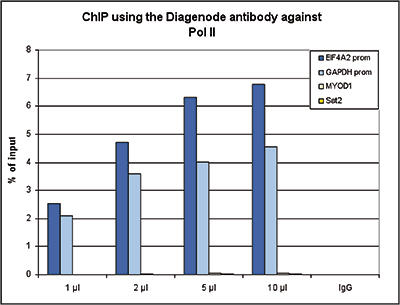
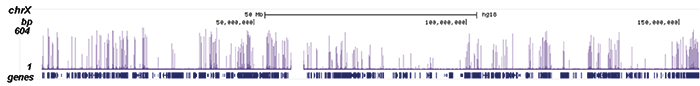
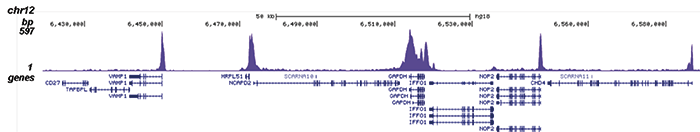
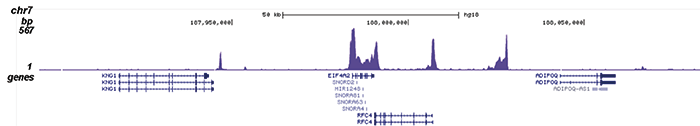
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Pol II Antibody - replaced by the antibody C15200253 (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15100055-100 Lot# 008). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Cotranscriptional demethylation induces global loss of H3K4me2 fromactive genes in Arabidopsis
Mori S. et al.
Based on studies of animals and yeasts, methylation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me1/2/3, for mono-, di-, and tri-methylation, respectively) is regarded as the key epigenetic modification of transcriptionally active genes. In plants, however, H3K4me2 correlates negatively with transcription, and the regulatory mechan... |
MLL-AF4 and a murinized pSer-variant thereof are turning on thenucleolar stress pathway.
Siemund Anna Lena and Hanewald Thomas and Kowarz Eric andMarschalek Rolf
BACKGROUND: Recent pathomolecular studies on the MLL-AF4 fusion protein revealed that the murinized version of MLL-AF4, the MLL-Af4 fusion protein, was able to induce leukemia when expressed in murine or human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (Lin et al. in Cancer Cell 30:737-749, 2016). In parallel, a group from... |
Human centromere formation activates transcription and opens chromatinfibre structure
Gilbert, Nick and Naughton, Catherine and Huidobro, Covadongaand Catacchio, Claudia and Buckle, Adam and Grimes, Graeme andNozawa, Ryu-Suke and Purgato, Stefania and Rocchi, Mariano
Human centromeres appear as constrictions on mitotic chromosomes and form a platform for kinetochore assembly in mitosis. Biophysical experiments led to a suggestion that repetitive DNA at centromeric regions form a compact scaffold necessary for function, but this was revised when neocentromeres were discovered on ... |
Conditional depletion of transcriptional kinases Ctk1 and Bur1 andeffects on co-transcriptional spliceosome assembly and pre-mRNA splicing.
Maudlin Isabella E and Beggs Jean D
From yeast to humans, pre-mRNA splicing occurs mainly co-transcriptionally, with splicing and transcription functionally coupled such that they influence one another. The recruitment model of co-transcriptional splicing proposes that core members of the transcription elongation machinery have the potential to influe... |
Transcriptional programming drives Ibrutinib-resistance evolution in mantlecell lymphoma.
Zhao, Xiaohong et al.
Ibrutinib, a bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, provokes robust clinical responses in aggressive mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), yet many patients relapse with lethal Ibrutinib-resistant (IR) disease. Here, using genomic, chemical proteomic, and drug screen profiling, we report that enhancer remodeling-mediated t... |
Slc6a8-Mediated Creatine Uptake and Accumulation Reprogram Macrophage Polarization via Regulating Cytokine Responses.
Ji L, Zhao X, Zhang B, Kang L, Song W, Zhao B, Xie W, Chen L, Hu X
Macrophage polarization is accompanied by drastic changes in L-arginine metabolism. Two L-arginine catalytic enzymes, iNOS and arginase 1, are well-characterized hallmark molecules of classically and alternatively activated macrophages, respectively. The third metabolic fate of L-arginine is the generation of creati... |
BCL2 Amplicon Loss and Transcriptional Remodeling Drives ABT-199 Resistance in B Cell Lymphoma Models.
Zhao X, Ren Y, Lawlor M, Shah BD, Park PMC, Lwin T, Wang X, Liu K, Wang M, Gao J, Li T, Xu M, Silva AS, Lee K, Zhang T, Koomen JM, Jiang H, Sudalagunta PR, Meads MB, Cheng F, Bi C, Fu K, Fan H, Dalton WS, Moscinski LC, Shain KH, Sotomayor EM, Wang GG, Gra
Drug-tolerant "persister" tumor cells underlie emergence of drug-resistant clones and contribute to relapse and disease progression. Here we report that resistance to the BCL-2 targeting drug ABT-199 in models of mantle cell lymphoma and double-hit lymphoma evolves from outgrowth of persister clones displaying loss ... |
Enhancers in the Peril lincRNA locus regulate distant but not local genes.
Groff AF, Barutcu AR, Lewandowski JP, Rinn JL
BACKGROUND: Recently, it has become clear that some promoters function as long-range regulators of gene expression. However, direct and quantitative assessment of enhancer activity at long intergenic noncoding RNA (lincRNA) or mRNA gene bodies has not been performed. To unbiasedly assess the enhancer capacity across... |
Gap junction protein Connexin-43 is a direct transcriptional regulator of N-cadherin in vivo.
Kotini M, Barriga EH, Leslie J, Gentzel M, Rauschenberger V, Schambony A, Mayor R
Connexins are the primary components of gap junctions, providing direct links between cells under many physiological processes. Here, we demonstrate that in addition to this canonical role, Connexins act as transcriptional regulators. We show that Connexin 43 (Cx43) controls neural crest cell migration in vivo by di... |
A Non-catalytic Function of SETD1A Regulates Cyclin K and the DNA Damage Response.
Hoshii T, Cifani P, Feng Z, Huang CH, Koche R, Chen CW, Delaney CD, Lowe SW, Kentsis A, Armstrong SA
MLL/SET methyltransferases catalyze methylation of histone 3 lysine 4 and play critical roles in development and cancer. We assessed MLL/SET proteins and found that SETD1A is required for survival of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Mutagenesis studies and CRISPR-Cas9 domain screening show the enzymatic SET domai... |
Predicting stimulation-dependent enhancer-promoter interactions from ChIP-Seq time course data
Dzida T. et al.
We have developed a machine learning approach to predict stimulation-dependent enhancer-promoter interactions using evidence from changes in genomic protein occupancy over time. The occupancy of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), RNA polymerase (Pol II) and histone marks H2AZ and H3K4me3 were measured over time us... |
Connexin43 controls N-cadherin transcription during collective cell migration
Kotini M. et al.
Connexins are the primary components of gap junctions, providing direct links between cells in many physiological processes, including cell migration and cancer metastasis. Exactly how cell migration is controlled by gap junctions remains a mystery. To shed light on this, we investigated the role of Connexin43 in co... |
PAFAH1B1 and the lncRNA NONHSAT073641 maintain an angiogenic phenotype in human endothelial cells
Josipovic I at al.
AIM:
Platelet-activating factor acetyl hydrolase 1B1 (PAFAH1B1, also known as Lis1) is a protein essentially involved in neurogenesis and mostly studied in the nervous system. As we observed a significant expression of PAFAH1B1 in the vascular system, we hypothesized that PAFAH1B1 is important during angiogenesis o... |
Spatiotemporal control of estrogen-responsive transcription in ERα-positive breast cancer cells.
P-Y Hsu, H-K Hsu, T-H Hsiao, Z Ye, E Wang, A L Profit, I Jatoi, Y Chen, N B Kirma, V X Jin, Z D Sharp and T H-M Huang
Recruitment of transcription machinery to target promoters for aberrant gene expression has been well studied, but underlying control directed by distant-acting enhancers remains unclear in cancer development. Our previous study demonstrated that distant estrogen response elements (DEREs) located on chromosome 20q13... |
The oncofusion protein FUS-ERG targets key hematopoietic regulators and modulates the all-trans retinoic acid signaling pathway in t(16;21) acute myeloid leukemia.
Sotoca AM1, Prange KH1, Reijnders B1, Mandoli A1, Nguyen LN1, Stunnenberg HG1, Martens JH
The ETS transcription factor ERG has been implicated as a major regulator of both normal and aberrant hematopoiesis. In acute myeloid leukemias harboring t(16;21), ERG function is deregulated due to a fusion with FUS/TLS resulting in the expression of a FUS-ERG oncofusion protein. How this oncofusion protein deregul... |
Composite macroH2A/NRF-1 Nucleosomes Suppress Noise and Generate Robustness in Gene Expression.
Lavigne MD, Vatsellas G, Polyzos A, Mantouvalou E, Sianidis G, Maraziotis I, Agelopoulos M, Thanos D
The histone variant macroH2A (mH2A) has been implicated in transcriptional repression, but the molecular mechanisms that contribute to global mH2A-dependent genome regulation remain elusive. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) coupled with transcriptional profiling in mH2A knockdown cells, we d... |
Persistent STAT5 activation in myeloid neoplasms recruits p53 into gene regulation.
Girardot M, Pecquet C, Chachoua I, Van Hees J, Guibert S, Ferrant A, Knoops L, Baxter EJ, Beer PA, Giraudier S, Moriggl R, Vainchenker W, Green AR, Constantinescu SN
STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) transcription factors are constitutively activated in most hematopoietic cancers. We previously identified a target gene, LPP/miR-28 (LIM domain containing preferred translocation partner in lipoma), induced by constitutive activation of STAT5, but not by trans... |
Principles of nucleation of H3K27 methylation during embryonic development.
van Heeringen SJ, Akkers RC, van Kruijsbergen I, Arif MA, Hanssen LL, Sharifi N, Veenstra GJ
During embryonic development, maintenance of cell identity and lineage commitment requires the Polycomb-group PRC2 complex, which catalyzes histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3). However, the developmental origins of this regulation are unknown. Here we show that H3K27me3 enrichment increases from blastula ... |
Integrative analysis of deep sequencing data identifies estrogen receptor early response genes and links ATAD3B to poor survival in breast cancer.
Ovaska K, Matarese F, Grote K, Charapitsa I, Cervera A, Liu C, Reid G, Seifert M, Stunnenberg HG, Hautaniemi S
Identification of responsive genes to an extra-cellular cue enables characterization of pathophysiologically crucial biological processes. Deep sequencing technologies provide a powerful means to identify responsive genes, which creates a need for computational methods able to analyze dynamic and multi-level deep se... |
Human β cell transcriptome analysis uncovers lncRNAs that are tissue-specific, dynamically regulated, and abnormally expressed in type 2 diabetes.
Morán I, Akerman I, van de Bunt M, Xie R, Benazra M, Nammo T, Arnes L, Nakić N, García-Hurtado J, Rodríguez-Seguí S, Pasquali L, Sauty-Colace C, Beucher A, Scharfmann R, van Arensbergen J, Johnson PR, Berry A, Lee C, Harkins T, Gmyr V, Pattou F, Kerr-Cont
A significant portion of the genome is transcribed as long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), several of which are known to control gene expression. The repertoire and regulation of lncRNAs in disease-relevant tissues, however, has not been systematically explored. We report a comprehensive strand-specific transcriptome map ... |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Analysis of Xenopus Embryos
Akkers RC, Jacobi UG, Veenstra GJ.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is a powerful technique to study epigenetic regulation and transcription factor binding events in the nucleus. It is based on immune-affinity capture of epitopes that have been cross-linked to genomic DNA in vivo. A readout of the extent to which the epitope is associated with pa... |
The transcriptional and epigenomic foundations of ground state pluripotency.
Marks H, Kalkan T, Menafra R, Denissov S, Jones K, Hofemeister H, Nichols J, Kranz A, Francis Stewart A, Smith A, Stunnenberg HG
Mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells grown in serum exhibit greater heterogeneity in morphology and expression of pluripotency factors than ES cells cultured in defined medium with inhibitors of two kinases (Mek and GSK3), a condition known as "2i" postulated to establish a naive ground state. We show that the transcript... |
Genome-wide profiling of LXR, RXR and PPARα in mouse liver reveals extensive sharing of binding sites.
Boergesen M, Pedersen TA, Gross B, van Heeringen SJ, Hagenbeek D, Bindesbøll C, Caron S, Lalloyer F, Steffensen KR, Nebb H, Gustafsson JA, Stunnenberg HG, Staels B, Mandrup S
The liver X receptors (LXRs) are nuclear receptors that form permissive heterodimers with retinoid X receptor (RXR) and are important regulators of lipid metabolism in the liver. We have recently shown that RXR agonist-induced hypertriglyceridemia and hepatic steatosis in mice is dependent on LXR and correlates with... |
The human histone H3 complement anno 2011.
Ederveen TH, Mandemaker IK, Logie C
Histones are highly basic, relatively small proteins that complex with DNA to form higher order structures that underlie chromosome topology. Of the four core histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4, it is H3 that is most heavily modified at the post-translational level. The human genome harbours 16 annotated bona fide histone... |
Coactivation of GR and NFKB alters the repertoire of their binding sites and target genes.
Rao NA, McCalman MT, Moulos P, Francoijs KJ, Chatziioannou A, Kolisis FN, Alexis MN, Mitsiou DJ, Stunnenberg HG
Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) exerts anti-inflammatory action in part by antagonizing proinflammatory transcription factors such as the nuclear factor kappa-b (NFKB). Here, we assess the crosstalk of activated GR and RELA (p65, major NFKB component) by global identification of their binding sites and target genes. We... |
UPF2 is a critical regulator of liver development, function and regeneration.
Thoren LA, Nørgaard GA, Weischenfeldt J, Waage J, Jakobsen JS, Damgaard I, Bergström FC, Blom AM, Borup R, Bisgaard HC, Porse BT
BACKGROUND: Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a post-transcriptional RNA surveillance process that facilitates the recognition and destruction of mRNAs bearing premature terminations codons (PTCs). Such PTC-containing (PTC+) mRNAs may arise from different processes, including erroneous processing and expression ... |
A hierarchy of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 acquisition in spatial gene regulation in Xenopus embryos.
Akkers RC, van Heeringen SJ, Jacobi UG, Janssen-Megens EM, Françoijs KJ, Stunnenberg HG, Veenstra GJ
Epigenetic mechanisms set apart the active and inactive regions in the genome of multicellular organisms to produce distinct cell fates during embryogenesis. Here, we report on the epigenetic and transcriptome genome-wide maps of gastrula-stage Xenopus tropicalis embryos using massive parallel sequencing of cDNA (RN... |
High-resolution analysis of epigenetic changes associated with X inactivation.
Marks H, Chow JC, Denissov S, Françoijs KJ, Brockdorff N, Heard E, Stunnenberg HG
Differentiation of female murine ES cells triggers silencing of one X chromosome through X-chromosome inactivation (XCI). Immunofluorescence studies showed that soon after Xist RNA coating the inactive X (Xi) undergoes many heterochromatic changes, including the acquisition of H3K27me3. However, the mechanisms that ... |
ChIP-Seq of ERalpha and RNA polymerase II defines genes differentially responding to ligands.
Welboren WJ, van Driel MA, et al.,
We used ChIP-Seq to map ERa-binding sites and to profile changes in RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) occupancy in MCF-7 cells in response to estradiol (E2), tamoxifen or fulvestrant. We identify 10 205 high confidence ERa-binding sites in response to E2 of which 68% contain an estrogen response element (ERE) and only 7% c... |