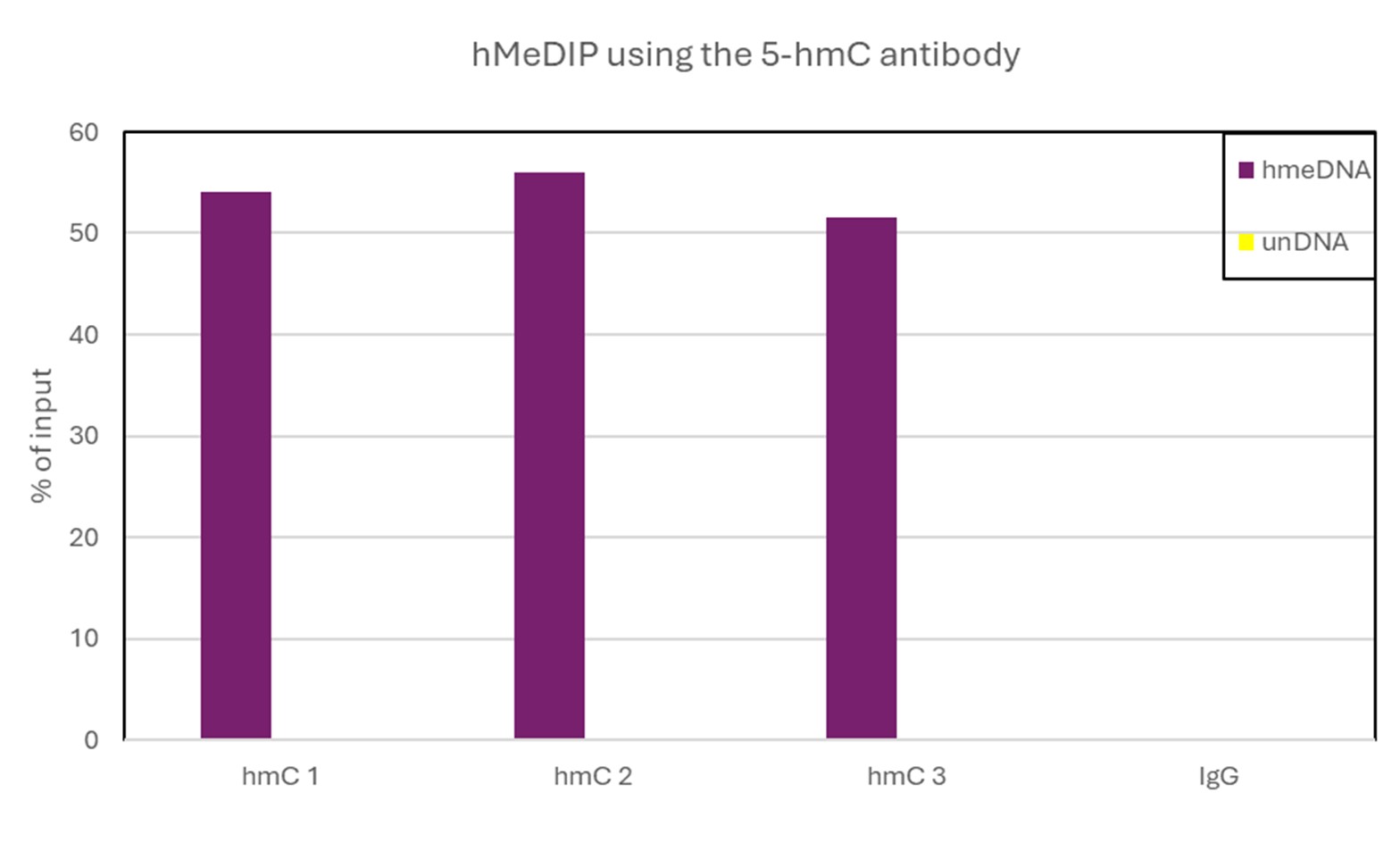
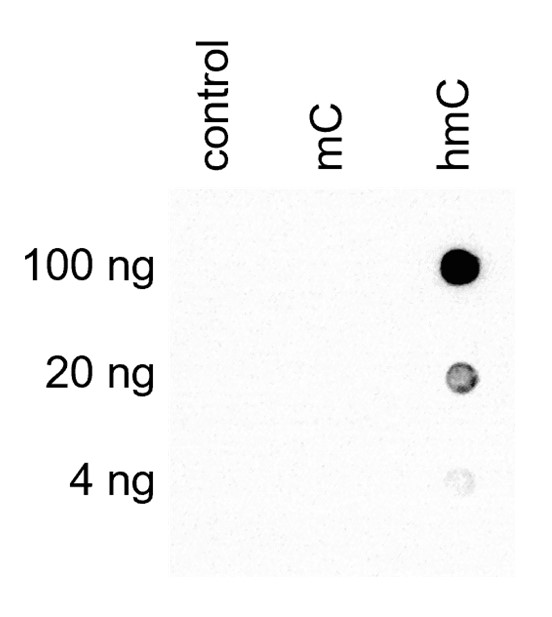
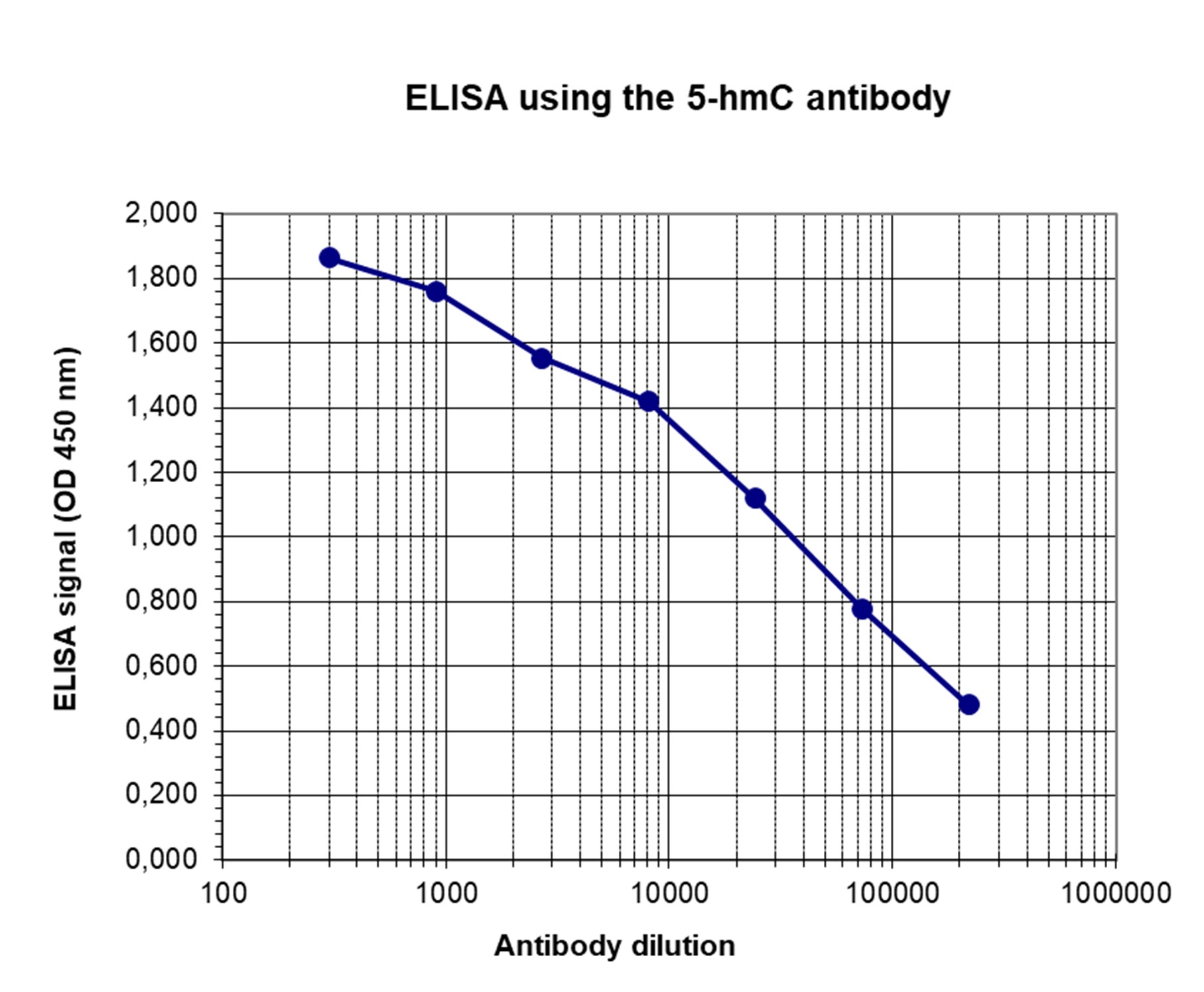
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) Antibody (mouse) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15200200-100 Lot# 002). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in circulating cell-free DNA as a potential diagnostic biomarker for SLE
Xinya Tong et al.
Background SLE is a complex autoimmune disease with heterogeneous manifestations and unpredictable outcomes. Early diagnosis is challenging due to non-specific symptoms, and current treatments only manage symptoms. Epigenetic alternations, including 5-Hydroxymethylome (5hmC) modifications, are important contr... |
RNA m5C oxidation by TET2 regulates chromatin state and leukaemogenesis
Zhongyu Zou et al.
Mutation of tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2 (encoded by TET2) drives myeloid malignancy initiation and progression1,2,3. TET2 deficiency is known to cause a globally opened chromatin state and activation of genes contributing to aberrant haematopoietic stem cell self-renewal4,5. However, the open chromatin obs... |
Bioengineering novel AAV9-mGULO-GT for multi-disease gene therapy:Targeting mutated GULO expression to cure scurvy and brain diseases.
Liu J. et al.
Current clinical breakthroughs in gene therapy have brought adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors to the forefront of gene delivery systems. Vitamin C deficiency due to GULO mutations is a genetic disorder affecting guinea pigs and humans. In our study, we used AAV9-mGULO GT to deliver the mouse GULO gene to guinea p... |
Epigenetic modifier alpha-ketoglutarate modulates aberrant gene bodymethylation and hydroxymethylation marks in diabetic heart.
Dhat R. et al.
BACKGROUND: Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Hyperglycemic myocardial microenvironment significantly alters chromatin architecture and the transcriptome, resulting in aberrant activation of signaling pathways in a diabetic heart. Epigenetic marks play vital roles in tra... |
Gene body DNA hydroxymethylation restricts the magnitude oftranscriptional changes during aging.
Occean J. R. et al.
DNA hydroxymethylation (5hmC) is the most abundant oxidative derivative of DNA methylation (5mC) and is typically enriched at enhancers and gene bodies of transcriptionally active and tissue-specific genes. Although aberrant genomic 5hmC has been implicated in many age-related diseases, the functional role of the mo... |
Relationship between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis based on DNA methylation
Ying Li, Bing Xie, Zhiqiang Jiang, Binbin Yuan
: The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis by analyzing the DNA methylation in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. The cancellous bone specimens were collected from a total of 12 hospitalized patients and divided into the osteoporosis group (OA), the osteoarthrit... |
TET3 prevents terminal differentiation of adult NSCs by a non-catalytic action at Snrpn.
Montalbán-Loro R, Lozano-Ureña A, Ito M, Krueger C, Reik W, Ferguson-Smith AC, Ferrón SR
Ten-eleven-translocation (TET) proteins catalyze DNA hydroxylation, playing an important role in demethylation of DNA in mammals. Remarkably, although hydroxymethylation levels are high in the mouse brain, the potential role of TET proteins in adult neurogenesis is unknown. We show here that a non-catalytic action o... |
miR-30a as Potential Therapeutics by Targeting TET1 through Regulation of Drp-1 Promoter Hydroxymethylation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Zhang S. et al.
Several recent studies have indicated that miR-30a plays critical roles in various biological processes and diseases. However, the mechanism of miR-30a participation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) regulation is ambiguous. Our previous study demonstrated that miR-30a may function as a novel therapeutic target... |
Dynamic interplay between locus-specific DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation regulates distinct biological pathways in prostate carcinogenesis
Kamdar SN, Ho LT, Kron KJ, Isserlin R, van der Kwast T, Zlotta AR, Fleshner NE, Bader G, Bapat B
Background
Despite the significant global loss of DNA hydroxymethylation marks in prostate cancer tissues, the locus-specific role of hydroxymethylation in prostate tumorigenesis is unknown. We characterized hydroxymethylation and methylation marks by performing whole-genome next-generation sequencing in represen... |
Hydroxymethylation of microRNA-365-3p Regulates Nociceptive Behaviors via Kcnh2
Pan Z, Zhang M, Ma T, Xue Z-Y, Li G-F, Hao L-Y, Zhu L-J, Li Y-Q, Ding H-L, Cao J-L
DNA 5-hydroxylmethylcytosine (5hmC) catalyzed by ten-eleven translocation methylcytosine dioxygenase (TET) occurs abundantly in neurons of mammals. However, the in vivo causal link between TET dysregulation and nociceptive modulation has not been established. Here, we found that spinal TET1 and TET3 were significant... |
The dual specificity phosphatase 2 gene is hypermethylated in human cancer and regulated by epigenetic mechanisms
Tanja Haag, Antje M. Richter, Martin B. Schneider, Adriana P. Jiménez and Reinhard H. Dammann
Dual specificity phosphatases are a class of tumor-associated proteins involved in the negative regulation of the MAP kinase pathway. Downregulation of the dual specificity phosphatase 2 (DUSP2) has been reported in cancer. Epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes by abnormal promoter methylation is ... |
Single-Base Resolution Analysis of 5-Formyl and 5-Carboxyl Cytosine Reveals Promoter DNA Methylation Dynamics.
Neri F, Incarnato D, Krepelova A, Rapelli S, Anselmi F, Parlato C, Medana C, Dal Bello F, Oliviero S
Ten eleven translocation (Tet) proteins oxidize 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC). 5fC and 5caC can be further excised by thymine-DNA glycosylase (Tdg). Here, we present a genome-wide approach, named methylation-assisted bisulfite seq... |
Dynamic reprogramming of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine during early porcine embryogenesis.
Cao Z, Zhou N, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wu R, Li Y, Zhang Y, Li N
DNA active demethylation is an important epigenetic phenomenon observed in porcine zygotes, yet its molecular origins are unknown. Our results show that 5-methylcytosine (5mC) converts into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) during the first cell cycle in porcine in vivo fertilization (IVV), IVF, and SCNT embryos, but n... |
Vitamin C induces Tet-dependent DNA demethylation and a blastocyst-like state in ES cells.
Blaschke K, Ebata KT, Karimi MM, Zepeda-Martínez JA, Goyal P, Mahapatra S, Tam A, Laird DJ, Hirst M, Rao A, Lorincz MC, Ramalho-Santos M
DNA methylation is a heritable epigenetic modification involved in gene silencing, imprinting, and the suppression of retrotransposons. Global DNA demethylation occurs in the early embryo and the germ line, and may be mediated by Tet (ten eleven translocation) enzymes, which convert 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydro... |
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine is associated with enhancers and gene bodies in human embryonic stem cells.
Stroud H, Feng S, Morey Kinney S, Pradhan S, Jacobsen SE
BACKGROUND: 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) was recently found to be abundantly present in certain cell types, including embryonic stem cells. There is growing evidence that TET proteins, which convert 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5hmC, play important biological roles. To further understand the function of 5hmC, an anal... |
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the mammalian zygote is linked with epigenetic reprogramming.
Wossidlo M, Nakamura T, Lepikhov K, Marques CJ, Zakhartchenko V, Boiani M, Arand J, Nakano T, Reik W, Walter J
The epigenomes of early mammalian embryos are extensively reprogrammed to acquire a totipotent developmental potential. A major initial event in this reprogramming is the active loss/demethylation of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in the zygote. Here, we report on findings that link this active demethylation to molecular me... |