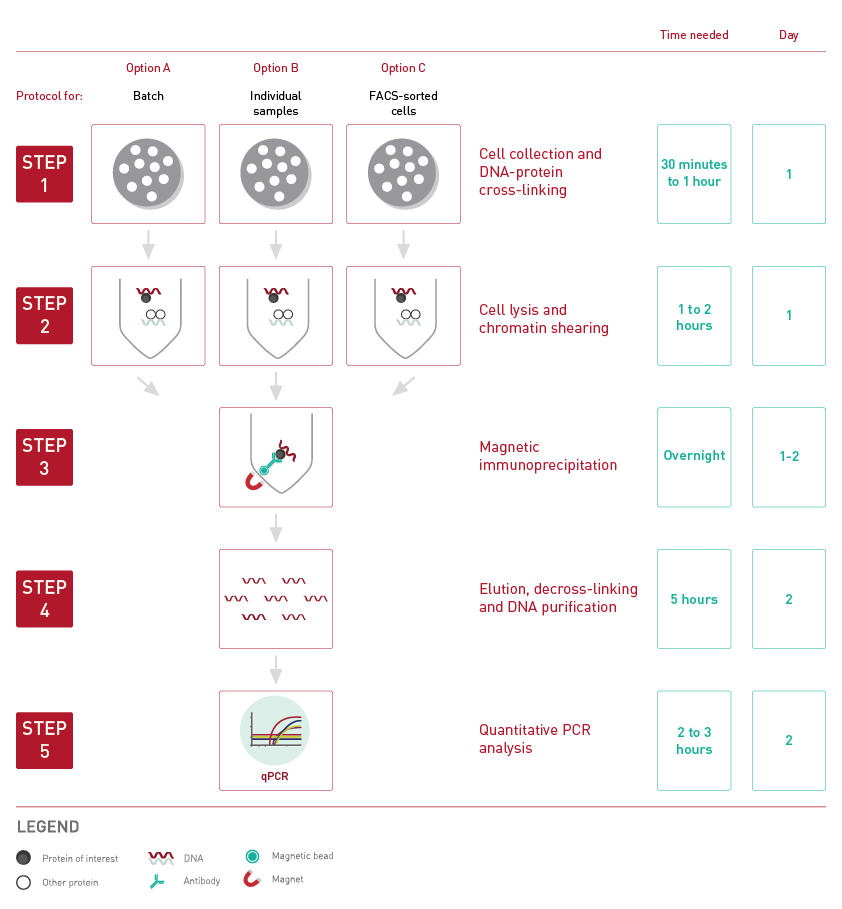
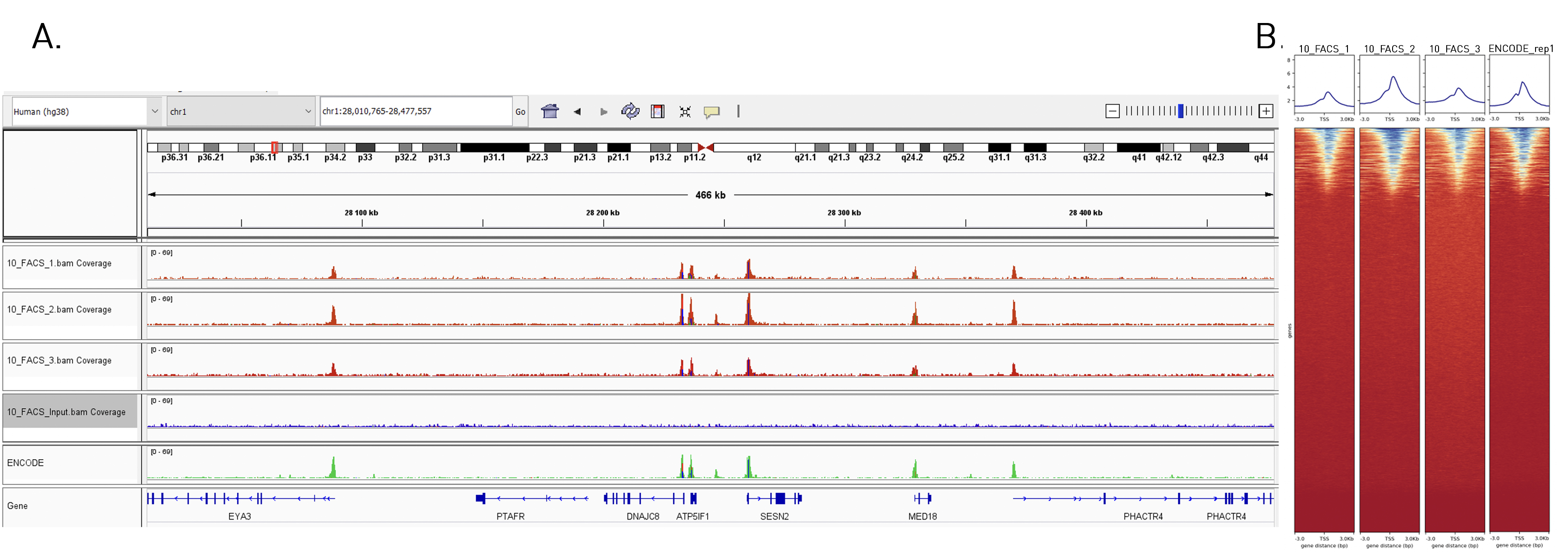
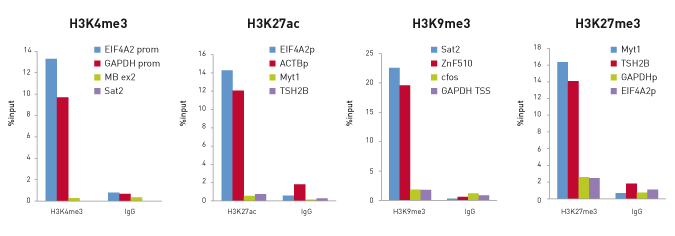
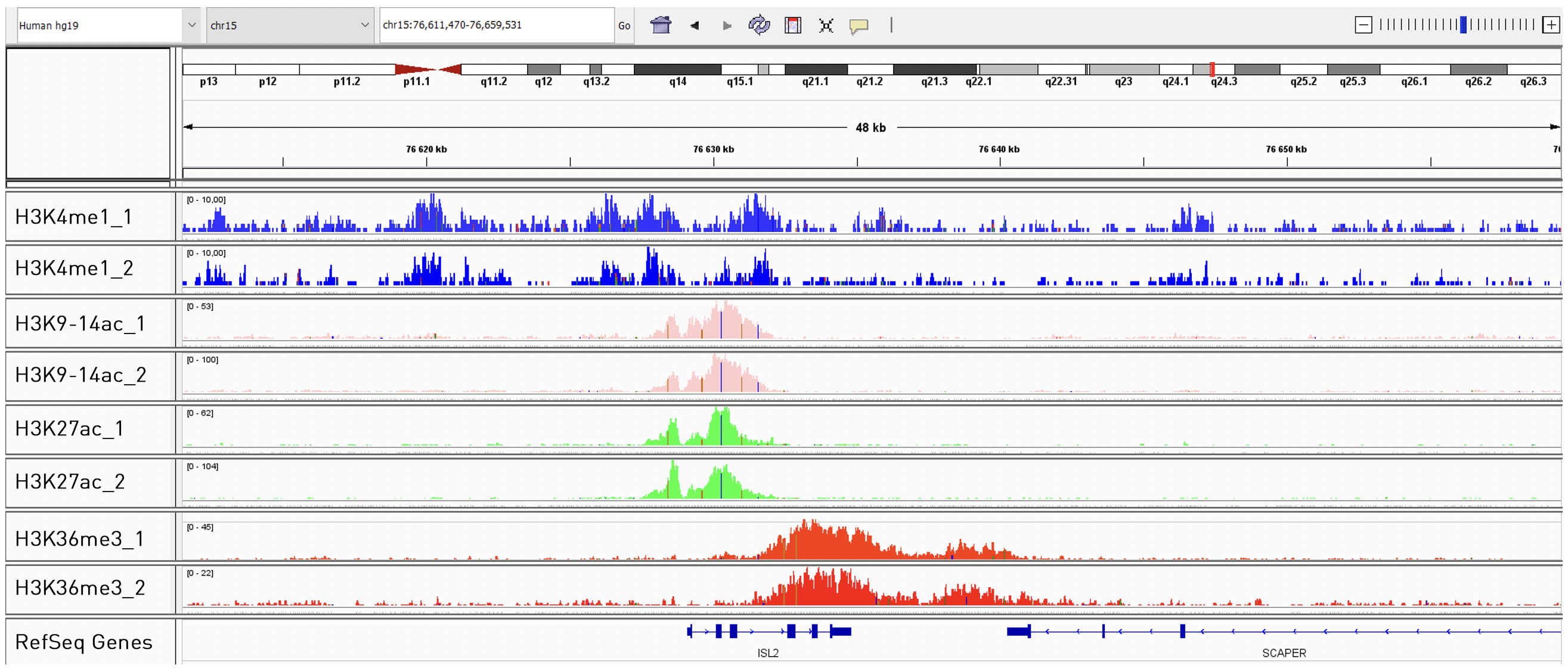
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: True MicroChIP-seq Kit (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C01010132). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Chromatin environment-dependent effects of DOT1L on gene expression in male germ cells
Manon Coulée et al.
The H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L is essential for multiple aspects of mammalian development where it has been shown to regulate gene expression. Here, by producing and integrating epigenomic and spike-in RNA-seq data, we decipher the molecular role of DOT1L during mouse spermatogenesis and show that it has opposite... |
Trithorax regulates long-term memory in Drosophila through epigenetic maintenance of mushroom body metabolic state and translation capacity
Nicholas Raun et al.
The role of epigenetics and chromatin in the maintenance of postmitotic neuronal cell identities is not well understood. Here, we show that the histone methyltransferase Trithorax (Trx) is required in postmitotic memory neurons of the Drosophila mushroom body (MB) to enable their capacity for long-term mem... |
PDGFRA is a conserved HAND2 effector during early cardiac development
Yanli Xu et al.
The basic helix–loop–helix transcription factor HAND2 has multiple roles during vertebrate organogenesis, including cardiogenesis. However, much remains to be uncovered about its mechanism of action. Here, we show the generation of several hand2 mutant alleles in zebrafish and demonstrate that ... |
Single-cell multi-omics, spatial transcriptomics and systematic perturbation decode circuitry of neural crest fate decisions
Hu Z. et al.
Cranial neural crest (NC) cells, which can migrate, adopt multiple fates, and form most of the craniofacial skeleton, are an excellent model for studying cell fate decisions. Using time-resolved single-cell multi-omics, spatial transcriptomics, and systematic Perturb-seq, we fully deciphered zebrafish cranial NC pro... |
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor cell intrinsically promotes resident memoryCD8 T cell differentiation and function.
Dean J. W. et al.
The Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr) regulates the differentiation and function of CD4 T cells; however, its cell-intrinsic role in CD8 T cells remains elusive. Herein we show that Ahr acts as a promoter of resident memory CD8 T cell (T) differentiation and function. Genetic ablation of Ahr in mouse CD... |
FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducingACE2.
Brevini Teresa et al.
Prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection through the modulation of viral host receptors, such as ACE2, could represent a new chemoprophylactic approach for COVID-19 complementing vaccination. However, the mechanisms controlling ACE2 expression remain elusive. Here, we identify the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) as a direct re... |
TCDD induces multigenerational alterations in the expression ofmicroRNA in the thymus through epigenetic modifications
Singh Narendra P et al.
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a potent AhR ligand, is an environmental contaminant that is known for mediating toxicity across generations. However, whether TCDD can induce multigenerational changes in the expression of miRNAs (miRs) has not been previously studied. In the current study, we investigate... |
Intranasal administration of Acinetobacter lwoffii in a murine model ofasthma induces IL-6-mediated protection associated with cecal microbiotachanges.
Alashkar A. B. et al.
BACKGROUND: Early-life exposure to certain environmental bacteria including Acinetobacter lwoffii (AL) has been implicated in protection from chronic inflammatory diseases including asthma later in life. However, the underlying mechanisms at the immune-microbe interface remain largely unknown. METHODS: The effects o... |
Epigenetic Mechanisms Mediating Cell State Transitions in Chondrocytes
Wuelling M. et al.
Epigenetic modifications play critical roles in regulating cell lineage differentiation, but the epigenetic mechanisms guiding specific differentiation steps within a cell lineage have rarely been investigated. To decipher such mechanisms, we used the defined transition from proliferating (PC) into hypertrophic chon... |
Single-cell-resolved dynamics of chromatin architecture delineate cell
and regulatory states in zebrafish embryos
McGarvey, Alison C. and Kopp, Wolfgang and Vučićević,
Dubravka and Mattonet, Kenny and Kempfer, Rieke and Hirsekorn,
Antje and Bilić, Ilija and Gil, Marine and Trinks, Alexandra
and Merks, Anne Margarete and Panáková, Daniela and Pombo,
Ana and Akalin, Al
DNA accessibility of cis-regulatory elements (CREs) dictates
transcriptional activity and drives cell differentiation during
development. While many genes regulating embryonic development have been
identified, the underlying CRE dynamics controlling their expression
remain largely uncharacterized. To address this, w... |
Autocrine Vitamin D-signaling switches off pro-inflammatory programsof Th1 cells
Chauss D.et al.
The molecular mechanisms governing orderly shutdown and retraction of CD4+ T helper (Th)1 responses remain poorly understood. Here, we show that complement triggers contraction of Th1 responses by inducing intrinsic expression of the vitamin D (VitD) receptor (VDR) and the VitD-activating enzyme CYP27B1, permitting ... |
Altered Chromatin States Drive Cryptic Transcription in AgingMammalian Stem Cells.
McCauley Brenna S et al.
A repressive chromatin state featuring trimethylated lysine 36 on histone H3 (H3K36me3) and DNA methylation suppresses cryptic transcription in embryonic stem cells. Cryptic transcription is elevated with age in yeast and nematodes, and reducing it extends yeast lifespan, though whether this occurs in mammals is unk... |
Inactivating histone deacetylase HDA promotes longevity by mobilizingtrehalose metabolism.
Yu, Ruofan et al.
Histone acetylations are important epigenetic markers for transcriptional activation in response to metabolic changes and various stresses. Using the high-throughput SEquencing-Based Yeast replicative Lifespan screen method and the yeast knockout collection, we demonstrate that the HDA complex, a class-II histone de... |
Histone H1 loss drives lymphoma by disrupting 3D chromatin architecture.
Yusufova, Nevin and Kloetgen, Andreas and Teater, Matt and Osunsade,Adewola and Camarillo, Jeannie M and Chin, Christopher R and Doane, AshleyS and Venters, Bryan J and Portillo-Ledesma, Stephanie and Conway, Josephand Phillip, Jude M and Elemento, Oli
Linker histone H1 proteins bind to nucleosomes and facilitate chromatin compaction, although their biological functions are poorly understood. Mutations in the genes that encode H1 isoforms B-E (H1B, H1C, H1D and H1E; also known as H1-5, H1-2, H1-3 and H1-4, respectively) are highly recurrent in B cell lymphoma... |
Increased H3K4me3 methylation and decreased miR-7113-5p expression lead toenhanced Wnt/β-catenin signaling in immune cells from PTSD patientsleading to inflammatory phenotype.
Bam, Marpe and Yang, Xiaoming and Busbee, Brandon P and Aiello, Allison Eand Uddin, Monica and Ginsberg, Jay P and Galea, Sandro and Nagarkatti,Prakash S and Nagarkatti, Mitzi
BACKGROUND: Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a psychiatric disorder accompanied by chronic peripheral inflammation. What triggers inflammation in PTSD is currently unclear. In the present study, we identified potential defects in signaling pathways in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from individual... |
Trans- and cis-acting effects of Firre on epigenetic features of theinactive X chromosome.
Fang, He and Bonora, Giancarlo and Lewandowski, Jordan P and Thakur,Jitendra and Filippova, Galina N and Henikoff, Steven and Shendure, Jay andDuan, Zhijun and Rinn, John L and Deng, Xinxian and Noble, William S andDisteche, Christine M
Firre encodes a lncRNA involved in nuclear organization. Here, we show that Firre RNA expressed from the active X chromosome maintains histone H3K27me3 enrichment on the inactive X chromosome (Xi) in somatic cells. This trans-acting effect involves SUZ12, reflecting interactions between Firre RNA and components of t... |
Age-associated cryptic transcription in mammalian stem cells is linked topermissive chromatin at cryptic promoters
McCauley B. S. et al.
Suppressing spurious cryptic transcription by a repressive intragenic chromatin state featuring trimethylated lysine 36 on histone H3 (H3K36me3) and DNA methylation is critical for maintaining self-renewal capacity in mouse embryonic stem cells. In yeast and nematodes, such cryptic transcription is elevated with age... |
Mutant EZH2 Induces a Pre-malignant Lymphoma Niche by Reprogramming the Immune Response.
Béguelin W, Teater M, Meydan C, Hoehn KB, Phillip JM, Soshnev AA, Venturutti L, Rivas MA, Calvo-Fernández MT, Gutierrez J, Camarillo JM, Takata K, Tarte K, Kelleher NL, Steidl C, Mason CE, Elemento O, Allis CD, Kleinstein SH, Melnick AM
Follicular lymphomas (FLs) are slow-growing, indolent tumors containing extensive follicular dendritic cell (FDC) networks and recurrent EZH2 gain-of-function mutations. Paradoxically, FLs originate from highly proliferative germinal center (GC) B cells with proliferation strictly dependent on interactions with T fo... |
Transferrin Receptor 1 Regulates Thermogenic Capacity and Cell Fate in Brown/Beige Adipocytes
Jin Li, Xiaohan Pan, Guihua Pan, Zijun Song, Yao He, Susu Zhang, Xueru Ye, Xiang Yang, Enjun Xie, Xinhui Wang, Xudong Mai, Xiangju Yin, Biyao Tang, Xuan Shu, Pengyu Chen, Xiaoshuang Dai, Ye Tian, Liheng Yao, Mulan Han, Guohuan Xu, Huijie Zhang, Jia Sun, H
Iron homeostasis is essential for maintaining cellular function in a wide range of cell types. However, whether iron affects the thermogenic properties of adipocytes is currently unknown. Using integrative analyses of multi-omics data, transferrin receptor 1 (Tfr1) is identified as a candidate for regulating thermog... |
Functionally Annotating Regulatory Elements in the Equine Genome Using Histone Mark ChIP-Seq.
Kingsley NB, Kern C, Creppe C, Hales EN, Zhou H, Kalbfleisch TS, MacLeod JN, Petersen JL, Finno CJ, Bellone RR
One of the primary aims of the Functional Annotation of ANimal Genomes (FAANG) initiative is to characterize tissue-specific regulation within animal genomes. To this end, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-Seq) to map four histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me... |
Wnt5a is a transcriptional target of Gli3 and Trps1 at the onset of chondrocyte hypertrophy.
Wuelling M, Schneider S, Schröther VA, Waterkamp C, Hoffmann D, Vortkamp A
During endochondral ossification, the differentiation of proliferating into hypertrophic chondrocytes is a key step determining the pace of bone formation and the future length of the skeletal elements. A variety of transcription factors are expressed at the onset of hypertrophy coordinating the expression of differ... |
Interaction of Sox2 with RNA binding proteins in mouse embryonic stem cells.
Samudyata , Amaral PP, Engström PG, Robson SC, Nielsen ML, Kouzarides T, Castelo-Branco G
Sox2 is a master transcriptional regulator of embryonic development. In this study, we determined the protein interactome of Sox2 in the chromatin and nucleoplasm of mouse embryonic stem (mES) cells. Apart from canonical interactions with pluripotency-regulating transcription factors, we identified interactions with... |
Development and epigenetic plasticity of murine Müller glia.
Dvoriantchikova G, Seemungal RJ, Ivanov D
The ability to regenerate the entire retina and restore lost sight after injury is found in some species and relies mostly on the epigenetic plasticity of Müller glia. To understand the role of mammalian Müller glia as a source of progenitors for retinal regeneration, we investigated changes in gene expres... |
Whsc1 links pluripotency exit with mesendoderm specification.
Tian TV, Di Stefano B, Stik G, Vila-Casadesús M, Sardina JL, Vidal E, Dasti A, Segura-Morales C, De Andrés-Aguayo L, Gómez A, Goldmann J, Jaenisch R, Graf T
How pluripotent stem cells differentiate into the main germ layers is a key question of developmental biology. Here, we show that the chromatin-related factor Whsc1 (also known as Nsd2 and MMSET) has a dual role in pluripotency exit and germ layer specification of embryonic stem cells. On induction of differentiatio... |
The epigenetic basis for the impaired ability of adult murine retinal pigment epithelium cells to regenerate retinal tissue.
Dvoriantchikova G, Seemungal RJ, Ivanov D
The epigenetic plasticity of amphibian retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) allows them to regenerate the entire retina, a trait known to be absent in mammals. In this study, we investigated the epigenetic plasticity of adult murine RPE to identify possible mechanisms that prevent mammalian RPE from regenerating retinal... |
Spatial confinement downsizes the inflammatory response of macrophages.
Jain N, Vogel V
Macrophages respond to chemical/metabolic and physical stimuli, but their effects cannot be readily decoupled in vivo during pro-inflammatory activation. Here, we show that preventing macrophage spreading by spatial confinement, as imposed by micropatterning, microporous substrates or cell crowding, suppresses late ... |
Automethylation-induced conformational switch in Clr4 (Suv39h) maintains epigenetic stability.
Iglesias N, Currie MA, Jih G, Paulo JA, Siuti N, Kalocsay M, Gygi SP, Moazed D
Histone H3 lysine 9 methylation (H3K9me) mediates heterochromatic gene silencing and is important for genome stability and the regulation of gene expression. The establishment and epigenetic maintenance of heterochromatin involve the recruitment of H3K9 methyltransferases to specific sites on DNA, followed by the re... |
Epigenetic inheritance mediated by coupling of RNAi and histone H3K9 methylation.
Yu R, Wang X, Moazed D
Histone post-translational modifications (PTMs) are associated with epigenetic states that form the basis for cell-type-specific gene expression. Once established, histone PTMs can be maintained by positive feedback involving enzymes that recognize a pre-existing histone modification and catalyse the same modificati... |
Insulin promoter in human pancreatic β cells contacts diabetes susceptibility loci and regulates genes affecting insulin metabolism.
Jian X, Felsenfeld G
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes involve a complex interplay between genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. Our laboratory has been interested in the physical interactions, in nuclei of human pancreatic β cells, between the insulin ( gene and other genes that are involved in insulin metabolism. We have ... |
Retinoid-Sensitive Epigenetic Regulation of the Hoxb Cluster Maintains Normal Hematopoiesis and Inhibits Leukemogenesis.
Qian P, De Kumar B, He XC, Nolte C, Gogol M, Ahn Y, Chen S, Li Z, Xu H, Perry JM, Hu D, Tao F, Zhao M, Han Y, Hall K, Peak A, Paulson A, Zhao C, Venkatraman A, Box A, Perera A, Haug JS, Parmely T, Li H, Krumlauf R, Li L
Hox genes modulate the properties of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and reacquired Hox expression in progenitors contributes to leukemogenesis. Here, our transcriptome and DNA methylome analyses revealed that Hoxb cluster and retinoid signaling genes are predominantly enriched in LT-HSCs, and this coordinate regula... |
Contrasting epigenetic states of heterochromatin in the different types of mouse pluripotent stem cells.
Tosolini M, Brochard V, Adenot P, Chebrout M, Grillo G, Navia V, Beaujean N, Francastel C, Bonnet-Garnier A, Jouneau A
Mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) represent naive and primed pluripotency states, respectively, and are maintained in vitro by specific signalling pathways. Furthermore, ESCs cultured in serum-free medium with two kinase inhibitors (2i-ESCs) are thought to be the ground naïve pl... |
Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 Regulate Microglia Function during Development, Homeostasis, and Neurodegeneration in a Context-Dependent Manner.
Datta M, Staszewski O, Raschi E, Frosch M, Hagemeyer N, Tay TL, Blank T, Kreutzfeldt M, Merkler D, Ziegler-Waldkirch S, Matthias P, Meyer-Luehmann M, Prinz M
Microglia as tissue macrophages contribute to the defense and maintenance of central nervous system (CNS) homeostasis. Little is known about the epigenetic signals controlling microglia function in vivo. We employed constitutive and inducible mutagenesis in microglia to delete two class I histone deacetylases, ... |