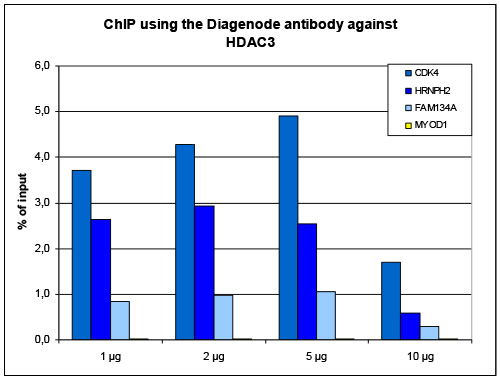
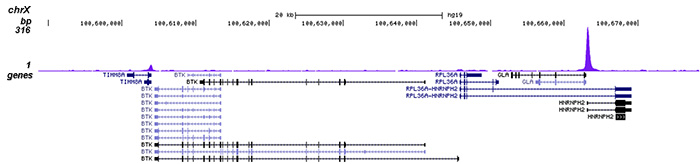
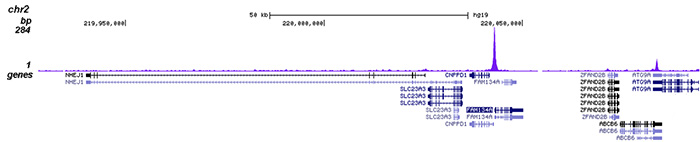
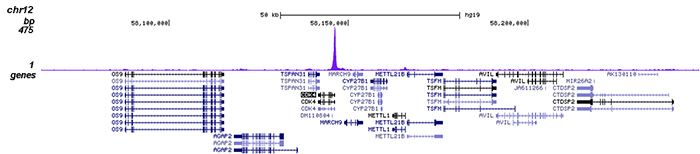
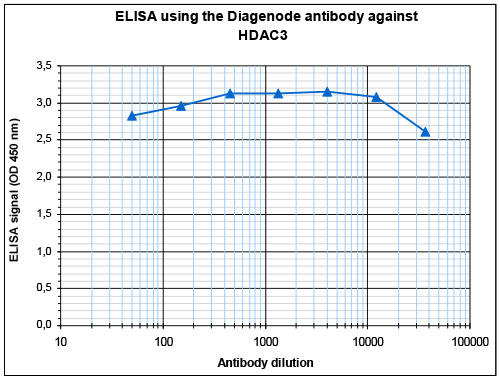
HDAC3 (UniProt/Swiss-Prot entry O15379) catalyses the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) and on some other non-histone substrates. Acetylation and deacetylation of these highly conserved lysine residues is important for the control of gene expression. When tethered to a promoter, HDAC3 represses transcription and therefore plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. HDAC3 probably participates in the regulation of transcription through its binding to the YY1 transcription factor, increasing YY1 repression. HDAC3 also downregulates p53 and is considered a potential tumor suppressor gene.
-
产品
剪切技术
Tagmentation
Chromatin studies
DNA methylation
- Bisulfite conversion
- Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation
- Methylbinding domain protein
- Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation
Genome editing (CRISPR/Cas9)
Antibodies
- All antibodies
- Sample size antibodies
- ChIP-seq grade antibodies
- ChIP-grade antibodies
- Western Blot Antibodies
- DNA modifications
- RNA modifications
- CRISPR/Cas9 antibodies
- CUT&Tag Antibodies
NGS Library preparation
- Library preparation for ChIP-seq
- Library preparation for RNA sequencing
- Library preparation for DNA sequencing
Automation
Reagents
- 服务
- 研究领域
- 资源
- 公司
-
联系人