Obtaining highly sensitive and highly specific antibodies is challenging for researchers.
Many antibodies that are used in experimental assays have limited validation behind them, and the
data given by the provider are not always lot-specific.
Consequently, researchers must often independently validate antibodies, a time-consuming and costly
process.
Diagenode has addressed these issues and provides:
- A rigorous QC process using stringent criteria for antibody validation
- Accessible validation data presented in our data sheets and website, obtained
with current lots of the antibodies
- Validation standardization - Every new lot is tested using the same stringent
criteria and compared to the previous lot before adding to the catalog.
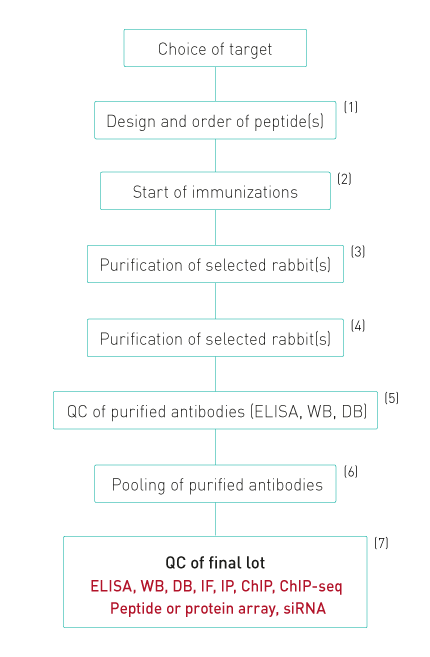
Diagenode’s antibody production and QC process
1. Peptides are designed to evoke a maximal immune response and coupled to KLH
2. Up to 20 rabbits arre immunized. Each rabbit is injected 6 times. Four bleeds are taken
from each rabbit.
3. All bleeds are tested by ELISA and WB. Antibodies against modified histones are also tested
for specificity against different peptides with related modifications by dot blot.
4. Only bleeds which show a single band of the expected size in WB or at least 90% specificity
in dot blot are selected for purification
5. The purified antibodies are again tested in ELISA, dot blot and WB.
6. Purifications that pass this QC are pooled together giving a final lot, which is again
tested.
7. The specificity of the final lot is further demonstrated by peptide or protein arrays.
Diagenode also has introduced WB combined with siRNA blocking of the target expression as an
additional validation procedure. Finally, the antibodies are validated in ChIP-seq
Stringent antibody validation criteria
Dot Blot
The specificity of antibodies against modified proteins (e.g. histones) is tested by dot blot.
The signal obtained with the specific peptide should be >70% of the total signal on the
blot for the highest peptide concentration.
Most of our antibodies against histone modifications exceed expectations with a specificity of >90%.
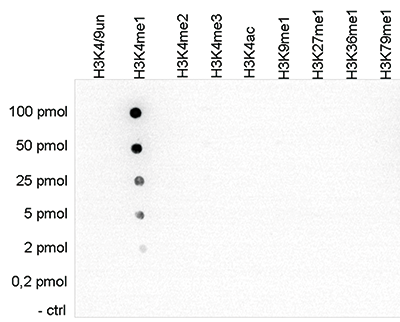
Figure 1. Cross reactivity tests using the Diagenode antibody directed against
H3K4me1
To test the cross reactivity of the Diagenode antibody against H3K4me1 (Cat. No. C15410194),
a Dot Blot analysis was performed with peptides containing other histone modifications and the
unmodified H3K4. One hundred to 0.2 pmol of the respective peptides were spotted on a membrane.
The antibody was used at a dilution of 1:5,000. Figure 1 shows a high specificity of the
antibody
for the modification of interest.
Modified histones peptide array
The specificity of antibodies against modified histones is further tested on peptide arrays.
These arrays contain 384 different peptides in duplicate with different combinations of H3, H4, H2A and H2B
modifications.
A specificity factor >30 and at least 5x higher than for any other
modification is required to pass this QC.
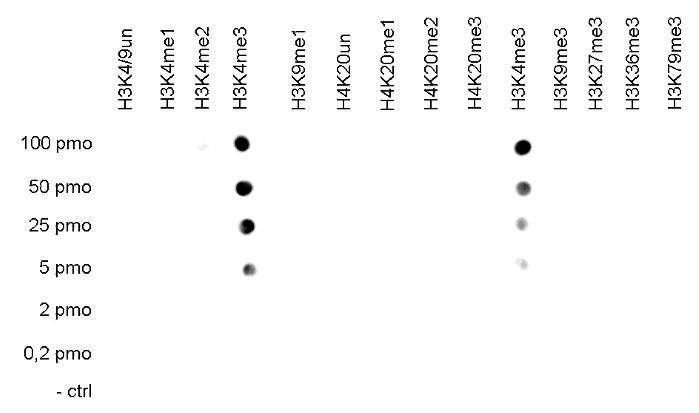
Figure 2. Cross reactivity tests using the Diagenode antibody directed against
H3K4me3
The specificity of the antibody was demonstrated by peptide array analyses on an array
containing 384 peptides with different combinations of modifications from histone H3, H4, H2A
and H2B. The antibody was used at a dilution of 1:2,000. Figure 2 shows a high specificity for
the peptides containing the H3K4me3 modification.
Western Blot
The overall specificity of the antibodies against histone modifications is tested in Western blot performed
on whole cell extracts,
histone extracts and recombinant histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. The following criteria are applied:
A specific signal <80% of the total signal in the lane containing the whole cell
extracts
Signal of other histones <10% of the total signal in the lane containing the histone
extracts
Signal with any of the recombinant histones <10% of the specific signal in the lane with
the histone extracts
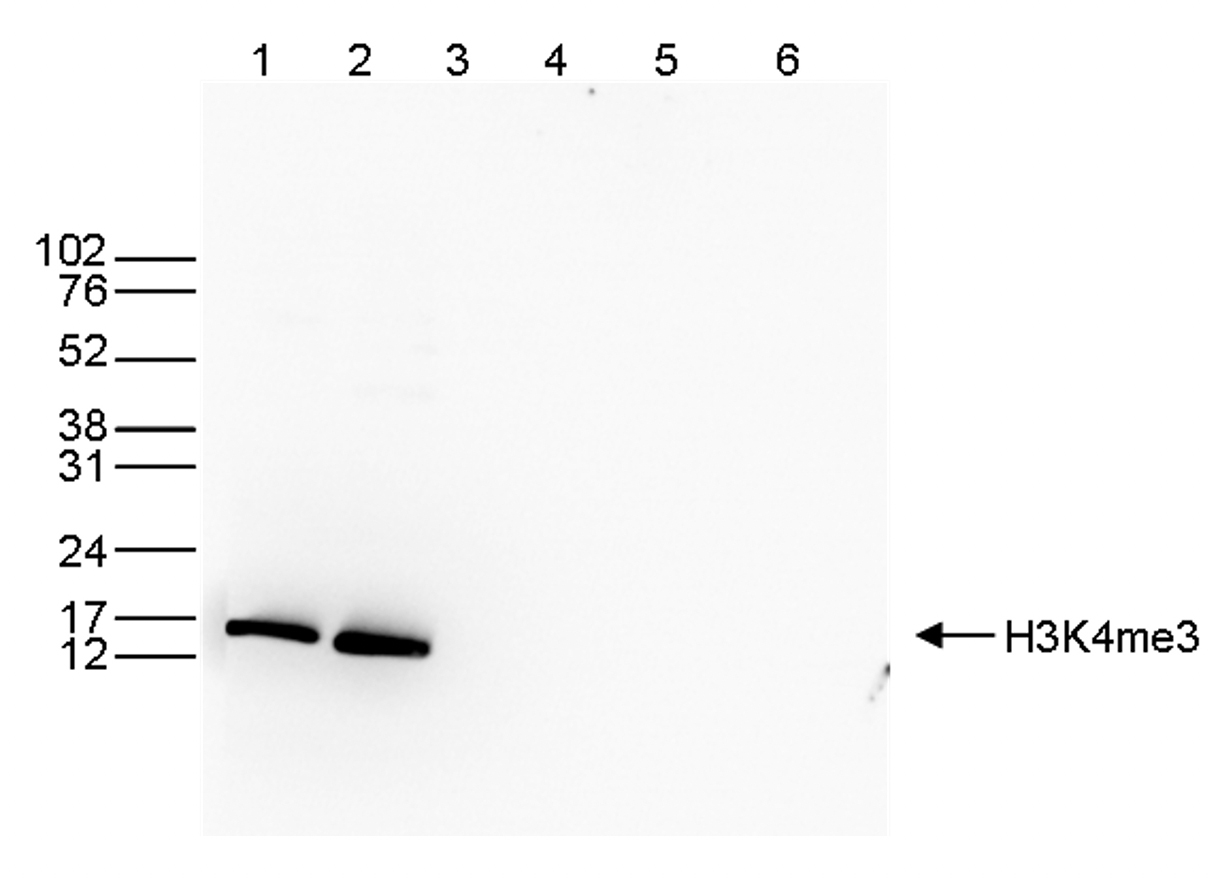
Figure 3. Western blot analysis using the Diagenode antibody directed against
H3K4me3
Western blot was performed on whole cell (40 μg, lane 1) and histone extracts (15 μg, lane 2)
from HeLa cells, and on 1 μg of recombinant histone H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 (lane 3, 4, 5 and 6,
respectively) using the Diagenode antibody against H3K4me3 (Cat. No. C15410003). The
antibody was diluted 1:1,000 in TBS-Tween containing 5% skimmed milk. The position of the
protein of interest is indicated on the right; the marker (in kDa) is shown on the left
siRNA Knockdown
The specificity of antibodies against non-histone proteins is further tested by siRNA knockdown.
If the antibody that recognizes the protein of interest is specific,
the Western blot of siRNA-treated cells will show a signal reduction of at least 60% compared to untreated
cells, as shown by the results below.
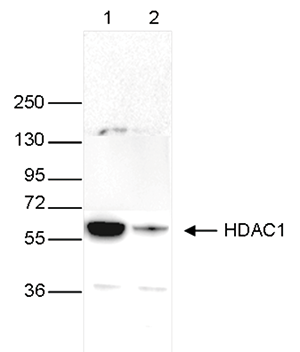
Figure 4. Western blot analysis using the Diagenode monoclonal antibody directed
against HDAC1
Whole cell extracts (40 μg) from HeLa cells transfected with HDAC1 siRNA (lane 2) and from an
untransfected control (lane 1) were analysed
by Western blot using the Diagenode antibody against HDAC1 (Cat. No. C15100144) diluted 1:1,000
in TBS-Tween containing 5% skimmed milk.
The position of the protein of interest is indicated on the right (expected size: 55 kDa); the
marker (in kDa) is shown on the left.
Immunofluorescence
Antibodies are validated in IF and DAPI is used in parallel to stain the nucleus of the cells.
Peptide blocking with specific and related peptides prior to the incubation is used for many antibodies
against histone modifications.
Epigenetic antibodies should only show a nuclear signal and this signal should disappear only after
incubation with the specific peptide.
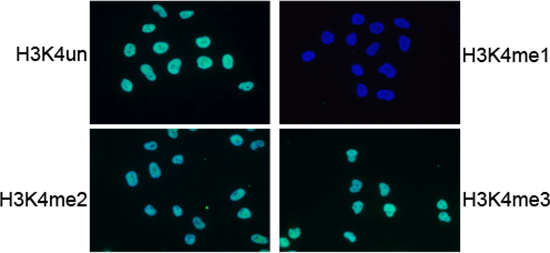
Figure 5. IF analysis using the Diagenode antibody directed against
H3K4me1
IF using the Diagenode H3K4me1 antibody (Cat. no. 15410194), diluted 1:200 after incubation with
4 different blocking peptides (H3K4un, H3K4me1, H3K4me2 and H3K4me3).
The image shows the merged staining with the antibody (green) and with DAPI (blue).
The green signal only disappears after blocking with the H3K4me1 peptide.
ChIP-grade
ChIP is performed according to our standardized protocol.
qPCR is performed using at least 2 positive and 2 negative control
targets.
To pass the ChIP QC, the antibody has to show the expected profile with a +/- ratio
>5.
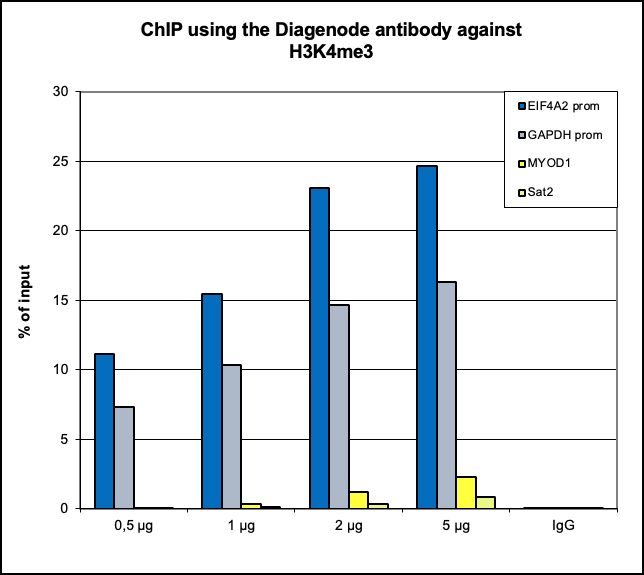
Figure 6. ChIP results obtained with the Diagenode antibody directed against
H3K4me3
ChIP assays were performed using human HeLa cells, the Diagenode antibody against H3K4me3 (Cat.
No. C15410003) and optimized PCR primer pairs for qPCR.
ChIP was performed with the “Auto Histone ChIP-seq” kit (Cat. No. C01010022), using sheared
chromatin from 1 million cells.
A titration consisting of 1, 2, 5 and 10 μg of antibody per ChIP experiment was analyzed.
IgG (2 μg/IP) was used as a negative IP control. Quantitative PCR was performed with primers
specific for the promoter of the active genes GAPDH and EIF4A2, used as positive controls, and
for
exon 2 of the inactive myoglobin (MB) gene and the Sat2 satellite repeat, used as negative
controls.
The figure shows the recovery, expressed as a % of input (the relative amount of
immunoprecipitated DNA compared to input DNA after qPCR analysis).
These results are in accordance with the observation that trimethylation of K4 at histone H3 is
associated with the promoters of active genes.
ChIP-seq grade
ChIP for ChIP-seq is performed on sheared chromatin with one of the Diagenode ChIP-seq kits.
Extensive bioinformatic analysis is applied on the obtained data and, if available, the results are compared
to
publicly available data (Encode).
An antibody passes the QC if it shows the expected profile with an overlap of >90% for the top 40 most
significant peaks and a %RIP at least as high as obtained with published data.
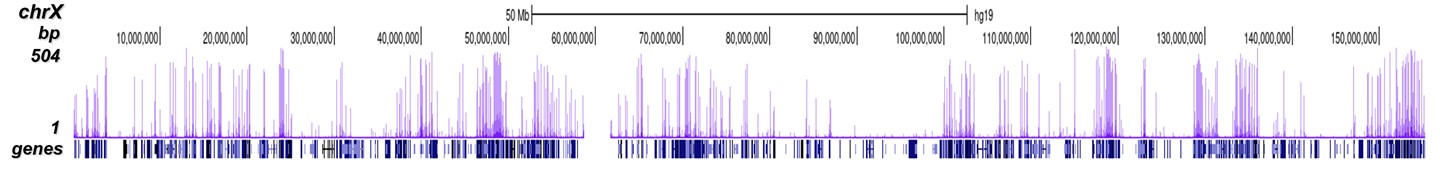
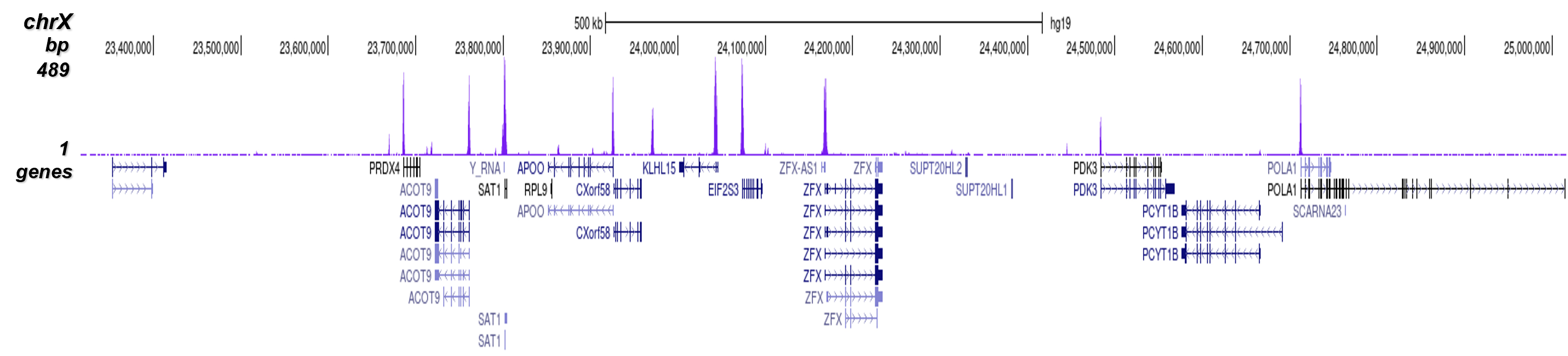
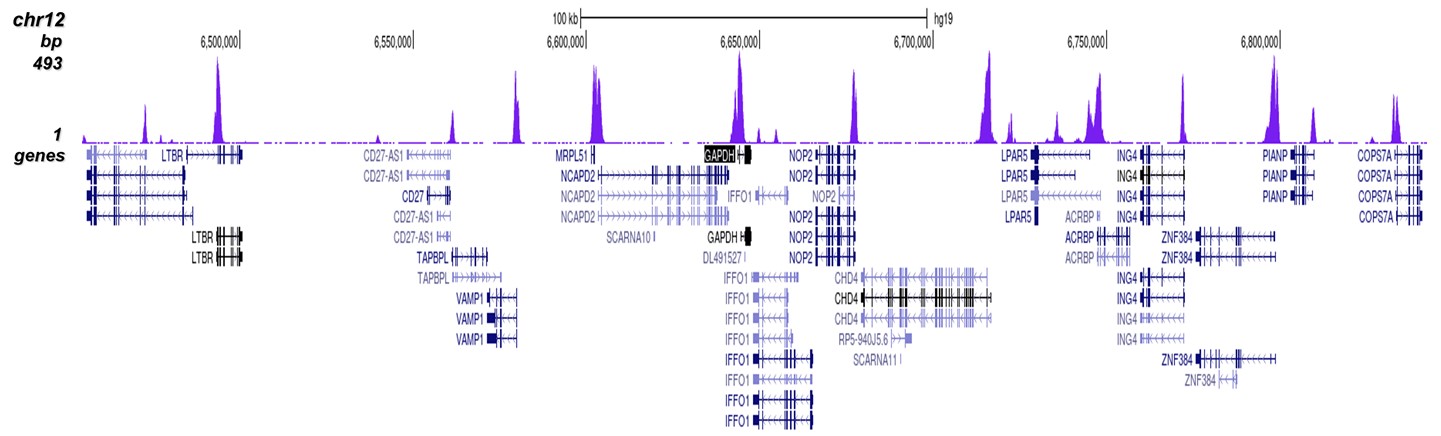
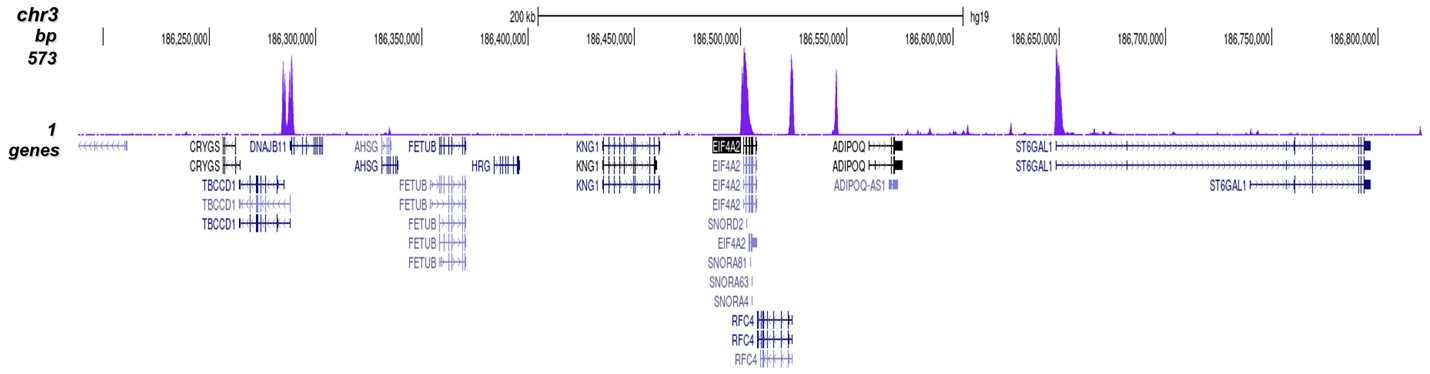
Figure 8. ChIP-seq results obtained with the Diagenode antibody directed against
H3K4me3
ChIP was performed on sheared chromatin from 1 million HeLaS3 cells using 1 μg of the Diagenode
antibody against H3K4me3 (Cat. No. C15410003) as described above.
The IP’d DNA was subsequently analysed on an Illumina Genome Analyzer.
Library preparation, cluster generation and sequencing were performed according to the
manufacturer’s instructions.
The 36 bp tags were aligned to the human genome using the ELAND algorithm.
Figure 7 shows the peak distribution along the complete sequence and a 600 kb region of the
X-chromosome (figure 8A and B) and in two regions surrounding the GAPDH and EIF4A2 positive
control
genes, respectively (figure 8C and D).
These results clearly show an enrichment of the H3K4 trimethylation at the promoters of active
genes.