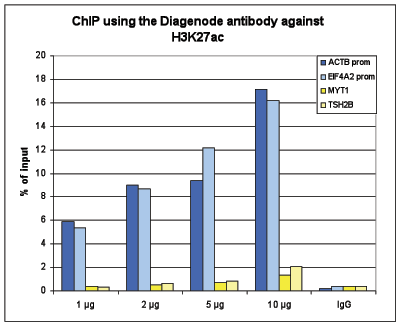
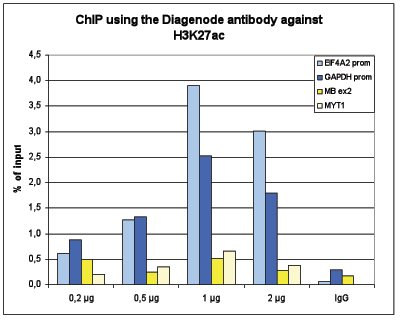
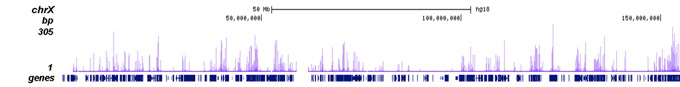
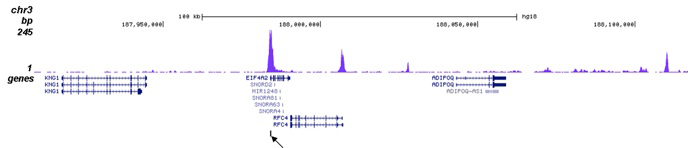
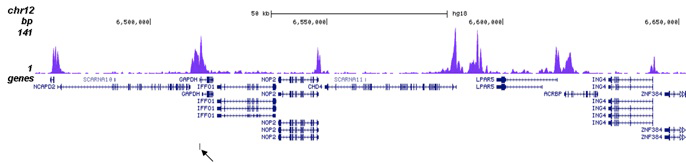
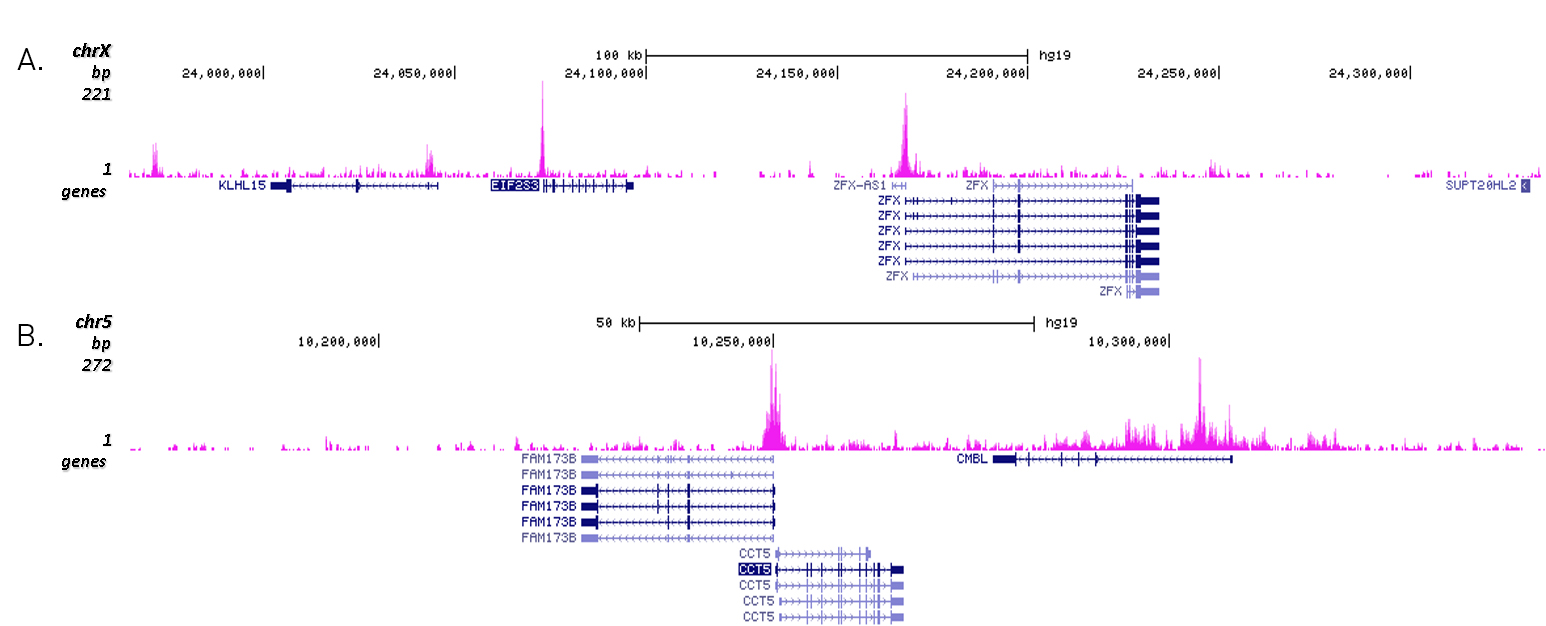
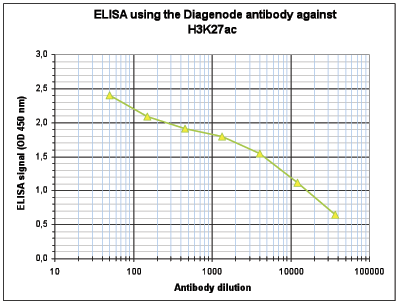
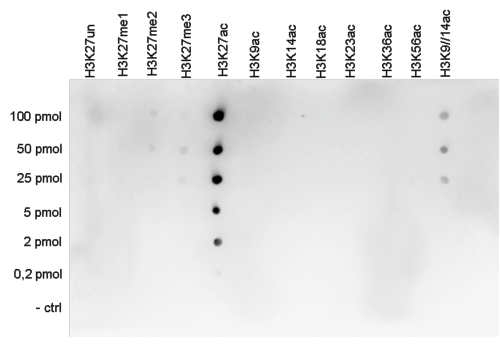
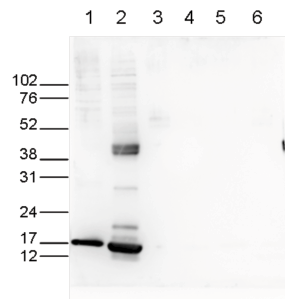
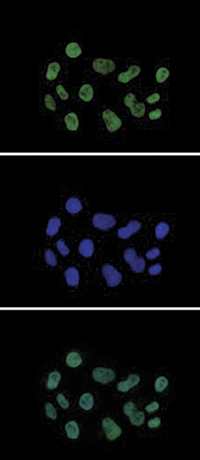
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K27ac polyclonal antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410196 Lot# A1723-0041D). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
CRISPR-based precise methylation of specific FUT8 promoter regions allows isolation of CHO cells with a fine-tuned glycoprofile
Jiménez Lancho, Víctor et al.
A major advantage of producing therapeutic proteins in mammalian cells is their ability to tailor proteins with human-like posttranslational modifications such as glycosylation, which ultimately defines aspects like stability, protein folding or immunogenicity. However, producing therapeutic proteins with a consis... |
Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B-cells from a hypoxia model of the germinal center requires external unsaturated fatty acids
Havey, Larissa et al.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) drives over 200,000 cancer cases annually, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, and classic Hodgkin lymphoma-malignancies that frequently originate from germinal centers (GCs), which are physiologically hypoxic (O2 < 1%). However, conventional transformation mode... |
Epigenomics of embryogenesis in turbot
Aramburu, Oscar et al.
Embryogenesis is the foundational step of ontogeny, where a complex organism emerges from a single totipotent cell. This process is orchestrated by changes in transcriptional regulation, influenced by chromatin accessibility and epigenetic modifications, enabling transcription factor accessibility. Epigenomic re... |
Disease-specific epigenetic deregulation of enhancers, transposons, and polycomb targets in acute promyelocytic leukemia
Zhong, Xiangfu et al.
Background: Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), characterized by a fusion between the PML and RARA genes and by a block in the myeloid maturation at the promyelocytic stage.
Methods: This study investigates the epigenetic landscape of APL by integrating ChIP-se... |
Upregulation of ALDH1 as an adaptive epigenetic response to anthracyclines in acute myeloid leukemia
Leonetti, Francesco et al.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a genetically heterogeneous malignancy characterized by the clonal proliferation of undifferentiated myeloid precursors in the bone marrow. Although standard induction regimens based on anthracyclines often achieve initial remission, up to 25% of patients exhibit primary refractor... |
Targeting histone H2B acetylated enhanceosomes via p300/CBP degradation in prostate cancer
Luo, Jie et al.
Prostate cancer is driven by oncogenic transcription factor enhanceosomes comprising chromatin and epigenetic regulators. The lysine acetyltransferases p300 and CREB-binding protein (CBP) are key cofactors that activate enhancers through histone acetylation. Here we identify p300/CBP-mediated multisite histone H... |
Combinatorial DNMTs and EZH2 inhibition reprograms the H3K27me3 and DNAme-mediated onco-epigenome to suppress multiple myeloma proliferation
Atienza Párraga, Alba et al.
Comprehensive epigenomic studies in multiple myeloma (MM) that unravel the connections between major epigenetic regulators, their intertwined collaboration and the potential of combinatorial targeting remain limited. Utilizing ChIP-seq, ATAC-seq, RNA-seq, and DNA methylation (DNAme) data, we generated whole-genome c... |
SUMO operates from a unique long tandem repeat to keep innate immunity in check
Goffeney, Amandine et al.
The SUMO pathway mainly functions to repress innate immunity in myeloid cells. Inactivating sumoylation triggers a strong, noncanonical, type I interferon (IFN1) response, amplified and coupled with inflammation upon stimulation. These findings transposed to pre-clinical models with the demonstration that sumoyl... |
Iron deficiency causes aspartate-sensitive dysfunction in CD8+ T cells
Teh, Megan R et al.
Iron is an irreplaceable co-factor for metabolism. Iron deficiency affects >1 billion people and decreased iron availability impairs immunity. Nevertheless, how iron deprivation impacts immune cell function remains poorly characterised. We interrogate how physiologically low iron availability affects CD8+&nbs... |
Epstein-Barr Virus-Driven B-Cell Transformation under Germinal Center Hypoxia Requires External Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Havey, Larissa et al.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) contributes to over 200,000 cancers annually, predominantly aggressive lymphomas originating from hypoxic germinal centers (< 1% O2). However, conventional models fail to recapitulate the physiologically relevant hypoxic microenvironment which profoundly influences B-cell metabolic remode... |
CRISPR screening identifies regulators of enhancer-mediated androgen receptor transcription in advanced prostate cancer
Rachel R. Xiang et al.
Amplification of the androgen receptor (AR) locus is the most frequent alteration in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Recently, it was discovered that an enhancer of the AR is co-amplified with the AR gene body and contributes to increased AR transcription and resistance to androgen de... |
MECOM is a master repressor of myeloid differentiation through dose control of CEBPA in acute myeloid leukemia
Dorien Pastoors et al.
Enhancer translocations, due to 3q26 rearrangements, drive out-of-context MECOM expression in an aggressive subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Direct depletion of MECOM using an endogenous auxin-inducible degron immediately upregulates expression of myeloid differentiation factor CEBPA. MECOM depletion is also... |
Interferon-gamma rescues FK506 dampened dendritic cell calcineurin-dependent responses to Aspergillus fumigatus via Stat3 to Stat1 switching
Amit Adlakha et al.
IScience Highlights
Calcineurin inhibitors block DC maturation in response to A. fumigatus
Lack of DC maturation impairs Th1 polarization in response to A. fumigatus
Interferon-γ restores maturation, promotes Th1 polarization and fungal killing
ChIPseq reveals in... |
NUP98 fusion proteins and KMT2A-MENIN antagonize PRC1.1 to drive gene expression in AML
Emily B. Heikamp et al.
Highlights
Degradation of NUP98-fp halts nascent transcription of key oncogenes within 1 h
NUP98-fp loss results in accumulation of PRC1.1 and repressive histone modifications
PRC1.1 is needed for stable gene repression but not for acute transcriptional changes
PRC1.1 is requi... |
Integrated multi-omics analysis of PBX1 in mouse adult neural stem- and progenitor cells identifies a transcriptional module that functionally links PBX1 to TCF3/4
Vera Laub et al.
Developmental transcription factors act in networks, but how these networks achieve cell- and tissue specificity is still poorly understood. Here, we explored pre-B cell leukemia homeobox 1 (PBX1) in adult neurogenesis combining genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic approaches. ChIP-seq analysis uncovered PBX1 bind... |
Trained immunity is regulated by T cell-induced CD40-TRAF6 signaling
Jacobs M.M.E. et al.
Trained immunity is characterized by histone modifications and metabolic changes in innate immune cells following exposure to inflammatory signals, leading to heightened responsiveness to secondary stimuli. Although our understanding of the molecular regulation of trained immunity has increased, the role of adaptive... |
Systematic prioritization of functional variants and effector genes underlying colorectal cancer risk
Law P.J. et al.
Genome-wide association studies of colorectal cancer (CRC) have identified 170 autosomal risk loci. However, for most of these, the functional variants and their target genes are unknown. Here, we perform statistical fine-mapping incorporating tissue-specific epigenetic annotations and massively parallel reporter as... |
Bivalent chromatin accommodates survivin and BRG1/SWI complex to activate DNA damage response in CD4+ cells
Chandrasekaran V. et al.
Background
Bivalent regions of chromatin (BvCR) are characterized by trimethylated lysine 4 (H3K4me3) and lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3K27me3) deposition which aid gene expression control during cell differentiation. The role of BvCR in post-transcriptional DNA damage response remains unidentified. Oncoprotein ... |
RNA sequestration in P-bodies sustains myeloid leukaemia
Srikanth Kodali et al.
Post-transcriptional mechanisms are fundamental safeguards of progenitor cell identity and are often dysregulated in cancer. Here, we identified regulators of P-bodies as crucial vulnerabilities in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) through genome-wide CRISPR screens in normal and malignant haematopoietic progenitors. We... |
Innate immune training restores pro-reparative myeloid functions to promote remyelination in the aged central nervous system
Tiwari V. et al.
The reduced ability of the central nervous system to regenerate with increasing age limits functional recovery following demyelinating injury. Previous work has shown that myelin debris can overwhelm the metabolic capacity of microglia, thereby impeding tissue regeneration in aging, but the underlying mechanisms are... |
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment
Perez R. F. at al.
Aging involves the deterioration of organismal function, leading to the emergence of multiple pathologies. Environmental stimuli, including lifestyle, can influence the trajectory of this process and may be used as tools in the pursuit of healthy aging. To evaluate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this context, ... |
Epigenomic signatures of sarcomatoid differentiation to guide the treatment of renal cell carcinoma
Talal El Zarif et al.
Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (sRCC) is associated with poor survival and a heightened response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Two major barriers to improving outcomes for sRCC are the limited understanding of its gene regulatory programs and the low diagnostic yield of tumor biopsie... |
Single-cell epigenomic reconstruction of developmental trajectories from pluripotency in human neural organoid systems
Fides Zenk et al.
Cell fate progression of pluripotent progenitors is strictly regulated, resulting in high human cell diversity. Epigenetic modifications also orchestrate cell fate restriction. Unveiling the epigenetic mechanisms underlying human cell diversity has been difficult. In this study, we use human brain and retina organoi... |
SURVIVIN IN SYNERGY WITH BAF/SWI COMPLEX BINDS BIVALENT CHROMATIN REGIONS AND ACTIVATES DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE IN CD4+ T CELLS
Chandrasekaran V. et al.
This study explores a regulatory role of oncoprotein survivin on the bivalent regions of chromatin (BvCR) characterized by concomitant deposition of trimethylated lysine of histone H3 at position 4 (H3K4me3) and 27 (H3K27me3).
Intersect between BvCR and chromatin sequences bound to survivin demonstrated their co-lo... |
Multiomics uncovers the epigenomic and transcriptomic response to viral and bacterial stimulation in turbot
Aramburu O. et al.
Uncovering the epigenomic regulation of immune responses is essential for a comprehensive understanding of host defence mechanisms but remains poorly described in farmed fish. Here, we report the first annotation of the innate immune regulatory response in the genome of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus), a farmed flatfi... |
Opposing gene regulatory programs governing myofiber development andmaturation revealed at single nucleus resolution.
Dos Santos M. et al.
Skeletal muscle fibers express distinct gene programs during development and maturation, but the underlying gene regulatory networks that confer stage-specific myofiber properties remain unknown. To decipher these distinctive gene programs and how they respond to neural activity, we generated a combined multi-omic s... |
Alterations in the hepatocyte epigenetic landscape in steatosis.
Maji Ranjan K. et al.
Fatty liver disease or the accumulation of fat in the liver, has been reported to affect the global population. This comes with an increased risk for the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Yet, little is known about the effects of a diet containing high fat and alcohol towards epigenet... |
Identification of a deltaNp63-Dependent Basal-Like ASubtype-Specific Transcribed Enhancer Program (B-STEP) in Aggressive Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.
Wang X. et al.
A major hurdle to the application of precision oncology in pancreatic cancer is the lack of molecular stratification approaches and targeted therapy for defined molecular subtypes. In this work, we sought to gain further insight and identify molecular and epigenetic signatures of the basal-like A pancreatic ductal a... |
The Fgf/Erf/NCoR1/2 repressive axis controls trophoblast cellfate.
Lackner A. et al.
Placental development relies on coordinated cell fate decisions governed by signalling inputs. However, little is known about how signalling cues are transformed into repressive mechanisms triggering lineage-specific transcriptional signatures. Here, we demonstrate that upon inhibition of the Fgf/Erk pathway in mous... |
Landscape of prostate-specific membrane antigen heterogeneity andregulation in AR-positive and AR-negative metastatic prostate cancer.
Bakht MK et al.
Tumor expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is lost in 15-20\% of men with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), yet the underlying mechanisms remain poorly defined. In androgen receptor (AR)-positive CRPC, we observed lower PSMA expression in liver lesions versus other sites, suggesting a r... |
Comprehensive epigenomic profiling reveals the extent of disease-specificchromatin states and informs target discovery in ankylosing spondylitis
Brown A.C. et al.
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a common, highly heritable inflammatory arthritis characterized by enthesitis of the spine and sacroiliac joints. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have revealed more than 100 genetic associations whose functional effects remain largely unresolved. Here, we present a comprehensiv... |
Chromatin profiling identifies transcriptional readthrough as a conservedmechanism for piRNA biogenesis in mosquitoes.
Qu J. et al.
The piRNA pathway in mosquitoes differs substantially from other model organisms, with an expanded PIWI gene family and functions in antiviral defense. Here, we define core piRNA clusters as genomic loci that show ubiquitous piRNA expression in both somatic and germline tissues. These core piRNA clusters are enriche... |
Epigenetic dosage identifies two major and functionally distinct beta cells ubtypes.
Dror E.et al.
The mechanisms that specify and stabilize cell subtypes remain poorly understood. Here, we identify two major subtypes of pancreatic β cells based on histone mark heterogeneity (beta HI and beta LO). Beta HI cells exhibit 4-fold higher levels of H3K27me3, distinct chromatin organization and compaction, a... |
Single substitution in H3.3G34 alters DNMT3A recruitment to causeprogressive neurodegeneration.
Khazaei S. et al.
Germline histone H3.3 amino acid substitutions, including H3.3G34R/V, cause severe neurodevelopmental syndromes. To understand how these mutations impact brain development, we generated H3.3G34R/V/W knock-in mice and identified strikingly distinct developmental defects for each mutation. H3.3G34R-mutants exhibited p... |
Histone remodeling reflects conserved mechanisms of bovine and humanpreimplantation development.
Zhou C. et al.
How histone modifications regulate changes in gene expression during preimplantation development in any species remains poorly understood. Using CUT\&Tag to overcome limiting amounts of biological material, we profiled two activating (H3K4me3 and H3K27ac) and two repressive (H3K9me3 and H3K27me3) marks in bovine... |
Epigenomic charting and functional annotation of risk loci in renal cellcarcinoma.
Nassar A. H. et al.
While the mutational and transcriptional landscapes of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) are well-known, the epigenome is poorly understood. We characterize the epigenome of clear cell (ccRCC), papillary (pRCC), and chromophobe RCC (chRCC) by using ChIP-seq, ATAC-Seq, RNA-seq, and SNP arrays. We integrate 153 individual da... |
Analyzing the Genome-Wide Distribution of Histone Marks byCUT\&Tag in Drosophila Embryos.
Zenk F. et al.
CUT&Tag is a method to map the genome-wide distribution of histone modifications and some chromatin-associated proteins. CUT&Tag relies on antibody-targeted chromatin tagmentation and can easily be scaled up or automatized. This protocol provides clear experimental guidelines and helpful considerations when ... |
K27M in canonical and noncanonical H3 variants occurs in distinctoligodendroglial cell lineages in brain midline gliomas.
Jessa Selin et al.
Canonical (H3.1/H3.2) and noncanonical (H3.3) histone 3 K27M-mutant gliomas have unique spatiotemporal distributions, partner alterations and molecular profiles. The contribution of the cell of origin to these differences has been challenging to uncouple from the oncogenic reprogramming induced by the mutation. Here... |
Identification of genomic binding sites and direct target genes for thetranscription factor DDIT3/CHOP.
Osman A. et al.
DDIT3 is a tightly regulated basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor and key regulator in cellular stress responses. It is involved in a variety of pathological conditions and may cause cell cycle block and apoptosis. It is also implicated in differentiation of some specialized cell types and as an oncogene... |
Viral transduction of primary human lymphoma B cells reveals mechanismsof NOTCH-mediated immune escape.
Mangolini M. et al.
Hotspot mutations in the PEST-domain of NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 are recurrently identified in B cell malignancies. To address how NOTCH-mutations contribute to a dismal prognosis, we have generated isogenic primary human tumor cells from patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL), diff... |
Linked-read whole-genome sequencing resolves common and privatestructural variants in multiple myeloma.
Peña-Pérez L. et al.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is an incurable and aggressive plasma cell malignancy characterized by a complex karyotype with multiple structural variants (SVs) and copy-number variations (CNVs). Linked-read whole-genome sequencing (lrWGS) allows for refined detection and reconstruction of SVs by providing long-range geneti... |
Vitamin D receptor and STAT6 interactome governs oesophagealepithelial barrier responses to IL-13 signalling.
Brusilovsky M. et al.
OBJECTIVE: The contribution of vitamin D (VD) deficiency to the pathogenesis of allergic diseases remains elusive. We aimed to define the impact of VD on oesophageal allergic inflammation. DESIGN: We assessed the genomic distribution and function of VD receptor (VDR) and STAT6 using histology, molecular imaging, mot... |
Epigenomic analysis reveals a dynamic and context-specific macrophageenhancer landscape associated with innate immune activation and tolerance.
Zhang P. et al.
BACKGROUND: Chromatin states and enhancers associate gene expression, cell identity and disease. Here, we systematically delineate the acute innate immune response to endotoxin in terms of human macrophage enhancer activity and contrast with endotoxin tolerance, profiling the coding and non-coding transcriptome, chr... |
Nuclear receptor RORγ inverse agonists/antagonists display tissue- andgene-context selectivity through distinct activities in altering chromatinaccessibility and master regulator SREBP2 occupancy.
Zou Hongye et al.
The nuclear receptor RORγ is a major driver of autoimmune diseases and certain types of cancer due to its aberrant function in T helper 17 (Th17) cell differentiation and tumor cholesterol metabolism, respectively. Compound screening using the classic receptor-coactivator interaction perturbation scheme led to... |
Immune disease variants modulate gene expression in regulatory CD4T cells.
Bossini-Castillo L. et al.
Identifying cellular functions dysregulated by disease-associated variants could implicate novel pathways for drug targeting or modulation in cell therapies. However, follow-up studies can be challenging if disease-relevant cell types are difficult to sample. Variants associated with immune diseases point toward the... |
CREBBP/EP300 acetyltransferase inhibition disrupts FOXA1-bound enhancers to inhibit the proliferation of ER+ breast cancer cells.
Bommi-Reddy A. et al.
Therapeutic targeting of the estrogen receptor (ER) is a clinically validated approach for estrogen receptor positive breast cancer (ER+ BC), but sustained response is limited by acquired resistance. Targeting the transcriptional coactivators required for estrogen receptor activity represents an alternative approach... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple Myeloma
Elina Alaterre et al.
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have been widely used to understand themolecular processes that drive MM biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape of MM wouldadvance our un... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple
Myeloma
Alaterre, Elina and Ovejero, Sara and Herviou, Laurie and de
Boussac, Hugues and Papadopoulos, Giorgio and Kulis, Marta and
Boireau, Stéphanie and Robert, Nicolas and Requirand, Guilhem
and Bruyer, Angélique and Cartron, Guillaume and Vincent,
Laure and M
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have
been widely used to understand the molecular processes that drive MM
biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,
progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the
epigenetic landscape of MM would advance our... |
Pre-configuring chromatin architecture with histone modifications guideshematopoietic stem cell formation in mouse embryos.
Li CC et al.
The gene activity underlying cell differentiation is regulated by a diverse set of transcription factors (TFs), histone modifications, chromatin structures and more. Although definitive hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are known to emerge via endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition (EHT), how the multi-layered epigen... |
Androgen receptor and MYC equilibration centralizes on developmentalsuper-enhancer
Guo H. et al.
Androgen receptor (AR) in prostate cancer (PCa) can drive transcriptional repression of multiple genes including MYC, and supraphysiological androgen is effective in some patients. Here, we show that this repression is independent of AR chromatin binding and driven by coactivator redistribution, and through chromati... |
Comparing the epigenetic landscape in myonuclei purified with a PCM1antibody from a fast/glycolytic and a slow/oxidative muscle.
Bengtsen Mads et al.
Muscle cells have different phenotypes adapted to different usage, and can be grossly divided into fast/glycolytic and slow/oxidative types. While most muscles contain a mixture of such fiber types, we aimed at providing a genome-wide analysis of the epigenetic landscape by ChIP-Seq in two muscle extremes, the fast/... |
p300 suppresses the transition of myelodysplastic syndromes to acutemyeloid leukemia
Man Na et al.
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) malignancies characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis and an increased risk of leukemia transformation. Epigenetic regulators are recurrently mutated in MDS, directly implicating epigenetic dysregulation in MDS pathogenesis. Here, we... |
Aiolos regulates eosinophil migration into tissues.
Felton Jennifer M et al.
Expression of Ikaros family transcription factor IKZF3 (Aiolos) increases during murine eosinophil lineage commitment and maturation. Herein, we investigated Aiolos expression and function in mature human and murine eosinophils. Murine eosinophils deficient in Aiolos demonstrated gene expression changes in pathways ... |
Enhanced targeted DNA methylation of the CMV and endogenous promoterswith dCas9-DNMT3A3L entails distinct subsequent histonemodification changes in CHO cells.
Marx Nicolas et al.
With the emergence of new CRISPR/dCas9 tools that enable site specific modulation of DNA methylation and histone modifications, more detailed investigations of the contribution of epigenetic regulation to the precise phenotype of cells in culture, including recombinant production subclones, is now possible. These al... |
Lasp1 regulates adherens junction dynamics and fibroblast transformationin destructive arthritis
Beckmann D. et al.
The LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (Lasp1) was originally cloned from metastatic breast cancer and characterised as an adaptor molecule associated with tumourigenesis and cancer cell invasion. However, the regulation of Lasp1 and its function in the aggressive transformation of cells is unclear. Here we use integrativ... |
Placental uptake and metabolism of 25(OH)Vitamin D determines itsactivity within the fetoplacental unit
Ashley, B. et al.
Pregnancy 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentrations are associated with maternal and fetal health outcomes, but the underlying mechanisms have not been elucidated. Using physiological human placental perfusion approaches and intact villous explants we demonstrate a role for the placenta in regulating the relation... |
Chromatin accessibility governs the differential response of cancer and T cells to arginine starvation.
Crump, N.T. et al.
Depleting the microenvironment of important nutrients such as arginine is a key strategy for immune evasion by cancer cells. Many tumors overexpress arginase, but it is unclear how these cancers, but not T cells, tolerate arginine depletion. In this study, we show that tumor cells synthesize arginine from citru... |
Sarcomere function activates a p53-dependent DNA damage response that promotes polyploidization and limits in vivo cell engraftment.
Pettinato, Anthony M. et al.
Human cardiac regeneration is limited by low cardiomyocyte replicative rates and progressive polyploidization by unclear mechanisms. To study this process, we engineer a human cardiomyocyte model to track replication and polyploidization using fluorescently tagged cyclin B1 and cardiac troponin T. Using time-lapse i... |
Androgen and glucocorticoid receptor direct distinct transcriptionalprograms by receptor-specific and shared DNA binding sites.
Kulik, Marina et al.
The glucocorticoid (GR) and androgen (AR) receptors execute unique functions in vivo, yet have nearly identical DNA binding specificities. To identify mechanisms that facilitate functional diversification among these transcription factor paralogs, we studied them in an equivalent cellular context. Analysis of chroma... |
USP22 Suppresses Expression in Acute Colitis and Inflammation-AssociatedColorectal Cancer.
Kosinsky, R. L. et al.
As a member of the 11-gene "death-from-cancer" gene expression signature, ubiquitin-specific protease 22 (USP22) has been considered an oncogene in various human malignancies, including colorectal cancer (CRC). We recently identified an unexpected tumor-suppressive function of USP22 in CRC and detected intestinal in... |
The epigenetic landscape in purified myonuclei from fast and slow muscles
Bengtsen, M. et al.
Muscle cells have different phenotypes adapted to different usage and can be grossly divided into fast/glycolytic and slow/oxidative types. While most muscles contain a mixture of such fiber types, we aimed at providing a genome-wide analysis of chromatin environment by ChIP-Seq in two muscle extremes, the almost co... |
Environmental enrichment induces epigenomic and genome organization changesrelevant for cognitive function
Espeso-Gil, S. et al.
In early development, the environment triggers mnemonic epigenomic programs resulting in memory and learning experiences to confer cognitive phenotypes into adulthood. To uncover how environmental stimulation impacts the epigenome and genome organization, we used the paradigm of environmental enrichment (EE) in youn... |
Chromatin dysregulation associated with NSD1 mutation in head and necksquamous cell carcinoma.
Farhangdoost, Nargess et al.
Chromatin dysregulation has emerged as an important mechanism of oncogenesis. To develop targeted treatments, it is important to understand the transcriptomic consequences of mutations in chromatin modifier genes. Recently, mutations in the histone methyltransferase gene nuclear receptor binding SET domain protein 1... |
Kmt2c mutations enhance HSC self-renewal capacity and convey a selectiveadvantage after chemotherapy.
Chen, Ran et al.
The myeloid tumor suppressor KMT2C is recurrently deleted in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML), particularly therapy-related MDS/AML (t-MDS/t-AML), as part of larger chromosome 7 deletions. Here, we show that KMT2C deletions convey a selective advantage to hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs... |
Stronger induction of trained immunity by mucosal BCG or MTBVAC vaccination compared to standard intradermal vaccination.
Vierboom, M.P.M. et al.
BCG vaccination can strengthen protection against pathogens through the induction of epigenetic and metabolic reprogramming of innate immune cells, a process called trained immunity. We and others recently demonstrated that mucosal or intravenous BCG better protects rhesus macaques from infection and TB disease than... |
Postoperative abdominal sepsis induces selective and persistent changes inCTCF binding within the MHC-II region of human monocytes.
Siegler B. et al.
BACKGROUND: Postoperative abdominal infections belong to the most common triggers of sepsis and septic shock in intensive care units worldwide. While monocytes play a central role in mediating the initial host response to infections, sepsis-induced immune dysregulation is characterized by a defective antigen present... |
Promoter-interacting expression quantitative trait loci are enriched forfunctional genetic variants.
Chandra V. et al.
Expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) studies provide associations of genetic variants with gene expression but fall short of pinpointing functionally important eQTLs. Here, using H3K27ac HiChIP assays, we mapped eQTLs overlapping active cis-regulatory elements that interact with their target gene promoters (pr... |
Histone H3.3G34-Mutant Interneuron Progenitors Co-opt PDGFRA for Gliomagenesis.
Chen C. et al.
Histone H3.3 glycine 34 to arginine/valine (G34R/V) mutations drive deadly gliomas and show exquisite regional and temporal specificity, suggesting a developmental context permissive to their effects. Here we show that 50\% of G34R/V tumors (n = 95) bear activating PDGFRA mutations that display strong selection... |
CDK4/6 inhibition reprograms the breast cancer enhancer landscape bystimulating AP-1 transcriptional activity
Watt, April C. and Cejas, Paloma and DeCristo, Molly J. and Metzger-Filho,Otto and Lam, Enid Y. N. and Qiu, Xintao and BrinJones, Haley and Kesten,Nikolas and Coulson, Rhiannon and Font-Tello, Alba and Lim, Klothilda andVadhi, Raga and Daniels, Veerle
Pharmacologic inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) were designed to induce cancer cell cycle arrest. Recent studies have suggested that these agents also exert other effects, influencing cancer cell immunogenicity, apoptotic responses and differentiation. Using cell-based and mouse models of breas... |
MITF is a driver oncogene and potential therapeutic target in kidneyangiomyolipoma tumors through transcriptional regulation of CYR61.
Zarei, Mahsa and Giannikou, Krinio and Du, Heng and Liu, Heng-Jia andDuarte, Melissa and Johnson, Sneha and Nassar, Amin H and Widlund, Hans Rand Henske, Elizabeth P and Long, Henry W and Kwiatkowski, David J
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is an autosomal dominant tumor suppressor syndrome, characterized by tumor development in multiple organs, including renal angiomyolipoma. Biallelic loss of TSC1 or TSC2 is a known genetic driver of angiomyolipoma development, however, whether an altered transcriptional repertoire co... |
Combined treatment with CBP and BET inhibitors reverses inadvertentactivation of detrimental super enhancer programs in DIPG cells.
Wiese, M and Hamdan, FH and Kubiak, K and Diederichs, C and Gielen, GHand Nussbaumer, G and Carcaboso, AM and Hulleman, E and Johnsen, SA andKramm, CM
Diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPG) are the most aggressive brain tumors in children with 5-year survival rates of only 2%. About 85% of all DIPG are characterized by a lysine-to-methionine substitution in histone 3, which leads to global H3K27 hypomethylation accompanied by H3K27 hyperacetylation. Hyperacetyla... |
OxLDL-mediated immunologic memory in endothelial cells.
Sohrabi Y, Lagache SMM, Voges VC, Semo D, Sonntag G, Hanemann I, Kahles F, Waltenberger J, Findeisen HM
Trained innate immunity describes the metabolic reprogramming and long-term proinflammatory activation of innate immune cells in response to different pathogen or damage associated molecular patterns, such as oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL). Here, we have investigated whether the regulatory networks of trai... |
The Human Integrator Complex Facilitates Transcriptional Elongation by Endonucleolytic Cleavage of Nascent Transcripts.
Beckedorff F, Blumenthal E, daSilva LF, Aoi Y, Cingaram PR, Yue J, Zhang A, Dokaneheifard S, Valencia MG, Gaidosh G, Shilatifard A, Shiekhattar R
Transcription by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) is pervasive in the human genome. However, the mechanisms controlling transcription at promoters and enhancers remain enigmatic. Here, we demonstrate that Integrator subunit 11 (INTS11), the catalytic subunit of the Integrator complex, regulates transcription at these loci... |
Prostate cancer reactivates developmental epigenomic programs during metastatic progression.
Pomerantz MM, Qiu X, Zhu Y, Takeda DY, Pan W, Baca SC, Gusev A, Korthauer KD, Severson TM, Ha G, Viswanathan SR, Seo JH, Nguyen HM, Zhang B, Pasaniuc B, Giambartolomei C, Alaiwi SA, Bell CA, O'Connor EP, Chabot MS, Stillman DR, Lis R, Font-Tello A, Li L,
Epigenetic processes govern prostate cancer (PCa) biology, as evidenced by the dependency of PCa cells on the androgen receptor (AR), a prostate master transcription factor. We generated 268 epigenomic datasets spanning two state transitions-from normal prostate epithelium to localized PCa to metastases-in specimens... |
Egr2-guided histone H2B monoubiquitination is required for peripheral nervous system myelination.
Wüst HM, Wegener A, Fröb F, Hartwig AC, Wegwitz F, Kari V, Schimmel M, Tamm ER, Johnsen SA, Wegner M, Sock E
Schwann cells are the nerve ensheathing cells of the peripheral nervous system. Absence, loss and malfunction of Schwann cells or their myelin sheaths lead to peripheral neuropathies such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in humans. During Schwann cell development and myelination chromatin is dramatically modified. How... |
FiTAc-seq: fixed-tissue ChIP-seq for H3K27ac profiling and super-enhancer analysis of FFPE tissues.
Font-Tello A, Kesten N, Xie Y, Taing L, Varešlija D, Young LS, Hamid AA, Van Allen EM, Sweeney CJ, Gjini E, Lako A, Hodi FS, Bellmunt J, Brown M, Cejas P, Long HW
Fixed-tissue ChIP-seq for H3K27 acetylation (H3K27ac) profiling (FiTAc-seq) is an epigenetic method for profiling active enhancers and promoters in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues. We previously developed a modified ChIP-seq protocol (FiT-seq) for chromatin profiling in FFPE. FiT-seq produces high-q... |
Genomic deregulation of PRMT5 supports growth and stress tolerance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Schnormeier AK, Pommerenke C, Kaufmann M, Drexler HG, Koeppel M
Patients suffering from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) display highly diverse clinical courses ranging from indolent cases to aggressive disease, with genetic and epigenetic features resembling this diversity. Here, we developed a comprehensive approach combining a variety of molecular and clinical data to pinpo... |
Integration of high-throughput reporter assays identify a critical enhancer of the Ikzf1 gene.
Alomairi J, Molitor AM, Sadouni N, Hussain S, Torres M, Saadi W, Dao LTM, Charbonnier G, Santiago-Algarra D, Andrau JC, Puthier D, Sexton T, Spicuglia S
The Ikzf1 locus encodes the lymphoid specific transcription factor Ikaros, which plays an essential role in both T and B cell differentiation, while deregulation or mutation of IKZF1/Ikzf1 is involved in leukemia. Tissue-specific and cell identity genes are usually associated with clusters of enhancers, also called ... |
Non-coding somatic mutations converge on the PAX8 pathway in ovarian cancer.
Corona RI, Seo JH, Lin X, Hazelett DJ, Reddy J, Fonseca MAS, Abassi F, Lin YG, Mhawech-Fauceglia PY, Shah SP, Huntsman DG, Gusev A, Karlan BY, Berman BP, Freedman ML, Gayther SA, Lawrenson K
The functional consequences of somatic non-coding mutations in ovarian cancer (OC) are unknown. To identify regulatory elements (RE) and genes perturbed by acquired non-coding variants, here we establish epigenomic and transcriptomic landscapes of primary OCs using H3K27ac ChIP-seq and RNA-seq, and then integrate th... |
LXR Activation Induces a Proinflammatory Trained Innate Immunity-Phenotype in Human Monocytes
Sohrabi Yahya, Sonntag Glenn V. H., Braun Laura C., Lagache Sina M. M., Liebmann Marie, Klotz Luisa, Godfrey Rinesh, Kahles Florian, Waltenberger Johannes, Findeisen Hannes M.
The concept of trained innate immunity describes a long-term proinflammatory memory in innate immune cells. Trained innate immunity is regulated through reprogramming of cellular metabolic pathways including cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis. Here, we have analyzed the role of Liver X Receptor (LXR), a key regula... |
Tissue alarmins and adaptive cytokine induce dynamic and distinct transcriptional responses in tissue-resident intraepithelial cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
Zorro MM, Aguirre-Gamboa R, Mayassi T, Ciszewski C, Barisani D, Hu S, Weersma RK, Withoff S, Li Y, Wijmenga C, Jabri B, Jonkers IH
The respective effects of tissue alarmins interleukin (IL)-15 and interferon beta (IFNβ), and IL-21 produced by T cells on the reprogramming of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) that cause tissue destruction in celiac disease is poorly understood. Transcriptomic and epigenetic profiling of primary intestinal CTLs ... |
AP-1 activity induced by co-stimulation is required for chromatin opening during T cell activation.
Yukawa M, Jagannathan S, Vallabh S, Kartashov AV, Chen X, Weirauch MT, Barski A
Activation of T cells is dependent on the organized and timely opening and closing of chromatin. Herein, we identify AP-1 as the transcription factor that directs most of this remodeling. Chromatin accessibility profiling showed quick opening of closed chromatin in naive T cells within 5 h of activation. These newly... |
Analysis of Histone Modifications in Rodent Pancreatic Islets by Native Chromatin Immunoprecipitation.
Sandovici I, Nicholas LM, O'Neill LP
The islets of Langerhans are clusters of cells dispersed throughout the pancreas that produce several hormones essential for controlling a variety of metabolic processes, including glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Studying the transcriptional control of pancreatic islet cells has important implications for ... |
Changes in H3K27ac at Gene Regulatory Regions in Porcine AlveolarMacrophages Following LPS or PolyIC Exposure.
Herrera-Uribe, Juber and Liu, Haibo and Byrne, Kristen A and Bond, Zahra Fand Loving, Crystal L and Tuggle, Christopher K
Changes in chromatin structure, especially in histone modifications (HMs), linked with chromatin accessibility for transcription machinery, are considered to play significant roles in transcriptional regulation. Alveolar macrophages (AM) are important immune cells for protection against pulmonary pathogens, and must... |
Charting the cis-regulome of activated B cells by coupling structural and functional genomics.
Chaudhri VK, Dienger-Stambaugh K, Wu Z, Shrestha M, Singh H
Cis-regulomes underlying immune-cell-specific genomic states have been extensively analyzed by structure-based chromatin profiling. By coupling such approaches with a high-throughput enhancer screen (self-transcribing active regulatory region sequencing (STARR-seq)), we assembled a functional cis-regulome for lipopo... |
Functionally Annotating Regulatory Elements in the Equine Genome Using Histone Mark ChIP-Seq.
Kingsley NB, Kern C, Creppe C, Hales EN, Zhou H, Kalbfleisch TS, MacLeod JN, Petersen JL, Finno CJ, Bellone RR
One of the primary aims of the Functional Annotation of ANimal Genomes (FAANG) initiative is to characterize tissue-specific regulation within animal genomes. To this end, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-Seq) to map four histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me... |
A Study of High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Origins Implicates the SOX18 Transcription Factor in Tumor Development.
Lawrenson K, Fonseca MAS, Liu AY, Segato Dezem F, Lee JM, Lin X, Corona RI, Abbasi F, Vavra KC, Dinh HQ, Gill NK, Seo JH, Coetzee S, Lin YG, Pejovic T, Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Rowat AC, Drapkin R, Karlan BY, Hazelett DJ, Freedman ML, Gayther SA, Noushmehr H
Fallopian tube secretory epithelial cells (FTSECs) are likely the main precursor cell type of high-grade serous ovarian cancers (HGSOCs), but these tumors may also arise from ovarian surface epithelial cells (OSECs). We profiled global landscapes of gene expression and active chromatin to characterize molecular simi... |
CREB5 Promotes Resistance to Androgen-Receptor Antagonists and Androgen Deprivation in Prostate Cancer.
Hwang JH, Seo JH, Beshiri ML, Wankowicz S, Liu D, Cheung A, Li J, Qiu X, Hong AL, Botta G, Golumb L, Richter C, So J, Sandoval GJ, Giacomelli AO, Ly SH, Han C, Dai C, Pakula H, Sheahan A, Piccioni F, Gjoerup O, Loda M, Sowalsky AG, Ellis L, Long H, Root D
Androgen-receptor (AR) inhibitors, including enzalutamide, are used for treatment of all metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancers (mCRPCs). However, some patients develop resistance or never respond. We find that the transcription factor CREB5 confers enzalutamide resistance in an open reading frame (ORF) ex... |
The Lineage Determining Factor GRHL2 Collaborates with FOXA1 to Establish a Targetable Pathway in Endocrine Therapy-Resistant Breast Cancer.
Cocce KJ, Jasper JS, Desautels TK, Everett L, Wardell S, Westerling T, Baldi R, Wright TM, Tavares K, Yllanes A, Bae Y, Blitzer JT, Logsdon C, Rakiec DP, Ruddy DA, Jiang T, Broadwater G, Hyslop T, Hall A, Laine M, Phung L, Greene GL, Martin LA, Pancholi S
Notwithstanding the positive clinical impact of endocrine therapies in estrogen receptor-alpha (ERα)-positive breast cancer, de novo and acquired resistance limits the therapeutic lifespan of existing drugs. Taking the position that resistance is nearly inevitable, we undertook a study to identify and exploit ... |
TET2 Regulates the Neuroinflammatory Response in Microglia.
Carrillo-Jimenez A, Deniz Ö, Niklison-Chirou MV, Ruiz R, Bezerra-Salomão K, Stratoulias V, Amouroux R, Yip PK, Vilalta A, Cheray M, Scott-Egerton AM, Rivas E, Tayara K, García-Domínguez I, Garcia-Revilla J, Fernandez-Martin JC, Espinosa-Oliva AM, Shen X,
Epigenomic mechanisms regulate distinct aspects of the inflammatory response in immune cells. Despite the central role for microglia in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration, little is known about their epigenomic regulation of the inflammatory response. Here, we show that Ten-eleven translocation 2 (TET2) methylc... |
Unique and Shared Epigenetic Programs of the CREBBP and EP300 Acetyltransferases in Germinal Center B Cells Reveal Targetable Dependencies in Lymphoma.
Meyer SN, Scuoppo C, Vlasevska S, Bal E, Holmes AB, Holloman M, Garcia-Ibanez L, Nataraj S, Duval R, Vantrimpont T, Basso K, Brooks N, Dalla-Favera R, Pasqualucci L
Inactivating mutations of the CREBBP and EP300 acetyltransferases are among the most common genetic alterations in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL). Here, we examined the relationship between these two enzymes in germinal center (GC) B cells, the normal counterpart of FL and DLBCL, ... |
Reactivation of super-enhancers by KLF4 in human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Tsompana M, Gluck C, Sethi I, Joshi I, Bard J, Nowak NJ, Sinha S, Buck MJ
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a disease of significant morbidity and mortality and rarely diagnosed in early stages. Despite extensive genetic and genomic characterization, targeted therapeutics and diagnostic markers of HNSCC are lacking due to the inherent heterogeneity and complexity of the dis... |
BET protein targeting suppresses the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in triple-negative breast cancer and elicits anti-tumor immune response.
Andrieu GP, Shafran JS, Smith CL, Belkina AC, Casey AN, Jafari N, Denis GV
Therapeutic strategies aiming to leverage anti-tumor immunity are being intensively investigated as they show promising results in cancer therapy. The PD-1/PD-L1 pathway constitutes an important target to restore functional anti-tumor immune response. Here, we report that BET protein inhibition suppresses PD-1/PD-L1... |
Activation of neuronal genes via LINE-1 elements upon global DNA demethylation in human neural progenitors.
Jönsson ME, Ludvik Brattås P, Gustafsson C, Petri R, Yudovich D, Pircs K, Verschuere S, Madsen S, Hansson J, Larsson J, Månsson R, Meissner A, Jakobsson J
DNA methylation contributes to the maintenance of genomic integrity in somatic cells, in part through the silencing of transposable elements. In this study, we use CRISPR-Cas9 technology to delete DNMT1, the DNA methyltransferase key for DNA methylation maintenance, in human neural progenitor cells (hNPCs). We obser... |
The alarmin S100A9 hampers osteoclast differentiation from human circulating precursors by reducing the expression of RANK.
Di Ceglie I, Blom AB, Davar R, Logie C, Martens JHA, Habibi E, Böttcher LM, Roth J, Vogl T, Goodyear CS, van der Kraan PM, van Lent PL, van den Bosch MH
The alarmin S100A8/A9 is implicated in sterile inflammation-induced bone resorption and has been shown to increase the bone-resorptive capacity of mature osteoclasts. Here, we investigated the effects of S100A9 on osteoclast differentiation from human CD14 circulating precursors. Hereto, human CD14 monocytes were is... |
Twist2 amplification in rhabdomyosarcoma represses myogenesis and promotes oncogenesis by redirecting MyoD DNA binding.
Li S, Chen K, Zhang Y, Barnes SD, Jaichander P, Zheng Y, Hassan M, Malladi VS, Skapek SX, Xu L, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN, Liu N
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is an aggressive pediatric cancer composed of myoblast-like cells. Recently, we discovered a unique muscle progenitor marked by the expression of the Twist2 transcription factor. Genomic analyses of 258 RMS patient tumors uncovered prevalent copy number amplification events and increased expre... |
Ep400 deficiency in Schwann cells causes persistent expression of early developmental regulators and peripheral neuropathy.
Fröb F, Sock E, Tamm ER, Saur AL, Hillgärtner S, Williams TJ, Fujii T, Fukunaga R, Wegner M
Schwann cells ensure efficient nerve impulse conduction in the peripheral nervous system. Their development is accompanied by defined chromatin changes, including variant histone deposition and redistribution. To study the importance of variant histones for Schwann cell development, we altered their genomic distribu... |
Acetate Promotes T Cell Effector Function during Glucose Restriction.
Qiu J, Villa M, Sanin DE, Buck MD, O'Sullivan D, Ching R, Matsushita M, Grzes KM, Winkler F, Chang CH, Curtis JD, Kyle RL, Van Teijlingen Bakker N, Corrado M, Haessler F, Alfei F, Edwards-Hicks J, Maggi LB, Zehn D, Egawa T, Bengsch B, Klein Geltink RI, Je
Competition for nutrients like glucose can metabolically restrict T cells and contribute to their hyporesponsiveness during cancer. Metabolic adaptation to the surrounding microenvironment is therefore key for maintaining appropriate cell function. For instance, cancer cells use acetate as a substrate alternati... |
Pervasive H3K27 Acetylation Leads to ERV Expression and a Therapeutic Vulnerability in H3K27M Gliomas.
Krug B, De Jay N, Harutyunyan AS, Deshmukh S, Marchione DM, Guilhamon P, Bertrand KC, Mikael LG, McConechy MK, Chen CCL, Khazaei S, Koncar RF, Agnihotri S, Faury D, Ellezam B, Weil AG, Ursini-Siegel J, De Carvalho DD, Dirks PB, Lewis PW, Salomoni P, Lupie
High-grade gliomas defined by histone 3 K27M driver mutations exhibit global loss of H3K27 trimethylation and reciprocal gain of H3K27 acetylation, respectively shaping repressive and active chromatin landscapes. We generated tumor-derived isogenic models bearing this mutation and show that it leads to pervasive H3K... |
Cardiac Reprogramming Factors Synergistically Activate Genome-wide Cardiogenic Stage-Specific Enhancers.
Hashimoto H, Wang Z, Garry GA, Malladi VS, Botten GA, Ye W, Zhou H, Osterwalder M, Dickel DE, Visel A, Liu N, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN
The cardiogenic transcription factors (TFs) Mef2c, Gata4, and Tbx5 can directly reprogram fibroblasts to induced cardiac-like myocytes (iCLMs), presenting a potential source of cells for cardiac repair. While activity of these TFs is enhanced by Hand2 and Akt1, their genomic targets and interactions during reprogram... |
Epigenetic modulation of a hardwired 3D chromatin landscape in two naive states of pluripotency.
Atlasi Y, Megchelenbrink W, Peng T, Habibi E, Joshi O, Wang SY, Wang C, Logie C, Poser I, Marks H, Stunnenberg HG
The mechanisms underlying enhancer activation and the extent to which enhancer-promoter rewiring contributes to spatiotemporal gene expression are not well understood. Using integrative and time-resolved analyses we show that the extensive transcriptome and epigenome resetting during the conversion between 'serum' a... |
Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing-Based CRISPRi Screening Resolves Molecular Drivers of Early Human Endoderm Development.
Genga RMJ, Kernfeld EM, Parsi KM, Parsons TJ, Ziller MJ, Maehr R
Studies in vertebrates have outlined conserved molecular control of definitive endoderm (END) development. However, recent work also shows that key molecular aspects of human END regulation differ even from rodents. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) to END offers a tractable system to study the mo... |
Long intergenic non-coding RNAs regulate human lung fibroblast function: Implications for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Hadjicharalambous MR, Roux BT, Csomor E, Feghali-Bostwick CA, Murray LA, Clarke DL, Lindsay MA
Phenotypic changes in lung fibroblasts are believed to contribute to the development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), a progressive and fatal lung disease. Long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) have been identified as novel regulators of gene expression and protein activity. In non-stimulated cells, we o... |
ARv7 Represses Tumor-Suppressor Genes in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.
Cato L, de Tribolet-Hardy J, Lee I, Rottenberg JT, Coleman I, Melchers D, Houtman R, Xiao T, Li W, Uo T, Sun S, Kuznik NC, Göppert B, Ozgun F, van Royen ME, Houtsmuller AB, Vadhi R, Rao PK, Li L, Balk SP, Den RB, Trock BJ, Karnes RJ, Jenkins RB, Klein EA,
Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer (PCa) benefits patients with early disease, but becomes ineffective as PCa progresses to a castration-resistant state (CRPC). Initially CRPC remains dependent on androgen receptor (AR) signaling, often through increased expression of full-length AR (ARfl) or expressio... |
A critical regulator of Bcl2 revealed by systematic transcript discovery of lncRNAs associated with T-cell differentiation.
Saadi W, Kermezli Y, Dao LTM, Mathieu E, Santiago-Algarra D, Manosalva I, Torres M, Belhocine M, Pradel L, Loriod B, Aribi M, Puthier D, Spicuglia S
Normal T-cell differentiation requires a complex regulatory network which supports a series of maturation steps, including lineage commitment, T-cell receptor (TCR) gene rearrangement, and thymic positive and negative selection. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are difficult to assess due to limited T-ce... |
The role of TCF3 as potential master regulator in blastemal Wilms tumors.
Kehl T, Schneider L, Kattler K, Stöckel D, Wegert J, Gerstner N, Ludwig N, Distler U, Tenzer S, Gessler M, Walter J, Keller A, Graf N, Meese E, Lenhof HP
Wilms tumors are the most common type of pediatric kidney tumors. While the overall prognosis for patients is favorable, especially tumors that exhibit a blastemal subtype after preoperative chemotherapy have a poor prognosis. For an improved risk assessment and therapy stratification, it is essential to identify th... |
Chromatin-Based Classification of Genetically Heterogeneous AMLs into Two Distinct Subtypes with Diverse Stemness Phenotypes.
Yi G, Wierenga ATJ, Petraglia F, Narang P, Janssen-Megens EM, Mandoli A, Merkel A, Berentsen K, Kim B, Matarese F, Singh AA, Habibi E, Prange KHM, Mulder AB, Jansen JH, Clarke L, Heath S, van der Reijden BA, Flicek P, Yaspo ML, Gut I, Bock C, Schuringa JJ
Global investigation of histone marks in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains limited. Analyses of 38 AML samples through integrated transcriptional and chromatin mark analysis exposes 2 major subtypes. One subtype is dominated by patients with NPM1 mutations or MLL-fusion genes, shows activation of the regulat... |
High-throughput ChIPmentation: freely scalable, single day ChIPseq data generation from very low cell-numbers.
Gustafsson C, De Paepe A, Schmidl C, Månsson R
BACKGROUND: Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled to sequencing (ChIP-seq) is widely used to map histone modifications and transcription factor binding on a genome-wide level. RESULTS: We present high-throughput ChIPmentation (HT-ChIPmentation) that eliminates the need for DNA purification prior to library amplifica... |
Comprehensive Analysis of Chromatin States in Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor Identifies Diverging Roles for SWI/SNF and Polycomb in Gene Regulation.
Erkek S, Johann PD, Finetti MA, Drosos Y, Chou HC, Zapatka M, Sturm D, Jones DTW, Korshunov A, Rhyzova M, Wolf S, Mallm JP, Beck K, Witt O, Kulozik AE, Frühwald MC, Northcott PA, Korbel JO, Lichter P, Eils R, Gajjar A, Roberts CWM, Williamson D, Hasselbla
Biallelic inactivation of SMARCB1, encoding a member of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, is the hallmark genetic aberration of atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors (ATRT). Here, we report how loss of SMARCB1 affects the epigenome in these tumors. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) on pri... |
DeltaNp63-dependent super enhancers define molecular identity in pancreatic cancer by an interconnected transcription factor network.
Hamdan FH, Johnsen SA
Molecular subtyping of cancer offers tremendous promise for the optimization of a precision oncology approach to anticancer therapy. Recent advances in pancreatic cancer research uncovered various molecular subtypes with tumors expressing a squamous/basal-like gene expression signature displaying a worse prognosis. ... |
TRPS1 Is a Lineage-Specific Transcriptional Dependency in Breast Cancer.
Witwicki RM, Ekram MB, Qiu X, Janiszewska M, Shu S, Kwon M, Trinh A, Frias E, Ramadan N, Hoffman G, Yu K, Xie Y, McAllister G, McDonald R, Golji J, Schlabach M, deWeck A, Keen N, Chan HM, Ruddy D, Rejtar T, Sovath S, Silver S, Sellers WR, Jagani Z, Hogart
Perturbed epigenomic programs play key roles in tumorigenesis, and chromatin modulators are candidate therapeutic targets in various human cancer types. To define singular and shared dependencies on DNA and histone modifiers and transcription factors in poorly differentiated adult and pediatric cancers, we conducted... |
The Itaconate Pathway Is a Central Regulatory Node Linking Innate Immune Tolerance and Trained Immunity
Domínguez-Andrés Jorge, Novakovic Boris, Li Yang, Scicluna Brendon P., Gresnigt Mark S., Arts Rob J.W., Oosting Marije, Moorlag Simone J.C.F.M., Groh Laszlo A., Zwaag Jelle, Koch Rebecca M., ter Horst Rob, Joosten Leo A.B., Wijmenga Cisca, Michelucci Ales
Sepsis involves simultaneous hyperactivation of the immune system and immune paralysis, leading to both organ dysfunction and increased susceptibility to secondary infections. Acute activation of myeloid cells induced itaconate synthesis, which subsequently mediated innate immune tolerance in human monocytes. In con... |
Impact of human sepsis on CCCTC-binding factor associated monocyte transcriptional response of Major Histocompatibility Complex II components.
Siegler BH, Uhle F, Lichtenstern C, Arens C, Bartkuhn M, Weigand MA, Weiterer S
BACKGROUND: Antigen presentation on monocyte surface to T-cells by Major Histocompatibility Complex, Class II (MHC-II) molecules is fundamental for pathogen recognition and efficient host response. Accordingly, loss of Major Histocompatibility Complex, Class II, DR (HLA-DR) surface expression indicates impaired mono... |
Mapping molecular landmarks of human skeletal ontogeny and pluripotent stem cell-derived articular chondrocytes.
Ferguson GB, Van Handel B, Bay M, Fiziev P, Org T, Lee S, Shkhyan R, Banks NW, Scheinberg M, Wu L, Saitta B, Elphingstone J, Larson AN, Riester SM, Pyle AD, Bernthal NM, Mikkola HK, Ernst J, van Wijnen AJ, Bonaguidi M, Evseenko D
Tissue-specific gene expression defines cellular identity and function, but knowledge of early human development is limited, hampering application of cell-based therapies. Here we profiled 5 distinct cell types at a single fetal stage, as well as chondrocytes at 4 stages in vivo and 2 stages during in vitro differen... |
Atopic asthma after rhinovirus-induced wheezing is associated with DNA methylation change in the SMAD3 gene promoter.
Lund RJ, Osmala M, Malonzo M, Lukkarinen M, Leino A, Salmi J, Vuorikoski S, Turunen R, Vuorinen T, Akdis C, Lähdesmäki H, Lahesmaa R, Jartti T
Children with rhinovirus-induced severe early wheezing have an increased risk of developing asthma later in life. The exact molecular mechanisms for this association are still mostly unknown. To identify potential changes in the transcriptional and epigenetic regulation in rhinovirus-associated atopic or nonatopic a... |
A Somatically Acquired Enhancer of the Androgen Receptor Is a Noncoding Driver in Advanced Prostate Cancer.
Takeda DY, Spisák S, Seo JH, Bell C, O'Connor E, Korthauer K, Ribli D, Csabai I, Solymosi N, Szállási Z, Stillman DR, Cejas P, Qiu X, Long HW, Tisza V, Nuzzo PV, Rohanizadegan M, Pomerantz MM, Hahn WC, Freedman ML
Increased androgen receptor (AR) activity drives therapeutic resistance in advanced prostate cancer. The most common resistance mechanism is amplification of this locus presumably targeting the AR gene. Here, we identify and characterize a somatically acquired AR enhancer located 650 kb centromeric to the ... |
Enhancer-driven transcriptional regulation is a potential key determinant for human visceral and subcutaneous adipocytes.
Liefke R, Bokelmann K, Ghadimi BM, Dango S
Obesity is characterized by the excess of body fat leading to impaired health. Abdominal fat is particularly harmful and is associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases and cancer. In contrast, subcutaneous fat is generally considered less detrimental. The mechanisms that establish the cellular characterist... |
Integrative multi-omics analysis of intestinal organoid differentiation
Rik GH Lindeboom, Lisa van Voorthuijsen1, Koen C Oost, Maria J Rodríguez-Colman, Maria V Luna-Velez, Cristina Furlan, Floriane Baraille, Pascal WTC Jansen, Agnès Ribeiro, Boudewijn MT Burgering, Hugo J Snippert, & Michiel Vermeulen
Intestinal organoids accurately recapitulate epithelial homeostasis in vivo, thereby representing a powerful in vitro system to investigate lineage specification and cellular differentiation. Here, we applied a multi-omics framework on stem cell-enriched and stem cell-depleted mouse intestinal organoids to obtain a ... |
The Polycomb-Dependent Epigenome Controls β Cell Dysfunction, Dedifferentiation, and Diabetes.
Lu TT, Heyne S, Dror E, Casas E, Leonhardt L, Boenke T, Yang CH, Sagar , Arrigoni L, Dalgaard K, Teperino R, Enders L, Selvaraj M, Ruf M, Raja SJ, Xie H, Boenisch U, Orkin SH, Lynn FC, Hoffman BG, Grün D, Vavouri T, Lempradl AM, Pospisilik JA
To date, it remains largely unclear to what extent chromatin machinery contributes to the susceptibility and progression of complex diseases. Here, we combine deep epigenome mapping with single-cell transcriptomics to mine for evidence of chromatin dysregulation in type 2 diabetes. We find two chromatin-state signat... |
The reference epigenome and regulatory chromatin landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Beekman R. et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a frequent hematological neoplasm in which underlying epigenetic alterations are only partially understood. Here, we analyze the reference epigenome of seven primary CLLs and the regulatory chromatin landscape of 107 primary cases in the context of normal B cell differentiation.... |
Increased H3K9 methylation and impaired expression of Protocadherins are associated with the cognitive dysfunctions of the Kleefstra syndrome.
Iacono G, Dubos A, Méziane H, Benevento M, Habibi E, Mandoli A, Riet F, Selloum M, Feil R, Zhou H, Kleefstra T, Kasri NN, van Bokhoven H, Herault Y, Stunnenberg HG
Kleefstra syndrome, a disease with intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders and other developmental defects is caused in humans by haploinsufficiency of EHMT1. Although EHMT1 and its paralog EHMT2 were shown to be histone methyltransferases responsible for deposition of the di-methylated H3K9 (H3K9me2), th... |
UTX-mediated enhancer and chromatin remodeling suppresses myeloid leukemogenesis through noncatalytic inverse regulation of ETS and GATA programs.
Gozdecka M, Meduri E, Mazan M, Tzelepis K, Dudek M, Knights AJ, Pardo M, Yu L, Choudhary JS, Metzakopian E, Iyer V, Yun H, Park N, Varela I, Bautista R, Collord G, Dovey O, Garyfallos DA, De Braekeleer E, Kondo S, Cooper J, Göttgens B, Bullinger L, Northc
The histone H3 Lys27-specific demethylase UTX (or KDM6A) is targeted by loss-of-function mutations in multiple cancers. Here, we demonstrate that UTX suppresses myeloid leukemogenesis through noncatalytic functions, a property shared with its catalytically inactive Y-chromosome paralog, UTY (or KDM6C). In keeping wi... |
Bcl11b, a novel GATA3-interacting protein, suppresses Th1 while limiting Th2 cell differentiation.
Fang D, Cui K, Hu G, Gurram RK, Zhong C, Oler AJ, Yagi R, Zhao M, Sharma S, Liu P, Sun B, Zhao K, Zhu J
GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3) acts as the master transcription factor for type 2 T helper (Th2) cell differentiation and function. However, it is still elusive how GATA3 function is precisely regulated in Th2 cells. Here, we show that the transcription factor B cell lymphoma 11b (Bcl11b), a previously unknown compo... |
The novel BET bromodomain inhibitor BI 894999 represses super-enhancer-associated transcription and synergizes with CDK9 inhibition in AML.
Gerlach D, Tontsch-Grunt U, Baum A, Popow J, Scharn D, Hofmann MH, Engelhardt H, Kaya O, Beck J, Schweifer N, Gerstberger T, Zuber J, Savarese F, Kraut N
Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) protein inhibitors have been reported as treatment options for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in preclinical models and are currently being evaluated in clinical trials. This work presents a novel potent and selective BET inhibitor (BI 894999), which has recently entered clinical t... |
Comparative Analysis of Immune Cells Reveals a Conserved Regulatory Lexicon.
Donnard E, Vangala P, Afik S, McCauley S, Nowosielska A, Kucukural A, Tabak B, Zhu X, Diehl W, McDonel P, Yosef N, Luban J, Garber M
Most well-characterized enhancers are deeply conserved. In contrast, genome-wide comparative studies of steady-state systems showed that only a small fraction of active enhancers are conserved. To better understand conservation of enhancer activity, we used a comparative genomics approach that integrates temporal ex... |
Epigenetic modifiers promote mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative metabolism leading to enhanced differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells.
Martine Uittenbogaard, Christine A. Brantner, Anne Chiaramello1
During neural development, epigenetic modulation of chromatin acetylation is part of a dynamic, sequential and critical process to steer the fate of multipotent neural progenitors toward a specific lineage. Pan-HDAC inhibitors (HDCis) trigger neuronal differentiation by generating an "acetylation" signature and prom... |
Ezh2 and Runx1 Mutations Collaborate to Initiate Lympho-Myeloid Leukemia in Early Thymic Progenitors.
Booth CAG, Barkas N, Neo WH, Boukarabila H, Soilleux EJ, Giotopoulos G, Farnoud N, Giustacchini A, Ashley N, Carrelha J, Jamieson L, Atkinson D, Bouriez-Jones T, Prinjha RK, Milne TA, Teachey DT, Papaemmanuil E, Huntly BJP, Jacobsen SEW, Mead AJ
Lympho-myeloid restricted early thymic progenitors (ETPs) are postulated to be the cell of origin for ETP leukemias, a therapy-resistant leukemia associated with frequent co-occurrence of EZH2 and RUNX1 inactivating mutations, and constitutively activating signaling pathway mutations. In a mouse model, we demonstrat... |
Allele-Specific Chromatin Recruitment and Therapeutic Vulnerabilities of ESR1 Activating Mutations.
Jeselsohn R, Bergholz JS, Pun M, Cornwell M, Liu W, Nardone A, Xiao T, Li W, Qiu X, Buchwalter G, Feiglin A, Abell-Hart K, Fei T, Rao P, Long H, Kwiatkowski N, Zhang T, Gray N, Melchers D, Houtman R, Liu XS, Cohen O, Wagle N, Winer EP, Zhao J, Brown M
Estrogen receptor α (ER) ligand-binding domain (LBD) mutations are found in a substantial number of endocrine treatment-resistant metastatic ER-positive (ER) breast cancers. We investigated the chromatin recruitment, transcriptional network, and genetic vulnerabilities in breast cancer models harboring the cli... |
Metabolic Induction of Trained Immunity through the Mevalonate Pathway.
Bekkering S, Arts RJW, Novakovic B, Kourtzelis I, van der Heijden CDCC, Li Y, Popa CD, Ter Horst R, van Tuijl J, Netea-Maier RT, van de Veerdonk FL, Chavakis T, Joosten LAB, van der Meer JWM, Stunnenberg H, Riksen NP, Netea MG
Innate immune cells can develop long-term memory after stimulation by microbial products during infections or vaccinations. Here, we report that metabolic signals can induce trained immunity. Pharmacological and genetic experiments reveal that activation of the cholesterol synthesis pathway, but not the synthesis of... |
BCG Vaccination Protects against Experimental Viral Infection in Humans through the Induction of Cytokines Associated with Trained Immunity.
Arts RJW, Moorlag SJCFM, Novakovic B, Li Y, Wang SY, Oosting M, Kumar V, Xavier RJ, Wijmenga C, Joosten LAB, Reusken CBEM, Benn CS, Aaby P, Koopmans MP, Stunnenberg HG, van Crevel R, Netea MG
The tuberculosis vaccine bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) has heterologous beneficial effects against non-related infections. The basis of these effects has been poorly explored in humans. In a randomized placebo-controlled human challenge study, we found that BCG vaccination induced genome-wide epigenetic repr... |
In Situ Fixation Redefines Quiescence and Early Activation of Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells
Machado L. et al.
Summary
State of the art techniques have been developed to isolate and analyze cells from various tissues, aiming to capture their in vivo state. However, the majority of cell isolation protocols involve lengthy mechanical and enzymatic dissociation steps followed by flow cytometry, exposing cells to stres... |
Genetic Predisposition to Multiple Myeloma at 5q15 Is Mediated by an ELL2 Enhancer Polymorphism
Li N. et al.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignancy of plasma cells. Genome-wide association studies have shown that variation at 5q15 influences MM risk. Here, we have sought to decipher the causal variant at 5q15 and the mechanism by which it influences tumorigenesis. We show that rs6877329 G > C resides in a predicted ... |
Chromosome contacts in activated T cells identify autoimmune disease candidate genes
Burren OS et al.
BACKGROUND:
Autoimmune disease-associated variants are preferentially found in regulatory regions in immune cells, particularly CD4+ T cells. Linking such regulatory regions to gene promoters in disease-relevant cell contexts facilitates identification of candidate disease genes.
RESULTS:
Within 4 h, act... |
Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Petersen R. et al.
Linking non-coding genetic variants associated with the risk of diseases or disease-relevant traits to target genes is a crucial step to realize GWAS potential in the introduction of precision medicine. Here we set out to determine the mechanisms underpinning variant association with platelet quantitative traits usi... |
c-Myc Antagonises the Transcriptional Activity of the Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer Affecting Key Gene Networks
Stefan J. Barfeld, Alfonso Urbanucci, Harri M. Itkonen, Ladan Fazli , Jessica L. Hicks , Bernd Thiede , Paul S. Rennie , Srinivasan Yegnasubramanian, Angelo M. DeMarzo , Ian G. Mills
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common non-cutaneous cancer in men. The androgen receptor (AR), a ligand-activated transcription factor, constitutes the main drug target for advanced cases of the disease. However, a variety of other transcription factors and signaling networks have been shown to be altered in pati... |
Epigenetically-driven anatomical diversity of synovial fibroblasts guides joint-specific fibroblast functions
Frank-Bertoncelj M, Trenkmann M, Klein K, Karouzakis E, Rehrauer H, Bratus A, Kolling C, Armaka M, Filer A, Michel BA, Gay RE, Buckley CD, Kollias G, Gay S, Ospelt C
A number of human diseases, such as arthritis and atherosclerosis, include characteristic pathology in specific anatomical locations. Here we show transcriptomic differences in synovial fibroblasts from different joint locations and that HOX gene signatures reflect the joint-specific origins of mouse and human synov... |
Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF10 suppresses TGFβ-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via a negative feedback mechanism
Mishra V.K. et al.
TGFβ-SMAD signaling exerts a contextual effect that suppresses malignant growth early in epithelial tumorigenesis but promotes metastasis at later stages. Longstanding challenges in resolving this functional dichotomy may uncover new strategies to treat advanced carcinomas. The Krüppel-like transcription f... |
RNF40 regulates gene expression in an epigenetic context-dependent manner
Xie W. et al.
BACKGROUND:
Monoubiquitination of H2B (H2Bub1) is a largely enigmatic histone modification that has been linked to transcriptional elongation. Because of this association, it has been commonly assumed that H2Bub1 is an exclusively positively acting histone modification and that increased H2Bub1 occupancy correlat... |
The non-coding variant rs1800734 enhances DCLK3 expression through long-range interaction and promotes colorectal cancer progression.
Liu N.Q. et al.
Genome-wide association studies have identified a great number of non-coding risk variants for colorectal cancer (CRC). To date, the majority of these variants have not been functionally studied. Identification of allele-specific transcription factor (TF) binding is of great importance to understand regulatory conse... |
DNA methylation heterogeneity defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma
Sheffield N.C. et al.
Developmental tumors in children and young adults carry few genetic alterations, yet they have diverse clinical presentation. Focusing on Ewing sarcoma, we sought to establish the prevalence and characteristics of epigenetic heterogeneity in genetically homogeneous cancers. We performed genome-scale DNA methylation ... |
Rapid Recall Ability of Memory T cells is Encoded in their Epigenome
Barski A. et al.
Even though T-cell receptor (TCR) stimulation together with co-stimulation is sufficient for the activation of both naïve and memory T cells, the memory cells are capable of producing lineage specific cytokines much more rapidly than the naïve cells. The mechanisms behind this rapid recall response of the ... |
FOXA1 Directs H3K4 Monomethylation at Enhancers via Recruitment of the Methyltransferase MLL3
Jozwik K.M. et al.
FOXA1 is a pioneer factor that binds to enhancer regions that are enriched in H3K4 mono- and dimethylation (H3K4me1 and H3K4me2). We performed a FOXA1 rapid immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry of endogenous proteins (RIME) screen in ERα-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells and found histone-lysine N-methyltran... |
Genetic Drivers of Epigenetic and Transcriptional Variation in Human Immune Cells
Chen L. et al.
Characterizing the multifaceted contribution of genetic and epigenetic factors to disease phenotypes is a major challenge in human genetics and medicine. We carried out high-resolution genetic, epigenetic, and transcriptomic profiling in three major human immune cell types (CD14+ monocytes, CD16+ neutrophils, ... |
β-Glucan Reverses the Epigenetic State of LPS-Induced Immunological Tolerance
Novakovic B. et al.
Innate immune memory is the phenomenon whereby innate immune cells such as monocytes or macrophages undergo functional reprogramming after exposure to microbial components such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We apply an integrated epigenomic approach to characterize the molecular events involved in LPS-induced to... |
The Hematopoietic Transcription Factors RUNX1 and ERG Prevent AML1-ETO Oncogene Overexpression and Onset of the Apoptosis Program in t(8;21) AMLs
Mandoli A. et al.
The t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-associated oncoprotein AML1-ETO disrupts normal hematopoietic differentiation. Here, we have investigated its effects on the transcriptome and epigenome in t(8,21) patient cells. AML1-ETO binding was found at promoter regions of active genes with high levels of histone acetyl... |
Neonatal monocytes exhibit a unique histone modification landscape
Bermick JR et al.
Background
Neonates have dampened expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and difficulty clearing pathogens. This makes them uniquely susceptible to infections, but the factors regulating neonatal-specific immune responses are poorly understood. Epigenetics, including histone modifications, can activate or silen... |
BRD4 localization to lineage-specific enhancers is associated with a distinct transcription factor repertoire
Najafova Z. et al.
Proper temporal epigenetic regulation of gene expression is essential for cell fate determination and tissue development. The Bromodomain-containing Protein-4 (BRD4) was previously shown to control the transcription of defined subsets of genes in various cell systems. In this study we examined the role of BRD4 in pr... |
reChIP-seq reveals widespread bivalency of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in CD4(+) memory T cells
Kinkley S et al.
The combinatorial action of co-localizing chromatin modifications and regulators determines chromatin structure and function. However, identifying co-localizing chromatin features in a high-throughput manner remains a technical challenge. Here we describe a novel reChIP-seq approach and tailored bioinformatic analys... |
Epigenetic dynamics of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation
Wallner S et al.
BACKGROUND:
Monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation involves major biochemical and structural changes. In order to elucidate the role of gene regulatory changes during this process, we used high-throughput sequencing to analyze the complete transcriptome and epigenome of human monocytes that were differentiated in... |
Chromatin accessibility maps of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia identify subtype-specific epigenome signatures and transcription regulatory networks
Rendeiro AF et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is characterized by substantial clinical heterogeneity, despite relatively few genetic alterations. To provide a basis for studying epigenome deregulation in CLL, here we present genome-wide chromatin accessibility maps for 88 CLL samples from 55 patients measured by the ATAC-seq ... |
Comprehensive genome and epigenome characterization of CHO cells in response to evolutionary pressures and over time
Feichtinger J, Hernández I, Fischer C, Hanscho M, Auer N, Hackl M, Jadhav V, Baumann M, Krempl PM, Schmidl C, Farlik M, Schuster M, Merkel A, Sommer A, Heath S, Rico D, Bock C, Thallinger GG, Borth N
The most striking characteristic of CHO cells is their adaptability, which enables efficient production of proteins as well as growth under a variety of culture conditions, but also results in genomic and phenotypic instability. To investigate the relative contribution of genomic and epigenetic modifications towards... |
ArrayNinja: An Open Source Platform for Unified Planning and Analysis of Microarray Experiments
Dickson BM, Cornett EM, Ramjan Z, Rothbart SB
Microarray-based proteomic platforms have emerged as valuable tools for studying various aspects of protein function, particularly in the field of chromatin biochemistry. Microarray technology itself is largely unrestricted in regard to printable material and platform design, and efficient multidimensional optimizat... |
MLL-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemias Activate BCL-2 through H3K79 Methylation and Are Sensitive to the BCL-2-Specific Antagonist ABT-199
Benito JM et al.
Targeted therapies designed to exploit specific molecular pathways in aggressive cancers are an exciting area of current research. Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL) mutations such as the t(4;11) translocation cause aggressive leukemias that are refractory to conventional treatment. The t(4;11) translocation produces an M... |
Glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor kappa-b affect three-dimensional chromatin organization
Kuznetsova T et al.
BACKGROUND:
The impact of signal-dependent transcription factors, such as glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor kappa-b, on the three-dimensional organization of chromatin remains a topic of discussion. The possible scenarios range from remodeling of higher order chromatin architecture by activated transcrip... |
Cell-Cycle-Dependent Reconfiguration of the DNA Methylome during Terminal Differentiation of Human B Cells into Plasma Cells
Caron G et al.
Molecular mechanisms underlying terminal differentiation of B cells into plasma cells are major determinants of adaptive immunity but remain only partially understood. Here we present the transcriptional and epigenomic landscapes of cell subsets arising from activation of human naive B cells and differentiation into... |
Non-coding recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
Xose S. Puente, Silvia Beà, Rafael Valdés-Mas, Neus Villamor, Jesús Gutiérrez-Abril et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is a frequent disease in which the genetic alterations determining the clinicobiological behaviour are not fully understood. Here we describe a comprehensive evaluation of the genomic landscape of 452 CLL cases and 54 patients with monoclonal B-lymphocytosis, a precursor disorder.... |
Epigenome mapping reveals distinct modes of gene regulation and widespread enhancer reprogramming by the oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1.
Tomazou EM, Sheffield NC, Schmidl C, Schuster M, Schönegger A, Datlinger P, Kubicek S, Bock C, Kovar H
Transcription factor fusion proteins can transform cells by inducing global changes of the transcriptome, often creating a state of oncogene addiction. Here, we investigate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this process, focusing on Ewing sarcoma cells that are dependent on the EWS-FLI1 fusion protein. We establi... |
Genome-wide and single-cell analyses reveal a context dependent relationship between CBP recruitment and gene expression.
Kasper LH, Qu C, Obenauer JC, McGoldrick DJ, Brindle PK
Genome-wide distribution of histone H3K18 and H3K27 acetyltransferases, CBP (CREBBP) and p300 (EP300), is used to map enhancers and promoters, but whether these elements functionally require CBP/p300 remains largely uncertain. Here we compared global CBP recruitment with gene expression in wild-type and CBP/p300 dou... |