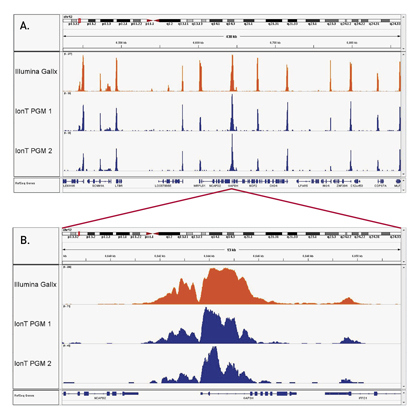
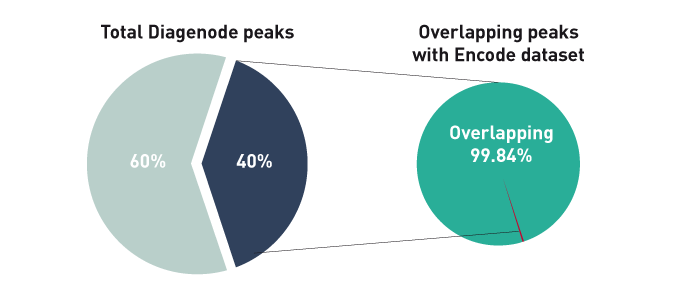
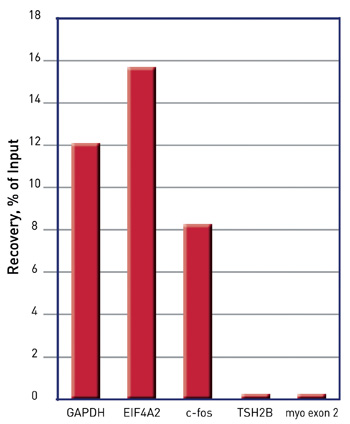
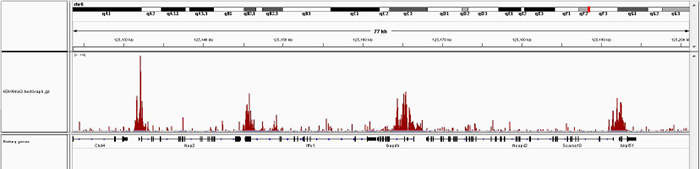
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: iDeal ChIP-seq kit for Histones (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C01010051). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
CRISPR-based precise methylation of specific FUT8 promoter regions allows isolation of CHO cells with a fine-tuned glycoprofile
Jiménez Lancho, Víctor et al.
A major advantage of producing therapeutic proteins in mammalian cells is their ability to tailor proteins with human-like posttranslational modifications such as glycosylation, which ultimately defines aspects like stability, protein folding or immunogenicity. However, producing therapeutic proteins with a consis... |
Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B-cells from a hypoxia model of the germinal center requires external unsaturated fatty acids
Havey, Larissa et al.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) drives over 200,000 cancer cases annually, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, and classic Hodgkin lymphoma-malignancies that frequently originate from germinal centers (GCs), which are physiologically hypoxic (O2 < 1%). However, conventional transformation mode... |
Disease-specific epigenetic deregulation of enhancers, transposons, and polycomb targets in acute promyelocytic leukemia
Zhong, Xiangfu et al.
Background: Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), characterized by a fusion between the PML and RARA genes and by a block in the myeloid maturation at the promyelocytic stage.
Methods: This study investigates the epigenetic landscape of APL by integrating ChIP-se... |
Targeting histone H2B acetylated enhanceosomes via p300/CBP degradation in prostate cancer
Luo, Jie et al.
Prostate cancer is driven by oncogenic transcription factor enhanceosomes comprising chromatin and epigenetic regulators. The lysine acetyltransferases p300 and CREB-binding protein (CBP) are key cofactors that activate enhancers through histone acetylation. Here we identify p300/CBP-mediated multisite histone H... |
Combinatorial DNMTs and EZH2 inhibition reprograms the H3K27me3 and DNAme-mediated onco-epigenome to suppress multiple myeloma proliferation
Atienza Párraga, Alba et al.
Comprehensive epigenomic studies in multiple myeloma (MM) that unravel the connections between major epigenetic regulators, their intertwined collaboration and the potential of combinatorial targeting remain limited. Utilizing ChIP-seq, ATAC-seq, RNA-seq, and DNA methylation (DNAme) data, we generated whole-genome c... |
Epstein-Barr Virus-Driven B-Cell Transformation under Germinal Center Hypoxia Requires External Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Havey, Larissa et al.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) contributes to over 200,000 cancers annually, predominantly aggressive lymphomas originating from hypoxic germinal centers (< 1% O2). However, conventional models fail to recapitulate the physiologically relevant hypoxic microenvironment which profoundly influences B-cell metabolic remode... |
Radial glia integrin avb8 regulates cell autonomous microglial TGFβ1 signaling that is necessary for microglial identity
Gabriel L. McKinsey et al.
Microglial diversity arises from the interplay between inherent genetic programs and external environmental signals. However, the mechanisms by which these processes develop and interact within the growing brain are not yet fully understood. Here, we show that radial glia-expressed integrin beta 8 (ITGB8) activates ... |
IER3: exploring its dual function as an oncogene and tumor suppressor
Meena Kanduri et al.
The IER3 gene has a complex role in cancer biology, acting either as a tumor suppressor or an oncogene, depending on the cancer type. This duality underscores the complexity and importance of molecular pathways in modulating cancer behavior. Despite its significance in cancer development, there is a dearth of studie... |
Chromatin environment-dependent effects of DOT1L on gene expression in male germ cells
Manon Coulée et al.
The H3K79 methyltransferase DOT1L is essential for multiple aspects of mammalian development where it has been shown to regulate gene expression. Here, by producing and integrating epigenomic and spike-in RNA-seq data, we decipher the molecular role of DOT1L during mouse spermatogenesis and show that it has opposite... |
RNA Pol-II transcripts in nucleolar associated domains of cancer cell nucleoli
Soumya Roy Chowdhury et al.
We performed a comparative study of the non-ribosomal gene content of nucleoli from seven cancer cell lines, using identical methods of purification and analysis. We identified unique chromosomal domains associated with the nucleolus (NADs) and genes within these domains (NAGs). Four cell lines have relatively few N... |
Interferon-gamma rescues FK506 dampened dendritic cell calcineurin-dependent responses to Aspergillus fumigatus via Stat3 to Stat1 switching
Amit Adlakha et al.
IScience Highlights
Calcineurin inhibitors block DC maturation in response to A. fumigatus
Lack of DC maturation impairs Th1 polarization in response to A. fumigatus
Interferon-γ restores maturation, promotes Th1 polarization and fungal killing
ChIPseq reveals in... |
ETV2/ER71 regulates hematovascular lineage generation and vascularization through an H3K9 demethylase, KDM4A
Min Seong Kim et al.
Highlights
Interaction of ETV2 and KDM4A decreases H3K9 trimethylation on hematovascular genes.
ETV2 and KDM4A cooperatively regulates the expression of hematovascular genes.
Mice lacking endothelial Etv2 and Kdm4a display a severe angiogenic impairment.
... |
Claudin-1 as a potential marker of stress-induced premature senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells
Agnieszka Gadecka et al.
Cellular senescence, a permanent state of cell cycle arrest, can result either from external stress and is then called stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS), or from the exhaustion of cell division potential giving rise to replicative senescence (RS). Despite numerous biomarkers distinguishing SIPS from RS rema... |
Innate immune training restores pro-reparative myeloid functions to promote remyelination in the aged central nervous system
Tiwari V. et al.
The reduced ability of the central nervous system to regenerate with increasing age limits functional recovery following demyelinating injury. Previous work has shown that myelin debris can overwhelm the metabolic capacity of microglia, thereby impeding tissue regeneration in aging, but the underlying mechanisms are... |
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment
Perez R. F. at al.
Aging involves the deterioration of organismal function, leading to the emergence of multiple pathologies. Environmental stimuli, including lifestyle, can influence the trajectory of this process and may be used as tools in the pursuit of healthy aging. To evaluate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this context, ... |
The landscape of RNA-chromatin interaction reveals small non-coding RNAs as essential mediators of leukemia maintenance
Haiyang Yun et al.
RNA constitutes a large fraction of chromatin. Spatial distribution and functional relevance of most of RNA-chromatin interactions remain unknown. We established a landscape analysis of RNA-chromatin interactions in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In total more than 50 million interactions were captured in an AM... |
Positive and negative feedback regulation of the TGF-β1 explains two equilibrium states in skin aging
Haga M. et al.
During aging, skin homeostasis is essential for maintaining appearance, as well as biological defense of the human body. In this study, we identified thrombospondin-1 (THBS1) and fibromodulin (FMOD) as positive and negative regulators, respectively, of the TGF-β1-SMAD4 axis in human skin aging, based on ... |
Chromatin profiling reveals TFAP4 as a critical transcriptional regulator of bovine satellite cell differentiation
Pengcheng Lyu et al.
Background
Satellite cells are myogenic precursor cells in adult skeletal muscle and play a crucial role in skeletal muscle regeneration, maintenance, and growth. Like embryonic myoblasts, satellite cells have the ability to proliferate, differentiate, and fuse to form multinucleated myofibers. In this study, we ai... |
LEO1 Is Required for Efficient Entry into Quiescence, Control of H3K9 Methylation and Gene Expression in Human Fibroblasts
Laurent M. et al.
(1) Background: The LEO1 (Left open reading frame 1) protein is a conserved subunit of the PAF1C complex (RNA polymerase II-associated factor 1 complex). PAF1C has well-established mechanistic functions in elongation of transcription and RNA processing. We previously showed, in fission yeast, that LEO1 controls hist... |
In skeletal muscle and neural crest cells, SMCHD1 regulates biologicalpathways relevant for Bosma syndrome and facioscapulohumeral dystrophyphenotype.
Laberthonnière C. et al.
Many genetic syndromes are linked to mutations in genes encoding factors that guide chromatin organization. Among them, several distinct rare genetic diseases are linked to mutations in SMCHD1 that encodes the structural maintenance of chromosomes flexible hinge domain containing 1 chromatin-associated factor. In hu... |
Neonatal immune challenge poses a sex-specific risk for epigeneticmicroglial reprogramming and behavioral impairment.
Schwabenland M. et al.
While the precise processes underlying a sex bias in the development of central nervous system (CNS) disorders are unknown, there is growing evidence that an early life immune activation can contribute to the disease pathogenesis. When we mimicked an early systemic viral infection or applied murine cytomegalovirus (... |
Reversible transitions between noradrenergic and mesenchymal tumoridentities define cell plasticity in neuroblastoma.
Thirant C. et al.
Noradrenergic and mesenchymal identities have been characterized in neuroblastoma cell lines according to their epigenetic landscapes and core regulatory circuitries. However, their relationship and relative contribution in patient tumors remain poorly defined. We now document spontaneous and reversible plasticity b... |
Epigenetic dosage identifies two major and functionally distinct beta cells ubtypes.
Dror E.et al.
The mechanisms that specify and stabilize cell subtypes remain poorly understood. Here, we identify two major subtypes of pancreatic β cells based on histone mark heterogeneity (beta HI and beta LO). Beta HI cells exhibit 4-fold higher levels of H3K27me3, distinct chromatin organization and compaction, a... |
Developmental phenomics suggests that H3K4 monomethylation confersmulti-level phenotypic robustness.
Gandara Lautaro et al.
How histone modifications affect animal development remains difficult to ascertain. Despite the prevalence of histone 3 lysine 4 monomethylation (H3K4me1) on enhancers, hypomethylation appears to have minor effects on phenotype and viability. Here, we genetically reduce H3K4me1 deposition in Drosophila melanogaster ... |
ΔNp63α facilitates proliferation and migration, and modulates the chromatin landscape in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells
Anghui Peng et al.
p63 plays a crucial role in epithelia-originating tumours; however, its role in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA) has not been completely explored. Our study revealed the oncogenic properties of p63 in iCCA and identified the major expressed isoform as ΔNp63α. We collected iCCA clinical data from Th... |
Repression and 3D-restructuring resolves regulatory conflicts inevolutionarily rearranged genomes.
Ringel A. et al.
Regulatory landscapes drive complex developmental gene expression, but it remains unclear how their integrity is maintained when incorporating novel genes and functions during evolution. Here, we investigated how a placental mammal-specific gene, Zfp42, emerged in an ancient vertebrate topologically associated domai... |
Effects of GSK-J4 on JMJD3 Histone Demethylase in Mouse Prostate Cancer Xenografts
Sanchez A. et al.
Background/aim: Histone methylation status is required to control gene expression. H3K27me3 is an epigenetic tri-methylation modification to histone H3 controlled by the demethylase JMJD3. JMJD3 is dysregulated in a wide range of cancers and has been shown to control the expression of a specific growth-modulato... |
Immune disease variants modulate gene expression in regulatory CD4T cells.
Bossini-Castillo L. et al.
Identifying cellular functions dysregulated by disease-associated variants could implicate novel pathways for drug targeting or modulation in cell therapies. However, follow-up studies can be challenging if disease-relevant cell types are difficult to sample. Variants associated with immune diseases point toward the... |
Broad domains of histone marks in the highly compact macronucleargenome.
Drews F. et al.
The unicellular ciliate contains a large vegetative macronucleus with several unusual characteristics, including an extremely high coding density and high polyploidy. As macronculear chromatin is devoid of heterochromatin, our study characterizes the functional epigenomic organization necessary for gene regulation a... |
CREBBP/EP300 acetyltransferase inhibition disrupts FOXA1-bound enhancers to inhibit the proliferation of ER+ breast cancer cells.
Bommi-Reddy A. et al.
Therapeutic targeting of the estrogen receptor (ER) is a clinically validated approach for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer (ER+ BC), but sustained response is limited by acquired resistance. Targeting the transcriptional coactivators required for estrogen receptor activity represents an alternative approach... |
Screening of ETO2-GLIS2-induced Super Enhancers identifiestargetable cooperative dependencies in acute megakaryoblastic leukemia.
Benbarche S. et al.
Super Enhancers (SEs) are clusters of regulatory elements associated with cell identity and disease. However, whether these elements are induced by oncogenes and can regulate gene modules cooperating for cancer cell transformation or maintenance remains elusive. To address this question, we conducted a genome-wide C... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple Myeloma
Elina Alaterre et al.
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have been widely used to understand themolecular processes that drive MM biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape of MM wouldadvance our un... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple
Myeloma
Alaterre, Elina and Ovejero, Sara and Herviou, Laurie and de
Boussac, Hugues and Papadopoulos, Giorgio and Kulis, Marta and
Boireau, Stéphanie and Robert, Nicolas and Requirand, Guilhem
and Bruyer, Angélique and Cartron, Guillaume and Vincent,
Laure and M
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have
been widely used to understand the molecular processes that drive MM
biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,
progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the
epigenetic landscape of MM would advance our... |
Developmental and Injury-induced Changes in DNA Methylation inRegenerative versus Non-regenerative Regions of the VertebrateCentral Nervous System
Reverdatto S. et al.
Background Because some of its CNS neurons (e.g., retinal ganglion cells after optic nerve crush (ONC)) regenerate axons throughout life, whereas others (e.g., hindbrain neurons after spinal cord injury (SCI)) lose this capacity as tadpoles metamorphose into frogs, the South African claw-toed frog, Xenopus laevis, o... |
Effects of GSK-J4 on JMJD3 Histone Demethylase in MouseProstate Cancer Xenografts.
Sanchez A. et al.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Histone methylation status is required to control gene expression. H3K27me3 is an epigenetic tri-methylation modification to histone H3 controlled by the demethylase JMJD3. JMJD3 is dysregulated in a wide range of cancers and has been shown to control the expression of a specific growth-modulatory ge... |
Sp1-Induced SETDB1 Overexpression Transcriptionally InhibitsHPGD in a β-Catenin-Dependent Manner and Promotes theProliferation and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer
Fan Y. et al.
Gastric cancer (GC) has high morbidity and mortality, the cure rate of surgical treatment and drug chemotherapy is not ideal. Therefore, development of new treatment strategies is necessary. We aimed to identify the mechanism underlying Sp1 regulation of GC progression. |
Epigenetic remodelling of enhancers in response to estrogen deprivationand re-stimulation.
Sklias Athena et al.
Estrogen hormones are implicated in a majority of breast cancers and estrogen receptor alpha (ER), the main nuclear factor mediating estrogen signaling, orchestrates a complex molecular circuitry that is not yet fully elucidated. Here, we investigated genome-wide DNA methylation, histone acetylation and transcriptio... |
An integrated multi-omics analysis identifies prognostic molecularsubtypes of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer
Lindskrog Sia Viborg et al.
The molecular landscape in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) is characterized by large biological heterogeneity with variable clinical outcomes. Here, we perform an integrative multi-omics analysis of patients diagnosed with NMIBC (n = 834). Transcriptomic analysis identifies four classes (1, ... |
Functional annotations of three domestic animal genomes provide vitalresources for comparative and agricultural research.
Kern C. et al.
Gene regulatory elements are central drivers of phenotypic variation and thus of critical importance towards understanding the genetics of complex traits. The Functional Annotation of Animal Genomes consortium was formed to collaboratively annotate the functional elements in animal genomes, starting with domesticate... |
Chromatin dysregulation associated with NSD1 mutation in head and necksquamous cell carcinoma.
Farhangdoost, Nargess et al.
Chromatin dysregulation has emerged as an important mechanism of oncogenesis. To develop targeted treatments, it is important to understand the transcriptomic consequences of mutations in chromatin modifier genes. Recently, mutations in the histone methyltransferase gene nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 1... |
A distinct metabolic response characterizes sensitivity to EZH2inhibition in multiple myeloma.
Nylund P. et al.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a heterogeneous haematological disease that remains clinically challenging. Increased activity of the epigenetic silencer EZH2 is a common feature in patients with poor prognosis. Previous findings have demonstrated that metabolic profiles can be sensitive markers for response to treatment i... |
A brain cyst load-associated antigen is a Toxoplasma gondii biomarker forserodetection of persistent parasites and chronic infection.
Dard C. et al.
BACKGROUND: Biomarker discovery remains a major challenge for predictive medicine, in particular, in the context of chronic diseases. This is true for the widespread protozoan Toxoplasma gondii which establishes long-lasting parasitism in metazoans, humans included. This microbe successively unfolds distinct genetic... |
Multi-omic comparison of Alzheimer's variants in human ESC-derivedmicroglia reveals convergence at APOE.
Liu, Tongfei and Zhu, Bing and Liu, Yan and Zhang, Xiaoming and Yin, Junand Li, Xiaoguang and Jiang, LuLin and Hodges, Andrew P and Rosenthal, SaraBrin and Zhou, Lisa and Yancey, Joel and McQuade, Amanda and Blurton-Jones,Mathew and Tanzi, Rudolph E an
Variations in many genes linked to sporadic Alzheimer's disease (AD) show abundant expression in microglia, but relationships among these genes remain largely elusive. Here, we establish isogenic human ESC-derived microglia-like cell lines (hMGLs) harboring AD variants in CD33, INPP5D, SORL1, and TREM2 loci and cura... |
Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Processivity Factor,ORF59, Binds to Canonical and Linker Histones, and ItsCarboxy Terminus Is Dispensable for Viral DNA Synthesis
Gutierrez IV et al.
Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is an oncogenic virus and the causative agent of potentially fatal malignancies. Lytic replication of KSHV is an essential part of the viral life cycle, allowing for virus dissemination within the infected host and shedding to infect naive hosts. |
Genomic profiling of T-cell activation suggests increased sensitivity ofmemory T cells to CD28 costimulation.
Glinos, Dafni A and Soskic, Blagoje and Williams, Cayman and Kennedy, Alanand Jostins, Luke and Sansom, David M and Trynka, Gosia
T-cell activation is a critical driver of immune responses. The CD28 costimulation is an essential regulator of CD4 T-cell responses, however, its relative importance in naive and memory T cells is not fully understood. Using different model systems, we observe that human memory T cells are more sensitive to CD28 co... |
H3K27M in Gliomas Causes a One-Step Decrease in H3K27 Methylation andReduced Spreading within the Constraints of H3K36 Methylation.
Harutyunyan, Ashot S and Chen, Haifen and Lu, Tianyuan and Horth, Cynthiaand Nikbakht, Hamid and Krug, Brian and Russo, Caterina and Bareke, Ericand Marchione, Dylan M and Coradin, Mariel and Garcia, Benjamin A andJabado, Nada and Majewski, Jacek
The discovery of H3K27M mutations in pediatric gliomas marked a new chapter in cancer epigenomics. Numerous studies have investigated the effect of this mutation on H3K27 trimethylation, but only recently have we started to realize its additional effects on the epigenome. Here, we use isogenic glioma H3K27M cell lin... |
Macrophage Immune Memory Controls Endometriosis in Mice and Humans.
Jeljeli, Mohamed and Riccio, Luiza G C and Chouzenoux, Sandrine and Moresi,Fabiana and Toullec, Laurie and Doridot, Ludivine and Nicco, Carole andBourdon, Mathilde and Marcellin, Louis and Santulli, Pietro and Abrão,Mauricio S and Chapron, Charles and
Endometriosis is a frequent, chronic, inflammatory gynecological disease characterized by the presence of ectopic endometrial tissue causing pain and infertility. Macrophages have a central role in lesion establishment and maintenance by driving chronic inflammation and tissue remodeling. Macrophages can be reprogra... |
Derivation of Intermediate Pluripotent Stem Cells Amenable to PrimordialGerm Cell Specification.
Yu L. et al.
Dynamic pluripotent stem cell (PSC) states are in vitro adaptations of pluripotency continuum in vivo. Previous studies have generated a number of PSCs with distinct properties. To date, however, no known PSCs have demonstrated dual competency for chimera formation and direct responsiveness to primordial g... |
Radiation-induced H3K9 methylation on E-cadherin promoter mediated byROS/Snail axis : Role of G9a signaling during lung epithelial-mesenchymaltransition.
Nagaraja, SunilGowda Sunnaghatta and Subramanian, Umadevi and Nagarajan,Devipriya
Lung cancer patients who have undergone radiotherapy developed severe complications such as pneumonitis and fibrosis. Upon irradiation, epithelial cells acquire mesenchymal phenotype via a process called epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), which plays a vital role in organ fibrosis. Several mechanisms have b... |
Formation of the CenH3-Deficient Holocentromere in Lepidoptera AvoidsActive Chromatin.
Senaratne, Aruni P and Muller, Héloïse and Fryer, Kelsey A and Kawamoto,Munetaka and Katsuma, Susumu and Drinnenberg, Ines A
Despite the essentiality for faithful chromosome segregation, centromere architectures are diverse among eukaryotes and embody two main configurations: mono- and holocentromeres, referring, respectively, to localized or unrestricted distribution of centromeric activity. Of the two, some holocentromeres offer the cur... |
Epigenetic regulation of the lineage specificity of primary human dermallymphatic and blood vascular endothelial cells.
Tacconi, Carlotta and He, Yuliang and Ducoli, Luca and Detmar, Michael
Lymphatic and blood vascular endothelial cells (ECs) share several molecular and developmental features. However, these two cell types possess distinct phenotypic signatures, reflecting their different biological functions. Despite significant advances in elucidating how the specification of lymphatic and blood vasc... |
N-Methyladenosine co-transcriptionally directs the demethylation of histoneH3K9me2.
Li, Y and Xia, L and Tan, K and Ye, X and Zuo, Z and Li, M and Xiao, R andWang, Z and Liu, X and Deng, M and Cui, J and Yang, M and Luo, Q and Liu, Sand Cao, X and Zhu, H and Liu, T and Hu, J and Shi, J and Xiao, S
A dynamic epigenome is critical for appropriate gene expression in development and health. Central to this is the intricate process of transcription, which integrates cellular signaling with chromatin changes, transcriptional machinery and modifications to messenger RNA, such as N-methyladenosine (mA), which is co-t... |
Combined deletion of Bap1, Nf2, and Cdkn2ab causes rapid onset of malignant mesothelioma in mice.
Badhai J, Pandey GK, Song JY, Krijgsman O, Bhaskaran R, Chandrasekaran G, Kwon MC, Bombardelli L, Monkhorst K, Grasso C, Zevenhoven J, van der Vliet J, Cozijnsen M, Krimpenfort P, Peeper D, van Lohuizen M, Berns A
We have generated mouse models of malignant mesothelioma (MM) based upon disruption of the Bap1, Nf2, and Cdkn2ab tumor suppressor loci in various combinations as also frequently observed in human MM. Inactivation of all three loci in the mesothelial lining of the thoracic cavity leads to a highly aggressive MM that... |
Restoration of KMT2C/MLL3 in human colorectal cancer cells reinforces genome-wide H3K4me1 profiles and influences cell growth and gene expression.
Larsson C, Cordeddu L, Siggens L, Pandzic T, Kundu S, He L, Ali MA, Pristovšek N, Hartman K, Ekwall K, Sjöblom T
BACKGROUND: The histone 3 lysine 4 (H3K4) monomethylase KMT2C is mutated across several cancer types; however, the effects of mutations on epigenome organization, gene expression, and cell growth are not clear. A frequently recurring mutation in colorectal cancer (CRC) with microsatellite instability is a single nuc... |
Multi-omic analysis of gametogenesis reveals a novel signature at the promoters and distal enhancers of active genes.
Crespo M, Damont A, Blanco M, Lastrucci E, Kennani SE, Ialy-Radio C, Khattabi LE, Terrier S, Louwagie M, Kieffer-Jaquinod S, Hesse AM, Bruley C, Chantalat S, Govin J, Fenaille F, Battail C, Cocquet J, Pflieger D
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression is tightly controlled by the dynamic modification of histones by chemical groups, the diversity of which has largely expanded over the past decade with the discovery of lysine acylations, catalyzed from acyl-coenzymes A. We investigated the dynamics of lysine acetylation and ... |
A MORC-driven transcriptional switch controls Toxoplasma developmental trajectories and sexual commitment.
Farhat DC, Swale C, Dard C, Cannella D, Ortet P, Barakat M, Sindikubwabo F, Belmudes L, De Bock PJ, Couté Y, Bougdour A, Hakimi MA
Toxoplasma gondii has a complex life cycle that is typified by asexual development that takes place in vertebrates, and sexual reproduction, which occurs exclusively in felids and is therefore less studied. The developmental transitions rely on changes in the patterns of gene expression, and recent studies have assi... |
MYCN amplification and ATRX mutations are incompatible in neuroblastoma.
Zeineldin M, Federico S, Chen X, Fan Y, Xu B, Stewart E, Zhou X, Jeon J, Griffiths L, Nguyen R, Norrie J, Easton J, Mulder H, Yergeau D, Liu Y, Wu J, Van Ryn C, Naranjo A, Hogarty MD, Kamiński MM, Valentine M, Pruett-Miller SM, Pappo A, Zhang J, Clay MR,
Aggressive cancers often have activating mutations in growth-controlling oncogenes and inactivating mutations in tumor-suppressor genes. In neuroblastoma, amplification of the MYCN oncogene and inactivation of the ATRX tumor-suppressor gene correlate with high-risk disease and poor prognosis. Here we show that ATRX ... |
A comprehensive epigenomic analysis of phenotypically distinguishable, genetically identical female and male Daphnia pulex.
Kvist J, Athanàsio CG, Pfrender ME, Brown JB, Colbourne JK, Mirbahai L
BACKGROUND: Daphnia species reproduce by cyclic parthenogenesis involving both sexual and asexual reproduction. The sex of the offspring is environmentally determined and mediated via endocrine signalling by the mother. Interestingly, male and female Daphnia can be genetically identical, yet display large difference... |
TIP60/P400/H4K12ac Plays a Role as a Heterochromatin Back-up Skeleton inBreast Cancer.
Idrissou, Mouhamed and Boisnier, Tiphanie and Sanchez, Anna and Khoufaf,Fatma Zohra Houfaf and Penault-Llorca, Frederique and Bignon, Yves-Jean andBernard-Gallon, Dominique
BACKGROUND/AIM: In breast cancer, initiation of carcinogenesis leads to epigenetic dysregulation, which can lead for example to the loss of the heterochromatin skeleton SUV39H1/H3K9me3/HP1 or the supposed secondary skeleton TIP60/P400/H4K12ac/BRD (2/4), which allows the maintenance of chromatin integrity and plastic... |
Changes in H3K27ac at Gene Regulatory Regions in Porcine AlveolarMacrophages Following LPS or PolyIC Exposure.
Herrera-Uribe, Juber and Liu, Haibo and Byrne, Kristen A and Bond, Zahra Fand Loving, Crystal L and Tuggle, Christopher K
Changes in chromatin structure, especially in histone modifications (HMs), linked with chromatin accessibility for transcription machinery, are considered to play significant roles in transcriptional regulation. Alveolar macrophages (AM) are important immune cells for protection against pulmonary pathogens, and must... |
Unraveling the role of H3K4 trimethylation and lncRNA HOTAIR in SATB1 and DUSP4-dependent survival of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophages
Subuddhi Arijita, Kumar Manish, Majumder Debayan, Sarkar Arijita, Ghosh Zhumur, Vasudevan Madavan, Kundu Manikuntala, Basu Joyoti
The modification of chromatin influences host transcriptional programs during bacterial infection, at times skewing the balance in favor of pathogen survival. To test the role of chromatin modifications during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, we analysed genome-wide deposition of H3K4me3 marks in macrophages in... |
Functionally Annotating Regulatory Elements in the Equine Genome Using Histone Mark ChIP-Seq.
Kingsley NB, Kern C, Creppe C, Hales EN, Zhou H, Kalbfleisch TS, MacLeod JN, Petersen JL, Finno CJ, Bellone RR
One of the primary aims of the Functional Annotation of ANimal Genomes (FAANG) initiative is to characterize tissue-specific regulation within animal genomes. To this end, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-Seq) to map four histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me... |
Trained immunity modulates inflammation-induced fibrosis.
Jeljeli M, Riccio LGC, Doridot L, Chêne C, Nicco C, Chouzenoux S, Deletang Q, Allanore Y, Kavian N, Batteux F
Chronic inflammation and fibrosis can result from inappropriately activated immune responses that are mediated by macrophages. Macrophages can acquire memory-like characteristics in response to antigen exposure. Here, we show the effect of BCG or low-dose LPS stimulation on macrophage phenotype, cytokine production,... |
Nucleome Dynamics during Retinal Development.
Norrie JL, Lupo MS, Xu B, Al Diri I, Valentine M, Putnam D, Griffiths L, Zhang J, Johnson D, Easton J, Shao Y, Honnell V, Frase S, Miller S, Stewart V, Zhou X, Chen X, Dyer MA
More than 8,000 genes are turned on or off as progenitor cells produce the 7 classes of retinal cell types during development. Thousands of enhancers are also active in the developing retinae, many having features of cell- and developmental stage-specific activity. We studied dynamic changes in the 3D chromatin land... |
Pervasive H3K27 Acetylation Leads to ERV Expression and a Therapeutic Vulnerability in H3K27M Gliomas.
Krug B, De Jay N, Harutyunyan AS, Deshmukh S, Marchione DM, Guilhamon P, Bertrand KC, Mikael LG, McConechy MK, Chen CCL, Khazaei S, Koncar RF, Agnihotri S, Faury D, Ellezam B, Weil AG, Ursini-Siegel J, De Carvalho DD, Dirks PB, Lewis PW, Salomoni P, Lupie
High-grade gliomas defined by histone 3 K27M driver mutations exhibit global loss of H3K27 trimethylation and reciprocal gain of H3K27 acetylation, respectively shaping repressive and active chromatin landscapes. We generated tumor-derived isogenic models bearing this mutation and show that it leads to pervasive H3K... |
Long intergenic non-coding RNAs regulate human lung fibroblast function: Implications for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Hadjicharalambous MR, Roux BT, Csomor E, Feghali-Bostwick CA, Murray LA, Clarke DL, Lindsay MA
Phenotypic changes in lung fibroblasts are believed to contribute to the development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), a progressive and fatal lung disease. Long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) have been identified as novel regulators of gene expression and protein activity. In non-stimulated cells, we o... |
Chromatin activity at GWAS loci identifies T cell states driving complex immune diseases
Blagoje Soskic, Eddie Cano-Gamez, Deborah J. Smyth, Wendy C. Rowan, Nikolina Nakic, Jorge Esparza-Gordillo, Lara Bossini-Castillo, David F. Tough, Christopher G. C. Larminie, Paola G. Bronson, David Wille, Gosia Trynka
Complex immune disease variants are enriched in active chromatin regions of T cells and macrophages. However, whether these variants function in specific cell states or stages of cell activation is unknown. We stimulated T cells and macrophages in the presence of thirteen different cytokine cocktails linked to immun... |
The Wnt-Driven Mll1 Epigenome Regulates Salivary Gland and Head and Neck Cancer.
Zhu Q, Fang L, Heuberger J, Kranz A, Schipper J, Scheckenbach K, Vidal RO, Sunaga-Franze DY, Müller M, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Sauer S, Birchmeier W
We identified a regulatory system that acts downstream of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in salivary gland and head and neck carcinomas. We show in a mouse tumor model of K14-Cre-induced Wnt/β-catenin gain-of-function and Bmpr1a loss-of-function mutations that tumor-propagating cells exhibit increased Mll1 activi... |
Generation of an equine biobank to be used for Functional Annotation of Animal Genomes project.
Burns EN, Bordbari MH, Mienaltowski MJ, Affolter VK, Barro MV, Gianino F, Gianino G, Giulotto E, Kalbfleisch TS, Katzman SA, Lassaline M, Leeb T, Mack M, Müller EJ, MacLeod JN, Ming-Whitfield B, Alanis CR, Raudsepp T, Scott E, Vig S, Zhou H, Petersen JL,
The Functional Annotation of Animal Genomes (FAANG) project aims to identify genomic regulatory elements in both sexes across multiple stages of development in domesticated animals. This study represents the first stage of the FAANG project for the horse, Equus caballus. A biobank of 80 tissue samples, two cell line... |
Cellular localization of the cell cycle inhibitor Cdkn1c controls growth arrest of adult skeletal muscle stem cells
Despoina Mademtzoglou, Yoko Asakura, Matthew J Borok, Sonia Alonso-Martin, Philippos Mourikis, Yusaku Kodaka, Amrudha Mohan, Atsushi Asakura, Frederic Relaix
Adult skeletal muscle maintenance and regeneration depend on efficient muscle stem cell (MuSC) functions. The mechanisms coordinating cell cycle with activation, renewal, and differentiation of MuSCs remain poorly understood. Here, we investigated how adult MuSCs are regulated by CDKN1c (p57kip2), a cyclin-dependent... |
Cellular localization of the cell cycle inhibitor Cdkn1c controls growth arrest of adult skeletal muscle stem cells
Despoina Mademtzoglou, Yoko Asakura, Matthew J Borok, Sonia Alonso-Martin, Philippos Mourikis, Yusaku Kodaka, Amrudha Mohan, Atsushi Asakura Is a corresponding author , Frederic Relaix
Adult skeletal muscle maintenance and regeneration depend on efficient muscle stem cell (MuSC) functions. The mechanisms coordinating cell cycle with activation, renewal, and differentiation of MuSCs remain poorly understood. Here, we investigated how adult MuSCs are regulated by CDKN1c (p57kip2), a cyclin-dependent... |
Genome-wide association study identifies multiple new loci associated with Ewing sarcoma susceptibility.
Machiela MJ, Grünewald TGP, Surdez D, Reynaud S, Mirabeau O, Karlins E, Rubio RA, Zaidi S, Grossetete-Lalami S, Ballet S, Lapouble E, Laurence V, Michon J, Pierron G, Kovar H, Gaspar N, Kontny U, González-Neira A, Picci P, Alonso J, Patino-Garcia A, Corra
Ewing sarcoma (EWS) is a pediatric cancer characterized by the EWSR1-FLI1 fusion. We performed a genome-wide association study of 733 EWS cases and 1346 unaffected individuals of European ancestry. Our study replicates previously reported susceptibility loci at 1p36.22, 10q21.3 and 15q15.1, and identifies new loci a... |
LSD1-ERRα complex requires NRF1 to positively regulate transcription and cell invasion.
Zhang L, Carnesecchi J, Cerutti C, Tribollet V, Périan S, Forcet C, Wong J, Vanacker JM
Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) exerts dual effects on histone H3, promoting transcriptional repression via Lys4 (H3K4) demethylation or transcriptional activation through Lys9 (H3K9) demethylation. These activities are often exerted at transcriptional start sites (TSSs) and depend on the type of enhancer-bound... |
UTX-mediated enhancer and chromatin remodeling suppresses myeloid leukemogenesis through noncatalytic inverse regulation of ETS and GATA programs.
Gozdecka M, Meduri E, Mazan M, Tzelepis K, Dudek M, Knights AJ, Pardo M, Yu L, Choudhary JS, Metzakopian E, Iyer V, Yun H, Park N, Varela I, Bautista R, Collord G, Dovey O, Garyfallos DA, De Braekeleer E, Kondo S, Cooper J, Göttgens B, Bullinger L, Northc
The histone H3 Lys27-specific demethylase UTX (or KDM6A) is targeted by loss-of-function mutations in multiple cancers. Here, we demonstrate that UTX suppresses myeloid leukemogenesis through noncatalytic functions, a property shared with its catalytically inactive Y-chromosome paralog, UTY (or KDM6C). In keeping wi... |
Reciprocal signalling by Notch-Collagen V-CALCR retains muscle stem cells in their niche.
Baghdadi MB, Castel D, Machado L, Fukada SI, Birk DE, Relaix F, Tajbakhsh S, Mourikis P
The cell microenvironment, which is critical for stem cell maintenance, contains both cellular and non-cellular components, including secreted growth factors and the extracellular matrix. Although Notch and other signalling pathways have previously been reported to regulate quiescence of stem cells, the co... |
Bcl11b, a novel GATA3-interacting protein, suppresses Th1 while limiting Th2 cell differentiation.
Fang D, Cui K, Hu G, Gurram RK, Zhong C, Oler AJ, Yagi R, Zhao M, Sharma S, Liu P, Sun B, Zhao K, Zhu J
GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) acts as the master transcription factor for type 2 T helper (Th2) cell differentiation and function. However, it is still elusive how GATA3 function is precisely regulated in Th2 cells. Here, we show that the transcription factor B cell lymphoma 11b (Bcl11b), a previously unknown compo... |
Epigenetic modifiers promote mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative metabolism leading to enhanced differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells.
Martine Uittenbogaard, Christine A. Brantner, Anne Chiaramello1
During neural development, epigenetic modulation of chromatin acetylation is part of a dynamic, sequential and critical process to steer the fate of multipotent neural progenitors toward a specific lineage. Pan-HDAC inhibitors (HDCis) trigger neuronal differentiation by generating an "acetylation" signature and prom... |
Selenite and methylseleninic acid epigenetically affects distinct gene sets in myeloid leukemia: A genome wide epigenetic analysis.
Khalkar P, Ali HA, Codó P, Argelich ND, Martikainen A, Arzenani MK, Lehmann S, Walfridsson J, Ungerstedt J, Fernandes AP
Selenium compounds have emerged as promising chemotherapeutic agents with proposed epigenetic effects, however the mechanisms and downstream effects are yet to be studied. Here we assessed the effects of the inorganic selenium compound selenite and the organic form methylseleninic acid (MSA) in a leukemic cell line ... |
BRACHYURY directs histone acetylation to target loci during mesoderm development.
Beisaw A. et al.
T-box transcription factors play essential roles in multiple aspects of vertebrate development. Here, we show that cooperative function of BRACHYURY (T) with histone-modifying enzymes is essential for mouse embryogenesis. A single point mutation (TY88A) results in decreased histone 3 lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) ... |
In Situ Fixation Redefines Quiescence and Early Activation of Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells
Machado L. et al.
Summary
State of the art techniques have been developed to isolate and analyze cells from various tissues, aiming to capture their in vivo state. However, the majority of cell isolation protocols involve lengthy mechanical and enzymatic dissociation steps followed by flow cytometry, exposing cells to stres... |
The Dynamic Epigenetic Landscape of the Retina During Development, Reprogramming, and Tumorigenesis.
Aldiri I. et al.
In the developing retina, multipotent neural progenitors undergo unidirectional differentiation in a precise spatiotemporal order. Here we profile the epigenetic and transcriptional changes that occur during retinogenesis in mice and humans. Although some progenitor genes and cell cycle genes were epigenetically sil... |
Genomic responses of mouse synovial fibroblasts during TNF-driven arthritogenesis greatly mimic those of human rheumatoid arthritis
Ntougkos E. et al.
OBJECTIVE:
Aberrant activation of synovial fibroblasts (SFs) is a key determinant in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We aimed to produce a map of gene expression and epigenetic changes occurring in this cell type during disease progression in the human TNF-transgenic model of arthritis, and identify ... |
Epigenetically-driven anatomical diversity of synovial fibroblasts guides joint-specific fibroblast functions
Frank-Bertoncelj M, Trenkmann M, Klein K, Karouzakis E, Rehrauer H, Bratus A, Kolling C, Armaka M, Filer A, Michel BA, Gay RE, Buckley CD, Kollias G, Gay S, Ospelt C
A number of human diseases, such as arthritis and atherosclerosis, include characteristic pathology in specific anatomical locations. Here we show transcriptomic differences in synovial fibroblasts from different joint locations and that HOX gene signatures reflect the joint-specific origins of mouse and human synov... |
Behavioral, transcriptomic and epigenetic responses to social challenge in honey bees
Shpigler H.Y. et al.
Understanding how social experiences are represented in the brain and shape future responses is a major challenge in the study of behavior. We addressed this problem by studying behavioral, transcriptomic and epigenetic responses to intrusion in honey bees. Previous research showed that initial exposure to an intrud... |
DNA methylation heterogeneity defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma
Sheffield N.C. et al.
Developmental tumors in children and young adults carry few genetic alterations, yet they have diverse clinical presentation. Focusing on Ewing sarcoma, we sought to establish the prevalence and characteristics of epigenetic heterogeneity in genetically homogeneous cancers. We performed genome-scale DNA methylation ... |
BMP restricts stemness of intestinal Lgr5(+) stem cells by directly suppressing their signature genes
Zhen Q. et al.
The intestinal epithelium possesses a remarkable self-renewal ability, which is mediated by actively proliferating Lgr5+ stem cells. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signalling represents one major counterforce that limits the hyperproliferation of intestinal epithelium, but the exact mechanism remains elusive. Here... |
HMCan-diff: a method to detect changes in histone modifications in cells with different genetic characteristics
Ashoor H. et al.
Comparing histone modification profiles between cancer and normal states, or across different tumor samples, can provide insights into understanding cancer initiation, progression and response to therapy. ChIP-seq histone modification data of cancer samples are distorted by copy number variation innate to any cancer... |
Epigenetic Networks Regulate the Transcriptional Program in Memory and Terminally Differentiated CD8+ T Cells
Rodriguez R.M. et al.
Epigenetic mechanisms play a critical role during differentiation of T cells by contributing to the formation of stable and heritable transcriptional patterns. To better understand the mechanisms of memory maintenance in CD8 + T cells, we performed genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation, histone marking (acetylated... |
Iterative Fragmentation Improves the Detection of ChIP-seq Peaks for Inactive Histone Marks
Laczik M. et al.
As chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) sequencing is becoming the dominant technique for studying chromatin modifications, new protocols surface to improve the method. Bioinformatics is also essential to analyze and understand the results, and precise analysis helps us to identify the effects of protocol optimizati... |
Comprehensive genome and epigenome characterization of CHO cells in response to evolutionary pressures and over time
Feichtinger J, Hernández I, Fischer C, Hanscho M, Auer N, Hackl M, Jadhav V, Baumann M, Krempl PM, Schmidl C, Farlik M, Schuster M, Merkel A, Sommer A, Heath S, Rico D, Bock C, Thallinger GG, Borth N
The most striking characteristic of CHO cells is their adaptability, which enables efficient production of proteins as well as growth under a variety of culture conditions, but also results in genomic and phenotypic instability. To investigate the relative contribution of genomic and epigenetic modifications towards... |
Brg1 coordinates multiple processes during retinogenesis and is a tumor suppressor in retinoblastoma
Aldiri I et al.
Retinal development requires precise temporal and spatial coordination of cell cycle exit, cell fate specification, cell migration and differentiation. When this process is disrupted, retinoblastoma, a developmental tumor of the retina, can form. Epigenetic modulators are central to precisely coordinating developmen... |
Epigenetic role of CCAAT box-binding transcription factor NF-Y on ID gene family in human embryonic carcinoma cells
Farideh Moeinvaziri and Maryam Shahhoseini
Nuclear factor Y (NF-Y) is a histone substitute protein that specifically binds to the CCAAT box of the target genes and thereby promotes their regulation. NF-Y transcription factor, with defined CCAAT element-binding activities, target a gene family that encodes a group of basic helix–loop–helix ID fact... |
The mycotoxin aflatoxin B1 stimulates Epstein–Barr virus-induced B-cell transformation in in vitro and in vivo experimental models
R. Accardi, H. Gruffat, C. Sirand, F. Fusil, T. Gheit, H. Hernandez-Vargas, F. Le Calvez-Kelm, A. Traverse-Glehen, F.-L. Cosset, E. Manet, C. P. Wild and M. Tommasino
Although Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection is widely distributed, certain EBV-driven malignancies are geographically restricted. EBV-associated Burkitt’s lymphoma (eBL) is endemic in children living in sub-Saharan Africa. This population is heavily exposed to food contaminated with the mycotoxin aflatox... |
Epigenome mapping reveals distinct modes of gene regulation and widespread enhancer reprogramming by the oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1.
Tomazou EM, Sheffield NC, Schmidl C, Schuster M, Schönegger A, Datlinger P, Kubicek S, Bock C, Kovar H
Transcription factor fusion proteins can transform cells by inducing global changes of the transcriptome, often creating a state of oncogene addiction. Here, we investigate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this process, focusing on Ewing sarcoma cells that are dependent on the EWS-FLI1 fusion protein. We establi... |
TRIM28 Represses Transcription of Endogenous Retroviruses in Neural Progenitor Cells.
Fasching L, Kapopoulou A, Sachdeva R, Petri R, Jönsson ME, Männe C, Turelli P, Jern P, Cammas F, Trono D, Jakobsson J
TRIM28 is a corepressor that mediates transcriptional silencing by establishing local heterochromatin. Here, we show that deletion of TRIM28 in neural progenitor cells (NPCs) results in high-level expression of two groups of endogenous retroviruses (ERVs): IAP1 and MMERVK10C. We find that NPCs use TRIM28-mediated hi... |
Centromeric histone H2B monoubiquitination promotes noncoding transcription and chromatin integrity.
Sadeghi L, Siggens L, Svensson JP, Ekwall K
Functional centromeres are essential for proper cell division. Centromeres are established largely by epigenetic processes resulting in incorporation of the histone H3 variant CENP-A. Here, we demonstrate the direct involvement of H2B monoubiquitination, mediated by RNF20 in humans or Brl1 in Schizosaccharomyces pom... |