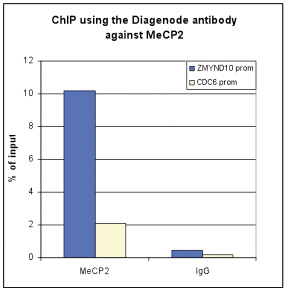
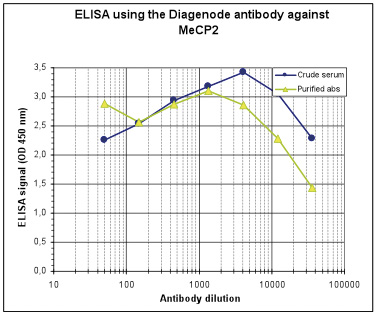
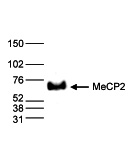
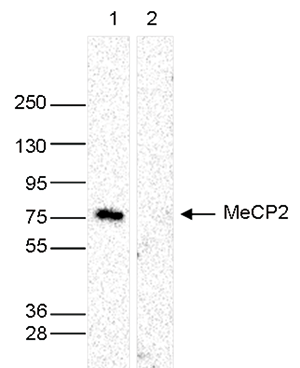
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: MeCP2 Antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410052 Lot# A20-001P). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Probing DNA damage in Rett syndrome neurons uncovers a role for MECP2 regulation of PARP1
Morales, A. et al.
Methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2)/Rett syndrome is characterized by a postnatal loss of neurophysiological function and regression of childhood development. While Rett neurons have been described as showing elevated senescence and P53 activity, here we show that molecular and physiological dysfunction in ne... |
Evidence of neuronal DNA damage in the brains of patients with Rett syndrome
Morales, Abril et al.
Rett syndrome is characterized by the postnatal loss of neurophysiological function and regression of childhood development. Because the syndrome is X linked, and males with MECP2 mutations generally do not survive birth, the study of this syndrome has been complicated by the fact that, in the female brain, a port... |
Mu opioid receptor expressing neurons in the rostral ventromedial medullaare the source of mechanical hypersensitivity induced by repeated restraintstress.
Imbe Hiroki and Ihara Hayato
Repeated exposure to psychophysical stress often causes an increase in sensitivity and response to pain. This phenomenon is commonly called stress-induced hyperalgesia (SIH). Although psychophysical stress is a well-known risk factor for numerous chronic pain syndromes, the neural mechanism underlying SIH has not ye... |
Epigenetic Silencing of OR and TAS2R Genes Expression inHuman Orbitofrontal Cortex At Early Stages of SporadicAlzheimer’s Disease
Alves Victoria Cunha et al.
Modulation of brain olfactory (OR) and taste receptors (TASR) expression was recently reported in neurological diseases. We explored the possible expression and regulation of selected OR and TASR genes in human orbitofrontal cortex of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and found that these are expressed and mar... |
Rett syndrome linked to defects in forming the MeCP2/Rbfox/LASRcomplex in mouse models
Jiang Yan et al.
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a severe neurological disorder and a leading cause of intellectual disability in young females. RTT is mainly caused by mutations found in the X-linked gene encoding methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2). Despite extensive studies, the molecular mechanism underlying RTT pathogenesis is still po... |
Environmental enrichment preserves a young DNA methylation landscape inthe aged mouse hippocampus
Zocher S. et al.
The decline of brain function during aging is associated with epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation. Lifestyle interventions can improve brain function during aging, but their influence on age-related epigenetic changes is unknown. Using genome-wide DNA methylation sequencing, we here show that experiencing ... |
MeCP2 controls neural stem cell fate specification throughmiR-199a-mediated inhibition of BMP-Smad signaling.
Nakashima H. et al.
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a severe neurological disorder, with impaired brain development caused by mutations in MECP2; however, the underlying mechanism remains elusive. We know from previous work that MeCP2 facilitates the processing of a specific microRNA, miR-199a, by associating with the Drosha complex to regulate... |
MeCP2 regulates gene expression through recognition of H3K27me3.
Lee, W and Kim, J and Yun, JM and Ohn, T and Gong, Q
MeCP2 plays a multifaceted role in gene expression regulation and chromatin organization. Interaction between MeCP2 and methylated DNA in the regulation of gene expression is well established. However, the widespread distribution of MeCP2 suggests it has additional interactions with chromatin. Here we demonstra... |
Genome-wide methylation in alcohol use disorder subjects: implications for an epigenetic regulation of the cortico-limbic glucocorticoid receptors (NR3C1).
Gatta E, Grayson DR, Auta J, Saudagar V, Dong E, Chen Y, Krishnan HR, Drnevich J, Pandey SC, Guidotti A
Environmental factors, including substance abuse and stress, cause long-lasting changes in the regulation of gene expression in the brain via epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation. We examined genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the prefrontal cortex (PFC, BA10) of 25 pairs of control and individuals wi... |
The L1 adhesion molecule normalizes neuritogenesis in Rett syndrome-derived neural precursor cells
Yoo M. et al.
Therapeutic intervention is an important need in ameliorating the severe consequences of Rett Syndrome (RTT), a neurological disorder caused by mutations in the X-linked gene methyl-CpG-binding protein-2 (MeCP2). Following previously observed morphological defects in induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived neur... |
Epigenetic regulation of RELN and GAD1 in the frontal cortex (FC) of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) subjects
Zhubi A. et al.
Both Reelin (RELN) and glutamate decarboxylase 67 (GAD1) have been implicated in the pathophysiology of Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). We have previously shown that both mRNAs are reduced in the cerebella (CB) of ASD subjects through a mechanism that involves increases in the amounts of MECP2 binding to the corres... |
The heparan sulfate sulfotransferase 3-OST3A (HS3ST3A) is a novel tumor regulator and a prognostic marker in breast cancer
Mao X, Gauche C, Coughtrie MW, Bui C, Gulberti S, Merhi-Soussi F, Ramalanjaona N, Bertin-Jung I, Diot A, Dumas D, De Freitas Caires N, Thompson AM, Bourdon JC, Ouzzine M, Fournel-Gigleux S
Heparan sulfate (HS) proteoglycan chains are key components of the breast tumor microenvironment that critically influence the behavior of cancer cells. It is established that abnormal synthesis and processing of HS play a prominent role in tumorigenesis, albeit mechanisms remain mostly obscure. HS function is mainl... |
Sequence features accurately predict genome-wide MeCP2 binding in vivo
Rube HT, Lee W, Hejna M, Chen H, Yasui DH, Hess JF, LaSalle JM, Song JS, Gong Q
Methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) is critical for proper brain development and expressed at near-histone levels in neurons, but the mechanism of its genomic localization remains poorly understood. Using high-resolution MeCP2-binding data, we show that DNA sequence features alone can predict binding with 88% accur... |
Adrenergic Repression of the Epigenetic Reader MeCP2 Facilitates Cardiac Adaptation in Chronic Heart Failure
Mayer SC. et al.
RATIONALE:
In chronic heart failure, increased adrenergic activation contributes to structural remodeling and altered gene expression. Although adrenergic signaling alters histone modifications, it is unknown, whether it also affects other epigenetic processes, including DNA methylation and its recognition.
OBJECT... |
Dynamic CCAAT/Enhancer Binding Protein-Associated Changes of DNA Methylation in the Angiotensinogen Gene.
Wang F, Demura M, Cheng Y, Zhu A, Karashima S, Yoneda T, Demura Y, Maeda Y, Namiki M, Ono K, Nakamura Y, Sasano H, Akagi T, Yamagishi M, Saijoh K, Takeda Y.
DNA methylation patterns are maintained in adult somatic cells. Recent findings, however, suggest that all methylation patterns are not preserved. We demonstrate that stimulatory signals can change the DNA methylation status at a CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (CEBP) binding site and a transcription start site and a... |
Survival motor neuron gene 2 silencing by DNA methylation correlates with spinal muscular atrophy disease severity and can be bypassed by histone deacetylase inhibition.
Hauke J, Riessland M, Lunke S, Eyüpoglu IY, Blümcke I, El-Osta A, Wirth B, Hahnen E
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a common neuromuscular disorder, is caused by homozygous absence of the survival motor neuron gene 1 (SMN1), while the disease severity is mainly influenced by the number of SMN2 gene copies. This correlation is not absolute, suggesting the existence of yet unknown factors modulating d... |