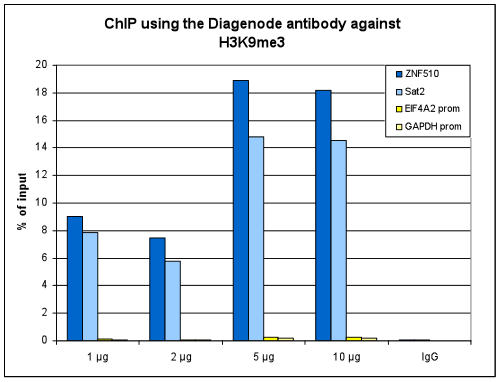
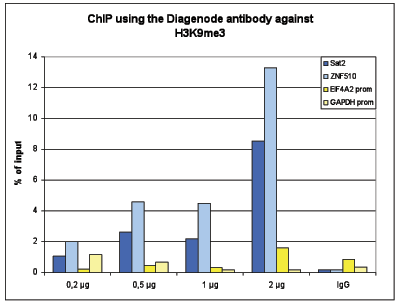
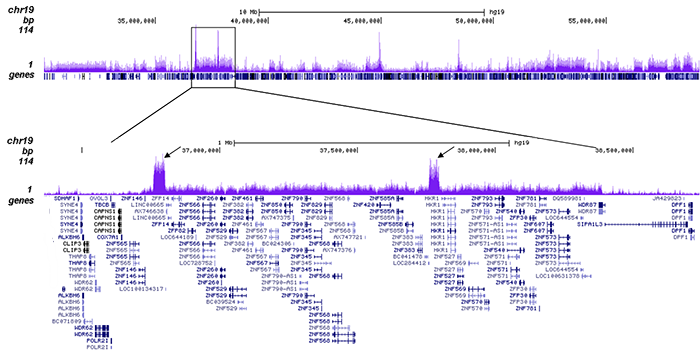
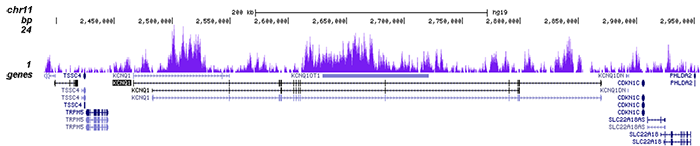
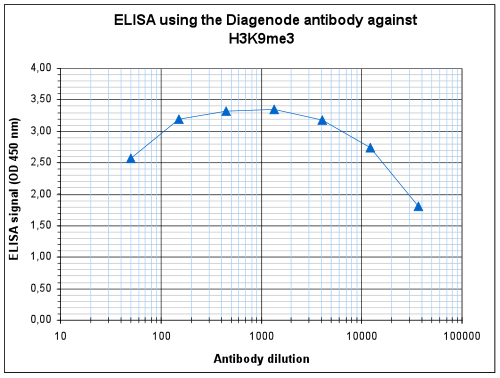
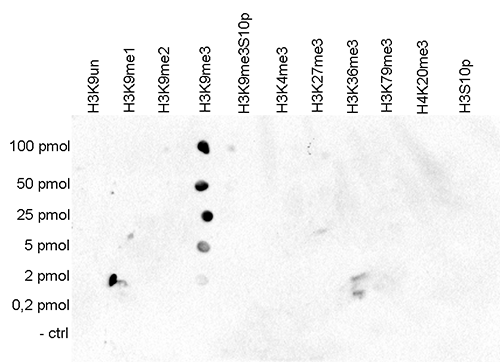
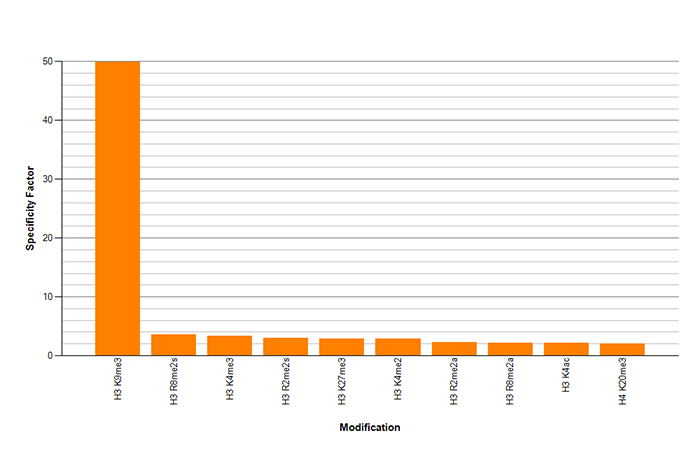
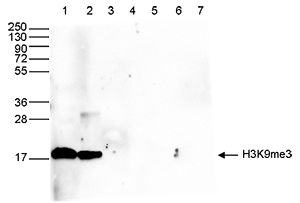
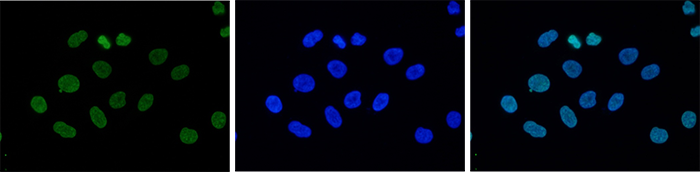
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K9me3 Antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410193-10 Lot# A0219P). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Coordinated control of genome-nuclear lamina interactions by topoisomerase 2B and lamin B receptor
van Schaik, Tom et al.
Lamina-associated domains (LADs) are megabase-sized genomic regions anchored to the nuclear lamina (NL). Factors controlling the interactions of the genome with the NL have largely remained elusive. Here, we identified DNA topoisomerase 2 beta (TOP2B) as a regulator of these interactions. TOP2B binds predominant... |
The senolytic cocktail, dasatinib and quercetin, impacts the chromatin structure of both young and senescent vascular smooth muscle cells
Agnieszka Gadecka et al.
One promising strategy to alleviate aging symptoms is the treatment with senolytics that is compounds which selectively eliminate senescent cells. Some therapies aim to reduce symptoms of cellular senescence without senescent cell eradication (senomorphic activity). However, senotherapies raise many questions concer... |
MECOM is a master repressor of myeloid differentiation through dose control of CEBPA in acute myeloid leukemia
Dorien Pastoors et al.
Enhancer translocations, due to 3q26 rearrangements, drive out-of-context MECOM expression in an aggressive subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Direct depletion of MECOM using an endogenous auxin-inducible degron immediately upregulates expression of myeloid differentiation factor CEBPA. MECOM depletion is also... |
Nuclear localization of MTHFD2 is required for correct mitosis progression
Natalia Pardo-Lorente et al.
Subcellular compartmentalization of metabolic enzymes establishes a unique metabolic environment that elicits specific cellular functions. Indeed, the nuclear translocation of certain metabolic enzymes is required for epigenetic regulation and gene expression control. Here, we show that the nuclear localization of t... |
Claudin-1 as a potential marker of stress-induced premature senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells
Agnieszka Gadecka et al.
Cellular senescence, a permanent state of cell cycle arrest, can result either from external stress and is then called stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS), or from the exhaustion of cell division potential giving rise to replicative senescence (RS). Despite numerous biomarkers distinguishing SIPS from RS rema... |
RNA sequestration in P-bodies sustains myeloid leukaemia
Srikanth Kodali et al.
Post-transcriptional mechanisms are fundamental safeguards of progenitor cell identity and are often dysregulated in cancer. Here, we identified regulators of P-bodies as crucial vulnerabilities in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) through genome-wide CRISPR screens in normal and malignant haematopoietic progenitors. We... |
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment
Perez R. F. at al.
Aging involves the deterioration of organismal function, leading to the emergence of multiple pathologies. Environmental stimuli, including lifestyle, can influence the trajectory of this process and may be used as tools in the pursuit of healthy aging. To evaluate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this context, ... |
In vitro production of cat-restricted Toxoplasma pre-sexual stages
Antunes, A.V. et al.
Sexual reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii, confined to the felid gut, remains largely uncharted owing to ethical concerns regarding the use of cats as model organisms. Chromatin modifiers dictate the developmental fate of the parasite during its multistage life cycle, but their targeting to stage-specific cistro... |
Alterations in the hepatocyte epigenetic landscape in steatosis.
Maji Ranjan K. et al.
Fatty liver disease or the accumulation of fat in the liver, has been reported to affect the global population. This comes with an increased risk for the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Yet, little is known about the effects of a diet containing high fat and alcohol towards epigenet... |
Chromatin profiling identifies transcriptional readthrough as a conservedmechanism for piRNA biogenesis in mosquitoes.
Qu J. et al.
The piRNA pathway in mosquitoes differs substantially from other model organisms, with an expanded PIWI gene family and functions in antiviral defense. Here, we define core piRNA clusters as genomic loci that show ubiquitous piRNA expression in both somatic and germline tissues. These core piRNA clusters are enriche... |
Epigenetic dosage identifies two major and functionally distinct beta cells ubtypes.
Dror E.et al.
The mechanisms that specify and stabilize cell subtypes remain poorly understood. Here, we identify two major subtypes of pancreatic β cells based on histone mark heterogeneity (beta HI and beta LO). Beta HI cells exhibit 4-fold higher levels of H3K27me3, distinct chromatin organization and compaction, a... |
Species-specific regulation of XIST by the JPX/FTX orthologs.
Rosspopoff O. et al.
X chromosome inactivation (XCI) is an essential process, yet it initiates with remarkable diversity in various mammalian species. XIST, the main trigger of XCI, is controlled in the mouse by an interplay of lncRNA genes (LRGs), some of which evolved concomitantly to XIST and have orthologues across all placental mam... |
Noncanonical regulation of imprinted gene Igf2 by amyloid-beta 1-42 inAlzheimer's disease.
Fertan E. et al.
Reduced insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) levels in Alzheimer's disease (AD) may be the mechanism relating age-related metabolic disorders to dementia. Since Igf2 is an imprinted gene, we examined age and sex differences in the relationship between amyloid-beta 1-42 (Aβ) accumulation and epigenetic regulation... |
Histone remodeling reflects conserved mechanisms of bovine and humanpreimplantation development.
Zhou C. et al.
How histone modifications regulate changes in gene expression during preimplantation development in any species remains poorly understood. Using CUT\&Tag to overcome limiting amounts of biological material, we profiled two activating (H3K4me3 and H3K27ac) and two repressive (H3K9me3 and H3K27me3) marks in bovine... |
Dietary methionine starvation impairs acute myeloid leukemia progression.
Cunningham A. et al.
Targeting altered tumor cell metabolism might provide an attractive opportunity for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). An amino acid dropout screen on primary leukemic stem cells and progenitor populations revealed a number of amino acid dependencies, of which methionine was one of the strongest. By using v... |
Dominant role of DNA methylation over H3K9me3 for IAP silencingin endoderm.
Wang Z. et al.
Silencing of endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) is largely mediated by repressive chromatin modifications H3K9me3 and DNA methylation. On ERVs, these modifications are mainly deposited by the histone methyltransferase Setdb1 and by the maintenance DNA methyltransferase Dnmt1. Knock-out of either Setdb1 or Dnmt1 leads to... |
bESCs from cloned embryos do not retain transcriptomic or epigenetic memory from somatic donor cells.
Navarro M. et al.
Embryonic stem cells (ESC) indefinitely maintain the pluripotent state of the blastocyst epiblast. Stem cells are invaluable for studying development and lineage commitment, and in livestock they constitute a useful tool for genomic improvement and in vitro breeding programs. Although these cells have been recently ... |
Epigenetic Mechanisms Mediating Cell State Transitions in Chondrocytes
Wuelling M. et al.
Epigenetic modifications play critical roles in regulating cell lineage differentiation, but the epigenetic mechanisms guiding specific differentiation steps within a cell lineage have rarely been investigated. To decipher such mechanisms, we used the defined transition from proliferating (PC) into hypertrophic chon... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple Myeloma
Elina Alaterre et al.
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have been widely used to understand themolecular processes that drive MM biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape of MM wouldadvance our un... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple
Myeloma
Alaterre, Elina and Ovejero, Sara and Herviou, Laurie and de
Boussac, Hugues and Papadopoulos, Giorgio and Kulis, Marta and
Boireau, Stéphanie and Robert, Nicolas and Requirand, Guilhem
and Bruyer, Angélique and Cartron, Guillaume and Vincent,
Laure and M
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have
been widely used to understand the molecular processes that drive MM
biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,
progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the
epigenetic landscape of MM would advance our... |
Enhanced targeted DNA methylation of the CMV and endogenous promoterswith dCas9-DNMT3A3L entails distinct subsequent histonemodification changes in CHO cells.
Marx Nicolas et al.
With the emergence of new CRISPR/dCas9 tools that enable site specific modulation of DNA methylation and histone modifications, more detailed investigations of the contribution of epigenetic regulation to the precise phenotype of cells in culture, including recombinant production subclones, is now possible. These al... |
Sarcomere function activates a p53-dependent DNA damage response that promotes polyploidization and limits in vivo cell engraftment.
Pettinato, Anthony M. et al.
Human cardiac regeneration is limited by low cardiomyocyte replicative rates and progressive polyploidization by unclear mechanisms. To study this process, we engineer a human cardiomyocyte model to track replication and polyploidization using fluorescently tagged cyclin B1 and cardiac troponin T. Using time-lapse i... |
Androgen and glucocorticoid receptor direct distinct transcriptionalprograms by receptor-specific and shared DNA binding sites.
Kulik, Marina et al.
The glucocorticoid (GR) and androgen (AR) receptors execute unique functions in vivo, yet have nearly identical DNA binding specificities. To identify mechanisms that facilitate functional diversification among these transcription factor paralogs, we studied them in an equivalent cellular context. Analysis of chroma... |
Environmental enrichment induces epigenomic and genome organization changesrelevant for cognitive function
Espeso-Gil, S. et al.
In early development, the environment triggers mnemonic epigenomic programs resulting in memory and learning experiences to confer cognitive phenotypes into adulthood. To uncover how environmental stimulation impacts the epigenome and genome organization, we used the paradigm of environmental enrichment (EE) in youn... |
TRF2 Mediates Replication Initiation within Human Telomeres to PreventTelomere Dysfunction.
Drosopoulos, William C and Deng, Zhong and Twayana, Shyam and Kosiyatrakul,Settapong T and Vladimirova, Olga and Lieberman, Paul M and Schildkraut,Carl L
The telomeric shelterin protein telomeric repeat-binding factor 2 (TRF2) recruits origin recognition complex (ORC) proteins, the foundational building blocks of DNA replication origins, to telomeres. We seek to determine whether TRF2-recruited ORC proteins give rise to functional origins in telomere repeat tracts. W... |