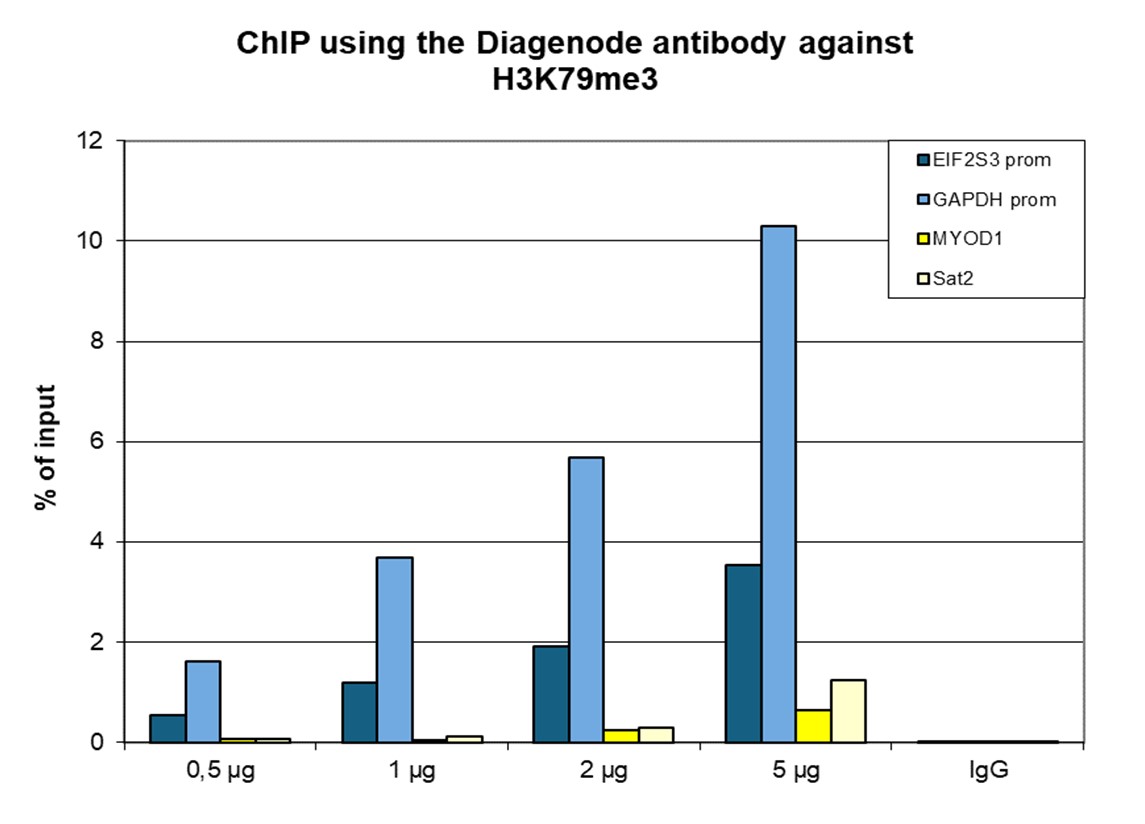
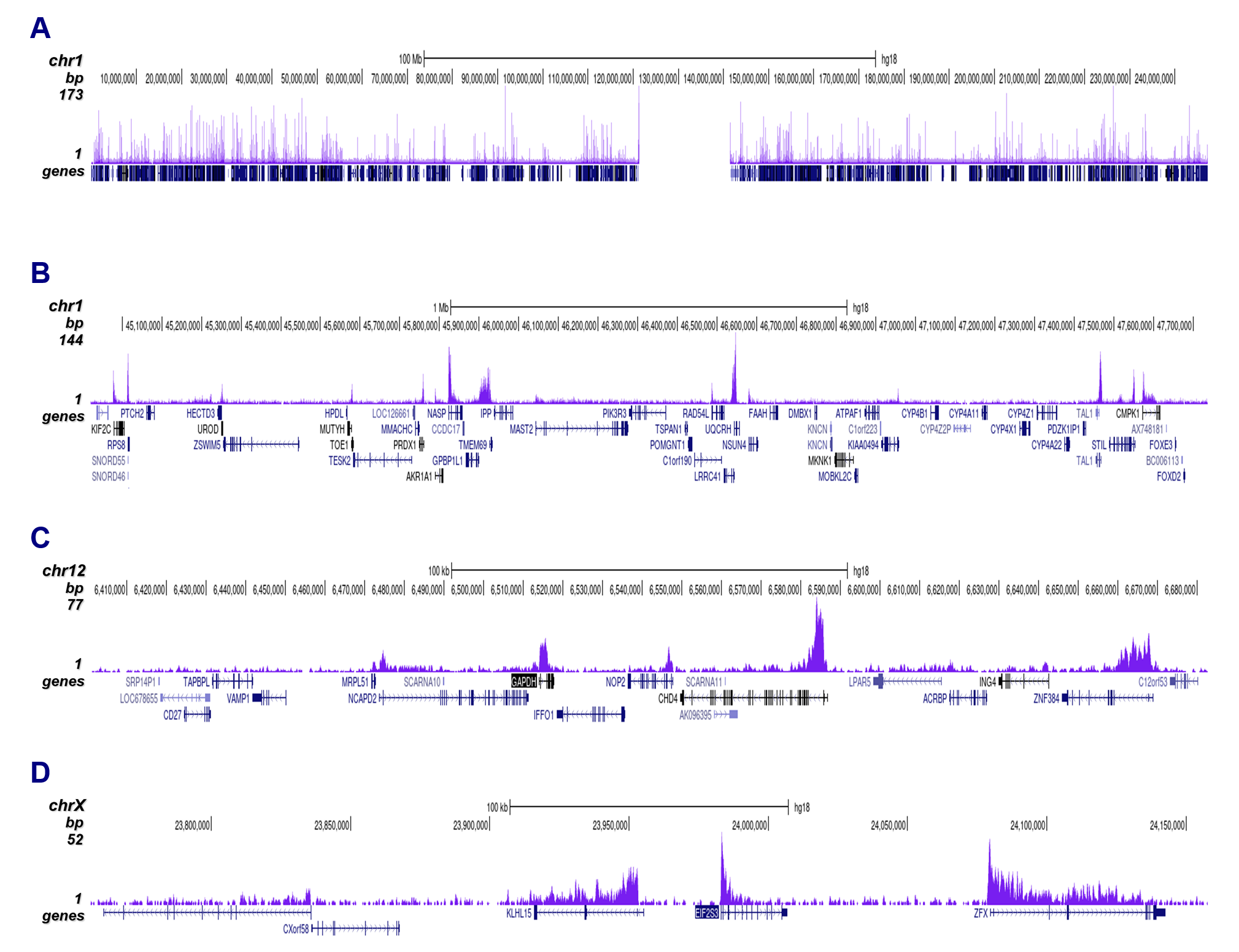
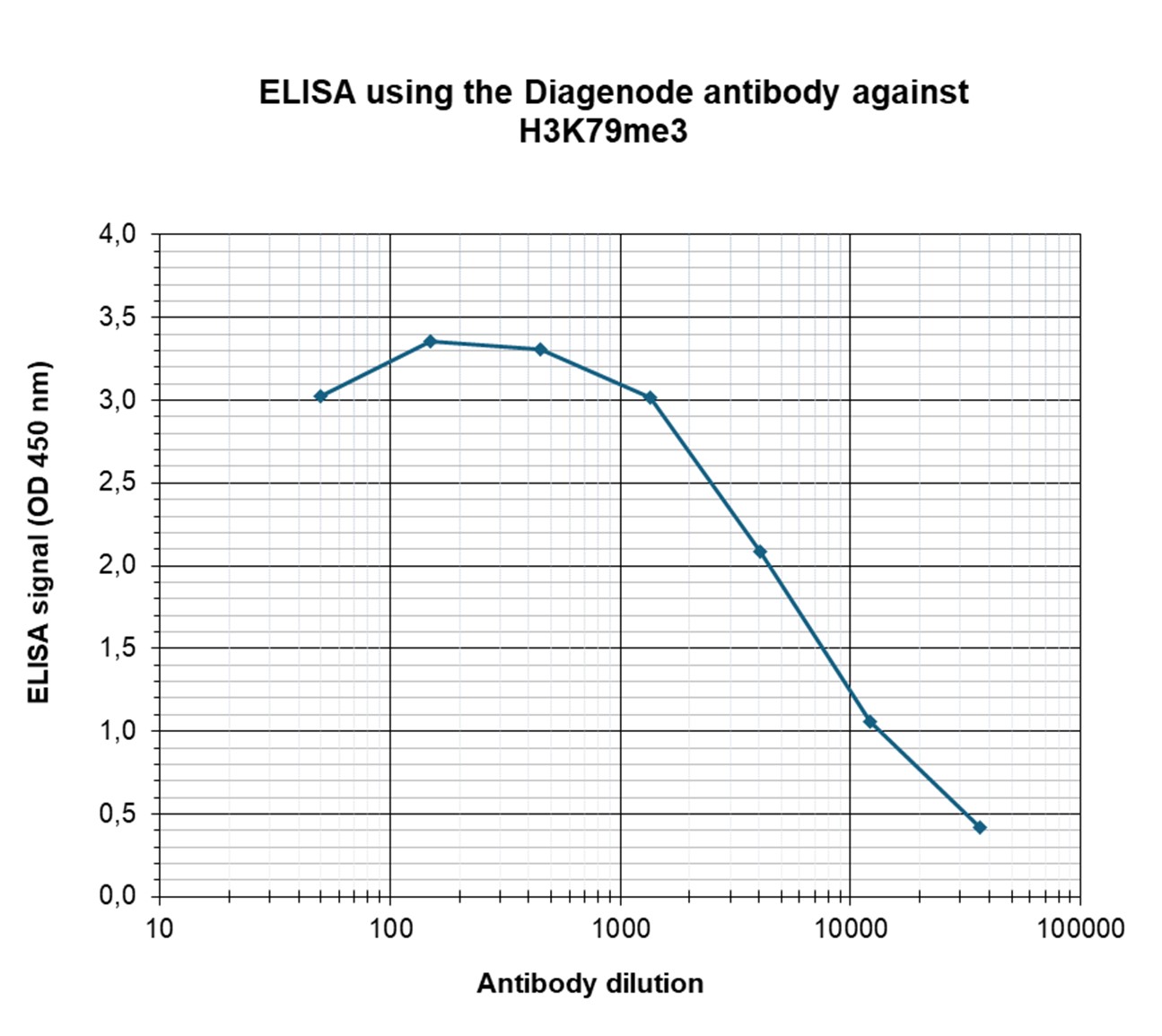
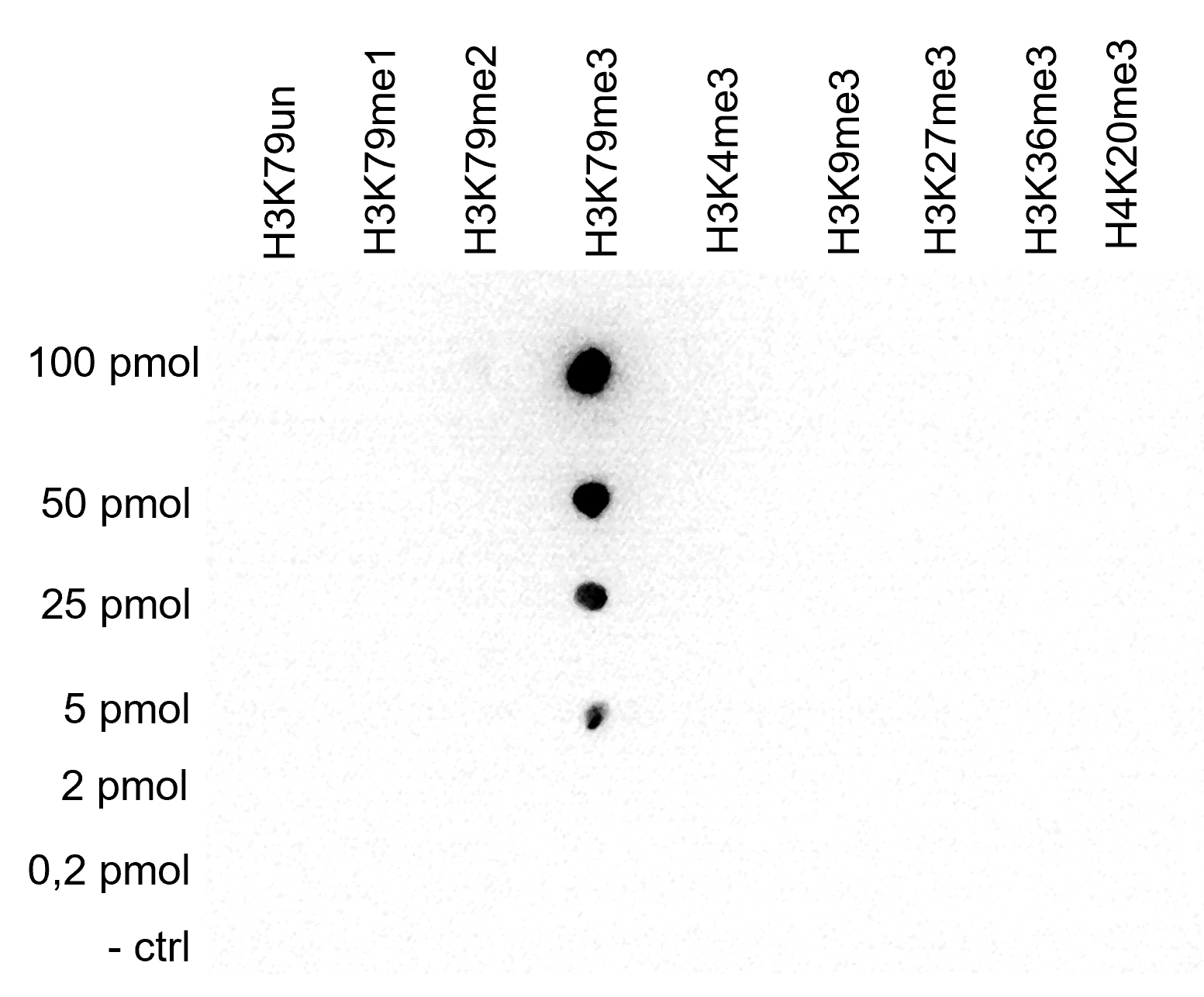
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K79me3 polyclonal antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410068-10 Lot# A2014P). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Distinct silencer states generate epigenetic states of heterochromatin.
Saxton Daniel S and Rine Jasper
Heterochromatic loci can exhibit different transcriptional states in genetically identical cells. A popular model posits that the inheritance of modified histones is sufficient for inheritance of the silenced state. However, silencing inheritance requires silencers and therefore cannot be driven by the inheritance o... |
DOT1L O-GlcNAcylation promotes its protein stability andMLL-fusion leukemia cell proliferation.
Song Tanjing et al.
Histone lysine methylation functions at the interface of the extracellular environment and intracellular gene expression. DOT1L is a versatile histone H3K79 methyltransferase with a prominent role in MLL-fusion leukemia, yet little is known about how DOT1L responds to extracellular stimuli. Here, we report that DOT1... |
The histone methyltransferase DOT1L is required for proper DNA damage response, DNA repair, and modulates chemotherapy responsiveness.
Kari V, Raul SK, Henck JM, Kitz J, Kramer F, Kosinsky RL, Übelmesser N, Mansour WY, Eggert J, Spitzner M, Najafova Z, Bastians H, Grade M, Gaedcke J, Wegwitz F, Johnsen SA
BACKGROUND: Disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like (DOT1L) is a non-SET domain containing methyltransferase known to catalyze mono-, di-, and tri-methylation of histone 3 on lysine 79 (H3K79me). DOT1L-mediated H3K79me has been implicated in chromatin-associated functions including gene transcription, heterochromati... |
Tri-methylation of H3K79 is decreased in TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer
Evanno E. et al.
BACKGROUND:
The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) enables epithelial cancer cells to acquire mesenchymal features and contributes to metastasis and resistance to treatment. This process involves epigenetic reprogramming for gene expression. We explored global histone modifications during TGF-β1-indu... |
DOT1L Activity Promotes Proliferation and Protects Cortical Neural Stem Cells from Activation of ATF4-DDIT3-Mediated ER Stress In Vitro
Roidl D, Hellbach N, Bovio PP, Villarreal A, Heidrich S, Nestel S, Grüning BA, Boenisch U, Vogel T
Growing evidence suggests that the lysine methyltransferase DOT1L/KMT4 has important roles in proliferation, survival, and differentiation of stem cells in development and in disease. We investigated the function of DOT1L in neural stem cells (NSCs) of the cerebral cortex. The pharmacological inhibition and shRNA-me... |
MLL-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemias Activate BCL-2 through H3K79 Methylation and Are Sensitive to the BCL-2-Specific Antagonist ABT-199
Benito JM et al.
Targeted therapies designed to exploit specific molecular pathways in aggressive cancers are an exciting area of current research. Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL) mutations such as the t(4;11) translocation cause aggressive leukemias that are refractory to conventional treatment. The t(4;11) translocation produces an M... |
Degree of recruitment of DOT1L to MLL-AF9 defines level of H3K79 Di- and tri-methylation on target genes and transformation potential.
Kuntimaddi A, Achille NJ, Thorpe J, Lokken AA, Singh R, Hemenway CS, Adli M, Zeleznik-Le NJ, Bushweller JH
The MLL gene is a common target of chromosomal translocations found in human leukemia. MLL-fusion leukemia has a consistently poor outcome. One of the most common translocation partners is AF9 (MLLT3). MLL-AF9 recruits DOT1L, a histone 3 lysine 79 methyltransferase (H3K79me1/me2/me3), leading to aberrant gene transc... |
Anticheckpoint pathways at telomeres in yeast
Ribeyre Cyril, Shore David
Telomeres hide (or ‘cap’) chromosome ends from DNA-damage surveillance mechanisms that arrest the cell cycle and promote repair, but the checkpoint status of telomeres is not well understood. Here we characterize the response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) flanked by varying amounts o... |
Promoter-exon relationship of H3 lysine 9, 27, 36 and 79 methylation on pluripotency-associated genes.
Barrand S, Andersen IS, Collas P
Evidence links pluripotency to a gene regulatory network organized by the transcription factors Oct4, Nanog and Sox2. Expression of these genes is controlled by epigenetic modifications on regulatory regions. However, little is known on profiles of trimethylated H3 lysine residues on coding regions of these genes in... |
Chromatin states of core pluripotency-associated genes in pluripotent, multipotent and differentiated cells.
Barrand S, Collas P
Oct4, Nanog and Sox2 constitute a core of transcription factors controlling pluripotency. Differentiation and reprogramming studies have unraveled a few epigenetic modifications associated in relation to the expression state of OCT4, NANOG and SOX2. There is, however, no comprehensive map of chromatin states on thes... |