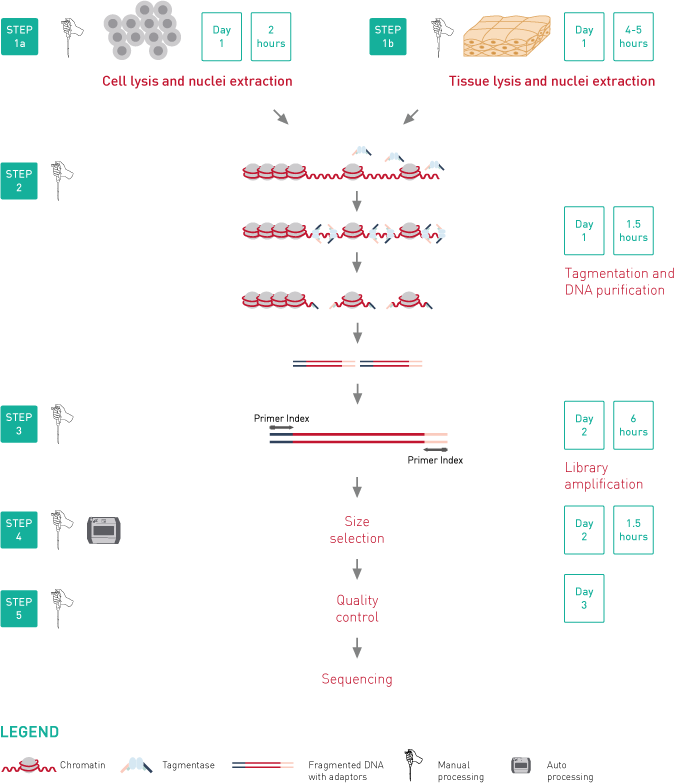
ATAC-seq, Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin, followed by next generation sequencing, is a key technology to easily identify the open regions of the chromatin. The protocol consists of 3 steps: nuclei preparation, tagmentation and library amplification. First, the cells/tissue undergo the lysis, ending with the crude nuclei. Then, the nuclei are incubated with a tagmentase (Tn5 transposase), which cuts the genomic regions associated with open chromatin and inserts the sequencing adaptors. Finally, the generated libraries are amplified and can be used for sequencing. High-throughput sequencing will then detect peaks, in open regions of the chromatin only, giving a map of the chromatin status in the whole genome of the sample.