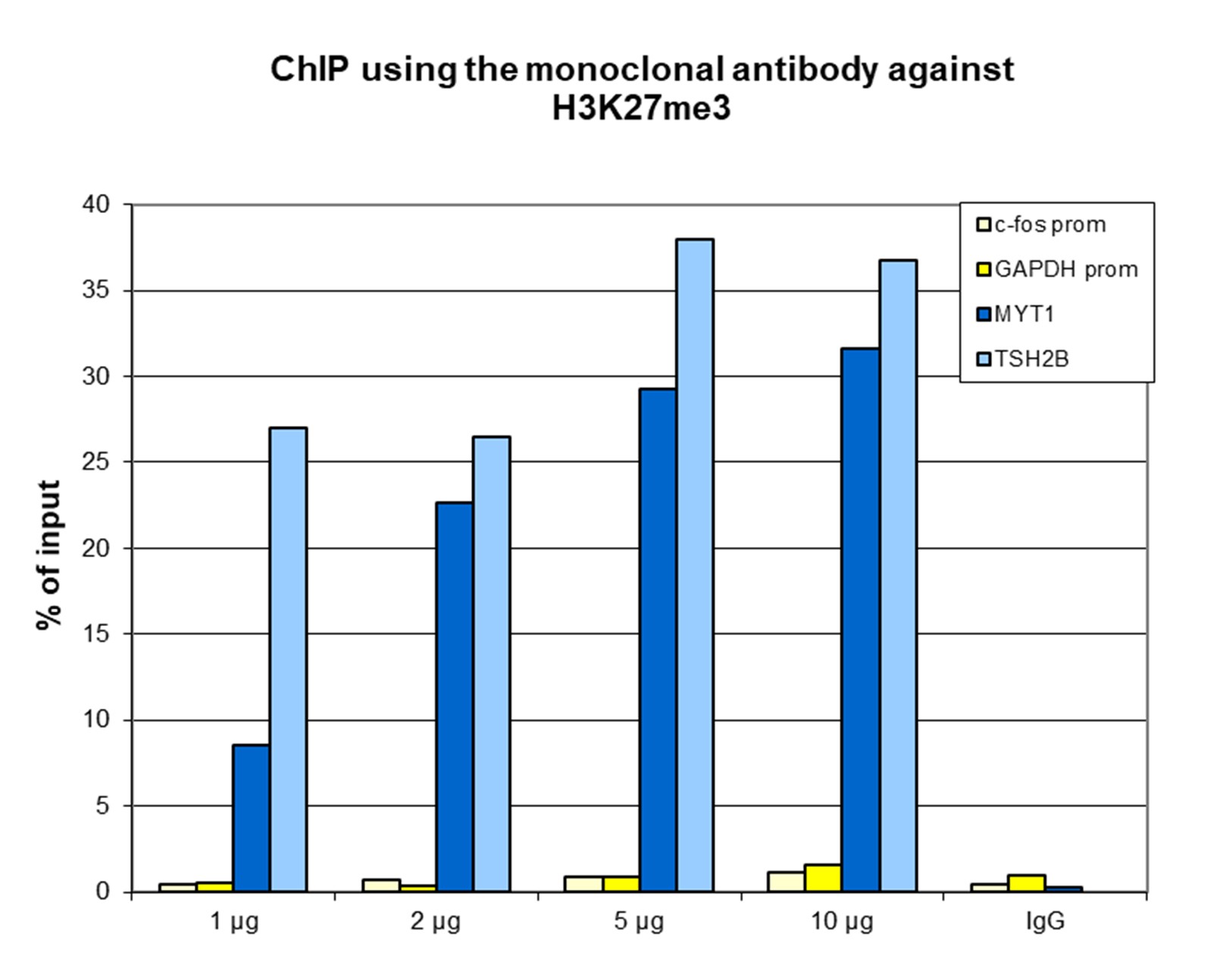
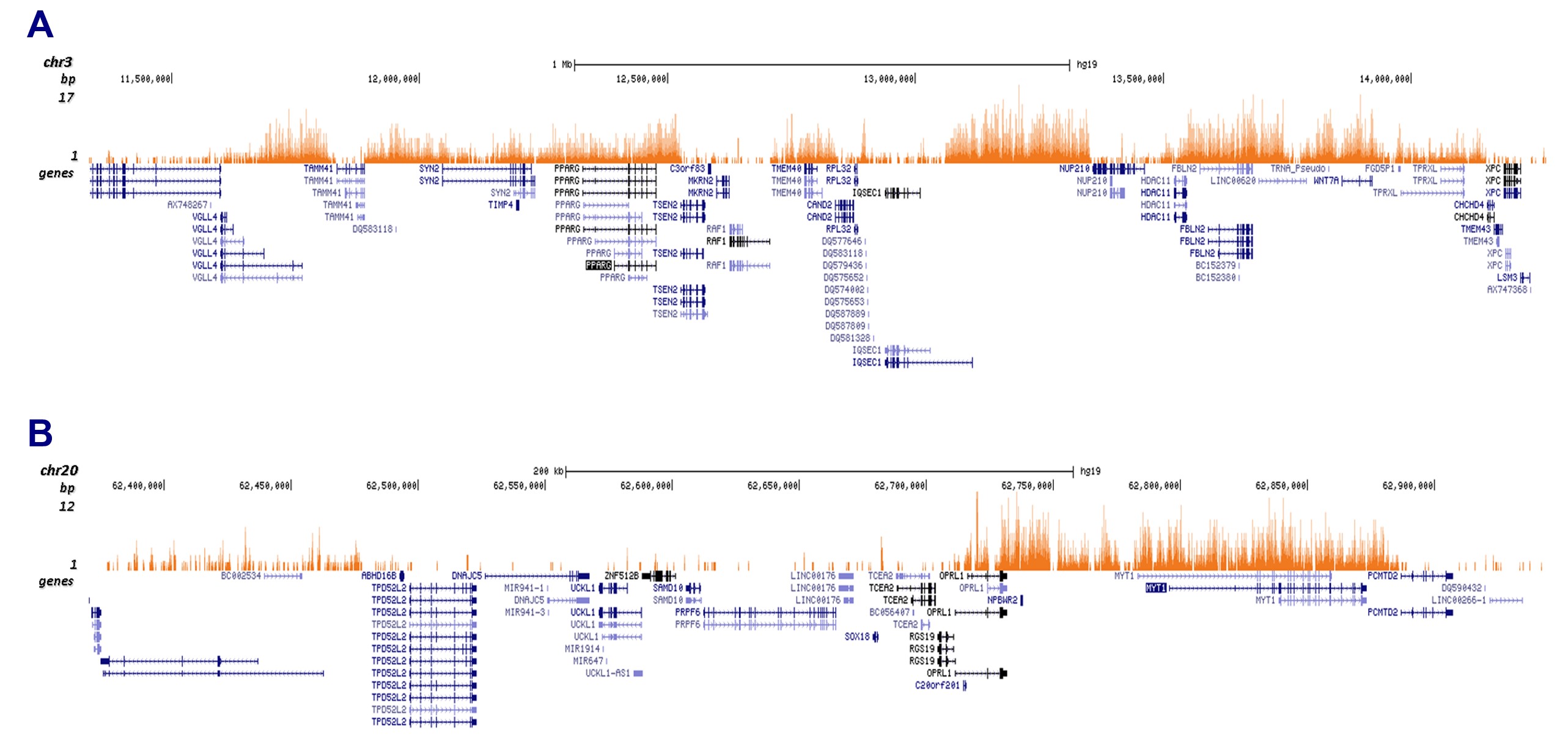
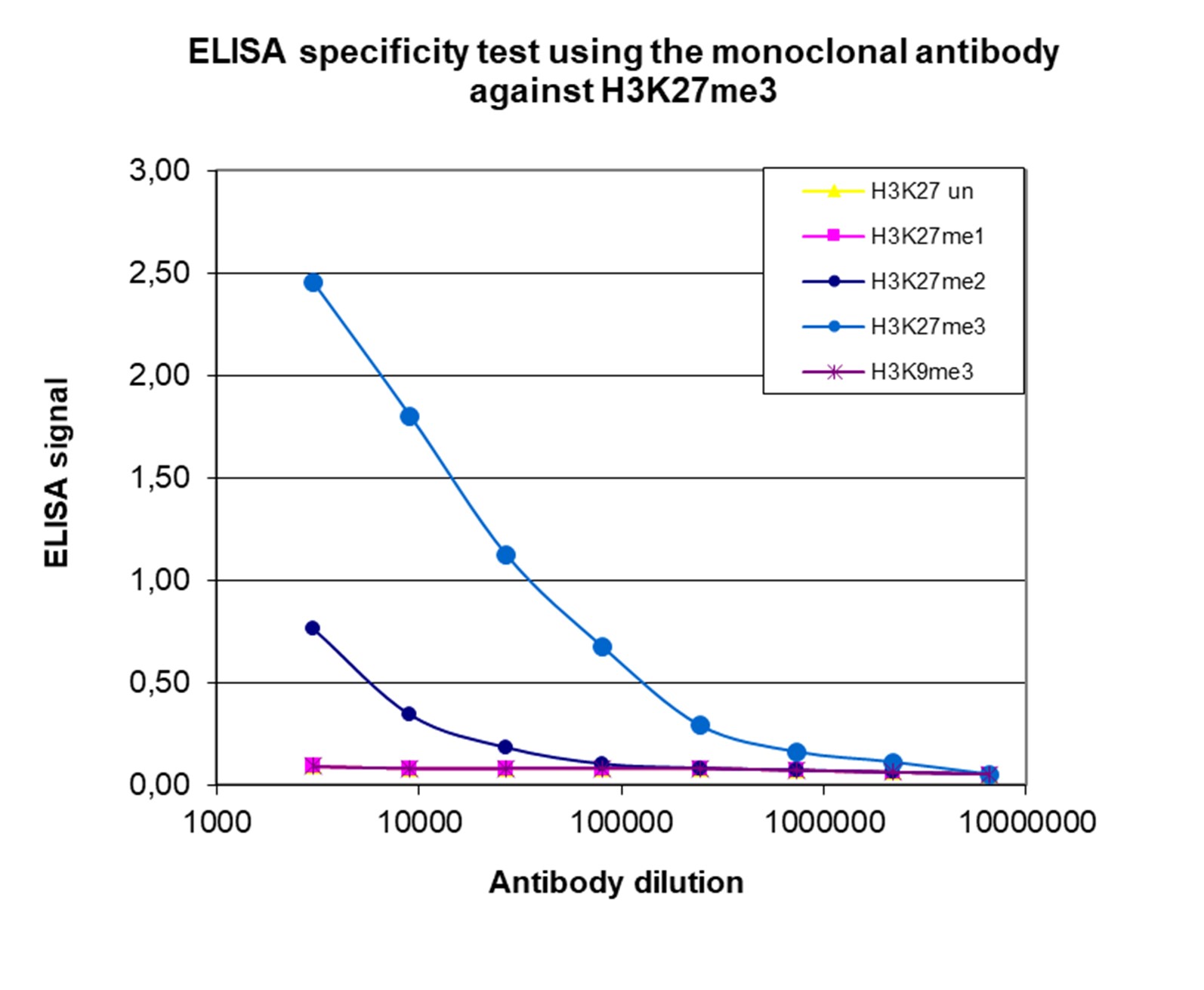
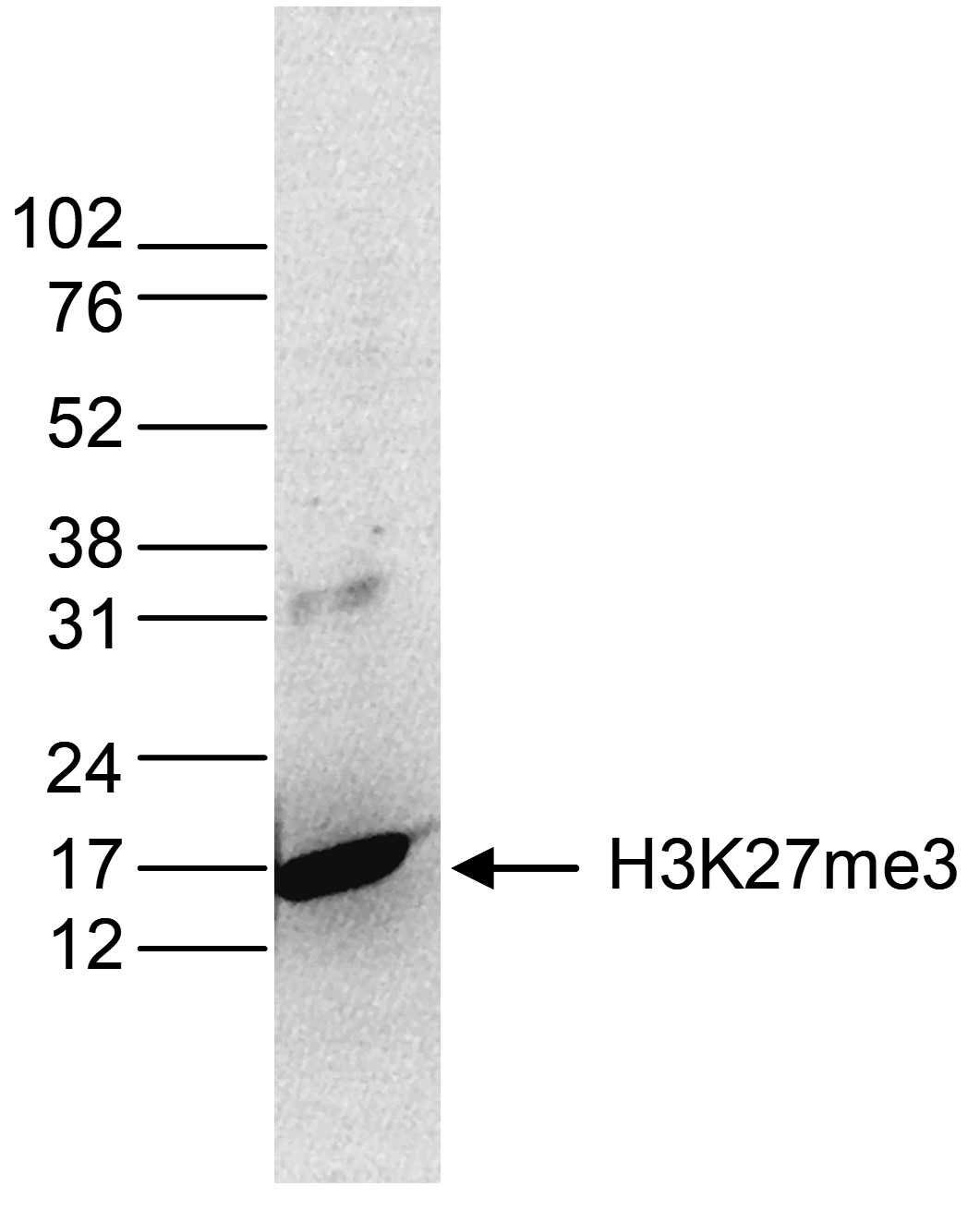
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K27me3 Antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15200181-10 Lot# 001-16). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
PHF19 drives the formation of PRC2 clusters to enhance motility in TNBC cells
Pelzer, Nina et al.
Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) is a key regulator of transcriptional repression and chromatin organization, essential in development and disease. While its enzymatic activity is well characterized, the factors governing PRC2 subnuclear organization, particularly in cancer cells, are largely unknown. Here, we... |
Constitutive expression of the transcriptional co-activator IκBζ promotes melanoma growth and immunotherapy resistance
Kolb, Antonia et al.
IκBζ, a rather unknown co-regulator of NF-κB, can either activate or repress a subset of NF-κB target genes. While its role as an inducibly expressed, transcriptional regulator of cytokines and chemokines in immune cells is established, IκBζ's function in solid cancer remains un... |
Chromatin profiling reveals TFAP4 as a critical transcriptional regulator of bovine satellite cell differentiation
Pengcheng Lyu et al.
Background
Satellite cells are myogenic precursor cells in adult skeletal muscle and play a crucial role in skeletal muscle regeneration, maintenance, and growth. Like embryonic myoblasts, satellite cells have the ability to proliferate, differentiate, and fuse to form multinucleated myofibers. In this study, we ai... |
Tracing the emergence of primordial germ cells from bilaminar disc rabbitembryos and pluripotent stem cells.
Kobayashi Toshihiro et al.
Rabbit embryos develop as bilaminar discs at gastrulation as in humans and most other mammals, whereas rodents develop as egg cylinders. Primordial germ cells (PGCs) appear to originate during gastrulation according to many systematic studies on mammalian embryos. Here, we show that rabbit PGC (rbPGC) specification ... |
Histone modification dynamics at H3K27 are associated with alteredtranscription of in planta induced genes in Magnaporthe oryzae.
Zhang, Wei and Huang, Jun and Cook, David E
Transcriptional dynamic in response to environmental and developmental cues are fundamental to biology, yet many mechanistic aspects are poorly understood. One such example is fungal plant pathogens, which use secreted proteins and small molecules, termed effectors, to suppress host immunity and promote colonization... |
Intergenerationally Maintained Histone H4 Lysine 16 Acetylation Is Instructive for Future Gene Activation.
Samata M, Alexiadis A, Richard G, Georgiev P, Nuebler J, Kulkarni T, Renschler G, Basilicata MF, Zenk FL, Shvedunova M, Semplicio G, Mirny L, Iovino N, Akhtar A
Before zygotic genome activation (ZGA), the quiescent genome undergoes reprogramming to transition into the transcriptionally active state. However, the mechanisms underlying euchromatin establishment during early embryogenesis remain poorly understood. Here, we show that histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation (H4K16ac) i... |
Pro-inflammatory cytokines activate hypoxia-inducible factor 3α via epigenetic changes in mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.
Cuomo F, Coppola A, Botti C, Maione C, Forte A, Scisciola L, Liguori G, Caiafa I, Ursini MV, Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Altucci L, Cobellis G
Human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (hMSCs) emerged as a promising therapeutic tool for ischemic disorders, due to their ability to regenerate damaged tissues, promote angiogenesis and reduce inflammation, leading to encouraging, but still limited results. The outcomes in clinical trials exploring hMSC therapy are ... |
Chemical Biology Approaches for Characterization of Epigenetic Regulators
Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Szewczyk MM, Prinos P, Lima-Fernandes E, Ackloo S, Arrowsmith CH
Chemical biology approaches are a powerful means to functionally characterize epigenetic regulators such as histone modifying enzymes. We outline experimental protocols and best practices for the cellular characterization and use of “chemical probes” that selectively inhibit protein methyltransferases, m... |
Germline organization in Strongyloides nematodes reveals alternative differentiation and regulation mechanisms.
Kulkarni A et al.
Nematodes of the genus Strongyloides are important parasites of vertebrates including man. Currently, little is known about their germline organization or reproductive biology and how this influences their parasitic life strategies. Here, we analyze the structure of the germline in several Strongyloides and closely ... |
An Orally Bioavailable Chemical Probe of the Lysine Methyltransferases EZH2 and EZH1.
Konze KD, Ma A, Li F, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Parton T, Macnevin CJ, Liu F, Gao C, Huang XP, Kuznetsova E, Rougie M, Jiang A, Pattenden SG, Norris JL, James LI, Roth BL, Brown PJ, Frye SV, Arrowsmith CH, Hahn KM, Wang GG, Vedadi M, Jin J
EZH2 or EZH1 is the catalytic subunit of the polycomb repressive complex 2 that catalyzes methylation of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27). The trimethylation of H3K27 (H3K27me3) is a transcriptionally repressive post-translational modification. Overexpression of EZH2 and hypertrimethylation of H3K27 have been implicated... |