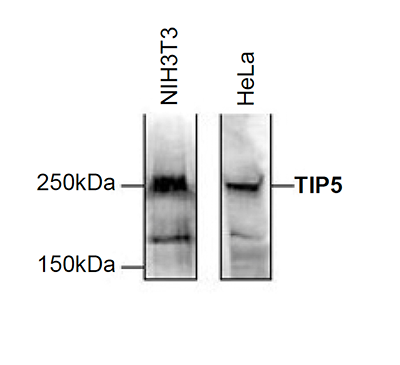
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: TIP5 polyclonal antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15310090 Lot# A300-004 ). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
The RNA helicase DHX9 establishes nucleolar heterochromatin, and this activity is required for embryonic stem cell differentiation
Leone S. et al.
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been implicated in the regulation of chromatin conformation and epigenetic patterns. lncRNA expression levels are widely taken as an indicator for functional properties. However, the role of RNA processing in modulating distinct features of the same lncRNA is less understood. The ... |
ING1 regulates rRNA levels by altering nucleolar chromatin structure and mTOR localization
Rajarajacholan U.K. et al.
Epigenetic, transcriptional and signaling processes in the nucleolus regulate rRNA transcription and cell growth. We report here that the tumor suppressor ING1b binds rDNA, regulates rDNA chromatin modifications and affects nucleolar localization of mTOR to modulate rRNA levels. ING1 represses rDNA transcription by ... |
BAZ2A (TIP5) is involved in epigenetic alterations in prostate cancer and its overexpression predicts disease recurrence.
Gu L, Frommel SC, Oakes CC, Simon R, Grupp K, Gerig CY, Bär D, Robinson MD, Baer C, Weiss M, Gu Z, Schapira M, Kuner R, Sültmann H, Provenzano M, , Yaspo ML, Brors B, Korbel J, Schlomm T, Sauter G, Eils R, Plass C, Santoro R
Prostate cancer is driven by a combination of genetic and/or epigenetic alterations. Epigenetic alterations are frequently observed in all human cancers, yet how aberrant epigenetic signatures are established is poorly understood. Here we show that the gene encoding BAZ2A (TIP5), a factor previously implicated in ep... |
lncRNA Maturation to Initiate Heterochromatin Formation in the Nucleolus Is Required for Exit from Pluripotency in ESCs.
Savić N, Bär D, Leone S, Frommel SC, Weber FA, Vollenweider E, Ferrari E, Ziegler U, Kaech A, Shakhova O, Cinelli P, Santoro R
The open chromatin of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) condenses into repressive heterochromatin as cells exit the pluripotent state. How the 3D genome organization is orchestrated and implicated in pluripotency and lineage specification is not understood. Here, we find that maturation of the long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) ... |
Interaction of nucleolin with ribosomal RNA genes and its role in RNA polymerase I transcription.
Cong R, Das S, Ugrinova I, Kumar S, Mongelard F, Wong J, Bouvet P
Nucleolin is a multi-functional nucleolar protein that is required for ribosomal RNA gene (rRNA) transcription in vivo, but the mechanism by which nucleolin modulates RNA polymerase I (RNAPI) transcription is not well understood. Nucleolin depletion results in an increase in the heterochromatin mark H3K9me2 and a de... |
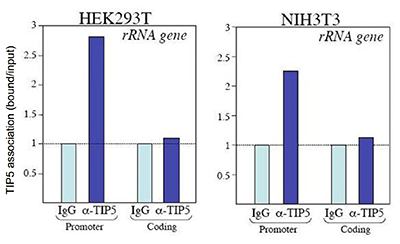
The NoRC complex mediates the heterochromatin formation and stability of silent rRNA genes and centromeric repeats
Guetg C, Lienemann P, Sirri V, Grummt I, Hernandez-Verdun D, Hottiger MO, Fussenegger M, Santoro R
Maintenance of specific heterochromatic domains is crucial for genome stability. In eukaryotic cells, a fraction of the tandem-repeated ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes is organized in the heterochromatic structures. The principal determinant of rDNA silencing is the nucleolar remodelling complex, NoRC, that consists of T... |
Chromatin remodeling by imitation switch (ISWI) class ATP-dependent remodelers is stimulated by histone variant H2A.Z.
Goldman JA, Garlick JD, Kingston RE
ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes rearrange nucleosomes by altering the position of DNA around the histone octamer. Although chromatin remodelers and the histone variant H2A.Z colocalize on transcriptional control regions, whether H2A.Z directly affects remodeler association or activity is unclear. We det... |
Epigenetic engineering of ribosomal RNA genes enhances protein production.
Santoro R, Lienemann P, Fussenegger M
Selection of mammalian high-producer cell lines remains a major challenge for the biopharmaceutical manufacturing industry. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes encode the major component of the ribosome but many rRNA gene copies are not transcribed due to epigenetic silencing by the nucleolar remodelling complex (NoRC) [6], ... |