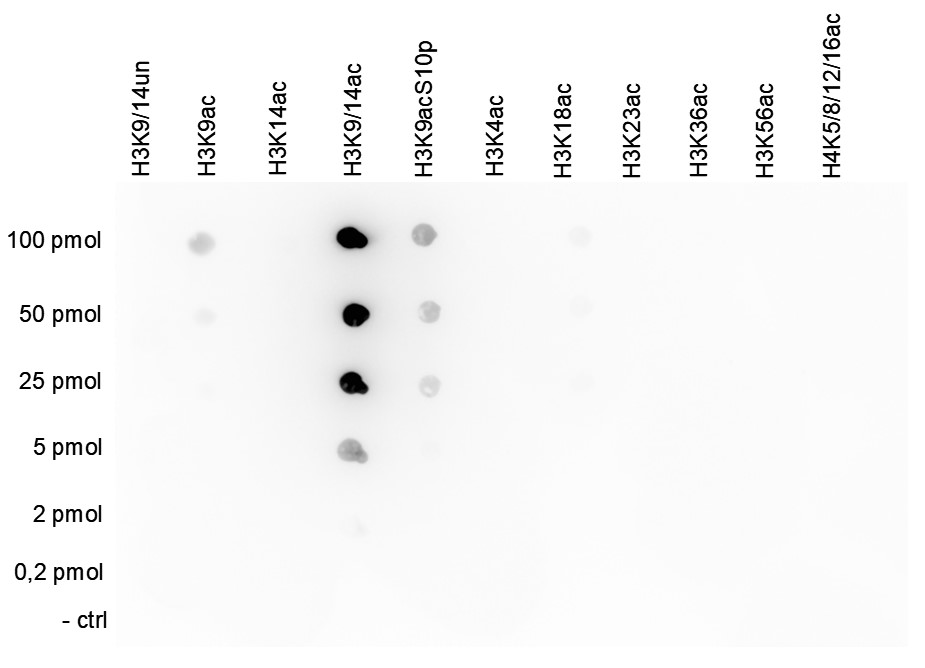
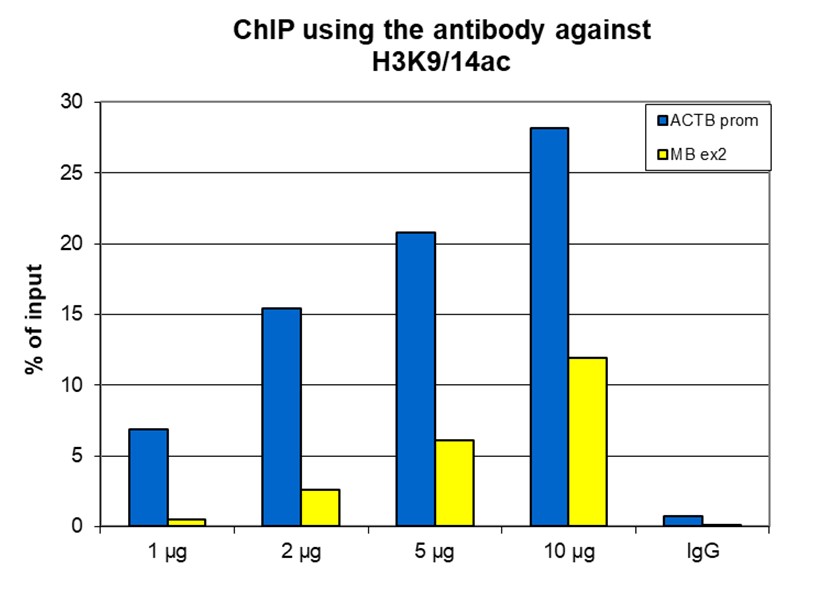
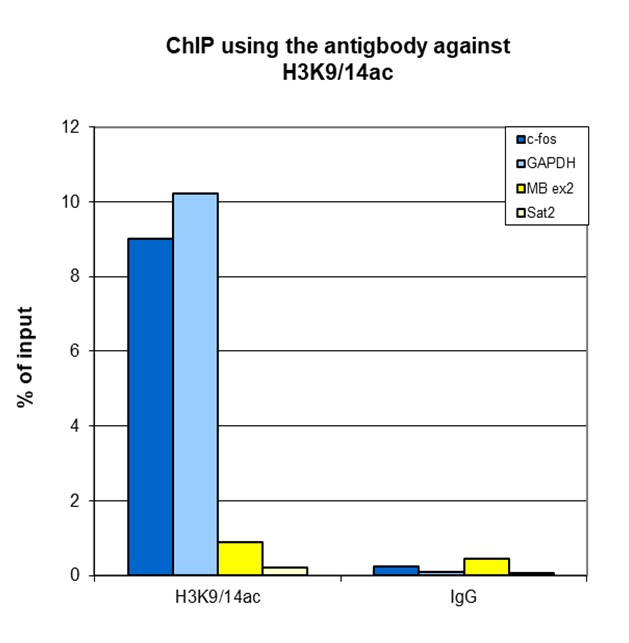
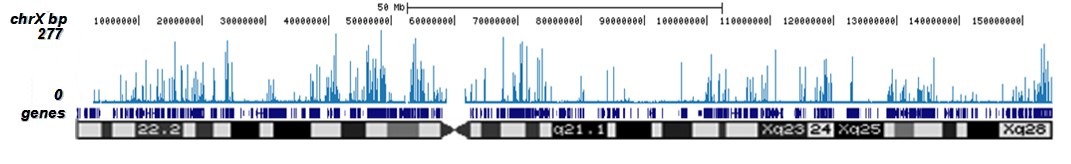
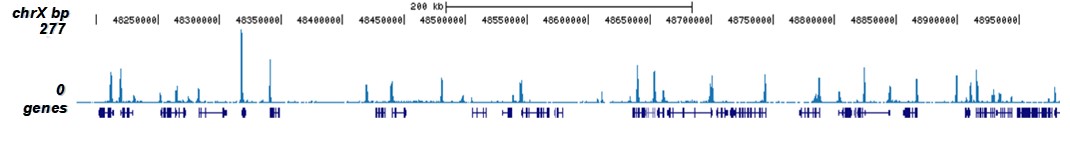
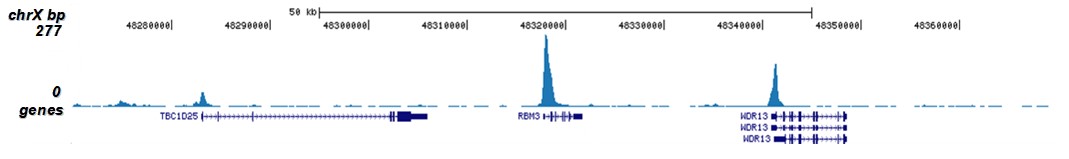
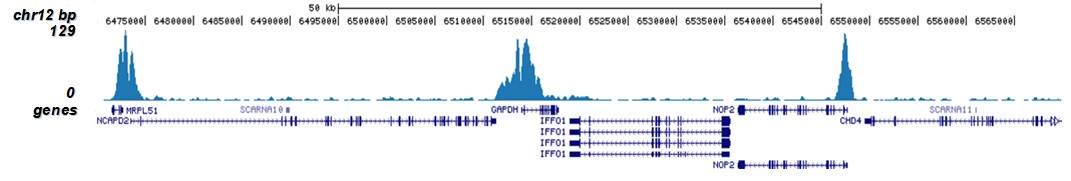
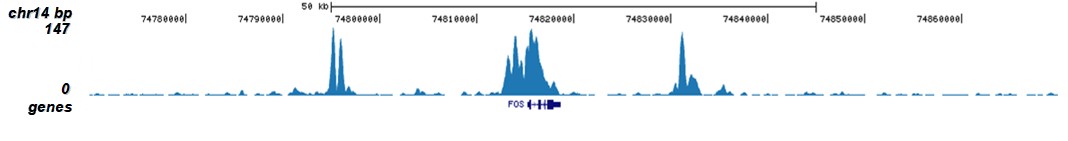
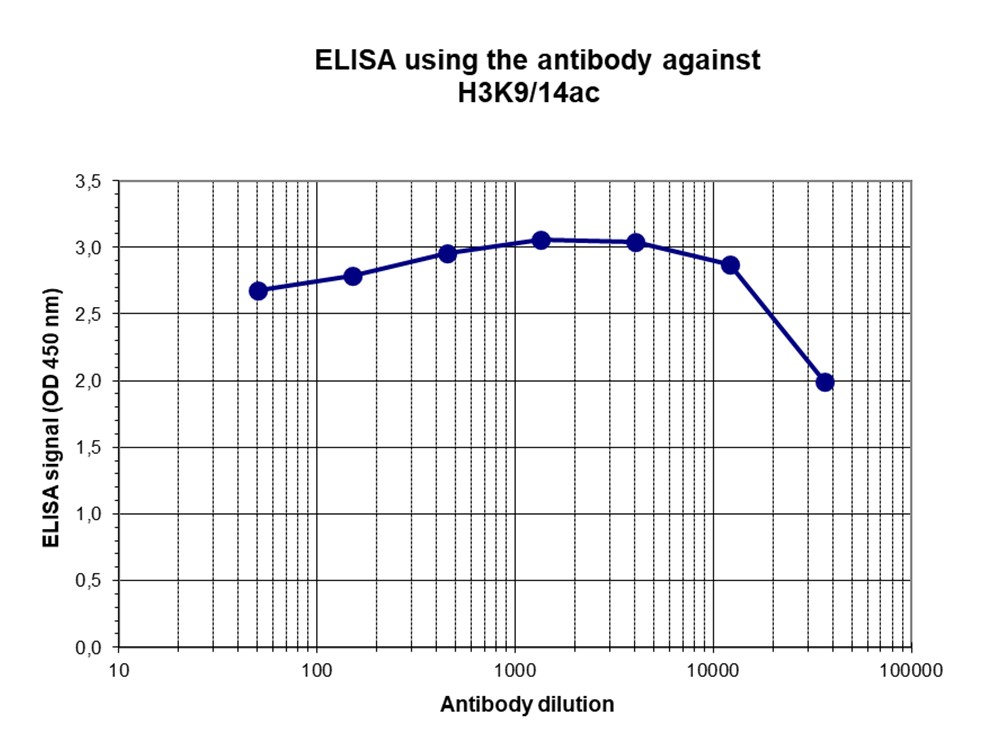
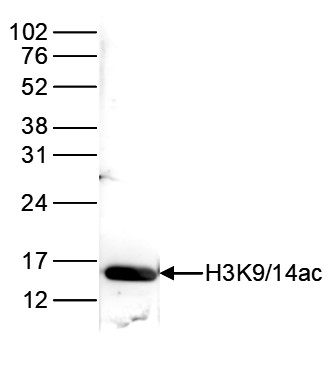
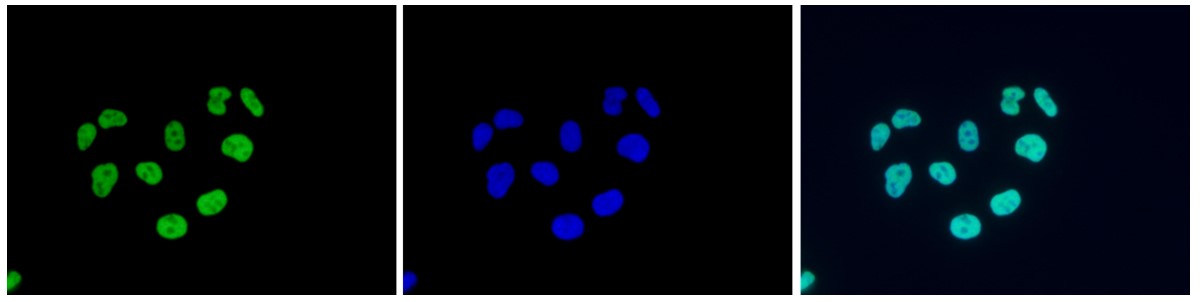
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K9/14ac polyclonal antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410005 Lot# A381-004). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Temporal modification of H3K9/14ac and H3K4me3 histone marksmediates mechano-responsive gene expression during the accommodationprocess in poplar
Ghosh R. et al.
Plants can attenuate their molecular response to repetitive mechanical stimulation as a function of their mechanical history. For instance, a single bending of stem is sufficient to attenuate the gene expression in poplar plants to the subsequent mechanical stimulation, and the state of desensitization can last for ... |
Efficacy of selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibition in mouse models ofPseudomonas aeruginosa infection: A new glimpse for reducinginflammation and infection in cystic fibrosis.
Brindisi M.et al.
The latest studies identified the histone deacetylase (HDAC) class of enzymes as strategic components of the complex molecular machinery underlying inflammation in cystic fibrosis (CF). Compelling new support has been provided for HDAC6 isoform as a key player in the generation of the dysregulated proinflammatory ph... |
Histone demethylase KDM2A suppresses EGF-TSPAN8 pathway toinhibit breast cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro.
Zhang Haomiao et al.
Metastasis is a major cause of breast cancer mortality and the current study found histone demethylase, KDM2A, expression to be negatively correlated with breast cancer metastasis. KDM2A knockdown greatly promoted migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. The histone demethylase activity of KDM2A downregulated ... |
Transferrin Receptor 1 Regulates Thermogenic Capacity and Cell Fate in Brown/Beige Adipocytes
Jin Li, Xiaohan Pan, Guihua Pan, Zijun Song, Yao He, Susu Zhang, Xueru Ye, Xiang Yang, Enjun Xie, Xinhui Wang, Xudong Mai, Xiangju Yin, Biyao Tang, Xuan Shu, Pengyu Chen, Xiaoshuang Dai, Ye Tian, Liheng Yao, Mulan Han, Guohuan Xu, Huijie Zhang, Jia Sun, H
Iron homeostasis is essential for maintaining cellular function in a wide range of cell types. However, whether iron affects the thermogenic properties of adipocytes is currently unknown. Using integrative analyses of multi-omics data, transferrin receptor 1 (Tfr1) is identified as a candidate for regulating thermog... |
Alteration of CTCF-associated chromatin neighborhood inhibits TAL1-driven oncogenic transcription program and leukemogenesis.
Li Y, Liao Z, Luo H, Benyoucef A, Kang Y, Lai Q, Dovat S, Miller B, Chepelev I, Li Y, Zhao K, Brand M, Huang S
Aberrant activation of the TAL1 is associated with up to 60% of T-ALL cases and is involved in CTCF-mediated genome organization within the TAL1 locus, suggesting that CTCF boundary plays a pathogenic role in T-ALL. Here, we show that -31-Kb CTCF binding site (-31CBS) serves as chromatin boundary that defines topolo... |
Integrative Proteomic Profiling Reveals PRC2-Dependent Epigenetic Crosstalk Maintains Ground-State Pluripotency.
van Mierlo G, Dirks RAM, De Clerck L, Brinkman AB, Huth M, Kloet SL, Saksouk N, Kroeze LI, Willems S, Farlik M, Bock C, Jansen JH, Deforce D, Vermeulen M, Déjardin J, Dhaenens M, Marks H
The pluripotent ground state is defined as a basal state free of epigenetic restrictions, which influence lineage specification. While naive embryonic stem cells (ESCs) can be maintained in a hypomethylated state with open chromatin when grown using two small-molecule inhibitors (2i)/leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)... |
The Hematopoietic Transcription Factors RUNX1 and ERG Prevent AML1-ETO Oncogene Overexpression and Onset of the Apoptosis Program in t(8;21) AMLs
Mandoli A. et al.
The t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-associated oncoprotein AML1-ETO disrupts normal hematopoietic differentiation. Here, we have investigated its effects on the transcriptome and epigenome in t(8,21) patient cells. AML1-ETO binding was found at promoter regions of active genes with high levels of histone acetyl... |
Role of Annexin gene and its regulation during zebrafish caudal fin regeneration
Saxena S, Purushothaman S, Meghah V, Bhatti B, Poruri A, Meena Lakshmi MG, Sarath Babu N, Murthy CL, Mandal KK, Kumar A, Idris MM
The molecular mechanism of epimorphic regeneration is elusive due to its complexity and limitation in mammals. Epigenetic regulatory mechanisms play a crucial role in development and regeneration. This investigation attempted to reveal the role of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms, such as histone H3 and H4 lysine ac... |
Germline organization in Strongyloides nematodes reveals alternative differentiation and regulation mechanisms.
Kulkarni A et al.
Nematodes of the genus Strongyloides are important parasites of vertebrates including man. Currently, little is known about their germline organization or reproductive biology and how this influences their parasitic life strategies. Here, we analyze the structure of the germline in several Strongyloides and closely ... |
VEGF-mediated cell survival in non-small-cell lung cancer: implications for epigenetic targeting of VEGF receptors as a therapeutic approach
Barr MP et al.
AIMS:
To evaluate the potential therapeutic utility of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) in targeting VEGF receptors in non-small-cell lung cancer.
MATERIALS & METHODS:
Non-small-cell lung cancer cells were screened for the VEGF receptors at the mRNA and protein levels, while cellular responses to vari... |
The oncofusion protein FUS-ERG targets key hematopoietic regulators and modulates the all-trans retinoic acid signaling pathway in t(16;21) acute myeloid leukemia.
Sotoca AM1, Prange KH1, Reijnders B1, Mandoli A1, Nguyen LN1, Stunnenberg HG1, Martens JH
The ETS transcription factor ERG has been implicated as a major regulator of both normal and aberrant hematopoiesis. In acute myeloid leukemias harboring t(16;21), ERG function is deregulated due to a fusion with FUS/TLS resulting in the expression of a FUS-ERG oncofusion protein. How this oncofusion protein deregul... |
Membrane-Bound Methyltransferase Complex VapA-VipC-VapB Guides Epigenetic Control of Fungal Development.
Sarikaya-Bayram O, Bayram O, Feussner K, Kim JH, Kim HS, Kaever A, Feussner I, Chae KS, Han DM, Han KH, Braus GH
Epigenetic and transcriptional control of gene expression must be coordinated in response to external signals to promote alternative multicellular developmental programs. The membrane-associated trimeric complex VapA-VipC-VapB controls a signal transduction pathway for fungal differentiation. The VipC-VapB methyltra... |
Histone deacetylase complex1 expression level titrates plant growth and abscisic Acid sensitivity in Arabidopsis.
Perrella G, Lopez-Vernaza MA, Carr C, Sani E, Gosselé V, Verduyn C, Kellermeier F, Hannah MA, Amtmann A
Histone deacetylation regulates gene expression during plant stress responses and is therefore an interesting target for epigenetic manipulation of stress sensitivity in plants. Unfortunately, overexpression of the core enzymes (histone deacetylases [HDACs]) has either been ineffective or has caused pleiotropic morp... |
IL-23 is pro-proliferative, epigenetically regulated and modulated by chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer.
Baird AM, Leonard J, Naicker KM, Kilmartin L, O'Byrne KJ, Gray SG
BACKGROUND: IL-23 is a member of the IL-6 super-family and plays key roles in cancer. Very little is currently known about the role of IL-23 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). METHODS: RT-PCR and chromatin immunopreciptiation (ChIP) were used to examine the levels, epigenetic regulation and effects of various dr... |
ERG and FLI1 binding sites demarcate targets for aberrant epigenetic regulation by AML1-ETO in acute myeloid leukemia.
Martens JH, Mandoli A, Simmer F, Wierenga BJ, Saeed S, Singh AA, Altucci L, Vellenga E, Stunnenberg HG
ERG and FLI1 are closely related members of the ETS family of transcription factors and have been identified as essential factors for the function and maintenance of normal hematopoietic stem cells. Here, genome-wide analysis revealed that both ERG and FLI1 occupy similar genomic regions as AML1-ETO in t(8;21) AMLs ... |
Pre-B cell to macrophage transdifferentiation without significant promoter DNA methylation changes.
Rodríguez-Ubreva J, Ciudad L, Gómez-Cabrero D, Parra M, Bussmann LH, di Tullio A, Kallin EM, Tegnér J, Graf T, Ballestar E
Transcription factor-induced lineage reprogramming or transdifferentiation experiments are essential for understanding the plasticity of differentiated cells. These experiments helped to define the specific role of transcription factors in conferring cell identity and played a key role in the development of the rege... |
IL-20 is epigenetically regulated in NSCLC and down regulates the expression of VEGF.
Baird AM, Gray SG, O'Byrne KJ
BACKGROUND: IL-20 is a pleiotrophic member of the IL-10 family and plays a role in skin biology and the development of haematopoietic cells. Recently, IL-20 has been demonstrated to have potential anti-angiogenic effects in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by down regulating COX-2. METHODS: The expression of IL-20... |
Epigenetic Regulation of Glucose Transporters in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
O'Byrne KJ, Baird AM, Kilmartin L, Leonard J, Sacevich C, Gray SG.
Due to their inherently hypoxic environment, cancer cells often resort to glycolysis, or the anaerobic breakdown of glucose to form ATP to provide for their energy needs, known as the Warburg effect. At the same time, overexpression of the insulin receptor in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is associated with an ... |
Epigenetic control of vascular smooth muscle cells in Marfan and non-Marfan thoracic aortic aneurysms.
Gomez D, Coyet A, Ollivier V, Jeunemaitre X, Jondeau G, Michel JB, Vranckx R
AIMS: Human thoracic aortic aneurysms (TAAs) are characterized by extracellular matrix breakdown associated with progressive smooth muscle cell (SMC) rarefaction. These features are present in all types of TAA: monogenic forms [mainly Marfan syndrome (MFS)], forms associated with bicuspid aortic valve (BAV), and deg... |
Regulation of EP receptors in non-small cell lung cancer by epigenetic modifications.
Gray SG, Al-Sarraf N, Baird AM, Cathcart MC, McGovern E, O'Byrne KJ.
BACKGROUND: Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 is frequently overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and results in increased levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE(2)), an important signalling molecule implicated in tumourigenesis. PGE(2) exerts its effects through the E prostanoid (EP) receptors (EPs1-4). METHODS: The ... |