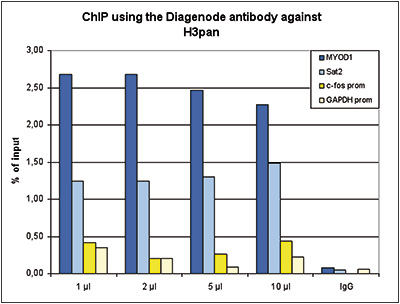
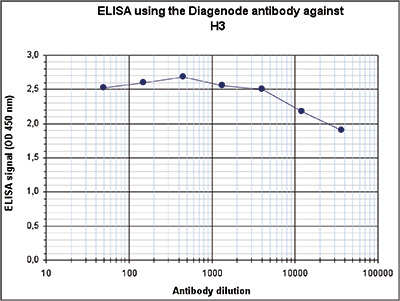
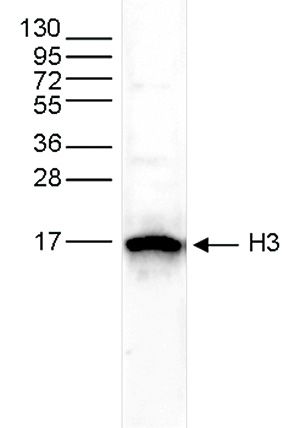
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3pan polyclonal antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15310135-20 Lot# A2566-001). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Epigenetic, transcriptional and phenotypic responses in Daphnia magna exposed to low-level ionizing radiation
Thaulow Jens, Song You, Lindeman Leif C., Kamstra Jorke H., Lee YeonKyeong, Xie Li, Aleström Peter, Salbu Brit, Tollefsen Knut Erik
Ionizing radiation is known to induce oxidative stress and DNA damage as well as epigenetic effects in aquatic organisms. Epigenetic changes can be part of the adaptive responses to protect organisms from radiation-induced damage, or act as drivers of toxicity pathways leading to adverse effects. To investigate the ... |
The 20S proteasome activator PA28γ controls the compaction of chromatin
Didier Fesquet, David Llères, Cristina Viganò, Francisca Méchali, Séverine Boulon, Robert Feil, Olivier Coux, Catherine Bonne-Andrea, Véronique Baldin
The nuclear PA28γ is known to activate the 20S proteasome, but its precise cellular functions remains unclear. Here, we identify PA28γ as a key factor that structures heterochromatin. We find that in human cells, a fraction of PA28γ-20S proteasome complexes localizes within HP1-linked heterochromat... |
The TGF-β profibrotic cascade targets ecto-5'-nucleotidase gene in proximal tubule epithelial cells and is a traceable marker of progressive diabetic kidney disease.
Cappelli C, Tellez A, Jara C, Alarcón S, Torres A, Mendoza P, Podestá L, Flores C, Quezada C, Oyarzún C, Martín RS
Progressive diabetic nephropathy (DN) and loss of renal function correlate with kidney fibrosis. Crosstalk between TGF-β and adenosinergic signaling contributes to the phenotypic transition of cells and to renal fibrosis in DN models. We evaluated the role of TGF-β on NT5E gene expression coding for the ec... |
Inhibition of methyltransferase activity of enhancer of zeste 2 leads to enhanced lipid accumulation and altered chromatin status in zebrafish.
den Broeder MJ, Ballangby J, Kamminga LM, Aleström P, Legler J, Lindeman LC, Kamstra JH
BACKGROUND: Recent studies indicate that exposure to environmental chemicals may increase susceptibility to developing metabolic diseases. This susceptibility may in part be caused by changes to the epigenetic landscape which consequently affect gene expression and lead to changes in lipid metabolism. The epigenetic... |
lncRNA KHPS1 Activates a Poised Enhancer by Triplex-Dependent Recruitment of Epigenomic Regulators.
Blank-Giwojna A, Postepska-Igielska A, Grummt I
Transcription of the proto-oncogene SPHK1 is regulated by KHPS1, an antisense RNA that activates SPHK1 expression by forming a triple-helical RNA-DNA-DNA structure at the SPHK1 enhancer. Triplex-mediated tethering of KHPS1 to its target gene is required for recruitment of E2F1 and p300 and transcription of the RNA d... |
Gamma radiation induces locus specific changes to histone modification enrichment in zebrafish and Atlantic salmon.
Lindeman LC, Kamstra JH, Ballangby J, Hurem S, Martín LM, Brede DA, Teien HC, Oughton DH, Salbu B, Lyche JL, Aleström P
Ionizing radiation is a recognized genotoxic agent, however, little is known about the role of the functional form of DNA in these processes. Post translational modifications on histone proteins control the organization of chromatin and hence control transcriptional responses that ultimately affect the phenotype. Th... |
SIRT7-Dependent Deacetylation of Fibrillarin Controls Histone H2A Methylation and rRNA Synthesis during the Cell Cycle.
Iyer-Bierhoff A, Krogh N, Tessarz P, Ruppert T, Nielsen H, Grummt I
Fibrillarin (FBL) is a dual-function nucleolar protein that catalyzes 2'-O methylation of pre-rRNA and methylation of histone H2A at glutamine 104 (H2AQ104me). The mechanisms that regulate FBL activity are unexplored. Here, we show that FBL is acetylated at several lysine residues by the acetyltransferase CBP and de... |
HIV-2/SIV viral protein X counteracts HUSH repressor complex.
Ghina Chougui, Soundasse Munir-Matloob, Roy Matkovic, Michaël M Martin, Marina Morel, Hichem Lahouassa, Marjorie Leduc, Bertha Cecilia Ramirez, Lucie Etienne and Florence Margottin-Goguet
To evade host immune defences, human immunodeficiency viruses 1 and 2 (HIV-1 and HIV-2) have evolved auxiliary proteins that target cell restriction factors. Viral protein X (Vpx) from the HIV-2/SIVsmm lineage enhances viral infection by antagonizing SAMHD1 (refs ), but this antagonism is not sufficient to explain a... |
The transcription factors Runx3 and ThPOK cross-regulate acquisition of cytotoxic function by human Th1 lymphocytes
Yasmina Serroukh et al
Cytotoxic CD4 (CD4CTX) T cells are emerging as an important component of antiviral and antitumor immunity, but the molecular basis of their development remains poorly understood. In the context of human cytomegalovirus infection, a significant proportion of CD4 T cells displays cytotoxic functions. We observed that ... |
The transcription factors Runx3 and ThPOK cross-regulate acquisition of cytotoxic function by human Th1 lymphocytes.
Serroukh Y, Gu-Trantien C, Hooshiar Kashani B, Defrance M, Vu Manh TP, Azouz A, Detavernier A, Hoyois A, Das J, Bizet M, Pollet E, Tabbuso T, Calonne E, van Gisbergen K, Dalod M, Fuks F, Goriely S, Marchant A
Cytotoxic CD4 (CD4) T cells are emerging as an important component of antiviral and antitumor immunity, but the molecular basis of their development remains poorly understood. In the context of human cytomegalovirus infection, a significant proportion of CD4 T cells displays cytotoxic functions. We observed that the... |
Phenotypic Plasticity through Transcriptional Regulation of the Evolutionary Hotspot Gene tan in Drosophila melanogaster
Gibert JM et al.
Phenotypic plasticity is the ability of a given genotype to produce different phenotypes in response to distinct environmental conditions. Phenotypic plasticity can be adaptive. Furthermore, it is thought to facilitate evolution. Although phenotypic plasticity is a widespread phenomenon, its molecular mechanisms are... |
Heat shock represses rRNA synthesis by inactivation of TIF-IA and lncRNA-dependent changes in nucleosome positioning
Zhao Z et al.
Attenuation of ribosome biogenesis in suboptimal growth environments is crucial for cellular homeostasis and genetic integrity. Here, we show that shutdown of rRNA synthesis in response to elevated temperature is brought about by mechanisms that target both the RNA polymerase I (Pol I) transcription machinery and th... |
Role of Annexin gene and its regulation during zebrafish caudal fin regeneration
Saxena S, Purushothaman S, Meghah V, Bhatti B, Poruri A, Meena Lakshmi MG, Sarath Babu N, Murthy CL, Mandal KK, Kumar A, Idris MM
The molecular mechanism of epimorphic regeneration is elusive due to its complexity and limitation in mammals. Epigenetic regulatory mechanisms play a crucial role in development and regeneration. This investigation attempted to reveal the role of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms, such as histone H3 and H4 lysine ac... |
Standardizing chromatin research: a simple and universal method for ChIP-seq
Laura Arrigoni, Andreas S. Richter, Emily Betancourt, Kerstin Bruder, Sarah Diehl, Thomas Manke and Ulrike Bönisch
Here we demonstrate that harmonization of ChIP-seq workflows across cell types and conditions is possible when obtaining chromatin from properly isolated nuclei. We established an ultrasound-based nuclei extraction method (Nuclei Extraction by Sonication) that is highly effective across various organisms, cell ... |
Nurr1 and Retinoid X Receptor Ligands Stimulate Ret Signaling in Dopamine Neurons and Can Alleviate α-Synuclein Disrupted Gene Expression
Volakakis N et al.
α-synuclein, a protein enriched in Lewy bodies and highly implicated in neurotoxicity in Parkinson's disease, is distributed both at nerve terminals and in the cell nucleus. Here we show that a nuclear derivative of α-synuclein induces more pronounced changes at the gene expression level in mouse primary... |
The Integrase Cofactor LEDGF/p75 Associates with Iws1 and Spt6 for Postintegration Silencing of HIV-1 Gene Expression in Latently Infected Cells.
Gérard A, Ségéral E, Naughtin M, Abdouni A, Charmeteau B, Cheynier R, Rain JC, Emiliani S
The persistence of a latent reservoir containing transcriptionally silent, but replication-competent, integrated provirus is a serious challenge to HIV eradication. HIV integration is under the control of LEDGF/p75, the cellular cofactor of viral integrase. Investigating possible postintegration roles for LEDGF/p75,... |
Endonuclease G preferentially cleaves 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-modified DNA creating a substrate for recombination.
Robertson AB, Robertson J, Fusser M, Klungland A
5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) has been suggested to be involved in various nucleic acid transactions and cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, demethylation of 5-methylcytosine and stem cell pluripotency. We have identified an activity that preferentially catalyzes the cleavage of double-strande... |
Nitric oxide-induced neuronal to glial lineage fate-change depends on NRSF/REST function in neural progenitor cells.
Bergsland M, Covacu R, Perez Estrada C, Svensson M, Brundin L
Degeneration of CNS tissue commonly occurs during neuroinflammatory conditions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and neurotrauma. During such conditions, neural stem/progenitor cell (NPC) populations have been suggested to provide new cells to degenerated areas. In the normal brain, NPCs from the SVZ generate neurons... |