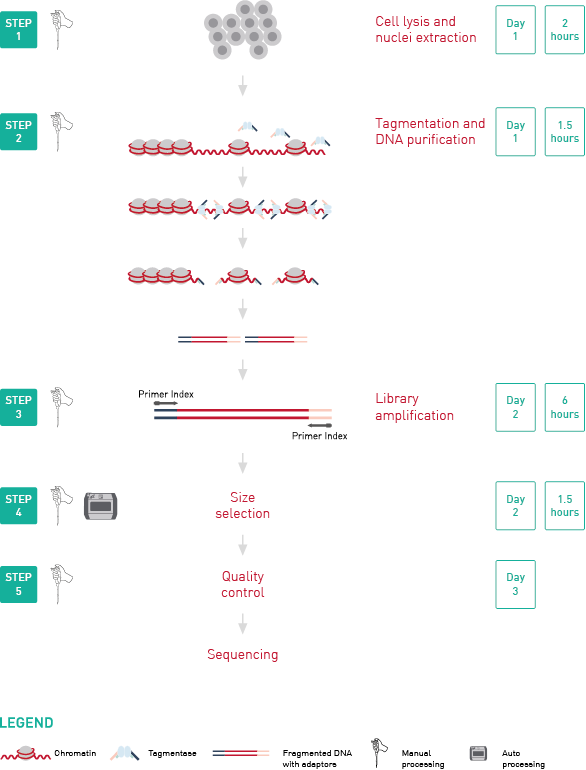
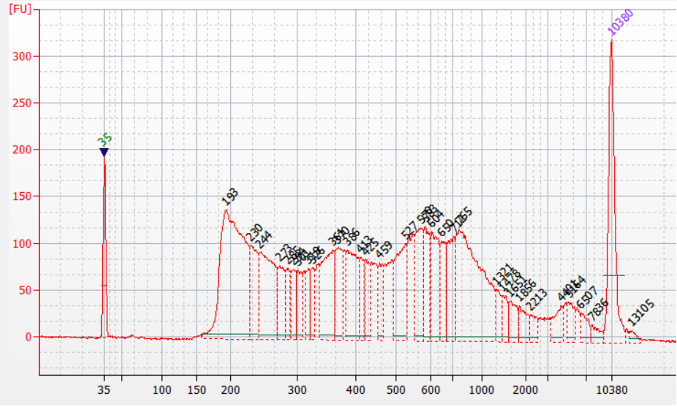
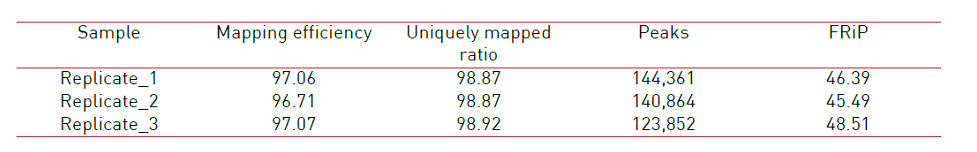
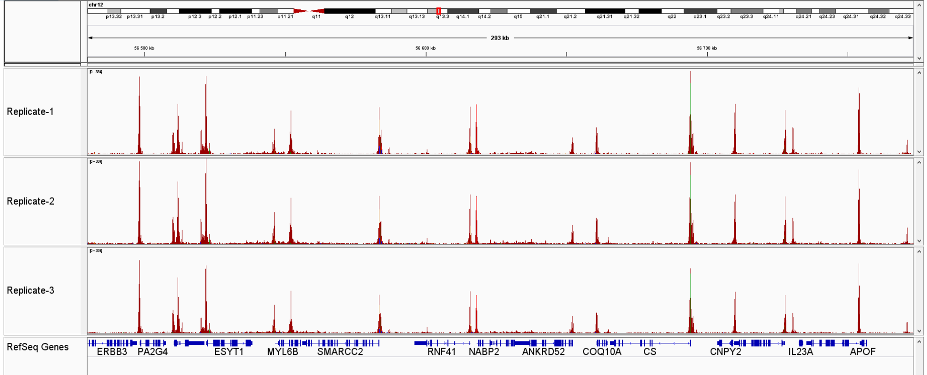
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: ATAC-seq kit (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C01080002). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Cervicovaginal microbiome alters transcriptomic and chromatin accessibility signatures across cervicovaginal epithelial barriers
Anton L, Cristancho AG, Ferguson B, Ravel J, Elovitz MA.
Background: The cervicovaginal microbiome plays a critical role in women's health with microbial communities dominated by Lactobacillus species considered optimal. In contrast, the depletion of lactobacilli and the presence of a diverse array of strict and facultative anaerobes, such as Gardnerella vaginalis, h... |
Retinoic acid and ascorbate synergize to suppress myeloid leukemia via TET2 activation
Leesang, Tiffany E et al.
Enhancing ten-eleven translocation 2 (TET2) activity through genetic or pharmacologic approaches, such as ascorbate supplementation, can slow myeloid malignancy progression. However, ascorbate alone may be insufficient to fully activate TET2 in malignant cells due to pharmacokinetic constraints and the need for ch... |
Interactions of the LINE-1 encoded ORF1p with proteins and chromatin converge on a role in neuronal physiology
Sinnassamy, Sandra et al.
Retrotransposons are emerging as novel regulators of embryonic and brain development. We recently demonstrated that the LINE-1–encoded protein ORF1p is abundantly expressed in adult mouse and human neurons, although its function remains unclear. Here, we characterize the ORF1p interactome in differentiated m... |
H1.3 depletion in AML cells prompts H1.2 redistribution, chromatin remodeling and cell cycle defects
Tellez-Quijorna, Clara et al.
Linker histone H1 variants play critical, yet distinct, roles in chromatin organization and gene regulation. However, very little is known about their specificity in cancer cells. In this study, we investigated the specificity of the H1.3 variant in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells. Through chromatin mapping and... |
Distinguishing benign from pathogenic duplications involving GPR101 and VGLL1-adjacent enhancers in the clinical setting with the bioinformatic tool POSTRE
Trivellin, Giampaolo et al.
Background:
Structural variants (SVs) that disrupt topologically associating domains (TADs) can cause disease by rewiring enhancer-promoter interactions. Duplications involving GPR101 are known to cause X-linked acrogigantism (X-LAG) by enabling aberrant expression of GPR101 through hijacking ... |
CRAMP1 drives linker histone expression to enable Polycomb repression
Matthews, Rachael E et al.
In contrast to the well-understood role of core histones in DNA packaging, the function of the linker histone (H1) remains enigmatic. Challenging the prevailing view that linker histones are a general feature of heterochromatin, here we show a critical requirement for H1 in Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) fun... |
Temporal and spatial niche partitioning in a retrotransposon community of the Drosophila melanogaster genome
Varoqui, Marion et al.
Transposable elements (TEs) are genetic parasites that can potentially threaten the stability of the genomes they colonize. Nonetheless, TEs persist within genomes and are rarely fully eliminated, with diverse TE families coexisting in varing copy numbers. The TE replication strategies that enable host organisms... |
Cervicovaginal microbiome alters transcriptomic and epigenomic signatures across cervicovaginal epithelial barriers
Lauren Anton et al.
Background
The cervicovaginal microbiome plays a critical role in women's health, with microbial communities dominated by Lactobacillus species considered optimal. In contrast, the depletion of lactobacilli and the presence of a diverse array of strict and facultative anaerobes, such as Gardnerella v... |
An ISWI-related chromatin remodeller regulates stage-specific gene expression in Toxoplasma gondii
Pachano, Belen et al.
ATP-dependent chromatin remodellers are specialized multiprotein machines that organize the genome in eukaryotic cells and regulate its accessibility by repositioning, ejecting or modifying nucleosomes. However, their role in Toxoplasma gondii is poorly understood. Here we show that T. gondii&n... |
Repression of oxidative phosphorylation by NR2F2, MTERF3 and GDF15 in human skin under high-glucose stress
S. Ley-Ngardigal et al.
Lifestyle factors such as a Western diet or metabolic diseases like diabetes disrupt glucose homeostasis and induce stress responses, yet their impact on skin metabolism and structural integrity remains poorly understood. Here, we performed multiomic and bioenergetic analyses of human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs), huma... |
CRISPR screening identifies regulators of enhancer-mediated androgen receptor transcription in advanced prostate cancer
Rachel R. Xiang et al.
Amplification of the androgen receptor (AR) locus is the most frequent alteration in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). Recently, it was discovered that an enhancer of the AR is co-amplified with the AR gene body and contributes to increased AR transcription and resistance to androgen de... |
Schistosoma mansoni antigen induced innate immune memory features mitochondrial biogenesis and can be inhibited by ovarian produced hormones
Juan Marcos Oviedo et al.
We have previously identified that S. mansoni infection induces a unique form of myeloid training that protects male but not female mice from high fat diet induced disease. Here we demonstrate that ovarian derived hormones account for this sex specific difference. Ovariectomy of females prior to infection ... |
Dynamic PRC1–CBX8 stabilizes a porous structure of chromatin condensates
Uckelmann, M., et al.
Abstract
The compaction of chromatin is a prevalent paradigm in gene repression. Chromatin compaction is commonly thought to repress transcription by restricting chromatin accessibility. However, the spatial organization and dynamics of chromatin compacted by gene-repressing factors are unknown. Here, using cryo-... |
Assessing the impact of whole genome duplication on gene expression and regulation during arachnid development
Madeleine E. Aase-Remedios et al.
Whole genome duplication (WGD) generates new genetic material that can contribute to the evolution of the regulation of developmental processes and phenotypic diversification. A WGD occurred in an ancestor of arachnopulmonates (spiders, scorpions, and their relatives), which provides an important independent compari... |
Spatial organizations of heterochromatin underpin nuclear structural integrity of ventricular cardiomyocytes against mechanical stress
Keita Fujiwara et al.
Highlights
Cardiomyocytes acquire characteristic spatial organizations of heterochromatin (SOH)
High levels of H2B-mCherry disrupt SOH, leading to nuclear elongation in cardiomyocytes
SOH disruption minimally impacts gene expression despite loosening global genome structure
SOH ... |
DNA demethylation triggers cell free DNA release in colorectal cancer cells
Valeria Pessei et al.
Background
Liquid biopsy based on cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analysis holds significant promise as a minimally invasive approach for the diagnosis, genotyping, and monitoring of solid malignancies. Human tumors release cfDNA in the bloodstream through a combination of events, including cell death, active and passive rel... |
Temporal and spatial niche partitioning in a retrotransposon community of the Drosophila genome
Varoqui M. et al.
Transposable elements (TEs), widespread genetic parasites, pose potential threats to the stability of their host genomes. Hence, the interactions observed today between TEs and their host genomes, as well as among the different TE species coexisting in the same host, likely reflect those that did not lead to the ext... |
Galectin 3-binding protein (LGALS3BP) depletion attenuates hepatic fibrosis by reducing transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) availability and inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis
Dae-Hwan Kim et al.
Background
Increased Galectin 3-binding protein (LGALS3BP) serum levels have been used to assess hepatic fibrosis stages and the severity of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Considering the crucial role of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in the emergence of these diseases, the present study tested... |
Patho-transcriptomic analysis of invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung (IMA): comparison with lung adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell features (SRCC)
William D. Stuart et al.
Background Invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma (IMA) comprises ∼5% of lung adenocarcinoma. There is no effective therapy for IMA when surgical resection is not possible. IMA is sometimes confused with adenocarcinoma with signet ring cell features (SRCC) pathologically since both adenocarcinomas feature tumor... |
Transient loss of Polycomb components induces an epigenetic cancer fate
V. Parreno et al.
Although cancer initiation and progression are generally associated with the accumulation of somatic mutations1,2, substantial epigenomic alterations underlie many aspects of tumorigenesis and cancer susceptibility3,4,5,6, suggesting that genetic mechanisms might not be the only drivers of malignant transformation7.... |
Systematic mapping of TF-mediated cell fate changes by a pooled induction coupled with scRNA-seq and multi-omics approaches
Lee M. et al.
Transcriptional regulation controls cellular functions through interactions between transcription factors (TFs) and their chromosomal targets. However, understanding the fate conversion potential of multiple TFs in an inducible manner remains limited. Here, we introduce iTF-seq as a method for identifying individual... |
Protocol to isolate nuclei from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii for ATAC sequencing
Santhanagopalan I. et al.
Highlights
Optimized isolation of nuclei from the green model alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Tag-free isolation from both cell-walled and cell wall-deficient algae strains
Key steps for an effective and fast isolation and quantification procedure of nuclei
Extracts at a quality suitabl... |
Interplay between coding and non-coding regulation drives the Arabidopsis seed-to-seedling transition
Trembley B.J.M. et al.
Translation of seed stored mRNAs is essential to trigger germination. However, when RNAPII re-engages RNA synthesis during the seed-to-seedling transition has remained in question. Combining csRNA-seq, ATAC-seq and smFISH in Arabidopsis thaliana we demonstrate that active transcription initiation is detect... |
The transcriptional regulatory network modulating human trophoblast stem cells to extravillous trophoblast differentiation
Kim M. et al.
During human pregnancy, extravillous trophoblasts play crucial roles in placental invasion into the maternal decidua and spiral artery remodeling. However, regulatory factors and their action mechanisms modulating human extravillous trophoblast specification have been unknown. By analyzing dynamic changes in transcr... |
DMSO derives Trophectoderm and Clonal Blastoid from Single Human Pluripotent Stem Cell
Alsolami S. et al.
Human naïve pluripotent stem cells (nPSCs) can differentiate into extra-embryonic trophectoderm (TE), a critical step in the generation of the integrated embryo model termed blastoid. The current paradigm of blastoid generation necessitates the aggregation of dozens of nPSCs treated with multiple small molecule... |
In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages
Antunes, A.V. et al.
Sexual reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii, confined to the felid gut, remains largely uncharted owing to ethical concerns regarding the use of cats as model organisms. Chromatin modifiers dictate the developmental fate of the parasite during its multistage life cycle, but their targeting to stage-specific cistro... |
Vaginal microbes alter epithelial transcriptomic and epigenomic modifications providing insight into the molecular mechanisms for susceptibility to adverse reproductive outcomes
Elovitz M. et al.
The cervicovaginal microbiome is highly associated with women's health with microbial communities dominated by Lactobacillus spp. being considered optimal. Conversely, a lack of lactobacilli and a high abundance of strict and facultative anaerobes including Gardnerella vaginalis, have been associated ... |
Inflammatory stress-mediated chromatin changes underlie dysfunction in endothelial cells
Liu H. et al.
Inflammatory stresses underlie endothelial dysfunction and contribute to the development of chronic cardiovascular disorders such as atherosclerosis and vascular fibrosis. The initial transcriptional response of endothelial cells to pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha is well established. However, very few ... |
Dynamic PRC1-CBX8 stabilizes a porous structure of chromatin condensates
Uckelmann M. et al.
The compaction of chromatin is a prevalent paradigm in gene repression. Chromatin compaction is commonly thought to repress transcription by restricting chromatin accessibility. However, the spatial organisation and dynamics of chromatin compacted by gene-repressing factors are unknown. Using cryo-electron tomograph... |
UMSBP2 is chromatin remodeler that functions in regulation of geneexpression and suppression of antigenic variation in trypanosomes.
Soni A. et al.
Universal Minicircle Sequence binding proteins (UMSBPs) are CCHC-type zinc-finger proteins that bind the single-stranded G-rich UMS sequence, conserved at the replication origins of minicircles in the kinetoplast DNA, the mitochondrial genome of kinetoplastids. Trypanosoma brucei UMSBP2 has been recently shown to co... |