How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Megaruptor® 2 (Hologic Diagenode Cat# B06010002). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Detection and Quantitation of DNA Damage on a Genome-wide ScaleUsing RADAR-seq.
Zatopek Kelly M et al.
The formation and persistence of DNA damage can impact biological processes such as DNA replication and transcription. To maintain genome stability and integrity, organisms rely on robust DNA damage repair pathways. Techniques to detect and locate DNA damage sites across a genome enable an understanding of the conse... |
Predictable and stable epimutations induced during clonal plantpropagation with embryonic transcription factor.
Wibowo Anjar Tri et al.
Clonal propagation is frequently used in commercial plant breeding and biotechnology programs because it minimizes genetic variation, yet it is not uncommon to observe clonal plants with stable phenotypic changes, a phenomenon known as somaclonal variation. Several studies have linked epigenetic modifications induce... |
Benchmarking second and third-generation sequencing platforms formicrobial metagenomics.
Meslier Victoria et al.
Shotgun metagenomic sequencing is a common approach for studying the taxonomic diversity and metabolic potential of complex microbial communities. Current methods primarily use second generation short read sequencing, yet advances in third generation long read technologies provide opportunities to overcome some of t... |
Mitochondrial RNA editing in Trypanoplasma borreli: new tools, newrevelations
Gerasimov Evgeny S. et al.
The kinetoplastids are unicellular flagellates that derive their name from the ‘kinetoplast’, a region within their single mitochondrion harboring its organellar genome of high DNA content, called kinetoplast (k) DNA. Some protein products of this mitochondrial genome are encoded as cryptogenes; their tr... |
Evaluation of the pathogenesis of non-typical strain with α-hemolysin,Vibrio parahaemolyticus 353, isolated from Chinese seafood throughcomparative genome and transcriptome analysis.
Zha Fei et al.
Vibrio parahaemolyticus outbreaks frequently occur, causing gastrointestinal sickness owing to the consumption of aquatic foods by various virulence factors; however, the mechanism of pathogenesis is still unknown. In this study, a non-typical strain of V. parahaemolyticus, named VP353, was isolated from shrimp in C... |
Rapid and comprehensive diagnostic method for repeat expansion diseasesusing nanopore sequencing.
Miyatake S. et al.
We developed a diagnostic method for repeat expansion diseases using a long-read sequencer to improve currently available, low throughput diagnostic methods. We employed the real-time target enrichment system of the nanopore GridION sequencer using the adaptive sampling option, in which software-based target assignm... |
Characterization of somatic structural variations in 528 Chineseindividuals with Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Cui H. et al.
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) demonstrates high genome instability. Here, we analyze 528 whole genomes to investigate structural variations' mechanisms and biological functions. SVs show multi-mode distributions in size, indicating distinct mutational processes. We develop a tool and define five types of... |
The Capparis spinosa var. herbacea genome provides the first genomicinstrument for a diversity and evolution study of the Capparaceae family.
Wang Lei et al.
BACKGROUND: The caper bush Capparis spinosa L., one of the most economically important species of Capparaceae, is a xerophytic shrub that is well adapted to drought and harsh environments. However, genetic studies on this species are limited because of the lack of its reference genome. FINDINGS: We sequenced and ass... |
Genomic Characterization and Antimicrobial Susceptibility ofDromedary-Associated from the Horn of Africa.
Akarsu H. et al.
Members of the family, particularly those of the genus Staphylococcus, encompass important human and animal pathogens. We collected and characterized strains from apparently healthy and diseased camels ( = 84) and cattle ( = 7) in Somalia and Kenya. We phenotypically characterized the strains, including their antimi... |
Complete Genome Sequences of the Soil Oxalotrophic BacteriumCupriavidus oxalaticus Strain Ox1 and Its DerivedmCherry-Tagged Strain.
Palmieri Fabio et al.
Here, we report the complete genome sequences of the soil oxalotrophic bacterium Cupriavidus oxalaticus Ox1 and a derived mCherry-tagged strain. The genome size is approximately 6.69 Mb, with a GC content of 66.9\%. The genome sequence of Ox1 contains a complete operon for the degradation and assimilation of ... |
The improved genome of the nematode Parapristionchus giblindavisiprovides insights into lineage-specific gene family evolution.
Röseler W. et al.
Nematodes such as Caenorhabditis elegans and Pristionchus pacificus are extremely successful model organisms for comparative biology. Several studies have shown that phenotypic novelty but also conserved processes are controlled by taxon-restricted genes. To trace back the evolution of such new or rapidly evolving g... |
The chromosome-level genome of Gypsophila paniculata reveals themolecular mechanism of floral development and ethylene insensitivity
Fan Li et al.
Gypsophila paniculata, belonging to the Caryophyllaceae of the Caryophyllales, is one of the worldwide famous cut flowers. It is commonly used as dried flowers, whereas the underlying mechanism of flower senescence has not yet been addressed. Here, we present a chromosome-scale genome assembly for G. paniculata with... |
Patients with biallelic GGC repeat expansions in NOTCH2NLCexhibiting a typical neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease phenotype.
Kameyama Shinichi et al.
We report two patients with autosomal dominant neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease (NIID) harboring the biallelic GGC repeat expansion in NOTCH2NLC to uncover the impact of repeat expansion zygosity on the clinical phenotype. The zygosity of the entire NOTCH2NLC GGC repeat expansion and DNA methylation were comp... |
A haplotype resolved chromosomal level avocado genome allows analysis ofnovel avocado genes
Onkar N. et al.
Avocado (Persea americana) is a member of the magnoliids, an early branching lineage of angiosperms that has high value globally with the fruit being highly nutritious. Here, we report a chromosome-level genome assembly for the commercial avocado cultivar Hass, which represents 80\% of the world’s avocado cons... |
Identification of Laportea bulbifera using the Complete ChloroplastGenome as a Super-Barcode
Wang Wenting et al.
Laportea bulbifera, a Miao medicine grown in karst areas, has exerts a unique curative effect on skin itching in the elderly, with an annual sales of > 100 million Yuan. Owing to the shortage of resources and large morphological variations in L. bulbifera, it is difficult to identify the species correctly using o... |
Oxford Nanopore R10.4 long-read sequencing enables the generation ofnear-finished bacterial genomes from pure cultures and metagenomes withoutshort-read or reference polishing.
Sereika Mantas et al.
Long-read Oxford Nanopore sequencing has democratized microbial genome sequencing and enables the recovery of highly contiguous microbial genomes from isolates or metagenomes. However, to obtain near-finished genomes it has been necessary to include short-read polishing to correct insertions and deletions derived fr... |
Complete Genome Sequences of Multidrug-Resistant Campylobactercoli Strains YH501, YH503, and YH504, from Retail Chicken.
He Yiping et al.
Campylobacter coli is an important foodborne pathogen that can cause inflammation of the intestine and diarrhea in humans. The complete genomes, including megaplasmids, of C. coli strains YH501, YH503, and YH504 from retail chicken were sequenced and assembled. Whole-genome analysis revealed a number of virulence an... |
High-Quality Genome Assembly of Nannochloris desiccata 2437 andIts Associated Bacterial Community.
Sanders Claire K et al.
High-quality genome sequences were generated for the nonaxenic marine microalga Nannochloris desiccata UTEX 2437 and eight of its associated environmental bacterial species. UTEX 2437 is diploid, and its 20.738-Mbp nuclear genome sequence is assembled in 29 contigs. |
Long-read Oxford nanopore sequencing reveals a de novo case of complexchromosomal rearrangement involving chromosomes 2, 7, and 13.
Xing Lingling et al.
BACKGROUND: Complex chromosomal rearrangements (CCRs) are associated with high reproductive risk, infertility, abnormalities in offspring, and recurrent miscarriage in women. It is essential to accurately characterize apparently balanced chromosome rearrangements in unaffected individuals. METHODS: A CCR young coupl... |
Accumulation of endosymbiont genomes in an insect autosome followed byendosymbiont replacement.
Tvedte Eric S. et al.
Eukaryotic genomes can acquire bacterial DNA via lateral gene transfer (LGT). A prominent source of LGT is Wolbachia, a widespread endosymbiont of arthropods and nematodes that is transmitted maternally through female germline cells. The DNA transfer from the Wolbachia endosymbiont wAna to Drosophila ananassae is ex... |
DNA Hypermethylation and a Specific Methylation Spectrum on theX Chromosome in Turner Syndrome as Determined by NanoporeSequencing
Fan Xin et al.
The molecular genetic mechanism of Turner syndrome (TS) still leaves much to be discovered. Methods: TS (45X0) patients and age-matched controls (46XX and 46XY) were selected. The nanopore sequencing combined with trio-whole exome sequencing (trio-WES) were used for the first time to investigate TS. Results: Thirtee... |
The genome sequence of Anoplius nigerrimus (Scopoli, 1763), a spiderwasp
Falk Steven and Broad Gavin
We present a genome assembly from an individual Anoplius nigerrimus (Arthropoda; Insecta; Hymenoptera; Pompilidae) of unknown sex. The genome sequence is 624 megabases in span. In total, 45.75\% of the assembly is scaffolded into 15 chromosomal pseudomolecules. The mitochondrial genome was also assembled and is 17.5... |
Familial long-read sequencing increases yield of de novo mutations.
Noyes Michelle D et al.
Studies of de novo mutation (DNM) have typically excluded some of the most repetitive and complex regions of the genome because these regions cannot be unambiguously mapped with short-read sequencing data. To better understand the genome-wide pattern of DNM, we generated long-read sequence data from an autism parent... |
Transposon activity, local duplications and propagation of structuralvariants across haplotypes drive the evolution of the Drosophila S2cell line.
Lewerentz Jacob et al.
BACKGROUND: Immortalized cell lines are widely used model systems whose genomes are often highly rearranged and polyploid. However, their genome structure is seldom deciphered and is thus not accounted for during analyses. We therefore used linked short- and long-read sequencing to perform haplotype-level reconstruc... |
Phylogenomics and Comparative Genomics Highlight SpecificGenetic Features in Species.
Sun Yi-Fei et al.
The species in Polyporales are ecologically and economically relevant wood decayers used in traditional medicine, but their genomic traits are still poorly documented. In the present study, we carried out a phylogenomic and comparative genomic analyses to better understand the genetic blueprint of this fungal lineag... |
Pushing the limits of HiFi assemblies reveals centromere diversity between two Arabidopsis thaliana genomes
Rabanal Fernando A. and Gräff Maike and Lanz Christa andFritschi Katrin and Llaca Victor and Lang Michelle andCarbonell-Bejerano Pablo and Henderson Ian and Weigel Detlef
Although long-read sequencing can often enable chromosome-level reconstruction of genomes, it is still unclear how one can routinely obtain gapless assemblies. In the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, other than the reference accession Col-0, all other accessions de novo assembled with long-reads unti... |
Chromosomal rearrangements with stable repertoires of genes andtransposable elements in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungus
Demené A. et al.
Chromosomal rearrangements have been largely described among eukaryotes, and may have important consequences on evolution of species. High genome plasticity has been often reported in Fungi, which may explain their apparent ability to quickly adapt to new environments. Cryphonectria parasitica, causing the Chestnut ... |
Genomic characterisation of three GES-producing Enterobacteralesisolated in the Czech Republic.
Finianos M. et al.
OBJECTIVES: The aim of the study is to characterise the genomic features of three GES-producing Enterobacterales isolates from Czech hospitals. METHODS: In 2020, during a routine screening of the hospital's surfaces in Prague General Hospital, two strains (CZ862 and CZ863) that belonged to the Enterobacter cloacae c... |
Improved chromosome-level genome assembly of the Glanville fritillarybutterfly () integrating Pacific Biosciences long reads and ahigh-density linkage map
Smolander Olli-Pekka et al.
Abstract Background The Glanville fritillary (Melitaea cinxia) butterfly is a model system for metapopulation dynamics research in fragmented landscapes. Here, we provide a chromosome-level assembly of the butterfly's genome produced from Pacific Biosciences sequencing of a pool of males, combined with a linkage map... |
PRINCESS: comprehensive detection of haplotype resolved SNVs, SVs,and methylation.
Mahmoud Medhat et al.
Long-read sequencing has been shown to have advantages in structural variation (SV) detection and methylation calling. Many studies focus either on SV, methylation, or phasing of SNV; however, only the combination of variants provides a comprehensive insight into the sample and thus enables novel findings in biology... |
Establishing community reference samples, data and call sets forbenchmarking cancer mutation detection using whole-genome sequencing.
Fang Li Tai et al.
The lack of samples for generating standardized DNA datasets for setting up a sequencing pipeline or benchmarking the performance of different algorithms limits the implementation and uptake of cancer genomics. Here, we describe reference call sets obtained from paired tumor-normal genomic DNA (gDNA) samples derived... |
LeafGo: Leaf to Genome, a quick workflow to produce high-quality denovo plant genomes using long-read sequencing technology.
Driguez Patrick et al.
Currently, different sequencing platforms are used to generate plant genomes and no workflow has been properly developed to optimize time, cost, and assembly quality. We present LeafGo, a complete de novo plant genome workflow, that starts from tissue and produces genomes with modest laboratory and bioinformatic res... |
Targeted long-read sequencing identifies missing disease-causingvariation.
Miller Danny E et al.
Despite widespread clinical genetic testing, many individuals with suspected genetic conditions lack a precise diagnosis, limiting their opportunity to take advantage of state-of-the-art treatments. In some cases, testing reveals difficult-to-evaluate structural differences, candidate variants that do not fully expl... |
Evidence of an epidemic spread of KPC-producing in Czech hospitals
Kraftova Lucie et al.
The aim of the present study is to describe the ongoing spread of the KPC-producing strains, which is evolving to an epidemic in Czech hospitals. During the period of 2018–2019, a total of 108 KPC-producing Enterobacterales were recovered from 20 hospitals. Analysis of long-read sequencing data revealed the pr... |
The USDA-ARS Ag100Pest Initiative: High-Quality GenomeAssemblies for Agricultural Pest Arthropod Research
Childers A.K. et al.
Simple Summary High-quality genome assemblies are essential tools for modern biological research. In the past, creating genome assemblies was prohibitively expensive and time-consuming for most non-model insect species due to, in part, the technical challenge of isolating the necessary quantity and quality of DNA fr... |
The American lobster genome reveals insights on longevity, neural, andimmune adaptations.
Polinski J. M. et al.
The American lobster, , is integral to marine ecosystems and supports an important commercial fishery. This iconic species also serves as a valuable model for deciphering neural networks controlling rhythmic motor patterns and olfaction. Here, we report a high-quality draft assembly of the genome with 25,284 predict... |
Analysis of the Coptis chinensis genome reveals the diversification ofprotoberberine-type alkaloids.
Liu Y. et al.
Chinese goldthread (Coptis chinensis Franch.), a member of the Ranunculales, represents an important early-diverging eudicot lineage with diverse medicinal applications. Here, we present a high-quality chromosome-scale genome assembly and annotation of C. chinensis. Phylogenetic and comparative genomic analyses reve... |
Infectivity assessment of porcine endogenous retrovirus usinghigh-throughput sequencing technologies.
Kono K. et al.
Xenogenic cell-based therapeutic products are expected to alleviate the chronic shortage of human donor organs. For example, porcine islet cell products are currently under development for the treatment of human diabetes. As porcine cells possess endogenous retrovirus (PERV), which can replicate in human cells in vi... |
Chromosomal inversion polymorphisms in two sympatric ascidian lineages.
Satou, Yutaka and Sato, Atsuko and Yasuo, Hitoyoshi and Mihirogi, Yukie andBishop, John and Fujie, Manabu and Kawamitsu, Mayumi and Hisata, Kanako andSatoh, Noriyuki
Chromosomal rearrangements can reduce fitness of heterozygotes and can thereby prevent gene flow. Therefore, such rearrangements can play a role in local adaptation and speciation. In particular, inversions are considered to be a major potential cause for chromosomal speciation. There are two closely related, partia... |
Complete vertebrate mitogenomes reveal widespread repeats and geneduplications.
Formenti G. et al.
BACKGROUND: Modern sequencing technologies should make the assembly of the relatively small mitochondrial genomes an easy undertaking. However, few tools exist that address mitochondrial assembly directly. RESULTS: As part of the Vertebrate Genomes Project (VGP) we develop mitoVGP, a fully automated pipeline for sim... |
Chromosomal rearrangements but no change of genes and transposable elementsrepertoires in an invasive forest-pathogenic fungus
Demené, A. et al.
Chromosomal rearrangements have been largely described among eukaryotes, and may have important consequences on evolution of species. High genome plasticity have been often reported in Fungi, that may explain their apparent ability to quickly adapt to new environments. Cryphonectria parasitica, causing the Chestnut ... |
A single nucleotide polymorphism variant located in the cis-regulatoryregion of the ABCG2 gene is associated with mallard egg colour.
Liu H. et al.
Avian egg coloration is shaped by natural selection, but its genetic basis remains unclear. Here, we used genome-wide association analysis and identity by descent to finely map green egg colour to a 179-kb region of Chr4 based on the resequencing of 352 ducks (Anas platyrhynchos) from a segregating population result... |
Genomic Characterization of VIM and MCR Co-Producers: The First TwoClinical Cases, in Italy.
Marchetti, Vittoria Mattioni and Bitar, Ibrahim and Sarti, Mario andFogato, Elena and Scaltriti, Erika and Bracchi, Chiara and Hrabak, Jaroslavand Pongolini, Stefano and Migliavacca, Roberta
BACKGROUND: the co-production of carbapenemases and -genes represents a worrisome event in the treatment of infections. The aim of the study was to characterize the genomic features of two clinical complex (ECC) isolates, co-producing VIM and MCR enzymes, in Italy. METHODS: species identification and antibiotic susc... |
Chromosome-scale genome assembly provides insights into the evolution andflavor synthesis of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims).
Xia Z. et al.
Passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) is an economically valuable fruit that is cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Here, we report an ~1341.7 Mb chromosome-scale genome assembly of passion fruit, with 98.91\% (~1327.18 Mb) of the assembly assigned to nine pseudochromosomes. T... |
Rapid and ongoing evolution of repetitive sequence structures in humancentromeres.
Suzuki Y. et al.
Our understanding of centromere sequence variation across human populations is limited by its extremely long nested repeat structures called higher-order repeats that are challenging to sequence. Here, we analyzed chromosomes 11, 17, and X using long-read sequencing data for 36 individuals from diverse populations i... |
Efficient hybrid de novo assembly of human genomes with WENGAN.
Di Genova A. et al.
Generating accurate genome assemblies of large, repeat-rich human genomes has proved difficult using only long, error-prone reads, and most human genomes assembled from long reads add accurate short reads to polish the consensus sequence. Here we report an algorithm for hybrid assembly, WENGAN, that provides very hi... |
Translating GWAS-identified loci for cardiac rhythm and rate using an in vivo image- and CRISPR/Cas9-based approach.
von der Heyde B, Emmanouilidou A, Mazzaferro E, Vicenzi S, Höijer I, Klingström T, Jumaa S, Dethlefsen O, Snieder H, de Geus E, Ameur A, Ingelsson E, Allalou A, Brooke HL, den Hoed M
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) identified eight loci that are associated with heart rate variability (HRV), but candidate genes in these loci remain uncharacterized. We developed an image- and CRISPR/Cas9-based pipeline to systematically characterize candidate genes for HRV in live zebrafi... |
Genomic Insight of VIM-harboring IncA Plasmid from a Clinical ST69Escherichia coli Strain in Italy
Mattioni, Marchetti Vittoria and Bitar, Ibrahim and Piazza, Aurora andMercato, Alessandra and Fogato, Elena and Hrabak, Jaroslav and Migliavacca,Roberta
Background: VIM (Verona Integron-encoded Metallo-beta-lactamase) is a member of the Metallo-Beta-Lactamases (MBLs), and is able to hydrolyze all beta-lactams antibiotics, except for monobactams, and including carbapenems. Here we characterize a VIM-producing IncA plasmid isolated from a clinical ST69 Escherichia col... |
Genomic Insight of VIM-harboring IncA Plasmid from a ClinicalST69 Escherichia coli Strain in Italy
Mattioni MV et al.
Background: VIM (Verona Integron-encoded Metallo-beta-lactamase) is a member of the Metallo-Beta-Lactamases (MBLs), and is able to hydrolyze all beta-lactams antibiotics, except for monobactams, and including carbapenems. Here we characterize a VIM-producing IncA plasmid isolated from a clinical ST69 Escherichia col... |
Diversity of Pectobacteriaceae Species in Potato Growing Regions in Northern Morocco.
Oulghazi S, Moumni M, Khayi S, Robic K, Sarfraz S, Lopez-Roques C, Vandecasteele C, Faure D
Dickeya and Pectobacterium pathogens are causative agents of several diseases that affect many crops worldwide. This work investigated the species diversity of these pathogens in Morocco, where Dickeya pathogens have only been isolated from potato fields recently. To this end, samplings were conducted in three major... |
Major Impacts of Widespread Structural Variation on Gene Expression and Crop Improvement in Tomato.
Alonge M, Wang X, Benoit M, Soyk S, Pereira L, Zhang L, Suresh H, Ramakrishnan S, Maumus F, Ciren D, Levy Y, Harel TH, Shalev-Schlosser G, Amsellem Z, Razifard H, Caicedo AL, Tieman DM, Klee H, Kirsche M, Aganezov S, Ranallo-Benavidez TR, Lemmon ZH, Kim J
Structural variants (SVs) underlie important crop improvement and domestication traits. However, resolving the extent, diversity, and quantitative impact of SVs has been challenging. We used long-read nanopore sequencing to capture 238,490 SVs in 100 diverse tomato lines. This panSV genome, along with 14 new referen... |
Host-Specific Evolutionary and Transmission Dynamics Shape the Functional Diversification of Staphylococcus epidermidis in Human Skin.
Zhou W, Spoto M, Hardy R, Guan C, Fleming E, Larson PJ, Brown JS, Oh J
Metagenomic inferences of bacterial strain diversity and infectious disease transmission studies largely assume a dominant, within-individual haplotype. We hypothesize that within-individual bacterial population diversity is critical for homeostasis of a healthy microbiome and infection risk. We characterized the&nb... |
LongQC: A Quality Control Tool for Third GenerationSequencing Long Read Data
Fukasawa Yoshinori et al.
We propose LongQC as an easy and automated quality control tool for genomic datasets generated by third generation sequencing (TGS) technologies such as Oxford Nanopore technologies (ONT) and SMRT sequencing from Pacific Bioscience (PacBio). Key statistics were optimized for long read data, and LongQC covers all maj... |
Genome Sequence of sp. Strain JOR-1, an Extremely Halophilic Archaeon from the Dead Sea.
Anton BP, DasSarma P, Martinez FL, DasSarma SL, Al Madadha M, Roberts RJ, DasSarma S
An extremely halophilic archaeon, sp. strain JOR-1, was isolated from the east coast of the Dead Sea, Kingdom of Jordan, and sequenced using single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing. The GC-rich 2.5-Mbp genome was composed of a circular chromosome and a megaplasmid. The genome contained 2,633 genes and was incorp... |
The round goby genome provides insights into mechanisms that may facilitate biological invasions.
Adrian-Kalchhauser I, Blomberg A, Larsson T, Musilova Z, Peart CR, Pippel M, Solbakken MH, Suurväli J, Walser JC, Wilson JY, Alm Rosenblad M, Burguera D, Gutnik S, Michiels N, Töpel M, Pankov K, Schloissnig S, Winkler S
BACKGROUND: The invasive benthic round goby (Neogobius melanostomus) is the most successful temperate invasive fish and has spread in aquatic ecosystems on both sides of the Atlantic. Invasive species constitute powerful in situ experimental systems to study fast adaptation and directional selection on short ecologi... |
The complete mitochondrial genome of Taxus cuspidata (Taxaceae): eight protein-coding genes have transferred to the nuclear genome.
Kan SL, Shen TT, Gong P, Ran JH, Wang XQ
BACKGROUND: Gymnosperms represent five of the six lineages of seed plants. However, most sequenced plant mitochondrial genomes (mitogenomes) have been generated for angiosperms, whereas mitogenomic sequences have been generated for only six gymnosperms. In particular, complete mitogenomes are available for all major... |
A highly contiguous genome assembly of the bat hawkmoth Hyles vespertilio (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae).
Pippel M, Jebb D, Patzold F, Winkler S, Vogel H, Myers G, Hiller M, Hundsdoerfer AK
BACKGROUND: Adapted to different ecological niches, moth species belonging to the Hyles genus exhibit a spectacular diversity of larval color patterns. These species diverged ∼7.5 million years ago, making this rather young genus an interesting system to study a wide range of questions including the process of s... |
Detection of Abrin-Like and Prepropulchellin-Like Toxin Genes and Transcripts Using Whole Genome Sequencing and Full-Length Transcript Sequencing of .
Hovde BT, Daligault HE, Hanschen ER, Kunde YA, Johnson MB, Starkenburg SR, Johnson SL
The sequenced genome and the leaf transcriptome of a near relative of and was analyzed to characterize the genetic basis of toxin gene expression. From the high-quality genome assembly, a total of 26 potential coding regions were identified that contain genes with abrin-like, pulchellin-like, and agglutinin-like hom... |
NanoSatellite: accurate characterization of expanded tandem repeat length and sequence through whole genome long-read sequencing on PromethION.
De Roeck A, De Coster W, Bossaerts L, Cacace R, De Pooter T, Van Dongen J, D'Hert S, De Rijk P, Strazisar M, Van Broeckhoven C, Sleegers K
Technological limitations have hindered the large-scale genetic investigation of tandem repeats in disease. We show that long-read sequencing with a single Oxford Nanopore Technologies PromethION flow cell per individual achieves 30× human genome coverage and enables accurate assessment of tandem repeats inclu... |
Genomic and phenotypic analyses of six offspring of a genome-edited hornless bull.
Young AE, Mansour TA, McNabb BR, Owen JR, Trott JF, Brown CT, Van Eenennaam AL
Genome editing followed by reproductive cloning was previously used to produce two hornless dairy bulls. We crossed one genome-edited dairy bull, homozygous for the dominant P Celtic POLLED allele, with horned cows (pp) and obtained six heterozygous (Pp) polled calves. The calves had no horns and were otherwise heal... |
Complete Genome Sequence of an Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O111:H8 Strain Recovered from a Large Outbreak in Japan Associated with Consumption of Raw Beef.
Sekizuka T, Lee K, Kimata K, Isobe J, Kuroda M, Iyoda S, Ohnishi M, Sata T, Watahiki M
We present the complete genome sequence of an enterohemorrhagic O111:H8 strain. This strain was isolated from a hemolytic-uremic syndrome patient and was responsible for a large outbreak associated with the consumption of raw beef in 2011. |
Long-read sequencing and haplotype linkage analysis enabled preimplantation genetic testing for patients carrying pathogenic inversions.
Zhang S, Liang F, Lei C, Wu J, Fu J, Yang Q, Luo X, Yu G, Wang D, Zhang Y, Lu D, Sun X, Liang Y, Xu C
BACKGROUND: Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) has already been applied in patients known to carry chromosomal structural variants to improve the clinical outcome of assisted reproduction. However, conventional molecular techniques are not capable of reliably distinguishing embryos that carry balanced inversion f... |
Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome.
Wenger AM, Peluso P, Rowell WJ, Chang PC, Hall RJ, Concepcion GT, Ebler J, Fungtammasan A, Kolesnikov A, Olson ND, Töpfer A, Alonge M, Mahmoud M, Qian Y, Chin CS, Phillippy AM, Schatz MC, Myers G, DePristo MA, Ruan J, Marschall T, Sedlazeck FJ, Zook JM, L
The DNA sequencing technologies in use today produce either highly accurate short reads or less-accurate long reads. We report the optimization of circular consensus sequencing (CCS) to improve the accuracy of single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing (PacBio) and generate highly accurate (99.8%) long high-fidelit... |
Reference genome and comparative genome analysis for the WHO reference strain for Mycobacterium bovis BCG Danish, the present tuberculosis vaccine.
Borgers K, Ou JY, Zheng PX, Tiels P, Van Hecke A, Plets E, Michielsen G, Festjens N, Callewaert N, Lin YC
BACKGROUND: Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (M. bovis BCG) is the only vaccine available against tuberculosis (TB). In an effort to standardize the vaccine production, three substrains, i.e. BCG Danish 1331, Tokyo 172-1 and Russia BCG-1 were established as the WHO reference strains. Both for BCG ... |
Long-read based de novo assembly of low-complexity metagenome samples results in finished genomes and reveals insights into strain diversity and an active phage system.
Somerville V, Lutz S, Schmid M, Frei D, Moser A, Irmler S, Frey JE, Ahrens CH
BACKGROUND: Complete and contiguous genome assemblies greatly improve the quality of subsequent systems-wide functional profiling studies and the ability to gain novel biological insights. While a de novo genome assembly of an isolated bacterial strain is in most cases straightforward, more informative data about co... |
A chromosome-scale genome assembly of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.).
Li Q, Li H, Huang W, Xu Y, Zhou Q, Wang S, Ruan J, Huang S, Zhang Z
BACKGROUND: Accurate and complete reference genome assemblies are fundamental for biological research. Cucumber is an important vegetable crop and model system for sex determination and vascular biology. Low-coverage Sanger sequences and high-coverage short Illumina sequences have been used to assemble draft cucumbe... |
Genome Sequence and Methylation Patterns of sp. Strain BOL3-1, the First Haloarchaeon Isolated and Cultured from Salar de Uyuni, Bolivia.
Priya DasSarma, Anton BP, DasSarma S, Laye VJ, Guzman D, Roberts RJ, DasSarma S
sp. strain BOL3-1 was isolated from Salar de Uyuni, Bolivia, and sequenced using single-molecule real-time sequencing. Its 3.7-Mbp genome was analyzed for gene content and methylation patterns and incorporated into the Haloarchaeal Genomes Database (http://halo.umbc.edu). The polyextremophilic character and high-ele... |
The Reference Genome Sequence of Scutellaria baicalensis Provides Insights into the Evolution of Wogonin Biosynthesis.
Zhao Q, Yang J, Cui MY, Liu J, Fang Y, Yan M, Qiu W, Shang H, Xu Z, Yidiresi R, Weng JK, Pluskal T, Vigouroux M, Steuernagel B, Wei Y, Yang L, Hu Y, Chen XY, Martin C
Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi is important in Chinese traditional medicine where preparations of dried roots, "Huang Qin," are used for liver and lung complaints and as complementary cancer treatments. We report a high-quality reference genome sequence for S. baicalensis where 93% of the 408.14-Mb genome has been a... |
Biocompatible N-acetyl cysteine reduces graphene oxide and persists at the surface as a green radical scavenger.
Palmieri V, Dalchiele EA, Perini G, Motta A, De Spirito M, Zanoni R, Marrani AG, Papi M
We demonstrate that N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) reduces graphene oxide (GO) at room temperature. This represents a new green method to produce reduced GO (rGO). NAC adheres to the rGO surface as demonstrated by several spectroscopy techniques and avoids GO-mediated oxidation of glutathione. This method offers new opport... |
The alternative reality of plant mitochondrial DNA
Alexander Kozik, Beth A. Rowan, Dean Lavelle, Lidija Berke, M. Eric Schranz, Richard W. Michelmore, and Alan C. Christensen
Plant mitochondrial genomes are usually assembled and displayed as circular maps based on the widely-held assumption that circular genome molecules are the primary form of mitochondrial DNA, despite evidence to the contrary. Many plant mitochondrial genomes have one or more pairs of large repeats that can act as sit... |
Characterizing the Major Structural Variant Alleles of the Human Genome.
Audano PA, Sulovari A, Graves-Lindsay TA, Cantsilieris S, Sorensen M, Welch AE, Dougherty ML, Nelson BJ, Shah A, Dutcher SK, Warren WC, Magrini V, McGrath SD, Li YI, Wilson RK, Eichler EE
In order to provide a comprehensive resource for human structural variants (SVs), we generated long-read sequence data and analyzed SVs for fifteen human genomes. We sequence resolved 99,604 insertions, deletions, and inversions including 2,238 (1.6 Mbp) that are shared among all discovery genomes with an additional... |
Complete Genome Sequence and Methylome Analysis of Micrococcus luteus SA211, a Halophilic, Lithium-Tolerant Actinobacterium from Argentina.
Martínez FL, Anton BP, DasSarma P, Rajal V, Irazusta V, Roberts RJ, DasSarma S
Micrococcus luteus has been found in a wide range of habitats. We report the complete genome sequence and methylome analysis of strain SA211 isolated from a hypersaline, lithium-rich, high-altitude salt flat in Argentina with single-molecule real-time sequencing. |
Reference genome for the WHO reference strain for Mycobacterium bovis BCG Danish, the present tuberculosis vaccine
Katlyn Borgersa,Jheng-Yang Ouc, Po-Xing Zhengc, Petra Tielsa, Annelies Van Heckea, Evelyn Pletsa, Gitte Michielsena, Nele Festjensa, Nico Callewaerta, Yao-Cheng Lin
Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (M. bovis BCG) is the only vaccine available against tuberculosis (TB). This study reports on an integrated genome analysis workflow for BCG, resulting in the completely assembled genome sequence of BCG Danish 1331 (07/270), one of the WHO reference strains for BCG... |
SMRT long reads and Direct Label and Stain optical maps allow the generation of a high-quality genome assembly for the European barn swallow (Hirundo rustica rustica).
Formenti G, Chiara M, Poveda L, Francoijs KJ, Bonisoli-Alquati A, Canova L, Gianfranceschi L, Horner DS, Saino N
Background: The barn swallow (Hirundo rustica) is a migratory bird that has been the focus of a large number of ecological, behavioural and genetic studies. To facilitate further population genetics and genomic studies, here we present a reference genome assembly for the European subspecies (H. r. rustica). Findings... |
Improved reference genome of Aedes aegypti informs arbovirus vector control.
Matthews BJ, Dudchenko O, Kingan SB, Koren S, Antoshechkin I, Crawford JE, Glassford WJ, Herre M, Redmond SN, Rose NH, Weedall GD, Wu Y, Batra SS, Brito-Sierra CA, Buckingham SD, Campbell CL, Chan S, Cox E, Evans BR, Fansiri T, Filipović I, Fontaine A, Gl
Female Aedes aegypti mosquitoes infect more than 400 million people each year with dangerous viral pathogens including dengue, yellow fever, Zika and chikungunya. Progress in understanding the biology of mosquitoes and developing the tools to fight them has been slowed by the lack of a high-quality genome assem... |
Whole-genome landscape of Medicago truncatula symbiotic genes.
Pecrix Y, Staton SE, Sallet E, Lelandais-Brière C, Moreau S, Carrère S, Blein T, Jardinaud MF, Latrasse D, Zouine M, Zahm M, Kreplak J, Mayjonade B, Satgé C, Perez M, Cauet S, Marande W, Chantry-Darmon C, Lopez-Roques C, Bouchez O, Bérard A, Debellé F, Mu
Advances in deciphering the functional architecture of eukaryotic genomes have been facilitated by recent breakthroughs in sequencing technologies, enabling a more comprehensive representation of genes and repeat elements in genome sequence assemblies, as well as more sensitive and tissue-specific analyses of gene e... |
Chromosome-scale assemblies of plant genomes using nanopore long reads and optical maps.
Belser C, Istace B, Denis E, Dubarry M, Baurens FC, Falentin C, Genete M, Berrabah W, Chèvre AM, Delourme R, Deniot G, Denoeud F, Duffé P, Engelen S, Lemainque A, Manzanares-Dauleux M, Martin G, Morice J, Noel B, Vekemans X, D'Hont A, Rousseau-Gueutin M,
Plant genomes are often characterized by a high level of repetitiveness and polyploid nature. Consequently, creating genome assemblies for plant genomes is challenging. The introduction of short-read technologies 10 years ago substantially increased the number of available plant genomes. Generally, these assemblies ... |
The Genomic Basis of Color Pattern Polymorphism in the Harlequin Ladybird.
Gautier M, Yamaguchi J, Foucaud J, Loiseau A, Ausset A, Facon B, Gschloessl B, Lagnel J, Loire E, Parrinello H, Severac D, Lopez-Roques C, Donnadieu C, Manno M, Berges H, Gharbi K, Lawson-Handley L, Zang LS, Vogel H, Estoup A, Prud'homme B
Many animal species comprise discrete phenotypic forms. A common example in natural populations of insects is the occurrence of different color patterns, which has motivated a rich body of ecological and genetic research [1-6]. The occurrence of dark, i.e., melanic, forms displaying discrete color patterns is f... |
Long-read sequence capture of the hemoglobin gene clusters across gadid species.
Hoff SNK, Baalsrud HT, Tooming-Klunderud A, Skage M, Richmond T, Obernosterer G, Shirzadi R, Tørresen OK, Jakobsen KS, Jentoft S
Combining high-throughput sequencing with targeted sequence capture has become an attractive tool to study specific genomic regions of interest. Most studies have so far focused on the exome using short-read technology. These approaches are not designed to capture intergenic regions needed to reconstruct genomic org... |
Genomic Structural Variations Within Five Continental Populations of .
Long E, Evans C, Chaston J, Udall JA
Chromosomal structural variations (SV) including insertions, deletions, inversions, and translocations occur within the genome and can have a significant effect on organismal phenotype. Some of these effects are caused by structural variations containing genes. Large structural variations represent a significant amo... |
Long-read sequencing identified a causal structural variant in an exome-negative case and enabled preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
Miao H, Zhou J, Yang Q, Liang F, Wang D, Ma N, Gao B, Du J, Lin G, Wang K, Zhang Q
Background: For a proportion of individuals judged clinically to have a recessive Mendelian disease, only one heterozygous pathogenic variant can be found from clinical whole exome sequencing (WES), posing a challenge to genetic diagnosis and genetic counseling. One possible reason is the limited ability to detect d... |
Long-read sequencing across the C9orf72 'GGGGCC' repeat expansion: implications for clinical use and genetic discovery efforts in human disease.
Ebbert MTW, Farrugia SL, Sens JP, Jansen-West K, Gendron TF, Prudencio M, McLaughlin IJ, Bowman B, Seetin M, DeJesus-Hernandez M, Jackson J, Brown PH, Dickson DW, van Blitterswijk M, Rademakers R, Petrucelli L, Fryer JD
BACKGROUND: Many neurodegenerative diseases are caused by nucleotide repeat expansions, but most expansions, like the C9orf72 'GGGGCC' (GC) repeat that causes approximately 5-7% of all amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD) cases, are too long to sequence using short-read sequencing te... |
The complete methylome of an entomopathogenic bacterium reveals the existence of loci with unmethylated Adenines.
Payelleville A, Legrand L, Ogier JC, Roques C, Roulet A, Bouchez O, Mouammine A, Givaudan A, Brillard J
DNA methylation can serve to control diverse phenomena in eukaryotes and prokaryotes, including gene regulation leading to cell differentiation. In bacteria, DNA methylomes (i.e., methylation state of each base of the whole genome) have been described for several species, but methylome profile variation during the l... |
Long-read sequence capture of the haemoglobin gene clusters across codfish species.
Hoff SNK, Baalsrud HT, Tooming-Klunderud A, Skage M, Richmond T, Obernosterer G, Shirzadi R, Tørresen OK, Jakobsen KS, Jentoft S
Combining high-throughput sequencing with targeted sequence capture has become an attractive tool to study specific genomic regions of interest. Most studies have so far focused on the exome using short-read technology. These approaches are not designed to capture intergenic regions needed to reconstruct genomic org... |
A high-quality genome sequence of Rosa chinensis to elucidate ornamental traits.
Hibrand Saint-Oyant L, Ruttink T, Hamama L, Kirov I, Lakhwani D, Zhou NN, Bourke PM, Daccord N, Leus L, Schulz D, Van de Geest H, Hesselink T, Van Laere K, Debray K, Balzergue S, Thouroude T, Chastellier A, Jeauffre J, Voisine L, Gaillard S, Borm TJA, Are
Rose is the world's most important ornamental plant, with economic, cultural and symbolic value. Roses are cultivated worldwide and sold as garden roses, cut flowers and potted plants. Roses are outbred and can have various ploidy levels. Our objectives were to develop a high-quality reference genome sequence for th... |
Overview of Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies.
Slatko BE, Gardner AF, Ausubel FM
High throughput DNA sequencing methodology (next generation sequencing; NGS) has rapidly evolved over the past 15 years and new methods are continually being commercialized. As the technology develops, so do increases in the number of corresponding applications for basic and applied science. The purpose of this revi... |
Draft genome of the Peruvian scallop Argopecten purpuratus.
Li C, Liu X, Liu B, Ma B, Liu F, Liu G, Shi Q, Wang C
Background: The Peruvian scallop, Argopecten purpuratus, is mainly cultured in southern Chile and Peru was introduced into China in the last century. Unlike other Argopecten scallops, the Peruvian scallop normally has a long life span of up to 7 to 10 years. Therefore, researchers have been using it to develop hybri... |
Genomic repeats, misassembly and reannotation: a case study with long-read resequencing of Porphyromonas gingivalis reference strains.
Acuña-Amador L, Primot A, Cadieu E, Roulet A, Barloy-Hubler F
BACKGROUND: Without knowledge of their genomic sequences, it is impossible to make functional models of the bacteria that make up human and animal microbiota. Unfortunately, the vast majority of publicly available genomes are only working drafts, an incompleteness that causes numerous problems and constitutes a majo... |
Single-Molecule Sequencing Reveals the Chromosome-Scale Genomic Architecture of the Nematode Model Organism Pristionchus pacificus.
Rödelsperger C. et al.
The nematode Pristionchus pacificus is an established model for integrative evolutionary biology and comparative studies with Caenorhabditis elegans. While an existing genome draft facilitated the identification of several genes controlling various developmental processes, its high degree of fragmentation complicate... |
De novo PacBio long-read and phased avian genome assemblies correct and add to reference genes generated with intermediate and short reads
Korlach J. et al.
Reference-quality genomes are expected to provide a resource for studying gene structure, function, and evolution. However, often genes of interest are not completely or accurately assembled, leading to unknown errors in analyses or additional cloning efforts for the correct sequences. A promising solution is long-r... |
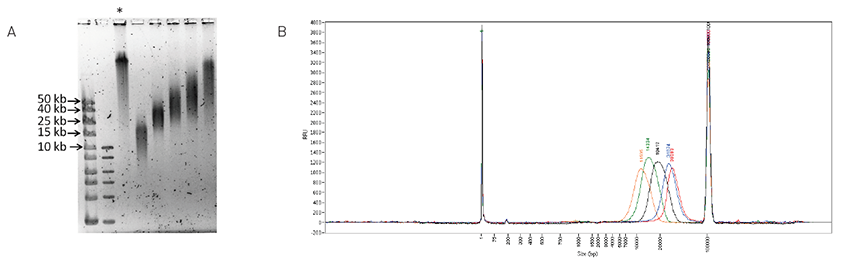
DNA fragmentation and quality control analysis
Wassim Lakhal, Irina Panteleeva, Sharon Squazzo, Rini Saxena, Jerome Kroonen, Steve Siembieda, Markus Tilmes & Jonathan Hagopian
Optimal data generation using NGS platforms relies on a few sample-preparation prerequisites, namely, precise DNA fragmentation, size-range analysis, and smear quantification. The Diagenode One, Bioruptor®, Megaruptor®, and Fragment Analyzer™ by Advanced Analytical ensure that these first cri... |