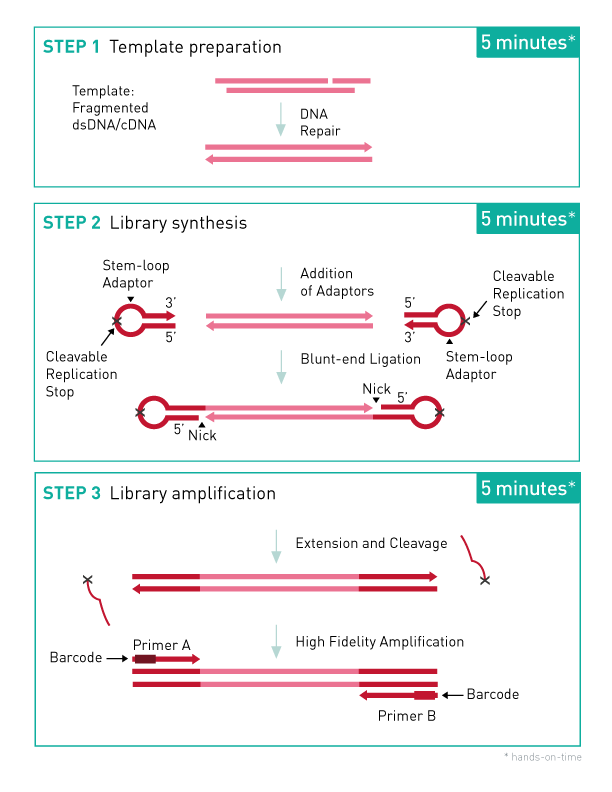
Step 1. Template Preparation provides efficient repair of the fragmented double-stranded DNA input.
In this step, the DNA is repaired and yields molecules with blunt ends.
Step 2. Library Synthesis. enables ligation of MicroPlex patented stem- loop adapters.
In the next step, stem-loop adaptors with blocked 5’ ends are ligated with high efficiency to the 5’ end of the genomic DNA, leaving a nick at the 3’ end. The adaptors cannot ligate to each other and do not have single- strand tails, both of which contribute to non-specific background found with many other NGS preparations.
Step 3. Library Amplification enables extension of the template, cleavage of the stem-loop adaptors, and amplification of the library. Illumina- compatible indexes are also introduced using a high-fidelity, highly- processive, low-bias DNA polymerase.
In the final step, the 3’ ends of the genomic DNA are extended to complete library synthesis and Illumina-compatible indexes are added through a high-fidelity amplification. Any remaining free adaptors are destroyed. Hands-on time and the risk of contamination are minimized by using a single tube and eliminating intermediate purifications.
Obtained libraries are purified, quantified and sized. The libraries pooling can be performed as well before sequencing.