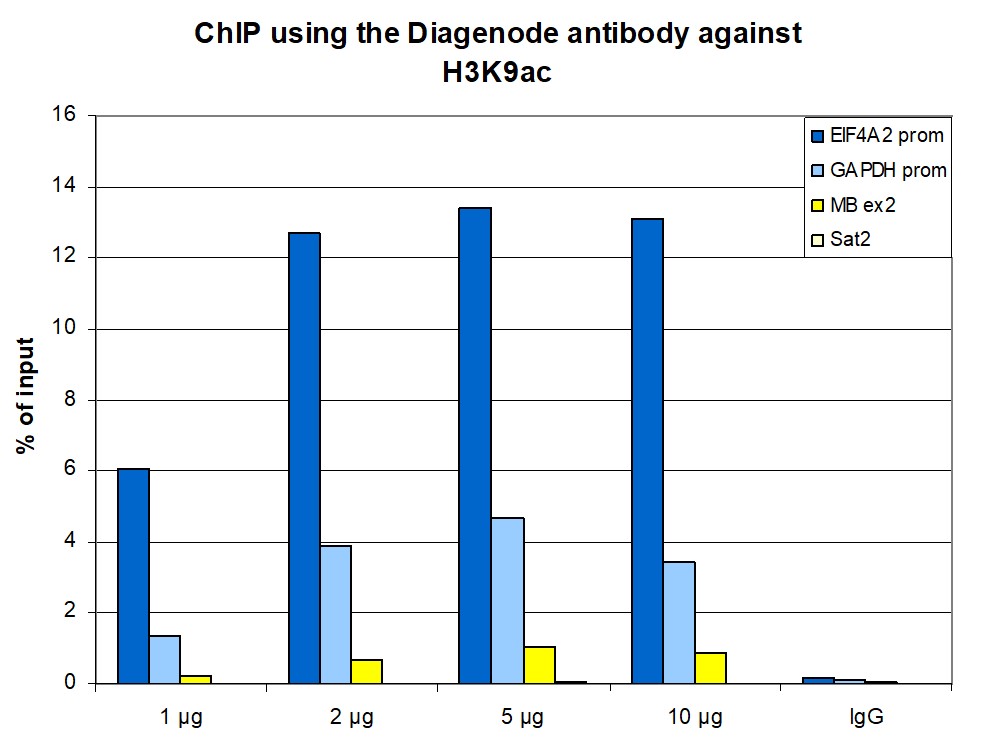
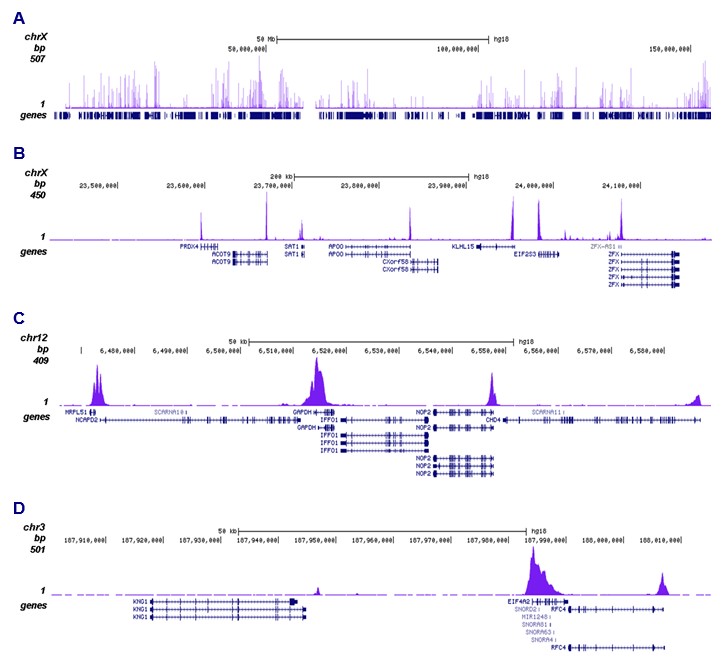
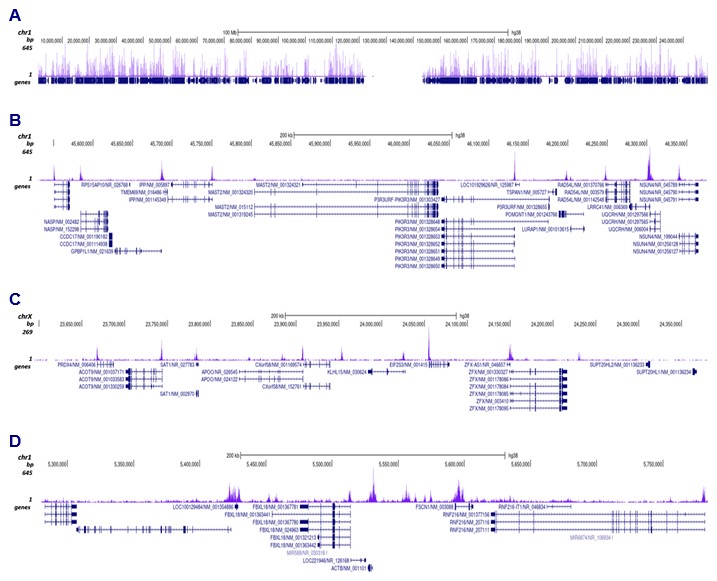
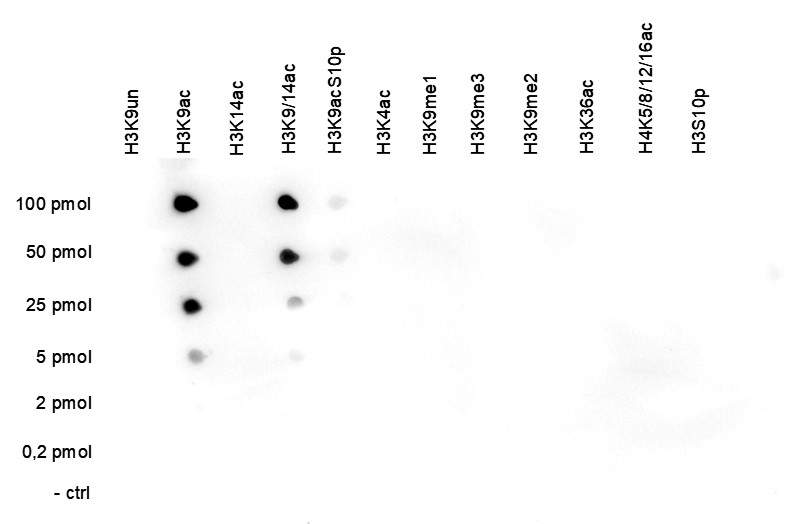
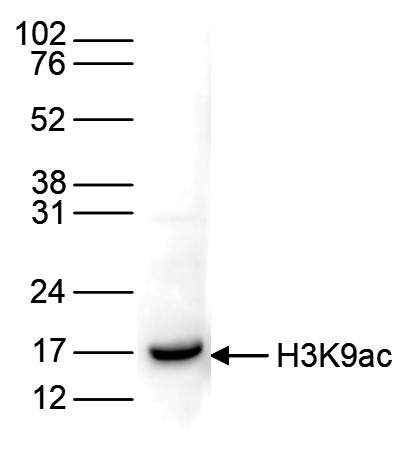
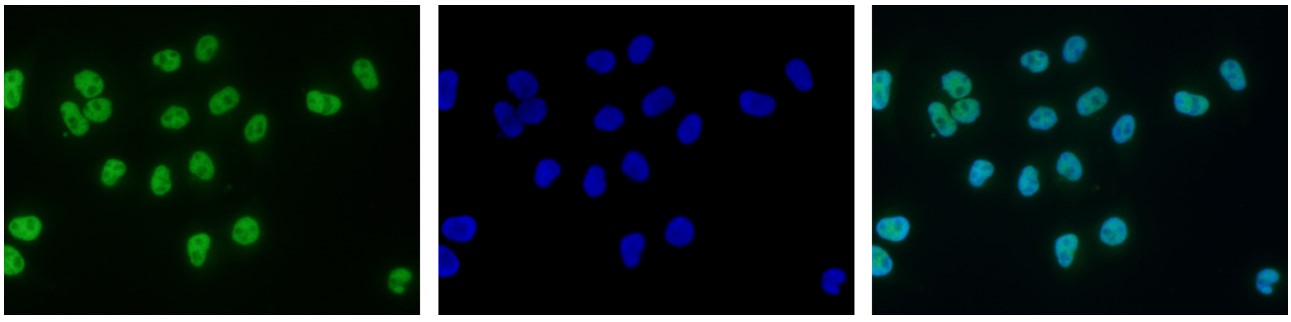
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K9ac Antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410004-10 Lot# A1435-0012D). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Noncanonical regulation of imprinted gene Igf2 by amyloid-beta 1-42 inAlzheimer's disease.
Fertan E. et al.
Reduced insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) levels in Alzheimer's disease (AD) may be the mechanism relating age-related metabolic disorders to dementia. Since Igf2 is an imprinted gene, we examined age and sex differences in the relationship between amyloid-beta 1-42 (Aβ) accumulation and epigenetic regulation... |
Analyzing the Genome-Wide Distribution of Histone Marks byCUT\&Tag in Drosophila Embryos.
Zenk F. et al.
CUT&Tag is a method to map the genome-wide distribution of histone modifications and some chromatin-associated proteins. CUT&Tag relies on antibody-targeted chromatin tagmentation and can easily be scaled up or automatized. This protocol provides clear experimental guidelines and helpful considerations when ... |
The histone acetyltransferase KAT6A is recruited to unmethylatedCpG islands via a DNA binding winged helix domain.
Weber L.M. et al.
The lysine acetyltransferase KAT6A (MOZ, MYST3) belongs to the MYST family of chromatin regulators, facilitating histone acetylation. Dysregulation of KAT6A has been implicated in developmental syndromes and the onset of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Previous work suggests that KAT6A is recruited to its genomic targ... |
HISTONE DEACETYLASE 15 and MOS4-Associated Complex subunits3A/3B coregulate intron retention of ABA-responsive genes.
Tu Yi-Tsung et al.
Histone deacetylases (HDAs) play an important role in transcriptional regulation of multiple biological processes. In this study, we investigated the function of HDA15 in abscisic acid (ABA) responses. We used immunopurification coupled with mass spectrometry-based proteomics to identify proteins interacting with HD... |
Broad domains of histone marks in the highly compact macronucleargenome.
Drews F. et al.
The unicellular ciliate contains a large vegetative macronucleus with several unusual characteristics, including an extremely high coding density and high polyploidy. As macronculear chromatin is devoid of heterochromatin, our study characterizes the functional epigenomic organization necessary for gene regulation a... |
CREBBP/EP300 acetyltransferase inhibition disrupts FOXA1-bound enhancers to inhibit the proliferation of ER+ breast cancer cells.
Bommi-Reddy A. et al.
Therapeutic targeting of the estrogen receptor (ER) is a clinically validated approach for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer (ER+ BC), but sustained response is limited by acquired resistance. Targeting the transcriptional coactivators required for estrogen receptor activity represents an alternative approach... |
Epigenetic, transcriptional and phenotypic responses in Daphnia magna exposed to low-level ionizing radiation
Thaulow Jens, Song You, Lindeman Leif C., Kamstra Jorke H., Lee YeonKyeong, Xie Li, Aleström Peter, Salbu Brit, Tollefsen Knut Erik
Ionizing radiation is known to induce oxidative stress and DNA damage as well as epigenetic effects in aquatic organisms. Epigenetic changes can be part of the adaptive responses to protect organisms from radiation-induced damage, or act as drivers of toxicity pathways leading to adverse effects. To investigate the ... |
An epigenetic map of malaria parasite development from host to vector.
Witmer K, Fraschka SA, Vlachou D, Bártfai R, Christophides GK
The malaria parasite replicates asexually in the red blood cells of its vertebrate host employing epigenetic mechanisms to regulate gene expression in response to changes in its environment. We used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing in conjunction with RNA sequencing to create an epigenomic and tr... |
USP22-dependent HSP90AB1 expression promotes resistance to HSP90 inhibition in mammary and colorectal cancer.
Kosinsky RL, Helms M, Zerche M, Wohn L, Dyas A, Prokakis E, Kazerouni ZB, Bedi U, Wegwitz F, Johnsen SA
As a member of the 11-gene "death-from-cancer" gene expression signature, overexpression of the Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 22 (USP22) was associated with poor prognosis in various human malignancies. To investigate the function of USP22 in cancer development and progression, we sought to detect common USP22-depende... |
Impact of human sepsis on CCCTC-binding factor associated monocyte transcriptional response of Major Histocompatibility Complex II components.
Siegler BH, Uhle F, Lichtenstern C, Arens C, Bartkuhn M, Weigand MA, Weiterer S
BACKGROUND: Antigen presentation on monocyte surface to T-cells by Major Histocompatibility Complex, Class II (MHC-II) molecules is fundamental for pathogen recognition and efficient host response. Accordingly, loss of Major Histocompatibility Complex, Class II, DR (HLA-DR) surface expression indicates impaired mono... |
SIRT1-dependent epigenetic regulation of H3 and H4 histone acetylation in human breast cancer
Khaldoun Rifaï et al.
Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed malignancy in women worldwide. It is well established that the complexity of carcinogenesis involves profound epigenetic deregulations that contribute to the tumorigenesis process. Deregulated H3 and H4 acetylated histone marks are amongst those alterations. Sirtuin-1 (... |
Epigenetic regulation of vascular NADPH oxidase expression and reactive oxygen species production by histone deacetylase-dependent mechanisms in experimental diabetes.
Manea SA, Antonescu ML, Fenyo IM, Raicu M, Simionescu M, Manea A
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by up-regulated NADPH oxidase (Nox) contribute to structural-functional alterations of the vascular wall in diabetes. Epigenetic mechanisms, such as histone acetylation, emerged as important regulators of gene expression in cardiovascular disorders. Since their role in diabete... |
Rapid Communication: The correlation between histone modifications and expression of key genes involved in accumulation of adipose tissue in the pig.
Kociucka B. et al.
Histone modification is a well-known epigenetic mechanism involved in regulation of gene expression; however, it has been poorly studied in adipose tissues of the pig. Understanding the molecular background of adipose tissue development and function is essential for improving production efficiency and meat quality. ... |
Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF10 suppresses TGFβ-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via a negative feedback mechanism
Mishra V.K. et al.
TGFβ-SMAD signaling exerts a contextual effect that suppresses malignant growth early in epithelial tumorigenesis but promotes metastasis at later stages. Longstanding challenges in resolving this functional dichotomy may uncover new strategies to treat advanced carcinomas. The Krüppel-like transcription f... |
Lhx2 interacts with the NuRD complex and regulates cortical neuron subtype determinants Fezf2 and Sox11
Muralidharan B. et al.
n the developing cerebral cortex, sequential transcriptional programs take neuroepithelial cells from proliferating progenitors to differentiated neurons with unique molecular identities. The regulatory changes that occur in the chromatin of the progenitors are not well understood. During deep layer neurogenesis, we... |
Chronic stress leads to epigenetic dysregulation in the neuropeptide-Y and cannabinoid CB1 receptor genes in the mouse cingulate cortex
Lomazzo E. et al.
Persistent stress triggers a variety of mechanisms, which may ultimately lead to the occurrence of anxiety- and depression-related disorders. Epigenetic modifications represent a mechanism by which chronic stress mediates long-term effects. Here, we analyzed brain tissue from mice exposed to chronic unpredictable st... |
H3K4 acetylation, H3K9 acetylation and H3K27 methylation in breast tumor molecular subtypes
Judes G et al.
AIM:
Here, we investigated how the St Gallen breast molecular subtypes displayed distinct histone H3 profiles.
PATIENTS & METHODS:
192 breast tumors divided into five St Gallen molecular subtypes (luminal A, luminal B HER2-, luminal B HER2+, HER2+ and basal-like) were evaluated for their histone H3 modifica... |
Epigenetic Modifications with DZNep, NaBu and SAHA in Luminal and Mesenchymal-like Breast Cancer Subtype Cells
Dagdemir A et al.
BACKGROUND/AIM:
Numerous studies have shown that breast cancer and epigenetic mechanisms have a very powerful interactive relation. The MCF7 cell line, representative of luminal subtype and the MDA-MB 231 cell line representative of mesenchymal-like subtype were treated respectively with a Histone Methyl Transferas... |
Molecular and Epigenetic Biomarkers in Luminal Androgen Receptor: A Triple Negative Breast Cancer Subtype
Judes G et al.
|
Role of Annexin gene and its regulation during zebrafish caudal fin regeneration
Saxena S, Purushothaman S, Meghah V, Bhatti B, Poruri A, Meena Lakshmi MG, Sarath Babu N, Murthy CL, Mandal KK, Kumar A, Idris MM
The molecular mechanism of epimorphic regeneration is elusive due to its complexity and limitation in mammals. Epigenetic regulatory mechanisms play a crucial role in development and regeneration. This investigation attempted to reveal the role of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms, such as histone H3 and H4 lysine ac... |
VEGF-mediated cell survival in non-small-cell lung cancer: implications for epigenetic targeting of VEGF receptors as a therapeutic approach
Barr MP et al.
AIMS:
To evaluate the potential therapeutic utility of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) in targeting VEGF receptors in non-small-cell lung cancer.
MATERIALS & METHODS:
Non-small-cell lung cancer cells were screened for the VEGF receptors at the mRNA and protein levels, while cellular responses to vari... |
Spatiotemporal control of estrogen-responsive transcription in ERα-positive breast cancer cells.
P-Y Hsu, H-K Hsu, T-H Hsiao, Z Ye, E Wang, A L Profit, I Jatoi, Y Chen, N B Kirma, V X Jin, Z D Sharp and T H-M Huang
Recruitment of transcription machinery to target promoters for aberrant gene expression has been well studied, but underlying control directed by distant-acting enhancers remains unclear in cancer development. Our previous study demonstrated that distant estrogen response elements (DEREs) located on chromosome 20q13... |
Deciphering the principles that govern mutually exclusive expression of Plasmodium falciparum clag3 genes
Rovira-Graells N, Crowley VM, Bancells C, Mira-Martínez S, de Pouplana LR, Cortés A
The product of the Plasmodium falciparum genes clag3.1 and clag3.2 plays a fundamental role in malaria parasite biology by determining solute transport into infected erythrocytes. Expression of the two clag3 genes is mutually exclusive, such that a single parasite expresses only one of the two genes at a time. Here ... |
Dendritic cell development requires histone deacetylase activity.
Chauvistré H, Küstermann C, Rehage N, Klisch T, Mitzka S, Felker P, Rose-John S, Zenke M, Seré KM
DCs develop from multipotent progenitors (MPPs), which commit into DC-restricted common dendritic cell progenitors (CDPs). CDPs further differentiate into classical DCs (cDCs) and plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs). Here, we studied the impact of histone acetylation on DC development in C57BL/6 mice by interfering with histone... |
Lysine-specific demethylase 1 regulates differentiation onset and migration of trophoblast stem cells.
Zhu D, Hölz S, Metzger E, Pavlovic M, Jandausch A, Jilg C, Galgoczy P, Herz C, Moser M, Metzger D, Günther T, Arnold SJ, Schüle R
Propagation and differentiation of stem cell populations are tightly regulated to provide sufficient cell numbers for tissue formation while maintaining the stem cell pool. Embryonic parts of the mammalian placenta are generated from differentiating trophoblast stem cells (TSCs) invading the maternal decidua. Here w... |
IL-23 is pro-proliferative, epigenetically regulated and modulated by chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer.
Baird AM, Leonard J, Naicker KM, Kilmartin L, O'Byrne KJ, Gray SG
BACKGROUND: IL-23 is a member of the IL-6 super-family and plays key roles in cancer. Very little is currently known about the role of IL-23 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). METHODS: RT-PCR and chromatin immunopreciptiation (ChIP) were used to examine the levels, epigenetic regulation and effects of various dr... |
Histone tail acetylation in brain occurs in an unpredictable fashion after death.
Barrachina M, Moreno J, Villar-Menéndez I, Juvés S, Ferrer I
Histone acetylation plays a role in the regulation of gene transcription. Yet it is not known whether post-mortem brain tissue is suitable for the analysis of histone acetylation. To examine this question, nucleosomes were isolated from frontal cortex of nine subjects which were obtained at short times after death a... |
IL-20 is epigenetically regulated in NSCLC and down regulates the expression of VEGF.
Baird AM, Gray SG, O'Byrne KJ
BACKGROUND: IL-20 is a pleiotrophic member of the IL-10 family and plays a role in skin biology and the development of haematopoietic cells. Recently, IL-20 has been demonstrated to have potential anti-angiogenic effects in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by down regulating COX-2. METHODS: The expression of IL-20... |
H3.5 is a novel hominid-specific histone H3 variant that is specifically expressed in the seminiferous tubules of human testes.
Schenk R, Jenke A, Zilbauer M, Wirth S, Postberg J
The incorporation of histone variants into chromatin plays an important role for the establishment of particular chromatin states. Six human histone H3 variants are known to date, not counting CenH3 variants: H3.1, H3.2, H3.3 and the testis-specific H3.1t as well as the recently described variants H3.X and H3.Y. We ... |
Epigenetic Regulation of Glucose Transporters in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
O'Byrne KJ, Baird AM, Kilmartin L, Leonard J, Sacevich C, Gray SG.
Due to their inherently hypoxic environment, cancer cells often resort to glycolysis, or the anaerobic breakdown of glucose to form ATP to provide for their energy needs, known as the Warburg effect. At the same time, overexpression of the insulin receptor in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is associated with an ... |
H2A.Z demarcates intergenic regions of the plasmodium falciparum epigenome that are dynamically marked by H3K9ac and H3K4me3.
Bártfai R, Hoeijmakers WA, Salcedo-Amaya AM, Smits AH, Janssen-Megens E, Kaan A, Treeck M, Gilberger TW, Françoijs KJ, Stunnenberg HG
Epigenetic regulatory mechanisms and their enzymes are promising targets for malaria therapeutic intervention; however, the epigenetic component of gene expression in P. falciparum is poorly understood. Dynamic or stable association of epigenetic marks with genomic features provides important clues about their funct... |
Histone modifications at the blastocyst Axin1(Fu) locus mark the heritability of in vitro culture-induced epigenetic alterations in mice.
Fernandez-Gonzalez R, Ramirez MA, Pericuesta E, Calle A, Gutierrez-Adan A
For epigenetic phenotypes to be passed on from one generation to the next, it is required that epigenetic marks between generations are not cleared during the two stages of epigenetic reprogramming: mammalian gametogenesis and preimplantation development. The molecular nature of the chromatin marks involved in these... |
Plasmodium falciparum heterochromatin protein 1 marks genomic loci linked to phenotypic variation of exported virulence factors.
Flueck C, Bartfai R, Volz J, Niederwieser I, Salcedo-Amaya AM, Alako BT, Ehlgen F, Ralph SA, Cowman AF, Bozdech Z, Stunnenberg HG, Voss TS
Epigenetic processes are the main conductors of phenotypic variation in eukaryotes. The malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum employs antigenic variation of the major surface antigen PfEMP1, encoded by 60 var genes, to evade acquired immune responses. Antigenic variation of PfEMP1 occurs through in situ switches in... |
A rapid micro chromatin immunoprecipitation assay (microChIP).
Dahl JA, Collas P
Interactions of proteins with DNA mediate many critical nuclear functions. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is a robust technique for studying protein-DNA interactions. Current ChIP assays, however, either require large cell numbers, which prevent their application to rare cell samples or small-tissue biopsies, ... |
Regulation of EP receptors in non-small cell lung cancer by epigenetic modifications.
Gray SG, Al-Sarraf N, Baird AM, Cathcart MC, McGovern E, O'Byrne KJ.
BACKGROUND: Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 is frequently overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and results in increased levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE(2)), an important signalling molecule implicated in tumourigenesis. PGE(2) exerts its effects through the E prostanoid (EP) receptors (EPs1-4). METHODS: The ... |