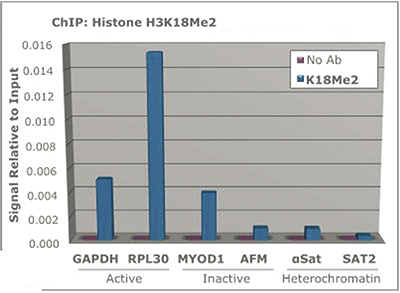
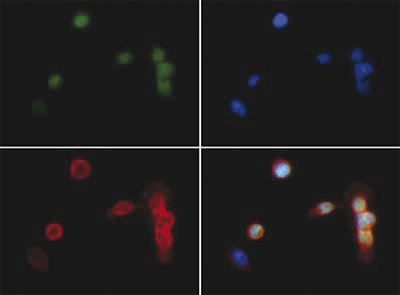
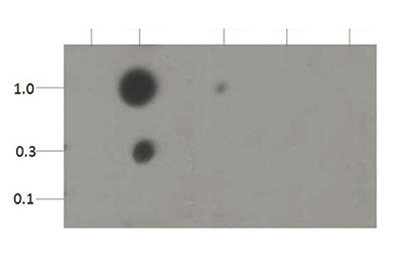
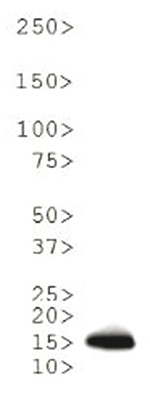The di-methylated K18 on histone H3 is a seemingly transient post-translational modification. H3K18 is better known to be acetylated, and occasionally mono-methylated. Suv39h1, a well-studied histone methyltransferase seems to be responsible for the transition of acetylation and methylation at this H3 modification site. The di-methylated K18 on H3 seems to be associated with embryological development and possibly implantation.