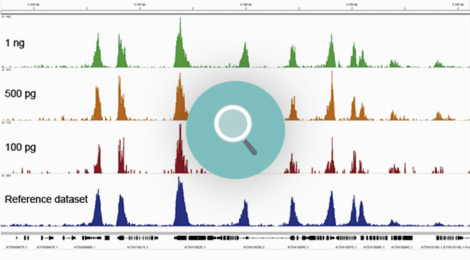
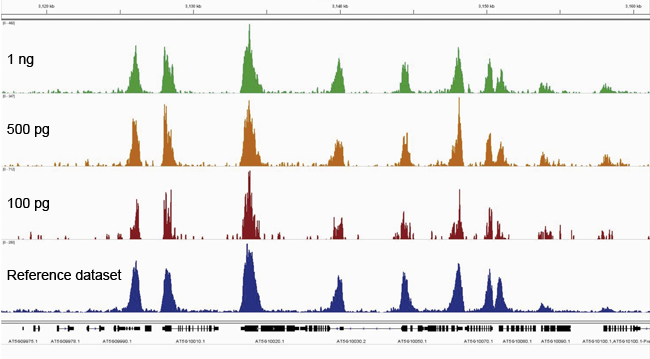
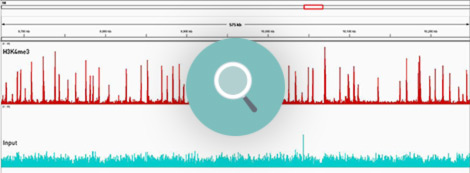
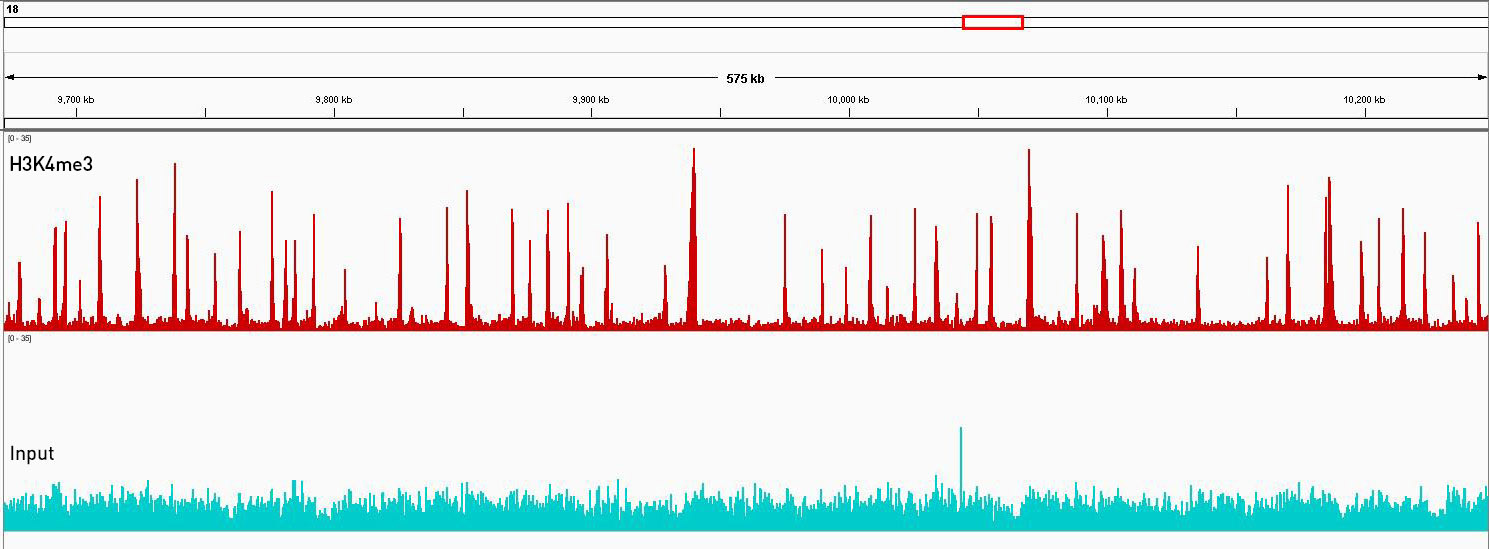
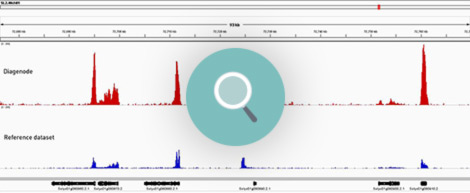
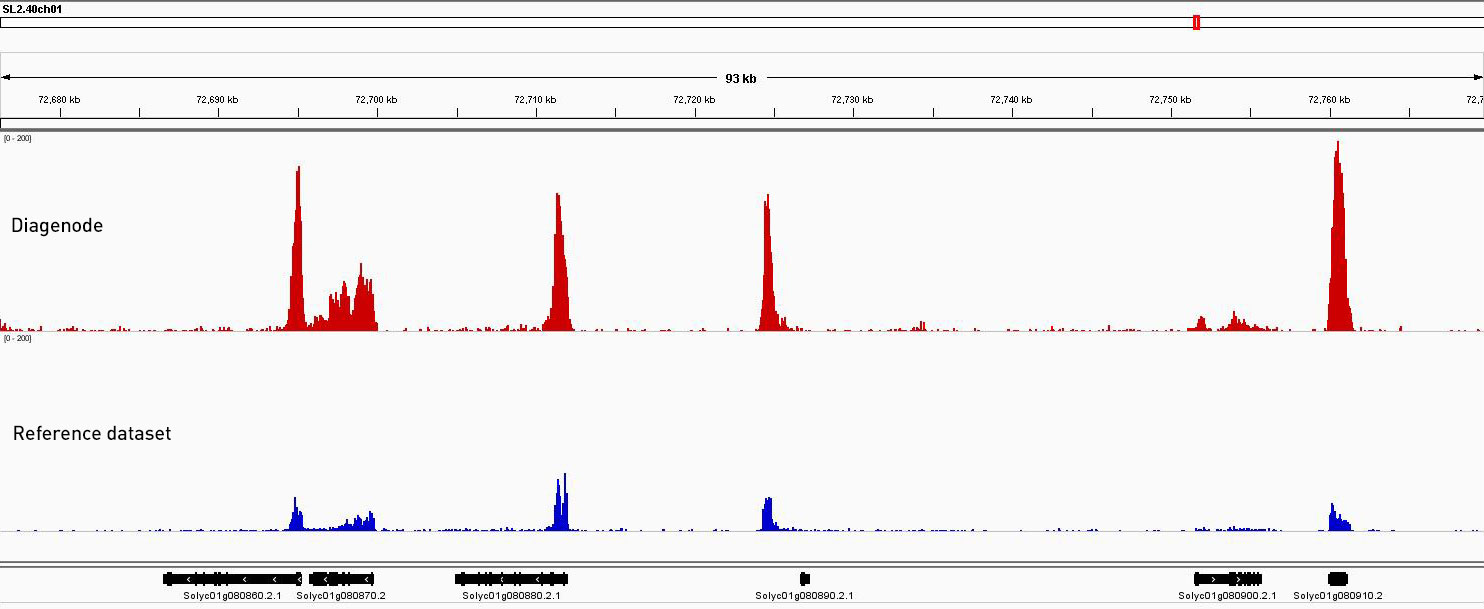
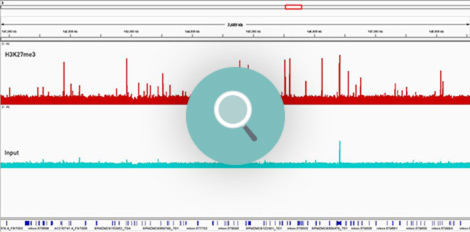
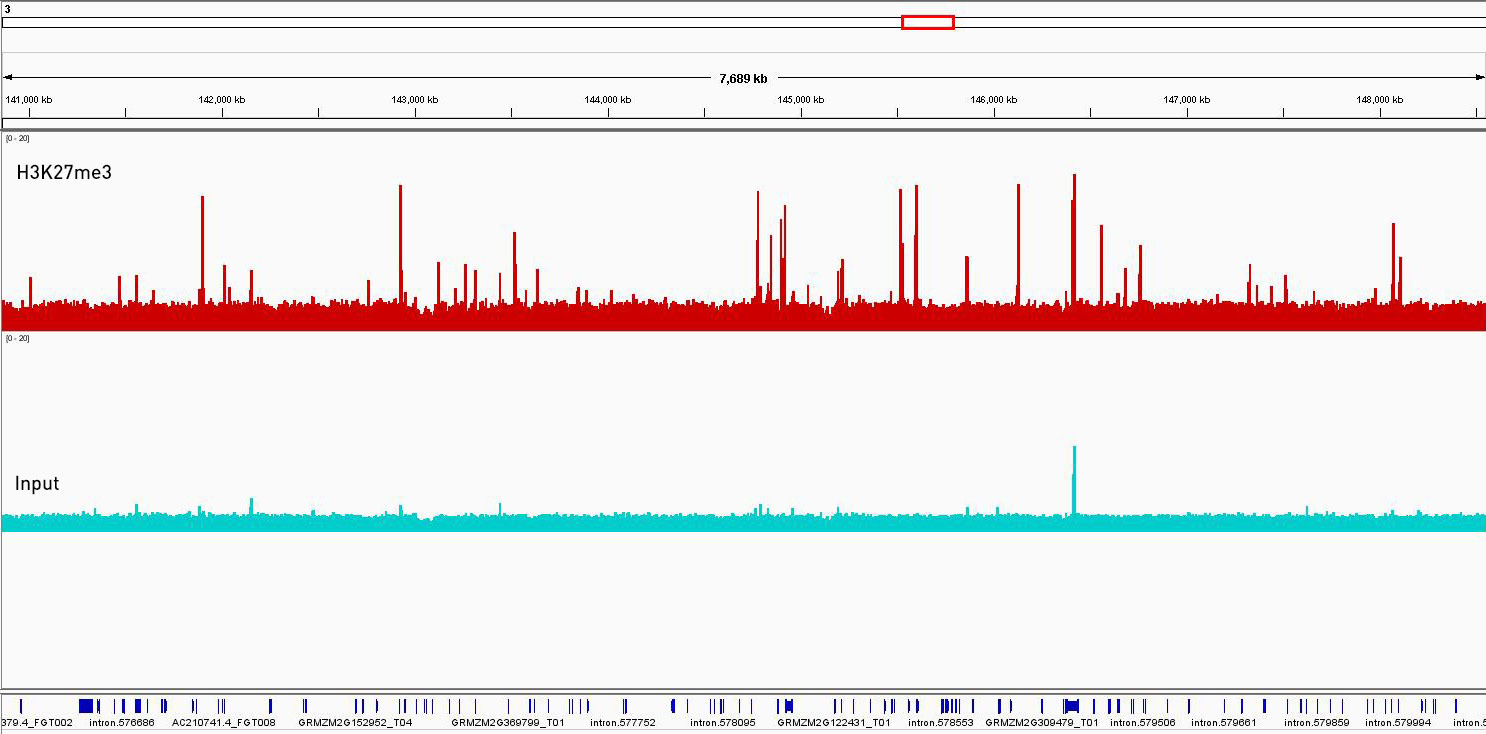
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Universal Plant ChIP-seq kit (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C01010152). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Temporal modification of H3K9/14ac and H3K4me3 histone marksmediates mechano-responsive gene expression during the accommodationprocess in poplar
Ghosh R. et al.
Plants can attenuate their molecular response to repetitive mechanical stimulation as a function of their mechanical history. For instance, a single bending of stem is sufficient to attenuate the gene expression in poplar plants to the subsequent mechanical stimulation, and the state of desensitization can last for ... |
Winter warming post floral initiation delays flowering via bud dormancyactivation and affects yield in a winter annual crop.
Lu Xiang et al.
Winter annual life history is conferred by the requirement for vernalization to promote the floral transition and control the timing of flowering. Here we show using winter oilseed rape that flowering time is controlled by inflorescence bud dormancy in addition to vernalization. Winter warming treatments given to pl... |
AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR 16 (StARF16) regulates defense gene StNPR1 upon infection with necrotrophic pathogen in potato.
Kalsi HS et al.
We demonstrate a new regulatory mechanism in the jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) mediated crosstalk in potato defense response, wherein, miR160 target StARF16 (a gene involved in growth and development) binds to the promoter of StNPR1 (a defense gene) and negatively regulates its expression to suppress th... |
GIF1 controls ear inflorescence architecture and floral development byregulating key genes in hormone biosynthesis and meristem determinacy inmaize.
Li Manfei et al.
BACKGROUND: Inflorescence architecture and floral development in flowering plants are determined by genetic control of meristem identity, determinacy, and maintenance. The ear inflorescence meristem in maize (Zea mays) initiates short branch meristems called spikelet pair meristems, thus unlike the tassel infloresce... |
Chromosomal variations of species revealed by FISH with rDNAs andcentromeric histone H3 variant associated DNAs
Liu Mao-Sen et al.
Lycoris species have various chromosome numbers and karyotypes, but all have a constant total number of chromosome major arms. In addition to three fundamental types, including metacentric (M-), telocentric (T-), and acrocentric (A-) chromosomes, chromosomes in various morphology and size were also observed in natur... |
Expression of in the Stem Cell Domain Is Required for ItsFunction in the Control of Floral Meristem Activity in Arabidopsis
Kwaśniewska K. et al.
In the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, the zinc-finger transcription factor KNUCKLES (KNU) plays an important role in the termination of floral meristem activity, a process that is crucial for preventing the overgrowth of flowers. The KNU gene is activated in floral meristems by the floral organ identity factor AG... |
Localization and characterization of Citrus centromeres by combining
half-tetrad analysis and CenH3-associated sequence profiling.
Xia, Qiang-Ming and Miao, Lu-Ke and Xie, Kai-Dong and Yin, Zhao-Ping and
Wu, Xiao-Meng and Chen, Chun-Li and Grosser, Jude W and Guo, Wen-Wu
KEY MESSAGE: The physical locations of citrus centromere are revealed
by combining genetic and immunological assays for the first time and nine
citrus centromere-specific markers for cytogenetics are mined. Centromere
localization is challenging, because highly redundant repetitive sequences
in centromeric regions m... |
StE(z)2, a Polycomb group methyltransferase and deposition of H3K27me3 andH3K4me3 regulate the expression of tuberization genes in potato.
Kumar, Amit and Kondhare, Kirtikumar R and Malankar, Nilam N and Banerjee,Anjan K
Polycomb Repressive Complex (PRC) group proteins regulate various developmental processes in plants by repressing the target genes via H3K27 trimethylation, whereas their function is antagonized by Trithorax group proteins-mediated H3K4 trimethylation. Tuberization in potato is widely studied, but the role of histon... |
The domesticated transposase ALP2 mediates formation of a novel Polycomb protein complex by direct interaction with MSI1, a core subunit of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2).
Velanis CN, Perera P, Thomson B, de Leau E, Liang SC, Hartwig B, Förderer A, Thornton H, Arede P, Chen J, Webb KM, Gümüs S, De Jaeger G, Page CA, Hancock CN, Spanos C, Rappsilber J, Voigt P, Turck F, Wellmer F, Goodrich J
A large fraction of plant genomes is composed of transposable elements (TE), which provide a potential source of novel genes through "domestication"-the process whereby the proteins encoded by TE diverge in sequence, lose their ability to catalyse transposition and instead acquire novel functions for their hosts. In... |
REDOX RESPONSIVE TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR1 (RRFT1) is involved in extracellular ATP regulated Arabidopsis thaliana seedling growth.
Zhu R, Dong X, Xue Y, Xu J, Zhang A, Feng M, Zhao Q, Xia S, Yin Y, He S, Li Y, Liu T, Kang E, Shang Z
Extracellular ATP (eATP) is an apoplastic signaling molecule that plays essential roles in the growth and development of plants. Arabidopsis seedlings have been reported to respond to eATP, however, the downstream signaling components are still not well understood. Here, we report that an ethylene responsive factor,... |
An inferred fitness consequence map of the rice genome.
Joly-Lopez Z, Platts AE, Gulko B, Choi JY, Groen SC, Zhong X, Siepel A, Purugganan MD
The extent to which sequence variation impacts plant fitness is poorly understood. High-resolution maps detailing the constraint acting on the genome, especially in regulatory sites, would be beneficial as functional annotation of noncoding sequences remains sparse. Here, we present a fitness consequence (fitCons) m... |
Transcription Factor Interplay between LEAFY and APETALA1/CAULIFLOWER during Floral Initiation
Goslin K. et al.
The transcription factors LEAFY (LFY) and APETALA1 (AP1), together with the AP1 paralog CAULIFLOWER (CAL), control the onset of flower development in a partially redundant manner. This redundancy is thought to be mediated, at least in part, through the regulation of a shared set of target genes. However, whether the... |
Characterization of the Polycomb-Group Mark H3K27me3 in Unicellular Algae
Mikulski P. et al.
Polycomb Group (PcG) proteins mediate chromatin repression in plants and animals by catalyzing H3K27 methylation and H2AK118/119 mono-ubiquitination through the activity of the Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) and PRC1, respectively. PcG proteins were extensively studied in higher plants, but their function and ... |
Nitric oxide modulates histone acetylation at stress genes by inhibition of histone deacetylases
Mengel A. et al.
Histone acetylation, which is an important mechanism to regulate gene expression, is controlled by the opposing action of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs). In animals, several HDACs are subjected to regulation by nitric oxide (NO), in plants however, it is unknown whether NO affects... |