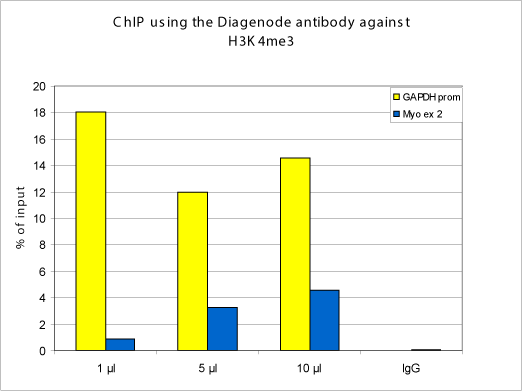
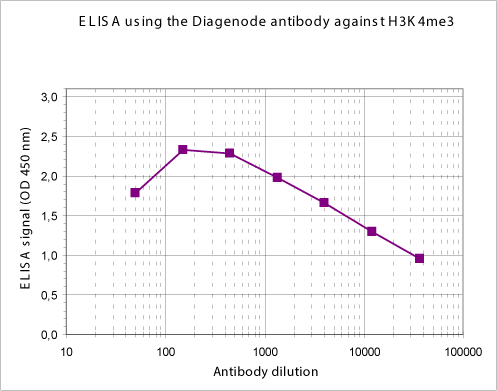
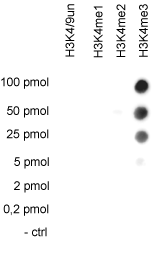
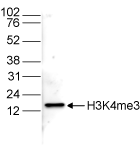
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K4me3 Antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15310003 Lot# A.49-001 ). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Neurons undergo IFNγ-driven persistent epigenetic shifts and synaptopathy in encephalitis
Shammas, Ghazal et al.
In infectious and autoimmune disorders of the central nervous system, neurons can become cognate immunological targets of cytotoxic T cells, leading to persistent functional and synaptic impairments. However, the molecular underpinnings of such irreversible alterations remain unclear. Using a cytotoxic T cell-driv... |
Single amino-acid mutation in a Drosoph ila melanogaster ribosomalprotein: An insight in uL11 transcriptional activity.
Grunchec H. et al.
The ribosomal protein uL11 is located at the basis of the ribosome P-stalk and plays a paramount role in translational efficiency. In addition, no mutant for uL11 is available suggesting that this gene is haplo-insufficient as many other Ribosomal Protein Genes (RPGs). We have previously shown that overexpression of... |
Epigenomic profiling of primate lymphoblastoid cell lines reveals theevolutionary patterns of epigenetic activities in gene regulatoryarchitectures
García-Pérez R. et al.
Changes in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression have a central role in evolution. Here, we extensively profiled a panel of human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan, and macaque lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs), using ChIP-seq for five histone marks, ATAC-seq and RNA-seq, further complemented with whole genome s... |
Physical and functional interaction between SET1/COMPASS complex component CFP-1 and a Sin3S HDAC complex in C. elegans.
Beurton F, Stempor P, Caron M, Appert A, Dong Y, Chen RA, Cluet D, Couté Y, Herbette M, Huang N, Polveche H, Spichty M, Bedet C, Ahringer J, Palladino F
The CFP1 CXXC zinc finger protein targets the SET1/COMPASS complex to non-methylated CpG rich promoters to implement tri-methylation of histone H3 Lys4 (H3K4me3). Although H3K4me3 is widely associated with gene expression, the effects of CFP1 loss vary, suggesting additional chromatin factors contribute to context d... |
The FZD7-TWIST1 axis is responsible for anoikis resistance and tumorigenesis in ovarian carcinoma.
Tan M, Asad M, Heong V, Wong MK, Tan TZ, Ye J, Kuay KT, Thiery JP, Scott C, Huang RY
Frizzled family receptor 7 (FZD7), a Wnt signaling receptor, is associated with the maintenance of stem cell properties and cancer progression. FZD7 has emerged as a potential therapeutic target because it is capable of transducing both canonical and noncanonical Wnt signals. In this study, we investigated the regul... |
Inhibiting Inflammation with Myeloid Cell-Specific Nanobiologics Promotes Organ Transplant Acceptance.
Braza MS, van Leent MMT, Lameijer M, Sanchez-Gaytan BL, Arts RJW, Pérez-Medina C, Conde P, Garcia MR, Gonzalez-Perez M, Brahmachary M, Fay F, Kluza E, Kossatz S, Dress RJ, Salem F, Rialdi A, Reiner T, Boros P, Strijkers GJ, Calcagno CC, Ginhoux F, Marazzi
Inducing graft acceptance without chronic immunosuppression remains an elusive goal in organ transplantation. Using an experimental transplantation mouse model, we demonstrate that local macrophage activation through dectin-1 and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) drives trained immunity-associated cytokine production duri... |
c-Myc Antagonises the Transcriptional Activity of the Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer Affecting Key Gene Networks
Stefan J. Barfeld, Alfonso Urbanucci, Harri M. Itkonen, Ladan Fazli , Jessica L. Hicks , Bernd Thiede , Paul S. Rennie , Srinivasan Yegnasubramanian, Angelo M. DeMarzo , Ian G. Mills
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common non-cutaneous cancer in men. The androgen receptor (AR), a ligand-activated transcription factor, constitutes the main drug target for advanced cases of the disease. However, a variety of other transcription factors and signaling networks have been shown to be altered in pati... |
GRHL2-miR-200-ZEB1 maintains the epithelial status of ovarian cancer through transcriptional regulation and histone modification
Chung VY, Tan TZ, Tan M, Wong MK, Kuay KT, Yang Z, Ye J, Muller J, Koh CM, Guccione E, Thiery JP, Huang RY
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a biological process by which polarized epithelial cells convert into a mesenchymal phenotype, has been implicated to contribute to the molecular heterogeneity of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Here we report that a transcription factor-Grainyhead-like 2 (GRHL2) maintains t... |
The complex pattern of epigenomic variation between natural yeast strains at single-nucleosome resolution.
Filleton F, Chuffart F, Nagarajan M, Bottin-Duplus H, Yvert G
BACKGROUND:
Epigenomic studies on humans and model species have revealed substantial inter-individual variation in histone modification profiles. However, the pattern of this variation has not been precisely characterized, particularly regarding which genomic features are enriched for variability and whether dist... |
Caenorhabditis elegans chromatin-associated proteins SET-2 and ASH-2 are differentially required for histone H3 Lys 4 methylation in embryos and adult germ cells.
Xiao Y, Bedet C, Robert VJ, Simonet T, Dunkelbarger S, Rakotomalala C, Soete G, Korswagen HC, Strome S, Palladino F
Methylation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me), a mark associated with gene activation, is mediated by SET1 and the related mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) histone methyltransferases (HMTs) across species. Mammals contain seven H3K4 HMTs, Set1A, Set1B, and MLL1-MLL5. The activity of SET1 and MLL proteins relies on protein... |