors. We report accurate classification of patients across all stages of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in plasma (area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.99) and demonstrate the validity of this assay to identify patients with RCC using urine cell-free DNA (cfDNA; AUROC of 0.86).</p>',
'date' => '2020-06-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32572266',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41591-020-0933-1',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 15:13:49',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 48 => array(
'id' => '3984',
'name' => 'Detection and discrimination of intracranial tumors using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Nassiri F, Chakravarthy A, Feng S, Shen SY, Nejad R, Zuccato JA, Voisin MR, Patil V, Horbinski C, Aldape K, Zadeh G, De Carvalho DD',
'description' => '<p>Definitive diagnosis of intracranial tumors relies on tissue specimens obtained by invasive surgery. Noninvasive diagnostic approaches provide an opportunity to avoid surgery and mitigate unnecessary risk to patients. In the present study, we show that DNA-methylation profiles from plasma reveal highly specific signatures to detect and accurately discriminate common primary intracranial tumors that share cell-of-origin lineages and can be challenging to distinguish using standard-of-care imaging.</p>',
'date' => '2020-06-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32572265',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41591-020-0932-2',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 15:14:45',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 49 => array(
'id' => '3942',
'name' => 'DNA methylation enzymes and PRC1 restrict B-cell Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein expression.',
'authors' => 'Guo R, Zhang Y, Teng M, Jiang C, Schineller M, Zhao B, Doench JG, O'Reilly RJ, Cesarman E, Giulino-Roth L, Gewurz BE',
'description' => '<p>To accomplish the remarkable task of lifelong infection, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) switches between four viral genome latency and lytic programmes to navigate the B-cell compartment and evade immune responses. The transforming programme, consisting of highly immunogenic EBV nuclear antigen (EBNA) and latent membrane proteins (LMPs), is expressed in newly infected B lymphocytes and in post-transplant lymphomas. On memory cell differentiation and in most EBV-associated Burkitt's lymphomas, all but one viral antigen are repressed for immunoevasion. To gain insights into the epigenetic mechanisms that restrict immunogenic oncoprotein expression, a genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screen was performed in EBV and Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Here, we show that the ubiquitin ligase ubiquitin-like PHD and RING finger domain-containing protein 1 (UHRF1) and its DNA methyltransferase partner DNA methyltransferase I (DNMT1) are critical for the restriction of EBNA and LMP expression. All UHRF1 reader and writer domains were necessary for silencing and DNMT3B was identified as an upstream viral genome CpG methylation initiator. Polycomb repressive complex I exerted a further layer of control over LMP expression, suggesting a second mechanism for latency programme switching. UHRF1, DNMT1 and DNMT3B are upregulated in germinal centre B cells, the Burkitt's lymphoma cell of origin, providing a molecular link between B-cell state and the EBV latency programme. These results suggest rational therapeutic targets to manipulate EBV oncoprotein expression.</p>',
'date' => '2020-05-18',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32424339',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41564-020-0724-y',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:24:57',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 50 => array(
'id' => '3926',
'name' => 'TET-Mediated Hypermethylation Primes SDH-Deficient Cells for HIF2α-Driven Mesenchymal Transition.',
'authors' => 'Morin A, Goncalves J, Moog S, Castro-Vega LJ, Job S, Buffet A, Fontenille MJ, Woszczyk J, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Letouzé E, Favier J',
'description' => '<p>Loss-of-function mutations in the SDHB subunit of succinate dehydrogenase predispose patients to aggressive tumors characterized by pseudohypoxic and hypermethylator phenotypes. The mechanisms leading to DNA hypermethylation and its contribution to SDH-deficient cancers remain undemonstrated. We examine the genome-wide distribution of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and their correlation with RNA expression in SDHB-deficient tumors and murine Sdhb cells. We report that DNA hypermethylation results from TET inhibition. Although it preferentially affects PRC2 targets and known developmental genes, PRC2 activity does not contribute to the DNA hypermethylator phenotype. We also prove, in vitro and in vivo, that TET silencing, although recapitulating the methylation profile of Sdhb cells, is not sufficient to drive their EMT-like phenotype, which requires additional HIF2α activation. Altogether, our findings reveal synergistic roles of TET repression and pseudohypoxia in the acquisition of metastatic traits, providing a rationale for targeting HIF2α and DNA methylation in SDH-associated malignancies.</p>',
'date' => '2020-03-31',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32234487',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.022',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:50:11',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 51 => array(
'id' => '3920',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Mantle Edge and Mantle Central from Pearl Oyster Pinctada fucata martensii.',
'authors' => 'Zhang J, Luo S, Gu Z, Deng Y, Jiao Y',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a type of epigenetic modification that alters gene expression without changing the DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. In this study, we identified six DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) genes and two methyl-CpG binding domain protein2 (MBD2) gene from Pinctada fucata martensii. We also analyzed the genome-wide DNA methylation levels of mantle edge (ME) and mantle central (MC) from P. f. martensii via methylated immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-Seq). Results revealed that both ME and MC had 122 million reads, and had 58,702 and 55,721 peaks, respectively. The obtained methylation patterns of gene elements and repeats showed that the methylation of the protein-coding genes, particularly intron and coding exons (CDSs), was more frequent than that of other genomic elements in the pearl oyster genome. We combined the methylation data with the RNA-seq data of the ME and MC of P. f. martensii and found that promoter, CDS, and intron methylation levels were positively correlated with gene expression levels except the highest gene expression level. We also identified 313 differential methylation genes (DMGs) and annotated 212 of them. These DMGs were significantly enriched in 30 pathways, such as amino acid and protein metabolism, energy metabolism, terpenoid synthesis, and immune-related pathways. This study comprehensively analyzed the methylomes of biomineralization-related tissues and helped enhance our understanding of the regulatory mechanism underlying shell formation.</p>',
'date' => '2020-03-06',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32140888',
'doi' => '10.1007/s10126-020-09957-4',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:58:42',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 52 => array(
'id' => '3859',
'name' => 'Preterm birth is associated with epigenetic programming of transgenerational hypertension in mice.',
'authors' => 'Dumeige L, Nehlich M, Viengchareun S, Perrot J, Pussard E, Lombès M, Martinerie L',
'description' => '<p>Renal and cardiovascular complications of prematurity are well established, notably the development of hypertension in adulthood. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Our objective was to investigate the impact of prematurity on the ontogenesis of renal corticosteroid pathways, to evaluate its implication in perinatal renal complications and in the emergence of hypertension in adulthood. Swiss CD1 pregnant mice were injected with lipopolysaccharides at 18 days of gestation (E18) to induce prematurity at E18.5. Pups were sacrificed at birth, 7 days and 6 months of life. Second (F2) and third (F3) generations, established by mating prematurely born adult females with wild-type males, were also analyzed. Former preterm males developed hypertension at M6 (P < 0.0001). We found robust activation of renal corticosteroid target gene transcription at birth in preterm mice (αENaC (+45%), Gilz (+85%)), independent of any change in mineralocorticoid or glucocorticoid receptor expression. The offspring of the preterm group displayed increased blood pressure in F2 and F3, associated with increased renal Gilz mRNA expression, despite similar MR or GR expression and plasma corticosteroid levels measured by LC-MS/MS. Gilz promoter methylation measured by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR was reduced with a negative correlation between methylation and expression (P = 0.0106). Our study demonstrates prematurity-related alterations in renal corticosteroid signaling pathways, with transgenerational inheritance of blood pressure dysregulation and epigenetic Gilz regulation up to the third generation. This study provides a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in essential hypertension, which could partly be due to perinatal epigenetic programming from previous generations.</p>',
'date' => '2020-01-24',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31974504',
'doi' => '10.1038/s12276-020-0373-5',
'modified' => '2020-03-20 17:55:50',
'created' => '2020-03-13 13:45:54',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 53 => array(
'id' => '3855',
'name' => 'Alteration in global DNA methylation status following preconditioning injury influences axon growth competence of the sensory neurons.',
'authors' => 'Shin HY, Kim K, Kwon MJ, Oh YJ, Kim EH, Kim HS, Hong CP, Lee JH, Lee K, Kim BG',
'description' => '<p>Preconditioning peripheral nerve injury primes the sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) to acquire axon regeneration competence. Transcription of a large set of regeneration-associated-genes (RAGs) contributes to the enhanced intrinsic axonal regeneration capacity. However, the mechanism underlying the coordinated upregulation of RAGs orchestrated by preconditioning injury is unclear. We sought to determine potential influence of DNA methylation change on transcriptional activation of RAGs in the L4-L6 DRGs following sciatic nerve injury. Genome-wide sequencing revealed that about 20% of the methylated DNA fragments were differentially methylated, and >3000 genes contained differentially methylated regions. Not only demethylation but also increased methylation was observed to a similar extent. The change in the global DNA methylation did not correlate with the gene expression level of most genes, including the well-documented RAGs. However, pharmacological inhibition or activation of DNA methylation markedly attenuated the axon growth capacity of the preconditioned DRG neurons. Pharmacological perturbation of DNA methylation resulted in simultaneous downregulation of many highly overlapping non-transcription factor RAGs, which was accompanied by a concurrent, robust upregulation of SOCS3 and Serpine1. Overexpression of SOCS3 and Serpine1 in the DRG neurons overrode injury-induced axon growth competence, corroborating their roles as the negative regulators of axon regeneration. We conclude that the injury-induced global alteration of DNA methylome strongly influences the axon growth competence in preconditioned DRG neurons. Our results also suggest a possibility that perturbing DNA methylome changes might lead to the upregulation of negative regulator RAGs thereby attenuating axon growth capacity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-01-08',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31926166',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113177',
'modified' => '2020-03-20 17:59:09',
'created' => '2020-03-13 13:45:54',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 54 => array(
'id' => '3814',
'name' => 'Lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced changes in rodent neural progenitors and rescues cognition.',
'authors' => 'Zanni G, Goto S, Fragopoulou AF, Gaudenzi G, Naidoo V, Di Martino E, Levy G, Dominguez CA, Dethlefsen O, Cedazo-Minguez A, Merino-Serrais P, Stamatakis A, Hermanson O, Blomgren K',
'description' => '<p>Cranial radiotherapy in children has detrimental effects on cognition, mood, and social competence in young cancer survivors. Treatments harnessing hippocampal neurogenesis are currently of great relevance in this context. Lithium, a well-known mood stabilizer, has both neuroprotective, pro-neurogenic as well as antitumor effects, and in the current study we introduced lithium treatment 4 weeks after irradiation. Female mice received a single 4 Gy whole-brain radiation dose on postnatal day (PND) 21 and were randomized to 0.24% Li2CO chow or normal chow from PND 49 to 77. Hippocampal neurogenesis was assessed on PND 77, 91, and 105. We found that lithium treatment had a pro-proliferative effect on neural progenitors, but neuronal integration occurred only after it was discontinued. Also, the treatment ameliorated deficits in spatial learning and memory retention observed in irradiated mice. Gene expression profiling and DNA methylation analysis identified two novel factors related to the observed effects, Tppp, associated with microtubule stabilization, and GAD2/65, associated with neuronal signaling. Our results show that lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced loss of hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive impairment even when introduced long after the injury. We propose that lithium treatment should be intermittent in order to first make neural progenitors proliferate and then, upon discontinuation, allow them to differentiate. Our findings suggest that pharmacological treatment of cognitive so-called late effects in childhood cancer survivors is possible.</p>',
'date' => '2019-11-14',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31723242',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41380-019-0584-0',
'modified' => '2019-12-05 10:58:44',
'created' => '2019-12-02 15:25:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 55 => array(
'id' => '3773',
'name' => 'Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA.',
'authors' => 'Shen SY, Burgener JM, Bratman SV, De Carvalho DD',
'description' => '<p>Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) comprises small DNA fragments derived from normal and tumor tissue that are released into the bloodstream. Recently, methylation profiling of cfDNA as a liquid biopsy tool has been gaining prominence due to the presence of tissue-specific markers in cfDNA. We have previously reported cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) as a sensitive, low-input, cost-efficient and bisulfite-free approach to profiling DNA methylomes of plasma cfDNA. cfMeDIP-seq is an extension of a previously published MeDIP-seq protocol and is adapted to allow for methylome profiling of samples with low input (ranging from 1 to 10 ng) of DNA, which is enabled by the addition of 'filler DNA' before immunoprecipitation. This protocol is not limited to plasma cfDNA; it can also be applied to other samples that are naturally sheared and at low availability (e.g., urinary cfDNA and cerebrospinal fluid cfDNA), and is potentially applicable to other applications beyond cancer detection, including prenatal diagnostics, cardiology and monitoring of immune response. The protocol presented here should enable any standard molecular laboratory to generate cfMeDIP-seq libraries from plasma cfDNA in ~3-4 d.</p>',
'date' => '2019-08-30',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31471598',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41596-019-0202-2',
'modified' => '2019-10-02 17:07:45',
'created' => '2019-10-02 16:16:55',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 56 => array(
'id' => '3761',
'name' => 'Single-base methylome profiling of the giant kelp Saccharina japonica reveals significant differences in DNA methylation to microalgae and plants.',
'authors' => 'Fan X, Han W, Teng L, Jiang P, Zhang X, Xu D, Li C, Pellegrini M, Wu C, Wang Y, Kaczurowski MJS, Lin X, Tirichine L, Mock T, Ye N',
'description' => '<p>Brown algae have convergently evolved plant-like body plans and reproductive cycles, which in plants are controlled by differential DNA methylation. Here we provide the first single-base methylome profiles of haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes of a multicellular alga. Although only c. 1.4% of cytosines in Saccharina japonica were methylated mainly at CHH sites and characterised by 5-methylcytosine (5mC), there were significant differences between life-cycle stages. DNA methyltransferase 2 (DNMT2), known to efficiently catalyze tRNA methylation, is assumed to methylate the genome of S. japonica in the structural context of tRNAs as the genome does not encode any other DNA methyltransferases. Circular and long non-coding RNA genes were the most strongly methylated regulatory elements in S. japonica. Differential expression of genes was negatively correlated with DNA methylation with the highest methylation levels measured in both haploid gametophytes. Hypomethylated and highly expressed genes in diploid sporophytes included genes involved in morphogenesis and halogen metabolism. Our data give evidence that cytosine methylation, although occurring at a low level, is significantly contributing to the formation of different life-cycle stages, tissue differentiation, and metabolism in brown algae.</p>',
'date' => '2019-08-16',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31419316',
'doi' => '10.1111/nph.16125',
'modified' => '2019-10-03 10:04:08',
'created' => '2019-10-02 16:16:55',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 57 => array(
'id' => '3720',
'name' => 'Genome-wide methylation in alcohol use disorder subjects: implications for an epigenetic regulation of the cortico-limbic glucocorticoid receptors (NR3C1).',
'authors' => 'Gatta E, Grayson DR, Auta J, Saudagar V, Dong E, Chen Y, Krishnan HR, Drnevich J, Pandey SC, Guidotti A',
'description' => '<p>Environmental factors, including substance abuse and stress, cause long-lasting changes in the regulation of gene expression in the brain via epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation. We examined genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the prefrontal cortex (PFC, BA10) of 25 pairs of control and individuals with alcohol use disorder (AUD), using the Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip. We identified 5254 differentially methylated CpGs (p < 0.005). Bioinformatic analyses highlighted biological processes containing genes related to stress adaptation, including the glucocorticoid receptor (encoded by NR3C1). Considering that alcohol is a stressor, we focused our attention on differentially methylated regions of the NR3C1 gene and validated the differential methylation of several genes in the NR3C1 network. Chronic alcohol drinking results in a significant increased methylation of the NR3C1 exon variant 1, with a particular increase in the levels of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine over 5-methylcytosine. These changes in DNA methylation were associated with reduced NR3C1 mRNA and protein expression levels in PFC, as well as other cortico-limbic regions of AUD subjects when compared with controls. Furthermore, we show that the expression of several stress-responsive genes (e.g., CRF, POMC, and FKBP5) is altered in the PFC of AUD subjects. These stress-response genes were also changed in the hippocampus, a region that is highly susceptible to stress. These data suggest that alcohol-dependent aberrant DNA methylation of NR3C1 and consequent changes in other stress-related genes might be fundamental in the pathophysiology of AUD and lay the groundwork for treatments targeting the epigenetic mechanisms regulating NR3C1 in AUD.</p>',
'date' => '2019-06-25',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31239533',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41380-019-0449-6',
'modified' => '2019-07-04 18:07:16',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 58 => array(
'id' => '3604',
'name' => 'DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene in a CUMS model of depression.',
'authors' => 'Xiang D, Xiao J, Fu L, Yao L, Wan Q, Xiao L, Zhu F, Wang G, Liu Z',
'description' => '<p>Tacr2, the gene encoding the NK2 receptor, belongs to G protein-coupled receptors. Accumulating evidence has indicated that the tachykinin receptors may contribute to the pathophysiology of depression. During the last decade, some studies have shown that Tacr2 activation is involved in the modulation of emotional processes. However, the extent, to which stress impacts Tacr2 expression remains unclear. The molecular mechanisms underlying depression also remain poorly understood. In this study, we subjected adult male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) to induce a depression-like phenotype. We then measured the body weight and performed the sucrose preference test, forced swimming test (FST) and open field test to detect the effects of stress on anhedonia and activity. Western blotting and real-time PCR were used to study the protein and mRNA expression levels of Tacr2, respectively, in the hypothalamus. To explore DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene, we used methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Additionally, we used the bisulfite sequencing PCR (BSP) to further verify the DNA methylation levels of the Tacr2 receptor gene in rats. We found that the CUMS-sensitive rats exhibited a decrease in body weight and sucrose preference, a decrease in the distance traveled, rearing frequency and velocity in the open field test, and an increase in immobility time in the FST. Compared with the expression in the control rats, Tacr2 protein and mRNA expression in the hypothalamus significantly increased in the CUMS-sensitive rats; however, the DNA methylation levels of the Tacr2 gene were significantly lower than in the control rats. In summary, according to our findings, the stress-induced increase in Tacr2 expression in the hypothalamus correlated with a specific decrease in DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene. These results may enrich the understanding of the pathological processes of depression and provide insights into therapeutic approaches for its treatment.</p>',
'date' => '2019-06-03',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30711443',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.bbr.2019.01.059',
'modified' => '2019-04-16 13:54:40',
'created' => '2019-04-16 12:25:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 59 => array(
'id' => '3666',
'name' => 'Epigenetic Alterations in Juvenile Spondyloarthritis Patients: a Preliminary Study of Selected Genes Promoter Methylation and Silencing',
'authors' => 'Lamot Lovro, Blažeković Antonela, Jerčić Kristina Gotovac, Ivković Tina Catela, Vidović Mandica, Lamot Mirta, Kapitanović Sanja, Borovečki Fran, Harjaček Miroslav',
'description' => '<p>Juvenile spondyloarthritis (jSpA) is a complex disease with both genetic and environmental factors contributing to etiology. Multiple studies have shown that epigenetic mechanisms could link the environment and gene expression and thus provide a potential explanation for external contribution in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, including rheumatic. Previously obtained gene signatures in jSpA patients revealed distinctive expression of important immune-related genes, though the mechanism(s) responsible for those alterations remained unknown. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the methylation levels of the TLR4, CXCR4, NLRP3, and PTPN12 gene promoter, along with the expression of several non-coding microRNAs (miR-150, miR-146a, miR-181a, and miR-223) in jSpA patients. Peripheral blood samples were obtained from 19 patients newly diagnosed with jSpA according to ILAR classification criteria for enthesitis-related arthritis (ErA) and seven gender- and age-matched subjects without any symptoms or signs of inflammatory disease. The expression of specific microRNAs was analyzed using qRT-PCR with predeveloped microRNA assays. DNA promoter region methylation status of selected genes was assessed by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) analysis. Fold enrichment of immunoprecipitated DNA differed significantly for NLRP3 promoter site, while the expression analysis of selected microRNAs showed no significant difference in fold change between jSpA patients and healthy controls. The results indicated that epigenetic modifications in the initial phase of the disease could be responsible for some of the expression alterations in jSpA patients. Since NLRP3 has a crucial role in inflammasome assembly and inflammasomes have been shown to shape microbiota, it is tempting to assume that dysbiosis in jSpA patients can at least partially be explained by reduced NLRP3 expression due to hypermethylation, stressing for the first time the epigenetic contribution to jSpA pathophysiology</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-09',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42399-019-00070-9',
'doi' => '10.1007/s42399-019-00070-9',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:53:06',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 60 => array(
'id' => '3846',
'name' => 'The methylation pattern of DNA and complex correlations with gene expressions during TuMV infection in Chinese cabbage',
'authors' => 'J. YU , L.-W. GAO , Y. YANG , C. LIU , R.-J. ZHANG , F.-F. SUN , L.-X. SONG , D. XIAO , T.-K. LIU , X.-L. HOU , and C.-W. ZHANG',
'description' => '<p>Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) is one of the most important economic crops. However, its yield and quality can be severely threatened by Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV). Emerging evidence indicates that epigenetic mechanisms, especially DNA methylation, play an important role in regulating gene expression. Therefore, identification of resistance genes modified by DNA methylation during the virus infection would provide a critical clue for improving disease resistance breeding programs. Here, we present detailed analysis for the correlation of DNA methylation and gene expression involved in several anti-pathogen pathways. We also found that different methylation patterns exist in different methylation sites (CG, CHG, and CHH, where H represents A, G, or T) and genomic regions. Furthermore, we identified disease-resistant genes related to the nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeats family, auxin, salicylic acid signaling transduction, cell wall biosynthesis, and protein degradation among the different methylated genes (DMGs) suggesting that these genes may be modified by DNA methylation and work together to activate an immune response. The identified DMGs are a valuable resource for discovering resistance genes. Our study not only provides valuable data for future biotechnology research and epigenetic studies, but also helps to explore how the epigenetic mechanisms modify antiviral pathways.</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-09',
'pmid' => 'https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337128882_The_methylation_pattern_of_DNA_and_complex_correlations_with_gene_expressions_during_TuMV_infection_in_Chinese_cabbage',
'doi' => '10.32615/bp.2019.073',
'modified' => '2020-02-20 11:12:23',
'created' => '2020-02-13 10:02:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 61 => array(
'id' => '3716',
'name' => 'Epigenetic control of the angiotensin-converting enzyme in endothelial cells during inflammation.',
'authors' => 'Mudersbach T, Siuda D, Kohlstedt K, Fleming I',
'description' => '<p>The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) plays a central role in the renin-angiotensin system, which is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. Alterations in ACE expression or activity are associated with various pathological phenotypes, particularly cardiovascular diseases. In human endothelial cells, ACE was shown to be negatively regulated by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α. To examine, whether or not, epigenetic factors were involved in ACE expression regulation, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and RNA interference experiments directed against regulators of DNA methylation homeostasis i.e., DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenases (TETs), were performed. TNFα stimulation enhanced DNA methylation in two distinct regions within the ACE promoter via a mechanism linked to DNMT3a and DNMT3b, but not to DNMT1. At the same time, TET1 protein expression was downregulated. In addition, DNA methylation decreased the binding affinity of the transcription factor MYC associated factor X to the ACE promoter. In conclusion, DNA methylation determines the TNFα-dependent regulation of ACE gene transcription and thus protein expression in human endothelial cells.</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31042763',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0216218',
'modified' => '2019-07-05 13:14:33',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 62 => array(
'id' => '3698',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in Tibetan and Yorkshire pigs under high-altitude hypoxia.',
'authors' => 'Zhang B, Ban D, Gou X, Zhang Y, Yang L, Chamba Y, Zhang H',
'description' => '<p>Background: Tibetan pigs, which inhabit the Tibetan Plateau, exhibit distinct phenotypic and physiological characteristics from those of lowland pigs and have adapted well to the extreme conditions at high altitude. However, the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of hypoxic adaptation in animals remain unclear. Methods: Whole-genome DNA methylation data were generated for heart tissues of Tibetan pigs grown in the highland (TH,  = 4) and lowland (TL,  = 4), as well as Yorkshire pigs grown in the highland (YH,  = 4) and lowland (YL,  = 4), using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing. Results: We obtained 480 million reads and detected 280679, 287224, 259066, and 332078 methylation enrichment peaks in TH, YH, TL, and YL, respectively. Pairwise TH vs. YH, TL vs. YL, TH vs. TL, and YH vs. YL comparisons revealed 6829, 11997, 2828, and 1286 differentially methylated regions (DMRs), respectively. These DMRs contained 384, 619, 192, and 92 differentially methylated genes (DMGs), respectively. DMGs that were enriched in the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signaling pathway and pathways involved in cancer and hypoxia-related processes were considered to be important candidate genes for high-altitude adaptation in Tibetan pigs. Conclusions: This study elucidates the molecular and epigenetic mechanisms involved in hypoxic adaptation in pigs and may help further understand human hypoxia-related diseases.</p>',
'date' => '2019-04-28',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30867905',
'doi' => '10.1186/s40104-019-0316-y',
'modified' => '2019-07-05 14:47:45',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 63 => array(
'id' => '3648',
'name' => 'Assessment and site-specific manipulation of DNA (hydroxy-)methylation during mouse corticogenesis.',
'authors' => 'Noack F, Pataskar A, Schneider M, Buchholz F, Tiwari VK, Calegari F',
'description' => '<p>Dynamic changes in DNA (hydroxy-)methylation are fundamental for stem cell differentiation. However, the signature of these epigenetic marks in specific cell types during corticogenesis is unknown. Moreover, site-specific manipulation of cytosine modifications is needed to reveal the significance and function of these changes. Here, we report the first assessment of (hydroxy-)methylation in neural stem cells, neurogenic progenitors, and newborn neurons during mammalian corticogenesis. We found that gain in hydroxymethylation and loss in methylation occur sequentially at specific cellular transitions during neurogenic commitment. We also found that these changes predominantly occur within enhancers of neurogenic genes up-regulated during neurogenesis and target of pioneer transcription factors. We further optimized the use of dCas9-Tet1 manipulation of (hydroxy-)methylation, locus-specifically, in vivo, showing the biological relevance of our observations for , a regulator of corticogenesis involved in developmental malformations and cognitive impairment. Together, our data reveal the dynamics of cytosine modifications in lineage-related cell types, whereby methylation is reduced and hydroxymethylation gained during the neurogenic lineage concurrently with up-regulation of pioneer transcription factors and activation of enhancers for neurogenic genes.</p>',
'date' => '2019-04-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30814272',
'doi' => '10.1038/nrg.2017.57',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:13:14',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 64 => array(
'id' => '3647',
'name' => 'DMSO induces drastic changes in human cellular processes and epigenetic landscape in vitro.',
'authors' => 'Verheijen M, Lienhard M, Schrooders Y, Clayton O, Nudischer R, Boerno S, Timmermann B, Selevsek N, Schlapbach R, Gmuender H, Gotta S, Geraedts J, Herwig R, Kleinjans J, Caiment F',
'description' => '<p>Though clinical trials for medical applications of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) reported toxicity in the 1960s, later, the FDA classified DMSO in the safest solvent category. DMSO became widely used in many biomedical fields and biological effects were overlooked. Meanwhile, biomedical science has evolved towards sensitive high-throughput techniques and new research areas, including epigenomics and microRNAs. Considering its wide use, especially for cryopreservation and in vitro assays, we evaluated biological effect of DMSO using these technological innovations. We exposed 3D cardiac and hepatic microtissues to medium with or without 0.1% DMSO and analyzed the transcriptome, proteome and DNA methylation profiles. In both tissue types, transcriptome analysis detected >2000 differentially expressed genes affecting similar biological processes, thereby indicating consistent cross-organ actions of DMSO. Furthermore, microRNA analysis revealed large-scale deregulations of cardiac microRNAs and smaller, though still massive, effects in hepatic microtissues. Genome-wide methylation patterns also revealed tissue-specificity. While hepatic microtissues demonstrated non-significant changes, findings from cardiac microtissues suggested disruption of DNA methylation mechanisms leading to genome-wide changes. The extreme changes in microRNAs and alterations in the epigenetic landscape indicate that DMSO is not inert. Its use should be reconsidered, especially for cryopreservation of embryos and oocytes, since it may impact embryonic development.</p>',
'date' => '2019-03-15',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30874586',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-019-40660-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:14:07',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 65 => array(
'id' => '3673',
'name' => 'Evidence of association of circulating epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers with suspected coronary heart disease evaluated by Cardiac Computed Tomography.',
'authors' => 'Infante T, Forte E, Schiano C, Punzo B, Cademartiri F, Cavaliere C, Salvatore M, Napoli C',
'description' => '<p>Circulating biomarkers available in clinical practice do not allow to stratify patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) prior the onset of a clinically relevant event. We evaluated the methylation status of specific genomic segments and gene expression in peripheral blood of patients undergoing Cardiac Computed Tomography (CCT) for CHD (n = 95). We choose to investigate cholesterol metabolism. Methylation and gene expression of low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), sterol regulatory element-binding factor 2 (SREBF2) and ATP-binding cassette transporter 1 (ABCA1) were evaluated by qRT-PCR. Calcium score (CACS), stenosis degree, total plaque volume (TPV), calcified plaque volume (CPV), non-calcified plaque volume (NCPV) and plaque burden (PB) were assessed in all CHD patients (n = 65). The percentage of methylation at the specific analyzed segment of LDLR promoter was higher in CHD patients vs healthy subjects (HS) (n = 30) (p = 0.001). LDLR, SREBF2 and ABCA1 mRNAs were up-regulated in CHD patients vs HS (p = 0.02; p = 0.019; p = 0.008). SREBF2 was overexpressed in patients with coronary stenosis ≥50% vs subjects with stenosis <50% (p = 0.036). After adjustment for risk factors and clinical features, ABCA1 (p = 0.005) and SREBF2 (p = 0.010) gene expression were identified as independent predictors of CHD and severity. ROC curve analysis revealed a good performance of ABCA1 on predicting CHD (AUC = 0.768; p<0.001) and of SREBF2 for the prediction of disease severity (AUC = 0.815; p<0.001). Moreover, adjusted multivariate analysis demonstrated SREBF2 as independent predictor of CPV, NCPV and TPV (p = 0.022; p = 0.002 and p = 0.006) and ABCA1 as independent predictor of NCPV and TPV (p = 0.002 and p = 0.013). CHD presence and characteristics are related to selected circulating transcriptional and epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers linked to cholesterol pathway. More extensive analysis of CHD phenotypes and circulating biomarkers might improve and personalize cardiovascular risk stratification in the clinical settings.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-23',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30673762',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0210909',
'modified' => '2019-07-01 11:27:58',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 66 => array(
'id' => '3655',
'name' => 'LncRNA Dnmt3aos regulates Dnmt3a expression leading to aberrant DNA methylation in macrophage polarization',
'authors' => 'Xueqin Li, Yingying Zhang, Mengying Zhang, Xiang Kong, Hui Yang, Min Zhong, Weiya Pei, Yang Xu, Xiaolong Zhu, Tianbing Chen, Jingjing Ye, and Kun ',
'description' => '<p>Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play key roles in various biological processes. However, the roles of lncRNAs in macrophage polarization remain largely unexplored. In this study, thousands of lncRNAs were identified that are differentially expressed in distinct polarized bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Among them, Dnmt3aos (DNA methyltransferase 3A, opposite strand), as a known lncRNA, locates on the antisense strand of Dnmt3a. Functional experiments further confirmed that Dnmt3aos were highly expressed in M(IL-4) macrophages and participated in the regulation of Dnmt3a expression, and played a key role in macrophage polarization. The DNA methylation profiles between the Dnmt3aos knockdown group and the control group in M(IL-4) macrophages were determined by MeDIP-seq technique for the first time, and the Dnmt3aos-Dnmt3a axis-mediated DNA methylation modification-regulated macrophage polarization related gene IFN-γ was identified. Our study will help to enrich our knowledge of the mechanism of macrophage polarization and will provide new insights for immunotherapy in macrophage-associated diseases.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-07',
'pmid' => 'https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/514307v1',
'doi' => '/',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:39:53',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 67 => array(
'id' => '3660',
'name' => 'Global distribution of DNA hydroxymethylation and DNA methylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.',
'authors' => 'Wernig-Zorc S, Yadav MP, Kopparapu PK, Bemark M, Kristjansdottir HL, Andersson PO, Kanduri C, Kanduri M',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has been a good model system to understand the functional role of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in cancer progression. More recently, an oxidized form of 5-mC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has gained lot of attention as a regulatory epigenetic modification with prognostic and diagnostic implications for several cancers. However, there is no global study exploring the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) levels in CLL. Herein, using mass spectrometry and hMeDIP-sequencing, we analysed the dynamics of 5-hmC during B cell maturation and CLL pathogenesis. RESULTS: We show that naïve B-cells had higher levels of 5-hmC and 5-mC compared to non-class switched and class-switched memory B-cells. We found a significant decrease in global 5-mC levels in CLL patients (n = 15) compared to naïve and memory B cells, with no changes detected between the CLL prognostic groups. On the other hand, global 5-hmC levels of CLL patients were similar to memory B cells and reduced compared to naïve B cells. Interestingly, 5-hmC levels were increased at regulatory regions such as gene-body, CpG island shores and shelves and 5-hmC distribution over the gene-body positively correlated with degree of transcriptional activity. Importantly, CLL samples showed aberrant 5-hmC and 5-mC pattern over gene-body compared to well-defined patterns in normal B-cells. Integrated analysis of 5-hmC and RNA-sequencing from CLL datasets identified three novel oncogenic drivers that could have potential roles in CLL development and progression. CONCLUSIONS: Thus, our study suggests that the global loss of 5-hmC, accompanied by its significant increase at the gene regulatory regions, constitute a novel hallmark of CLL pathogenesis. Our combined analysis of 5-mC and 5-hmC sequencing provided insights into the potential role of 5-hmC in modulating gene expression changes during CLL pathogenesis.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30616658',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13072‑018‑0252‑7',
'modified' => '2019-07-01 11:46:16',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 68 => array(
'id' => '3430',
'name' => 'Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Shen SY, Singhania R, Fehringer G, Chakravarthy A, Roehrl MHA, Chadwick D, Zuzarte PC, Borgida A, Wang TT, Li T, Kis O, Zhao Z, Spreafico A, Medina TDS, Wang Y, Roulois D, Ettayebi I, Chen Z, Chow S, Murphy T, Arruda A, O'Kane GM, Liu J, Mansour M, McPher',
'description' => '<p>The use of liquid biopsies for cancer detection and management is rapidly gaining prominence. Current methods for the detection of circulating tumour DNA involve sequencing somatic mutations using cell-free DNA, but the sensitivity of these methods may be low among patients with early-stage cancer given the limited number of recurrent mutations. By contrast, large-scale epigenetic alterations-which are tissue- and cancer-type specific-are not similarly constrained and therefore potentially have greater ability to detect and classify cancers in patients with early-stage disease. Here we develop a sensitive, immunoprecipitation-based protocol to analyse the methylome of small quantities of circulating cell-free DNA, and demonstrate the ability to detect large-scale DNA methylation changes that are enriched for tumour-specific patterns. We also demonstrate robust performance in cancer detection and classification across an extensive collection of plasma samples from several tumour types. This work sets the stage to establish biomarkers for the minimally invasive detection, interception and classification of early-stage cancers based on plasma cell-free DNA methylation patterns.</p>',
'date' => '2018-11-14',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30429608',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41586-018-0703-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-11 16:22:54',
'created' => '2018-12-04 09:51:07',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 69 => array(
'id' => '3511',
'name' => 'Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation to identify genes and pathways associated with male sterility in soybean',
'authors' => 'Han Shaohuai, Li Yanwei, Li Jiajia, Zhang Hao, Ding Xianlong, He Tingting, Gai Junyi, Yang Shouping',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification, which is important for gene expression regulation. Although genome-wide DNA methylation studies have been reported in several plant species, the difference in the methylation pattern between the cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) line and its maintainer in soybean remains unclear. We compared genome-wide DNA methylation between the soybean CMS line NJCMS1A and its maintainer NJCMS1B using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) technology. The results showed that the methylation level was higher in transposable elements (TEs) than promoter and intron; however, the methylation levels varied among different types of TEs with the highest level for long terminal repeats (LTRs) and the lowest for transcription start sites (TSS) and transcription termination sites (TTS). We observed 178 differentially methylated genes (DMGs) between NJCMS1A and NJCMS1B, including 156 hypomethylated and 22 hyper-methylated genes in NJCMS1A compared to NJCMS1B. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis showed that 114 DMGs were annotated to one or more GO categories, among which four GO terms were significantly enriched. KEGG pathway analysis showed that 18 DMGs were significantly enriched in 10 metabolism pathways, including homologous recombination, purine metabolism, proteasome, non-homologous end-joining, and pyrimidine</p>',
'date' => '2018-09-16',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11032-018-0875-1',
'doi' => '10.1007/s11032-018-0875-1',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:44:53',
'created' => '2019-02-27 12:54:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 70 => array(
'id' => '3585',
'name' => 'Folic acid supplementation alters the DNA methylation profile and improves insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed mice.',
'authors' => 'Li W, Tang R, Ma F, Ouyang S, Liu Z, Wu J',
'description' => '<p>Folic acid (FA) supplementation may protect from obesity and insulin resistance, the effects and mechanism of FA on chronic high-fat-diet-induced obesity-related metabolic disorders are not well elucidated. We adopted a genome-wide approach to directly examine whether FA supplementation affects the DNA methylation profile of mouse adipose tissue and identify the functional consequences of these changes. Mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), normal diet (ND) or an HFD supplemented with folic acid (20 μg/ml in drinking water) for 10 weeks, epididymal fat was harvested, and genome-wide DNA methylation analyses were performed using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Mice exposed to the HFD expanded their adipose mass, which was accompanied by a significant increase in circulating glucose and insulin levels. FA supplementation reduced the fat mass and serum glucose levels and improved insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. MeDIP-seq revealed distribution of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) throughout the adipocyte genome, with more hypermethylated regions in HFD mice. Methylome profiling identified DMRs associated with 3787 annotated genes from HFD mice in response to FA supplementation. Pathway analyses showed novel DNA methylation changes in adipose genes associated with insulin secretion, pancreatic secretion and type 2 diabetes. The differential DNA methylation corresponded to changes in the adipose tissue gene expression of Adcy3 and Rapgef4 in mice exposed to a diet containing FA. FA supplementation improved insulin resistance, decreased the fat mass, and induced DNA methylation and gene expression changes in genes associated with obesity and insulin secretion in obese mice fed a HFD.</p>',
'date' => '2018-09-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29986310',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.05.010',
'modified' => '2019-04-17 15:33:46',
'created' => '2019-04-16 12:25:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 71 => array(
'id' => '3633',
'name' => 'Embryonic germ cell extracts erase imprinted genes and improve the efficiency of induced pluripotent stem cells.',
'authors' => 'Hu J, Zhao Q, Feng Y, Li N, Gu Y, Sun R, Duan L, Wu Y, Shan Z, Lei L',
'description' => '<p>Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have the potential to be useful in the treatment of human diseases. While prior studies have reported multiple methods to generate iPSCs, DNA methylation continues to limit the totipotency and reprogramming efficiency of iPSCs. Here, we first show the competency of embryonic germ cells (EGCs) as a reprogramming catalyst capable of effectively promoting reprogramming induced by four defined factors, including Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc. Combining EGC extracts with these four factors resulted in formation of more embryonic stem cell-like colonies than did factors alone. Notably, expression of imprinted genes was higher with combined induction than with factors alone. Moreover, iPSCs derived from the combined inductors tended to have more global hypomethylation. Our research not only provides evidence that EGC extracts could activate DNA demethylation and reprogram imprinted genes, but also establishes a new way to enhance reprogramming of iPSCs, which remains a critical safety concern for potential use of iPSCs in regenerative medicine.</p>',
'date' => '2018-07-19',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30026469',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-018-29339-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:30:27',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 72 => array(
'id' => '3393',
'name' => 'Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos.',
'authors' => 'Sussarellu R, Lebreton M, Rouxel J, Akcha F, Rivière G',
'description' => '<p>Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better understand whether the embryotoxic effects of copper in Crassostrea gigas could be mediated by alterations in gene expression, and the putative role of DNA methylation, which is known to contribute to gene regulation in early embryo development. For that purpose, oyster embryos were exposed to 4 nominal copper concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 μg L Cu) during early development assays. Embryotoxicity was monitored through the oyster embryo-larval bioassay at the D-larva stage 24 h post fertilization (hpf) and genotoxicity at gastrulation 7 hpf. In parallel, the relative expression of 15 genes encoding putative homeotic, biomineralization and DNA methylation proteins was measured at three developmental stages (3 hpf morula stage, 7 hpf gastrula stage, 24 hpf D-larvae stage) using RT-qPCR. Global DNA content in methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine were measured by HPLC and gene-specific DNA methylation levels were monitored using MeDIP-qPCR. A significant increase in larval abnormalities was observed from copper concentrations of 10 μg L, while significant genotoxic effects were detected at 1 μg L and above. All the selected genes presented a stage-dependent expression pattern, which was impaired for some homeobox and DNA methylation genes (Notochord, HOXA1, HOX2, Lox5, DNMT3b and CXXC-1) after copper exposure. While global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) at gastrula stage didn't show significant changes between experimental conditions, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its degradation product, decreased upon copper treatment. The DNA methylation of exons and the transcript levels were correlated in control samples for HOXA1 but such a correlation was diminished following copper exposure. The methylation level of some specific gene regions (HoxA1, Hox2, Engrailed2 and Notochord) displayed changes upon copper exposure. Such changes were gene and exon-specific and no obvious global trends could be identified. Our study suggests that the embryotoxic effects of copper in oysters could involve homeotic gene expression impairment possibly by changing DNA methylation levels.</p>',
'date' => '2018-03-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29353135',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.001',
'modified' => '2018-11-09 12:21:38',
'created' => '2018-11-08 12:59:45',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 73 => array(
'id' => '3448',
'name' => 'Aberrant methylated key genes of methyl group metabolism within the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinogenesis.',
'authors' => 'Erichsen L, Ghanjati F, Beermann A, Poyet C, Hermanns T, Schulz WA, Seifert HH, Wild PJ, Buser L, Kröning A, Braunstein S, Anlauf M, Jankowiak S, Hassan M, Bendhack ML, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Santourlidis S',
'description' => '<p>Urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common cancer of the urinary bladder causes severe morbidity and mortality, e.g. about 40.000 deaths in the EU annually, and incurs considerable costs for the health system due to the need for prolonged treatments and long-term monitoring. Extensive aberrant DNA methylation is described to prevail in urothelial carcinoma and is thought to contribute to genetic instability, altered gene expression and tumor progression. However, it is unknown how this epigenetic alteration arises during carcinogenesis. Intact methyl group metabolism is required to ensure maintenance of cell-type specific methylomes and thereby genetic integrity and proper cellular function. Here, using two independent techniques for detecting DNA methylation, we observed DNA hypermethylation of the 5'-regulatory regions of the key methyl group metabolism genes ODC1, AHCY and MTHFR in early urothelial carcinoma. These hypermethylation events are associated with genome-wide DNA hypomethylation which is commonly associated with genetic instability. We therefore infer that hypermethylation of methyl group metabolism genes acts in a feed-forward cycle to promote additional DNA methylation changes and suggest a new hypothesis on the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinoma.</p>',
'date' => '2018-02-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29472622',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-018-21932-7',
'modified' => '2019-02-15 21:31:04',
'created' => '2019-02-14 15:01:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 74 => array(
'id' => '3325',
'name' => 'Integrative omics data analyses of repeated dose toxicity of valproic acid in vitro reveal new mechanisms of steatosis induction',
'authors' => 'van Breda S.G.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is a very potent anti-cancer and neuro-protective drug probably by its HDAC inhibiting properties, which may cause steatosis in the liver. The present study investigates the effect of repetitive VPA treatment of primary human hepatocytes (PHH) on whole genome gene expression-, DNA methylation-, and miRNA changes, using microarrays and integrated data analyses. PHH were exposed to a non-cytotoxic dose of VPA for 5days daily which induced lipid accumulation. Part of the PHH was left untreated for 3days for studying the persistence of 'omics' changes. VPA treatment appeared to inhibit the expression of the transcription factors HNF1A and ONECUT1. HNF1A interacted with 41 differentially expressed genes of which 12 were also differentially methylated. None of the genes present in this network were regulated by a DE-miR. The subnetwork of ONECUT1 consisted of 44 differentially expressed genes of which 15 were differentially methylated, and 3 were regulated by a DE-miR. A number of genes in the networks are involved in fatty acid metabolism, and may contribute to the development of steatosis by increasing oxidative stress thereby causing mitochondrial dysfunction, and by shifting metabolism of VPA towards β-oxidation due to reduced glucuronidation. Part of the changes remained persistent after washing out of VPA, like PMAIP1 which is associated with cellular stress in liver of patients with NASH. The MMP2 gene showed the highest number of interactions with other persistently expressed genes, among which LCN2 which is a key modulator of lipid homeostasis. Furthermore, VPA modulated the expression and DNA methylation level of nuclear receptors and their target genes involved in the adverse outcome pathway of steatosis, thereby expanding our current knowledge of the pathway. In particular, VPA modulated PPARγ, and PPARα, AHR and CD36 on both the gene expression and the DNA methylation level, thereby inhibiting β-oxidation and increasing uptake of fatty acid into the hepatocytes, respectively. Overall, our integrative data analyses identified novel genes modulated by VPA, which provide more insight into the mechanisms of repeated dose toxicity of VPA, leading to steatosis.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-15',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29154799',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-02-06 09:28:05',
'created' => '2018-02-06 09:28:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 75 => array(
'id' => '3316',
'name' => 'Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos',
'authors' => 'Rossana Sussarellu, Morgane Lebreton, Julien Rouxel, Farida Akcha, Guillaume Rivière ',
'description' => '<p id="spar0045">Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better understand whether the embryotoxic effects of copper in <em>Crassostrea gigas</em> could be mediated by alterations in gene expression, and the putative role of DNA methylation, which is known to contribute to gene regulation in early embryo development.</p>
<p id="spar0050">For that purpose, oyster embryos were exposed to 4 nominal copper concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 μg L<sup>−1</sup> Cu<sup>2+</sup>) during early development assays. Embryotoxicity was monitored through the oyster embryo-larval bioassay at the D-larva stage 24 h post fertilization (hpf) and genotoxicity at gastrulation 7 hpf. In parallel, the relative expression of 15 genes encoding putative homeotic, biomineralization and DNA methylation proteins was measured at three developmental stages (3 hpf morula stage, 7 hpf gastrula stage, 24 hpf D-larvae stage) using RT-qPCR. Global DNA content in methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine were measured by HPLC and gene-specific DNA methylation levels were monitored using MeDIP-qPCR.</p>
<p id="spar0055">A significant increase in larval abnormalities was observed from copper concentrations of 10 μg L<sup>−1</sup>, while significant genotoxic effects were detected at 1 μg L<sup>−1</sup> and above. All the selected genes presented a stage-dependent expression pattern, which was impaired for some homeobox and DNA methylation genes (<em>Notochord, HOXA1, HOX2, Lox5, DNMT3b and CXXC-1</em>) after copper exposure. While global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) at gastrula stage didn’t show significant changes between experimental conditions, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its degradation product, decreased upon copper treatment. The DNA methylation of exons and the transcript levels were correlated in control samples for <em>HOXA1</em> but such a correlation was diminished following copper exposure. The methylation level of some specific gene regions (<em>HoxA1, Hox2, Engrailed2</em> and <em>Notochord</em>) displayed changes upon copper exposure. Such changes were gene and exon-specific and no obvious global trends could be identified. Our study suggests that the embryotoxic effects of copper in oysters could involve homeotic gene expression impairment possibly by changing DNA methylation levels.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-03',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166445X18300018?via%3Dihub',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.001',
'modified' => '2018-01-14 01:21:09',
'created' => '2018-01-14 01:21:09',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 76 => array(
'id' => '3383',
'name' => 'Genome-wide analysis of day/night DNA methylation differences in Populus nigra.',
'authors' => 'Ding C.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is an important mechanism of epigenetic modification. Methylation changes during stress responses and developmental processes have been well studied; however, their role in plant adaptation to the day/night cycle is poorly understood. In this study, we detected global methylation patterns in leaves of the black poplar Populus nigra 'N46' at 8:00 and 24:00 by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). We found 10,027 and 10,242 genes to be methylated in the 8:00 and 24:00 samples, respectively. The methylated genes appeared to be involved in multiple biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components, suggesting important roles for DNA methylation in poplar cells. Comparing the 8:00 and 24:00 samples, only 440 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) overlapped with genic regions, including 193 hyper- and 247 hypo-methylated DMRs, and may influence the expression of 137 downstream genes. Most hyper-methylated genes were associated with transferase activity, kinase activity, and phosphotransferase activity, whereas most hypo-methylated genes were associated with protein binding, ATP binding, and adenyl ribonucleotide binding, suggesting that different biological processes were activated during the day and night. Our results indicated that methylated genes were prevalent in the poplar genome, but that only a few of these participated in diurnal gene expression regulation.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-02',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29293569',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-08-07 09:45:38',
'created' => '2018-08-07 09:45:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 77 => array(
'id' => '3384',
'name' => 'Obligatory and facilitative allelic variation in the DNA methylome within common disease-associated loci',
'authors' => 'Bell C.G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Integrating epigenetic data with genome-wide association study (GWAS) results can reveal disease mechanisms. The genome sequence itself also shapes the epigenome, with CpG density and transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) strongly encoding the DNA methylome. Therefore, genetic polymorphism impacts on the observed epigenome. Furthermore, large genetic variants alter epigenetic signal dosage. Here, we identify DNA methylation variability between GWAS-SNP risk and non-risk haplotypes. In three subsets comprising 3128 MeDIP-seq peripheral-blood DNA methylomes, we find 7173 consistent and functionally enriched Differentially Methylated Regions. 36.8% can be attributed to common non-SNP genetic variants. CpG-SNPs, as well as facilitative TFBS-motifs, are also enriched. Highlighting their functional potential, CpG-SNPs strongly associate with allele-specific DNase-I hypersensitivity sites. Our results demonstrate strong DNA methylation allelic differences driven by obligatory or facilitative genetic effects, with potential direct or regional disease-related repercussions. These allelic variations require disentangling from pure tissue-specific modifications, may influence array studies, and imply underestimated population variability in current reference epigenomes.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-02',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29295990',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-08-07 10:13:12',
'created' => '2018-08-07 10:13:12',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 78 => array(
'id' => '3449',
'name' => 'Epigenetic alterations in TRAMP mice: epigenome DNA methylation profiling using MeDIP-seq.',
'authors' => 'Li W, Huang Y, Sargsyan D, Khor TO, Guo Y, Shu L, Yang AY, Zhang C, Paredes-Gonzalez X, Verzi M, Hart RP, Kong AN',
'description' => '<p>Purpose: We investigated the genomic DNA methylation profile of prostate cancer in transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) cancer model and to analyze the crosstalk among targeted genes and the related functional pathways. Methods: Prostate DNA samples from 24-week-old TRAMP and C57BL/6 male mice were isolated. The DNA methylation profiles were analyzed by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) followed by next-generation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Canonical pathways, diseases and function and network analyses of the different samples were then performed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software. Some target genes with significant difference in methylation were selected for validation using methylation specific primers (MSP) and qPCR. Results: TRAMP mice undergo extensive aberrant CpG hyper- and hypo-methylation. There were 2147 genes with a significant (log2-change ≥ 2) change in CpG methylation between the two groups, as mapped by the IPA software. Among these genes, the methylation of 1105 and 1042 genes was significantly decreased and increased, respectively, in TRAMP prostate tumors. The top associated disease identified by IPA was adenocarcinoma; however, the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-, histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2)-, glutathione S-transferase pi (GSTP1)- and polyubiquitin-C (UBC)-related pathways showed significantly altered methylation profiles based on the canonical pathway and network analyses. MSP and qPCR results of genes of interests corroborated with MeDIP-seq findings. Conclusions: This is the first MeDIP-seq with IPA analysis of the TRAMP model to provide novel insight into the genome-wide methylation profile of prostate cancer. Studies on epigenetics, such as DNA methylation, will potentially provide novel avenues and strategies for further development of biomarkers targeted for treatment and prevention approaches for prostate cancer.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29344347',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13578-018-0201-y',
'modified' => '2019-02-15 21:41:39',
'created' => '2019-02-14 15:01:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 79 => array(
'id' => '3508',
'name' => 'Analysis of DNA methylome and transcriptome profiling following Gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application in Nicotiana tabacum L.',
'authors' => 'Manoharlal Raman, Saiprasad G. V. S., Kaikala Vinay, Suresh Kumar R., Kovařík Ales',
'description' => '<p>The present work investigated a comprehensive genome-wide landscape of DNA methylome and its relationship with transcriptome upon gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application under practical field conditions in solanaceae model, Nicotiana tabacum L. Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation-Sequencing (MeDIP-Seq) analysis uncovered over 82% (18,456) of differential methylated regions (DMRs) in intergenic-region. Within protein-coding region, 2339 and 1685 of identified DMRs were observed in genebody- and promoter-region, respectively. Microarray study revealed 7032 differential expressed genes (DEGs) with 3507 and 3525 genes displaying upand down-regulation, respectively. Integration analysis revealed 520 unique non-redundant annotated DMRs overlapping with DEGs. Our results indicated that GA3 induced DNA hypo- as well as hyper-methylation were associated with both gene-silencing and -activation. No complete biasness or correlation was observed in either of the promoter- or genebody-regions, which otherwise showed an overall trend towards GA3 induced global DNA hypo-methylation. Taken together, our results suggested that differential DNA methylation mediated by GA3 may only play a permissive role in regulating the gene expression.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40502-018-0393-5',
'doi' => '10.1007/s40502-018-0393-5',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:43:47',
'created' => '2019-02-27 12:54:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 80 => array(
'id' => '3334',
'name' => 'Data on novel DNA methylation changes induced by valproic acid in human hepatocytes',
'authors' => 'Wolters J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is a widely prescribed antiepileptic drug in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis. However the exact mechanism of the steatosis formation is unknown. The data presented in this DIB publication is used to further investigate the VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in patterns of methylation. Therefore, primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were exposed to VPA at a concentration which was shown to cause steatosis without inducing overt cytotoxicity. VPA was administered for 5 days daily to PHHs. Furthermore, after 5 days VPA-treatment parts of the PHHs were followed for a 3 days washout. Differentially methylated DNA regions (DMRs) were identified by using the 'Methylated DNA Immuno-Precipitation - sequencing' (MeDIP-seq) method. The data presented in this DIB demonstrate induced steatosis pathways by all DMRs during VPA-treatment, covering interesting drug-induced steatosis genes (persistent DMRs upon terminating VPA treatment and the <i>EP300</i> network). This was illustrated in our associated article (Wolters et al., 2017) [1]. MeDIP-seq raw data are available on ArrayExpress (accession number: E-MTAB-4437).</p>',
'date' => '2017-11-10',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29201983',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-02-08 17:16:22',
'created' => '2018-02-08 17:16:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 81 => array(
'id' => '3283',
'name' => 'Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Methylation Patterns Induced by Valproic Acid in Human Hepatocytes',
'authors' => 'Wolters J.E.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is one of the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis through mitochondrial dysfunction. The aim of this study is to further investigate VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in patterns of methylation in nuclear DNA (nDNA) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Therefore, primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were exposed to an incubation concentration of VPA that was shown to cause steatosis without inducing overt cytotoxicity. VPA was administered daily for 5 days, and this was followed by a 3 day washout (WO). Methylated DNA regions (DMRs) were identified by using the methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-sequencing (MeDIP-seq) method. The nDNA DMRs after VPA treatment could indeed be classified into oxidative stress- and steatosis-related pathways. In particular, networks of the steatosis-related gene EP300 provided novel insight into the mechanisms of toxicity induced by VPA treatment. Furthermore, we suggest that VPA induces a crosstalk between nDNA hypermethylation and mtDNA hypomethylation that plays a role in oxidative stress and steatosis development. Although most VPA-induced methylation patterns appeared reversible upon terminating VPA treatment, 31 nDNA DMRs (including 5 zinc finger protein genes) remained persistent after the WO period. Overall, we have shown that MeDIP-seq analysis is highly informative in disclosing novel mechanisms of VPA-induced toxicity in PHHs. Our results thus provide a prototype for the novel generation of interesting methylation biomarkers for repeated dose liver toxicity in vitro.</p>',
'date' => '2017-10-16',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28853863',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-24 09:33:19',
'created' => '2017-10-24 09:33:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 82 => array(
'id' => '3271',
'name' => ' Genome methylation and regulatory functions for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chicken embryos',
'authors' => 'Zhang Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Tibetan chickens have unique adaptations to the extreme high-altitude environment that they inhabit. Epigenetic DNA methylation affects many biological processes, including hypoxic adaptation; however, the regulatory genes for DNA methylation in hypoxic adaptation remain unknown. In this study, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation with high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) was used to provide an atlas of the DNA methylomes of the heart tissue of hypoxic highland Tibetan and lowland Chahua chicken embryos. A total of 31.2 gigabases of sequence data were generated from six MeDIP-seq libraries. We identified 1,049 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and 695 related differentially methylated genes (DMGs) between the two chicken breeds. The DMGs are involved in vascular smooth muscle contraction, VEGF signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, and other hypoxia-related pathways. Five candidate genes that had low methylation (<i>EDNRA</i>, <i>EDNRB2</i>,<i> BMPR1B</i>,<i> BMPRII</i>, and <i>ITGA2</i>) might play key regulatory roles in the adaptation to hypoxia in Tibetan chicken embryos. Our study provides significant explanations for the functions of genes and their epigenetic regulation for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chickens.</p>',
'date' => '2017-10-06',
'pmid' => 'https://peerj.com/articles/3891/',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-13 17:02:21',
'created' => '2017-10-13 17:02:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 83 => array(
'id' => '3265',
'name' => 'Emerging Role of One-Carbon Metabolism and DNA Methylation Enrichment on δ-Containing GABAA Receptor Expression in the Cerebellum of Subjects with Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD',
'authors' => 'Gatta E. et al.',
'description' => '<section class="abstract">
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Background</div>
<p>Cerebellum is an area of the brain particularly sensitive to the effects of acute and chronic alcohol consumption. Alcohol exposure decreases cerebellar Purkinje cell output by increasing GABA release from Golgi cells onto extrasynaptic α<sub>6</sub>/δ-containing GABA<sub>A</sub> receptors located on glutamatergic granule cells. Here, we studied whether chronic alcohol consumption induces changes in GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor subunit expression and whether these changes are associated with alterations in epigenetic mechanisms via DNA methylation.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Methods</div>
<p>We used a cohort of postmortem cerebellum from control and chronic alcoholics, here defined as alcohol use disorders subjects (n=25/group). <em>S</em>-adenosyl-methionine/<em>S</em>-adenosyl-homocysteine were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. mRNA levels of various genes were assessed by reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Promoter methylation enrichment was assessed using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and hydroxy-methylated DNA immunoprecipitation assays.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Results</div>
<p>mRNAs encoding key enzymes of 1-carbon metabolism that determine the <em>S</em>-adenosyl-methionine/<em>S</em>-adenosyl-homocysteine ratio were increased, indicating higher “methylation index” in alcohol use disorder subjects. We found that increased methylation of the promoter of the δ subunit GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor was associated with reduced mRNA and protein levels in the cerebellum of alcohol use disorder subjects. No changes were observed in α<sub>1</sub>- or α<sub>6</sub>-containing GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor subunits. The expression of DNA-methyltransferases (1, 3A, and 3B) was unaltered, whereas the mRNA level of TET1, which participates in the DNA demethylation pathway, was decreased. Hence, increased methylation of the δ subunit GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor promoter may result from alcohol-induced reduction of DNA demethylation.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Conclusion</div>
<p>Together, these results support the hypothesis that aberrant DNA methylation pathways may be involved in cerebellar pathophysiology of alcoholism. Furthermore, this work provides novel evidence for a central role of DNA methylation mechanisms in the alcohol-induced neuroadaptive changes of human cerebellar GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor function.</p>
</section>
</section>',
'date' => '2017-08-19',
'pmid' => 'https://academic.oup.com/ijnp/article/doi/10.1093/ijnp/pyx075/4085582/Emerging-role-of-one-carbon-metabolism-and-DNA',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-09 16:11:05',
'created' => '2017-10-09 16:11:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 84 => array(
'id' => '3251',
'name' => 'Coordinate Regulation of TET2 and EBNA2 Control DNA Methylation State of Latent Epstein-Barr Virus',
'authors' => 'Lu F. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and its associated carcinogenesis are regulated by dynamic changes in DNA methylation of both virus and host genomes. We show here that the Ten-Eleven Translocation 2 (TET2) gene, implicated in hydroxymethylation and active DNA demethylation, is a key regulator of EBV latency type DNA methylation patterning. EBV latency types are defined by DNA methylation patterns that restrict expression of viral latency genes. We show that TET2 mRNA and protein expression correlate with the highly demethylated EBV type III latency program permissive for expression of EBNA2, EBNA3s, and LMP transcripts. We show that shRNA depletion of TET2 results in a decrease in latency gene expression, but can also trigger a switch to lytic gene expression. TET2 depletion results in the loss of hydroxymethylated cytosine, and corresponding increase in cytosine methylation at key regulatory regions on the viral and host genomes. This also corresponded to a loss of RBP-jκ binding, and decreased histone H3K4 trimethylation at these sites. Furthermore, we show that the TET2 gene, itself, is regulated similar to the EBV genome. ChIP-Seq revealed that TET2 gene contains EBNA2-dependent RBP-jκ and EBF1 binding sites, and is subject to DNA methylation associated transcriptional silencing similar to EBV latency type III genomes. Finally, we provide evidence that TET2 colocalizes with EBNA2-EBF1-RBP-jκ binding sites, and can interact with EBNA2 by co-immunoprecipitation. Taken together, these findings indicate that TET2 gene transcripts are regulated similarly to EBV type III latency genes, and that TET2 protein is a cofactor of EBNA2 and co-regulator of the EBV type III latency program and DNA methylation state..<b>IMPORTANCE</b> Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and carcinogenesis involves the selective epigenetic modification of viral and cellular genes. Here, we show that TET2, a cellular tumor suppressor involved in active DNA demethylation, plays a central role in regulating DNA methylation state during EBV latency. TET2 is coordinately regulated and functionally interacts with the viral oncogene EBNA2. TET2 and EBNA2 function cooperatively to demethylate genes important for EBV-driven B cells growth transformation.</p>',
'date' => '2017-08-07',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28794029',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-09-26 09:54:39',
'created' => '2017-09-26 09:54:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 85 => array(
'id' => '3237',
'name' => 'Intracellular adenosine regulates epigenetic programming in endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis',
'authors' => 'Xu Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The nucleoside adenosine is a potent regulator of vascular homeostasis, but it remains unclear how expression or function of the adenosine-metabolizing enzyme adenosine kinase (ADK) and the intracellular adenosine levels influence angiogenesis. We show here that hypoxia lowered the expression of ADK and increased the levels of intracellular adenosine in human endothelial cells. Knockdown (KD) of ADK elevated intracellular adenosine, promoted proliferation, migration, and angiogenic sprouting in human endothelial cells. Additionally, mice deficient in endothelial ADK displayed increased angiogenesis as evidenced by the rapid development of the retinal and hindbrain vasculature, increased healing of skin wounds, and prompt recovery of arterial blood flow in the ischemic hindlimb. Mechanistically, hypomethylation of the promoters of a series of pro-angiogenic genes, especially for VEGFR2 in ADK KD cells, was demonstrated by the Infinium methylation assay. Methylation-specific PCR, bisulfite sequencing, and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation further confirmed hypomethylation in the promoter region of VEGFR2 in ADK-deficient endothelial cells. Accordingly, loss or inactivation of ADK increased VEGFR2 expression and signaling in endothelial cells. Based on these findings, we propose that ADK downregulation-induced elevation of intracellular adenosine levels in endothelial cells in the setting of hypoxia is one of the crucial intrinsic mechanisms that promote angiogenesis.</p>',
'date' => '2017-07-17',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28751580',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-08-29 09:15:21',
'created' => '2017-08-29 09:15:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 86 => array(
'id' => '3216',
'name' => 'Vitamin C induces specific demethylation of H3K9me2 in mouse embryonic stem cells via Kdm3a/b',
'authors' => 'Kevin T. Ebata, Kathryn Mesh, Shichong Liu, Misha Bilenky, Alexander Fekete, Michael G. Acker, Martin Hirst, Benjamin A. Garcia and Miguel Ramalho-Santos',
'description' => '<section xmlns="" xmlns:fn="http://www.w3.org/2005/xpath-functions" xmlns:meta="http://www.springer.com/app/meta" class="Abstract" id="Abs1" lang="en">
<div class="js-CollapseSection">
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec1">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Background</h3>
<p id="Par1" class="Para">Histone methylation patterns regulate gene expression and are highly dynamic during development. The erasure of histone methylation is carried out by histone demethylase enzymes. We had previously shown that vitamin C enhances the activity of Tet enzymes in embryonic stem (ES) cells, leading to DNA demethylation and activation of germline genes.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec2">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Results</h3>
<p id="Par2" class="Para">We report here that vitamin C induces a remarkably specific demethylation of histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) in naïve ES cells. Vitamin C treatment reduces global levels of H3K9me2, but not other histone methylation marks analyzed, as measured by western blot, immunofluorescence and mass spectrometry. Vitamin C leads to widespread loss of H3K9me2 at large chromosomal domains as well as gene promoters and repeat elements. Vitamin C-induced loss of H3K9me2 occurs rapidly within 24 h and is reversible. Importantly, we found that the histone demethylases Kdm3a and Kdm3b are required for vitamin C-induced demethylation of H3K9me2. Moreover, we show that vitamin C-induced Kdm3a/b-mediated H3K9me2 demethylation and Tet-mediated DNA demethylation are independent processes at specific loci. Lastly, we document Kdm3a/b are partially required for the upregulation of germline genes by vitamin C.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec3">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p id="Par3" class="Para">These results reveal a specific role for vitamin C in histone demethylation in ES cells and document that DNA methylation and H3K9me2 cooperate to silence germline genes in pluripotent cells.</p>
</div>
</div>
</section>',
'date' => '2017-07-12',
'pmid' => 'https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-017-0143-3',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-017-0143-3',
'modified' => '2017-08-23 14:47:51',
'created' => '2017-07-29 08:04:03',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 87 => array(
'id' => '3205',
'name' => 'Dynamics of DNA methylomes underlie oyster development',
'authors' => 'Riviere G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a critical epigenetic regulator of development in mammals and social insects, but its significance in development outside these groups is not understood. Here we investigated the genome-wide dynamics of DNA methylation in a mollusc model, the oyster Crassostrea gigas, from the egg to the completion of organogenesis. Large-scale methylation maps reveal that the oyster genome displays a succession of methylated and non methylated regions, which persist throughout development. Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) are strongly regulated during cleavage and metamorphosis. The distribution and levels of methylated DNA within genomic features (exons, introns, promoters, repeats and transposons) show different developmental lansdscapes marked by a strong increase in the methylation of exons against introns after metamorphosis. Kinetics of methylation in gene-bodies correlate to their transcription regulation and to distinct functional gene clusters, and DMRs at cleavage and metamorphosis bear the genes functionally related to these steps, respectively. This study shows that DNA methylome dynamics underlie development through transcription regulation in the oyster, a lophotrochozoan species. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of such epigenetic regulation outside vertebrates and ecdysozoan models, bringing new insights into the evolution and the epigenetic regulation of developmental processes.</p>',
'date' => '2017-06-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28594821',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-07-03 10:24:12',
'created' => '2017-07-03 10:24:12',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 88 => array(
'id' => '3186',
'name' => 'MeDIP-seq and nCpG analyses illuminate sexually dimorphic methylation of gonadal development genes with high historic methylation in turtle hatchlings with temperature-dependent sex determination',
'authors' => 'Radhakrishnan S. et al.',
'description' => '<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec1">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Background</h3>
<p id="Par1" class="Para">DNA methylation alters gene expression but not DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. Temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) epitomizes phenotypic plasticity where environmental temperature drives embryonic sexual fate, as occurs commonly in turtles. Importantly, the temperature-specific transcription of two genes underlying gonadal differentiation is known to be induced by differential methylation in TSD fish, turtle and alligator. Yet, how extensive is the link between DNA methylation and TSD remains unclear. Here we test for broad differences in genome-wide DNA methylation between male and female hatchling gonads of the TSD painted turtle <em xmlns="" class="EmphasisTypeItalic">Chrysemys picta</em> using methyl DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing, to identify differentially methylated candidates for future study. We also examine the genome-wide nCpG distribution (which affects DNA methylation) in painted turtles and test for historic methylation in genes regulating vertebrate gonadogenesis.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec2">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Results</h3>
<p id="Par2" class="Para">Turtle global methylation was consistent with other vertebrates (57% of the genome, 78% of all CpG dinucleotides). Numerous genes predicted to regulate turtle gonadogenesis exhibited sex-specific methylation and were proximal to methylated repeats. nCpG distribution predicted actual turtle DNA methylation and was bimodal in gene promoters (as other vertebrates) and introns (unlike other vertebrates). Differentially methylated genes, including regulators of sexual development, had lower nCpG content indicative of higher historic methylation.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec3">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p id="Par3" class="Para">Ours is the first evidence suggesting that sexually dimorphic DNA methylation is pervasive in turtle gonads (perhaps mediated by repeat methylation) and that it targets numerous regulators of gonadal development, consistent with the hypothesis that it may regulate thermosensitive transcription in TSD vertebrates. However, further research during embryogenesis will help test this hypothesis and the alternative that instead, most differential methylation observed in hatchlings is the by-product of sexual differentiation and not its cause.</p>
</div>',
'date' => '2017-05-19',
'pmid' => 'https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-017-0136-2',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-05-22 10:21:02',
'created' => '2017-05-22 10:21:02',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 89 => array(
'id' => '3210',
'name' => 'Protective vaccination and blood-stage malaria modify DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver of Balb/c mice.',
'authors' => 'Al-Quraishy S. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation are increasingly recognized to be critical for vaccination efficacy and outcome of different infectious diseases, but corresponding information is scarcely available for host defense against malaria. In the experimental blood-stage malaria Plasmodium chabaudi, we investigate the possible effects of a blood-stage vaccine on DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver, known as effector against blood-stage malaria, using DNA methylation microarrays. Naturally susceptible Balb/c mice acquire, by protective vaccination, the potency to survive P. chabaudi malaria and, concomitantly, modifications of constitutive DNA methylation of promoters of numerous genes in the liver; specifically, promoters of 256 genes are hyper(=up)- and 345 genes are hypo(=down)-methylated (p < 0.05). Protective vaccination also leads to changes in promoter DNA methylation upon challenge with P. chabaudi at peak parasitemia on day 8 post infection (p.i.), when 571 and 1013 gene promoters are up- and down-methylated, respectively, in relation to constitutive DNA methylation (p < 0.05). Gene set enrichment analyses reveal that both vaccination and P. chabaudi infections mainly modify promoters of those genes which are most statistically enriched with functions relating to regulation of transcription. Genes with down-methylated promoters encompass those encoding CX3CL1, GP130, and GATA2, known to be involved in monocyte recruitment, IL-6 trans-signaling, and onset of erythropoiesis, respectively. Our data suggest that vaccination may epigenetically improve parts of several effector functions of the liver against blood-stage malaria, as, e.g., recruitment of monocyte/macrophage to the liver accelerated liver regeneration and extramedullary hepatic erythropoiesis, thus leading to self-healing of otherwise lethal P. chabaudi blood-stage malaria.</p>',
'date' => '2017-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28315013',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-07-07 16:36:58',
'created' => '2017-07-07 16:36:58',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 90 => array(
'id' => '3184',
'name' => 'Comparative analysis of MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq and estimation of gene expression changes in a rodent model of schizophrenia',
'authors' => 'Neary J.L. et al.',
'description' => '<p>We conducted a comparative study of multiplexed affinity enrichment sequence methodologies (MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq) in a rodent model of schizophrenia, induced by in utero methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) exposure. We also examined related gene expression changes using a pooled sample approach. MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq identified 769 and 1771 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) between F2 offspring of MAM-exposed rats and saline control rats, respectively. The assays showed good concordance, with ~ 56% of MBD-seq-detected DMRs being identified by or proximal to MeDIP-seq DMRs. There was no significant overlap between DMRs and differentially expressed genes, suggesting that DNA methylation regulatory effects may act upon more distal genes, or are too subtle to detect using our approach. Methylation and gene expression gene ontology enrichment analyses identified biological processes important to schizophrenia pathophysiology, including neuron differentiation, prepulse inhibition, amphetamine response, and glutamatergic synaptic transmission regulation, reinforcing the utility of the MAM rodent model for schizophrenia research.</p>',
'date' => '2017-03-29',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S088875431730023X',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-05-22 09:53:51',
'created' => '2017-05-22 09:53:51',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 91 => array(
'id' => '3148',
'name' => 'Overexpression of LINE-1 Retrotransposons in Autism Brain',
'authors' => 'Shpyleva S. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Long interspersed nuclear elements-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are mobile DNA sequences that are capable of duplication and insertion (retrotransposition) within the genome. Recently, retrotransposition of L1 was shown to occur within human brain leading to somatic mosaicism in hippocampus and cerebellum. Because unregulated L1 activity can promote genomic instability and mutagenesis, multiple mechanisms including epigenetic chromatin condensation have evolved to effectively repress L1 expression. Nonetheless, L1 expression has been shown to be increased in patients with Rett syndrome and schizophrenia. Based on this evidence and our reports of oxidative stress and epigenetic dysregulation in autism cerebellum, we sought to determine whether L1 expression was increased in autism brain. The results indicated that L1 expression was significantly elevated in the autism cerebellum but not in BA9, BA22, or BA24. The binding of repressive MeCP2 and histone H3K9me3 to L1 sequences was significantly lower in autism cerebellum suggesting that relaxation of epigenetic repression may have contributed to increased expression. Further, the increase in L1 expression was inversely correlated with glutathione redox status consistent with reports indicating that L1 expression is increased under pro-oxidant conditions. Finally, the expression of transcription factor FOXO3, sensor of oxidative stress, was significantly increased and positively associated with L1 expression and negatively associated with glutathione redox status. While these novel results are an important first step, future understanding of the contribution of elevated L1 expression to neuronal CNVs and genomic instability in autism will depend on emerging cell-specific genomic technologies, a challenge that warrants future investigation.</p>',
'date' => '2017-02-20',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28220356',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-03-24 17:12:49',
'created' => '2017-03-24 17:12:49',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 92 => array(
'id' => '3092',
'name' => 'Integrative "-Omics" Analysis in Primary Human Hepatocytes Unravels Persistent Mechanisms of Cyclosporine A-Induced Cholestasis',
'authors' => 'Wolters J.E. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Cyclosporine A (CsA) is an undecapeptide with strong immunosuppressant activities and is used a lot after organ transplantation. Furthermore, it may induce cholestasis in the liver. In general, the drug-induced cholestasis (DIC) pathway includes genes involved in the uptake, synthesis, conjugation, and secretion of bile acids. However, whether CsA-induced changes in the cholestasis pathway in vitro are persistent for repeated dose toxicity has not yet been investigated. To explore this, primary human hepatocytes (PHH) were exposed to a subcytotoxic dose of 30 μM CsA daily for 3 and 5 days. To investigate the persistence of induced changes upon terminating CsA exposure after 5 days, a subset of PHH was subjected to a washout period (WO-period) of 3 days. Multiple -omics analyses, comprising whole genome analysis of DNA methylation, gene expression, and microRNA expression, were performed. The CsA-treatment resulted after 3 and 5 days, respectively, in 476 and 20 differentially methylated genes (DMGs), 1353 and 1481 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and in 22 and 29 differentially expressed microRNAs (DE-miRs). Cholestasis-related pathways appeared induced during CsA-treatment. Interestingly, 828 persistent DEGs and 6 persistent DE-miRs but no persistent DMGs were found after the WO-period. These persistent DEGs and DE-miRs showed concordance for 22 genes. Furthermore, 29 persistent DEGs changed into the same direction as observed in livers from cholestasis patients. None of those 29 DEGs which among others relate to oxidative stress and lipid metabolism are yet present in the DIC pathway or cholestasis adverse outcome pathway (AOP) thus presenting novel findings. In summary, we have demonstrated for the first time a persistent impact of repeated dose administration of CsA on genes and microRNAs related to DIC in the gold standard human liver in vitro model with PHH.</p>',
'date' => '2016-12-19',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27989131',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-01-03 10:33:43',
'created' => '2017-01-03 10:33:43',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 93 => array(
'id' => '3086',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA promoter methylation and transcriptome analysis in human adipose tissue unravels novel candidate genes for obesity',
'authors' => 'Keller M. et al.',
'description' => '<h4 id="absSec_1">Objective/methods</h4>
<p id="abspara0010">DNA methylation plays an important role in obesity and related metabolic complications. We examined genome-wide DNA promoter methylation along with mRNA profiles in paired samples of human subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) and omental visceral adipose tissue (OVAT) from non-obese <em>vs.</em> obese individuals.</p>
<h4 id="absSec_2">Results</h4>
<p id="abspara0015">We identified negatively correlated methylation and expression of several obesity-associated genes in our discovery dataset and <em>in silico</em> replicated <em>ETV6</em> in two independent cohorts. Further, we identified six adipose tissue depot-specific genes (<em>HAND2</em>, <em>HOXC6</em>, <em>PPARG</em>, <em>SORBS2</em>, <em>CD36</em>, and <em>CLDN1</em>). The effects were further supported in additional independent cohorts. Our top hits might play a role in adipogenesis and differentiation, obesity, lipid metabolism, and adipose tissue expandability. Finally, we show that <em>in vitro</em> methylation of <em>SORBS2</em> directly represses gene expression.</p>
<h4 id="absSec_3">Conclusions</h4>
<p id="abspara0020">Taken together, our data show distinct tissue specific epigenetic alterations which associate with obesity.</p>',
'date' => '2016-11-16',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212877816302757',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-12-21 10:36:19',
'created' => '2016-12-21 10:36:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 94 => array(
'id' => '3061',
'name' => 'Novel regional age-associated DNA methylation changes within human common disease-associated loci',
'authors' => 'Bell CG et al.',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Advancing age progressively impacts on risk and severity of chronic disease. It also modifies the epigenome, with changes in DNA methylation, due to both random drift and variation within specific functional loci.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">In a discovery set of 2238 peripheral-blood genome-wide DNA methylomes aged 19-82 years, we identify 71 age-associated differentially methylated regions within the linkage disequilibrium blocks of the single nucleotide polymorphisms from the NIH genome-wide association study catalogue. This included 52 novel regions, 29 within loci not covered by 450 k or 27 k Illumina array, and with enrichment for DNase-I Hypersensitivity sites across the full range of tissues. These age-associated differentially methylated regions also show marked enrichment for enhancers and poised promoters across multiple cell types. In a replication set of 2084 DNA methylomes, 95.7 % of the age-associated differentially methylated regions showed the same direction of ageing effect, with 80.3 % and 53.5 % replicated to p < 0.05 and p < 1.85 × 10<sup>-8</sup>, respectively.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">By analysing the functionally enriched disease and trait-associated regions of the human genome, we identify novel epigenetic ageing changes, which could be useful biomarkers or provide mechanistic insights into age-related common diseases.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2016-09-26',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27663977',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-11-04 10:56:10',
'created' => '2016-11-02 09:54:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 95 => array(
'id' => '3058',
'name' => 'Inheritable Silencing of Endogenous Genes by Hit-and-Run Targeted Epigenetic Editing',
'authors' => 'Amabile A. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Gene silencing is instrumental to interrogate gene function and holds promise for therapeutic applications. Here, we repurpose the endogenous retroviruses' silencing machinery of embryonic stem cells to stably silence three highly expressed genes in somatic cells by epigenetics. This was achieved by transiently expressing combinations of engineered transcriptional repressors that bind to and synergize at the target locus to instruct repressive histone marks and de novo DNA methylation, thus ensuring long-term memory of the repressive epigenetic state. Silencing was highly specific, as shown by genome-wide analyses, sharply confined to the targeted locus without spreading to nearby genes, resistant to activation induced by cytokine stimulation, and relieved only by targeted DNA demethylation. We demonstrate the portability of this technology by multiplex gene silencing, adopting different DNA binding platforms and interrogating thousands of genomic loci in different cell types, including primary T lymphocytes. Targeted epigenome editing might have broad application in research and medicine.</p>',
'date' => '2016-09-22',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27662090',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-10-27 15:48:08',
'created' => '2016-10-27 15:48:08',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 96 => array(
'id' => '3047',
'name' => 'Trichloroethylene-Induced DNA Methylation Changes in Male F344 Rat Liver',
'authors' => 'Jiang Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Trichloroethylene (TCE), a common environmental contaminant, causes hepatocellular carcinoma in mice but not in rats. To understand the mechanisms of the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE, we examined the methylation status of DNA in the liver of rats exposed to TCE at 0 or 1000 mg/kg b.w. for 5 days using MeDIP-chip, bisulfite sequencing, COBRA, and LC-MS/MS. The related mRNA expression levels were measured by qPCR. Although no global DNA methylation change was detected, 806 genes were hypermethylated and 186 genes were hypomethylated. The genes with hypermethylated DNA were enriched in endocytosis, MAPK, and cAMP signaling pathways. We further confirmed the hypermethylation of Uhrf2 DNA and the hypomethylation of Hadhb DNA, which were negatively correlated with their mRNA expression levels. The transcriptional levels of Jun, Ihh, and Tet2 were significantly downregulated, whereas Cdkn1a was overexpressed. No mRNA expression change was found for Mki67, Myc, Uhrf1, and Dnmt1. In conclusion, TCE-induced DNA methylation changes in rats appear to suppress instead of promote hepatocarcinogenesis, which might play a role in the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE.</p>',
'date' => '2016-09-21',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27618143',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-10-10 11:10:05',
'created' => '2016-10-10 11:10:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 97 => array(
'id' => '3001',
'name' => 'Dynamic Interplay between the Transcriptome and Methylome in Response to Oxidative and Alkylating Stress',
'authors' => 'Deferme L et al.',
'description' => '<p>In recent years, it has been shown that free radicals not only react directly with DNA but also regulate epigenetic processes such as DNA methylation, which may be relevant within the context of, for example, tumorigenesis. However, how these free radicals impact the epigenome remains unclear. We therefore investigated whether methyl and hydroxyl radicals, formed by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBH), change temporal DNA methylation patterns and how this interferes with genome-wide gene expression. At three time points, TBH-induced radicals in HepG2 cells were identified by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Total 5-methylcytosine (5mC) levels were determined by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry and genome-wide changes in 5mC and gene expression by microarrays. Induced methylome changes rather represent an adaptive response to the oxidative stress-related reactions observed in the transcriptome. More specifically, we found that methyl radicals did not induce DNA methylation directly. An initial oxidative and alkylating stress-related response of the transcriptome during the early phase of TBH treatment was followed by an epigenetic response associated with cell survival signaling. Also, we identified genes of which the expression seems directly regulated by DNA methylation. This work suggests an important role of the methylome in counter-regulating primary oxidative and alkylating stress responses in the transcriptome to restore normal cell function. Altogether, the methylome may play an important role in counter-regulating primary oxidative and alkylating stress responses in the transcriptome presumably to restore normal cell function.</p>',
'date' => '2016-08-24',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27509014',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-08-25 17:17:48',
'created' => '2016-08-25 17:17:48',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 98 => array(
'id' => '2984',
'name' => 'Efficiency of methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing for whole-genome DNA methylation analysis',
'authors' => 'Jeong HM et al.',
'description' => '<p><abstracttext label="AIMS" nlmcategory="OBJECTIVE">We compared four common methods for measuring DNA methylation levels and recommended the most efficient method in terms of cost and coverage.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>MATERIALS & METHODS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="MATERIALS & METHODS" nlmcategory="METHODS">The DNA methylation status of liver and stomach tissues was profiled using four different methods, whole-genome bisulphite sequencing (WG-BS), targeted bisulphite sequencing (Targeted-BS), methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing (MeDIP-BS). We calculated DNA methylation levels using each method and compared the results.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">MeDIP-BS yielded the most similar DNA methylation profile to WG-BS, with 20 times less data, suggesting remarkable cost savings and coverage efficiency compared with the other methods.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">MeDIP-BS is a practical cost-effective method for analyzing whole-genome DNA methylation that is highly accurate at base-pair resolution.</abstracttext></p>',
'date' => '2016-06-08',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27266718',
'doi' => ' 10.2217/epi-2016-0038',
'modified' => '2016-07-26 09:17:24',
'created' => '2016-07-26 09:17:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 99 => array(
'id' => '2904',
'name' => 'Aflatoxin B1 induces persistent epigenomic effects in primary human hepatocytes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma',
'authors' => 'Linda Rieswijka, Sandra M.H. Claessena, Otto Bekersc, Marcel van Herwijnena, Daniël H.J. Theunissena, Danyel G.J. Jennena, Theo M.C.M. de Koka, Jos C.S. Kleinjansa,Simone G.J. van Bredaa',
'description' => '<p><span>Chronic exposure to aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) has, in certain regions in the world, been strongly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. AFB1 is a very potent hepatotoxic and carcinogenic mycotoxin which is frequently reported as a food contaminant. Epigenetic modifications provoked by environmental exposures, such as AFB1, may create a persistent epigenetic footprint. Deregulation of epigenetic mechanisms has actually been reported in HCC patients following AFB1 exposure; however, no attempts have yet been made to investigate early effects on the epigenome level which may be persistent on longer term, thereby possibly initiating carcinogenic events. In this study, we aim to identify methyl DNA-mRNA-interactions representative for a persistent epigenetic footprint associated with the early onset of AFB1-induced HCC. For this, primary human hepatocytes were exposed to 0.3 μM of AFB1 for 5 days. Persistent epigenetic effects were measured 3 days after terminating the carcinogenic exposure. Whole genome DNA methylation changes and whole genome transcriptomic analysis were analyzed applying microarray technologies, and cross-omics interactions were evaluated. Upon combining transcriptomics data with results on DNA methylation, a range of persistent hyper- and hypo-methylated genes was identified which also appeared affected on the transcriptome level. For six of the hypo-methylated and up-regulated genes, namely TXNRD1, PCNA, CCNK, DIAPH3, RAB27A and HIST1H2BF, a clear role in carcinogenic events could be identified. This study is the first to report on a carcinogen-induced persistent impact on the epigenetic footprint in relation with the transcriptome which could be indicative for the early onset of AFB1-related development of HCC.</span></p>',
'date' => '2016-05-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0300483X16300427',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.tox.2016.05.002',
'modified' => '2016-05-13 14:13:03',
'created' => '2016-05-08 07:29:28',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 100 => array(
'id' => '2855',
'name' => 'Paternal B Vitamin Intake Is a Determinant of Growth, Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Tumor Volume in Female Apc1638N Mouse Offspring',
'authors' => 'Sabet JA, Park LK, Iyer LK, Tai AK, Koh GY, Pfalzer AC, Parnell LD, Mason JB, Liu Z, Byun AJ, Crott JW',
'description' => '<h3>Background</h3>
<p>The importance of maternal nutrition to offspring health and risk of disease is well established. Emerging evidence suggests paternal diet may affect offspring health as well.</p>
<h3>Objective</h3>
<p>In the current study we sought to determine whether modulating pre-conception paternal B vitamin intake alters intestinal tumor formation in offspring. Additionally, we sought to identify potential mechanisms for the observed weight differential among offspring by profiling hepatic gene expression and lipid content.</p>
<h3>Methods</h3>
<p>Male Apc<sup>1638N</sup> mice (prone to intestinal tumor formation) were fed diets containing replete (control, CTRL), mildly deficient (DEF), or supplemental (SUPP) quantities of vitamins B<sub>2</sub>, B<sub>6</sub>, B<sub>12</sub>, and folate for 8 weeks before mating with control-fed wild type females. Wild type offspring were euthanized at weaning and hepatic gene expression profiled. Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring were fed a replete diet and euthanized at 28 weeks of age to assess tumor burden.</p>
<h3>Results</h3>
<p>No differences in intestinal tumor incidence or burden were found between male Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring of different paternal diet groups. Although in female Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring there were no differences in tumor incidence or multiplicity, a stepwise increase in tumor volume with increasing paternal B vitamin intake was observed. Interestingly, female offspring of SUPP and DEF fathers had a significantly lower body weight than those of CTRL fed fathers. Moreover, hepatic trigylcerides and cholesterol were elevated 3-fold in adult female offspring of SUPP fathers. Weanling offspring of the same fathers displayed altered expression of several key lipid-metabolism genes. Hundreds of differentially methylated regions were identified in the paternal sperm in response to DEF and SUPP diets. Aside from a few genes including Igf2, there was a striking lack of overlap between these genes differentially methylated in sperm and differentially expressed in offspring.</p>
<h3>Conclusions</h3>
<p>In this animal model, modulation of paternal B vitamin intake prior to mating alters offspring weight gain, lipid metabolism and tumor growth in a sex-specific fashion. These results highlight the need to better define how paternal nutrition affects the health of offspring.</p>',
'date' => '2016-03-11',
'pmid' => 'http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0151579#abstract0',
'doi' => ' 10.1371/journal.pone.0151579',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 10:26:38',
'created' => '2016-03-15 10:26:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 101 => array(
'id' => '2977',
'name' => 'Regulation of miR-200c/141 expression by intergenic DNA-looping and transcriptional read-through',
'authors' => 'Batista L et al.',
'description' => '<p>The miR-200 family members have been implicated in stress responses and ovarian tumorigenesis. Here, we find that miR-200c/141 transcription is intimately linked to the transcription of the proximal upstream gene PTPN6 (SHP1) in all physiological conditions tested. PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 are transcriptionally co-regulated by two complementary mechanisms. First, a bypass of the regular PTPN6 polyadenylation signal allows the transcription of the downstream miR-200c/141. Second, the promoters of the PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 transcription units physically interact through a 3-dimensional DNA loop and exhibit similar epigenetic regulation. Our findings highlight that transcription of intergenic miRNAs is a novel outcome of transcriptional read-through and reveal a yet unexplored type of DNA loop associating two closely located promoters. These mechanisms have significant relevance in ovarian cancers and stress response, pathophysiological conditions in which miR-200c/141 exert key functions.</p>',
'date' => '2016-01-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26725650',
'doi' => '10.1038/ncomms9959',
'modified' => '2016-07-07 10:27:25',
'created' => '2016-07-07 10:27:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 102 => array(
'id' => '2951',
'name' => 'Maternal immune activation induces GAD1 and GAD2 promoter remodeling in the offspring prefrontal cortex',
'authors' => 'Labouesse MA et al.',
'description' => '<p>Maternal infection during pregnancy increases the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in the offspring. In addition to its influence on other neuronal systems, this early-life environmental adversity has been shown to negatively affect cortical γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) functions in adult life, including impaired prefrontal expression of enzymes required for GABA synthesis. The underlying molecular processes, however, remain largely unknown. In the present study, we explored whether epigenetic modifications represent a mechanism whereby maternal infection during pregnancy can induce such GABAergic impairments in the offspring. We used an established mouse model of prenatal immune challenge that is based on maternal treatment with the viral mimetic poly(I:C). We found that prenatal immune activation increased prefrontal levels of 5-methylated cytosines (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylated cytosines (5hmC) in the promoter region of GAD1, which encodes the 67-kDa isoform of the GABA-synthesising enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67). The early-life challenge also increased 5mC levels at the promoter region of GAD2, which encodes the 65-kDa GAD isoform (GAD65). These effects were accompanied by elevated GAD1 and GAD2 promoter binding of methyl CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) and by reduced GAD67 and GAD65 mRNA expression. Moreover, the epigenetic modifications at the GAD1 promoter correlated with prenatal infection-induced impairments in working memory and social interaction. Our study thus highlights that hypermethylation of GAD1 and GAD2 promoters may be an important molecular mechanism linking prenatal infection to presynaptic GABAergic impairments and associated behavioral and cognitive abnormalities in the offspring.</p>',
'date' => '2015-12-02',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26575259',
'doi' => ' 10.1080/15592294.2015.1114202',
'modified' => '2016-06-10 16:32:32',
'created' => '2016-06-10 16:32:32',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 103 => array(
'id' => '2860',
'name' => 'DNA methylation profiling: comparison of genome-wide sequencing methods and the Infinium Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip',
'authors' => 'Walker DL, Bhagwate AV, Baheti S, Smalley RL, Hilker CA, Sun Z, Cunningham JM',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>AIMS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="AIMS" nlmcategory="OBJECTIVE">To compare the performance of four sequence-based and one microarray methods for DNA methylation profiling.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>METHODS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="METHODS" nlmcategory="METHODS">DNA from two cell lines were profiled by reduced representation bisulfite sequencing, methyl capture sequencing (SS-Meth Seq), NimbleGen SeqCapEpi CpGiant(Nimblegen MethSeq), methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) and the Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip (Meth450K).</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS & CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS & CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">Despite differences in genome-wide coverage, high correlation and concordance were observed between different methods. Significant overlap of differentially methylated regions was identified between sequenced-based platforms. MeDIP provided the best coverage for the whole genome and gene body regions, while RRBS and Nimblegen MethSeq were superior for CpGs in CpG islands and promoters. Methylation analyses can be achieved by any of the five methods but understanding their differences may better address the research question being posed.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-12-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26192535',
'doi' => '10.2217/EPI.15.64',
'modified' => '2016-03-16 11:06:05',
'created' => '2016-03-16 11:06:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 104 => array(
'id' => '2892',
'name' => 'High cortisol in 5-year-old children causes loss of DNA methylation in SINE retrotransposons: a possible role for ZNF263 in stress-related diseases',
'authors' => 'Nätt D, Johansson I, Faresjö T, Ludvigsson J, Thorsell A',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Childhood stress leads to increased risk of many adult diseases, such as major depression and cardiovascular disease. Studies show that adults with experienced childhood stress have specific epigenetic changes, but to understand the pathways that lead to disease, we also need to study the epigenetic link prospectively in children.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Here, we studied a homogenous group of 48 5-year-old children. By combining hair cortisol measurements (a well-documented biomarker for chronic stress), with whole-genome DNA-methylation sequencing, we show that high cortisol associates with a genome-wide decrease in DNA methylation and targets short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs; a type of retrotransposon) and genes important for calcium transport: phenomena commonly affected in stress-related diseases and in biological aging. More importantly, we identify a zinc-finger transcription factor, ZNF263, whose binding sites where highly overrepresented in regions experiencing methylation loss. This type of zinc-finger protein has previously shown to be involved in the defense against retrotransposons.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">Our results show that stress in preschool children leads to changes in DNA methylation similar to those seen in biological aging. We suggest that this may affect future disease susceptibility by alterations in the epigenetic mechanisms that keep retrotransposons dormant. Future treatments for stress- and age-related diseases may therefore seek to target zinc-finger proteins that epigenetically control retrotransposon reactivation, such as ZNF263.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-09-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26339299',
'doi' => ' 10.1186/s13148-015-0123-z',
'modified' => '2016-04-14 10:03:28',
'created' => '2016-04-14 10:03:28',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 105 => array(
'id' => '2857',
'name' => 'Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo',
'authors' => 'Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associated with disturbed blood flow. DNA methylation is a powerful epigenetic regulator of endothelial transcription recently associated with flow characteristics. We investigated differential DNA methylation in flow region-specific aortic endothelial cells in vivo in adult domestic male and female swine.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Genome-wide DNA methylation was profiled in endothelial cells (EC) isolated from two robust locations of differing patho-susceptibility:--an athero-susceptible site located at the inner curvature of the aortic arch (AA) and an athero-protected region in the descending thoracic (DT) aorta. Complete methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) identified over 5500 endothelial differentially methylated regions (DMRs). DMR density was significantly enriched in exons and 5'UTR sequences of annotated genes, 60 of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. The set of DMR-associated genes was enriched in transcriptional regulation, pattern specification HOX loci, oxidative stress and the ER stress adaptive pathway, all categories linked to athero-susceptible endothelium. Examination of the relationship between DMR and mRNA in HOXA genes demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between CpG island promoter methylation and gene expression. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) confirmed differential CpG methylation of HOXA genes, the ER stress gene ATF4, inflammatory regulator microRNA-10a and ARHGAP25 that encodes a negative regulator of Rho GTPases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Gender-specific DMRs associated with ciliogenesis that may be linked to defects in cilia development were also identified in AA DMRs.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">An endothelial methylome analysis identifies epigenetic DMR characteristics associated with transcriptional regulation in regions of atherosusceptibility in swine aorta in vivo. The data represent the first methylome blueprint for spatio-temporal analyses of lesion susceptibility predisposing to endothelial dysfunction in complex flow environments in vivo.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-07-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12864-015-1656-4',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'created' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Testimonial' => array(),
'Area' => array(),
'SafetySheet' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '656',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS US en',
'language' => 'en',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-US-en-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'US',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:56:19',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:56:19',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '654',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS GB en',
'language' => 'en',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-GB-en-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'GB',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:28',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:28',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '649',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE fr',
'language' => 'fr',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-fr-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:52:41',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:52:41',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '653',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS FR fr',
'language' => 'fr',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-FR-fr-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'FR',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:02',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:02',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '652',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS ES es',
'language' => 'es',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-ES-es-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'ES',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:54:39',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:54:39',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '651',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS DE de',
'language' => 'de',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-DE-de-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'DE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:54:02',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:54:02',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '655',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS JP ja',
'language' => 'ja',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-JP-ja-1_1.pdf',
'countries' => 'JP',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:55',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:55',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 7 => array(
'id' => '650',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE nl',
'language' => 'nl',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-nl-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
)
)
$meta_canonical = 'https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns'
$country = 'US'
$countries_allowed = array(
(int) 0 => 'CA',
(int) 1 => 'US',
(int) 2 => 'IE',
(int) 3 => 'GB',
(int) 4 => 'DK',
(int) 5 => 'NO',
(int) 6 => 'SE',
(int) 7 => 'FI',
(int) 8 => 'NL',
(int) 9 => 'BE',
(int) 10 => 'LU',
(int) 11 => 'FR',
(int) 12 => 'DE',
(int) 13 => 'CH',
(int) 14 => 'AT',
(int) 15 => 'ES',
(int) 16 => 'IT',
(int) 17 => 'PT'
)
$outsource = false
$other_formats = array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
)
)
$pro = array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsGroup' => array(
'id' => '10',
'product_id' => '1879',
'group_id' => '7'
)
)
$edit = ''
$testimonials = ''
$featured_testimonials = ''
$related_products = '<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit"><img src="/img/product/reagents/diamag02.png" alt="some alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">B04000001</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-1819" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/1819" id="CartAdd/1819Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="1819" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'B04000001',
'240',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'B04000001',
'240',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit" data-reveal-id="cartModal-1819" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17031043-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2597" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2597" id="CartAdd/2597Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2597" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17031043-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17031043-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2597" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17031046-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2599" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2599" id="CartAdd/2599Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2599" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'C17031046-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'C17031046-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2599" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17021042-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2593" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2593" id="CartAdd/2593Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2593" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17021042-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17021042-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2593" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17021045-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2595" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2595" id="CartAdd/2595Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2595" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'C17021045-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'C17021045-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2595" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/auto-magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns"><img src="/img/product/kits/methyl-kit-icon.png" alt="Methylation kit icon" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C02010014</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit - ordering reference: C0...</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/bioruptorpico2"><img src="/img/product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-1.jpg" alt="Bioruptor Pico" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">B01080010</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: QUOTE MODAL --><div id="quoteModal-3046" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<h3>Get a quote</h3><p class="lead">You are about to request a quote for <strong>Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device</strong>. Fill out the form below and we will be in touch with you very soon.</p><p><small>All <span style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</span> fields are mandatory</small></p>
</div>
</div>
<form action="/en/quotes/quote?id=3046" id="Quote-3046" class="quote" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][product_id]" value="3046" id="QuoteProductId"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][formLoaded6tY4bPYk]" value="c0sveHAvS0dieWhxT3RCV3dlb3pnUT09" id="QuoteFormLoaded6tY4bPYk"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][product_rfq_tag]" value="bioruptorpico2" id="QuoteProductRfqTag"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][source_quote]" value="modal quote" id="QuoteSourceQuote"/>
<div class="row collapse">
<h2>Contact Information</h2>
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">First name <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][first_name]" placeholder="john" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteFirstName" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Last name <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][last_name]" placeholder="doe" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteLastName" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Company <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][company]" placeholder="Organisation / Institute" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteCompany" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Phone number</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][phone_number]" placeholder="+1 862 209-4680" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuotePhoneNumber"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">City</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][city]" placeholder="Denville" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteCity"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Country <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<select name="data[Quote][country]" required="required" class="triggers" id="country_selector_quote-3046">
<option value="">-- select a country --</option>
<option value="AF">Afghanistan</option>
<option value="AX">Åland Islands</option>
<option value="AL">Albania</option>
<option value="DZ">Algeria</option>
<option value="AS">American Samoa</option>
<option value="AD">Andorra</option>
<option value="AO">Angola</option>
<option value="AI">Anguilla</option>
<option value="AQ">Antarctica</option>
<option value="AG">Antigua and Barbuda</option>
<option value="AR">Argentina</option>
<option value="AM">Armenia</option>
<option value="AW">Aruba</option>
<option value="AU">Australia</option>
<option value="AT">Austria</option>
<option value="AZ">Azerbaijan</option>
<option value="BS">Bahamas</option>
<option value="BH">Bahrain</option>
<option value="BD">Bangladesh</option>
<option value="BB">Barbados</option>
<option value="BY">Belarus</option>
<option value="BE">Belgium</option>
<option value="BZ">Belize</option>
<option value="BJ">Benin</option>
<option value="BM">Bermuda</option>
<option value="BT">Bhutan</option>
<option value="BO">Bolivia</option>
<option value="BQ">Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba</option>
<option value="BA">Bosnia and Herzegovina</option>
<option value="BW">Botswana</option>
<option value="BV">Bouvet Island</option>
<option value="BR">Brazil</option>
<option value="IO">British Indian Ocean Territory</option>
<option value="BN">Brunei Darussalam</option>
<option value="BG">Bulgaria</option>
<option value="BF">Burkina Faso</option>
<option value="BI">Burundi</option>
<option value="KH">Cambodia</option>
<option value="CM">Cameroon</option>
<option value="CA">Canada</option>
<option value="CV">Cape Verde</option>
<option value="KY">Cayman Islands</option>
<option value="CF">Central African Republic</option>
<option value="TD">Chad</option>
<option value="CL">Chile</option>
<option value="CN">China</option>
<option value="CX">Christmas Island</option>
<option value="CC">Cocos (Keeling) Islands</option>
<option value="CO">Colombia</option>
<option value="KM">Comoros</option>
<option value="CG">Congo</option>
<option value="CD">Congo, The Democratic Republic of the</option>
<option value="CK">Cook Islands</option>
<option value="CR">Costa Rica</option>
<option value="CI">Côte d'Ivoire</option>
<option value="HR">Croatia</option>
<option value="CU">Cuba</option>
<option value="CW">Curaçao</option>
<option value="CY">Cyprus</option>
<option value="CZ">Czech Republic</option>
<option value="DK">Denmark</option>
<option value="DJ">Djibouti</option>
<option value="DM">Dominica</option>
<option value="DO">Dominican Republic</option>
<option value="EC">Ecuador</option>
<option value="EG">Egypt</option>
<option value="SV">El Salvador</option>
<option value="GQ">Equatorial Guinea</option>
<option value="ER">Eritrea</option>
<option value="EE">Estonia</option>
<option value="ET">Ethiopia</option>
<option value="FK">Falkland Islands (Malvinas)</option>
<option value="FO">Faroe Islands</option>
<option value="FJ">Fiji</option>
<option value="FI">Finland</option>
<option value="FR">France</option>
<option value="GF">French Guiana</option>
<option value="PF">French Polynesia</option>
<option value="TF">French Southern Territories</option>
<option value="GA">Gabon</option>
<option value="GM">Gambia</option>
<option value="GE">Georgia</option>
<option value="DE">Germany</option>
<option value="GH">Ghana</option>
<option value="GI">Gibraltar</option>
<option value="GR">Greece</option>
<option value="GL">Greenland</option>
<option value="GD">Grenada</option>
<option value="GP">Guadeloupe</option>
<option value="GU">Guam</option>
<option value="GT">Guatemala</option>
<option value="GG">Guernsey</option>
<option value="GN">Guinea</option>
<option value="GW">Guinea-Bissau</option>
<option value="GY">Guyana</option>
<option value="HT">Haiti</option>
<option value="HM">Heard Island and McDonald Islands</option>
<option value="VA">Holy See (Vatican City State)</option>
<option value="HN">Honduras</option>
<option value="HK">Hong Kong</option>
<option value="HU">Hungary</option>
<option value="IS">Iceland</option>
<option value="IN">India</option>
<option value="ID">Indonesia</option>
<option value="IR">Iran, Islamic Republic of</option>
<option value="IQ">Iraq</option>
<option value="IE">Ireland</option>
<option value="IM">Isle of Man</option>
<option value="IL">Israel</option>
<option value="IT">Italy</option>
<option value="JM">Jamaica</option>
<option value="JP">Japan</option>
<option value="JE">Jersey</option>
<option value="JO">Jordan</option>
<option value="KZ">Kazakhstan</option>
<option value="KE">Kenya</option>
<option value="KI">Kiribati</option>
<option value="KP">Korea, Democratic People's Republic of</option>
<option value="KR">Korea, Republic of</option>
<option value="KW">Kuwait</option>
<option value="KG">Kyrgyzstan</option>
<option value="LA">Lao People's Democratic Republic</option>
<option value="LV">Latvia</option>
<option value="LB">Lebanon</option>
<option value="LS">Lesotho</option>
<option value="LR">Liberia</option>
<option value="LY">Libya</option>
<option value="LI">Liechtenstein</option>
<option value="LT">Lithuania</option>
<option value="LU">Luxembourg</option>
<option value="MO">Macao</option>
<option value="MK">Macedonia, Republic of</option>
<option value="MG">Madagascar</option>
<option value="MW">Malawi</option>
<option value="MY">Malaysia</option>
<option value="MV">Maldives</option>
<option value="ML">Mali</option>
<option value="MT">Malta</option>
<option value="MH">Marshall Islands</option>
<option value="MQ">Martinique</option>
<option value="MR">Mauritania</option>
<option value="MU">Mauritius</option>
<option value="YT">Mayotte</option>
<option value="MX">Mexico</option>
<option value="FM">Micronesia, Federated States of</option>
<option value="MD">Moldova</option>
<option value="MC">Monaco</option>
<option value="MN">Mongolia</option>
<option value="ME">Montenegro</option>
<option value="MS">Montserrat</option>
<option value="MA">Morocco</option>
<option value="MZ">Mozambique</option>
<option value="MM">Myanmar</option>
<option value="NA">Namibia</option>
<option value="NR">Nauru</option>
<option value="NP">Nepal</option>
<option value="NL">Netherlands</option>
<option value="NC">New Caledonia</option>
<option value="NZ">New Zealand</option>
<option value="NI">Nicaragua</option>
<option value="NE">Niger</option>
<option value="NG">Nigeria</option>
<option value="NU">Niue</option>
<option value="NF">Norfolk Island</option>
<option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands</option>
<option value="NO">Norway</option>
<option value="OM">Oman</option>
<option value="PK">Pakistan</option>
<option value="PW">Palau</option>
<option value="PS">Palestine, State of</option>
<option value="PA">Panama</option>
<option value="PG">Papua New Guinea</option>
<option value="PY">Paraguay</option>
<option value="PE">Peru</option>
<option value="PH">Philippines</option>
<option value="PN">Pitcairn</option>
<option value="PL">Poland</option>
<option value="PT">Portugal</option>
<option value="PR">Puerto Rico</option>
<option value="QA">Qatar</option>
<option value="RE">Réunion</option>
<option value="RO">Romania</option>
<option value="RU">Russian Federation</option>
<option value="RW">Rwanda</option>
<option value="BL">Saint Barthélemy</option>
<option value="SH">Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha</option>
<option value="KN">Saint Kitts and Nevis</option>
<option value="LC">Saint Lucia</option>
<option value="MF">Saint Martin (French part)</option>
<option value="PM">Saint Pierre and Miquelon</option>
<option value="VC">Saint Vincent and the Grenadines</option>
<option value="WS">Samoa</option>
<option value="SM">San Marino</option>
<option value="ST">Sao Tome and Principe</option>
<option value="SA">Saudi Arabia</option>
<option value="SN">Senegal</option>
<option value="RS">Serbia</option>
<option value="SC">Seychelles</option>
<option value="SL">Sierra Leone</option>
<option value="SG">Singapore</option>
<option value="SX">Sint Maarten (Dutch part)</option>
<option value="SK">Slovakia</option>
<option value="SI">Slovenia</option>
<option value="SB">Solomon Islands</option>
<option value="SO">Somalia</option>
<option value="ZA">South Africa</option>
<option value="GS">South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands</option>
<option value="ES">Spain</option>
<option value="LK">Sri Lanka</option>
<option value="SD">Sudan</option>
<option value="SR">Suriname</option>
<option value="SS">South Sudan</option>
<option value="SJ">Svalbard and Jan Mayen</option>
<option value="SZ">Swaziland</option>
<option value="SE">Sweden</option>
<option value="CH">Switzerland</option>
<option value="SY">Syrian Arab Republic</option>
<option value="TW">Taiwan</option>
<option value="TJ">Tajikistan</option>
<option value="TZ">Tanzania</option>
<option value="TH">Thailand</option>
<option value="TL">Timor-Leste</option>
<option value="TG">Togo</option>
<option value="TK">Tokelau</option>
<option value="TO">Tonga</option>
<option value="TT">Trinidad and Tobago</option>
<option value="TN">Tunisia</option>
<option value="TR">Turkey</option>
<option value="TM">Turkmenistan</option>
<option value="TC">Turks and Caicos Islands</option>
<option value="TV">Tuvalu</option>
<option value="UG">Uganda</option>
<option value="UA">Ukraine</option>
<option value="AE">United Arab Emirates</option>
<option value="GB">United Kingdom</option>
<option value="US" selected="selected">United States</option>
<option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands</option>
<option value="UY">Uruguay</option>
<option value="UZ">Uzbekistan</option>
<option value="VU">Vanuatu</option>
<option value="VE">Venezuela</option>
<option value="VN">Viet Nam</option>
<option value="VG">Virgin Islands, British</option>
<option value="VI">Virgin Islands, U.S.</option>
<option value="WF">Wallis and Futuna</option>
<option value="EH">Western Sahara</option>
<option value="YE">Yemen</option>
<option value="ZM">Zambia</option>
<option value="ZW">Zimbabwe</option>
</select><script>
$('#country_selector_quote-3046').selectize();
</script><br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">State</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" maxlength="3" type="text"/><br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Email <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][email]" placeholder="email@address.com" maxlength="255" type="email" id="QuoteEmail" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse" id="email_v">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Email verification<sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][email_v]" autocomplete="nope" type="text" id="QuoteEmailV"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Comment</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<textarea name="data[Quote][comment]" placeholder="Additional comments" cols="30" rows="6" id="QuoteComment"></textarea> </div>
</div>
<!------------SERVICES PARTICULAR FORM START---------------->
<!------------DATA TO POPULATE REGARDING SPECIFIC SERVICES----->
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<div class="recaptcha"><div id="recaptcha6776db64c3be6"></div></div> </div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<button id="submit_btn-3046" class="alert button expand" form="Quote-3046" type="submit">Contact me</button> </div>
</div>
</form><script>
var pardotFormHandlerURL = 'https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2022-10-10/36b1c';
function postToPardot(formAction, id) {
$('#pardot-form-handler').load(function(){
$('#Quote-' + id).attr('action', formAction);
$('#Quote-' + id).submit();
});
$('#pardot-form-handler').attr('src', pardotFormHandlerURL + '?' + $('#Quote-' + id).serialize());
}
$(document).ready(function() {
$('body').append('<iframe id="pardot-form-handler" height="0" width="0" style="position:absolute; left:-100000px; top:-100000px" src="javascript:false;"></iframe>');
$('#Quote-3046').attr('action','javascript:postToPardot(\'' + $('#Quote-3046').attr('action') + '\', 3046)');
});
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").click(function (e) {
if($(this).closest('form')[0].checkValidity()){
e.preventDefault();
//disable the submit button
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").attr("disabled", true);
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").html("Processing...");
//submit the form
$("#Quote-3046").submit();
}
})
</script>
<script>
if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'US') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AL">Alabama (AL)</option><option value="AK">Alaska (AK)</option><option value="AZ">Arizona (AZ)</option><option value="AR">Arkansas (AR)</option><option value="CA">California (CA)</option><option value="CO">Colorado (CO)</option><option value="CT">Connecticut (CT)</option><option value="DE">Delaware (DE)</option><option value="FL">Florida (FL)</option><option value="GA">Georgia (GA)</option><option value="HI">Hawaii (HI)</option><option value="ID">Idaho (ID)</option><option value="IL">Illinois (IL)</option><option value="IN">Indiana (IN)</option><option value="IA">Iowa (IA)</option><option value="KS">Kansas (KS)</option><option value="KY">Kentucky (KY)</option><option value="LA">Louisiana (LA)</option><option value="ME">Maine (ME)</option><option value="MD">Maryland (MD)</option><option value="MA">Massachusetts (MA)</option><option value="MI">Michigan (MI)</option><option value="MN">Minnesota (MN)</option><option value="MS">Mississippi (MS)</option><option value="MO">Missouri (MO)</option><option value="MT">Montana (MT)</option><option value="NE">Nebraska (NE)</option><option value="NV">Nevada (NV)</option><option value="NH">New Hampshire (NH)</option><option value="NJ">New Jersey (NJ)</option><option value="NM">New Mexico (NM)</option><option value="NY">New York (NY)</option><option value="NC">North Carolina (NC)</option><option value="ND">North Dakota (ND)</option><option value="OH">Ohio (OH)</option><option value="OK">Oklahoma (OK)</option><option value="OR">Oregon (OR)</option><option value="PA">Pennsylvania (PA)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="RI">Rhode Island (RI)</option><option value="SC">South Carolina (SC)</option><option value="SD">South Dakota (SD)</option><option value="TN">Tennessee (TN)</option><option value="TX">Texas (TX)</option><option value="UT">Utah (UT)</option><option value="VT">Vermont (VT)</option><option value="VA">Virginia (VA)</option><option value="WA">Washington (WA)</option><option value="WV">West Virginia (WV)</option><option value="WI">Wisconsin (WI)</option><option value="WY">Wyoming (WY)</option><option value="DC">District of Columbia (DC)</option><option value="AS">American Samoa (AS)</option><option value="GU">Guam (GU)</option><option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands (MP)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands (UM)</option><option value="VI">Virgin Islands (VI)</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'CA') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AB">Alberta (AB)</option><option value="BC">British Columbia (BC)</option><option value="MB">Manitoba (MB)</option><option value="NB">New Brunswick (NB)</option><option value="NL">Newfoundland and Labrador (NL)</option><option value="NS">Nova Scotia (NS)</option><option value="ON">Ontario (ON)</option><option value="PE">Prince Edward Island (PE)</option><option value="QC">Quebec (QC)</option><option value="SK">Saskatchewan (SK)</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'DE') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="BW">Baden-Württemberg (BW)</option><option value="BY">Bayern (BY)</option><option value="BE">Berlin (BE)</option><option value="BB">Brandeburg (BB)</option><option value="HB">Bremen (HB)</option><option value="HH">Hamburg (HH)</option><option value="HE">Hessen (HE)</option><option value="MV">Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV)</option><option value="NI">Niedersachsen (NI)</option><option value="NW">Nordrhein-Westfalen (NW)</option><option value="RP">Rheinland-Pfalz (RP)</option><option value="SL">Saarland (SL)</option><option value="SN">Sachsen (SN)</option><option value ="SA">Sachsen-Anhalt (SA)</option><option value="SH">Schleswig-Holstein (SH)</option><option value="TH">Thüringen</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().hide();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<input name="data[Quote][state]" maxlength="255" type="text" id="state-3046" value="">');
}
$("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").change(function() {
if (this.value == 'US') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AL">Alabama (AL)</option><option value="AK">Alaska (AK)</option><option value="AZ">Arizona (AZ)</option><option value="AR">Arkansas (AR)</option><option value="CA">California (CA)</option><option value="CO">Colorado (CO)</option><option value="CT">Connecticut (CT)</option><option value="DE">Delaware (DE)</option><option value="FL">Florida (FL)</option><option value="GA">Georgia (GA)</option><option value="HI">Hawaii (HI)</option><option value="ID">Idaho (ID)</option><option value="IL">Illinois (IL)</option><option value="IN">Indiana (IN)</option><option value="IA">Iowa (IA)</option><option value="KS">Kansas (KS)</option><option value="KY">Kentucky (KY)</option><option value="LA">Louisiana (LA)</option><option value="ME">Maine (ME)</option><option value="MD">Maryland (MD)</option><option value="MA">Massachusetts (MA)</option><option value="MI">Michigan (MI)</option><option value="MN">Minnesota (MN)</option><option value="MS">Mississippi (MS)</option><option value="MO">Missouri (MO)</option><option value="MT">Montana (MT)</option><option value="NE">Nebraska (NE)</option><option value="NV">Nevada (NV)</option><option value="NH">New Hampshire (NH)</option><option value="NJ">New Jersey (NJ)</option><option value="NM">New Mexico (NM)</option><option value="NY">New York (NY)</option><option value="NC">North Carolina (NC)</option><option value="ND">North Dakota (ND)</option><option value="OH">Ohio (OH)</option><option value="OK">Oklahoma (OK)</option><option value="OR">Oregon (OR)</option><option value="PA">Pennsylvania (PA)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="RI">Rhode Island (RI)</option><option value="SC">South Carolina (SC)</option><option value="SD">South Dakota (SD)</option><option value="TN">Tennessee (TN)</option><option value="TX">Texas (TX)</option><option value="UT">Utah (UT)</option><option value="VT">Vermont (VT)</option><option value="VA">Virginia (VA)</option><option value="WA">Washington (WA)</option><option value="WV">West Virginia (WV)</option><option value="WI">Wisconsin (WI)</option><option value="WY">Wyoming (WY)</option><option value="DC">District of Columbia (DC)</option><option value="AS">American Samoa (AS)</option><option value="GU">Guam (GU)</option><option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands (MP)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands (UM)</option><option value="VI">Virgin Islands (VI)</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if (this.value == 'CA') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AB">Alberta (AB)</option><option value="BC">British Columbia (BC)</option><option value="MB">Manitoba (MB)</option><option value="NB">New Brunswick (NB)</option><option value="NL">Newfoundland and Labrador (NL)</option><option value="NS">Nova Scotia (NS)</option><option value="ON">Ontario (ON)</option><option value="PE">Prince Edward Island (PE)</option><option value="QC">Quebec (QC)</option><option value="SK">Saskatchewan (SK)</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if (this.value == 'DE') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="BW">Baden-Württemberg (BW)</option><option value="BY">Bayern (BY)</option><option value="BE">Berlin (BE)</option><option value="BB">Brandeburg (BB)</option><option value="HB">Bremen (HB)</option><option value="HH">Hamburg (HH)</option><option value="HE">Hessen (HE)</option><option value="MV">Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV)</option><option value="NI">Niedersachsen (NI)</option><option value="NW">Nordrhein-Westfalen (NW)</option><option value="RP">Rheinland-Pfalz (RP)</option><option value="SL">Saarland (SL)</option><option value="SN">Sachsen (SN)</option><option value ="SA">Sachsen-Anhalt (SA)</option><option value="SH">Schleswig-Holstein (SH)</option><option value="TH">Thüringen</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().hide();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<input name="data[Quote][state]" maxlength="255" type="text" id="state-3046" value="">');
}
});
</script>
<a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: QUOTE MODAL --><a href="#" id="bioruptorpico2" data-reveal-id="quoteModal-3046" class="quote_btn" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Bioruptor® Pico sonication device</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
'
$related = array(
'id' => '3046',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://go.diagenode.com/bioruptor-upgrade"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-br-trade.png" /></a></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p><span>The Bioruptor® Pico is the latest innovation in shearing and represents a new breakthrough as an all-in-one shearing system capable of shearing samples from 150 bp to 1 kb. </span>Since 2004, Diagenode has accumulated <strong>shearing expertise</strong> to design the Bioruptor® Pico and guarantee the best experience with the <strong>sample preparation</strong> for <strong>number of applications -- in various fields of studies</strong> including environmental research, toxicology, genomics and epigenomics, cancer research, stem cells and development, neuroscience, clinical applications, agriculture, and many more.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
</div>
<p>The Bioruptor Pico shearing accessories and consumables have been developed to allow <strong>flexibility in sample volumes</strong> (20 µl - 2 ml) and a <strong>fast parallel processing of samples</strong> (up to 16 samples simultaneously). <span>The built-in cooling system (Bioruptor® Cooler) ensures high precision <strong>temperature control</strong>. The <strong>user-friendly interface</strong> has been designed for any researcher, providing an easy and advanced modes that give both beginners and experienced users the right level of control. </span></p>
<p>In addition, Diagenode provides fully-validated tubes that remain <strong>budget-friendly with low operating cost</strong> (< 1€/$/DNA sample) and shearing kits for best sample quality. <span></span></p>
<p><strong>Application versatility</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>DNA shearing for Next-Generation-Sequencing</li>
<li>Chromatin shearing</li>
<li>RNA shearing</li>
<li>Protein extraction from tissues and cells (also for mass spectrometry)</li>
<li>FFPE DNA extraction</li>
<li>Protein aggregation studies</li>
<li>CUT&RUN - shearing of input DNA for NGS</li>
</ul>
<div style="background-color: #f1f3f4; margin: 10px; padding: 50px;">
<p><strong>Bioruptor Pico: Recommended for CUT&RUN sequencing for input DNA</strong><br /><br /> By combining antibody-targeted controlled cleavage by MNase and NGS, <strong>CUT&RUN sequencing</strong> can be used to identify protein-DNA binding sites genome-wide. CUT&RUN works by using the DNA cleaving activity of a Protein A-fused MNase to isolate DNA that is bound by a protein of interest. This targeted digestion is controlled by the addition of calcium, which MNase requires for its nuclease activity. After MNase digestion, short DNA fragments are released and can then be purified for subsequent library preparation and high-throughput sequencing. While CUT&RUN does not require mechanical shearing chromatin given the enzymatic approach, sonication is highly recommended for the fragmentation of the input DNA (used to compare the enriched sample) in order to be compatible with downstream NGS. The Bioruptor Pico is the ideal instrument of choice for generating optimal DNA fragments with a tight distribution, assuring excellent library prep and excellent sequencing results for your CUT&RUN assay.<br /><br /> <strong>Explore the Bioruptor Pico now.</strong></p>
</div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for Chromatin shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-reproducibility-is-priority.jpg" /></center></div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/pages/form-demo"> <img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for RNA shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-request-demo.jpg" /></a></center></div>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label1' => 'Specifications',
'info1' => '<center><img alt="Ultrasonic Sonicator" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-table.jpg" /></center>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label2' => 'View accessories & consumables for Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico',
'info2' => '<h3>Shearing Accessories</h3>
<table style="width: 641px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Catalog number</td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Throughput</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-2-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.2 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201144</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">16 samples</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.65 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201143</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">12 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 1.5 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201140</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-sonication-accessories-for-bioruptor-standard-plus-pico-1-pack">15 ml sonication accessories</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01200016</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Shearing Consumables</h3>
<table style="width: 646px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;">Catalog Number</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/02ml-microtubes-for-bioruptor-pico">0.2 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010020</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-500-tubes">0.65 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010011</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-with-caps-300-tubes">1.5 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010016</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-50-pc">15 ml Pico Tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010017</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-sonication-beads-50-rxns">15 ml Pico Tubes & sonication beads</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C01020031</span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/shearing_technology/bioruptor_accessories/TDS-BioruptorTubes.pdf">Find datasheet for Diagenode tubes here</a></p>
<p><a href="../documents/bioruptor-organigram-tubes">Which tubes for which Bioruptor®?</a></p>',
'label3' => 'Available shearing Kits',
'info3' => '<p>Diagenode has optimized a range of solutions for <strong>successful chromatin preparation</strong>. Chromatin EasyShear Kits together with the Pico ultrasonicator combine the benefits of efficient cell lysis and chromatin shearing, while keeping epitopes accessible to the antibody, critical for efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation. Each Chromatin EasyShear Kit provides optimized reagents and a thoroughly validated protocol according to your specific experimental needs. SDS concentration is adapted to each workflow taking into account target-specific requirements.</p>
<p>For best results, choose your desired ChIP kit followed by the corresponding Chromatin EasyShear Kit (to optimize chromatin shearing ). The Chromatin EasyShear Kits can be used independently of Diagenode’s ChIP kits for chromatin preparation prior to any chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol. Choose an appropriate kit for your specific experimental needs.</p>
<h2>Kit choice guide</h2>
<table style="border: 0;" valign="center">
<tbody>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<th class="text-center"></th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE TYPE</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE INPUT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">KIT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SDS<br /> CONCENTRATION</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">NUCLEI<br /> ISOLATION</th>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="5"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-histones.png" /></td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">< 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-optimization-kit-high-sds-100-million-cells">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />High SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">1%</td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/cross-unvalid-green.jpg" width="18" height="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">> 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">PLANT TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-plant-chip-seq-kit">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />for Plant</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.5%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="6"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-tf.png" /></td>
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="extra-spaced">
<h3>Guide for optimal chromatin preparation using Chromatin EasyShear Kits <i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/pages/chromatin-prep-easyshear-kit-guide">Read more</a></h3>
</div>
<p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B01080010',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'B01080010-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '00-Machine',
'price_EUR' => '27600',
'price_USD' => '31000',
'price_GBP' => '24000',
'price_JPY' => '4522260',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '77500',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => true,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '',
'slug' => 'bioruptorpico2',
'meta_title' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'modified' => '2024-12-19 15:08:43',
'created' => '2020-01-09 16:27:17',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
'id' => '4858',
'product_id' => '1879',
'related_id' => '3046'
),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1803',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-1.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:55:07',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:52:54',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '1804',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-2.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:08',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:08',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '1805',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-3.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:46',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:46',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '1806',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-4.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:56',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:56',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '1807',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-5.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:54:06',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:54:06',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '1772',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B010600010.jpg',
'alt' => 'B010600010',
'modified' => '2018-02-14 15:41:46',
'created' => '2018-02-14 15:41:46',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
)
)
$rrbs_service = array(
(int) 0 => (int) 1894,
(int) 1 => (int) 1895
)
$chipseq_service = array(
(int) 0 => (int) 2683,
(int) 1 => (int) 1835,
(int) 2 => (int) 1836,
(int) 3 => (int) 2684,
(int) 4 => (int) 1838,
(int) 5 => (int) 1839,
(int) 6 => (int) 1856
)
$labelize = object(Closure) {
}
$old_catalog_number = ' <span style="color:#CCC">(mc-magme-048)</span>'
$country_code = 'US'
$other_format = array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
)
$label = '<img src="/img/banners/banner-customizer-back.png" alt=""/>'
$document = array(
'id' => '1166',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit ',
'description' => '',
'image_id' => null,
'type' => 'Manual',
'url' => 'files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-manual-c02010020-21',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => '',
'modified' => '2022-11-22 15:50:08',
'created' => '2022-11-22 15:41:49',
'ProductsDocument' => array(
'id' => '3257',
'product_id' => '1879',
'document_id' => '1166'
)
)
$sds = array(
'id' => '650',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE nl',
'language' => 'nl',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-nl-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
'id' => '1194',
'product_id' => '1879',
'safety_sheet_id' => '650'
)
)
$publication = array(
'id' => '2857',
'name' => 'Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo',
'authors' => 'Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associated with disturbed blood flow. DNA methylation is a powerful epigenetic regulator of endothelial transcription recently associated with flow characteristics. We investigated differential DNA methylation in flow region-specific aortic endothelial cells in vivo in adult domestic male and female swine.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Genome-wide DNA methylation was profiled in endothelial cells (EC) isolated from two robust locations of differing patho-susceptibility:--an athero-susceptible site located at the inner curvature of the aortic arch (AA) and an athero-protected region in the descending thoracic (DT) aorta. Complete methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) identified over 5500 endothelial differentially methylated regions (DMRs). DMR density was significantly enriched in exons and 5'UTR sequences of annotated genes, 60 of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. The set of DMR-associated genes was enriched in transcriptional regulation, pattern specification HOX loci, oxidative stress and the ER stress adaptive pathway, all categories linked to athero-susceptible endothelium. Examination of the relationship between DMR and mRNA in HOXA genes demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between CpG island promoter methylation and gene expression. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) confirmed differential CpG methylation of HOXA genes, the ER stress gene ATF4, inflammatory regulator microRNA-10a and ARHGAP25 that encodes a negative regulator of Rho GTPases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Gender-specific DMRs associated with ciliogenesis that may be linked to defects in cilia development were also identified in AA DMRs.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">An endothelial methylome analysis identifies epigenetic DMR characteristics associated with transcriptional regulation in regions of atherosusceptibility in swine aorta in vivo. The data represent the first methylome blueprint for spatio-temporal analyses of lesion susceptibility predisposing to endothelial dysfunction in complex flow environments in vivo.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-07-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12864-015-1656-4',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'created' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
'id' => '550',
'product_id' => '1879',
'publication_id' => '2857'
)
)
$externalLink = ' <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682" target="_blank"><i class="fa fa-external-link"></i></a>'include - APP/View/Products/view.ctp, line 755
View::_evaluate() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 971
View::_render() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 933
View::render() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 473
Controller::render() - CORE/Cake/Controller/Controller.php, line 963
ProductsController::slug() - APP/Controller/ProductsController.php, line 1052
ReflectionMethod::invokeArgs() - [internal], line ??
Controller::invokeAction() - CORE/Cake/Controller/Controller.php, line 491
Dispatcher::_invoke() - CORE/Cake/Routing/Dispatcher.php, line 193
Dispatcher::dispatch() - CORE/Cake/Routing/Dispatcher.php, line 167
[main] - APP/webroot/index.php, line 118
Notice (8): Undefined variable: campaign_id [APP/View/Products/view.ctp, line 755]Code Context<!-- BEGIN: REQUEST_FORM MODAL -->
<div id="request_formModal" class="reveal-modal medium" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<?= $this->element('Forms/simple_form', array('solution_of_interest' => $solution_of_interest, 'header' => $header, 'message' => $message, 'campaign_id' => $campaign_id)) ?>
$viewFile = '/home/website-server/www/app/View/Products/view.ctp'
$dataForView = array(
'language' => 'en',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'product' => array(
'Product' => array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'locale' => 'eng'
),
'Antibody' => array(
'host' => '*****',
'id' => null,
'name' => null,
'description' => null,
'clonality' => null,
'isotype' => null,
'lot' => null,
'concentration' => null,
'reactivity' => null,
'type' => null,
'purity' => null,
'classification' => null,
'application_table' => null,
'storage_conditions' => null,
'storage_buffer' => null,
'precautions' => null,
'uniprot_acc' => null,
'slug' => null,
'meta_keywords' => null,
'meta_description' => null,
'modified' => null,
'created' => null,
'select_label' => null
),
'Slave' => array(),
'Group' => array(
'Group' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Master' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Product' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Related' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Application' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Category' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Document' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Feature' => array(),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Promotion' => array(),
'Protocol' => array(),
'Publication' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 7 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 8 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 9 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 10 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 11 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 12 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 13 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 14 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 15 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 16 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 17 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 18 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 19 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 20 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 21 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 22 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 23 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 24 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 25 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 26 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 27 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 28 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 29 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 30 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 31 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 32 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 33 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 34 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 35 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 36 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 37 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 38 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 39 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 40 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 41 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 42 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 43 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 44 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 45 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 46 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 47 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 48 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 49 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 50 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 51 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 52 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 53 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 54 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 55 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 56 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 57 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 58 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 59 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 60 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 61 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 62 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 63 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 64 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 65 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 66 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 67 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 68 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 69 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 70 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 71 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 72 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 73 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 74 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 75 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 76 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 77 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 78 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 79 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 80 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 81 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 82 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 83 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 84 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 85 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 86 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 87 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 88 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 89 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 90 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 91 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 92 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 93 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 94 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 95 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 96 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 97 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 98 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 99 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 100 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 101 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 102 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 103 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 104 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 105 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
'Testimonial' => array(),
'Area' => array(),
'SafetySheet' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 1 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 2 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 3 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 4 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 5 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 6 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
(int) 7 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'meta_canonical' => 'https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns'
)
$language = 'en'
$meta_keywords = ''
$meta_description = 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.'
$meta_title = 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA'
$product = array(
'Product' => array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'locale' => 'eng'
),
'Antibody' => array(
'host' => '*****',
'id' => null,
'name' => null,
'description' => null,
'clonality' => null,
'isotype' => null,
'lot' => null,
'concentration' => null,
'reactivity' => null,
'type' => null,
'purity' => null,
'classification' => null,
'application_table' => null,
'storage_conditions' => null,
'storage_buffer' => null,
'precautions' => null,
'uniprot_acc' => null,
'slug' => null,
'meta_keywords' => null,
'meta_description' => null,
'modified' => null,
'created' => null,
'select_label' => null
),
'Slave' => array(),
'Group' => array(
'Group' => array(
'id' => '7',
'name' => 'C02010021',
'product_id' => '1880',
'modified' => '2016-02-18 17:02:55',
'created' => '2016-02-18 17:02:55'
),
'Master' => array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
),
'Product' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Related' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1819',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'description' => '<p>The DiaMag02 is a powerful magnet which has been designed for controlled and rapid isolation of your DNA bound to magnetic beads. It allows for processing 16 samples at a time.</p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B04000001',
'old_catalog_number' => 'kch-816-001',
'sf_code' => 'B04000001-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '250',
'price_USD' => '240',
'price_GBP' => '220',
'price_JPY' => '40960',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '600',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit',
'meta_title' => 'DiaMag02 - magnetic rack',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'DiaMag02 - magnetic rack',
'modified' => '2019-06-11 16:27:35',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '2597',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1043-050, -500 is specific to a CpG region of the TSH2B gene from rat. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17031043-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1043-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17031043-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:06:44',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '2599',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1046-050, -500 is specific to a promoter region of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from rat. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17031046-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1046-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17031046-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:05:49',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '2593',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair cat # pp-1042-050, -500 is specific to a CpG region of the TSH2B gene from mouse. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17021042-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1042-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17021042-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'modified' => '2015-09-02 11:10:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '2595',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'description' => '<p><span>The primer pair Cat. No. C17021045 is specific to a promoter region of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from mouse. The primers are optimized to be used in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).</span></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '50 µl',
'catalog_number' => 'C17021045-50',
'old_catalog_number' => 'pp-1045-050',
'sf_code' => 'C17021045-D001-000014',
'type' => 'FRE',
'search_order' => '01-Accessory',
'price_EUR' => '60',
'price_USD' => '60',
'price_GBP' => '50',
'price_JPY' => '9830',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '150',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul',
'meta_title' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'modified' => '2021-01-18 10:00:33',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array([maximum depth reached])
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '2945',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit - ordering reference: C02010021',
'description' => '<p><span></span>The reference C02010014 has been replaced by <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns">C02010021</a><span>. </span> </p>
<p><span>Perform </span><strong>MeDIP</strong><span><span> </span>(Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation) <span>on the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/sx-8g-ip-star-compact-automated-system-1-unit" target="_blank">SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System</a> </span>followed by<span> </span></span><strong>qPCR</strong><span><span> </span>to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using </span><span>5-methylcytosine</span><span><span> </span>antibody. Our kit contains high quality reagents to get the h</span><span>ighest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</span></p>
<p>Diagenode’s Auto MagMeDIP qPCR is available in two formats (10 and 48 IPs) and has been optimized on the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/sx-8g-ip-star-compact-automated-system-1-unit" target="_blank">SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System</a> enabling highly reproducible results and allowing for high throughput assays.</p>
<h3><span>Characteristics</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Generate highly consistent results with internal controls in 24h</li>
<li>Minimize error with many reagents in 1 tube</li>
<li>Optimized purification (DIB - DNA isolation buffer)</li>
<li>Allows direct correlation between IP’d material & methylation status</li>
</ul>
<p style="text-align: center;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/magmedip-kit-validated-using-bioruptor.jpg" alt="MagMeDIP kit validated using Bioruptor" /></p>
<p><strong><em>Figure 1.</em></strong><em><span> </span><strong>IP results obtained with Diagenode Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit.</strong><span> </span>MeDIP assays were performed manually using DNA from blood, Gm12878, Hela and U20S cells and the Auto MagMeDIP qPCR kit (Diagenode). The DNA was prepared with the XL GenDNA Extraction Module included. The IP was performed including the kit meDNA and unDNA spike-in controls, together with the human DNA sample controls. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs also included in this kit.</em></p>
<p style="text-align: center;"><em><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/AutomatedMeDIP_9h.png" alt="" width="678" height="365" /></em></p>
<p style="text-align: justify;"><em><strong>Figure<span> </span>2. Automated MeDIP (9h). </strong>IP reaction was performed on the SX-8G IP-Star® Automated System with the anti-5-mC antibody. Methylated and unmethylated DNA were used as internal controls. Unmethylated DNA region of GADPH and a methylated DNA region of AlphaX1 were used to test DNA sample-IP efficiency. DNA has been isolated by using DNA Isolation Buffer (DIB).</em></p>
<p></p>',
'label1' => '',
'info1' => '',
'label2' => '',
'info2' => '',
'label3' => '',
'info3' => '',
'format' => '48 rxns',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010014',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'C02010014-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '',
'price_USD' => '',
'price_GBP' => '',
'price_JPY' => '',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'Japan',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => true,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'auto-magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x48',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x48',
'modified' => '2023-03-20 12:50:08',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '3046',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://go.diagenode.com/bioruptor-upgrade"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-br-trade.png" /></a></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p><span>The Bioruptor® Pico is the latest innovation in shearing and represents a new breakthrough as an all-in-one shearing system capable of shearing samples from 150 bp to 1 kb. </span>Since 2004, Diagenode has accumulated <strong>shearing expertise</strong> to design the Bioruptor® Pico and guarantee the best experience with the <strong>sample preparation</strong> for <strong>number of applications -- in various fields of studies</strong> including environmental research, toxicology, genomics and epigenomics, cancer research, stem cells and development, neuroscience, clinical applications, agriculture, and many more.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
</div>
<p>The Bioruptor Pico shearing accessories and consumables have been developed to allow <strong>flexibility in sample volumes</strong> (20 µl - 2 ml) and a <strong>fast parallel processing of samples</strong> (up to 16 samples simultaneously). <span>The built-in cooling system (Bioruptor® Cooler) ensures high precision <strong>temperature control</strong>. The <strong>user-friendly interface</strong> has been designed for any researcher, providing an easy and advanced modes that give both beginners and experienced users the right level of control. </span></p>
<p>In addition, Diagenode provides fully-validated tubes that remain <strong>budget-friendly with low operating cost</strong> (< 1€/$/DNA sample) and shearing kits for best sample quality. <span></span></p>
<p><strong>Application versatility</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>DNA shearing for Next-Generation-Sequencing</li>
<li>Chromatin shearing</li>
<li>RNA shearing</li>
<li>Protein extraction from tissues and cells (also for mass spectrometry)</li>
<li>FFPE DNA extraction</li>
<li>Protein aggregation studies</li>
<li>CUT&RUN - shearing of input DNA for NGS</li>
</ul>
<div style="background-color: #f1f3f4; margin: 10px; padding: 50px;">
<p><strong>Bioruptor Pico: Recommended for CUT&RUN sequencing for input DNA</strong><br /><br /> By combining antibody-targeted controlled cleavage by MNase and NGS, <strong>CUT&RUN sequencing</strong> can be used to identify protein-DNA binding sites genome-wide. CUT&RUN works by using the DNA cleaving activity of a Protein A-fused MNase to isolate DNA that is bound by a protein of interest. This targeted digestion is controlled by the addition of calcium, which MNase requires for its nuclease activity. After MNase digestion, short DNA fragments are released and can then be purified for subsequent library preparation and high-throughput sequencing. While CUT&RUN does not require mechanical shearing chromatin given the enzymatic approach, sonication is highly recommended for the fragmentation of the input DNA (used to compare the enriched sample) in order to be compatible with downstream NGS. The Bioruptor Pico is the ideal instrument of choice for generating optimal DNA fragments with a tight distribution, assuring excellent library prep and excellent sequencing results for your CUT&RUN assay.<br /><br /> <strong>Explore the Bioruptor Pico now.</strong></p>
</div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for Chromatin shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-reproducibility-is-priority.jpg" /></center></div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/pages/form-demo"> <img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for RNA shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-request-demo.jpg" /></a></center></div>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label1' => 'Specifications',
'info1' => '<center><img alt="Ultrasonic Sonicator" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-table.jpg" /></center>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label2' => 'View accessories & consumables for Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico',
'info2' => '<h3>Shearing Accessories</h3>
<table style="width: 641px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Catalog number</td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Throughput</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-2-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.2 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201144</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">16 samples</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.65 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201143</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">12 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 1.5 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201140</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-sonication-accessories-for-bioruptor-standard-plus-pico-1-pack">15 ml sonication accessories</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01200016</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Shearing Consumables</h3>
<table style="width: 646px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;">Catalog Number</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/02ml-microtubes-for-bioruptor-pico">0.2 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010020</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-500-tubes">0.65 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010011</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-with-caps-300-tubes">1.5 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010016</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-50-pc">15 ml Pico Tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010017</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-sonication-beads-50-rxns">15 ml Pico Tubes & sonication beads</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C01020031</span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/shearing_technology/bioruptor_accessories/TDS-BioruptorTubes.pdf">Find datasheet for Diagenode tubes here</a></p>
<p><a href="../documents/bioruptor-organigram-tubes">Which tubes for which Bioruptor®?</a></p>',
'label3' => 'Available shearing Kits',
'info3' => '<p>Diagenode has optimized a range of solutions for <strong>successful chromatin preparation</strong>. Chromatin EasyShear Kits together with the Pico ultrasonicator combine the benefits of efficient cell lysis and chromatin shearing, while keeping epitopes accessible to the antibody, critical for efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation. Each Chromatin EasyShear Kit provides optimized reagents and a thoroughly validated protocol according to your specific experimental needs. SDS concentration is adapted to each workflow taking into account target-specific requirements.</p>
<p>For best results, choose your desired ChIP kit followed by the corresponding Chromatin EasyShear Kit (to optimize chromatin shearing ). The Chromatin EasyShear Kits can be used independently of Diagenode’s ChIP kits for chromatin preparation prior to any chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol. Choose an appropriate kit for your specific experimental needs.</p>
<h2>Kit choice guide</h2>
<table style="border: 0;" valign="center">
<tbody>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<th class="text-center"></th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE TYPE</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE INPUT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">KIT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SDS<br /> CONCENTRATION</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">NUCLEI<br /> ISOLATION</th>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="5"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-histones.png" /></td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">< 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-optimization-kit-high-sds-100-million-cells">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />High SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">1%</td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/cross-unvalid-green.jpg" width="18" height="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">> 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">PLANT TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-plant-chip-seq-kit">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />for Plant</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.5%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="6"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-tf.png" /></td>
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="extra-spaced">
<h3>Guide for optimal chromatin preparation using Chromatin EasyShear Kits <i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/pages/chromatin-prep-easyshear-kit-guide">Read more</a></h3>
</div>
<p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B01080010',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'B01080010-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '00-Machine',
'price_EUR' => '27600',
'price_USD' => '31000',
'price_GBP' => '24000',
'price_JPY' => '4522260',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '77500',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => true,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '',
'slug' => 'bioruptorpico2',
'meta_title' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'modified' => '2024-12-19 15:08:43',
'created' => '2020-01-09 16:27:17',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'Image' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Application' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '7',
'position' => '10',
'parent_id' => '1',
'name' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'description' => '<div class="row extra-spaced">
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3>Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns"><span>The Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation is based on the affinity purification of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA using, respectively, an antibody directed against 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in the case of MeDIP or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in the case of hMeDIP.</span><br />
<h2></h2>
<h2>How it works</h2>
<p>In brief, Methyl DNA IP is performed as follows: Genomic DNA from cultured cells or tissues is prepared, sheared, and then denatured. Then, immunoselection and immunoprecipitation can take place using the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads. After isolation and purification is performed, the IP’d methylated DNA is ready for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<h2>Applications</h2>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> qPCR analysis</a></div>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-seq-package-V2-x10" class="center alert radius button"> NGS analysis </a></div>
<h2>Advantages</h2>
<ul style="font-size: 19px;" class="nobullet">
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Unaffected</strong> DNA</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>High enrichment</strong> yield</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Robust</strong> & <strong>reproducible</strong> techniques</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>NGS</strong> compatible</li>
</ul>
<h2></h2>
</div>
</div>
<div id="gtx-trans" style="position: absolute; left: 17px; top: 652.938px;">
<div class="gtx-trans-icon"></div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'slug' => 'methylated-dna-immunoprecipitation',
'meta_keywords' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation,Epigenetic,DNA Methylation,qPCR,5 methylcytosine (5-mC)',
'meta_description' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation method is based on the affinity purification of methylated DNA using an antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine (5-mC). ',
'meta_title' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation(MeDIP) - Dna methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2021-08-19 12:08:03',
'created' => '2014-09-14 05:33:34',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '1',
'position' => '9',
'parent_id' => null,
'name' => 'DNA Methylation',
'description' => '<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns">
<div style="text-align: justify;" class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h2>Complete solutions for DNA methylation studies</h2>
<p>Whether you are experienced or new to the field of DNA methylation, Diagenode has everything you need to make your assay as easy and convenient as possible while ensuring consistent data between samples and experiments. Diagenode offers sonication instruments, reagent kits, high quality antibodies, and high-throughput automation capability to address all of your specific DNA methylation analysis requirements.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns text-center"><a href="../landing-pages/dna-methylation-grant-applications"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-dna-grant.png" alt="" /></a></div>
<div style="text-align: justify;" class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark and is the most widely studied topic in epigenetics. <em>In vivo</em>, DNA is methylated following DNA replication and is involved in a number of biological processes including the regulation of imprinted genes, X chromosome inactivation. and tumor suppressor gene silencing in cancer cells. Methylation often occurs in cytosine-guanine rich regions of DNA (CpG islands), which are commonly upstream of promoter regions.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns"><br /><br />
<ul class="accordion" data-accordion="">
<li class="accordion-navigation"><a href="#dnamethyl"><i class="fa fa-caret-right"></i> Learn more</a>
<div id="dnamethyl" class="content">5-methylcytosine (5-mC) has been known for a long time as the only modification of DNA for epigenetic regulation. In 2009, however, Kriaucionis discovered a second methylated cytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC). The so-called 6th base, is generated by enzymatic conversion of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine by the TET family of oxygenases. Early reports suggested that 5-hmC may represent an intermediate of active demethylation in a new pathway which demethylates DNA, converting 5-mC to cytosine. Recent evidence fuel this hypothesis suggesting that further oxidation of the hydroxymethyl group leads to a formyl or carboxyl group followed by either deformylation or decarboxylation. The formyl and carboxyl groups of 5-formylcytosine (5-fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5-caC) could be enzymatically removed without excision of the base.
<p class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/categories/kits_dna/dna_methylation_variants.jpg" /></p>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
<br />
<h2>Main DNA methylation technologies</h2>
<p style="text-align: justify;">Overview of the <span style="font-weight: 400;">three main approaches for studying DNA methylation.</span></p>
<div class="row">
<ol>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Chemical modification with bisulfite – Bisulfite conversion</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Enrichment of methylated DNA (including MeDIP and MBD)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Treatment with methylation-sensitive or dependent restriction enzymes</span></li>
</ol>
<p><span style="font-weight: 400;"> </span></p>
<div class="row">
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th></th>
<th>Description</th>
<th width="350">Features</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><strong>Bisulfite conversion</strong></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">Chemical conversion of unmethylated cytosine to uracil. Methylated cytosines are protected from this conversion allowing to determine DNA methylation at single nucleotide resolution.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Single nucleotide resolution</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Quantitative analysis - methylation rate (%)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Gold standard and well studied</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Compatible with automation</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><b>Methylated DNA enrichment</b></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">(Hydroxy-)Methylated DNA is enriched by using specific antibodies (hMeDIP or MeDIP) or proteins (MBD) that specifically bind methylated CpG sites in fragmented genomic DNA.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Resolution depends on the fragment size of the enriched methylated DNA (300 bp)</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Qualitative analysis</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Compatible with automation</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><strong>Restriction enzyme-based digestion</strong></td>
<td><span style="font-weight: 400;">Use of (hydroxy)methylation-sensitive or (hydroxy)methylation-dependent restriction enzymes for DNA methylation analysis at specific sites.</span></td>
<td>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Determination of methylation status is limited by the enzyme recognition site</span></li>
<li style="font-weight: 400;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">Easy to use</span></li>
</ul>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="large-12 columns"></div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => true,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'slug' => 'epigenetics-dna-methylation',
'meta_keywords' => 'Epigenetics, DNA Methylation,5-hmC monoclonal antibody,hMeDIP,Bisulfite conversion,Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'meta_description' => 'Complete, optimized solutions for analyzing DNA methylation manually or on our automated system.',
'meta_title' => 'DNA Methylation - Bisulfite sequencing - Epigenetics | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2019-03-25 10:07:27',
'created' => '2015-05-03 13:47:53',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '6',
'position' => '10',
'parent_id' => '1',
'name' => 'メチル化DNA結合タンパク質',
'description' => '<div class="row">
<div class="large-12 columns">MBD方法は、メチル化DNAに対するH6-GST-MBD融合タンパク質の非常に高い親和性に基づいています。 このタンパク質は、N末端His6タグを含むグルタチオン-S-トランスフェラーゼ(GST)とのC末端融合物として、ヒトMeCP2のメチル結合ドメイン(MBD)を含有します。 このH6-GST-MBD融合タンパク質を用いて、メチル化CpGを含むDNAを特異的に単離する事が可能です。<br /><br />DiagenodeのMethylCap®キットは、二本鎖DNAの高濃縮と、メチル化CpG密度の関数における微分分画を可能にします。 分画はサンプルの複雑さを軽減し、次世代のシーケンシングを容易にします。 MethylCapアッセイに先立ち、DNAを最初に抽出し、Picoruptorソニケーターを用いて断片化します。<br />
<h3>概要</h3>
<p class="text-center"><br /><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/applications/methyl_binding_domain_overview.jpg" /></p>
</div>
</div>',
'in_footer' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => false,
'slug' => 'methylbinding-domain-protein',
'meta_keywords' => 'Epigenetic,Methylbinding Domain Protein,MBD,DNA methylation,DNA replication,MethylCap,MethylCap assay,',
'meta_description' => 'Methylbinding Domain Protein(MBD) approach is based on the very high affinity of a H6-GST-MBD fusion protein for methylated DNA. This protein consists of the methyl binding domain (MBD) of human MeCP2, as a C-terminal fusion with Glutathione-S-transferase',
'meta_title' => 'Epigenetic Methylbinding Domain Protein(MBD) - DNA methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2019-03-22 12:32:12',
'created' => '2015-06-02 17:05:42',
'ProductsApplication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Category' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '52',
'position' => '2',
'parent_id' => '12',
'name' => 'Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-seq-package-V2-x10"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/b-email-magmedip.png" /></a></p>
<p>The Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation is based on the affinity purification of methylated and hydroxymethylated DNA using, respectively, an antibody directed against 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in the case of MeDIP or 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in the case of hMeDIP.</p>
<h2>How it works</h2>
<p>In brief, Methyl DNA IP is performed as follows: Genomic DNA from cultured cells or tissues is prepared, sheared, and then denatured. Then, immunoselection and immunoprecipitation can take place using the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads. After isolation and purification is performed, the IP’d methylated DNA is ready for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<h2>Applications</h2>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> qPCR analysis</a></div>
<div align="center"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns" class="center alert radius button"> NGS analysis </a></div>
<h2>Advantages</h2>
<ul style="font-size: 19px;" class="nobullet">
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Unaffected</strong> DNA</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>High enrichment</strong> yield</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>Robust</strong> & <strong>reproducible</strong> techniques</li>
<li><i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <strong>NGS</strong> compatible</li>
</ul>
<h2></h2>',
'no_promo' => false,
'in_menu' => true,
'online' => true,
'tabular' => true,
'hide' => false,
'all_format' => false,
'is_antibody' => false,
'slug' => 'methylated-dna-immunoprecipitation',
'cookies_tag_id' => null,
'meta_keywords' => 'Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation,DNA methylation',
'meta_description' => 'Diagenode provides Antibody-based isolation of methylated DNA for DNA immunoprecipitation ',
'meta_title' => 'Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation for DNA Methylation | Diagenode',
'modified' => '2022-11-25 10:46:50',
'created' => '2015-07-08 09:30:57',
'ProductsCategory' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
),
'CookiesTag' => array([maximum depth reached])
)
),
'Document' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1166',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit ',
'description' => '',
'image_id' => null,
'type' => 'Manual',
'url' => 'files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-manual-c02010020-21',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => '',
'modified' => '2022-11-22 15:50:08',
'created' => '2022-11-22 15:41:49',
'ProductsDocument' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Feature' => array(),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1796',
'name' => 'https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/C02010020-magmedip-qpcr.jpg',
'alt' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10',
'modified' => '2019-04-24 17:06:59',
'created' => '2019-04-24 17:04:52',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Promotion' => array(),
'Protocol' => array(),
'Publication' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '4989',
'name' => 'Differential methylation of circulating free DNA assessed through cfMeDiP as a new tool for breast cancer diagnosis and detection of BRCA1/2 mutation',
'authors' => 'Piera Grisolia et al.',
'description' => '<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Background</h3>
<p>Recent studies have highlighted the importance of the cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylation profile in detecting breast cancer (BC) and its different subtypes. We investigated whether plasma cfDNA methylation, using cell-free Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation and High-Throughput Sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq), may be informative in characterizing breast cancer in patients with BRCA1/2 germline mutations for early cancer detection and response to therapy.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Methods</h3>
<p>We enrolled 23 BC patients with germline mutation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, 19 healthy controls without BRCA1/2 mutation, and two healthy individuals who carried BRCA1/2 mutations. Blood samples were collected for all study subjects at the diagnosis, and plasma was isolated by centrifugation. Cell-free DNA was extracted from 1 mL of plasma, and cfMeDIP-seq was performed for each sample. Shallow whole genome sequencing was performed on the immuno-precipitated samples. Then, the differentially methylated 300-bp regions (DMRs) between 25 BRCA germline mutation carriers and 19 non-carriers were identified. DMRs were compared with tumor-specific regions from public datasets to perform an unbiased analysis. Finally, two statistical classifiers were trained based on the GLMnet and random forest model to evaluate if the identified DMRs could discriminate BRCA-positive from healthy samples.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Results</h3>
<p>We identified 7,095 hypermethylated and 212 hypomethylated regions in 25 BRCA germline mutation carriers compared to 19 controls. These regions discriminate tumors from healthy samples with high accuracy and sensitivity. We show that the circulating tumor DNA of BRCA1/2 mutant breast cancers is characterized by the hypomethylation of genes involved in DNA repair and cell cycle. We uncovered the TFs associated with these DRMs and identified that proteins of the Erythroblast Transformation Specific (ETS) family are particularly active in the hypermethylated regions. Finally, we assessed that these regions could discriminate between BRCA positives from healthy samples with an AUC of 0.95, a sensitivity of 88%, and a specificity of 94.74%.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p>Our study emphasizes the importance of tumor cell-derived DNA methylation in BC, reporting a different methylation profile between patients carrying mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2, and wild-type controls. Our minimally invasive approach could allow early cancer diagnosis, assessment of minimal residual disease, and monitoring of response to therapy.</p>',
'date' => '2024-10-15',
'pmid' => 'https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-024-05734-2',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-05734-2',
'modified' => '2024-10-18 11:43:43',
'created' => '2024-10-18 11:43:43',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '4981',
'name' => 'Prediction of brain metastasis development with DNA methylation signatures',
'authors' => 'Jeffrey A. Zuccato et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Brain metastases (BMs) are the most common and among the deadliest brain tumors. Currently, there are no reliable predictors of BM development from primary cancer, which limits early intervention. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most common BM source and here we obtained 402 tumor and plasma samples from a large cohort of patients with LUAD with or without BM (</span><i>n</i><span> = 346). LUAD DNA methylation signatures were evaluated to build and validate an accurate model predicting BM development from LUAD, which was integrated with clinical factors to provide comprehensive patient-specific BM risk probabilities in a nomogram. Additionally, immune and cell interaction gene sets were differentially methylated at promoters in BM versus paired primary LUAD and had aligning dysregulation in the proteome. Immune cells were differentially abundant in BM versus LUAD. Finally, liquid biomarkers identified from methylated cell-free DNA sequenced in plasma were used to generate and validate accurate classifiers for early BM detection. Overall, LUAD methylomes can be leveraged to predict and noninvasively identify BM, moving toward improved patient outcomes with personalized treatment.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-10-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03286-y',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03286-y',
'modified' => '2024-10-11 09:58:45',
'created' => '2024-10-11 09:58:45',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '4957',
'name' => 'Association between TNF-α, cortisol levels, and exposure to PM10 and PM2.5: a pilot study',
'authors' => 'Dolcini J. et al.',
'description' => '<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Purpose</h3>
<p>The most harmful atmospheric pollutant for human health is particulate matter (PM). We analyzed the correlation between short-term lag exposure to PM10 and PM2.5, salivary cortisol and TNF-α level, and methylation levels of the TNF-α promoter.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Methods</h3>
<p>A pilot study including 20 subjects. Eight salivary samples for each subject at various times of the day were collected for comparing cortisol levels and TNFα detection. TNFα promoter methylation levels on salivary DNA were analyzed. Regression analyses were performed using generalized linear mixed models between the different outcomes and 4, 3, 2 and 1 day’s lag values of PM10/PM2.5.Generalized additive mixed model (GAMM) was used to evaluate any potential deviation from linearity.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Results</h3>
<p>Area under the curve with respect to the ground (AUCg) showed a statistically positive association with 4-, 3-, 2-, and 1-day lag of exposure to PM10. Area under the curve with respect to the increase (AUCi) showed a statistically negative association with 4-, 3- and 1-day lag of exposure to PM10. TNFα showed statistically significant association with both exposures, PM10 and PM2.5, at 4-, 3-, 2-, and 1-day lag.</p>
<h3 class="c-article__sub-heading" data-test="abstract-sub-heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p>Regarding cortisol levels there is an increase of overall hormone levels but a less dynamism of the system to answer to external stressors. Increase of TNF-α may reflect increased levels of oxidative stress and inflammation due to pollution exposure.</p>',
'date' => '2024-08-07',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12302-024-00961-2',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-024-00961-2',
'modified' => '2024-09-02 10:01:14',
'created' => '2024-09-02 10:00:08',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '4942',
'name' => 'Epigenomic signatures of sarcomatoid differentiation to guide the treatment of renal cell carcinoma',
'authors' => 'Talal El Zarif et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (sRCC) is associated with poor survival and a heightened response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Two major barriers to improving outcomes for sRCC are the limited understanding of its gene regulatory programs and the low diagnostic yield of tumor biopsies due to spatial heterogeneity. Herein, we characterized the epigenomic landscape of sRCC by profiling 107 epigenomic libraries from tissue and plasma samples from 50 patients with RCC and healthy volunteers. By profiling histone modifications and DNA methylation, we identified highly recurrent epigenomic reprogramming enriched in sRCC. Furthermore, CRISPRa experiments implicated the transcription factor FOSL1 in activating sRCC-associated gene regulatory programs, and </span><em>FOSL1</em><span><span> </span>expression was associated with the response to ICIs in RCC in two randomized clinical trials. Finally, we established a blood-based diagnostic approach using detectable sRCC epigenomic signatures in patient plasma, providing a framework for discovering epigenomic correlates of tumor histology via liquid biopsy.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-25',
'pmid' => 'https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(24)00678-8',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114350',
'modified' => '2024-06-24 10:33:29',
'created' => '2024-06-24 10:33:29',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '4947',
'name' => 'Detecting small cell transformation in patients with advanced EGFR mutant lung adenocarcinoma through epigenomic cfDNA profiling',
'authors' => 'Talal El Zarif et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Purpose: Histologic transformation to small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a mechanism of treatment resistance in patients with advanced oncogene-driven lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) that currently requires histologic review for diagnosis. Herein, we sought to develop an epigenomic cell-free (cf)DNA-based approach to non-invasively detect small cell transformation in patients with EGFR mutant (EGFRm) LUAD. Experimental Design: To characterize the epigenomic landscape of transformed (t)SCLC relative to LUAD and de novo SCLC, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) to profile the histone modifications H3K27ac, H3K4me3, and H3K27me3, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq), assay for transposase-accessible chromatin sequencing (ATAC-seq), and RNA sequencing on 26 lung cancer patient-derived xenograft (PDX) tumors. We then generated and analyzed H3K27ac ChIP-seq, MeDIP-seq, and whole genome sequencing cfDNA data from 1 ml aliquots of plasma from patients with EGFRm LUAD with or without tSCLC. Results: Analysis of 126 epigenomic libraries from the lung cancer PDXs revealed widespread epigenomic reprogramming between LUAD and tSCLC, with a large number of differential H3K27ac (n=24,424), DNA methylation (n=3,298), and chromatin accessibility (n=16,352) sites between the two histologies. Tumor-informed analysis of each of these three epigenomic features in cfDNA resulted in accurate non-invasive discrimination between patients with EGFRm LUAD versus tSCLC (AUROC=0.82-0.87). A multi-analyte cfDNA-based classifier integrating these three epigenomic features discriminated between EGFRm LUAD versus tSCLC with an AUROC of 0.94. Conclusions: These data demonstrate the feasibility of detecting small cell transformation in patients with EGFRm LUAD through epigenomic cfDNA profiling of 1 ml of patient plasma.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-24',
'pmid' => 'https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article/doi/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0466/746147/Detecting-small-cell-transformation-in-patients',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0466',
'modified' => '2024-07-04 14:50:38',
'created' => '2024-07-04 14:50:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '4949',
'name' => 'Prostate cancer detection through unbiased capture of methylated cell-free DNA',
'authors' => 'Ermira Lleshi et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Prostate cancer screening using prostate-specific antigen (PSA) has been shown to reduce mortality but with substantial overdiagnosis, leading to unnecessary biopsies. The identification of a highly specific biomarker using liquid biopsies, represents an unmet need in the diagnostic pathway for prostate cancer. In this study, we employed a method that enriches for methylated cell-free DNA fragments coupled with a machine learning algorithm which enabled the detection of metastatic and localised cancers with AUCs of 0.96 and 0.74, respectively. The model also detected 51.8% (14/27) of localised and 88.7% (79/89) of metastatic cancer patients in an external dataset. Furthermore, we show that the differentially methylated regions reflect epigenetic and transcriptomic changes at the tissue level. Notably, these regions are significantly enriched for biologically relevant pathways associated with the regulation of cellular proliferation and TGF-beta signalling. This demonstrates the potential of circulating tumour DNA methylation for prostate cancer detection and prognostication.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-06-20',
'pmid' => 'https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004224015554',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110330',
'modified' => '2024-07-04 15:29:13',
'created' => '2024-07-04 15:29:13',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '4921',
'name' => 'A Pre-Leukemic DNA Methylation Signature in Healthy Individuals at Higher Risk for Developing Myeloid Malignancy',
'authors' => 'Zhentang Lao et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Purpose: DNA methylation alterations are widespread in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), some of which appear to have evolved independently of somatic mutations in epigenetic regulators. While the presence of somatic mutations in peripheral blood can predict the risk of development of AML and MDS, its accuracy remains unsatisfactory. Experimental Design: We performed global DNA methylation profiling in a case-control study nested within Singapore Chinese Health Study to evaluate if DNA methylation alterations were associated with AML/MDS development. Targeted deep sequencing and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) were performed on peripheral blood collected a median of 9.9 years prior to diagnosis of AML or MDS, together with age-matched still healthy individuals as controls. Results: Sixty-six individuals who developed AML or MDS displayed significant DNA methylation changes in the peripheral blood compared with 167 age- and gender-matched controls who did not develop AML/MDS during the follow up period. Alterations in methylation in the differentially methylation regions (DMRs) were associated with increased odds of developing AML/MDS. Conclusions: The epigenetic changes may be acquired independently and prior to somatic mutations that relevant for AML/MDS development. The association between methylation changes and the risk of pre-AML/MDS in these individuals was considerably stronger than somatic mutations, suggesting that methylation changes could be used as biomarkers for pre- AML/MDS screening.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-03-04',
'pmid' => 'https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article-abstract/doi/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3804/735044/A-Pre-Leukemic-DNA-Methylation-Signature-in?redirectedFrom=fulltext',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-3804',
'modified' => '2024-03-12 16:50:46',
'created' => '2024-03-12 16:50:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 7 => array(
'id' => '4912',
'name' => 'Neurofibromin 1 controls metabolic balance and Notch-dependent quiescence of murine juvenile myogenic progenitors',
'authors' => 'Wei X. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Patients affected by neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) frequently show muscle weakness with unknown etiology. Here we show that, in mice, Neurofibromin 1 (</span><i>Nf1</i><span>) is not required in muscle fibers, but specifically in early postnatal myogenic progenitors (MPs), where<span> </span></span><i>Nf1</i><span><span> </span>loss led to cell cycle exit and differentiation blockade, depleting the MP pool resulting in reduced myonuclear accretion as well as reduced muscle stem cell numbers. This was caused by precocious induction of stem cell quiescence coupled to metabolic reprogramming of MPs impinging on glycolytic shutdown, which was conserved in muscle fibers. We show that a Mek/Erk/NOS pathway hypersensitizes<span> </span></span><i>Nf1</i><span>-deficient MPs to Notch signaling, consequently, early postnatal Notch pathway inhibition ameliorated premature quiescence, metabolic reprogramming and muscle growth. This reveals an unexpected role of Ras/Mek/Erk signaling supporting postnatal MP quiescence in concert with Notch signaling, which is controlled by Nf1 safeguarding coordinated muscle growth and muscle stem cell pool establishment. Furthermore, our data suggest transmission of metabolic reprogramming across cellular differentiation, affecting fiber metabolism and function in NF1.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-02-15',
'pmid' => 'https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-45618-z',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-45618-z',
'modified' => '2024-02-22 12:22:26',
'created' => '2024-02-22 12:22:26',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 8 => array(
'id' => '4892',
'name' => 'Promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions are associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival',
'authors' => 'Rivera‑Peña B. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) can be used as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets in precision medicine workflows. DNA from 21 HNSCC and 10 healthy oral tissue samples was hybridized to a genome‑wide tiling array to identify DMRs in a discovery cohort. Downstream analyses identified differences in promoter DNA methylation patterns in oral, laryngeal and oropharyngeal anatomical regions associated with tumor differentiation, nodal involvement and survival. Genome‑wide DMR analysis showed 2,565 DMRs common to the three subsites. A total of 738 DMRs were unique to laryngeal cancer (n=7), 889 DMRs were unique to oral cavity cancer (n=10) and 363 DMRs were unique to pharyngeal cancer (n=6). Based on the genome‑wide analysis and a Gene Ontology analysis, 10 candidate genes were selected to test for prognostic value and association with clinicopathological features. </span><em>TIMP3</em><span><span> </span>was associated with tumor differentiation in oral cavity cancer (P=0.039),<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span><span> </span>was associated with nodal involvement in pharyngeal cancer (P=0.017) and<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span><span> </span>was associated with tumor differentiation in laryngeal cancer (P=0.040). A total of five candidate genes were selected,<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>CDH1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span>,<span> </span></span><em>CALCA</em><span><span> </span>and<span> </span></span><em>TIMP3</em><span>, for a prevalence study in a larger validation cohort: Oral cavity cancer samples (n=42), pharyngeal cancer tissues (n=25) and laryngeal cancer samples (n=52).<span> </span></span><em>PAX1</em><span><span> </span>hypermethylation differed across HNSCC anatomic subsites (P=0.029), and was predominantly detected in laryngeal cancer. Kaplan‑Meier survival analysis (P=0.043) and Cox regression analysis of overall survival (P=0.001) showed that<span> </span></span><em>DAPK1</em><span><span> </span>methylation is associated with better prognosis in HNSCC. The findings of the present study showed that the HNSCC subsites oral cavity, pharynx and larynx display substantial differences in aberrant DNA methylation patterns, which may serve as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.</span></p>',
'date' => '2024-01-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/ol.2024.14223/abstract',
'doi' => ' https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2024.14223',
'modified' => '2024-01-11 08:48:03',
'created' => '2024-01-11 08:48:03',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 9 => array(
'id' => '4732',
'name' => 'Cerebrospinal fluid methylome-based liquid biopsies for accuratemalignant brain neoplasm classification.',
'authors' => 'Zuccato Jeffrey A et al.',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Resolving the differential diagnosis between brain metastases (BM), glioblastomas (GBM), and central nervous system lymphomas (CNSL) is an important dilemma for the clinical management of the main three intra-axial brain tumor types. Currently, treatment decisions require invasive diagnostic surgical biopsies that carry risks and morbidity. This study aimed to utilize methylomes from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), a biofluid proximal to brain tumors, for reliable non-invasive classification that addresses limitations associated with low target abundance in existing approaches. METHODS: Binomial GLMnet classifiers of tumor type were built, in fifty iterations of 80\% discovery sets, using CSF methylomes obtained from 57 BM, GBM, CNSL, and non-neoplastic control patients. Publicly-available tissue methylation profiles (N=197) on these entities and normal brain parenchyma were used for validation and model optimization. RESULTS: Models reliably distinguished between BM (area under receiver operating characteristic curve [AUROC]=0.93, 95\% confidence interval [CI]: 0.71-1.0), GBM (AUROC=0.83, 95\% CI: 0.63-1.0), and CNSL (AUROC=0.91, 95\% CI: 0.66-1.0) in independent 20\% validation sets. For validation, CSF-based methylome signatures reliably distinguished between tumor types within external tissue samples and tumors from non-neoplastic controls in CSF and tissue. CSF methylome signals were observed to align closely with tissue signatures for each entity. An additional set of optimized CSF-based models, built using tumor-specific features present in tissue data, showed enhanced classification accuracy. CONCLUSIONS: CSF methylomes are reliable for liquid biopsy-based classification of the major three malignant brain tumor types. We discuss how liquid biopsies may impact brain cancer management in the future by avoiding surgical risks, classifying unbiopsiable tumors, and guiding surgical planning when resection is indicated.</p>',
'date' => '2023-08-03',
'pmid' => 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36455236/',
'doi' => '10.1093/neuonc/noac264',
'modified' => '2023-10-13 08:50:06',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 10 => array(
'id' => '4803',
'name' => 'Transgenerational endocrine disruptor effects of cadmium in zebrafish andcontribution of standing epigenetic variation to adaptation.',
'authors' => 'Pierron F. et al.',
'description' => '<p><span>Evidence has emerged that environmentally-induced epigenetic changes can have long-lasting effects on gene transcription across generations. These recent findings highlight the need to investigate the transgenerational impacts of pollutants to assess their long term effects on populations. In this study, we investigated the transgenerational effect of cadmium on zebrafish across 4 generations. A first whole methylome approach carried out on fish of the first two generations led us to focus our investigations on the estradiol receptor alpha gene (esr1). We observed a sex-dependent transgenerational inheritance of Cd-induced DNA methylation changes up to the last generation. These changes were associated with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that were themselves at the origin of the creation or deletion of methylation sites. Thus, Cd-induced genetic selection gave rise to DNA methylation changes. We also analyzed the transcription level of various sections of esr1 as well as estrogen responsive genes. While Cd triggered transgenerational disorders, Cd-induced epigenetic changes in esr1 contributed to the rapid transgenerational adaptation of fish to Cd. Our results provide insight into the processes underpinning rapid adaptation and highlight the need to maintain genetic diversity within natural populations to bolster the resilience of species faced with the global environmental changes.</span></p>',
'date' => '2023-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37163897',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131579',
'modified' => '2023-06-15 08:44:52',
'created' => '2023-06-13 21:11:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 11 => array(
'id' => '4843',
'name' => 'Differentiation block in acute myeloid leukemia regulated by intronicsequences of FTO',
'authors' => 'Camera F. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Iroquois transcription factor gene IRX3 is highly expressed in 20–30\% of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and contributes to the pathognomonic differentiation block. Intron 8 FTO sequences ∼220kB downstream of IRX3 exhibit histone acetylation, DNA methylation, and contacts with the IRX3 promoter, which correlate with IRX3 expression. Deletion of these intronic elements confirms a role in positively regulating IRX3. RNAseq revealed long non-coding (lnc) transcripts arising from this locus. FTO-lncAML knockdown (KD) induced differentiation of AML cells, loss of clonogenic activity, and reduced FTO intron 8:IRX3 promoter contacts. While both FTO-lncAML KD and IRX3 KD induced differentiation, FTO-lncAML but not IRX3 KD led to HOXA downregulation suggesting transcript activity in trans. FTO-lncAMLhigh AML samples expressed higher levels of HOXA and lower levels of differentiation genes. Thus, a regulatory module in FTO intron 8 consisting of clustered enhancer elements and a long non-coding RNA is active in human AML, impeding myeloid differentiation.</p>',
'date' => '2023-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589004223013962',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.isci.2023.107319',
'modified' => '2023-08-01 14:14:01',
'created' => '2023-08-01 15:59:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 12 => array(
'id' => '4777',
'name' => 'Epigenetic modifier alpha-ketoglutarate modulates aberrant gene bodymethylation and hydroxymethylation marks in diabetic heart.',
'authors' => 'Dhat R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Hyperglycemic myocardial microenvironment significantly alters chromatin architecture and the transcriptome, resulting in aberrant activation of signaling pathways in a diabetic heart. Epigenetic marks play vital roles in transcriptional reprogramming during the development of DCM. The current study is aimed to profile genome-wide DNA (hydroxy)methylation patterns in the hearts of control and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats and decipher the effect of modulation of DNA methylation by alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), a TET enzyme cofactor, on the progression of DCM. METHODS: Diabetes was induced in male adult Wistar rats with an intraperitoneal injection of STZ. Diabetic and vehicle control animals were randomly divided into groups with/without AKG treatment. Cardiac function was monitored by performing cardiac catheterization. Global methylation (5mC) and hydroxymethylation (5hmC) patterns were mapped in the Left ventricular tissue of control and diabetic rats with the help of an enrichment-based (h)MEDIP-sequencing technique by using antibodies specific for 5mC and 5hmC. Sequencing data were validated by performing (h)MEDIP-qPCR analysis at the gene-specific level, and gene expression was analyzed by qPCR. The mRNA and protein expression of enzymes involved in the DNA methylation and demethylation cycle were analyzed by qPCR and western blotting. Global 5mC and 5hmC levels were also assessed in high glucose-treated DNMT3B knockdown H9c2 cells. RESULTS: We found the increased expression of DNMT3B, MBD2, and MeCP2 with a concomitant accumulation of 5mC and 5hmC, specifically in gene body regions of diabetic rat hearts compared to the control. Calcium signaling was the most significantly affected pathway by cytosine modifications in the diabetic heart. Additionally, hypermethylated gene body regions were associated with Rap1, apelin, and phosphatidyl inositol signaling, while metabolic pathways were most affected by hyperhydroxymethylation. AKG supplementation in diabetic rats reversed aberrant methylation patterns and restored cardiac function. Hyperglycemia also increased 5mC and 5hmC levels in H9c2 cells, which was normalized by DNMT3B knockdown or AKG supplementation. CONCLUSION: This study demonstrates that reverting hyperglycemic damage to cardiac tissue might be possible by erasing adverse epigenetic signatures by supplementing epigenetic modulators such as AKG along with an existing antidiabetic treatment regimen.</p>',
'date' => '2023-04-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37101286',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13072-023-00489-4',
'modified' => '2023-06-12 09:20:54',
'created' => '2023-05-05 12:34:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 13 => array(
'id' => '4611',
'name' => 'Pre-diagnosis plasma cell-free DNA methylome profiling up to sevenyears prior to clinical detection reveals early signatures of breast cancer',
'authors' => 'Cheng N. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Profiling of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has been well demonstrated to be a potential non-invasive screening tool for early cancer detection. However, limited studies have investigated the detectability of cfDNA methylation markers that are predictive of cancers in asymptomatic individuals. We performed cfDNA methylation profiling using cell-free DNA methylation immunoprecipitation sequencing (cfMeDIP-Seq) in blood collected from individuals up to seven years before a breast cancer diagnosis in addition to matched cancer-free controls. We identified differentially methylated cfDNA signatures that discriminated cancer-free controls from pre-diagnosis breast cancer cases in a discovery cohort that is used to build a classification model. We show that predictive models built from pre-diagnosis cfDNA hypermethylated regions can accurately predict early breast cancers in an independent test set (AUC=0.930) and are generalizable to late-stage breast cancers cases at the time of diagnosis (AUC=0.912). Characterizing the top hypermethylated cfDNA regions revealed significant enrichment for hypermethylation in external bulk breast cancer tissues compared to peripheral blood leukocytes and breast normal tissues. Our findings demonstrate that cfDNA methylation markers predictive of breast cancers can be detected in blood among asymptomatic individuals up to six years prior to clinical detection.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2023.01.30.23285027',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.01.30.23285027',
'modified' => '2023-04-04 08:34:20',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 14 => array(
'id' => '4612',
'name' => 'Cell-free multi-omics analysis reveals tumor status-informativesignatures in gastrointestinal cancer patients’ plasma',
'authors' => 'Tao Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>During cancer development, host’s tumorigenesis and immune signals are released to and informed by circulating molecules, like cell-free DNA (cfDNA) and RNA (cfRNA) in blood. However, these two kinds of molecules are still not systematically compared in gastrointestinal cancer. Here, we profiled 4 types of cell-free omics data from colorectal and stomach cancer patients, and assayed 15 types of genomic, epi-genomic, and transcriptomic variations. First, we demonstrated that the multi-omics data were more capable of detecting cancer genes than the single-omics data, where cfRNAs were more sensitive and informative than cfDNAs in terms of detection ratio, variation type, altered number, and enriched functional pathway. Moreover, we revealed several peripheral immune signatures that were suppressed in cancer patients and originated from specific circulating and tumor-microenvironment cells. Particularly, we defined a γδ-T-cell score and a cancer-associated-fibroblast (CAF) score using the cfRNA-seq data of 143 cancer patients. They were informative of clinical status like cancer stage, tumor size, and survival. In summary, our work reveals the cell-free multi-molecular landscape of colorectal and stomach cancer, and provides a potential monitoring utility in blood for the personalized cancer treatment.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2023.01.31.526431',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.01.31.526431',
'modified' => '2023-04-04 08:36:37',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 15 => array(
'id' => '4674',
'name' => 'Methylation and expression of glucocorticoid receptor exon-1 variants andFKBP5 in teenage suicide-completers.',
'authors' => 'Rizavi H. et al.',
'description' => '<p>A dysregulated hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis has repeatedly been demonstrated to play a fundamental role in psychiatric disorders and suicide, yet the mechanisms underlying this dysregulation are not clear. Decreased expression of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene, which is also susceptible to epigenetic modulation, is a strong indicator of impaired HPA axis control. In the context of teenage suicide-completers, we have systematically analyzed the 5'UTR of the GR gene to determine the expression levels of all GR exon-1 transcript variants and their epigenetic state. We also measured the expression and the epigenetic state of the FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP5/FKBP51), an important modulator of GR activity. Furthermore, steady-state DNA methylation levels depend upon the interplay between enzymes that promote DNA methylation and demethylation activities, thus we analyzed DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), ten-eleven translocation enzymes (TETs), and growth arrest- and DNA-damage-inducible proteins (GADD45). Focusing on both the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus, our results show decreased expression in specific GR exon-1 variants and a strong correlation of DNA methylation changes with gene expression in the PFC. FKBP5 expression is also increased in both areas suggesting a decreased GR sensitivity to cortisol binding. We also identified aberrant expression of DNA methylating and demethylating enzymes in both brain regions. These findings enhance our understanding of the complex transcriptional regulation of GR, providing evidence of epigenetically mediated reprogramming of the GR gene, which could lead to possible epigenetic influences that result in lasting modifications underlying an individual's overall HPA axis response and resilience to stress.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36781843',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41398-023-02345-1',
'modified' => '2023-04-14 09:26:37',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 16 => array(
'id' => '4675',
'name' => 'Bridging biological cfDNA features and machine learning approaches.',
'authors' => 'Moser T. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Liquid biopsies (LBs), particularly using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), are expected to revolutionize precision oncology and blood-based cancer screening. Recent technological improvements, in combination with the ever-growing understanding of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) biology, are enabling the detection of tumor-specific changes with extremely high resolution and new analysis concepts beyond genetic alterations, including methylomics, fragmentomics, and nucleosomics. The interrogation of a large number of markers and the high complexity of data render traditional correlation methods insufficient. In this regard, machine learning (ML) algorithms are increasingly being used to decipher disease- and tissue-specific signals from cfDNA. Here, we review recent insights into biological ctDNA features and how these are incorporated into sophisticated ML applications.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36792446',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.tig.2023.01.004',
'modified' => '2023-04-14 09:28:00',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 17 => array(
'id' => '4823',
'name' => 'Gene body DNA hydroxymethylation restricts the magnitude oftranscriptional changes during aging.',
'authors' => 'Occean J. R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC) is the most abundant oxidative derivative of DNA methylation (5mC) and is typically enriched at enhancers and gene bodies of transcriptionally active and tissue-specific genes. Although aberrant genomic 5hmC has been implicated in many age-related diseases, the functional role of the modification in aging remains largely unknown. Here, we report that 5hmC is stably enriched in multiple aged organs. Using the liver and cerebellum as model organs, we show that 5hmC accumulates in gene bodies associated with tissue-specific function and thereby restricts the magnitude of gene expression changes during aging. Mechanistically, we found that 5hmC decreases binding affinity of splicing factors compared to unmodified cytosine and 5mC, and is correlated with age-related alternative splicing events, suggesting RNA splicing as a potential mediator of 5hmC’s transcriptionally restrictive function. Furthermore, we show that various age-related contexts, such as prolonged quiescence and senescence, are partially responsible for driving the accumulation of 5hmC with age. We provide evidence that this age-related function is conserved in mouse and human tissues, and further show that the modification is altered by regimens known to modulate lifespan. Our findings reveal that 5hmC is a regulator of tissue-specific function and may play a role in regulating longevity.</p>',
'date' => '2023-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36824863',
'doi' => '10.1101/2023.02.15.528714',
'modified' => '2023-06-14 08:39:26',
'created' => '2023-06-13 22:16:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 18 => array(
'id' => '4711',
'name' => 'Neonatal inflammation increases hippocampal KCC2 expression throughmethylation-mediated TGF-β1 downregulation leading to impairedhippocampal cognitive function and synaptic plasticity in adult mice.',
'authors' => 'Rong J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The mechanisms by which neonatal inflammation leads to cognitive deficits in adulthood remain poorly understood. Inhibitory GABAergic synaptic transmission plays a vital role in controlling learning, memory and synaptic plasticity. Since early-life inflammation has been reported to adversely affect the GABAergic synaptic transmission, the aim of this study was to investigate whether and how neonatal inflammation affects GABAergic synaptic transmission resulting in cognitive impairment. Neonatal mice received a daily subcutaneous injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 50 μg/kg) or saline on postnatal days 3-5. It was found that blocking GABAergic synaptic transmission reversed the deficit in hippocampus-dependent memory or the induction failure of long-term potentiation in the dorsal CA1 in adult LPS mice. An increase of mIPSCs amplitude was further detected in adult LPS mice indicative of postsynaptic potentiation of GABAergic transmission. Additionally, neonatal LPS resulted in the increased expression and function of K-Cl-cotransporter 2 (KCC2) and the decreased expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) in the dorsal CA1 during adulthood. The local TGF-β1 overexpression improved KCC2 expression and function, synaptic plasticity and memory of adult LPS mice. Adult LPS mice show hypermethylation of TGFb1 promoter and negatively correlate with reduced TGF-β1 transcripts. 5-Aza-deoxycytidine restored the changes in TGFb1 promoter methylation and TGF-β1 expression. Altogether, the results suggest that hypermethylation-induced reduction of TGF-β1 leads to enhanced GABAergic synaptic inhibition through increased KCC2 expression, which is a underlying mechanism of neonatal inflammation-induced hippocampus-dependent memory impairment in adult mice.</p>',
'date' => '2023-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36691035',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12974-023-02697-x',
'modified' => '2023-04-05 08:42:07',
'created' => '2023-02-28 12:19:11',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 19 => array(
'id' => '4589',
'name' => 'Impact of FecB Mutation on Ovarian DNA Methylome inSmall-Tail Han Sheep.',
'authors' => 'Xie L. et al.',
'description' => '<p>UNLABELLED: Booroola fecundity (FecB) gene, a mutant of bone morphogenetic protein 1B (BMPR-1B) that was discovered in Booroola Merino, was the first prolificacy gene identified in sheep related to increased ovulation rate and litter size. The mechanism of FecB impact on reproduction is unclear. METHODS: In this study, adult Han ewes with homozygous FecB(B)/FecB(B) mutations (Han BB group) and ewes with FecB(+)/FecB(+) wildtype (Han ++ group) were selected. Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) was used to identify differences in methylated genes in ovary tissue. RESULTS: We examined differences in DNA methylation patterns between HanBB and Han ++ sheep. In both sheep, methylated reads were mainly distributed at the gene body regions, CpG islands and introns. The differentially methylated genes were enriched in neurotrophy in signaling pathway, Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) signaling pathway, Wnt signaling pathway, oocyte meiosis, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway, etc. Differentially-methylated genes were co-analyzed with differentially-expressed mRNAs. Several genes which could be associated with female reproduction were identified, such as FOXP3 (forkhead box P3), TMEFF2 (Transmembrane Protein with EGF Like and Two Follistatin Like Domains 2) and ADAT2 (Adenosine Deaminase TRNA Specific 2). CONCLUSIONS: We constructed a MeDIP-seq based methylomic study to investigate the ovarian DNA methylation differences between Small-Tail Han sheep with homozygous FecB mutant and wildtype, and successfully identified FecB gene-associated differentially-methylated genes. This study has provided information with which to understand the mechanisms of FecB gene-induced hyperprolificacy in sheep.</p>',
'date' => '2023-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36672944',
'doi' => '10.3390/genes14010203',
'modified' => '2023-04-11 10:04:29',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 20 => array(
'id' => '4631',
'name' => 'Consistent DNA Hypomethylations in Prostate Cancer.',
'authors' => 'Araúzo-Bravo M.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>With approximately 1.4 million men annually diagnosed with prostate cancer (PCa) worldwide, PCa remains a dreaded threat to life and source of devastating morbidity. In recent decades, a significant decrease in age-specific PCa mortality has been achieved by increasing prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening and improving treatments. Nevertheless, upcoming, augmented recommendations against PSA screening underline an escalating disproportion between the benefit and harm of current diagnosis/prognosis and application of radical treatment standards. Undoubtedly, new potent diagnostic and prognostic tools are urgently needed to alleviate this tensed situation. They should allow a more reliable early assessment of the upcoming threat, in order to enable applying timely adjusted and personalized therapy and monitoring. Here, we present a basic study on an epigenetic screening approach by Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP). We identified genes associated with hypomethylated CpG islands in three PCa sample cohorts. By adjusting our computational biology analyses to focus on single CpG-enriched 60-nucleotide-long DNA probes, we revealed numerous consistently differential methylated DNA segments in PCa. They were associated among other genes with and . These can be used for early discrimination, and might contribute to a new epigenetic tumor classification system of PCa. Our analysis shows that we can dissect short, differential methylated CpG-rich DNA fragments and combinations of them that are consistently present in all tumors. We name them tumor cell-specific differential methylated CpG dinucleotide signatures (TUMS).</p>',
'date' => '2022-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36613831',
'doi' => '10.3390/ijms24010386',
'modified' => '2023-03-28 09:03:47',
'created' => '2023-02-21 09:59:46',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 21 => array(
'id' => '4488',
'name' => 'Cell-free DNA methylation-defined prognostic subgroups in small celllung cancer identified by leukocyte methylation subtraction',
'authors' => 'Ul Haq Sami et al.',
'description' => '<p>Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) methylome is understudied. Here, we comprehensively profile SCLC using cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from plasma of 74 SCLC patients pre-treatment and from 20 non-cancer participants, genomic DNA (gDNA) from peripheral blood leukocytes from the same 74 patients and 7 accompanying circulating-tumour-cell patient-derived xenografts (CDX) underwent cfMeDIP-seq. PeRIpheral blood leukocyte MEthylation (PRIME) subtraction to improve tumour specificity. SCLC cfDNA methylation is distinct from non-cancer but correlates with CDX tumor methylation. PRIME and k-means consensus identified two methylome clusters with prognostic associations that related to axon guidance, neuroactive ligand−receptor interaction, pluripotency of stem cells, and differentially methylated at long noncoding RNA and other repeats features. We comprehensively profiled the SCLC methylome in a large patient cohort and identified methylome clusters with prognostic associations. Our work demonstrates the potential of liquid biopsies in examining SCLC biology encoded in the methylome.</p>',
'date' => '2022-11-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.isci.2022.105487',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.isci.2022.105487',
'modified' => '2022-11-18 12:35:39',
'created' => '2022-11-15 09:26:20',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 22 => array(
'id' => '4547',
'name' => 'The cell-free DNA methylome captures distinctions between localized andmetastatic prostate tumors.',
'authors' => 'Chen Sujun et al.',
'description' => '<p>Metastatic prostate cancer remains a major clinical challenge and metastatic lesions are highly heterogeneous and difficult to biopsy. Liquid biopsy provides opportunities to gain insights into the underlying biology. Here, using the highly sensitive enrichment-based sequencing technology, we provide analysis of 60 and 175 plasma DNA methylomes from patients with localized and metastatic prostate cancer, respectively. We show that the cell-free DNA methylome can capture variations beyond the tumor. A global hypermethylation in metastatic samples is observed, coupled with hypomethylation in the pericentromeric regions. Hypermethylation at the promoter of a glucocorticoid receptor gene NR3C1 is associated with a decreased immune signature. The cell-free DNA methylome is reflective of clinical outcomes and can distinguish different disease types with 0.989 prediction accuracy. Finally, we show the ability of predicting copy number alterations from the data, providing opportunities for joint genetic and epigenetic analysis on limited biological samples.</p>',
'date' => '2022-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36309516',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41467-022-34012-2',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:30:03',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 23 => array(
'id' => '4550',
'name' => 'A SOX2-engineered epigenetic silencer factor represses the glioblastomagenetic program and restrains tumor development.',
'authors' => 'Benedetti V. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Current therapies remain unsatisfactory in preventing the recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), which leads to poor patient survival. By rational engineering of the transcription factor SOX2, a key promoter of GBM malignancy, together with the Kruppel-associated box and DNA methyltransferase3A/L catalytic domains, we generated a synthetic repressor named SOX2 epigenetic silencer (SES), which induces the transcriptional silencing of its original targets. By doing so, SES kills both glioma cell lines and patient-derived cancer stem cells in vitro and in vivo. SES expression, through local viral delivery in mouse xenografts, induces strong regression of human tumors and survival rescue. Conversely, SES is not harmful to neurons and glia, also thanks to a minimal promoter that restricts its expression in mitotically active cells, rarely present in the brain parenchyma. Collectively, SES produces a significant silencing of a large fraction of the SOX2 transcriptional network, achieving high levels of efficacy in repressing aggressive brain tumors.</p>',
'date' => '2022-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35921410/',
'doi' => '10.1126/sciadv.abn3986',
'modified' => '2023-09-28 11:26:02',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 24 => array(
'id' => '4551',
'name' => 'mTORC1 is required for epigenetic silencing during β-cell functionalmaturation.',
'authors' => 'Ni Qicheng et al.',
'description' => '<p>OBJECTIVE: The mechanistic target of rapamycin comple×1 (mTORC1) is a key molecule that links nutrients, hormones, and growth factors to cell growth/function. Our previous studies have shown that mTORC1 is required for β-cell functional maturation and identity maintenance; however, the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. This work aimed to understand the underlying epigenetic mechanisms of mTORC1 in regulating β-cell functional maturation. METHODS: We performed Microarray, MeDIP-seq and ATAC-seq analysis to explore the abnormal epigenetic regulation in 8-week-old immature βRapKO islets. Moreover, DNMT3A was overexpressed in βRapKO islets by lentivirus, and the transcriptome changes and GSIS function were analyzed. RESULTS: We identified two major epigenetic silencing mechanisms, DNMT3A-dependent DNA methylation and PRC2-dependent H3K27me3 modification, which are responsible for functional immaturity of Raptor-deficient β-cell. Overexpression of DNMT3A partially reversed the immature transcriptome pattern and restored the impaired GSIS in Raptor-deficient β-cells. Moreover, we found that Raptor directly regulated PRC2/EED2 and H3K27me3 expression levels, as well as a group of immature genes marked with H3K27me3. Combined with ATAC-seq, MeDIP-seq and ChIP-seq, we identified β-cell immature genes with either DNA methylation and/or H3K27me3 modification. CONCLUSION: The present study advances our understanding of the nutrient sensor mTORC1, by integrating environmental nutrient supply and epigenetic modification, i.e., DNMT3A-mediated DNA methylation and PRC2-mediated histone methylation in regulating β-cell identity and functional maturation, and therefore may impact the disease risk of type 2 diabetes.</p>',
'date' => '2022-08-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35940555',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101559',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:09:58',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 25 => array(
'id' => '4391',
'name' => 'Detection of ovarian cancer using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Lu Huaiwu et al. ',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a highly lethal gynecologic cancer, and it is hard to diagnose at an early stage. Clinically, there are no ovarian cancer-specific markers for early detection. Here, we demonstrate the use of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) methylomes to detect ovarian cancer, especially the early-stage OC. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Plasma from 74 epithelial ovarian cancer patients, 86 healthy volunteers, and 20 patients with benign pelvic masses was collected. The cfDNA methylomes of these samples were generated by cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq). The differentially methylated regions (DMRs) were identified by the contrasts between tumor and non-tumor groups, and the discrimination performance was evaluated with the iterative training and testing method. RESULTS: The DMRs identified for cfDNA methylomes can well discriminate tumor groups and non-tumor groups (ROC values from 0.86 to 0.98). The late-stage top 300 DMRs are more late-stage-specific and failed to detect early-stage OC. However, the early-stage markers have the potential to discriminate all-stage OCs from non-tumor samples. CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrates that cfDNA methylomes generated with cfMeDIP-seq could be used to identify OC-specific biomarkers for OC, especially early OC detection. To detect early-stage OC, the biomarkers should be directly identified from early OC plasma samples rather than mix-stage ones. Further exploration of DMRs from a k larger early-stage OC cohort is warranted.</p>',
'date' => '2022-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35681212',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13148-022-01285-9',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:19:10',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 26 => array(
'id' => '4438',
'name' => 'A genome-wide screen reveals new regulators of the 2-cell-like cell state',
'authors' => 'Defossez Pierre-Antoine et al.',
'description' => '<p>In mammals, only the zygote and blastomeres of the early embryo are fully totipotent. This totipotency is mirrored in vitro by mouse "2-cell-like cells" (2CLCs), which appear at low frequency in cultures of Embryonic Stem cells (ESCs). Because totipotency is incompletely understood, we carried out a genomewide CRISPR KO screen in mouse ESCs, searching for mutants that reactivate the expression of Dazl, a robust 2-cell-like marker. Using secondary screens, we identify four mutants that reactivate not just Dazl, but also a broader 2-cell-like signature: the E3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor SPOP, the Zinc Finger transcription factor ZBTB14, MCM3AP, a component of the RNA processing complex TREX-2, and the lysine demethylase KDM5C. Functional experiments show how these factors link to known players of the 2 celllike state. These results extend our knowledge of totipotency, a key phase of organismal life.</p>',
'date' => '2022-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.21203%2Frs.3.rs-1561018%2Fv1',
'doi' => '10.21203/rs.3.rs-1561018/v1',
'modified' => '2022-09-28 09:23:42',
'created' => '2022-09-08 16:32:20',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 27 => array(
'id' => '4394',
'name' => 'Heat stress during grain filling regulates seed germination throughalterations of DNA methylation in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).',
'authors' => 'Sakai Yuki et al.',
'description' => '<p>KEY MESSAGE: Alterations in DNA methylation levels of ROS, GA and ABA related gene promoters cause transcriptional changes upon imbibition to induce seed germination in barley seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling. Environmental changes, especially changes in temperature, during seed development affect germination in several plant species. We have previously shown that heat stress during rice grain filling alters DNA methylation, an epigenetic mark important for gene silencing, regulates transcript levels of phytohormone metabolism genes, and delays seed germination. However, whether this phenomenon is present in other plant species remained to be elucidated. In this study, we compared seeds germination of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) plants grown at 15 °C (control) or 25 °C (heat stress) during grain filling. Heat stress during grain filling significantly promoted seed germination in comparison with the control. The phytohormone gibberellic acid (GA) and reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidases promote seed germination, whereas phytohormone abscisic acid (ABA) suppresses seed germination. We found that in heat-stressed seeds, genes related to ABA biosynthesis (HvNCED1 and 2) were significantly suppressed, whereas genes related to ABA catabolism (HvABA8'OH) and GA biosynthesis (HvHA20ox, HvGA3ox), and NADPH oxidase (HvRboh) genes were significantly upregulated after imbibition. Using MeDIP-qPCR, we showed that the promoters of HvNCED were hyper-methylated, and those of HvABA8'OH1, HvABA8'OH3, HvGA3ox2, and HvRbohF2 were hypo-methylated in heat treated seeds. Taken together, our data suggest that heat stress during grain filling affects DNA methylation of germination-related genes and promotes seed germination in barley.</p>',
'date' => '2022-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35581415',
'doi' => '10.1007/s11103-022-01278-5',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:24:13',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 28 => array(
'id' => '4398',
'name' => 'Hexokinase 2 is a transcriptional target and a positive modulator ofAHR signalling.',
'authors' => 'Watzky M. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) regulates the expression of numerous genes in response to activation by agonists including xenobiotics. Although it is well appreciated that environmental signals and cell intrinsic features may modulate this transcriptional response, how it is mechanistically achieved remains poorly understood. We show that hexokinase 2 (HK2) a metabolic enzyme fuelling cancer cell growth, is a transcriptional target of AHR as well as a modulator of its activity. Expression of HK2 is positively regulated by AHR upon exposure to agonists both in human cells and in mice lung tissues. Conversely, over-expression of HK2 regulates the abundance of many proteins involved in the regulation of AHR signalling and these changes are linked with altered AHR expression levels and transcriptional activity. HK2 expression also shows a negative correlation with AHR promoter methylation in tumours, and these tumours with high HK2 expression and low AHR methylation are associated with a worse overall survival in patients. In sum, our study provides novel insights into how AHR signalling is regulated which may help our understanding of the context-specific effects of this pathway and may have implications in cancer.</p>',
'date' => '2022-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1093%2Fnar%2Fgkac360',
'doi' => '10.1093/nar/gkac360',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:32:40',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 29 => array(
'id' => '4561',
'name' => 'Corticosterone induces discrete epigenetic signatures in the dorsal andventral hippocampus that depend upon sex and genotype: focus on methylatedNr3c1 gene.',
'authors' => 'Caradonna S. G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The genomic effects of circulating glucocorticoids are particularly relevant in cortico-limbic structures, which express a high concentration of steroid hormone receptors. To date, no studies have investigated genomic differences in hippocampal subregions, namely the dorsal (dHPC) and ventral (vHPC) hippocampus, in preclinical models treated with exogenous glucocorticoids. Chronic oral corticosterone (CORT) in mouse is a pharmacological approach that disrupts the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, increases affective behavior, and induces genomic changes after stress in the HPC of wildtype (WT) mice and mice heterozygous for the gene coding for brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met (hMet), a variant associated with genetic susceptibility to stress. Using RNA-sequencing, we investigated the genomic signatures of oral CORT in the dHPC and vHPC of WT and hMet male and female mice, and examined sex and genotype differences in response to oral CORT. Males under CORT showed lower glycemia and increased anxiety- and depression-like behavior compared to females that showed instead opposite affective behavior in response to CORT. Rank-rank-hypergeometric overlap (RRHO) was used to identify genes from a continuous gradient of significancy that were concordant across groups. RRHO showed that CORT-induced differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in WT mice and hMet mice converged in the dHPC of males and females, while in the vHPC, DEGs converged in males and diverged in females. The vHPC showed a higher number of DEGs compared to the dHPC and exhibited sex differences related to glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-binding genes and epigenetic modifiers. Methyl-DNA-immunoprecipitation in the vHPC revealed differential methylation of the exons 1 and 1 of the GR gene (Nr3c1) in hMet females. Together, we report behavioral and endocrinological sex differences in response to CORT, as well as epigenetic signatures that i) differ in the dHPC and vHPC,ii) are distinct in males and females, and iii) implicate differential methylation of Nr3c1 selectively in hMet females.</p>',
'date' => '2022-03-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35296634',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41398-022-01864-7',
'modified' => '2022-11-24 10:03:20',
'created' => '2022-11-24 08:49:52',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 30 => array(
'id' => '4364',
'name' => 'Methionine Metabolism Controls the B-cell EBV Epigenome andViral Latency',
'authors' => 'Guo R. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) subverts host epigenetic pathways to switch between viral latency programs, colonize the B-cell compartment and reactivate. Within memory B-cells, the reservoir for lifelong infection, EBV genomic DNA and histone methylation marks restrict gene expression. But, this epigenetic strategy also enables EBV-infected tumors, including Burkitt lymphomas to evade immune detection. Little is known about host cell metabolic pathways that support EBV epigenome landscapes. We therefore used amino acid restriction, metabolomic and CRISPR approaches to identify that an abundant methionine supply, and interconnecting methionine and folate cycles, maintain Burkitt EBV gene silencing. Methionine restriction, or methionine cycle perturbation, hypomethylated EBV genomes, de-repressed latent membrane protein and lytic gene expression. Methionine metabolism also shaped EBV latency gene regulation required for B-cell immortalization. Dietary methionine restriction altered murine Burkitt xenograft metabolomes and de-repressed EBV immunogens in vivo. These results highlight epigenetic/immunometabolism crosstalk supporting the EBV B-cell lifecycle and suggest therapeutic approaches.</p>',
'date' => '2022-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1101%2F2022.02.24.481783',
'doi' => '10.1101/2022.02.24.481783',
'modified' => '2022-08-04 15:50:37',
'created' => '2022-08-04 14:55:36',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 31 => array(
'id' => '4281',
'name' => 'Integrating SNPs-based genetic risk factor with blood epigenomicresponse of differentially arsenic-exposed rural subjects revealsdisease-associated signaling pathways.',
'authors' => 'Rehman Muhammad Yasir Abdur et al.',
'description' => '<p>Arsenic (As) contamination in groundwater is responsible for numerous adverse health outcomes among millions of people. Epigenetic alterations are among the most widely studied mechanisms of As toxicity. To understand how As exposure alters gene expression through epigenetic modifications, a systematic genome-wide study was designed to address the impact of multiple important single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) related to As exposure on the methylome of drinking water As-exposed rural subjects from Pakistan. Urinary As levels were used to stratify subjects into low, medium and high exposure groups. Genome-wide DNA methylation was investigated using MeDIP in combination with NimbleGen 2.1 M Deluxe Promotor arrays. Transcriptome levels were measured using Agilent 8 × 60 K expression arrays. Genotyping of selected SNPs (As3MT, DNMT1a, ERCC2, EGFR and MTHFR) was measured and an integrated genetic risk factor for each respondent was calculated by assigning a specific value to the measured genotypes based on known risk allele numbers. To select a representative model related to As exposure we compared 9 linear mixed models comprising of model 1 (including the genetic risk factor), model 2 (without the genetic risk factor) and models with individual SNPs incorporated into the methylome data. Pathway analysis was performed using ConsensusPathDB. Model 1 comprising the integrated genetic risk factor disclosed biochemical pathways including muscle contraction, cardio-vascular diseases, ATR signaling, GPCR signaling, methionine metabolism and chromatin modification in association with hypo- and hyper-methylated gene targets. A unique pathway (direct P53 effector) was found associated with the individual DNMT1a polymorphism due to hyper-methylation of CSE1L and TRRAP. Most importantly, we provide here the first evidence of As-associated DNA methylation in relation with gene expression of ATR, ATF7IP, TPM3, UBE2J2. We report the first evidence that integrating SNPs data with methylome data generates a more representative epigenome profile and discloses a better insight in disease risks of As-exposed individuals.</p>',
'date' => '2022-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.envpol.2021.118279',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118279',
'modified' => '2022-05-23 10:04:20',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 32 => array(
'id' => '4404',
'name' => 'Stella regulates the Development of Female Germline Stem Cells byModulating Chromatin Structure and DNA Methylation.',
'authors' => 'Hou Changliang et al.',
'description' => '<p>Female germline stem cells (FGSCs) have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into oocytes. , encoded by a maternal effect gene, plays an important role in oogenesis and early embryonic development. However, its function in FGSCs remains unclear. In this study, we showed that CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of promoted FGSC proliferation and reduced the level of genome-wide DNA methylation of FGSCs. Conversely, overexpression led to the opposite results, and enhanced FGSC differentiation. We also performed an integrative analysis of chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq), high-throughput genome-wide chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C), and use of our published epigenetic data. Results indicated that the binding sites of STELLA and active histones H3K4me3 and H3K27ac were enriched near the TAD boundaries. Hi-C analysis showed that overexpression attenuated the interaction within TADs, and interestingly enhanced the TAD boundary strength in STELLA-associated regions. Taking these findings together, our study not only reveals the role of in regulating DNA methylation and chromatin structure, but also provides a better understanding of FGSC development.</p>',
'date' => '2022-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9066111/',
'doi' => '10.7150/ijbs.69240',
'modified' => '2022-08-11 14:54:29',
'created' => '2022-08-11 12:14:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 33 => array(
'id' => '4302',
'name' => 'Examining age-dependent DNA methylation patterns and gene expression inthe male and female mouse hippocampus.',
'authors' => 'Chinn Carlene A et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a well-characterized epigenetic modification involved in numerous molecular and cellular functions. Methylation patterns have also been associated with aging mechanisms. However, how DNA methylation patterns change within key brain regions involved in memory formation in an age- and sex-specific manner remains unclear. Here, we performed reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) from mouse dorsal hippocampus - which is necessary for the formation and consolidation of specific types of memories - in young and aging mice of both sexes. Overall, our findings demonstrate that methylation levels within the dorsal hippocampus are divergent between sexes during aging in genomic features correlating to mRNA functionality, transcription factor binding sites, and gene regulatory elements. These results define age-related changes in the methylome across genomic features and build a foundation for investigating potential target genes regulated by DNA methylation in an age- and sex-specific manner.</p>',
'date' => '2021-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1016%2Fj.neurobiolaging.2021.08.006',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.08.006',
'modified' => '2022-05-30 09:54:05',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 34 => array(
'id' => '4100',
'name' => 'Therapy-induced DNA methylation inactivates MCT1 and renders tumor cells vulnerable to MCT4 inhibition',
'authors' => 'Catherine Vander Linden, Cyril Corbet, Estelle Bastien, Ruben Martherus, Céline Guilbaud, Laurenne Petit, Loris Wauthier, Axelle Loriot, Charles De Smet, Olivier Feron',
'description' => '<p><span>Metabolic plasticity in cancer cells makes use of metabolism-targeting agents very challenging. Drug-induced metabolic rewiring may, however, uncover vulnerabilities that can be exploited. We report that resistance to glycolysis inhibitor 3-bromopyruvate (3-BrPA) arises from DNA methylation in treated cancer cells and subsequent silencing of the monocarboxylate transporter MCT1. We observe that, unexpectedly, 3-BrPA-resistant cancer cells mostly rely on glycolysis to sustain their growth, with MCT4 as an essential player to support lactate flux. This shift makes cancer cells particularly suited to adapt to hypoxic conditions and resist OXPHOS inhibitors and anti-proliferative chemotherapy. In contrast, blockade of MCT4 activity in 3-BrPA-exposed cancer cells with diclofenac or genetic knockout, inhibits growth of derived spheroids and tumors in mice. This study supports a potential mode of collateral lethality according to which metabolic adaptation of tumor cells to a first-line therapy makes them more responsive to a second-line treatment.</span></p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.cell.com/cell-reports/fulltext/S2211-1247(21)00551-9#%20',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109202',
'modified' => '2021-06-03 16:04:34',
'created' => '2021-06-03 14:16:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 35 => array(
'id' => '4330',
'name' => 'Epigenetic Plasticity Enables CNS-Trafficking of EBV-infectedB Lymphocytes',
'authors' => 'Soldan S. S. et al. ',
'description' => '<p>Subpopulations of B-lymphocytes traffic to different sites and organs to provide diverse and tissue-specific functions. Here, we provide evidence that epigenetic differences confer a neuroinvasive phenotype. An EBV+ B cell lymphoma cell line (M14) with low frequency trafficking to the CNS was neuroadapted to generate a highly neuroinvasive B-cell population (MUN14). MUN14 B cells efficiently infiltrated the CNS within one week and produced neurological pathologies. We compared the gene expression profiles of viral and cellular genes using RNA-Seq and identified one viral (EBNA1) and several cellular gene candidates, including secreted phosphoprotein 1/osteopontin (SPP1/OPN), neuron navigator 3 (NAV3), CXCR4, and germinal center-associated signaling and motility protein (GCSAM) that were selectively upregulated in MUN14. ATAC-Seq and ChIP-qPCR revealed that these gene expression changes correlated with epigenetic changes at gene regulatory elements. The neuroinvasive phenotype could be attenuated with a neutralizing antibody to OPN, confirming the functional role of this protein in trafficking EBV+ B cells to the CNS. These studies indicate that B-cell trafficking to the CNS can be acquired by epigenetic adaptations and provide a new model to study B-cell neuroinvasion associated CNS lymphoma and autoimmune disease of the CNS, including multiple sclerosis (MS).</p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34106998',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.ppat.1009618',
'modified' => '2022-08-03 16:11:53',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 36 => array(
'id' => '4354',
'name' => 'Dnmt1 has de novo activity targeted to transposable elements',
'authors' => 'Haggerty C. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation plays a critical role during development, particularly in repressing retrotransposons. The mammalian methylation landscape is dependent on the combined activities of the canonical maintenance enzyme Dnmt1 and the de novo Dnmts, 3a and 3b. Here, we demonstrate that Dnmt1 displays de novo methylation activity in vitro and in vivo with specific retrotransposon targeting. We used whole-genome bisulfite and long-read Nanopore sequencing in genetically engineered methylation-depleted mouse embryonic stem cells to provide an in-depth assessment and quantification of this activity. Utilizing additional knockout lines and molecular characterization, we show that the de novo methylation activity of Dnmt1 depends on Uhrf1, and its genomic recruitment overlaps with regions that enrich for Uhrf1, Trim28 and H3K9 trimethylation. Our data demonstrate that Dnmt1 can catalyze DNA methylation in both a de novo and maintenance context, especially at retrotransposons, where this mechanism may provide additional stability for long-term repression and epigenetic propagation throughout development.</p>',
'date' => '2021-06-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34140676',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41594-021-00603-8',
'modified' => '2022-08-03 16:55:11',
'created' => '2022-05-19 10:41:50',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 37 => array(
'id' => '4135',
'name' => 'Alterations of DNA Methylation Caused by Cold Plasma Treatment Restore Delayed Germination of Heat-Stressed Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seeds',
'authors' => 'Suriyasak, C. et al. ',
'description' => '<p>In rice (Oryza sativa L.), seeds exposed to heat stress during grain filling exhibit delayed germination because of DNA methylation levels at promoters of abscisic acid (ABA, a germination-inhibiting hormone) catabolism genes and α-amylase (starchhydrolyzing enzyme) genes, affecting their expression levels. Cold atmospheric plasma is known as an innovative and sustainable energy that has positive effects on the growth and development of many plant species. We, therefore, treated seeds that matured under heat stress with cold plasma and found that subsequent germination was significantly restored; genes involved in ABA biosynthesis (OsNCED2 and OsNCED5) were downregulated, whereas genes involved in ABA catabolism (OsABA8′OH1 and OsABA8′OH3) and α-amylase genes (OsAmy1A, OsAmy1C, OsAmy3B, and OsAmy3E) were upregulated. Cold plasma treatment caused significant hypermethylation of the OsNCED5 promoter and hypomethylation of OsAmy1C and OsAmy3E promoters, which matched their expression patterns. We suggest that cold plasma treatment can significantly improve the germination of rice seeds affected by heat stress by affecting epigenetic regulation.</p>',
'date' => '2021-02-01',
'pmid' => 'https://doi.org/10.1021%2Facsagscitech.0c00070',
'doi' => '10.1021/acsagscitech.0c00070',
'modified' => '2021-12-10 17:15:10',
'created' => '2021-12-06 15:53:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 38 => array(
'id' => '4057',
'name' => 'Prenatal Stress Leads to the Altered Maturation of Corticostriatal SynapticPlasticity and Related Behavioral Impairments Through EpigeneticModifications of Dopamine D2 Receptor in Mice.',
'authors' => 'Li, Yingchun and Rong, Jing and Zhong, Haiquan and Liang, Min and Zhu,Chunting and Chang, Fei and Zhou, Rong',
'description' => '<p>Prenatal stress (PRS) had a long-term adverse effect on motor behaviors. Corticostriatal synaptic plasticity, a cellular basis for motor controlling, has been proven to participate in the pathogenesis of many behavior disorders. Based on the reports about the involvement of epigenetic DNA alterations in PRS-induced long-term effects, this research investigated the influence of PRS on the development and maturation of corticostriatal synaptic plasticity and related behaviors and explored the underlying epigenetic mechanism. Subjects were male offspring of dams that were exposed to stress three times per day from the 10th day of pregnancy until delivery. The development and maturation of plasticity at corticostriatal synapses, dopamine signaling, behavioral habituation, and DNA methylation were examined and analyzed. Control mice expressed long-term potentiation (LTP) at corticostriatal synapses during postnatal days (PD) 12-14 and produced long-term depression (LTD) during PD 20-60. However, PRS mice exhibited sustained LTP during PD 12-60. The treatment with dopamine 2 receptor (D2R) agonist quinpirole recovered striatal LTD and improved the impaired behavioral habituation in PD 45 adult PRS mice. Additionally, adult PRS mice showed reduced D2R, excess DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), increased binding of DNMT1 to D2R promoter, and hypermethylation at D2R promoter in the striatum. The DNMT1 inhibitor 5-aza-deoxycytidine restored striatal synaptic plasticity and improved behavioral habituation in adult PRS mice via D2R-mediated dopamine signaling. DNMT1-associated D2R hypermethylation is responsible for altering the maturation of plasticity at corticostriatal synapses and impairing the behavioral habituation in PRS mice.</p>',
'date' => '2021-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32935231',
'doi' => '10.1007/s12035-020-02127-6',
'modified' => '2021-02-19 17:23:03',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 39 => array(
'id' => '4200',
'name' => 'Comparative genome-wide methylation analysis of longissimus dorsi musclesin Yorkshire and Wannanhua pigs.',
'authors' => 'Li, X-J et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation was one of the earliest discovered epigenetic modifications in vertebrates, and is an important epigenetic mechanism involved in the expression of genes in many biological processes, including muscle growth and development. Its effects on economically important traits are evidenced in reported differences in meat quality traits between Chinese indigenous pig breeds (Wannanhua pig) and Western commercial pig breeds (Yorkshire pig), and this presents a unique model for analyzing the effects of DNA methylation on these traits. In the present study, a whole genome DNA methylation analysis was performed on the two breeds using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation. GO functional enrichment and pathway enrichment analyses identified differentially methylated genes primarily associated with fatty acid metabolism, biological processes of muscle development and signaling pathways related to muscle development and pork quality. Differentially methylated genes were verified by sodium pyrosequencing, and the results were consistent with the sequencing results. The results of the integrative analysis between DNA methylation and gene expression revealed that the DNA methylation levels showed a significantly negative correlation with gene expression levels around the transcription start site of genes. In total, 41 genes were both differentially expressed and methylated; these genes were related to fat metabolism, lipid metabolism and skeletal muscle development. This study could help further explore the molecular mechanisms and phenotypic differences in pig growth and development among different breeds.</p>',
'date' => '2020-12-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33301219',
'doi' => '10.1111/age.13029',
'modified' => '2022-01-06 14:43:32',
'created' => '2021-12-06 15:53:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 40 => array(
'id' => '4041',
'name' => 'Mechanism of delayed seed germination caused by high temperature duringgrain filling in rice (Oryza sativa L.).',
'authors' => 'Suriyasak, Chetphilin and Oyama, Yui and Ishida, Toshiaki and Mashiguchi,Kiyoshi and Yamaguchi, Shinjiro and Hamaoka, Norimitsu and Iwaya-Inoue,Mari and Ishibashi, Yushi',
'description' => '<p>High temperature during grain filling considerably reduces yield and quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.); however, how high temperature affects seed germination of the next generation is not yet well understood. Here, we report that seeds from plants exposed to high temperature during the grain filling stage germinated significantly later than seeds from unstressed plants. This delay remained even after dormancy release treatments, suggesting that it was not due to primary seed dormancy determined during grain filling. In imbibed embryos of heat-stressed seeds, expression of abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis genes (OsNCEDs) was higher than in those of control seeds, whereas that of ABA catabolism genes (OsABA8'OHs) was lower. In the aleurone layer, despite no change in GA signaling as evidenced by no effect of heat stress on OsGAMYB gene expression, the transcripts of α-amylase genes OsAmy1C, OsAmy3B, and OsAmy3E were significantly down-regulated in heat-stressed seeds in comparison with controls. Changes in promoter methylation levels were consistent with transcriptional changes of ABA catabolism-related and α-amylase genes. These data suggest that high temperature during grain filling results in DNA methylation of ABA catabolism-related and α-amylase gene promoters, delaying germination of heat-stressed seeds.</p>',
'date' => '2020-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33060675',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-020-74281-9',
'modified' => '2021-02-19 12:09:29',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 41 => array(
'id' => '4094',
'name' => 'Network integration and modelling of dynamic drug responses at multi-omicslevels.',
'authors' => 'Selevsek, Nathalie and Caiment, Florian and Nudischer, Ramona and Gmuender,Hans and Agarkova, Irina and Atkinson, Francis L and Bachmann, Ivo andBaier, Vanessa and Barel, Gal and Bauer, Chris and Boerno, Stefan and Bosc,Nicolas and Clayton, Olivia and ',
'description' => '<p>Uncovering cellular responses from heterogeneous genomic data is crucial for molecular medicine in particular for drug safety. This can be realized by integrating the molecular activities in networks of interacting proteins. As proof-of-concept we challenge network modeling with time-resolved proteome, transcriptome and methylome measurements in iPSC-derived human 3D cardiac microtissues to elucidate adverse mechanisms of anthracycline cardiotoxicity measured with four different drugs (doxorubicin, epirubicin, idarubicin and daunorubicin). Dynamic molecular analysis at in vivo drug exposure levels reveal a network of 175 disease-associated proteins and identify common modules of anthracycline cardiotoxicity in vitro, related to mitochondrial and sarcomere function as well as remodeling of extracellular matrix. These in vitro-identified modules are transferable and are evaluated with biopsies of cardiomyopathy patients. This to our knowledge most comprehensive study on anthracycline cardiotoxicity demonstrates a reproducible workflow for molecular medicine and serves as a template for detecting adverse drug responses from complex omics data.</p>',
'date' => '2020-10-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33060801',
'doi' => '10.1038/s42003-020-01302-8',
'modified' => '2021-03-17 17:16:56',
'created' => '2021-02-18 10:21:53',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 42 => array(
'id' => '4009',
'name' => 'Frataxin gene editing rescues Friedreich's ataxia pathology in dorsal rootganglia organoid-derived sensory neurons.',
'authors' => 'Mazzara, PG and Muggeo, S and Luoni, M and Massimino, L and Zaghi, M andValverde, PT and Brusco, S and Marzi, MJ and Palma, C and Colasante, Gand Iannielli, A and Paulis, M and Cordiglieri, C and Giannelli, SG andPodini, P and Gellera, C and Ta',
'description' => '<p>Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is an autosomal-recessive neurodegenerative and cardiac disorder which occurs when transcription of the FXN gene is silenced due to an excessive expansion of GAA repeats into its first intron. Herein, we generate dorsal root ganglia organoids (DRG organoids) by in vitro differentiation of human iPSCs. Bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing show that DRG organoids present a transcriptional signature similar to native DRGs and display the main peripheral sensory neuronal and glial cell subtypes. Furthermore, when co-cultured with human intrafusal muscle fibers, DRG organoid sensory neurons contact their peripheral targets and reconstitute the muscle spindle proprioceptive receptors. FRDA DRG organoids model some molecular and cellular deficits of the disease that are rescued when the entire FXN intron 1 is removed, and not with the excision of the expanded GAA tract. These results strongly suggest that removal of the repressed chromatin flanking the GAA tract might contribute to rescue FXN total expression and fully revert the pathological hallmarks of FRDA DRG neurons.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-21',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32826895',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41467-020-17954-3',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:12:57',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 43 => array(
'id' => '4017',
'name' => 'Integrated analysis of DNA methylation profile of HLA-G gene andimaging in coronary heart disease: Pilot study.',
'authors' => 'Schiano, C and Benincasa, G and Infante, T and Franzese, M and Castaldo, Rand Fiorito, C and Mansueto, G and Grimaldi, V and Della, Valle G andFatone, G and Soricelli, A and Nicoletti, GF and Ruocco, A and Mauro, Cand Salvatore, M and Napoli, C',
'description' => '<p>AIMS: Immune endothelial inflammation, underlying coronary heart disease (CHD) related phenotypes, could provide new insight into the pathobiology of the disease. We investigated DNA methylation level of the unique CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients and evaluated the correlation with cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) features. METHODS: Thirty-two patients that underwent CCTA for suspected CHD were enrolled for this study. Obstructive CHD group included fourteen patients, in which there was a stenosis greater than or equal to 50\% in one or more of the major coronary arteries detected; whereas subjects with Calcium (Ca) Score = 0, uninjured coronaries and with no obstructive CHD (no critical stenosis, NCS) were considered as control subjects (n = 18). For both groups, DNA methylation profile of the whole 5'UTR-CpG island of HLA-G was measured. The plasma soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) levels were detected in all subjects by specific ELISA assay. Statistical analysis was performed using R software. RESULTS: For the first time, our study reported that 1) a significant hypomethylation characterized three specific fragments (B, C and F) of the 5'UTR-CpG island (p = 0.05) of HLA-G gene in CHD patients compared to control group; 2) the hypomethylation level of one specific fragment of 161bp (+616/+777) positively correlated with coronary Ca score, a relevant parameter of CCTA (p<0.05) between two groups evaluated and was predictive for disease severity. CONCLUSIONS: Reduced levels of circulating HLA-G molecules could derive from epigenetic marks. Epigenetics phenomena induce hypomethylation of specific regions into 5'UTR-CpG island of HLA-G gene in CHD patients with obstructive non critical stenosis vs coronary stenosis individuals.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-13',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32790754',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0236951',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:37:03',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 44 => array(
'id' => '4021',
'name' => 'Comparative DNA methylome analysis of estrus ewes reveals the complexregulatory pathways of sheep fecundity.',
'authors' => 'Miao, X and Luo, Q and Xie, L and Zhao, H and Qin, X',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND/AIMS: Sheep are important livestock with variant ovulation rate and fertility. Dorset sheep is a typical breed with low prolificacy, whereas Small Tail Han sheep with FecB mutation (HanBB) have hyperprolificacy. Our previous studies have revealed the gene expression difference between the ovaries from Dorset and HanBB sheep contributes to the difference of fecundity, however, what leads to these gene expression difference remains unclear. DNA methylation, an important epigenetic process, plays a crucial role in gene expression regulation. METHODS: In the present study, we constructed a methylated DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) strategy to investigate the differentially methylated genes between the Dorset and HanBB ovaries. RESULTS: Our findings suggest the genes involved in immune response, branched-chain amino acid metabolism, cell growth and cell junction were differentially methylated in or around the gene body regions. CONCLUSIONS: These findings provide prospective insights on the epigenetic basis of sheep fecundity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32753034',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12958-020-00633-9',
'modified' => '2020-12-16 17:45:28',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 45 => array(
'id' => '4028',
'name' => 'Methylation in pericytes after acute injury promotes chronic kidneydisease.',
'authors' => 'Chou, YH and Pan, SY and Shao, YH and Shih, HM and Wei, SY andLai, CF and Chiang, WC and Schrimpf, C and Yang, KC and Lai, LC andChen, YM and Chu, TS and Lin, SL',
'description' => '<p>The origin and fate of renal myofibroblasts is not clear after acute kidney injury (AKI). Here, we demonstrate that myofibroblasts were activated from quiescent pericytes (qPericytes) and the cell numbers increased after ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced AKI (IRI-AKI). Myofibroblasts underwent apoptosis during renal recovery but one-fifth of them survived in the recovered kidneys on day 28 after IRI-AKI and their cell numbers increased again after day 56. Microarray data showed the distinctive gene expression patterns of qPericytes, activated pericytes (aPericytes, myofibroblasts), and inactivated pericytes (iPericytes) isolated from kidneys before, on day 7, and on day 28 after IRI-AKI. Hypermethylation of the Acta2 repressor Ybx2 during IRI-AKI resulted in epigenetic modification of iPericytes to promote the transition to chronic kidney disease (CKD) and aggravated fibrogenesis induced by a second AKI induced by adenine. Mechanistically, transforming growth factor-β1 decreased the binding of YBX2 to the promoter of Acta2 and induced Ybx2 hypermethylation, thereby increasing α-smooth muscle actin expression in aPericytes. Demethylation by 5-azacytidine recovered the microvascular stabilizing function of aPericytes, reversed the profibrotic property of iPericytes, prevented AKI-CKD transition, and attenuated fibrogenesis induced by a second adenine-AKI. In conclusion, intervention to erase hypermethylation of pericytes after AKI provides a strategy to stop the transition to CKD.</p>',
'date' => '2020-08-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32749240',
'doi' => '10.1172/JCI135773.',
'modified' => '2020-12-18 13:25:55',
'created' => '2020-10-12 14:54:59',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 46 => array(
'id' => '3998',
'name' => 'Integrated epigenetic biomarkers in circulating cell-free DNA as a robust classifier for pancreatic cancer.',
'authors' => 'Cao F, Wei A, Hu X, He Y, Zhang J, Xia L, Tu K, Yuan J, Guo Z, Liu H, Xie D, Li A',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: The high lethal rate of pancreatic cancer is partly due to a lack of efficient biomarkers for screening and early diagnosis. We attempted to develop effective and noninvasive methods using 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) markers from circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for the detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). RESULTS: A 24-feature 5mC model that can accurately discriminate PDAC from healthy controls (area under the curve (AUC) = 0.977, sensitivity = 0.824, specificity = 1) and a 5hmC prediction model with 27 features demonstrated excellent detection power in two distinct validation sets (AUC = 0.992 and 0.960, sensitivity = 0.786 and 0.857, specificity = 1 and 0.993). The 51-feature model combining 5mC and 5hmC markers outperformed both of the individual models, with an AUC of 0.997 (sensitivity = 0.938, specificity = 0.955) and particularly an improvement in the prediction sensitivity of PDAC. In addition, the weighted diagnosis score (wd-score) calculated with the 5hmC model can distinguish stage I patients from stage II-IV patients. CONCLUSIONS: Both 5mC and 5hmC biomarkers in cfDNA are effective in PDAC detection, and the 5mC-5hmC integrated model significantly improve the detection sensitivity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-07-23',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32703318',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13148-020-00898-2',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 14:43:06',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 47 => array(
'id' => '3985',
'name' => 'Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Nuzzo PV, Berchuck JE, Korthauer K, Spisak S, Nassar AH, Abou Alaiwi S, Chakravarthy A, Shen SY, Bakouny Z, Boccardo F, Steinharter J, Bouchard G, Curran CR, Pan W, Baca SC, Seo JH, Lee GM, Michaelson MD, Chang SL, Waikar SS, Sonpavde G, Irizarry RA, Pome',
'description' => '<p>Improving early cancer detection has the potential to substantially reduce cancer-related mortality. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) is a highly sensitive assay capable of detecting early-stage tumors. We report accurate classification of patients across all stages of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in plasma (area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.99) and demonstrate the validity of this assay to identify patients with RCC using urine cell-free DNA (cfDNA; AUROC of 0.86).</p>',
'date' => '2020-06-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32572266',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41591-020-0933-1',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 15:13:49',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 48 => array(
'id' => '3984',
'name' => 'Detection and discrimination of intracranial tumors using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Nassiri F, Chakravarthy A, Feng S, Shen SY, Nejad R, Zuccato JA, Voisin MR, Patil V, Horbinski C, Aldape K, Zadeh G, De Carvalho DD',
'description' => '<p>Definitive diagnosis of intracranial tumors relies on tissue specimens obtained by invasive surgery. Noninvasive diagnostic approaches provide an opportunity to avoid surgery and mitigate unnecessary risk to patients. In the present study, we show that DNA-methylation profiles from plasma reveal highly specific signatures to detect and accurately discriminate common primary intracranial tumors that share cell-of-origin lineages and can be challenging to distinguish using standard-of-care imaging.</p>',
'date' => '2020-06-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32572265',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41591-020-0932-2',
'modified' => '2020-09-01 15:14:45',
'created' => '2020-08-21 16:41:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 49 => array(
'id' => '3942',
'name' => 'DNA methylation enzymes and PRC1 restrict B-cell Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein expression.',
'authors' => 'Guo R, Zhang Y, Teng M, Jiang C, Schineller M, Zhao B, Doench JG, O'Reilly RJ, Cesarman E, Giulino-Roth L, Gewurz BE',
'description' => '<p>To accomplish the remarkable task of lifelong infection, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) switches between four viral genome latency and lytic programmes to navigate the B-cell compartment and evade immune responses. The transforming programme, consisting of highly immunogenic EBV nuclear antigen (EBNA) and latent membrane proteins (LMPs), is expressed in newly infected B lymphocytes and in post-transplant lymphomas. On memory cell differentiation and in most EBV-associated Burkitt's lymphomas, all but one viral antigen are repressed for immunoevasion. To gain insights into the epigenetic mechanisms that restrict immunogenic oncoprotein expression, a genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screen was performed in EBV and Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Here, we show that the ubiquitin ligase ubiquitin-like PHD and RING finger domain-containing protein 1 (UHRF1) and its DNA methyltransferase partner DNA methyltransferase I (DNMT1) are critical for the restriction of EBNA and LMP expression. All UHRF1 reader and writer domains were necessary for silencing and DNMT3B was identified as an upstream viral genome CpG methylation initiator. Polycomb repressive complex I exerted a further layer of control over LMP expression, suggesting a second mechanism for latency programme switching. UHRF1, DNMT1 and DNMT3B are upregulated in germinal centre B cells, the Burkitt's lymphoma cell of origin, providing a molecular link between B-cell state and the EBV latency programme. These results suggest rational therapeutic targets to manipulate EBV oncoprotein expression.</p>',
'date' => '2020-05-18',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32424339',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41564-020-0724-y',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:24:57',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 50 => array(
'id' => '3926',
'name' => 'TET-Mediated Hypermethylation Primes SDH-Deficient Cells for HIF2α-Driven Mesenchymal Transition.',
'authors' => 'Morin A, Goncalves J, Moog S, Castro-Vega LJ, Job S, Buffet A, Fontenille MJ, Woszczyk J, Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Letouzé E, Favier J',
'description' => '<p>Loss-of-function mutations in the SDHB subunit of succinate dehydrogenase predispose patients to aggressive tumors characterized by pseudohypoxic and hypermethylator phenotypes. The mechanisms leading to DNA hypermethylation and its contribution to SDH-deficient cancers remain undemonstrated. We examine the genome-wide distribution of 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and their correlation with RNA expression in SDHB-deficient tumors and murine Sdhb cells. We report that DNA hypermethylation results from TET inhibition. Although it preferentially affects PRC2 targets and known developmental genes, PRC2 activity does not contribute to the DNA hypermethylator phenotype. We also prove, in vitro and in vivo, that TET silencing, although recapitulating the methylation profile of Sdhb cells, is not sufficient to drive their EMT-like phenotype, which requires additional HIF2α activation. Altogether, our findings reveal synergistic roles of TET repression and pseudohypoxia in the acquisition of metastatic traits, providing a rationale for targeting HIF2α and DNA methylation in SDH-associated malignancies.</p>',
'date' => '2020-03-31',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32234487',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.022',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:50:11',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 51 => array(
'id' => '3920',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Mantle Edge and Mantle Central from Pearl Oyster Pinctada fucata martensii.',
'authors' => 'Zhang J, Luo S, Gu Z, Deng Y, Jiao Y',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a type of epigenetic modification that alters gene expression without changing the DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. In this study, we identified six DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) genes and two methyl-CpG binding domain protein2 (MBD2) gene from Pinctada fucata martensii. We also analyzed the genome-wide DNA methylation levels of mantle edge (ME) and mantle central (MC) from P. f. martensii via methylated immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-Seq). Results revealed that both ME and MC had 122 million reads, and had 58,702 and 55,721 peaks, respectively. The obtained methylation patterns of gene elements and repeats showed that the methylation of the protein-coding genes, particularly intron and coding exons (CDSs), was more frequent than that of other genomic elements in the pearl oyster genome. We combined the methylation data with the RNA-seq data of the ME and MC of P. f. martensii and found that promoter, CDS, and intron methylation levels were positively correlated with gene expression levels except the highest gene expression level. We also identified 313 differential methylation genes (DMGs) and annotated 212 of them. These DMGs were significantly enriched in 30 pathways, such as amino acid and protein metabolism, energy metabolism, terpenoid synthesis, and immune-related pathways. This study comprehensively analyzed the methylomes of biomineralization-related tissues and helped enhance our understanding of the regulatory mechanism underlying shell formation.</p>',
'date' => '2020-03-06',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/32140888',
'doi' => '10.1007/s10126-020-09957-4',
'modified' => '2020-08-17 10:58:42',
'created' => '2020-08-10 12:12:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 52 => array(
'id' => '3859',
'name' => 'Preterm birth is associated with epigenetic programming of transgenerational hypertension in mice.',
'authors' => 'Dumeige L, Nehlich M, Viengchareun S, Perrot J, Pussard E, Lombès M, Martinerie L',
'description' => '<p>Renal and cardiovascular complications of prematurity are well established, notably the development of hypertension in adulthood. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Our objective was to investigate the impact of prematurity on the ontogenesis of renal corticosteroid pathways, to evaluate its implication in perinatal renal complications and in the emergence of hypertension in adulthood. Swiss CD1 pregnant mice were injected with lipopolysaccharides at 18 days of gestation (E18) to induce prematurity at E18.5. Pups were sacrificed at birth, 7 days and 6 months of life. Second (F2) and third (F3) generations, established by mating prematurely born adult females with wild-type males, were also analyzed. Former preterm males developed hypertension at M6 (P < 0.0001). We found robust activation of renal corticosteroid target gene transcription at birth in preterm mice (αENaC (+45%), Gilz (+85%)), independent of any change in mineralocorticoid or glucocorticoid receptor expression. The offspring of the preterm group displayed increased blood pressure in F2 and F3, associated with increased renal Gilz mRNA expression, despite similar MR or GR expression and plasma corticosteroid levels measured by LC-MS/MS. Gilz promoter methylation measured by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-qPCR was reduced with a negative correlation between methylation and expression (P = 0.0106). Our study demonstrates prematurity-related alterations in renal corticosteroid signaling pathways, with transgenerational inheritance of blood pressure dysregulation and epigenetic Gilz regulation up to the third generation. This study provides a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms involved in essential hypertension, which could partly be due to perinatal epigenetic programming from previous generations.</p>',
'date' => '2020-01-24',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31974504',
'doi' => '10.1038/s12276-020-0373-5',
'modified' => '2020-03-20 17:55:50',
'created' => '2020-03-13 13:45:54',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 53 => array(
'id' => '3855',
'name' => 'Alteration in global DNA methylation status following preconditioning injury influences axon growth competence of the sensory neurons.',
'authors' => 'Shin HY, Kim K, Kwon MJ, Oh YJ, Kim EH, Kim HS, Hong CP, Lee JH, Lee K, Kim BG',
'description' => '<p>Preconditioning peripheral nerve injury primes the sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) to acquire axon regeneration competence. Transcription of a large set of regeneration-associated-genes (RAGs) contributes to the enhanced intrinsic axonal regeneration capacity. However, the mechanism underlying the coordinated upregulation of RAGs orchestrated by preconditioning injury is unclear. We sought to determine potential influence of DNA methylation change on transcriptional activation of RAGs in the L4-L6 DRGs following sciatic nerve injury. Genome-wide sequencing revealed that about 20% of the methylated DNA fragments were differentially methylated, and >3000 genes contained differentially methylated regions. Not only demethylation but also increased methylation was observed to a similar extent. The change in the global DNA methylation did not correlate with the gene expression level of most genes, including the well-documented RAGs. However, pharmacological inhibition or activation of DNA methylation markedly attenuated the axon growth capacity of the preconditioned DRG neurons. Pharmacological perturbation of DNA methylation resulted in simultaneous downregulation of many highly overlapping non-transcription factor RAGs, which was accompanied by a concurrent, robust upregulation of SOCS3 and Serpine1. Overexpression of SOCS3 and Serpine1 in the DRG neurons overrode injury-induced axon growth competence, corroborating their roles as the negative regulators of axon regeneration. We conclude that the injury-induced global alteration of DNA methylome strongly influences the axon growth competence in preconditioned DRG neurons. Our results also suggest a possibility that perturbing DNA methylome changes might lead to the upregulation of negative regulator RAGs thereby attenuating axon growth capacity.</p>',
'date' => '2020-01-08',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31926166',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113177',
'modified' => '2020-03-20 17:59:09',
'created' => '2020-03-13 13:45:54',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 54 => array(
'id' => '3814',
'name' => 'Lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced changes in rodent neural progenitors and rescues cognition.',
'authors' => 'Zanni G, Goto S, Fragopoulou AF, Gaudenzi G, Naidoo V, Di Martino E, Levy G, Dominguez CA, Dethlefsen O, Cedazo-Minguez A, Merino-Serrais P, Stamatakis A, Hermanson O, Blomgren K',
'description' => '<p>Cranial radiotherapy in children has detrimental effects on cognition, mood, and social competence in young cancer survivors. Treatments harnessing hippocampal neurogenesis are currently of great relevance in this context. Lithium, a well-known mood stabilizer, has both neuroprotective, pro-neurogenic as well as antitumor effects, and in the current study we introduced lithium treatment 4 weeks after irradiation. Female mice received a single 4 Gy whole-brain radiation dose on postnatal day (PND) 21 and were randomized to 0.24% Li2CO chow or normal chow from PND 49 to 77. Hippocampal neurogenesis was assessed on PND 77, 91, and 105. We found that lithium treatment had a pro-proliferative effect on neural progenitors, but neuronal integration occurred only after it was discontinued. Also, the treatment ameliorated deficits in spatial learning and memory retention observed in irradiated mice. Gene expression profiling and DNA methylation analysis identified two novel factors related to the observed effects, Tppp, associated with microtubule stabilization, and GAD2/65, associated with neuronal signaling. Our results show that lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced loss of hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive impairment even when introduced long after the injury. We propose that lithium treatment should be intermittent in order to first make neural progenitors proliferate and then, upon discontinuation, allow them to differentiate. Our findings suggest that pharmacological treatment of cognitive so-called late effects in childhood cancer survivors is possible.</p>',
'date' => '2019-11-14',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31723242',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41380-019-0584-0',
'modified' => '2019-12-05 10:58:44',
'created' => '2019-12-02 15:25:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 55 => array(
'id' => '3773',
'name' => 'Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA.',
'authors' => 'Shen SY, Burgener JM, Bratman SV, De Carvalho DD',
'description' => '<p>Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) comprises small DNA fragments derived from normal and tumor tissue that are released into the bloodstream. Recently, methylation profiling of cfDNA as a liquid biopsy tool has been gaining prominence due to the presence of tissue-specific markers in cfDNA. We have previously reported cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) as a sensitive, low-input, cost-efficient and bisulfite-free approach to profiling DNA methylomes of plasma cfDNA. cfMeDIP-seq is an extension of a previously published MeDIP-seq protocol and is adapted to allow for methylome profiling of samples with low input (ranging from 1 to 10 ng) of DNA, which is enabled by the addition of 'filler DNA' before immunoprecipitation. This protocol is not limited to plasma cfDNA; it can also be applied to other samples that are naturally sheared and at low availability (e.g., urinary cfDNA and cerebrospinal fluid cfDNA), and is potentially applicable to other applications beyond cancer detection, including prenatal diagnostics, cardiology and monitoring of immune response. The protocol presented here should enable any standard molecular laboratory to generate cfMeDIP-seq libraries from plasma cfDNA in ~3-4 d.</p>',
'date' => '2019-08-30',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31471598',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41596-019-0202-2',
'modified' => '2019-10-02 17:07:45',
'created' => '2019-10-02 16:16:55',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 56 => array(
'id' => '3761',
'name' => 'Single-base methylome profiling of the giant kelp Saccharina japonica reveals significant differences in DNA methylation to microalgae and plants.',
'authors' => 'Fan X, Han W, Teng L, Jiang P, Zhang X, Xu D, Li C, Pellegrini M, Wu C, Wang Y, Kaczurowski MJS, Lin X, Tirichine L, Mock T, Ye N',
'description' => '<p>Brown algae have convergently evolved plant-like body plans and reproductive cycles, which in plants are controlled by differential DNA methylation. Here we provide the first single-base methylome profiles of haploid gametophytes and diploid sporophytes of a multicellular alga. Although only c. 1.4% of cytosines in Saccharina japonica were methylated mainly at CHH sites and characterised by 5-methylcytosine (5mC), there were significant differences between life-cycle stages. DNA methyltransferase 2 (DNMT2), known to efficiently catalyze tRNA methylation, is assumed to methylate the genome of S. japonica in the structural context of tRNAs as the genome does not encode any other DNA methyltransferases. Circular and long non-coding RNA genes were the most strongly methylated regulatory elements in S. japonica. Differential expression of genes was negatively correlated with DNA methylation with the highest methylation levels measured in both haploid gametophytes. Hypomethylated and highly expressed genes in diploid sporophytes included genes involved in morphogenesis and halogen metabolism. Our data give evidence that cytosine methylation, although occurring at a low level, is significantly contributing to the formation of different life-cycle stages, tissue differentiation, and metabolism in brown algae.</p>',
'date' => '2019-08-16',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31419316',
'doi' => '10.1111/nph.16125',
'modified' => '2019-10-03 10:04:08',
'created' => '2019-10-02 16:16:55',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 57 => array(
'id' => '3720',
'name' => 'Genome-wide methylation in alcohol use disorder subjects: implications for an epigenetic regulation of the cortico-limbic glucocorticoid receptors (NR3C1).',
'authors' => 'Gatta E, Grayson DR, Auta J, Saudagar V, Dong E, Chen Y, Krishnan HR, Drnevich J, Pandey SC, Guidotti A',
'description' => '<p>Environmental factors, including substance abuse and stress, cause long-lasting changes in the regulation of gene expression in the brain via epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation. We examined genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the prefrontal cortex (PFC, BA10) of 25 pairs of control and individuals with alcohol use disorder (AUD), using the Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip. We identified 5254 differentially methylated CpGs (p < 0.005). Bioinformatic analyses highlighted biological processes containing genes related to stress adaptation, including the glucocorticoid receptor (encoded by NR3C1). Considering that alcohol is a stressor, we focused our attention on differentially methylated regions of the NR3C1 gene and validated the differential methylation of several genes in the NR3C1 network. Chronic alcohol drinking results in a significant increased methylation of the NR3C1 exon variant 1, with a particular increase in the levels of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine over 5-methylcytosine. These changes in DNA methylation were associated with reduced NR3C1 mRNA and protein expression levels in PFC, as well as other cortico-limbic regions of AUD subjects when compared with controls. Furthermore, we show that the expression of several stress-responsive genes (e.g., CRF, POMC, and FKBP5) is altered in the PFC of AUD subjects. These stress-response genes were also changed in the hippocampus, a region that is highly susceptible to stress. These data suggest that alcohol-dependent aberrant DNA methylation of NR3C1 and consequent changes in other stress-related genes might be fundamental in the pathophysiology of AUD and lay the groundwork for treatments targeting the epigenetic mechanisms regulating NR3C1 in AUD.</p>',
'date' => '2019-06-25',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31239533',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41380-019-0449-6',
'modified' => '2019-07-04 18:07:16',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 58 => array(
'id' => '3604',
'name' => 'DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene in a CUMS model of depression.',
'authors' => 'Xiang D, Xiao J, Fu L, Yao L, Wan Q, Xiao L, Zhu F, Wang G, Liu Z',
'description' => '<p>Tacr2, the gene encoding the NK2 receptor, belongs to G protein-coupled receptors. Accumulating evidence has indicated that the tachykinin receptors may contribute to the pathophysiology of depression. During the last decade, some studies have shown that Tacr2 activation is involved in the modulation of emotional processes. However, the extent, to which stress impacts Tacr2 expression remains unclear. The molecular mechanisms underlying depression also remain poorly understood. In this study, we subjected adult male Sprague Dawley (SD) rats to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) to induce a depression-like phenotype. We then measured the body weight and performed the sucrose preference test, forced swimming test (FST) and open field test to detect the effects of stress on anhedonia and activity. Western blotting and real-time PCR were used to study the protein and mRNA expression levels of Tacr2, respectively, in the hypothalamus. To explore DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene, we used methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Additionally, we used the bisulfite sequencing PCR (BSP) to further verify the DNA methylation levels of the Tacr2 receptor gene in rats. We found that the CUMS-sensitive rats exhibited a decrease in body weight and sucrose preference, a decrease in the distance traveled, rearing frequency and velocity in the open field test, and an increase in immobility time in the FST. Compared with the expression in the control rats, Tacr2 protein and mRNA expression in the hypothalamus significantly increased in the CUMS-sensitive rats; however, the DNA methylation levels of the Tacr2 gene were significantly lower than in the control rats. In summary, according to our findings, the stress-induced increase in Tacr2 expression in the hypothalamus correlated with a specific decrease in DNA methylation of the Tacr2 gene. These results may enrich the understanding of the pathological processes of depression and provide insights into therapeutic approaches for its treatment.</p>',
'date' => '2019-06-03',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30711443',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.bbr.2019.01.059',
'modified' => '2019-04-16 13:54:40',
'created' => '2019-04-16 12:25:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 59 => array(
'id' => '3666',
'name' => 'Epigenetic Alterations in Juvenile Spondyloarthritis Patients: a Preliminary Study of Selected Genes Promoter Methylation and Silencing',
'authors' => 'Lamot Lovro, Blažeković Antonela, Jerčić Kristina Gotovac, Ivković Tina Catela, Vidović Mandica, Lamot Mirta, Kapitanović Sanja, Borovečki Fran, Harjaček Miroslav',
'description' => '<p>Juvenile spondyloarthritis (jSpA) is a complex disease with both genetic and environmental factors contributing to etiology. Multiple studies have shown that epigenetic mechanisms could link the environment and gene expression and thus provide a potential explanation for external contribution in the pathogenesis of numerous diseases, including rheumatic. Previously obtained gene signatures in jSpA patients revealed distinctive expression of important immune-related genes, though the mechanism(s) responsible for those alterations remained unknown. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the methylation levels of the TLR4, CXCR4, NLRP3, and PTPN12 gene promoter, along with the expression of several non-coding microRNAs (miR-150, miR-146a, miR-181a, and miR-223) in jSpA patients. Peripheral blood samples were obtained from 19 patients newly diagnosed with jSpA according to ILAR classification criteria for enthesitis-related arthritis (ErA) and seven gender- and age-matched subjects without any symptoms or signs of inflammatory disease. The expression of specific microRNAs was analyzed using qRT-PCR with predeveloped microRNA assays. DNA promoter region methylation status of selected genes was assessed by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) analysis. Fold enrichment of immunoprecipitated DNA differed significantly for NLRP3 promoter site, while the expression analysis of selected microRNAs showed no significant difference in fold change between jSpA patients and healthy controls. The results indicated that epigenetic modifications in the initial phase of the disease could be responsible for some of the expression alterations in jSpA patients. Since NLRP3 has a crucial role in inflammasome assembly and inflammasomes have been shown to shape microbiota, it is tempting to assume that dysbiosis in jSpA patients can at least partially be explained by reduced NLRP3 expression due to hypermethylation, stressing for the first time the epigenetic contribution to jSpA pathophysiology</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-09',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s42399-019-00070-9',
'doi' => '10.1007/s42399-019-00070-9',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:53:06',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 60 => array(
'id' => '3846',
'name' => 'The methylation pattern of DNA and complex correlations with gene expressions during TuMV infection in Chinese cabbage',
'authors' => 'J. YU , L.-W. GAO , Y. YANG , C. LIU , R.-J. ZHANG , F.-F. SUN , L.-X. SONG , D. XIAO , T.-K. LIU , X.-L. HOU , and C.-W. ZHANG',
'description' => '<p>Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) is one of the most important economic crops. However, its yield and quality can be severely threatened by Turnip mosaic virus (TuMV). Emerging evidence indicates that epigenetic mechanisms, especially DNA methylation, play an important role in regulating gene expression. Therefore, identification of resistance genes modified by DNA methylation during the virus infection would provide a critical clue for improving disease resistance breeding programs. Here, we present detailed analysis for the correlation of DNA methylation and gene expression involved in several anti-pathogen pathways. We also found that different methylation patterns exist in different methylation sites (CG, CHG, and CHH, where H represents A, G, or T) and genomic regions. Furthermore, we identified disease-resistant genes related to the nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeats family, auxin, salicylic acid signaling transduction, cell wall biosynthesis, and protein degradation among the different methylated genes (DMGs) suggesting that these genes may be modified by DNA methylation and work together to activate an immune response. The identified DMGs are a valuable resource for discovering resistance genes. Our study not only provides valuable data for future biotechnology research and epigenetic studies, but also helps to explore how the epigenetic mechanisms modify antiviral pathways.</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-09',
'pmid' => 'https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337128882_The_methylation_pattern_of_DNA_and_complex_correlations_with_gene_expressions_during_TuMV_infection_in_Chinese_cabbage',
'doi' => '10.32615/bp.2019.073',
'modified' => '2020-02-20 11:12:23',
'created' => '2020-02-13 10:02:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 61 => array(
'id' => '3716',
'name' => 'Epigenetic control of the angiotensin-converting enzyme in endothelial cells during inflammation.',
'authors' => 'Mudersbach T, Siuda D, Kohlstedt K, Fleming I',
'description' => '<p>The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) plays a central role in the renin-angiotensin system, which is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. Alterations in ACE expression or activity are associated with various pathological phenotypes, particularly cardiovascular diseases. In human endothelial cells, ACE was shown to be negatively regulated by tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α. To examine, whether or not, epigenetic factors were involved in ACE expression regulation, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and RNA interference experiments directed against regulators of DNA methylation homeostasis i.e., DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenases (TETs), were performed. TNFα stimulation enhanced DNA methylation in two distinct regions within the ACE promoter via a mechanism linked to DNMT3a and DNMT3b, but not to DNMT1. At the same time, TET1 protein expression was downregulated. In addition, DNA methylation decreased the binding affinity of the transcription factor MYC associated factor X to the ACE promoter. In conclusion, DNA methylation determines the TNFα-dependent regulation of ACE gene transcription and thus protein expression in human endothelial cells.</p>',
'date' => '2019-05-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/31042763',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0216218',
'modified' => '2019-07-05 13:14:33',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 62 => array(
'id' => '3698',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in Tibetan and Yorkshire pigs under high-altitude hypoxia.',
'authors' => 'Zhang B, Ban D, Gou X, Zhang Y, Yang L, Chamba Y, Zhang H',
'description' => '<p>Background: Tibetan pigs, which inhabit the Tibetan Plateau, exhibit distinct phenotypic and physiological characteristics from those of lowland pigs and have adapted well to the extreme conditions at high altitude. However, the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of hypoxic adaptation in animals remain unclear. Methods: Whole-genome DNA methylation data were generated for heart tissues of Tibetan pigs grown in the highland (TH,  = 4) and lowland (TL,  = 4), as well as Yorkshire pigs grown in the highland (YH,  = 4) and lowland (YL,  = 4), using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing. Results: We obtained 480 million reads and detected 280679, 287224, 259066, and 332078 methylation enrichment peaks in TH, YH, TL, and YL, respectively. Pairwise TH vs. YH, TL vs. YL, TH vs. TL, and YH vs. YL comparisons revealed 6829, 11997, 2828, and 1286 differentially methylated regions (DMRs), respectively. These DMRs contained 384, 619, 192, and 92 differentially methylated genes (DMGs), respectively. DMGs that were enriched in the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signaling pathway and pathways involved in cancer and hypoxia-related processes were considered to be important candidate genes for high-altitude adaptation in Tibetan pigs. Conclusions: This study elucidates the molecular and epigenetic mechanisms involved in hypoxic adaptation in pigs and may help further understand human hypoxia-related diseases.</p>',
'date' => '2019-04-28',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30867905',
'doi' => '10.1186/s40104-019-0316-y',
'modified' => '2019-07-05 14:47:45',
'created' => '2019-07-04 10:42:34',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 63 => array(
'id' => '3648',
'name' => 'Assessment and site-specific manipulation of DNA (hydroxy-)methylation during mouse corticogenesis.',
'authors' => 'Noack F, Pataskar A, Schneider M, Buchholz F, Tiwari VK, Calegari F',
'description' => '<p>Dynamic changes in DNA (hydroxy-)methylation are fundamental for stem cell differentiation. However, the signature of these epigenetic marks in specific cell types during corticogenesis is unknown. Moreover, site-specific manipulation of cytosine modifications is needed to reveal the significance and function of these changes. Here, we report the first assessment of (hydroxy-)methylation in neural stem cells, neurogenic progenitors, and newborn neurons during mammalian corticogenesis. We found that gain in hydroxymethylation and loss in methylation occur sequentially at specific cellular transitions during neurogenic commitment. We also found that these changes predominantly occur within enhancers of neurogenic genes up-regulated during neurogenesis and target of pioneer transcription factors. We further optimized the use of dCas9-Tet1 manipulation of (hydroxy-)methylation, locus-specifically, in vivo, showing the biological relevance of our observations for , a regulator of corticogenesis involved in developmental malformations and cognitive impairment. Together, our data reveal the dynamics of cytosine modifications in lineage-related cell types, whereby methylation is reduced and hydroxymethylation gained during the neurogenic lineage concurrently with up-regulation of pioneer transcription factors and activation of enhancers for neurogenic genes.</p>',
'date' => '2019-04-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30814272',
'doi' => '10.1038/nrg.2017.57',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:13:14',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 64 => array(
'id' => '3647',
'name' => 'DMSO induces drastic changes in human cellular processes and epigenetic landscape in vitro.',
'authors' => 'Verheijen M, Lienhard M, Schrooders Y, Clayton O, Nudischer R, Boerno S, Timmermann B, Selevsek N, Schlapbach R, Gmuender H, Gotta S, Geraedts J, Herwig R, Kleinjans J, Caiment F',
'description' => '<p>Though clinical trials for medical applications of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) reported toxicity in the 1960s, later, the FDA classified DMSO in the safest solvent category. DMSO became widely used in many biomedical fields and biological effects were overlooked. Meanwhile, biomedical science has evolved towards sensitive high-throughput techniques and new research areas, including epigenomics and microRNAs. Considering its wide use, especially for cryopreservation and in vitro assays, we evaluated biological effect of DMSO using these technological innovations. We exposed 3D cardiac and hepatic microtissues to medium with or without 0.1% DMSO and analyzed the transcriptome, proteome and DNA methylation profiles. In both tissue types, transcriptome analysis detected >2000 differentially expressed genes affecting similar biological processes, thereby indicating consistent cross-organ actions of DMSO. Furthermore, microRNA analysis revealed large-scale deregulations of cardiac microRNAs and smaller, though still massive, effects in hepatic microtissues. Genome-wide methylation patterns also revealed tissue-specificity. While hepatic microtissues demonstrated non-significant changes, findings from cardiac microtissues suggested disruption of DNA methylation mechanisms leading to genome-wide changes. The extreme changes in microRNAs and alterations in the epigenetic landscape indicate that DMSO is not inert. Its use should be reconsidered, especially for cryopreservation of embryos and oocytes, since it may impact embryonic development.</p>',
'date' => '2019-03-15',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30874586',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-019-40660-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:14:07',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 65 => array(
'id' => '3673',
'name' => 'Evidence of association of circulating epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers with suspected coronary heart disease evaluated by Cardiac Computed Tomography.',
'authors' => 'Infante T, Forte E, Schiano C, Punzo B, Cademartiri F, Cavaliere C, Salvatore M, Napoli C',
'description' => '<p>Circulating biomarkers available in clinical practice do not allow to stratify patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) prior the onset of a clinically relevant event. We evaluated the methylation status of specific genomic segments and gene expression in peripheral blood of patients undergoing Cardiac Computed Tomography (CCT) for CHD (n = 95). We choose to investigate cholesterol metabolism. Methylation and gene expression of low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), sterol regulatory element-binding factor 2 (SREBF2) and ATP-binding cassette transporter 1 (ABCA1) were evaluated by qRT-PCR. Calcium score (CACS), stenosis degree, total plaque volume (TPV), calcified plaque volume (CPV), non-calcified plaque volume (NCPV) and plaque burden (PB) were assessed in all CHD patients (n = 65). The percentage of methylation at the specific analyzed segment of LDLR promoter was higher in CHD patients vs healthy subjects (HS) (n = 30) (p = 0.001). LDLR, SREBF2 and ABCA1 mRNAs were up-regulated in CHD patients vs HS (p = 0.02; p = 0.019; p = 0.008). SREBF2 was overexpressed in patients with coronary stenosis ≥50% vs subjects with stenosis <50% (p = 0.036). After adjustment for risk factors and clinical features, ABCA1 (p = 0.005) and SREBF2 (p = 0.010) gene expression were identified as independent predictors of CHD and severity. ROC curve analysis revealed a good performance of ABCA1 on predicting CHD (AUC = 0.768; p<0.001) and of SREBF2 for the prediction of disease severity (AUC = 0.815; p<0.001). Moreover, adjusted multivariate analysis demonstrated SREBF2 as independent predictor of CPV, NCPV and TPV (p = 0.022; p = 0.002 and p = 0.006) and ABCA1 as independent predictor of NCPV and TPV (p = 0.002 and p = 0.013). CHD presence and characteristics are related to selected circulating transcriptional and epigenetic-sensitive biomarkers linked to cholesterol pathway. More extensive analysis of CHD phenotypes and circulating biomarkers might improve and personalize cardiovascular risk stratification in the clinical settings.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-23',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30673762',
'doi' => '10.1371/journal.pone.0210909',
'modified' => '2019-07-01 11:27:58',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 66 => array(
'id' => '3655',
'name' => 'LncRNA Dnmt3aos regulates Dnmt3a expression leading to aberrant DNA methylation in macrophage polarization',
'authors' => 'Xueqin Li, Yingying Zhang, Mengying Zhang, Xiang Kong, Hui Yang, Min Zhong, Weiya Pei, Yang Xu, Xiaolong Zhu, Tianbing Chen, Jingjing Ye, and Kun ',
'description' => '<p>Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play key roles in various biological processes. However, the roles of lncRNAs in macrophage polarization remain largely unexplored. In this study, thousands of lncRNAs were identified that are differentially expressed in distinct polarized bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Among them, Dnmt3aos (DNA methyltransferase 3A, opposite strand), as a known lncRNA, locates on the antisense strand of Dnmt3a. Functional experiments further confirmed that Dnmt3aos were highly expressed in M(IL-4) macrophages and participated in the regulation of Dnmt3a expression, and played a key role in macrophage polarization. The DNA methylation profiles between the Dnmt3aos knockdown group and the control group in M(IL-4) macrophages were determined by MeDIP-seq technique for the first time, and the Dnmt3aos-Dnmt3a axis-mediated DNA methylation modification-regulated macrophage polarization related gene IFN-γ was identified. Our study will help to enrich our knowledge of the mechanism of macrophage polarization and will provide new insights for immunotherapy in macrophage-associated diseases.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-07',
'pmid' => 'https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/514307v1',
'doi' => '/',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:39:53',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 67 => array(
'id' => '3660',
'name' => 'Global distribution of DNA hydroxymethylation and DNA methylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.',
'authors' => 'Wernig-Zorc S, Yadav MP, Kopparapu PK, Bemark M, Kristjansdottir HL, Andersson PO, Kanduri C, Kanduri M',
'description' => '<p>BACKGROUND: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has been a good model system to understand the functional role of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in cancer progression. More recently, an oxidized form of 5-mC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has gained lot of attention as a regulatory epigenetic modification with prognostic and diagnostic implications for several cancers. However, there is no global study exploring the role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) levels in CLL. Herein, using mass spectrometry and hMeDIP-sequencing, we analysed the dynamics of 5-hmC during B cell maturation and CLL pathogenesis. RESULTS: We show that naïve B-cells had higher levels of 5-hmC and 5-mC compared to non-class switched and class-switched memory B-cells. We found a significant decrease in global 5-mC levels in CLL patients (n = 15) compared to naïve and memory B cells, with no changes detected between the CLL prognostic groups. On the other hand, global 5-hmC levels of CLL patients were similar to memory B cells and reduced compared to naïve B cells. Interestingly, 5-hmC levels were increased at regulatory regions such as gene-body, CpG island shores and shelves and 5-hmC distribution over the gene-body positively correlated with degree of transcriptional activity. Importantly, CLL samples showed aberrant 5-hmC and 5-mC pattern over gene-body compared to well-defined patterns in normal B-cells. Integrated analysis of 5-hmC and RNA-sequencing from CLL datasets identified three novel oncogenic drivers that could have potential roles in CLL development and progression. CONCLUSIONS: Thus, our study suggests that the global loss of 5-hmC, accompanied by its significant increase at the gene regulatory regions, constitute a novel hallmark of CLL pathogenesis. Our combined analysis of 5-mC and 5-hmC sequencing provided insights into the potential role of 5-hmC in modulating gene expression changes during CLL pathogenesis.</p>',
'date' => '2019-01-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30616658',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13072‑018‑0252‑7',
'modified' => '2019-07-01 11:46:16',
'created' => '2019-06-21 14:55:31',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 68 => array(
'id' => '3430',
'name' => 'Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes.',
'authors' => 'Shen SY, Singhania R, Fehringer G, Chakravarthy A, Roehrl MHA, Chadwick D, Zuzarte PC, Borgida A, Wang TT, Li T, Kis O, Zhao Z, Spreafico A, Medina TDS, Wang Y, Roulois D, Ettayebi I, Chen Z, Chow S, Murphy T, Arruda A, O'Kane GM, Liu J, Mansour M, McPher',
'description' => '<p>The use of liquid biopsies for cancer detection and management is rapidly gaining prominence. Current methods for the detection of circulating tumour DNA involve sequencing somatic mutations using cell-free DNA, but the sensitivity of these methods may be low among patients with early-stage cancer given the limited number of recurrent mutations. By contrast, large-scale epigenetic alterations-which are tissue- and cancer-type specific-are not similarly constrained and therefore potentially have greater ability to detect and classify cancers in patients with early-stage disease. Here we develop a sensitive, immunoprecipitation-based protocol to analyse the methylome of small quantities of circulating cell-free DNA, and demonstrate the ability to detect large-scale DNA methylation changes that are enriched for tumour-specific patterns. We also demonstrate robust performance in cancer detection and classification across an extensive collection of plasma samples from several tumour types. This work sets the stage to establish biomarkers for the minimally invasive detection, interception and classification of early-stage cancers based on plasma cell-free DNA methylation patterns.</p>',
'date' => '2018-11-14',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30429608',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41586-018-0703-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-11 16:22:54',
'created' => '2018-12-04 09:51:07',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 69 => array(
'id' => '3511',
'name' => 'Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation to identify genes and pathways associated with male sterility in soybean',
'authors' => 'Han Shaohuai, Li Yanwei, Li Jiajia, Zhang Hao, Ding Xianlong, He Tingting, Gai Junyi, Yang Shouping',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is an epigenetic modification, which is important for gene expression regulation. Although genome-wide DNA methylation studies have been reported in several plant species, the difference in the methylation pattern between the cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) line and its maintainer in soybean remains unclear. We compared genome-wide DNA methylation between the soybean CMS line NJCMS1A and its maintainer NJCMS1B using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation combined with high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) technology. The results showed that the methylation level was higher in transposable elements (TEs) than promoter and intron; however, the methylation levels varied among different types of TEs with the highest level for long terminal repeats (LTRs) and the lowest for transcription start sites (TSS) and transcription termination sites (TTS). We observed 178 differentially methylated genes (DMGs) between NJCMS1A and NJCMS1B, including 156 hypomethylated and 22 hyper-methylated genes in NJCMS1A compared to NJCMS1B. Gene Ontology (GO) analysis showed that 114 DMGs were annotated to one or more GO categories, among which four GO terms were significantly enriched. KEGG pathway analysis showed that 18 DMGs were significantly enriched in 10 metabolism pathways, including homologous recombination, purine metabolism, proteasome, non-homologous end-joining, and pyrimidine</p>',
'date' => '2018-09-16',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11032-018-0875-1',
'doi' => '10.1007/s11032-018-0875-1',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:44:53',
'created' => '2019-02-27 12:54:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 70 => array(
'id' => '3585',
'name' => 'Folic acid supplementation alters the DNA methylation profile and improves insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-fed mice.',
'authors' => 'Li W, Tang R, Ma F, Ouyang S, Liu Z, Wu J',
'description' => '<p>Folic acid (FA) supplementation may protect from obesity and insulin resistance, the effects and mechanism of FA on chronic high-fat-diet-induced obesity-related metabolic disorders are not well elucidated. We adopted a genome-wide approach to directly examine whether FA supplementation affects the DNA methylation profile of mouse adipose tissue and identify the functional consequences of these changes. Mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD), normal diet (ND) or an HFD supplemented with folic acid (20 μg/ml in drinking water) for 10 weeks, epididymal fat was harvested, and genome-wide DNA methylation analyses were performed using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Mice exposed to the HFD expanded their adipose mass, which was accompanied by a significant increase in circulating glucose and insulin levels. FA supplementation reduced the fat mass and serum glucose levels and improved insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. MeDIP-seq revealed distribution of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) throughout the adipocyte genome, with more hypermethylated regions in HFD mice. Methylome profiling identified DMRs associated with 3787 annotated genes from HFD mice in response to FA supplementation. Pathway analyses showed novel DNA methylation changes in adipose genes associated with insulin secretion, pancreatic secretion and type 2 diabetes. The differential DNA methylation corresponded to changes in the adipose tissue gene expression of Adcy3 and Rapgef4 in mice exposed to a diet containing FA. FA supplementation improved insulin resistance, decreased the fat mass, and induced DNA methylation and gene expression changes in genes associated with obesity and insulin secretion in obese mice fed a HFD.</p>',
'date' => '2018-09-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29986310',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.05.010',
'modified' => '2019-04-17 15:33:46',
'created' => '2019-04-16 12:25:30',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 71 => array(
'id' => '3633',
'name' => 'Embryonic germ cell extracts erase imprinted genes and improve the efficiency of induced pluripotent stem cells.',
'authors' => 'Hu J, Zhao Q, Feng Y, Li N, Gu Y, Sun R, Duan L, Wu Y, Shan Z, Lei L',
'description' => '<p>Patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have the potential to be useful in the treatment of human diseases. While prior studies have reported multiple methods to generate iPSCs, DNA methylation continues to limit the totipotency and reprogramming efficiency of iPSCs. Here, we first show the competency of embryonic germ cells (EGCs) as a reprogramming catalyst capable of effectively promoting reprogramming induced by four defined factors, including Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc. Combining EGC extracts with these four factors resulted in formation of more embryonic stem cell-like colonies than did factors alone. Notably, expression of imprinted genes was higher with combined induction than with factors alone. Moreover, iPSCs derived from the combined inductors tended to have more global hypomethylation. Our research not only provides evidence that EGC extracts could activate DNA demethylation and reprogram imprinted genes, but also establishes a new way to enhance reprogramming of iPSCs, which remains a critical safety concern for potential use of iPSCs in regenerative medicine.</p>',
'date' => '2018-07-19',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/30026469',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-018-29339-0',
'modified' => '2019-06-07 10:30:27',
'created' => '2019-06-06 12:11:18',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 72 => array(
'id' => '3393',
'name' => 'Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos.',
'authors' => 'Sussarellu R, Lebreton M, Rouxel J, Akcha F, Rivière G',
'description' => '<p>Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better understand whether the embryotoxic effects of copper in Crassostrea gigas could be mediated by alterations in gene expression, and the putative role of DNA methylation, which is known to contribute to gene regulation in early embryo development. For that purpose, oyster embryos were exposed to 4 nominal copper concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 μg L Cu) during early development assays. Embryotoxicity was monitored through the oyster embryo-larval bioassay at the D-larva stage 24 h post fertilization (hpf) and genotoxicity at gastrulation 7 hpf. In parallel, the relative expression of 15 genes encoding putative homeotic, biomineralization and DNA methylation proteins was measured at three developmental stages (3 hpf morula stage, 7 hpf gastrula stage, 24 hpf D-larvae stage) using RT-qPCR. Global DNA content in methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine were measured by HPLC and gene-specific DNA methylation levels were monitored using MeDIP-qPCR. A significant increase in larval abnormalities was observed from copper concentrations of 10 μg L, while significant genotoxic effects were detected at 1 μg L and above. All the selected genes presented a stage-dependent expression pattern, which was impaired for some homeobox and DNA methylation genes (Notochord, HOXA1, HOX2, Lox5, DNMT3b and CXXC-1) after copper exposure. While global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) at gastrula stage didn't show significant changes between experimental conditions, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its degradation product, decreased upon copper treatment. The DNA methylation of exons and the transcript levels were correlated in control samples for HOXA1 but such a correlation was diminished following copper exposure. The methylation level of some specific gene regions (HoxA1, Hox2, Engrailed2 and Notochord) displayed changes upon copper exposure. Such changes were gene and exon-specific and no obvious global trends could be identified. Our study suggests that the embryotoxic effects of copper in oysters could involve homeotic gene expression impairment possibly by changing DNA methylation levels.</p>',
'date' => '2018-03-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29353135',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.001',
'modified' => '2018-11-09 12:21:38',
'created' => '2018-11-08 12:59:45',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 73 => array(
'id' => '3448',
'name' => 'Aberrant methylated key genes of methyl group metabolism within the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinogenesis.',
'authors' => 'Erichsen L, Ghanjati F, Beermann A, Poyet C, Hermanns T, Schulz WA, Seifert HH, Wild PJ, Buser L, Kröning A, Braunstein S, Anlauf M, Jankowiak S, Hassan M, Bendhack ML, Araúzo-Bravo MJ, Santourlidis S',
'description' => '<p>Urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common cancer of the urinary bladder causes severe morbidity and mortality, e.g. about 40.000 deaths in the EU annually, and incurs considerable costs for the health system due to the need for prolonged treatments and long-term monitoring. Extensive aberrant DNA methylation is described to prevail in urothelial carcinoma and is thought to contribute to genetic instability, altered gene expression and tumor progression. However, it is unknown how this epigenetic alteration arises during carcinogenesis. Intact methyl group metabolism is required to ensure maintenance of cell-type specific methylomes and thereby genetic integrity and proper cellular function. Here, using two independent techniques for detecting DNA methylation, we observed DNA hypermethylation of the 5'-regulatory regions of the key methyl group metabolism genes ODC1, AHCY and MTHFR in early urothelial carcinoma. These hypermethylation events are associated with genome-wide DNA hypomethylation which is commonly associated with genetic instability. We therefore infer that hypermethylation of methyl group metabolism genes acts in a feed-forward cycle to promote additional DNA methylation changes and suggest a new hypothesis on the molecular etiology of urothelial carcinoma.</p>',
'date' => '2018-02-22',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29472622',
'doi' => '10.1038/s41598-018-21932-7',
'modified' => '2019-02-15 21:31:04',
'created' => '2019-02-14 15:01:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 74 => array(
'id' => '3325',
'name' => 'Integrative omics data analyses of repeated dose toxicity of valproic acid in vitro reveal new mechanisms of steatosis induction',
'authors' => 'van Breda S.G.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is a very potent anti-cancer and neuro-protective drug probably by its HDAC inhibiting properties, which may cause steatosis in the liver. The present study investigates the effect of repetitive VPA treatment of primary human hepatocytes (PHH) on whole genome gene expression-, DNA methylation-, and miRNA changes, using microarrays and integrated data analyses. PHH were exposed to a non-cytotoxic dose of VPA for 5days daily which induced lipid accumulation. Part of the PHH was left untreated for 3days for studying the persistence of 'omics' changes. VPA treatment appeared to inhibit the expression of the transcription factors HNF1A and ONECUT1. HNF1A interacted with 41 differentially expressed genes of which 12 were also differentially methylated. None of the genes present in this network were regulated by a DE-miR. The subnetwork of ONECUT1 consisted of 44 differentially expressed genes of which 15 were differentially methylated, and 3 were regulated by a DE-miR. A number of genes in the networks are involved in fatty acid metabolism, and may contribute to the development of steatosis by increasing oxidative stress thereby causing mitochondrial dysfunction, and by shifting metabolism of VPA towards β-oxidation due to reduced glucuronidation. Part of the changes remained persistent after washing out of VPA, like PMAIP1 which is associated with cellular stress in liver of patients with NASH. The MMP2 gene showed the highest number of interactions with other persistently expressed genes, among which LCN2 which is a key modulator of lipid homeostasis. Furthermore, VPA modulated the expression and DNA methylation level of nuclear receptors and their target genes involved in the adverse outcome pathway of steatosis, thereby expanding our current knowledge of the pathway. In particular, VPA modulated PPARγ, and PPARα, AHR and CD36 on both the gene expression and the DNA methylation level, thereby inhibiting β-oxidation and increasing uptake of fatty acid into the hepatocytes, respectively. Overall, our integrative data analyses identified novel genes modulated by VPA, which provide more insight into the mechanisms of repeated dose toxicity of VPA, leading to steatosis.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-15',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29154799',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-02-06 09:28:05',
'created' => '2018-02-06 09:28:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 75 => array(
'id' => '3316',
'name' => 'Copper induces expression and methylation changes of early development genes in Crassostrea gigas embryos',
'authors' => 'Rossana Sussarellu, Morgane Lebreton, Julien Rouxel, Farida Akcha, Guillaume Rivière ',
'description' => '<p id="spar0045">Copper contamination is widespread along coastal areas and exerts adverse effects on marine organisms such as mollusks. In the Pacific oyster, copper induces severe developmental abnormalities during early life stages; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms are largely unknown. This study aims to better understand whether the embryotoxic effects of copper in <em>Crassostrea gigas</em> could be mediated by alterations in gene expression, and the putative role of DNA methylation, which is known to contribute to gene regulation in early embryo development.</p>
<p id="spar0050">For that purpose, oyster embryos were exposed to 4 nominal copper concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 20 μg L<sup>−1</sup> Cu<sup>2+</sup>) during early development assays. Embryotoxicity was monitored through the oyster embryo-larval bioassay at the D-larva stage 24 h post fertilization (hpf) and genotoxicity at gastrulation 7 hpf. In parallel, the relative expression of 15 genes encoding putative homeotic, biomineralization and DNA methylation proteins was measured at three developmental stages (3 hpf morula stage, 7 hpf gastrula stage, 24 hpf D-larvae stage) using RT-qPCR. Global DNA content in methylcytosine and hydroxymethylcytosine were measured by HPLC and gene-specific DNA methylation levels were monitored using MeDIP-qPCR.</p>
<p id="spar0055">A significant increase in larval abnormalities was observed from copper concentrations of 10 μg L<sup>−1</sup>, while significant genotoxic effects were detected at 1 μg L<sup>−1</sup> and above. All the selected genes presented a stage-dependent expression pattern, which was impaired for some homeobox and DNA methylation genes (<em>Notochord, HOXA1, HOX2, Lox5, DNMT3b and CXXC-1</em>) after copper exposure. While global DNA methylation (5-methylcytosine) at gastrula stage didn’t show significant changes between experimental conditions, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine, its degradation product, decreased upon copper treatment. The DNA methylation of exons and the transcript levels were correlated in control samples for <em>HOXA1</em> but such a correlation was diminished following copper exposure. The methylation level of some specific gene regions (<em>HoxA1, Hox2, Engrailed2</em> and <em>Notochord</em>) displayed changes upon copper exposure. Such changes were gene and exon-specific and no obvious global trends could be identified. Our study suggests that the embryotoxic effects of copper in oysters could involve homeotic gene expression impairment possibly by changing DNA methylation levels.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-03',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166445X18300018?via%3Dihub',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.01.001',
'modified' => '2018-01-14 01:21:09',
'created' => '2018-01-14 01:21:09',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 76 => array(
'id' => '3383',
'name' => 'Genome-wide analysis of day/night DNA methylation differences in Populus nigra.',
'authors' => 'Ding C.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is an important mechanism of epigenetic modification. Methylation changes during stress responses and developmental processes have been well studied; however, their role in plant adaptation to the day/night cycle is poorly understood. In this study, we detected global methylation patterns in leaves of the black poplar Populus nigra 'N46' at 8:00 and 24:00 by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). We found 10,027 and 10,242 genes to be methylated in the 8:00 and 24:00 samples, respectively. The methylated genes appeared to be involved in multiple biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components, suggesting important roles for DNA methylation in poplar cells. Comparing the 8:00 and 24:00 samples, only 440 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) overlapped with genic regions, including 193 hyper- and 247 hypo-methylated DMRs, and may influence the expression of 137 downstream genes. Most hyper-methylated genes were associated with transferase activity, kinase activity, and phosphotransferase activity, whereas most hypo-methylated genes were associated with protein binding, ATP binding, and adenyl ribonucleotide binding, suggesting that different biological processes were activated during the day and night. Our results indicated that methylated genes were prevalent in the poplar genome, but that only a few of these participated in diurnal gene expression regulation.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-02',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29293569',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-08-07 09:45:38',
'created' => '2018-08-07 09:45:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 77 => array(
'id' => '3384',
'name' => 'Obligatory and facilitative allelic variation in the DNA methylome within common disease-associated loci',
'authors' => 'Bell C.G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Integrating epigenetic data with genome-wide association study (GWAS) results can reveal disease mechanisms. The genome sequence itself also shapes the epigenome, with CpG density and transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) strongly encoding the DNA methylome. Therefore, genetic polymorphism impacts on the observed epigenome. Furthermore, large genetic variants alter epigenetic signal dosage. Here, we identify DNA methylation variability between GWAS-SNP risk and non-risk haplotypes. In three subsets comprising 3128 MeDIP-seq peripheral-blood DNA methylomes, we find 7173 consistent and functionally enriched Differentially Methylated Regions. 36.8% can be attributed to common non-SNP genetic variants. CpG-SNPs, as well as facilitative TFBS-motifs, are also enriched. Highlighting their functional potential, CpG-SNPs strongly associate with allele-specific DNase-I hypersensitivity sites. Our results demonstrate strong DNA methylation allelic differences driven by obligatory or facilitative genetic effects, with potential direct or regional disease-related repercussions. These allelic variations require disentangling from pure tissue-specific modifications, may influence array studies, and imply underestimated population variability in current reference epigenomes.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-02',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29295990',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-08-07 10:13:12',
'created' => '2018-08-07 10:13:12',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 78 => array(
'id' => '3449',
'name' => 'Epigenetic alterations in TRAMP mice: epigenome DNA methylation profiling using MeDIP-seq.',
'authors' => 'Li W, Huang Y, Sargsyan D, Khor TO, Guo Y, Shu L, Yang AY, Zhang C, Paredes-Gonzalez X, Verzi M, Hart RP, Kong AN',
'description' => '<p>Purpose: We investigated the genomic DNA methylation profile of prostate cancer in transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) cancer model and to analyze the crosstalk among targeted genes and the related functional pathways. Methods: Prostate DNA samples from 24-week-old TRAMP and C57BL/6 male mice were isolated. The DNA methylation profiles were analyzed by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) followed by next-generation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Canonical pathways, diseases and function and network analyses of the different samples were then performed using the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software. Some target genes with significant difference in methylation were selected for validation using methylation specific primers (MSP) and qPCR. Results: TRAMP mice undergo extensive aberrant CpG hyper- and hypo-methylation. There were 2147 genes with a significant (log2-change ≥ 2) change in CpG methylation between the two groups, as mapped by the IPA software. Among these genes, the methylation of 1105 and 1042 genes was significantly decreased and increased, respectively, in TRAMP prostate tumors. The top associated disease identified by IPA was adenocarcinoma; however, the cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-, histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2)-, glutathione S-transferase pi (GSTP1)- and polyubiquitin-C (UBC)-related pathways showed significantly altered methylation profiles based on the canonical pathway and network analyses. MSP and qPCR results of genes of interests corroborated with MeDIP-seq findings. Conclusions: This is the first MeDIP-seq with IPA analysis of the TRAMP model to provide novel insight into the genome-wide methylation profile of prostate cancer. Studies on epigenetics, such as DNA methylation, will potentially provide novel avenues and strategies for further development of biomarkers targeted for treatment and prevention approaches for prostate cancer.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.pubmed.gov/29344347',
'doi' => '10.1186/s13578-018-0201-y',
'modified' => '2019-02-15 21:41:39',
'created' => '2019-02-14 15:01:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 79 => array(
'id' => '3508',
'name' => 'Analysis of DNA methylome and transcriptome profiling following Gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application in Nicotiana tabacum L.',
'authors' => 'Manoharlal Raman, Saiprasad G. V. S., Kaikala Vinay, Suresh Kumar R., Kovařík Ales',
'description' => '<p>The present work investigated a comprehensive genome-wide landscape of DNA methylome and its relationship with transcriptome upon gibberellin A3 (GA3) foliar application under practical field conditions in solanaceae model, Nicotiana tabacum L. Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation-Sequencing (MeDIP-Seq) analysis uncovered over 82% (18,456) of differential methylated regions (DMRs) in intergenic-region. Within protein-coding region, 2339 and 1685 of identified DMRs were observed in genebody- and promoter-region, respectively. Microarray study revealed 7032 differential expressed genes (DEGs) with 3507 and 3525 genes displaying upand down-regulation, respectively. Integration analysis revealed 520 unique non-redundant annotated DMRs overlapping with DEGs. Our results indicated that GA3 induced DNA hypo- as well as hyper-methylation were associated with both gene-silencing and -activation. No complete biasness or correlation was observed in either of the promoter- or genebody-regions, which otherwise showed an overall trend towards GA3 induced global DNA hypo-methylation. Taken together, our results suggested that differential DNA methylation mediated by GA3 may only play a permissive role in regulating the gene expression.</p>',
'date' => '2018-01-01',
'pmid' => 'https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40502-018-0393-5',
'doi' => '10.1007/s40502-018-0393-5',
'modified' => '2022-05-18 18:43:47',
'created' => '2019-02-27 12:54:44',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 80 => array(
'id' => '3334',
'name' => 'Data on novel DNA methylation changes induced by valproic acid in human hepatocytes',
'authors' => 'Wolters J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is a widely prescribed antiepileptic drug in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis. However the exact mechanism of the steatosis formation is unknown. The data presented in this DIB publication is used to further investigate the VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in patterns of methylation. Therefore, primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were exposed to VPA at a concentration which was shown to cause steatosis without inducing overt cytotoxicity. VPA was administered for 5 days daily to PHHs. Furthermore, after 5 days VPA-treatment parts of the PHHs were followed for a 3 days washout. Differentially methylated DNA regions (DMRs) were identified by using the 'Methylated DNA Immuno-Precipitation - sequencing' (MeDIP-seq) method. The data presented in this DIB demonstrate induced steatosis pathways by all DMRs during VPA-treatment, covering interesting drug-induced steatosis genes (persistent DMRs upon terminating VPA treatment and the <i>EP300</i> network). This was illustrated in our associated article (Wolters et al., 2017) [1]. MeDIP-seq raw data are available on ArrayExpress (accession number: E-MTAB-4437).</p>',
'date' => '2017-11-10',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29201983',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2018-02-08 17:16:22',
'created' => '2018-02-08 17:16:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 81 => array(
'id' => '3283',
'name' => 'Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Methylation Patterns Induced by Valproic Acid in Human Hepatocytes',
'authors' => 'Wolters J.E.J. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Valproic acid (VPA) is one of the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drugs in the world. Despite its pharmacological importance, it may cause liver toxicity and steatosis through mitochondrial dysfunction. The aim of this study is to further investigate VPA-induced mechanisms of steatosis by analyzing changes in patterns of methylation in nuclear DNA (nDNA) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Therefore, primary human hepatocytes (PHHs) were exposed to an incubation concentration of VPA that was shown to cause steatosis without inducing overt cytotoxicity. VPA was administered daily for 5 days, and this was followed by a 3 day washout (WO). Methylated DNA regions (DMRs) were identified by using the methylated DNA immunoprecipitation-sequencing (MeDIP-seq) method. The nDNA DMRs after VPA treatment could indeed be classified into oxidative stress- and steatosis-related pathways. In particular, networks of the steatosis-related gene EP300 provided novel insight into the mechanisms of toxicity induced by VPA treatment. Furthermore, we suggest that VPA induces a crosstalk between nDNA hypermethylation and mtDNA hypomethylation that plays a role in oxidative stress and steatosis development. Although most VPA-induced methylation patterns appeared reversible upon terminating VPA treatment, 31 nDNA DMRs (including 5 zinc finger protein genes) remained persistent after the WO period. Overall, we have shown that MeDIP-seq analysis is highly informative in disclosing novel mechanisms of VPA-induced toxicity in PHHs. Our results thus provide a prototype for the novel generation of interesting methylation biomarkers for repeated dose liver toxicity in vitro.</p>',
'date' => '2017-10-16',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28853863',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-24 09:33:19',
'created' => '2017-10-24 09:33:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 82 => array(
'id' => '3271',
'name' => ' Genome methylation and regulatory functions for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chicken embryos',
'authors' => 'Zhang Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Tibetan chickens have unique adaptations to the extreme high-altitude environment that they inhabit. Epigenetic DNA methylation affects many biological processes, including hypoxic adaptation; however, the regulatory genes for DNA methylation in hypoxic adaptation remain unknown. In this study, methylated DNA immunoprecipitation with high-throughput sequencing (MeDIP-seq) was used to provide an atlas of the DNA methylomes of the heart tissue of hypoxic highland Tibetan and lowland Chahua chicken embryos. A total of 31.2 gigabases of sequence data were generated from six MeDIP-seq libraries. We identified 1,049 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and 695 related differentially methylated genes (DMGs) between the two chicken breeds. The DMGs are involved in vascular smooth muscle contraction, VEGF signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway, and other hypoxia-related pathways. Five candidate genes that had low methylation (<i>EDNRA</i>, <i>EDNRB2</i>,<i> BMPR1B</i>,<i> BMPRII</i>, and <i>ITGA2</i>) might play key regulatory roles in the adaptation to hypoxia in Tibetan chicken embryos. Our study provides significant explanations for the functions of genes and their epigenetic regulation for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chickens.</p>',
'date' => '2017-10-06',
'pmid' => 'https://peerj.com/articles/3891/',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-13 17:02:21',
'created' => '2017-10-13 17:02:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 83 => array(
'id' => '3265',
'name' => 'Emerging Role of One-Carbon Metabolism and DNA Methylation Enrichment on δ-Containing GABAA Receptor Expression in the Cerebellum of Subjects with Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD',
'authors' => 'Gatta E. et al.',
'description' => '<section class="abstract">
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Background</div>
<p>Cerebellum is an area of the brain particularly sensitive to the effects of acute and chronic alcohol consumption. Alcohol exposure decreases cerebellar Purkinje cell output by increasing GABA release from Golgi cells onto extrasynaptic α<sub>6</sub>/δ-containing GABA<sub>A</sub> receptors located on glutamatergic granule cells. Here, we studied whether chronic alcohol consumption induces changes in GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor subunit expression and whether these changes are associated with alterations in epigenetic mechanisms via DNA methylation.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Methods</div>
<p>We used a cohort of postmortem cerebellum from control and chronic alcoholics, here defined as alcohol use disorders subjects (n=25/group). <em>S</em>-adenosyl-methionine/<em>S</em>-adenosyl-homocysteine were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography. mRNA levels of various genes were assessed by reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Promoter methylation enrichment was assessed using methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and hydroxy-methylated DNA immunoprecipitation assays.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Results</div>
<p>mRNAs encoding key enzymes of 1-carbon metabolism that determine the <em>S</em>-adenosyl-methionine/<em>S</em>-adenosyl-homocysteine ratio were increased, indicating higher “methylation index” in alcohol use disorder subjects. We found that increased methylation of the promoter of the δ subunit GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor was associated with reduced mRNA and protein levels in the cerebellum of alcohol use disorder subjects. No changes were observed in α<sub>1</sub>- or α<sub>6</sub>-containing GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor subunits. The expression of DNA-methyltransferases (1, 3A, and 3B) was unaltered, whereas the mRNA level of TET1, which participates in the DNA demethylation pathway, was decreased. Hence, increased methylation of the δ subunit GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor promoter may result from alcohol-induced reduction of DNA demethylation.</p>
</section>
<section class="sec">
<div class="title -title">Conclusion</div>
<p>Together, these results support the hypothesis that aberrant DNA methylation pathways may be involved in cerebellar pathophysiology of alcoholism. Furthermore, this work provides novel evidence for a central role of DNA methylation mechanisms in the alcohol-induced neuroadaptive changes of human cerebellar GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor function.</p>
</section>
</section>',
'date' => '2017-08-19',
'pmid' => 'https://academic.oup.com/ijnp/article/doi/10.1093/ijnp/pyx075/4085582/Emerging-role-of-one-carbon-metabolism-and-DNA',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-10-09 16:11:05',
'created' => '2017-10-09 16:11:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 84 => array(
'id' => '3251',
'name' => 'Coordinate Regulation of TET2 and EBNA2 Control DNA Methylation State of Latent Epstein-Barr Virus',
'authors' => 'Lu F. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and its associated carcinogenesis are regulated by dynamic changes in DNA methylation of both virus and host genomes. We show here that the Ten-Eleven Translocation 2 (TET2) gene, implicated in hydroxymethylation and active DNA demethylation, is a key regulator of EBV latency type DNA methylation patterning. EBV latency types are defined by DNA methylation patterns that restrict expression of viral latency genes. We show that TET2 mRNA and protein expression correlate with the highly demethylated EBV type III latency program permissive for expression of EBNA2, EBNA3s, and LMP transcripts. We show that shRNA depletion of TET2 results in a decrease in latency gene expression, but can also trigger a switch to lytic gene expression. TET2 depletion results in the loss of hydroxymethylated cytosine, and corresponding increase in cytosine methylation at key regulatory regions on the viral and host genomes. This also corresponded to a loss of RBP-jκ binding, and decreased histone H3K4 trimethylation at these sites. Furthermore, we show that the TET2 gene, itself, is regulated similar to the EBV genome. ChIP-Seq revealed that TET2 gene contains EBNA2-dependent RBP-jκ and EBF1 binding sites, and is subject to DNA methylation associated transcriptional silencing similar to EBV latency type III genomes. Finally, we provide evidence that TET2 colocalizes with EBNA2-EBF1-RBP-jκ binding sites, and can interact with EBNA2 by co-immunoprecipitation. Taken together, these findings indicate that TET2 gene transcripts are regulated similarly to EBV type III latency genes, and that TET2 protein is a cofactor of EBNA2 and co-regulator of the EBV type III latency program and DNA methylation state..<b>IMPORTANCE</b> Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) latency and carcinogenesis involves the selective epigenetic modification of viral and cellular genes. Here, we show that TET2, a cellular tumor suppressor involved in active DNA demethylation, plays a central role in regulating DNA methylation state during EBV latency. TET2 is coordinately regulated and functionally interacts with the viral oncogene EBNA2. TET2 and EBNA2 function cooperatively to demethylate genes important for EBV-driven B cells growth transformation.</p>',
'date' => '2017-08-07',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28794029',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-09-26 09:54:39',
'created' => '2017-09-26 09:54:39',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 85 => array(
'id' => '3237',
'name' => 'Intracellular adenosine regulates epigenetic programming in endothelial cells to promote angiogenesis',
'authors' => 'Xu Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>The nucleoside adenosine is a potent regulator of vascular homeostasis, but it remains unclear how expression or function of the adenosine-metabolizing enzyme adenosine kinase (ADK) and the intracellular adenosine levels influence angiogenesis. We show here that hypoxia lowered the expression of ADK and increased the levels of intracellular adenosine in human endothelial cells. Knockdown (KD) of ADK elevated intracellular adenosine, promoted proliferation, migration, and angiogenic sprouting in human endothelial cells. Additionally, mice deficient in endothelial ADK displayed increased angiogenesis as evidenced by the rapid development of the retinal and hindbrain vasculature, increased healing of skin wounds, and prompt recovery of arterial blood flow in the ischemic hindlimb. Mechanistically, hypomethylation of the promoters of a series of pro-angiogenic genes, especially for VEGFR2 in ADK KD cells, was demonstrated by the Infinium methylation assay. Methylation-specific PCR, bisulfite sequencing, and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation further confirmed hypomethylation in the promoter region of VEGFR2 in ADK-deficient endothelial cells. Accordingly, loss or inactivation of ADK increased VEGFR2 expression and signaling in endothelial cells. Based on these findings, we propose that ADK downregulation-induced elevation of intracellular adenosine levels in endothelial cells in the setting of hypoxia is one of the crucial intrinsic mechanisms that promote angiogenesis.</p>',
'date' => '2017-07-17',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28751580',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-08-29 09:15:21',
'created' => '2017-08-29 09:15:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 86 => array(
'id' => '3216',
'name' => 'Vitamin C induces specific demethylation of H3K9me2 in mouse embryonic stem cells via Kdm3a/b',
'authors' => 'Kevin T. Ebata, Kathryn Mesh, Shichong Liu, Misha Bilenky, Alexander Fekete, Michael G. Acker, Martin Hirst, Benjamin A. Garcia and Miguel Ramalho-Santos',
'description' => '<section xmlns="" xmlns:fn="http://www.w3.org/2005/xpath-functions" xmlns:meta="http://www.springer.com/app/meta" class="Abstract" id="Abs1" lang="en">
<div class="js-CollapseSection">
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec1">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Background</h3>
<p id="Par1" class="Para">Histone methylation patterns regulate gene expression and are highly dynamic during development. The erasure of histone methylation is carried out by histone demethylase enzymes. We had previously shown that vitamin C enhances the activity of Tet enzymes in embryonic stem (ES) cells, leading to DNA demethylation and activation of germline genes.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec2">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Results</h3>
<p id="Par2" class="Para">We report here that vitamin C induces a remarkably specific demethylation of histone H3 lysine 9 dimethylation (H3K9me2) in naïve ES cells. Vitamin C treatment reduces global levels of H3K9me2, but not other histone methylation marks analyzed, as measured by western blot, immunofluorescence and mass spectrometry. Vitamin C leads to widespread loss of H3K9me2 at large chromosomal domains as well as gene promoters and repeat elements. Vitamin C-induced loss of H3K9me2 occurs rapidly within 24 h and is reversible. Importantly, we found that the histone demethylases Kdm3a and Kdm3b are required for vitamin C-induced demethylation of H3K9me2. Moreover, we show that vitamin C-induced Kdm3a/b-mediated H3K9me2 demethylation and Tet-mediated DNA demethylation are independent processes at specific loci. Lastly, we document Kdm3a/b are partially required for the upregulation of germline genes by vitamin C.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec3">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p id="Par3" class="Para">These results reveal a specific role for vitamin C in histone demethylation in ES cells and document that DNA methylation and H3K9me2 cooperate to silence germline genes in pluripotent cells.</p>
</div>
</div>
</section>',
'date' => '2017-07-12',
'pmid' => 'https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-017-0143-3',
'doi' => 'https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-017-0143-3',
'modified' => '2017-08-23 14:47:51',
'created' => '2017-07-29 08:04:03',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 87 => array(
'id' => '3205',
'name' => 'Dynamics of DNA methylomes underlie oyster development',
'authors' => 'Riviere G. et al.',
'description' => '<p>DNA methylation is a critical epigenetic regulator of development in mammals and social insects, but its significance in development outside these groups is not understood. Here we investigated the genome-wide dynamics of DNA methylation in a mollusc model, the oyster Crassostrea gigas, from the egg to the completion of organogenesis. Large-scale methylation maps reveal that the oyster genome displays a succession of methylated and non methylated regions, which persist throughout development. Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) are strongly regulated during cleavage and metamorphosis. The distribution and levels of methylated DNA within genomic features (exons, introns, promoters, repeats and transposons) show different developmental lansdscapes marked by a strong increase in the methylation of exons against introns after metamorphosis. Kinetics of methylation in gene-bodies correlate to their transcription regulation and to distinct functional gene clusters, and DMRs at cleavage and metamorphosis bear the genes functionally related to these steps, respectively. This study shows that DNA methylome dynamics underlie development through transcription regulation in the oyster, a lophotrochozoan species. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of such epigenetic regulation outside vertebrates and ecdysozoan models, bringing new insights into the evolution and the epigenetic regulation of developmental processes.</p>',
'date' => '2017-06-08',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28594821',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-07-03 10:24:12',
'created' => '2017-07-03 10:24:12',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 88 => array(
'id' => '3186',
'name' => 'MeDIP-seq and nCpG analyses illuminate sexually dimorphic methylation of gonadal development genes with high historic methylation in turtle hatchlings with temperature-dependent sex determination',
'authors' => 'Radhakrishnan S. et al.',
'description' => '<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec1">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Background</h3>
<p id="Par1" class="Para">DNA methylation alters gene expression but not DNA sequence and mediates some cases of phenotypic plasticity. Temperature-dependent sex determination (TSD) epitomizes phenotypic plasticity where environmental temperature drives embryonic sexual fate, as occurs commonly in turtles. Importantly, the temperature-specific transcription of two genes underlying gonadal differentiation is known to be induced by differential methylation in TSD fish, turtle and alligator. Yet, how extensive is the link between DNA methylation and TSD remains unclear. Here we test for broad differences in genome-wide DNA methylation between male and female hatchling gonads of the TSD painted turtle <em xmlns="" class="EmphasisTypeItalic">Chrysemys picta</em> using methyl DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing, to identify differentially methylated candidates for future study. We also examine the genome-wide nCpG distribution (which affects DNA methylation) in painted turtles and test for historic methylation in genes regulating vertebrate gonadogenesis.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec2">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Results</h3>
<p id="Par2" class="Para">Turtle global methylation was consistent with other vertebrates (57% of the genome, 78% of all CpG dinucleotides). Numerous genes predicted to regulate turtle gonadogenesis exhibited sex-specific methylation and were proximal to methylated repeats. nCpG distribution predicted actual turtle DNA methylation and was bimodal in gene promoters (as other vertebrates) and introns (unlike other vertebrates). Differentially methylated genes, including regulators of sexual development, had lower nCpG content indicative of higher historic methylation.</p>
</div>
<div xmlns:func="http://oscar.fig.bmc.com" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" class="AbstractSection" id="ASec3">
<h3 xmlns="" class="Heading">Conclusions</h3>
<p id="Par3" class="Para">Ours is the first evidence suggesting that sexually dimorphic DNA methylation is pervasive in turtle gonads (perhaps mediated by repeat methylation) and that it targets numerous regulators of gonadal development, consistent with the hypothesis that it may regulate thermosensitive transcription in TSD vertebrates. However, further research during embryogenesis will help test this hypothesis and the alternative that instead, most differential methylation observed in hatchlings is the by-product of sexual differentiation and not its cause.</p>
</div>',
'date' => '2017-05-19',
'pmid' => 'https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-017-0136-2',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-05-22 10:21:02',
'created' => '2017-05-22 10:21:02',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 89 => array(
'id' => '3210',
'name' => 'Protective vaccination and blood-stage malaria modify DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver of Balb/c mice.',
'authors' => 'Al-Quraishy S. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation are increasingly recognized to be critical for vaccination efficacy and outcome of different infectious diseases, but corresponding information is scarcely available for host defense against malaria. In the experimental blood-stage malaria Plasmodium chabaudi, we investigate the possible effects of a blood-stage vaccine on DNA methylation of gene promoters in the liver, known as effector against blood-stage malaria, using DNA methylation microarrays. Naturally susceptible Balb/c mice acquire, by protective vaccination, the potency to survive P. chabaudi malaria and, concomitantly, modifications of constitutive DNA methylation of promoters of numerous genes in the liver; specifically, promoters of 256 genes are hyper(=up)- and 345 genes are hypo(=down)-methylated (p < 0.05). Protective vaccination also leads to changes in promoter DNA methylation upon challenge with P. chabaudi at peak parasitemia on day 8 post infection (p.i.), when 571 and 1013 gene promoters are up- and down-methylated, respectively, in relation to constitutive DNA methylation (p < 0.05). Gene set enrichment analyses reveal that both vaccination and P. chabaudi infections mainly modify promoters of those genes which are most statistically enriched with functions relating to regulation of transcription. Genes with down-methylated promoters encompass those encoding CX3CL1, GP130, and GATA2, known to be involved in monocyte recruitment, IL-6 trans-signaling, and onset of erythropoiesis, respectively. Our data suggest that vaccination may epigenetically improve parts of several effector functions of the liver against blood-stage malaria, as, e.g., recruitment of monocyte/macrophage to the liver accelerated liver regeneration and extramedullary hepatic erythropoiesis, thus leading to self-healing of otherwise lethal P. chabaudi blood-stage malaria.</p>',
'date' => '2017-05-01',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28315013',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-07-07 16:36:58',
'created' => '2017-07-07 16:36:58',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 90 => array(
'id' => '3184',
'name' => 'Comparative analysis of MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq and estimation of gene expression changes in a rodent model of schizophrenia',
'authors' => 'Neary J.L. et al.',
'description' => '<p>We conducted a comparative study of multiplexed affinity enrichment sequence methodologies (MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq) in a rodent model of schizophrenia, induced by in utero methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) exposure. We also examined related gene expression changes using a pooled sample approach. MBD-seq and MeDIP-seq identified 769 and 1771 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) between F2 offspring of MAM-exposed rats and saline control rats, respectively. The assays showed good concordance, with ~ 56% of MBD-seq-detected DMRs being identified by or proximal to MeDIP-seq DMRs. There was no significant overlap between DMRs and differentially expressed genes, suggesting that DNA methylation regulatory effects may act upon more distal genes, or are too subtle to detect using our approach. Methylation and gene expression gene ontology enrichment analyses identified biological processes important to schizophrenia pathophysiology, including neuron differentiation, prepulse inhibition, amphetamine response, and glutamatergic synaptic transmission regulation, reinforcing the utility of the MAM rodent model for schizophrenia research.</p>',
'date' => '2017-03-29',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S088875431730023X',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-05-22 09:53:51',
'created' => '2017-05-22 09:53:51',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 91 => array(
'id' => '3148',
'name' => 'Overexpression of LINE-1 Retrotransposons in Autism Brain',
'authors' => 'Shpyleva S. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Long interspersed nuclear elements-1 (LINE-1 or L1) are mobile DNA sequences that are capable of duplication and insertion (retrotransposition) within the genome. Recently, retrotransposition of L1 was shown to occur within human brain leading to somatic mosaicism in hippocampus and cerebellum. Because unregulated L1 activity can promote genomic instability and mutagenesis, multiple mechanisms including epigenetic chromatin condensation have evolved to effectively repress L1 expression. Nonetheless, L1 expression has been shown to be increased in patients with Rett syndrome and schizophrenia. Based on this evidence and our reports of oxidative stress and epigenetic dysregulation in autism cerebellum, we sought to determine whether L1 expression was increased in autism brain. The results indicated that L1 expression was significantly elevated in the autism cerebellum but not in BA9, BA22, or BA24. The binding of repressive MeCP2 and histone H3K9me3 to L1 sequences was significantly lower in autism cerebellum suggesting that relaxation of epigenetic repression may have contributed to increased expression. Further, the increase in L1 expression was inversely correlated with glutathione redox status consistent with reports indicating that L1 expression is increased under pro-oxidant conditions. Finally, the expression of transcription factor FOXO3, sensor of oxidative stress, was significantly increased and positively associated with L1 expression and negatively associated with glutathione redox status. While these novel results are an important first step, future understanding of the contribution of elevated L1 expression to neuronal CNVs and genomic instability in autism will depend on emerging cell-specific genomic technologies, a challenge that warrants future investigation.</p>',
'date' => '2017-02-20',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28220356',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-03-24 17:12:49',
'created' => '2017-03-24 17:12:49',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 92 => array(
'id' => '3092',
'name' => 'Integrative "-Omics" Analysis in Primary Human Hepatocytes Unravels Persistent Mechanisms of Cyclosporine A-Induced Cholestasis',
'authors' => 'Wolters J.E. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Cyclosporine A (CsA) is an undecapeptide with strong immunosuppressant activities and is used a lot after organ transplantation. Furthermore, it may induce cholestasis in the liver. In general, the drug-induced cholestasis (DIC) pathway includes genes involved in the uptake, synthesis, conjugation, and secretion of bile acids. However, whether CsA-induced changes in the cholestasis pathway in vitro are persistent for repeated dose toxicity has not yet been investigated. To explore this, primary human hepatocytes (PHH) were exposed to a subcytotoxic dose of 30 μM CsA daily for 3 and 5 days. To investigate the persistence of induced changes upon terminating CsA exposure after 5 days, a subset of PHH was subjected to a washout period (WO-period) of 3 days. Multiple -omics analyses, comprising whole genome analysis of DNA methylation, gene expression, and microRNA expression, were performed. The CsA-treatment resulted after 3 and 5 days, respectively, in 476 and 20 differentially methylated genes (DMGs), 1353 and 1481 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and in 22 and 29 differentially expressed microRNAs (DE-miRs). Cholestasis-related pathways appeared induced during CsA-treatment. Interestingly, 828 persistent DEGs and 6 persistent DE-miRs but no persistent DMGs were found after the WO-period. These persistent DEGs and DE-miRs showed concordance for 22 genes. Furthermore, 29 persistent DEGs changed into the same direction as observed in livers from cholestasis patients. None of those 29 DEGs which among others relate to oxidative stress and lipid metabolism are yet present in the DIC pathway or cholestasis adverse outcome pathway (AOP) thus presenting novel findings. In summary, we have demonstrated for the first time a persistent impact of repeated dose administration of CsA on genes and microRNAs related to DIC in the gold standard human liver in vitro model with PHH.</p>',
'date' => '2016-12-19',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27989131',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2017-01-03 10:33:43',
'created' => '2017-01-03 10:33:43',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 93 => array(
'id' => '3086',
'name' => 'Genome-wide DNA promoter methylation and transcriptome analysis in human adipose tissue unravels novel candidate genes for obesity',
'authors' => 'Keller M. et al.',
'description' => '<h4 id="absSec_1">Objective/methods</h4>
<p id="abspara0010">DNA methylation plays an important role in obesity and related metabolic complications. We examined genome-wide DNA promoter methylation along with mRNA profiles in paired samples of human subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) and omental visceral adipose tissue (OVAT) from non-obese <em>vs.</em> obese individuals.</p>
<h4 id="absSec_2">Results</h4>
<p id="abspara0015">We identified negatively correlated methylation and expression of several obesity-associated genes in our discovery dataset and <em>in silico</em> replicated <em>ETV6</em> in two independent cohorts. Further, we identified six adipose tissue depot-specific genes (<em>HAND2</em>, <em>HOXC6</em>, <em>PPARG</em>, <em>SORBS2</em>, <em>CD36</em>, and <em>CLDN1</em>). The effects were further supported in additional independent cohorts. Our top hits might play a role in adipogenesis and differentiation, obesity, lipid metabolism, and adipose tissue expandability. Finally, we show that <em>in vitro</em> methylation of <em>SORBS2</em> directly represses gene expression.</p>
<h4 id="absSec_3">Conclusions</h4>
<p id="abspara0020">Taken together, our data show distinct tissue specific epigenetic alterations which associate with obesity.</p>',
'date' => '2016-11-16',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2212877816302757',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-12-21 10:36:19',
'created' => '2016-12-21 10:36:19',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 94 => array(
'id' => '3061',
'name' => 'Novel regional age-associated DNA methylation changes within human common disease-associated loci',
'authors' => 'Bell CG et al.',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Advancing age progressively impacts on risk and severity of chronic disease. It also modifies the epigenome, with changes in DNA methylation, due to both random drift and variation within specific functional loci.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">In a discovery set of 2238 peripheral-blood genome-wide DNA methylomes aged 19-82 years, we identify 71 age-associated differentially methylated regions within the linkage disequilibrium blocks of the single nucleotide polymorphisms from the NIH genome-wide association study catalogue. This included 52 novel regions, 29 within loci not covered by 450 k or 27 k Illumina array, and with enrichment for DNase-I Hypersensitivity sites across the full range of tissues. These age-associated differentially methylated regions also show marked enrichment for enhancers and poised promoters across multiple cell types. In a replication set of 2084 DNA methylomes, 95.7 % of the age-associated differentially methylated regions showed the same direction of ageing effect, with 80.3 % and 53.5 % replicated to p < 0.05 and p < 1.85 × 10<sup>-8</sup>, respectively.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">By analysing the functionally enriched disease and trait-associated regions of the human genome, we identify novel epigenetic ageing changes, which could be useful biomarkers or provide mechanistic insights into age-related common diseases.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2016-09-26',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27663977',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-11-04 10:56:10',
'created' => '2016-11-02 09:54:21',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 95 => array(
'id' => '3058',
'name' => 'Inheritable Silencing of Endogenous Genes by Hit-and-Run Targeted Epigenetic Editing',
'authors' => 'Amabile A. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Gene silencing is instrumental to interrogate gene function and holds promise for therapeutic applications. Here, we repurpose the endogenous retroviruses' silencing machinery of embryonic stem cells to stably silence three highly expressed genes in somatic cells by epigenetics. This was achieved by transiently expressing combinations of engineered transcriptional repressors that bind to and synergize at the target locus to instruct repressive histone marks and de novo DNA methylation, thus ensuring long-term memory of the repressive epigenetic state. Silencing was highly specific, as shown by genome-wide analyses, sharply confined to the targeted locus without spreading to nearby genes, resistant to activation induced by cytokine stimulation, and relieved only by targeted DNA demethylation. We demonstrate the portability of this technology by multiplex gene silencing, adopting different DNA binding platforms and interrogating thousands of genomic loci in different cell types, including primary T lymphocytes. Targeted epigenome editing might have broad application in research and medicine.</p>',
'date' => '2016-09-22',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27662090',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-10-27 15:48:08',
'created' => '2016-10-27 15:48:08',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 96 => array(
'id' => '3047',
'name' => 'Trichloroethylene-Induced DNA Methylation Changes in Male F344 Rat Liver',
'authors' => 'Jiang Y. et al.',
'description' => '<p>Trichloroethylene (TCE), a common environmental contaminant, causes hepatocellular carcinoma in mice but not in rats. To understand the mechanisms of the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE, we examined the methylation status of DNA in the liver of rats exposed to TCE at 0 or 1000 mg/kg b.w. for 5 days using MeDIP-chip, bisulfite sequencing, COBRA, and LC-MS/MS. The related mRNA expression levels were measured by qPCR. Although no global DNA methylation change was detected, 806 genes were hypermethylated and 186 genes were hypomethylated. The genes with hypermethylated DNA were enriched in endocytosis, MAPK, and cAMP signaling pathways. We further confirmed the hypermethylation of Uhrf2 DNA and the hypomethylation of Hadhb DNA, which were negatively correlated with their mRNA expression levels. The transcriptional levels of Jun, Ihh, and Tet2 were significantly downregulated, whereas Cdkn1a was overexpressed. No mRNA expression change was found for Mki67, Myc, Uhrf1, and Dnmt1. In conclusion, TCE-induced DNA methylation changes in rats appear to suppress instead of promote hepatocarcinogenesis, which might play a role in the species-specific hepatocarcinogenecity of TCE.</p>',
'date' => '2016-09-21',
'pmid' => 'https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27618143',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-10-10 11:10:05',
'created' => '2016-10-10 11:10:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 97 => array(
'id' => '3001',
'name' => 'Dynamic Interplay between the Transcriptome and Methylome in Response to Oxidative and Alkylating Stress',
'authors' => 'Deferme L et al.',
'description' => '<p>In recent years, it has been shown that free radicals not only react directly with DNA but also regulate epigenetic processes such as DNA methylation, which may be relevant within the context of, for example, tumorigenesis. However, how these free radicals impact the epigenome remains unclear. We therefore investigated whether methyl and hydroxyl radicals, formed by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBH), change temporal DNA methylation patterns and how this interferes with genome-wide gene expression. At three time points, TBH-induced radicals in HepG2 cells were identified by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Total 5-methylcytosine (5mC) levels were determined by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry and genome-wide changes in 5mC and gene expression by microarrays. Induced methylome changes rather represent an adaptive response to the oxidative stress-related reactions observed in the transcriptome. More specifically, we found that methyl radicals did not induce DNA methylation directly. An initial oxidative and alkylating stress-related response of the transcriptome during the early phase of TBH treatment was followed by an epigenetic response associated with cell survival signaling. Also, we identified genes of which the expression seems directly regulated by DNA methylation. This work suggests an important role of the methylome in counter-regulating primary oxidative and alkylating stress responses in the transcriptome to restore normal cell function. Altogether, the methylome may play an important role in counter-regulating primary oxidative and alkylating stress responses in the transcriptome presumably to restore normal cell function.</p>',
'date' => '2016-08-24',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27509014',
'doi' => '',
'modified' => '2016-08-25 17:17:48',
'created' => '2016-08-25 17:17:48',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 98 => array(
'id' => '2984',
'name' => 'Efficiency of methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing for whole-genome DNA methylation analysis',
'authors' => 'Jeong HM et al.',
'description' => '<p><abstracttext label="AIMS" nlmcategory="OBJECTIVE">We compared four common methods for measuring DNA methylation levels and recommended the most efficient method in terms of cost and coverage.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>MATERIALS & METHODS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="MATERIALS & METHODS" nlmcategory="METHODS">The DNA methylation status of liver and stomach tissues was profiled using four different methods, whole-genome bisulphite sequencing (WG-BS), targeted bisulphite sequencing (Targeted-BS), methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) and methylated DNA immunoprecipitation bisulphite sequencing (MeDIP-BS). We calculated DNA methylation levels using each method and compared the results.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">MeDIP-BS yielded the most similar DNA methylation profile to WG-BS, with 20 times less data, suggesting remarkable cost savings and coverage efficiency compared with the other methods.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">MeDIP-BS is a practical cost-effective method for analyzing whole-genome DNA methylation that is highly accurate at base-pair resolution.</abstracttext></p>',
'date' => '2016-06-08',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27266718',
'doi' => ' 10.2217/epi-2016-0038',
'modified' => '2016-07-26 09:17:24',
'created' => '2016-07-26 09:17:24',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 99 => array(
'id' => '2904',
'name' => 'Aflatoxin B1 induces persistent epigenomic effects in primary human hepatocytes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma',
'authors' => 'Linda Rieswijka, Sandra M.H. Claessena, Otto Bekersc, Marcel van Herwijnena, Daniël H.J. Theunissena, Danyel G.J. Jennena, Theo M.C.M. de Koka, Jos C.S. Kleinjansa,Simone G.J. van Bredaa',
'description' => '<p><span>Chronic exposure to aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) has, in certain regions in the world, been strongly associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. AFB1 is a very potent hepatotoxic and carcinogenic mycotoxin which is frequently reported as a food contaminant. Epigenetic modifications provoked by environmental exposures, such as AFB1, may create a persistent epigenetic footprint. Deregulation of epigenetic mechanisms has actually been reported in HCC patients following AFB1 exposure; however, no attempts have yet been made to investigate early effects on the epigenome level which may be persistent on longer term, thereby possibly initiating carcinogenic events. In this study, we aim to identify methyl DNA-mRNA-interactions representative for a persistent epigenetic footprint associated with the early onset of AFB1-induced HCC. For this, primary human hepatocytes were exposed to 0.3 μM of AFB1 for 5 days. Persistent epigenetic effects were measured 3 days after terminating the carcinogenic exposure. Whole genome DNA methylation changes and whole genome transcriptomic analysis were analyzed applying microarray technologies, and cross-omics interactions were evaluated. Upon combining transcriptomics data with results on DNA methylation, a range of persistent hyper- and hypo-methylated genes was identified which also appeared affected on the transcriptome level. For six of the hypo-methylated and up-regulated genes, namely TXNRD1, PCNA, CCNK, DIAPH3, RAB27A and HIST1H2BF, a clear role in carcinogenic events could be identified. This study is the first to report on a carcinogen-induced persistent impact on the epigenetic footprint in relation with the transcriptome which could be indicative for the early onset of AFB1-related development of HCC.</span></p>',
'date' => '2016-05-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0300483X16300427',
'doi' => '10.1016/j.tox.2016.05.002',
'modified' => '2016-05-13 14:13:03',
'created' => '2016-05-08 07:29:28',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 100 => array(
'id' => '2855',
'name' => 'Paternal B Vitamin Intake Is a Determinant of Growth, Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal Tumor Volume in Female Apc1638N Mouse Offspring',
'authors' => 'Sabet JA, Park LK, Iyer LK, Tai AK, Koh GY, Pfalzer AC, Parnell LD, Mason JB, Liu Z, Byun AJ, Crott JW',
'description' => '<h3>Background</h3>
<p>The importance of maternal nutrition to offspring health and risk of disease is well established. Emerging evidence suggests paternal diet may affect offspring health as well.</p>
<h3>Objective</h3>
<p>In the current study we sought to determine whether modulating pre-conception paternal B vitamin intake alters intestinal tumor formation in offspring. Additionally, we sought to identify potential mechanisms for the observed weight differential among offspring by profiling hepatic gene expression and lipid content.</p>
<h3>Methods</h3>
<p>Male Apc<sup>1638N</sup> mice (prone to intestinal tumor formation) were fed diets containing replete (control, CTRL), mildly deficient (DEF), or supplemental (SUPP) quantities of vitamins B<sub>2</sub>, B<sub>6</sub>, B<sub>12</sub>, and folate for 8 weeks before mating with control-fed wild type females. Wild type offspring were euthanized at weaning and hepatic gene expression profiled. Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring were fed a replete diet and euthanized at 28 weeks of age to assess tumor burden.</p>
<h3>Results</h3>
<p>No differences in intestinal tumor incidence or burden were found between male Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring of different paternal diet groups. Although in female Apc<sup>1638N</sup> offspring there were no differences in tumor incidence or multiplicity, a stepwise increase in tumor volume with increasing paternal B vitamin intake was observed. Interestingly, female offspring of SUPP and DEF fathers had a significantly lower body weight than those of CTRL fed fathers. Moreover, hepatic trigylcerides and cholesterol were elevated 3-fold in adult female offspring of SUPP fathers. Weanling offspring of the same fathers displayed altered expression of several key lipid-metabolism genes. Hundreds of differentially methylated regions were identified in the paternal sperm in response to DEF and SUPP diets. Aside from a few genes including Igf2, there was a striking lack of overlap between these genes differentially methylated in sperm and differentially expressed in offspring.</p>
<h3>Conclusions</h3>
<p>In this animal model, modulation of paternal B vitamin intake prior to mating alters offspring weight gain, lipid metabolism and tumor growth in a sex-specific fashion. These results highlight the need to better define how paternal nutrition affects the health of offspring.</p>',
'date' => '2016-03-11',
'pmid' => 'http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0151579#abstract0',
'doi' => ' 10.1371/journal.pone.0151579',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 10:26:38',
'created' => '2016-03-15 10:26:38',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 101 => array(
'id' => '2977',
'name' => 'Regulation of miR-200c/141 expression by intergenic DNA-looping and transcriptional read-through',
'authors' => 'Batista L et al.',
'description' => '<p>The miR-200 family members have been implicated in stress responses and ovarian tumorigenesis. Here, we find that miR-200c/141 transcription is intimately linked to the transcription of the proximal upstream gene PTPN6 (SHP1) in all physiological conditions tested. PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 are transcriptionally co-regulated by two complementary mechanisms. First, a bypass of the regular PTPN6 polyadenylation signal allows the transcription of the downstream miR-200c/141. Second, the promoters of the PTPN6 and miR-200c/141 transcription units physically interact through a 3-dimensional DNA loop and exhibit similar epigenetic regulation. Our findings highlight that transcription of intergenic miRNAs is a novel outcome of transcriptional read-through and reveal a yet unexplored type of DNA loop associating two closely located promoters. These mechanisms have significant relevance in ovarian cancers and stress response, pathophysiological conditions in which miR-200c/141 exert key functions.</p>',
'date' => '2016-01-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26725650',
'doi' => '10.1038/ncomms9959',
'modified' => '2016-07-07 10:27:25',
'created' => '2016-07-07 10:27:25',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 102 => array(
'id' => '2951',
'name' => 'Maternal immune activation induces GAD1 and GAD2 promoter remodeling in the offspring prefrontal cortex',
'authors' => 'Labouesse MA et al.',
'description' => '<p>Maternal infection during pregnancy increases the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in the offspring. In addition to its influence on other neuronal systems, this early-life environmental adversity has been shown to negatively affect cortical γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) functions in adult life, including impaired prefrontal expression of enzymes required for GABA synthesis. The underlying molecular processes, however, remain largely unknown. In the present study, we explored whether epigenetic modifications represent a mechanism whereby maternal infection during pregnancy can induce such GABAergic impairments in the offspring. We used an established mouse model of prenatal immune challenge that is based on maternal treatment with the viral mimetic poly(I:C). We found that prenatal immune activation increased prefrontal levels of 5-methylated cytosines (5mC) and 5-hydroxymethylated cytosines (5hmC) in the promoter region of GAD1, which encodes the 67-kDa isoform of the GABA-synthesising enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD67). The early-life challenge also increased 5mC levels at the promoter region of GAD2, which encodes the 65-kDa GAD isoform (GAD65). These effects were accompanied by elevated GAD1 and GAD2 promoter binding of methyl CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) and by reduced GAD67 and GAD65 mRNA expression. Moreover, the epigenetic modifications at the GAD1 promoter correlated with prenatal infection-induced impairments in working memory and social interaction. Our study thus highlights that hypermethylation of GAD1 and GAD2 promoters may be an important molecular mechanism linking prenatal infection to presynaptic GABAergic impairments and associated behavioral and cognitive abnormalities in the offspring.</p>',
'date' => '2015-12-02',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26575259',
'doi' => ' 10.1080/15592294.2015.1114202',
'modified' => '2016-06-10 16:32:32',
'created' => '2016-06-10 16:32:32',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 103 => array(
'id' => '2860',
'name' => 'DNA methylation profiling: comparison of genome-wide sequencing methods and the Infinium Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip',
'authors' => 'Walker DL, Bhagwate AV, Baheti S, Smalley RL, Hilker CA, Sun Z, Cunningham JM',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>AIMS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="AIMS" nlmcategory="OBJECTIVE">To compare the performance of four sequence-based and one microarray methods for DNA methylation profiling.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>METHODS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="METHODS" nlmcategory="METHODS">DNA from two cell lines were profiled by reduced representation bisulfite sequencing, methyl capture sequencing (SS-Meth Seq), NimbleGen SeqCapEpi CpGiant(Nimblegen MethSeq), methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) and the Human Methylation 450 Bead Chip (Meth450K).</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS & CONCLUSION:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS & CONCLUSION" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">Despite differences in genome-wide coverage, high correlation and concordance were observed between different methods. Significant overlap of differentially methylated regions was identified between sequenced-based platforms. MeDIP provided the best coverage for the whole genome and gene body regions, while RRBS and Nimblegen MethSeq were superior for CpGs in CpG islands and promoters. Methylation analyses can be achieved by any of the five methods but understanding their differences may better address the research question being posed.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-12-01',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26192535',
'doi' => '10.2217/EPI.15.64',
'modified' => '2016-03-16 11:06:05',
'created' => '2016-03-16 11:06:05',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 104 => array(
'id' => '2892',
'name' => 'High cortisol in 5-year-old children causes loss of DNA methylation in SINE retrotransposons: a possible role for ZNF263 in stress-related diseases',
'authors' => 'Nätt D, Johansson I, Faresjö T, Ludvigsson J, Thorsell A',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Childhood stress leads to increased risk of many adult diseases, such as major depression and cardiovascular disease. Studies show that adults with experienced childhood stress have specific epigenetic changes, but to understand the pathways that lead to disease, we also need to study the epigenetic link prospectively in children.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Here, we studied a homogenous group of 48 5-year-old children. By combining hair cortisol measurements (a well-documented biomarker for chronic stress), with whole-genome DNA-methylation sequencing, we show that high cortisol associates with a genome-wide decrease in DNA methylation and targets short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs; a type of retrotransposon) and genes important for calcium transport: phenomena commonly affected in stress-related diseases and in biological aging. More importantly, we identify a zinc-finger transcription factor, ZNF263, whose binding sites where highly overrepresented in regions experiencing methylation loss. This type of zinc-finger protein has previously shown to be involved in the defense against retrotransposons.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">Our results show that stress in preschool children leads to changes in DNA methylation similar to those seen in biological aging. We suggest that this may affect future disease susceptibility by alterations in the epigenetic mechanisms that keep retrotransposons dormant. Future treatments for stress- and age-related diseases may therefore seek to target zinc-finger proteins that epigenetically control retrotransposon reactivation, such as ZNF263.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-09-04',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26339299',
'doi' => ' 10.1186/s13148-015-0123-z',
'modified' => '2016-04-14 10:03:28',
'created' => '2016-04-14 10:03:28',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 105 => array(
'id' => '2857',
'name' => 'Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo',
'authors' => 'Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associated with disturbed blood flow. DNA methylation is a powerful epigenetic regulator of endothelial transcription recently associated with flow characteristics. We investigated differential DNA methylation in flow region-specific aortic endothelial cells in vivo in adult domestic male and female swine.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Genome-wide DNA methylation was profiled in endothelial cells (EC) isolated from two robust locations of differing patho-susceptibility:--an athero-susceptible site located at the inner curvature of the aortic arch (AA) and an athero-protected region in the descending thoracic (DT) aorta. Complete methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) identified over 5500 endothelial differentially methylated regions (DMRs). DMR density was significantly enriched in exons and 5'UTR sequences of annotated genes, 60 of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. The set of DMR-associated genes was enriched in transcriptional regulation, pattern specification HOX loci, oxidative stress and the ER stress adaptive pathway, all categories linked to athero-susceptible endothelium. Examination of the relationship between DMR and mRNA in HOXA genes demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between CpG island promoter methylation and gene expression. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) confirmed differential CpG methylation of HOXA genes, the ER stress gene ATF4, inflammatory regulator microRNA-10a and ARHGAP25 that encodes a negative regulator of Rho GTPases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Gender-specific DMRs associated with ciliogenesis that may be linked to defects in cilia development were also identified in AA DMRs.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">An endothelial methylome analysis identifies epigenetic DMR characteristics associated with transcriptional regulation in regions of atherosusceptibility in swine aorta in vivo. The data represent the first methylome blueprint for spatio-temporal analyses of lesion susceptibility predisposing to endothelial dysfunction in complex flow environments in vivo.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-07-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12864-015-1656-4',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'created' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
),
'Testimonial' => array(),
'Area' => array(),
'SafetySheet' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '656',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS US en',
'language' => 'en',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-US-en-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'US',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:56:19',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:56:19',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '654',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS GB en',
'language' => 'en',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-GB-en-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'GB',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:28',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:28',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '649',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE fr',
'language' => 'fr',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-fr-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:52:41',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:52:41',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '653',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS FR fr',
'language' => 'fr',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-FR-fr-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'FR',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:02',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:02',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '652',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS ES es',
'language' => 'es',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-ES-es-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'ES',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:54:39',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:54:39',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '651',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS DE de',
'language' => 'de',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-DE-de-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'DE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:54:02',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:54:02',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 6 => array(
'id' => '655',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS JP ja',
'language' => 'ja',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-JP-ja-1_1.pdf',
'countries' => 'JP',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:55:55',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:55:55',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 7 => array(
'id' => '650',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE nl',
'language' => 'nl',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-nl-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
)
)
$meta_canonical = 'https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns'
$country = 'US'
$countries_allowed = array(
(int) 0 => 'CA',
(int) 1 => 'US',
(int) 2 => 'IE',
(int) 3 => 'GB',
(int) 4 => 'DK',
(int) 5 => 'NO',
(int) 6 => 'SE',
(int) 7 => 'FI',
(int) 8 => 'NL',
(int) 9 => 'BE',
(int) 10 => 'LU',
(int) 11 => 'FR',
(int) 12 => 'DE',
(int) 13 => 'CH',
(int) 14 => 'AT',
(int) 15 => 'ES',
(int) 16 => 'IT',
(int) 17 => 'PT'
)
$outsource = false
$other_formats = array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
)
)
$pro = array(
'id' => '1879',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<p> <span>Features</span></p>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species</strong></li>
</ul>
<div class="small-12 medium-3 large-3 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="208" height="221" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-9 large-9 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP Kit x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '10 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010020',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-A10',
'sf_code' => 'C02010020-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '315',
'price_USD' => '390',
'price_GBP' => '295',
'price_JPY' => '51615',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '975',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => false,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => false,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x10-10-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:56:31',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20',
'ProductsGroup' => array(
'id' => '10',
'product_id' => '1879',
'group_id' => '7'
)
)
$edit = ''
$testimonials = ''
$featured_testimonials = ''
$related_products = '<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit"><img src="/img/product/reagents/diamag02.png" alt="some alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">B04000001</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-1819" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/1819" id="CartAdd/1819Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="1819" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'B04000001',
'240',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack',
'B04000001',
'240',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="diamag02-magnetic-rack-1-unit" data-reveal-id="cartModal-1819" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">DiaMag 0.2ml - magnetic rack</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17031043-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2597" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2597" id="CartAdd/2597Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2597" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17031043-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17031043-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="rat-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2597" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Rat TSH2B coding region primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17031046-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2599" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2599" id="CartAdd/2599Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2599" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'C17031046-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair',
'C17031046-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="rat-gapdh-promoter-0-3-kb-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2599" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Rat GAPDH promoter +0.3 kb primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17021042-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2593" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2593" id="CartAdd/2593Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2593" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17021042-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair',
'C17021042-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="mouse-tsh2b-coding-region-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2593" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Mouse TSH2B coding region primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul"><img src="/img/grey-logo.jpg" alt="default alt" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C17021045-50</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: ADD TO CART MODAL --><div id="cartModal-2595" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<form action="/en/carts/add/2595" id="CartAdd/2595Form" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Cart][product_id]" value="2595" id="CartProductId"/>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<p>Add <input name="data[Cart][quantity]" placeholder="1" value="1" min="1" style="width:60px;display:inline" type="number" id="CartQuantity" required="required"/> <strong> Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair</strong> to my shopping cart.</p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'C17021045-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="checkout" id="checkout" value="checkout" type="submit">Checkout</button> </div>
<div class="small-6 medium-6 large-6 columns">
<button class="alert small button expand" onclick="$(this).addToCart('Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair',
'C17021045-50',
'60',
$('#CartQuantity').val());" name="keepshop" id="keepshop" type="submit">Keep shopping</button> </div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</form><a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: ADD TO CART MODAL --><a href="#" id="mouse-gapdh-promoter-primer-pair-50-ul" data-reveal-id="cartModal-2595" class="" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-cart-plus"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Mouse GAPDH promoter primer pair</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/auto-magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns"><img src="/img/product/kits/methyl-kit-icon.png" alt="Methylation kit icon" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">C02010014</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Auto MagMeDIP qPCR Kit - ordering reference: C0...</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
<li>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 columns">
<a href="/en/p/bioruptorpico2"><img src="/img/product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-1.jpg" alt="Bioruptor Pico" class="th"/></a> </div>
<div class="small-12 columns">
<div class="small-6 columns" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px;margin-left:-1px">
<span class="success label" style="">B01080010</span>
</div>
<div class="small-6 columns text-right" style="padding-left:0px;padding-right:0px;margin-top:-6px">
<!--a href="#" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a-->
<!-- BEGIN: QUOTE MODAL --><div id="quoteModal-3046" class="reveal-modal small" data-reveal aria-labelledby="modalTitle" aria-hidden="true" role="dialog">
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-12 large-12 columns">
<h3>Get a quote</h3><p class="lead">You are about to request a quote for <strong>Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device</strong>. Fill out the form below and we will be in touch with you very soon.</p><p><small>All <span style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</span> fields are mandatory</small></p>
</div>
</div>
<form action="/en/quotes/quote?id=3046" id="Quote-3046" class="quote" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8"><div style="display:none;"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="POST"/></div><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][product_id]" value="3046" id="QuoteProductId"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][formLoaded6tY4bPYk]" value="c0sveHAvS0dieWhxT3RCV3dlb3pnUT09" id="QuoteFormLoaded6tY4bPYk"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][product_rfq_tag]" value="bioruptorpico2" id="QuoteProductRfqTag"/><input type="hidden" name="data[Quote][source_quote]" value="modal quote" id="QuoteSourceQuote"/>
<div class="row collapse">
<h2>Contact Information</h2>
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">First name <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][first_name]" placeholder="john" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteFirstName" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Last name <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][last_name]" placeholder="doe" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteLastName" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Company <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][company]" placeholder="Organisation / Institute" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteCompany" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Phone number</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][phone_number]" placeholder="+1 862 209-4680" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuotePhoneNumber"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">City</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][city]" placeholder="Denville" maxlength="255" type="text" id="QuoteCity"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Country <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<select name="data[Quote][country]" required="required" class="triggers" id="country_selector_quote-3046">
<option value="">-- select a country --</option>
<option value="AF">Afghanistan</option>
<option value="AX">Åland Islands</option>
<option value="AL">Albania</option>
<option value="DZ">Algeria</option>
<option value="AS">American Samoa</option>
<option value="AD">Andorra</option>
<option value="AO">Angola</option>
<option value="AI">Anguilla</option>
<option value="AQ">Antarctica</option>
<option value="AG">Antigua and Barbuda</option>
<option value="AR">Argentina</option>
<option value="AM">Armenia</option>
<option value="AW">Aruba</option>
<option value="AU">Australia</option>
<option value="AT">Austria</option>
<option value="AZ">Azerbaijan</option>
<option value="BS">Bahamas</option>
<option value="BH">Bahrain</option>
<option value="BD">Bangladesh</option>
<option value="BB">Barbados</option>
<option value="BY">Belarus</option>
<option value="BE">Belgium</option>
<option value="BZ">Belize</option>
<option value="BJ">Benin</option>
<option value="BM">Bermuda</option>
<option value="BT">Bhutan</option>
<option value="BO">Bolivia</option>
<option value="BQ">Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba</option>
<option value="BA">Bosnia and Herzegovina</option>
<option value="BW">Botswana</option>
<option value="BV">Bouvet Island</option>
<option value="BR">Brazil</option>
<option value="IO">British Indian Ocean Territory</option>
<option value="BN">Brunei Darussalam</option>
<option value="BG">Bulgaria</option>
<option value="BF">Burkina Faso</option>
<option value="BI">Burundi</option>
<option value="KH">Cambodia</option>
<option value="CM">Cameroon</option>
<option value="CA">Canada</option>
<option value="CV">Cape Verde</option>
<option value="KY">Cayman Islands</option>
<option value="CF">Central African Republic</option>
<option value="TD">Chad</option>
<option value="CL">Chile</option>
<option value="CN">China</option>
<option value="CX">Christmas Island</option>
<option value="CC">Cocos (Keeling) Islands</option>
<option value="CO">Colombia</option>
<option value="KM">Comoros</option>
<option value="CG">Congo</option>
<option value="CD">Congo, The Democratic Republic of the</option>
<option value="CK">Cook Islands</option>
<option value="CR">Costa Rica</option>
<option value="CI">Côte d'Ivoire</option>
<option value="HR">Croatia</option>
<option value="CU">Cuba</option>
<option value="CW">Curaçao</option>
<option value="CY">Cyprus</option>
<option value="CZ">Czech Republic</option>
<option value="DK">Denmark</option>
<option value="DJ">Djibouti</option>
<option value="DM">Dominica</option>
<option value="DO">Dominican Republic</option>
<option value="EC">Ecuador</option>
<option value="EG">Egypt</option>
<option value="SV">El Salvador</option>
<option value="GQ">Equatorial Guinea</option>
<option value="ER">Eritrea</option>
<option value="EE">Estonia</option>
<option value="ET">Ethiopia</option>
<option value="FK">Falkland Islands (Malvinas)</option>
<option value="FO">Faroe Islands</option>
<option value="FJ">Fiji</option>
<option value="FI">Finland</option>
<option value="FR">France</option>
<option value="GF">French Guiana</option>
<option value="PF">French Polynesia</option>
<option value="TF">French Southern Territories</option>
<option value="GA">Gabon</option>
<option value="GM">Gambia</option>
<option value="GE">Georgia</option>
<option value="DE">Germany</option>
<option value="GH">Ghana</option>
<option value="GI">Gibraltar</option>
<option value="GR">Greece</option>
<option value="GL">Greenland</option>
<option value="GD">Grenada</option>
<option value="GP">Guadeloupe</option>
<option value="GU">Guam</option>
<option value="GT">Guatemala</option>
<option value="GG">Guernsey</option>
<option value="GN">Guinea</option>
<option value="GW">Guinea-Bissau</option>
<option value="GY">Guyana</option>
<option value="HT">Haiti</option>
<option value="HM">Heard Island and McDonald Islands</option>
<option value="VA">Holy See (Vatican City State)</option>
<option value="HN">Honduras</option>
<option value="HK">Hong Kong</option>
<option value="HU">Hungary</option>
<option value="IS">Iceland</option>
<option value="IN">India</option>
<option value="ID">Indonesia</option>
<option value="IR">Iran, Islamic Republic of</option>
<option value="IQ">Iraq</option>
<option value="IE">Ireland</option>
<option value="IM">Isle of Man</option>
<option value="IL">Israel</option>
<option value="IT">Italy</option>
<option value="JM">Jamaica</option>
<option value="JP">Japan</option>
<option value="JE">Jersey</option>
<option value="JO">Jordan</option>
<option value="KZ">Kazakhstan</option>
<option value="KE">Kenya</option>
<option value="KI">Kiribati</option>
<option value="KP">Korea, Democratic People's Republic of</option>
<option value="KR">Korea, Republic of</option>
<option value="KW">Kuwait</option>
<option value="KG">Kyrgyzstan</option>
<option value="LA">Lao People's Democratic Republic</option>
<option value="LV">Latvia</option>
<option value="LB">Lebanon</option>
<option value="LS">Lesotho</option>
<option value="LR">Liberia</option>
<option value="LY">Libya</option>
<option value="LI">Liechtenstein</option>
<option value="LT">Lithuania</option>
<option value="LU">Luxembourg</option>
<option value="MO">Macao</option>
<option value="MK">Macedonia, Republic of</option>
<option value="MG">Madagascar</option>
<option value="MW">Malawi</option>
<option value="MY">Malaysia</option>
<option value="MV">Maldives</option>
<option value="ML">Mali</option>
<option value="MT">Malta</option>
<option value="MH">Marshall Islands</option>
<option value="MQ">Martinique</option>
<option value="MR">Mauritania</option>
<option value="MU">Mauritius</option>
<option value="YT">Mayotte</option>
<option value="MX">Mexico</option>
<option value="FM">Micronesia, Federated States of</option>
<option value="MD">Moldova</option>
<option value="MC">Monaco</option>
<option value="MN">Mongolia</option>
<option value="ME">Montenegro</option>
<option value="MS">Montserrat</option>
<option value="MA">Morocco</option>
<option value="MZ">Mozambique</option>
<option value="MM">Myanmar</option>
<option value="NA">Namibia</option>
<option value="NR">Nauru</option>
<option value="NP">Nepal</option>
<option value="NL">Netherlands</option>
<option value="NC">New Caledonia</option>
<option value="NZ">New Zealand</option>
<option value="NI">Nicaragua</option>
<option value="NE">Niger</option>
<option value="NG">Nigeria</option>
<option value="NU">Niue</option>
<option value="NF">Norfolk Island</option>
<option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands</option>
<option value="NO">Norway</option>
<option value="OM">Oman</option>
<option value="PK">Pakistan</option>
<option value="PW">Palau</option>
<option value="PS">Palestine, State of</option>
<option value="PA">Panama</option>
<option value="PG">Papua New Guinea</option>
<option value="PY">Paraguay</option>
<option value="PE">Peru</option>
<option value="PH">Philippines</option>
<option value="PN">Pitcairn</option>
<option value="PL">Poland</option>
<option value="PT">Portugal</option>
<option value="PR">Puerto Rico</option>
<option value="QA">Qatar</option>
<option value="RE">Réunion</option>
<option value="RO">Romania</option>
<option value="RU">Russian Federation</option>
<option value="RW">Rwanda</option>
<option value="BL">Saint Barthélemy</option>
<option value="SH">Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha</option>
<option value="KN">Saint Kitts and Nevis</option>
<option value="LC">Saint Lucia</option>
<option value="MF">Saint Martin (French part)</option>
<option value="PM">Saint Pierre and Miquelon</option>
<option value="VC">Saint Vincent and the Grenadines</option>
<option value="WS">Samoa</option>
<option value="SM">San Marino</option>
<option value="ST">Sao Tome and Principe</option>
<option value="SA">Saudi Arabia</option>
<option value="SN">Senegal</option>
<option value="RS">Serbia</option>
<option value="SC">Seychelles</option>
<option value="SL">Sierra Leone</option>
<option value="SG">Singapore</option>
<option value="SX">Sint Maarten (Dutch part)</option>
<option value="SK">Slovakia</option>
<option value="SI">Slovenia</option>
<option value="SB">Solomon Islands</option>
<option value="SO">Somalia</option>
<option value="ZA">South Africa</option>
<option value="GS">South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands</option>
<option value="ES">Spain</option>
<option value="LK">Sri Lanka</option>
<option value="SD">Sudan</option>
<option value="SR">Suriname</option>
<option value="SS">South Sudan</option>
<option value="SJ">Svalbard and Jan Mayen</option>
<option value="SZ">Swaziland</option>
<option value="SE">Sweden</option>
<option value="CH">Switzerland</option>
<option value="SY">Syrian Arab Republic</option>
<option value="TW">Taiwan</option>
<option value="TJ">Tajikistan</option>
<option value="TZ">Tanzania</option>
<option value="TH">Thailand</option>
<option value="TL">Timor-Leste</option>
<option value="TG">Togo</option>
<option value="TK">Tokelau</option>
<option value="TO">Tonga</option>
<option value="TT">Trinidad and Tobago</option>
<option value="TN">Tunisia</option>
<option value="TR">Turkey</option>
<option value="TM">Turkmenistan</option>
<option value="TC">Turks and Caicos Islands</option>
<option value="TV">Tuvalu</option>
<option value="UG">Uganda</option>
<option value="UA">Ukraine</option>
<option value="AE">United Arab Emirates</option>
<option value="GB">United Kingdom</option>
<option value="US" selected="selected">United States</option>
<option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands</option>
<option value="UY">Uruguay</option>
<option value="UZ">Uzbekistan</option>
<option value="VU">Vanuatu</option>
<option value="VE">Venezuela</option>
<option value="VN">Viet Nam</option>
<option value="VG">Virgin Islands, British</option>
<option value="VI">Virgin Islands, U.S.</option>
<option value="WF">Wallis and Futuna</option>
<option value="EH">Western Sahara</option>
<option value="YE">Yemen</option>
<option value="ZM">Zambia</option>
<option value="ZW">Zimbabwe</option>
</select><script>
$('#country_selector_quote-3046').selectize();
</script><br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">State</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" maxlength="3" type="text"/><br />
</div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Email <sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][email]" placeholder="email@address.com" maxlength="255" type="email" id="QuoteEmail" required="required"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse" id="email_v">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Email verification<sup style="font-size:16px;color:red;">*</sup></span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<input name="data[Quote][email_v]" autocomplete="nope" type="text" id="QuoteEmailV"/> </div>
</div>
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
<span class="prefix">Comment</span>
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<textarea name="data[Quote][comment]" placeholder="Additional comments" cols="30" rows="6" id="QuoteComment"></textarea> </div>
</div>
<!------------SERVICES PARTICULAR FORM START---------------->
<!------------DATA TO POPULATE REGARDING SPECIFIC SERVICES----->
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<div class="recaptcha"><div id="recaptcha6776db64c3be6"></div></div> </div>
</div>
<br />
<div class="row collapse">
<div class="small-3 large-2 columns">
</div>
<div class="small-9 large-10 columns">
<button id="submit_btn-3046" class="alert button expand" form="Quote-3046" type="submit">Contact me</button> </div>
</div>
</form><script>
var pardotFormHandlerURL = 'https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2022-10-10/36b1c';
function postToPardot(formAction, id) {
$('#pardot-form-handler').load(function(){
$('#Quote-' + id).attr('action', formAction);
$('#Quote-' + id).submit();
});
$('#pardot-form-handler').attr('src', pardotFormHandlerURL + '?' + $('#Quote-' + id).serialize());
}
$(document).ready(function() {
$('body').append('<iframe id="pardot-form-handler" height="0" width="0" style="position:absolute; left:-100000px; top:-100000px" src="javascript:false;"></iframe>');
$('#Quote-3046').attr('action','javascript:postToPardot(\'' + $('#Quote-3046').attr('action') + '\', 3046)');
});
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").click(function (e) {
if($(this).closest('form')[0].checkValidity()){
e.preventDefault();
//disable the submit button
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").attr("disabled", true);
$("#Quote-3046 #submit_btn-3046").html("Processing...");
//submit the form
$("#Quote-3046").submit();
}
})
</script>
<script>
if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'US') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AL">Alabama (AL)</option><option value="AK">Alaska (AK)</option><option value="AZ">Arizona (AZ)</option><option value="AR">Arkansas (AR)</option><option value="CA">California (CA)</option><option value="CO">Colorado (CO)</option><option value="CT">Connecticut (CT)</option><option value="DE">Delaware (DE)</option><option value="FL">Florida (FL)</option><option value="GA">Georgia (GA)</option><option value="HI">Hawaii (HI)</option><option value="ID">Idaho (ID)</option><option value="IL">Illinois (IL)</option><option value="IN">Indiana (IN)</option><option value="IA">Iowa (IA)</option><option value="KS">Kansas (KS)</option><option value="KY">Kentucky (KY)</option><option value="LA">Louisiana (LA)</option><option value="ME">Maine (ME)</option><option value="MD">Maryland (MD)</option><option value="MA">Massachusetts (MA)</option><option value="MI">Michigan (MI)</option><option value="MN">Minnesota (MN)</option><option value="MS">Mississippi (MS)</option><option value="MO">Missouri (MO)</option><option value="MT">Montana (MT)</option><option value="NE">Nebraska (NE)</option><option value="NV">Nevada (NV)</option><option value="NH">New Hampshire (NH)</option><option value="NJ">New Jersey (NJ)</option><option value="NM">New Mexico (NM)</option><option value="NY">New York (NY)</option><option value="NC">North Carolina (NC)</option><option value="ND">North Dakota (ND)</option><option value="OH">Ohio (OH)</option><option value="OK">Oklahoma (OK)</option><option value="OR">Oregon (OR)</option><option value="PA">Pennsylvania (PA)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="RI">Rhode Island (RI)</option><option value="SC">South Carolina (SC)</option><option value="SD">South Dakota (SD)</option><option value="TN">Tennessee (TN)</option><option value="TX">Texas (TX)</option><option value="UT">Utah (UT)</option><option value="VT">Vermont (VT)</option><option value="VA">Virginia (VA)</option><option value="WA">Washington (WA)</option><option value="WV">West Virginia (WV)</option><option value="WI">Wisconsin (WI)</option><option value="WY">Wyoming (WY)</option><option value="DC">District of Columbia (DC)</option><option value="AS">American Samoa (AS)</option><option value="GU">Guam (GU)</option><option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands (MP)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands (UM)</option><option value="VI">Virgin Islands (VI)</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'CA') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AB">Alberta (AB)</option><option value="BC">British Columbia (BC)</option><option value="MB">Manitoba (MB)</option><option value="NB">New Brunswick (NB)</option><option value="NL">Newfoundland and Labrador (NL)</option><option value="NS">Nova Scotia (NS)</option><option value="ON">Ontario (ON)</option><option value="PE">Prince Edward Island (PE)</option><option value="QC">Quebec (QC)</option><option value="SK">Saskatchewan (SK)</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if ($("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").val() == 'DE') {
var val = $("#state-3046").val();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="BW">Baden-Württemberg (BW)</option><option value="BY">Bayern (BY)</option><option value="BE">Berlin (BE)</option><option value="BB">Brandeburg (BB)</option><option value="HB">Bremen (HB)</option><option value="HH">Hamburg (HH)</option><option value="HE">Hessen (HE)</option><option value="MV">Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV)</option><option value="NI">Niedersachsen (NI)</option><option value="NW">Nordrhein-Westfalen (NW)</option><option value="RP">Rheinland-Pfalz (RP)</option><option value="SL">Saarland (SL)</option><option value="SN">Sachsen (SN)</option><option value ="SA">Sachsen-Anhalt (SA)</option><option value="SH">Schleswig-Holstein (SH)</option><option value="TH">Thüringen</option></select>');
if (val.length == 2) {
$("#state-3046").val(val);
}
$("#state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().hide();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<input name="data[Quote][state]" maxlength="255" type="text" id="state-3046" value="">');
}
$("#Quote-3046 #country_selector_quote-3046.selectized").change(function() {
if (this.value == 'US') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AL">Alabama (AL)</option><option value="AK">Alaska (AK)</option><option value="AZ">Arizona (AZ)</option><option value="AR">Arkansas (AR)</option><option value="CA">California (CA)</option><option value="CO">Colorado (CO)</option><option value="CT">Connecticut (CT)</option><option value="DE">Delaware (DE)</option><option value="FL">Florida (FL)</option><option value="GA">Georgia (GA)</option><option value="HI">Hawaii (HI)</option><option value="ID">Idaho (ID)</option><option value="IL">Illinois (IL)</option><option value="IN">Indiana (IN)</option><option value="IA">Iowa (IA)</option><option value="KS">Kansas (KS)</option><option value="KY">Kentucky (KY)</option><option value="LA">Louisiana (LA)</option><option value="ME">Maine (ME)</option><option value="MD">Maryland (MD)</option><option value="MA">Massachusetts (MA)</option><option value="MI">Michigan (MI)</option><option value="MN">Minnesota (MN)</option><option value="MS">Mississippi (MS)</option><option value="MO">Missouri (MO)</option><option value="MT">Montana (MT)</option><option value="NE">Nebraska (NE)</option><option value="NV">Nevada (NV)</option><option value="NH">New Hampshire (NH)</option><option value="NJ">New Jersey (NJ)</option><option value="NM">New Mexico (NM)</option><option value="NY">New York (NY)</option><option value="NC">North Carolina (NC)</option><option value="ND">North Dakota (ND)</option><option value="OH">Ohio (OH)</option><option value="OK">Oklahoma (OK)</option><option value="OR">Oregon (OR)</option><option value="PA">Pennsylvania (PA)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="RI">Rhode Island (RI)</option><option value="SC">South Carolina (SC)</option><option value="SD">South Dakota (SD)</option><option value="TN">Tennessee (TN)</option><option value="TX">Texas (TX)</option><option value="UT">Utah (UT)</option><option value="VT">Vermont (VT)</option><option value="VA">Virginia (VA)</option><option value="WA">Washington (WA)</option><option value="WV">West Virginia (WV)</option><option value="WI">Wisconsin (WI)</option><option value="WY">Wyoming (WY)</option><option value="DC">District of Columbia (DC)</option><option value="AS">American Samoa (AS)</option><option value="GU">Guam (GU)</option><option value="MP">Northern Mariana Islands (MP)</option><option value="PR">Puerto Rico (PR)</option><option value="UM">United States Minor Outlying Islands (UM)</option><option value="VI">Virgin Islands (VI)</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if (this.value == 'CA') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="AB">Alberta (AB)</option><option value="BC">British Columbia (BC)</option><option value="MB">Manitoba (MB)</option><option value="NB">New Brunswick (NB)</option><option value="NL">Newfoundland and Labrador (NL)</option><option value="NS">Nova Scotia (NS)</option><option value="ON">Ontario (ON)</option><option value="PE">Prince Edward Island (PE)</option><option value="QC">Quebec (QC)</option><option value="SK">Saskatchewan (SK)</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else if (this.value == 'DE') {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<select name="data[Quote][state]" id="state-3046" required><option disabled selected value> -- select a state -- </option><option value="BW">Baden-Württemberg (BW)</option><option value="BY">Bayern (BY)</option><option value="BE">Berlin (BE)</option><option value="BB">Brandeburg (BB)</option><option value="HB">Bremen (HB)</option><option value="HH">Hamburg (HH)</option><option value="HE">Hessen (HE)</option><option value="MV">Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV)</option><option value="NI">Niedersachsen (NI)</option><option value="NW">Nordrhein-Westfalen (NW)</option><option value="RP">Rheinland-Pfalz (RP)</option><option value="SL">Saarland (SL)</option><option value="SN">Sachsen (SN)</option><option value ="SA">Sachsen-Anhalt (SA)</option><option value="SH">Schleswig-Holstein (SH)</option><option value="TH">Thüringen</option></select>');
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().show();
} else {
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").parent().parent().hide();
$("#Quote-3046 #state-3046").replaceWith('<input name="data[Quote][state]" maxlength="255" type="text" id="state-3046" value="">');
}
});
</script>
<a class="close-reveal-modal" aria-label="Close">×</a></div><!-- END: QUOTE MODAL --><a href="#" id="bioruptorpico2" data-reveal-id="quoteModal-3046" class="quote_btn" style="color:#B21329"><i class="fa fa-info-circle"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="small-12 columns" >
<h6 style="height:60px">Bioruptor® Pico sonication device</h6>
</div>
</div>
</li>
'
$related = array(
'id' => '3046',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico sonication device',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://go.diagenode.com/bioruptor-upgrade"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-br-trade.png" /></a></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p><span>The Bioruptor® Pico is the latest innovation in shearing and represents a new breakthrough as an all-in-one shearing system capable of shearing samples from 150 bp to 1 kb. </span>Since 2004, Diagenode has accumulated <strong>shearing expertise</strong> to design the Bioruptor® Pico and guarantee the best experience with the <strong>sample preparation</strong> for <strong>number of applications -- in various fields of studies</strong> including environmental research, toxicology, genomics and epigenomics, cancer research, stem cells and development, neuroscience, clinical applications, agriculture, and many more.</p>
</div>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
</div>
<p>The Bioruptor Pico shearing accessories and consumables have been developed to allow <strong>flexibility in sample volumes</strong> (20 µl - 2 ml) and a <strong>fast parallel processing of samples</strong> (up to 16 samples simultaneously). <span>The built-in cooling system (Bioruptor® Cooler) ensures high precision <strong>temperature control</strong>. The <strong>user-friendly interface</strong> has been designed for any researcher, providing an easy and advanced modes that give both beginners and experienced users the right level of control. </span></p>
<p>In addition, Diagenode provides fully-validated tubes that remain <strong>budget-friendly with low operating cost</strong> (< 1€/$/DNA sample) and shearing kits for best sample quality. <span></span></p>
<p><strong>Application versatility</strong>:</p>
<ul>
<li>DNA shearing for Next-Generation-Sequencing</li>
<li>Chromatin shearing</li>
<li>RNA shearing</li>
<li>Protein extraction from tissues and cells (also for mass spectrometry)</li>
<li>FFPE DNA extraction</li>
<li>Protein aggregation studies</li>
<li>CUT&RUN - shearing of input DNA for NGS</li>
</ul>
<div style="background-color: #f1f3f4; margin: 10px; padding: 50px;">
<p><strong>Bioruptor Pico: Recommended for CUT&RUN sequencing for input DNA</strong><br /><br /> By combining antibody-targeted controlled cleavage by MNase and NGS, <strong>CUT&RUN sequencing</strong> can be used to identify protein-DNA binding sites genome-wide. CUT&RUN works by using the DNA cleaving activity of a Protein A-fused MNase to isolate DNA that is bound by a protein of interest. This targeted digestion is controlled by the addition of calcium, which MNase requires for its nuclease activity. After MNase digestion, short DNA fragments are released and can then be purified for subsequent library preparation and high-throughput sequencing. While CUT&RUN does not require mechanical shearing chromatin given the enzymatic approach, sonication is highly recommended for the fragmentation of the input DNA (used to compare the enriched sample) in order to be compatible with downstream NGS. The Bioruptor Pico is the ideal instrument of choice for generating optimal DNA fragments with a tight distribution, assuring excellent library prep and excellent sequencing results for your CUT&RUN assay.<br /><br /> <strong>Explore the Bioruptor Pico now.</strong></p>
</div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for Chromatin shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-reproducibility-is-priority.jpg" /></center></div>
<div class="extra-spaced"><center><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/pages/form-demo"> <img alt="Bioruptor Sonication for RNA shearing" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-request-demo.jpg" /></a></center></div>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label1' => 'Specifications',
'info1' => '<center><img alt="Ultrasonic Sonicator" src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/shearing_technologies/pico-table.jpg" /></center>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'label2' => 'View accessories & consumables for Bioruptor<sup>®</sup> Pico',
'info2' => '<h3>Shearing Accessories</h3>
<table style="width: 641px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Catalog number</td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;">Throughput</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-2-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.2 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201144</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">16 samples</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 0.65 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201143</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">12 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 38px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 38px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-tube-holder-dock-for-bioruptor-pico">Tube holder for 1.5 ml tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01201140</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 38px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 300px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-sonication-accessories-for-bioruptor-standard-plus-pico-1-pack">15 ml sonication accessories</a></td>
<td style="width: 171px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">B01200016</span></td>
<td style="width: 160px; text-align: center; height: 37px;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">6 samples<br /></span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<h3>Shearing Consumables</h3>
<table style="width: 646px;">
<thead>
<tr style="background-color: #dddddd; height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><strong>Name</strong></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;">Catalog Number</td>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/02ml-microtubes-for-bioruptor-pico">0.2 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010020</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/0-65-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-500-tubes">0.65 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010011</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/1-5-ml-bioruptor-microtubes-with-caps-300-tubes">1.5 ml Pico Microtubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010016</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-50-pc">15 ml Pico Tubes</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C30010017</span></td>
</tr>
<tr style="height: 37px;">
<td style="width: 286px; height: 37px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/15-ml-bioruptor-tubes-sonication-beads-50-rxns">15 ml Pico Tubes & sonication beads</a></td>
<td style="width: 76px; height: 37px; text-align: center;"><span style="font-weight: 400;">C01020031</span></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/shearing_technology/bioruptor_accessories/TDS-BioruptorTubes.pdf">Find datasheet for Diagenode tubes here</a></p>
<p><a href="../documents/bioruptor-organigram-tubes">Which tubes for which Bioruptor®?</a></p>',
'label3' => 'Available shearing Kits',
'info3' => '<p>Diagenode has optimized a range of solutions for <strong>successful chromatin preparation</strong>. Chromatin EasyShear Kits together with the Pico ultrasonicator combine the benefits of efficient cell lysis and chromatin shearing, while keeping epitopes accessible to the antibody, critical for efficient chromatin immunoprecipitation. Each Chromatin EasyShear Kit provides optimized reagents and a thoroughly validated protocol according to your specific experimental needs. SDS concentration is adapted to each workflow taking into account target-specific requirements.</p>
<p>For best results, choose your desired ChIP kit followed by the corresponding Chromatin EasyShear Kit (to optimize chromatin shearing ). The Chromatin EasyShear Kits can be used independently of Diagenode’s ChIP kits for chromatin preparation prior to any chromatin immunoprecipitation protocol. Choose an appropriate kit for your specific experimental needs.</p>
<h2>Kit choice guide</h2>
<table style="border: 0;" valign="center">
<tbody>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<th class="text-center"></th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE TYPE</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SAMPLE INPUT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">KIT</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">SDS<br /> CONCENTRATION</th>
<th class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">NUCLEI<br /> ISOLATION</th>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="5"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-histones.png" /></td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">< 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-optimization-kit-high-sds-100-million-cells">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />High SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">1%</td>
<td class="text-center" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/cross-unvalid-green.jpg" width="18" height="20" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">> 100,000</td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-ultra-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Ultra Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">< 0.1%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff; border-bottom: 1px solid #dedede;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">PLANT TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-shearing-plant-chip-seq-kit">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />for Plant</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.5%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="7"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td rowspan="6"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/label-tf.png" /></td>
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">CELLS</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;"><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/chromatin-easyshear-kit-low-sds">Chromatin EasyShear Kit<br />Low SDS</a></td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center" style="font-size: 17px;">0.2%</td>
<td rowspan="3" class="text-center"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/valid.png" width="20" height="16" /></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">TISSUE</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td class="text-center">
<div class="label alert" style="font-size: 17px;">FFPE SAMPLES</div>
</td>
<td class="text-center"></td>
</tr>
<tr style="background: #fff;">
<td colspan="6"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<div class="extra-spaced">
<h3>Guide for optimal chromatin preparation using Chromatin EasyShear Kits <i class="fa fa-arrow-circle-right"></i> <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/pages/chromatin-prep-easyshear-kit-guide">Read more</a></h3>
</div>
<p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</p>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
<div id="ConnectiveDocSignExtentionInstalled" data-extension-version="1.0.4"></div>',
'format' => '1 unit',
'catalog_number' => 'B01080010',
'old_catalog_number' => '',
'sf_code' => 'B01080010-',
'type' => 'ACC',
'search_order' => '00-Machine',
'price_EUR' => '27600',
'price_USD' => '31000',
'price_GBP' => '24000',
'price_JPY' => '4522260',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '77500',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => true,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '',
'slug' => 'bioruptorpico2',
'meta_title' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Bioruptor® Pico sonication device',
'modified' => '2024-12-19 15:08:43',
'created' => '2020-01-09 16:27:17',
'ProductsRelated' => array(
'id' => '4858',
'product_id' => '1879',
'related_id' => '3046'
),
'Image' => array(
(int) 0 => array(
'id' => '1803',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-1.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:55:07',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:52:54',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 1 => array(
'id' => '1804',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-2.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:08',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:08',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 2 => array(
'id' => '1805',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-3.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:46',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:46',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 3 => array(
'id' => '1806',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-4.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:53:56',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:53:56',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 4 => array(
'id' => '1807',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B01080000-5.jpg',
'alt' => 'Bioruptor Pico',
'modified' => '2020-01-10 10:54:06',
'created' => '2020-01-10 10:54:06',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
),
(int) 5 => array(
'id' => '1772',
'name' => 'product/shearing_technologies/B010600010.jpg',
'alt' => 'B010600010',
'modified' => '2018-02-14 15:41:46',
'created' => '2018-02-14 15:41:46',
'ProductsImage' => array(
[maximum depth reached]
)
)
)
)
$rrbs_service = array(
(int) 0 => (int) 1894,
(int) 1 => (int) 1895
)
$chipseq_service = array(
(int) 0 => (int) 2683,
(int) 1 => (int) 1835,
(int) 2 => (int) 1836,
(int) 3 => (int) 2684,
(int) 4 => (int) 1838,
(int) 5 => (int) 1839,
(int) 6 => (int) 1856
)
$labelize = object(Closure) {
}
$old_catalog_number = ' <span style="color:#CCC">(mc-magme-048)</span>'
$country_code = 'US'
$other_format = array(
'id' => '1880',
'antibody_id' => null,
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit',
'description' => '<p><a href="https://www.diagenode.com/files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/buttons/bt-manual.png" /></a></p>
<p>Perform <strong>MeDIP</strong> (<strong>Me</strong>thylated <strong>D</strong>NA <strong>I</strong>mmuno<strong>p</strong>recipitation) followed by qPCR or NGS to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using a highly sensitive 5-methylcytosine antibody. Our MagMeDIP kit contains high quality reagents to get the highest enrichment of methylated DNA with an optimized user-friendly protocol.</p>
<h3><span>Features</span></h3>
<ul>
<li>Starting DNA amount: <strong>10 ng – 1 µg</strong></li>
<li>Content: <strong>all reagents included</strong> for DNA extraction, immunoprecipitation (including the 5-mC antibody, spike-in controls and their corresponding qPCR primer pairs) as well as DNA isolation after IP.</li>
<li>Application: <strong>qPCR</strong> and <strong>NGS</strong></li>
<li>Robust method, <strong>superior enrichment</strong>, and easy-to-use protocol</li>
<li><strong>High reproducibility</strong> between replicates and repetitive experiments</li>
<li>Compatible with <strong>all species </strong></li>
</ul>
<p> </p>
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center></center><center></center><center></center><center><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/banners/banner-nature-publication-580.png" alt="Click here to read more about MeDIP " caption="false" width="80%" /></a></center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns">
<h3 style="text-align: justify;">Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes<br /><a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30429608" target="_blank">Read the publication</a></h3>
<h3 class="c-article-title u-h1" data-test="article-title" itemprop="name headline" style="text-align: justify;">Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA<br /><a href="https://www.nature.com/articles/s41596-019-0202-2" target="_blank" title="cfMeDIP-seq Nature Method">Read the method</a></h3>
</div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<div class="row">
<div class="small-12 medium-4 large-4 columns"><center>
<script>// <![CDATA[
var date = new Date(); var heure = date.getHours(); var jour = date.getDay(); var semaine = Math.floor(date.getDate() / 7) + 1; if (jour === 2 && ( (heure >= 9 && heure < 9.5) || (heure >= 18 && heure < 18.5) )) { document.write('<a href="https://us02web.zoom.us/j/85467619762"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-ON.gif"></a>'); } else { document.write('<a href="https://go.diagenode.com/l/928883/2023-04-26/3kq1v"><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/epicafe-OFF.png"></a>'); }
// ]]></script>
</center></div>
<div class="small-12 medium-8 large-8 columns"><br />
<p></p>
</div>
</div>
<h3></h3>',
'label1' => 'MagMeDIP workflow',
'info1' => '<p>DNA methylation occurs primarily as 5-methylcytosine (5-mC), and the Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit takes advantage of a specific antibody targeting this 5-mC to immunoprecipitate methylated DNA, which can be thereafter directly analyzed by qPCR or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).</p>
<h3><span>How it works</span></h3>
<p>In brief, after the cell collection and lysis, the genomic DNA is extracted, sheared, and then denatured. In the next step the antibody directed against 5 methylcytosine and antibody binding beads are used for immunoselection and immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA fragments. Then, the IP’d methylated DNA is isolated and can be used for any subsequent analysis as qPCR, amplification, hybridization on microarrays or next generation sequencing.</p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MagMeDIP-workflow.png" width="70%" alt="5-methylcytosine" caption="false" /></center>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label2' => 'MeDIP-qPCR',
'info2' => '<p>The kit MagMeDIP contains all reagents necessary for a complete MeDIP-qPCR workflow. Two MagMeDIP protocols have been validated: for manual processing as well as for automated processing, using the Diagenode’s IP-Star Compact Automated System (please refer to the kit manual).</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Complete kit</strong> including DNA extraction module, IP antibody and reagents, DNA isolation buffer</li>
<li><strong>Quality control of the IP:</strong> due to methylated and unmethylated DNA spike-in controls and their associated qPCR primers</li>
<li><strong>Easy to use</strong> with user-friendly magnetic beads and rack</li>
<li><strong>Highly validated protocol</strong></li>
<li>Automated protocol supplied</li>
</ul>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/fig1-magmedipkit.png" width="85%" alt="Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation" caption="false" /></center>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><em><strong>Figure 1.</strong> Immunoprecipitation results obtained with Diagenode MagMeDIP Kit</em></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;">MeDIP assays were performed manually using 1 µg or 50 ng gDNA from blood cells with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode). The IP was performed with the Methylated and Unmethylated spike-in controls included in the kit, together with the human DNA samples. The DNA was isolated/purified using DIB. Afterwards, qPCR was performed using the primer pairs included in this kit.</p>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>',
'label3' => 'MeDIP-seq',
'info3' => '<p>For DNA methylation analysis on the whole genome, MagMeDIP kit can be coupled with Next-Generation Sequencing. To perform MeDIP-sequencing we recommend the following strategy:</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Choose a library preparation solution which is compatible with the starting amount of DNA you are planning to use (from 10 ng to 1 μg). It can be a home-made solution or a commercial one.</li>
<li>Choose the indexing system that fits your needs considering the following features:</li>
<ul>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>Single-indexing, combinatorial dual-indexing or unique dual-indexing</li>
<li>Number of barcodes</li>
<li>Full-length adaptors containing the barcodes or barcoding at the final amplification step</li>
<li>Presence / absence of Unique Molecular Identifiers (for PCR duplicates removal)</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</ul>
<li>Standard library preparation protocols are compatible with double-stranded DNA only, therefore the first steps of the library preparation (end repair, A-tailing, adaptor ligation and clean-up) will have to be performed on sheared DNA, before the IP.</li>
</ul>
<p style="padding-left: 30px;"><strong>CAUTION:</strong> As the immunoprecipitation step occurs at the middle of the library preparation workflow, single-tube solutions for library preparation are usually not compatible with MeDIP-sequencing.</p>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>For DNA isolation after the IP, we recommend using the <a href="https://www.diagenode.com/en/p/ipure-kit-v2-x24" title="IPure kit v2">IPure kit v2</a> (available separately, Cat. No. C03010014) instead of DNA isolation Buffer.</li>
</ul>
<ul style="list-style-type: circle;">
<li>Perform library amplification after the DNA isolation following the standard protocol of the chosen library preparation solution.</li>
</ul>
<h3><span>MeDIP-seq workflow</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/MeDIP-seq-workflow.png" width="110%" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit x10 workflow" caption="false" /></center>
<h3><span>Example of results</span></h3>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-specificity.png" alt="MagMeDIP qPCR Kit Result" caption="false" width="951" height="488" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 1. qPCR analysis of external spike-in DNA controls (methylated and unmethylated) after IP.</strong> Samples were prepared using 1μg – 100ng -10ng sheared human gDNA with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-saturation-analysis.png" alt=" MagMeDIP kit " caption="false" width="951" height="461" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 2. Saturation analysis.</strong> Clean reads were aligned to the human genome (hg19) using Burrows-Wheeler aligner (BWA) algorithm after which duplicated and unmapped reads were removed resulting in a mapping efficiency >98% for all samples. Quality and validity check of the mapped MeDIP-seq data was performed using MEDIPS R package. Saturation plots show that all sets of reads have sufficient complexity and depth to saturate the coverage profile of the reference genome and that this is reproducible between replicates and repetitive experiments (data shown for 50 ng gDNA input: left panel = replicate a, right panel = replicate b).</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<center><img src="https://www.diagenode.com/img/product/kits/medip-libraries-prep.png" alt="MagMeDIP x10 " caption="false" width="951" height="708" /></center>
<p></p>
<p style="font-size: 0.9em;"><strong>Figure 3. Sequencing profiles of MeDIP-seq libraries prepared from different starting amounts of sheared gDNA on the positive and negative methylated control regions.</strong> MeDIP-seq libraries were prepared from decreasing starting amounts of gDNA (1 μg (green), 50 ng (red), and 10ng (blue)) originating from human blood with the MagMeDIP kit (Diagenode) and a commercially available library prep kit. DNA isolation after IP has been performed with IPure kit V2 (Diagenode). IP and corresponding INPUT samples were sequenced on Illumina NovaSeq SP with 2x50 PE reads. The reads were mapped to the human genome (hg19) with bwa and the alignments were loaded into IGV (the tracks use an identical scale). The top IGV figure shows the TSH2B (also known as H2BC1) gene (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The TSH2B gene is coding for a histone variant that does not occur in blood cells, and it is known to be silenced by methylation. Accordingly, we see a high coverage in the vicinity of this gene. The bottom IGV figure shows the GADPH locus (marked by blue boxes in the bottom track) and its surroundings. The GADPH gene is a highly active transcription region and should not be methylated, resulting in no reads accumulation following MeDIP-seq experiment.</p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<ul>
<script async="" src="https://edge.fullstory.com/s/fs.js" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="chrome-extension://hhojmcideegachlhfgfdhailpfhgknjm/web_accessible_resources/index.js"></script>
</ul>
</ul>',
'format' => '48 rxns (IP)',
'catalog_number' => 'C02010021',
'old_catalog_number' => 'mc-magme-048',
'sf_code' => 'C02010021-',
'type' => 'RFR',
'search_order' => '04-undefined',
'price_EUR' => '760',
'price_USD' => '770',
'price_GBP' => '695',
'price_JPY' => '124525',
'price_CNY' => '',
'price_AUD' => '1925',
'country' => 'ALL',
'except_countries' => 'None',
'quote' => false,
'in_stock' => false,
'featured' => true,
'no_promo' => false,
'online' => true,
'master' => true,
'last_datasheet_update' => '0000-00-00',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-x48-48-rxns',
'meta_title' => 'MagMeDIP Kit for efficient immunoprecipitation of methylated DNA | Diagenode',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => 'Perform Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (MeDIP) to estimate DNA methylation status of your sample using highly specific 5-mC antibody. This kit allows the preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries.',
'modified' => '2024-12-04 16:52:47',
'created' => '2015-06-29 14:08:20'
)
$label = '<img src="/img/banners/banner-customizer-back.png" alt=""/>'
$document = array(
'id' => '1166',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP Kit ',
'description' => '',
'image_id' => null,
'type' => 'Manual',
'url' => 'files/products/kits/magmedip-kit-manual-C02010020-21.pdf',
'slug' => 'magmedip-kit-manual-c02010020-21',
'meta_keywords' => '',
'meta_description' => '',
'modified' => '2022-11-22 15:50:08',
'created' => '2022-11-22 15:41:49',
'ProductsDocument' => array(
'id' => '3257',
'product_id' => '1879',
'document_id' => '1166'
)
)
$sds = array(
'id' => '650',
'name' => 'MagMeDIP qPCR Kit SDS BE nl',
'language' => 'nl',
'url' => 'files/SDS/MagMeDIP/SDS-C02010020-MagMeDIP_qPCR_Kit-BE-nl-1_0.pdf',
'countries' => 'BE',
'modified' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'created' => '2020-07-01 16:53:22',
'ProductsSafetySheet' => array(
'id' => '1194',
'product_id' => '1879',
'safety_sheet_id' => '650'
)
)
$publication = array(
'id' => '2857',
'name' => 'Arterial endothelial methylome: differential DNA methylation in athero-susceptible disturbed flow regions in vivo',
'authors' => 'Jiang YZ1, Manduchi E2, Stoeckert CJ Jr3, Davies PF',
'description' => '<div class="">
<h4>BACKGROUND:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="BACKGROUND" nlmcategory="BACKGROUND">Atherosclerosis is a heterogeneously distributed disease of arteries in which the endothelium plays an important central role. Spatial transcriptome profiling of endothelium in pre-lesional arteries has demonstrated differential phenotypes primed for athero-susceptibility at hemodynamic sites associated with disturbed blood flow. DNA methylation is a powerful epigenetic regulator of endothelial transcription recently associated with flow characteristics. We investigated differential DNA methylation in flow region-specific aortic endothelial cells in vivo in adult domestic male and female swine.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>RESULTS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="RESULTS" nlmcategory="RESULTS">Genome-wide DNA methylation was profiled in endothelial cells (EC) isolated from two robust locations of differing patho-susceptibility:--an athero-susceptible site located at the inner curvature of the aortic arch (AA) and an athero-protected region in the descending thoracic (DT) aorta. Complete methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (MeDIP-seq) identified over 5500 endothelial differentially methylated regions (DMRs). DMR density was significantly enriched in exons and 5'UTR sequences of annotated genes, 60 of which are linked to cardiovascular disease. The set of DMR-associated genes was enriched in transcriptional regulation, pattern specification HOX loci, oxidative stress and the ER stress adaptive pathway, all categories linked to athero-susceptible endothelium. Examination of the relationship between DMR and mRNA in HOXA genes demonstrated a significant inverse relationship between CpG island promoter methylation and gene expression. Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) confirmed differential CpG methylation of HOXA genes, the ER stress gene ATF4, inflammatory regulator microRNA-10a and ARHGAP25 that encodes a negative regulator of Rho GTPases involved in cytoskeleton remodeling. Gender-specific DMRs associated with ciliogenesis that may be linked to defects in cilia development were also identified in AA DMRs.</abstracttext></p>
<h4>CONCLUSIONS:</h4>
<p><abstracttext label="CONCLUSIONS" nlmcategory="CONCLUSIONS">An endothelial methylome analysis identifies epigenetic DMR characteristics associated with transcriptional regulation in regions of atherosusceptibility in swine aorta in vivo. The data represent the first methylome blueprint for spatio-temporal analyses of lesion susceptibility predisposing to endothelial dysfunction in complex flow environments in vivo.</abstracttext></p>
</div>',
'date' => '2015-07-07',
'pmid' => 'http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682',
'doi' => '10.1186/s12864-015-1656-4',
'modified' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'created' => '2016-03-15 13:45:22',
'ProductsPublication' => array(
'id' => '550',
'product_id' => '1879',
'publication_id' => '2857'
)
)
$externalLink = ' <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26148682" target="_blank"><i class="fa fa-external-link"></i></a>'include - APP/View/Products/view.ctp, line 755
View::_evaluate() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 971
View::_render() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 933
View::render() - CORE/Cake/View/View.php, line 473
Controller::render() - CORE/Cake/Controller/Controller.php, line 963
ProductsController::slug() - APP/Controller/ProductsController.php, line 1052
ReflectionMethod::invokeArgs() - [internal], line ??
Controller::invokeAction() - CORE/Cake/Controller/Controller.php, line 491
Dispatcher::_invoke() - CORE/Cake/Routing/Dispatcher.php, line 193
Dispatcher::dispatch() - CORE/Cake/Routing/Dispatcher.php, line 167
[main] - APP/webroot/index.php, line 118
×