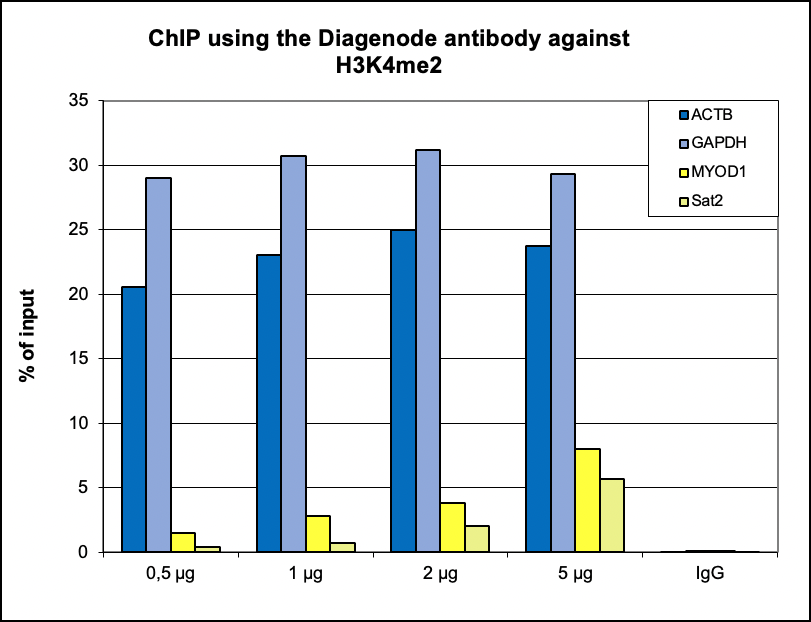
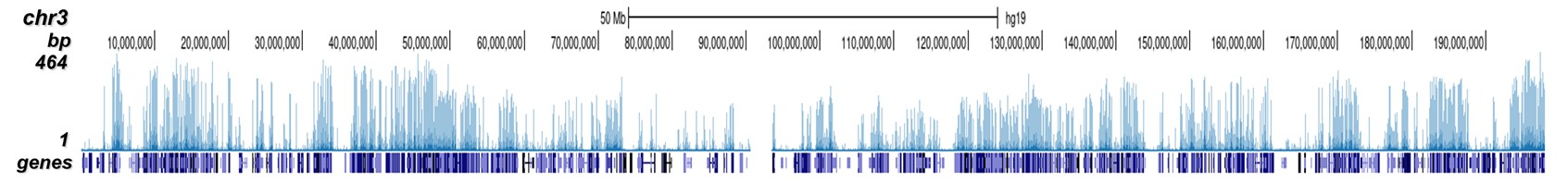
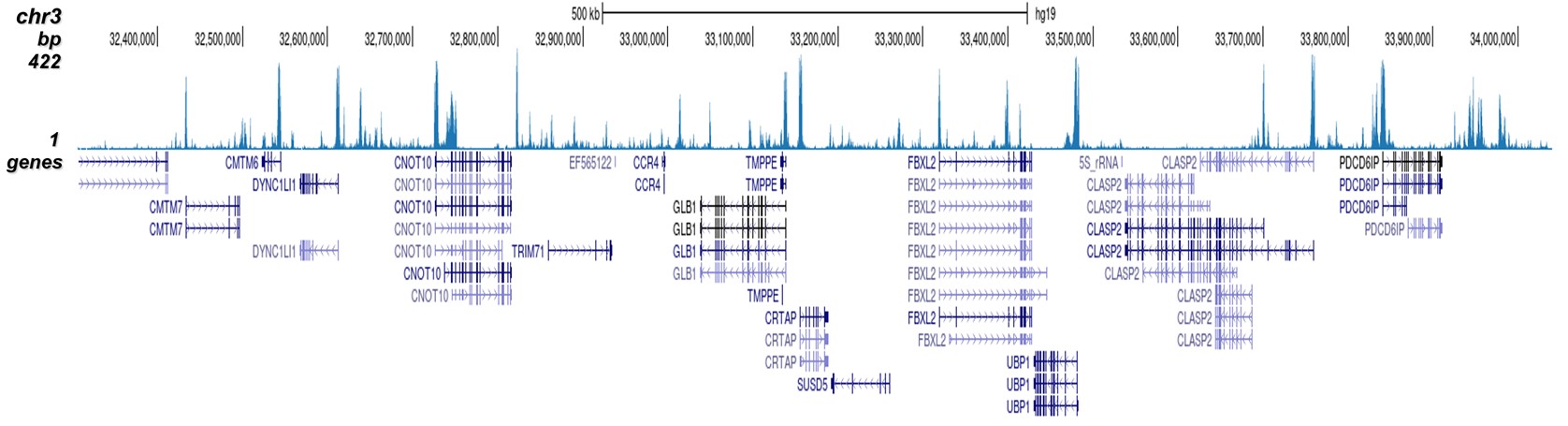
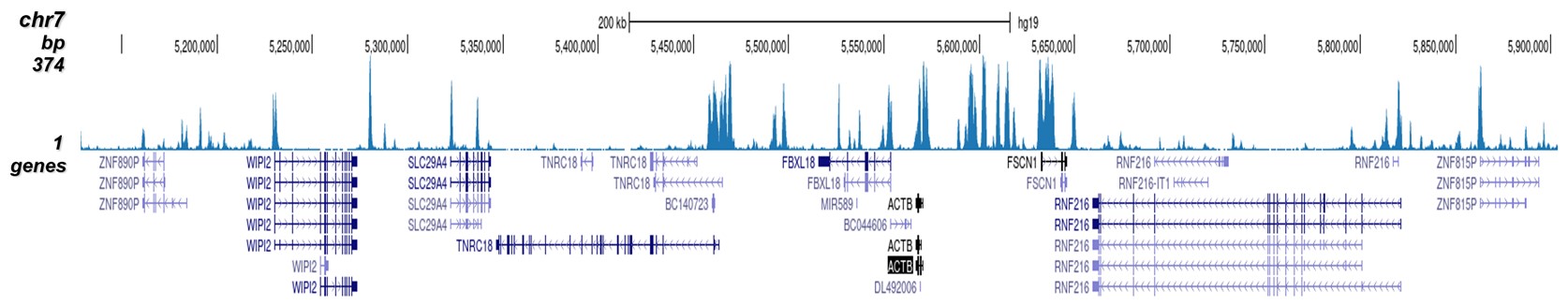
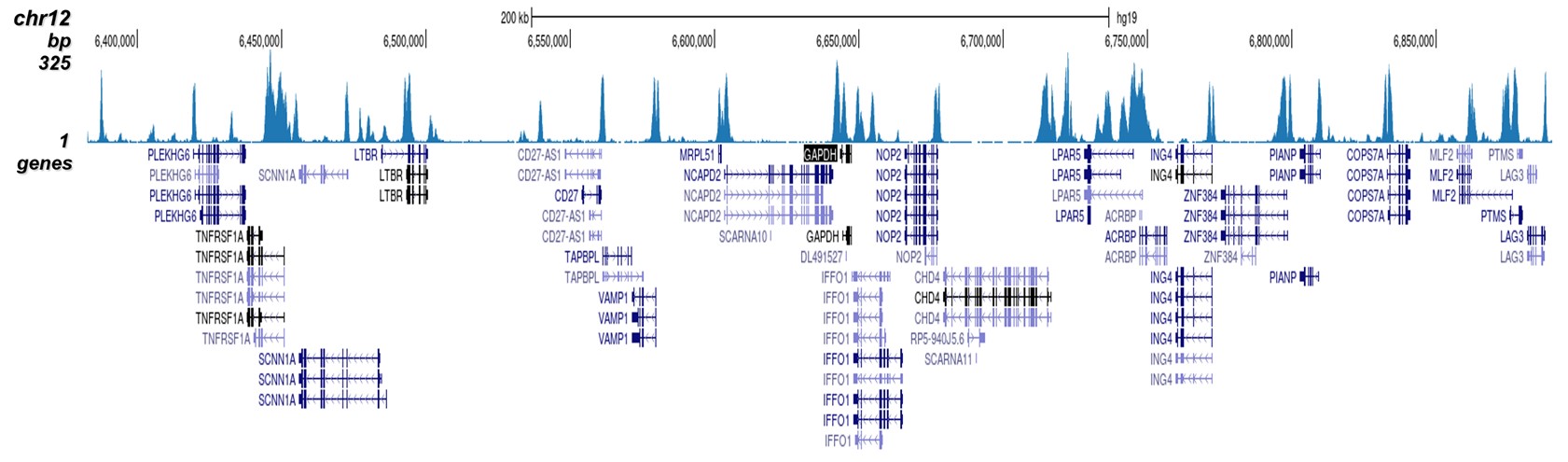
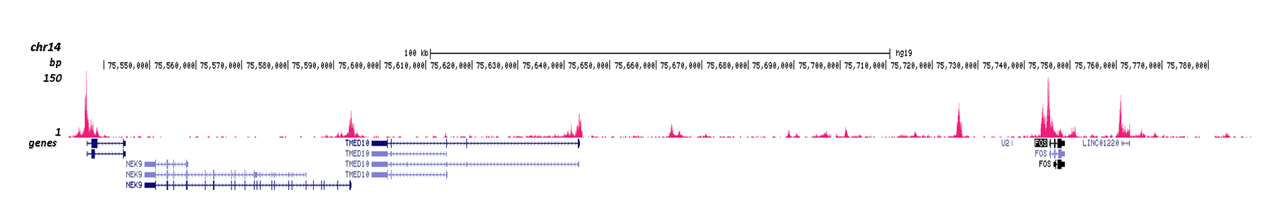
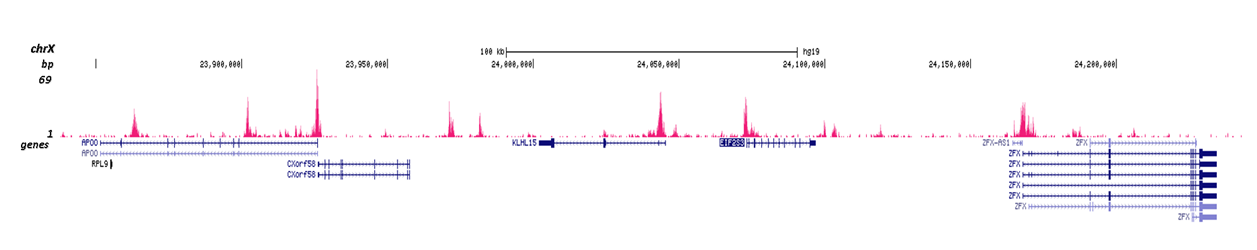
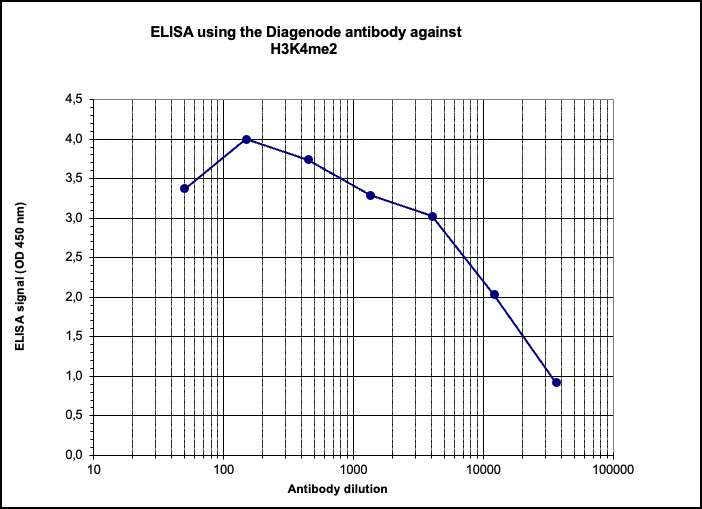
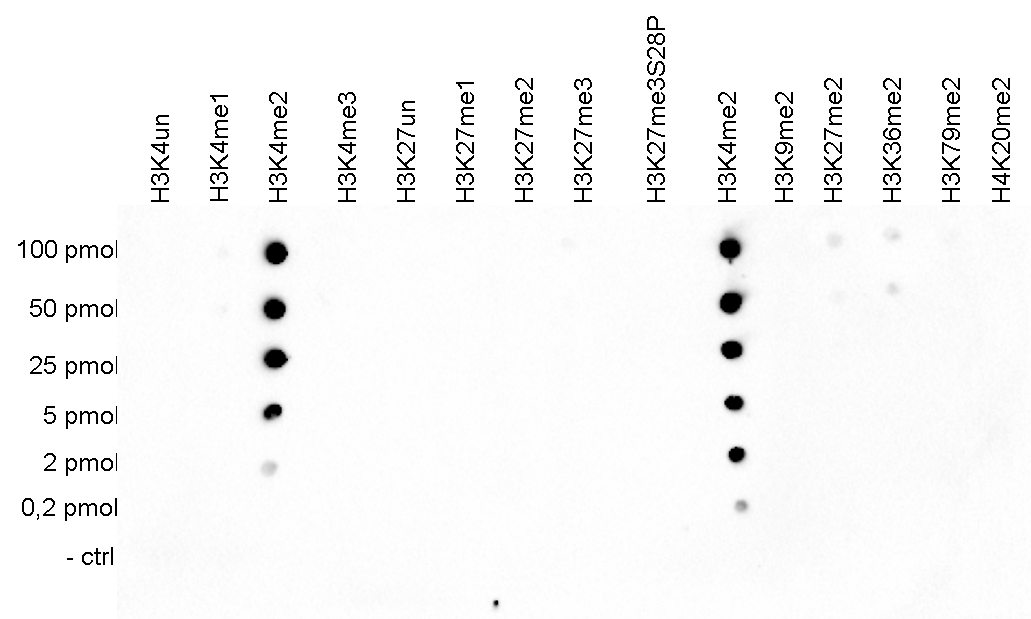
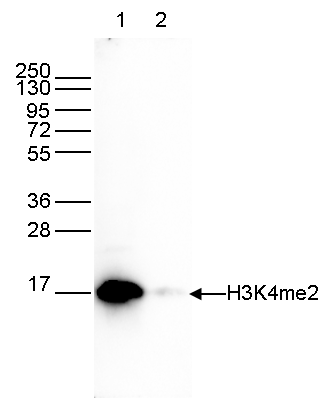
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K4me2 Antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410035 Lot# A936-0023). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Plasma cell-free DNA chromatin immunoprecipitation profiling depicts phenotypic and clinical heterogeneity in advanced prostate cancer
Sipola, Joonatan et al.
Cell phenotype underlies prostate cancer presentation and treatment resistance and can be regulated by epigenomic features. However, the osteotropic tendency of prostate cancer limits access to metastatic tissue, meaning most prior insights into prostate cancer chromatin biology are from preclinical models that do n... |
Epigenomic signatures of sarcomatoid differentiation to guide the treatment of renal cell carcinoma
Talal El Zarif et al.
Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation (sRCC) is associated with poor survival and a heightened response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Two major barriers to improving outcomes for sRCC are the limited understanding of its gene regulatory programs and the low diagnostic yield of tumor biopsie... |
Epigenomic charting and functional annotation of risk loci in renal cellcarcinoma.
Nassar A. H. et al.
While the mutational and transcriptional landscapes of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) are well-known, the epigenome is poorly understood. We characterize the epigenome of clear cell (ccRCC), papillary (pRCC), and chromophobe RCC (chRCC) by using ChIP-seq, ATAC-Seq, RNA-seq, and SNP arrays. We integrate 153 individual da... |
Heterocycle-containing tranylcypromine derivatives endowed with highanti-LSD1 activity.
Fioravanti R. et al.
As regioisomers/bioisosteres of , a 4-phenylbenzamide tranylcypromine (TCP) derivative previously disclosed by us, we report here the synthesis and biological evaluation of some (hetero)arylbenzoylamino TCP derivatives -, in which the 4-phenyl moiety of was shifted at the benzamide C3 position or replaced by 2- or 3... |
DNA sequence and chromatin modifiers cooperate to confer epigeneticbistability at imprinting control regions.
Butz S. et al.
Genomic imprinting is regulated by parental-specific DNA methylation of imprinting control regions (ICRs). Despite an identical DNA sequence, ICRs can exist in two distinct epigenetic states that are memorized throughout unlimited cell divisions and reset during germline formation. Here, we systematically study the ... |
Histone lysine demethylase inhibition reprograms prostate cancermetabolism and mechanics.
Chianese Ugo and Papulino Chiara and Passaro Eugenia andEvers Tom Mj and Babaei Mehrad and Toraldo Antonella andDe Marchi Tommaso and Niméus Emma and Carafa Vincenzo andNicoletti Maria Maddalena and Del Gaudio Nunzio andIaccarino Nunzia an
OBJECTIVE: Aberrant activity of androgen receptor (AR) is the primary cause underlying development and progression of prostate cancer (PCa) and castration-resistant PCa (CRPC). Androgen signaling regulates gene transcription and lipid metabolism, facilitating tumor growth and therapy resistance in early and advanced... |
The CpG Island-Binding Protein SAMD1 Contributes to anUnfavorable Gene Signature in HepG2 Hepatocellular CarcinomaCells.
Simon C. et al.
The unmethylated CpG island-binding protein SAMD1 is upregulated in many human cancer types, but its cancer-related role has not yet been investigated. Here, we used the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 as a cancer model and investigated the cellular and transcriptional roles of SAMD1 using ChIP-Seq and RNA-... |
The SAM domain-containing protein 1 (SAMD1) acts as a repressivechromatin regulator at unmethylated CpG islands
Stielow B. et al.
CpG islands (CGIs) are key regulatory DNA elements at most promoters, but how they influence the chromatin status and transcription remains elusive. Here, we identify and characterize SAMD1 (SAM domain-containing protein 1) as an unmethylated CGI-binding protein. SAMD1 has an atypical winged-helix domain that direct... |
Inhibition of Histone Demethylases LSD1 and UTX Regulates ERα Signaling in Breast Cancer.
Benedetti R, Dell'Aversana C, De Marchi T, Rotili D, Liu NQ, Novakovic B, Boccella S, Di Maro S, Cosconati S, Baldi A, Niméus E, Schultz J, Höglund U, Maione S, Papulino C, Chianese U, Iovino F, Federico A, Mai A, Stunnenberg HG, Nebbioso A, Altucci L
In breast cancer, Lysine-specific demethylase-1 (LSD1) and other lysine demethylases (KDMs), such as Lysine-specific demethylase 6A also known as Ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat, X chromosome (UTX), are co-expressed and co-localize with estrogen receptors (ERs), suggesting the potential use of hybr... |
ChIP-seq of plasma cell-free nucleosomes identifies cell-of-origin geneexpression programs
Sadeh, Ronen and Sharkia, Israa and Fialkoff, Gavriel and Rahat, Ayelet andGutin, Jenia and Chappleboim, Alon and Nitzan, Mor and Fox-Fisher, Ilanaand Neiman, Daniel and Meler, Guy and Kamari, Zahala and Yaish, Dayana andPeretz, Tamar and Hubert, Ayala
Blood cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is derived from fragmented chromatin in dying cells. As such, it remains associated with histones that may retain the covalent modifications present in the cell of origin. Until now this rich epigenetic information carried by cell-free nucleosomes has not been explored at the genome level... |
The Wnt-Driven Mll1 Epigenome Regulates Salivary Gland and Head and Neck Cancer.
Zhu Q, Fang L, Heuberger J, Kranz A, Schipper J, Scheckenbach K, Vidal RO, Sunaga-Franze DY, Müller M, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Sauer S, Birchmeier W
We identified a regulatory system that acts downstream of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in salivary gland and head and neck carcinomas. We show in a mouse tumor model of K14-Cre-induced Wnt/β-catenin gain-of-function and Bmpr1a loss-of-function mutations that tumor-propagating cells exhibit increased Mll1 activi... |
Histone variant H2A.Z deposition and acetylation directs the canonical Notch signaling response.
Giaimo BD, Ferrante F, Vallejo DM, Hein K, Gutierrez-Perez I, Nist A, Stiewe T, Mittler G, Herold S, Zimmermann T, Bartkuhn M, Schwarz P, Oswald F, Dominguez M, Borggrefe T
A fundamental as yet incompletely understood feature of Notch signal transduction is a transcriptional shift from repression to activation that depends on chromatin regulation mediated by transcription factor RBP-J and associated cofactors. Incorporation of histone variants alter the functional properties of chromat... |
The Arabidopsis LDL1/2-HDA6 histone modification complex is functionally associated with CCA1/LHY in regulation of circadian clock genes.
Hung FY, Chen FF, Li C, Chen C, Lai YC, Chen JH, Cui Y, Wu K
In Arabidopsis, the circadian clock central oscillator genes are important cellular components to generate and maintain circadian rhythms. There is a negative feedback loop between the morning expressed CCA1 (CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1)/LHY (LATE ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL) and evening expressed TOC1 (TIMING OF CAB EXPRE... |
SETBP1 induces transcription of a network of development genes by acting as an epigenetic hub.
Piazza R, Magistroni V, Redaelli S, Mauri M, Massimino L, Sessa A, Peronaci M, Lalowski M, Soliymani R, Mezzatesta C, Pirola A, Banfi F, Rubio A, Rea D, Stagno F, Usala E, Martino B, Campiotti L, Merli M, Passamonti F, Onida F, Morotti A, Pavesi F, Bregni
SETBP1 variants occur as somatic mutations in several hematological malignancies such as atypical chronic myeloid leukemia and as de novo germline mutations in the Schinzel-Giedion syndrome. Here we show that SETBP1 binds to gDNA in AT-rich promoter regions, causing activation of gene expression through recruitment ... |
A CLK3-HMGA2 Alternative Splicing Axis Impacts Human Hematopoietic Stem Cell Molecular Identity throughout Development.
Cesana M, Guo MH, Cacchiarelli D, Wahlster L, Barragan J, Doulatov S, Vo LT, Salvatori B, Trapnell C, Clement K, Cahan P, Tsanov KM, Sousa PM, Tazon-Vega B, Bolondi A, Giorgi FM, Califano A, Rinn JL, Meissner A, Hirschhorn JN, Daley GQ
While gene expression dynamics have been extensively cataloged during hematopoietic differentiation in the adult, less is known about transcriptome diversity of human hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) during development. To characterize transcriptional and post-transcriptional changes in HSCs during development, we le... |
Overexpression of histone demethylase Fbxl10 leads to enhanced migration in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.
Rohde M. et al.
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing, immune responses and invasive tumors all require the orchestrated movement of cells to specific locations. Histone demethylase proteins alter transcription ... |
A novel microscopy-based high-throughput screening method to identify proteins that regulate global histone modification levels.
Baas R, Lelieveld D, van Teeffelen H, Lijnzaad P, Castelijns B, van Schaik FM, Vermeulen M, Egan DA, Timmers HT, de Graaf P
Posttranslational modifications of histones play an important role in the regulation of gene expression and chromatin structure in eukaryotes. The balance between chromatin factors depositing (writers) and removing (erasers) histone marks regulates the steady-state levels of chromatin modifications. Here we describe... |
The H3K4me3 histone demethylase Fbxl10 is a regulator of chemokine expression, cellular morphology and the metabolome of fibroblasts
Janzer A, Stamm K, Becker A, Zimmer A, Buettner R, Kirfel J
Fbxl10 (Jhdm1b/Kdm2b) is a conserved and ubiquitously expressed member of the JHDM (JmjC-domain-containing histone demethy-lase) family. Fbxl10 was implicated in the demethylation of H3K4me3 or H3K36me2 thereby removing active chromatin marks and inhibiting gene transcription. Apart from the JmjC domain, Fbxl10 cons... |