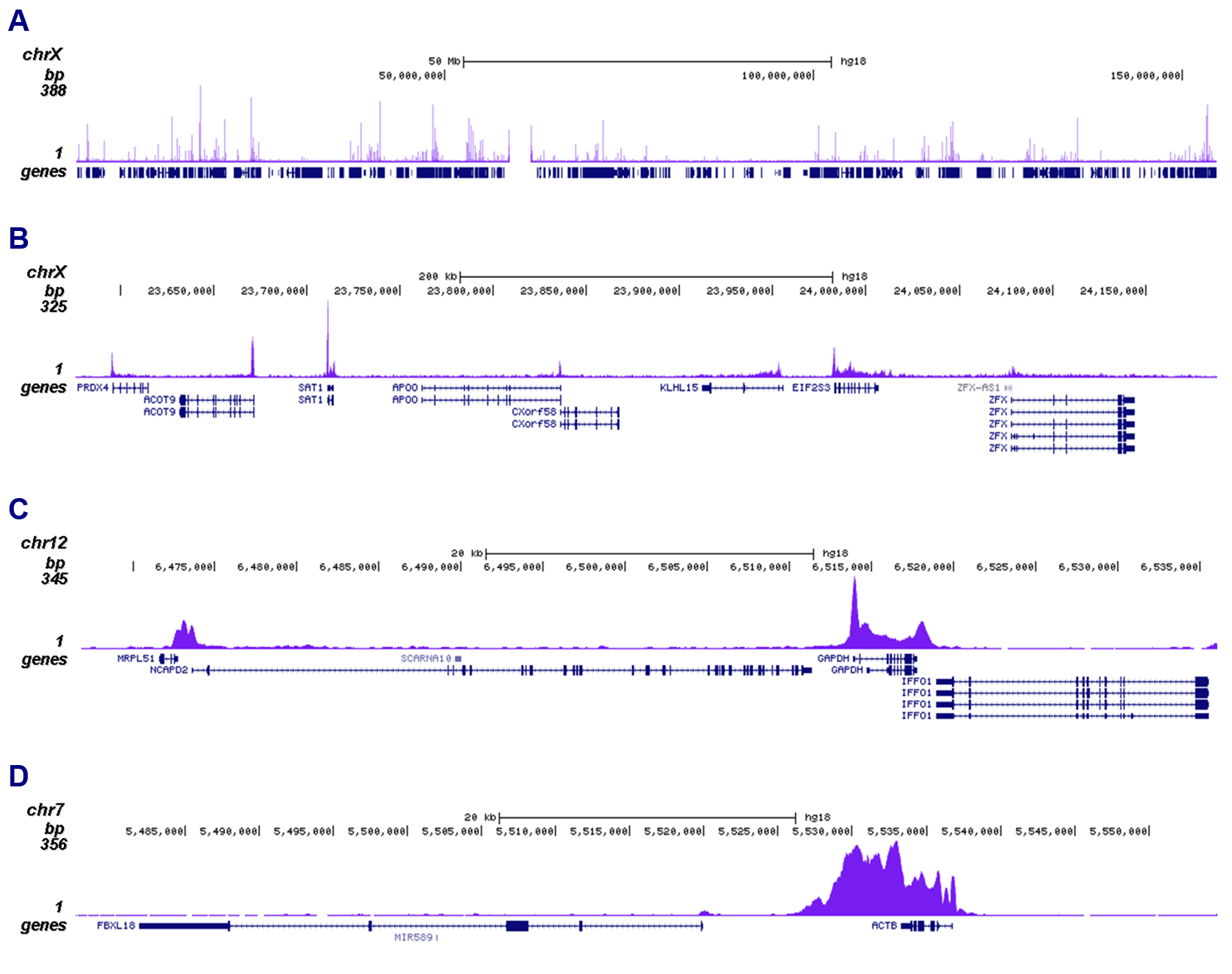
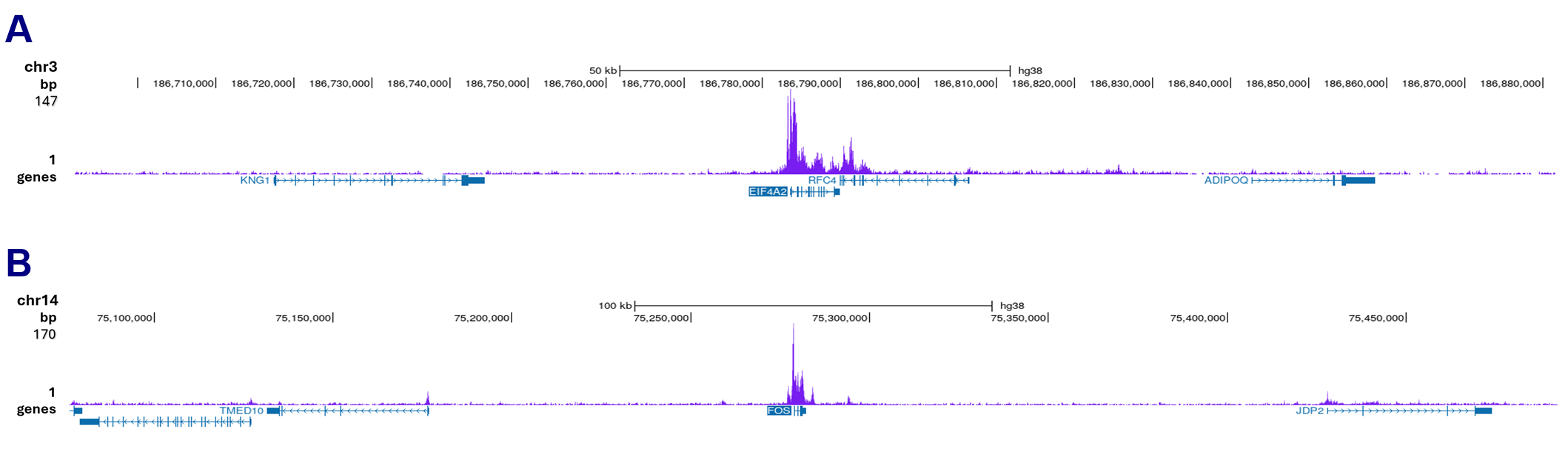
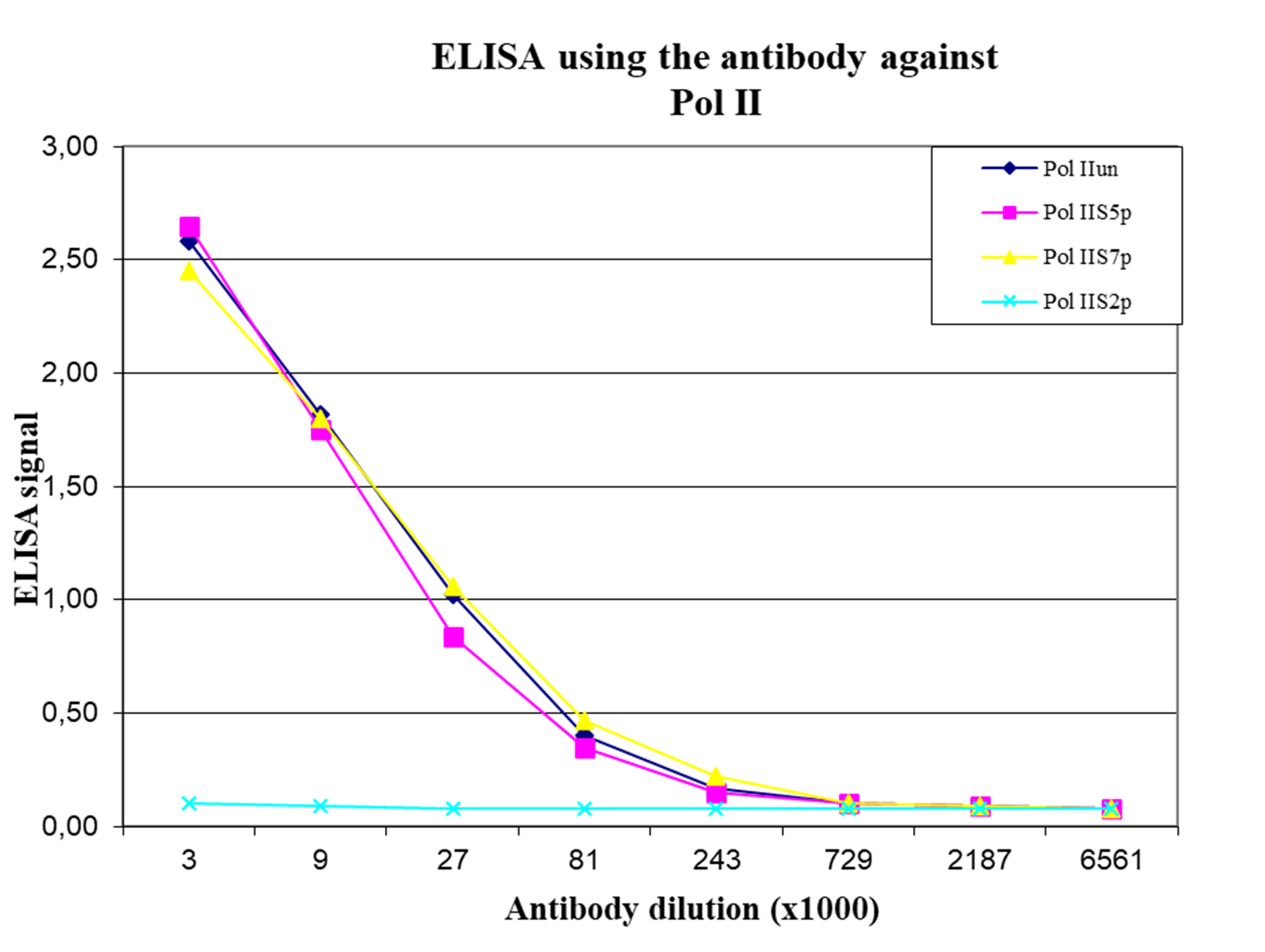
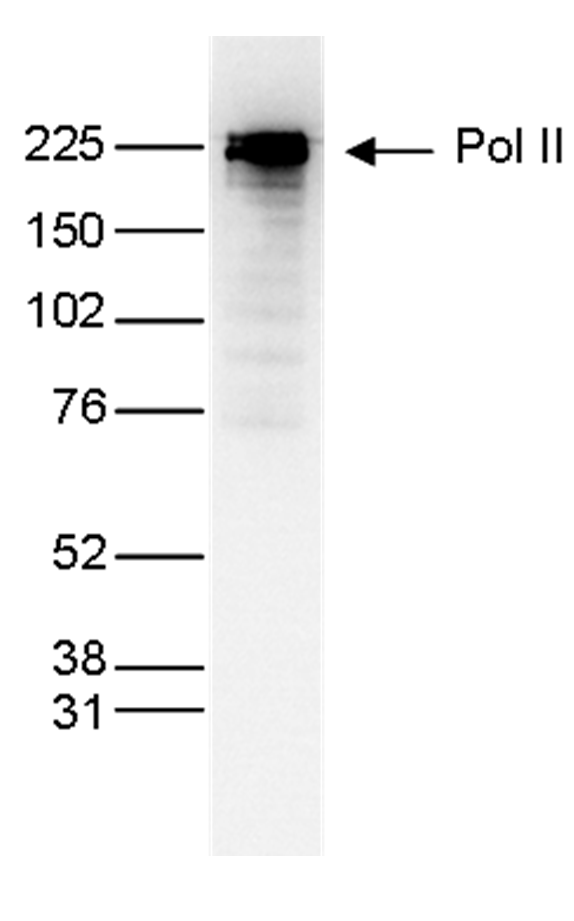
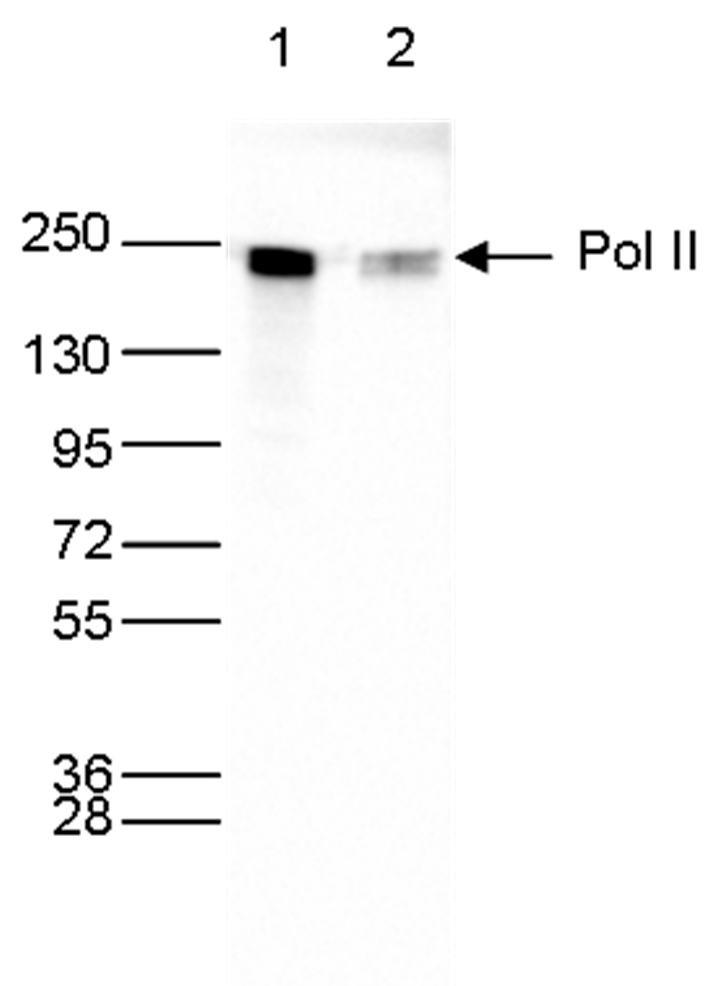
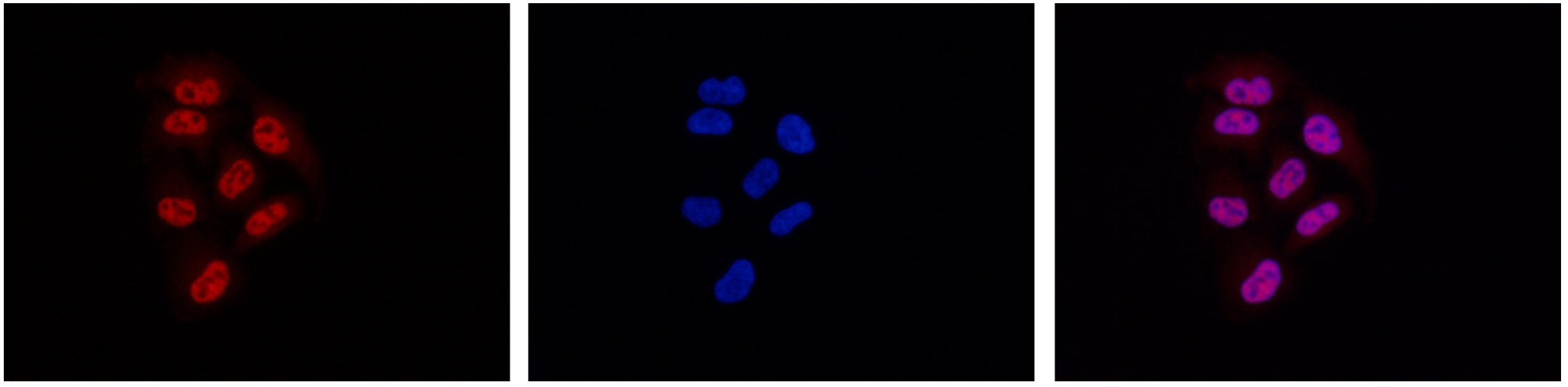
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: Pol II Antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15200004 Lot# 001-15). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Sox8 is essential for vertebrate gastrulation
Moreira, Sofia et al.
Gastrulation is a fundamental developmental process during which germ layers are formed and the body axes are defined by the precise orchestration of cell movements and fate specification. Here, we identify the SOXE transcription factor Sox8 as a pivotal regulator of Xenopus laevis gastrulation. We show that Sox8 ... |
HIRA supports hepatitis B virus minichromosome establishment andtranscriptional activity in infected hepatocytes.
Locatelli M. et al.
BACKGROUND \& AIMS: Upon Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, partially double stranded viral DNA converts into a covalently-closed-circular chromatinized episomal structure (cccDNA). This form represents the long-lived genomic reservoir responsible for viral persistence in the infected liver. While the involvemen... |
NR4A1 regulates expression of immediate early genes, suppressingreplication stress in cancer.
Guo Hongshan et al.
Deregulation of oncogenic signals in cancer triggers replication stress. Immediate early genes (IEGs) are rapidly and transiently expressed following stressful signals, contributing to an integrated response. Here, we find that the orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 localizes across the gene body and 3' UTR of IEGs, wher... |
Vulnerability of drug-resistant EML4-ALK rearranged lung cancer to transcriptional inhibition.
Paliouras AR, Buzzetti M, Shi L, Donaldson IJ, Magee P, Sahoo S, Leong HS, Fassan M, Carter M, Di Leva G, Krebs MG, Blackhall F, Lovly CM, Garofalo M
A subset of lung adenocarcinomas is driven by the EML4-ALK translocation. Even though ALK inhibitors in the clinic lead to excellent initial responses, acquired resistance to these inhibitors due to on-target mutations or parallel pathway alterations is a major clinical challenge. Exploring these mechanisms of resis... |
High density of unrepaired genomic ribonucleotides leads to Topoisomerase 1-mediated severe growth defects in absence of ribonucleotide reductase.
Cerritelli SM, Iranzo J, Sharma S, Chabes A, Crouch RJ, Tollervey D, Hage AE
Cellular levels of ribonucleoside triphosphates (rNTPs) are much higher than those of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs), thereby influencing the frequency of incorporation of ribonucleoside monophosphates (rNMPs) by DNA polymerases (Pol) into DNA. RNase H2-initiated ribonucleotide excision repair (RER) effic... |
Recombination may occur in the absence of transcription in the immunoglobulin heavy chain recombination centre.
Oudinet C, Braikia FZ, Dauba A, Khamlichi AA
Developing B cells undergo V(D)J recombination to generate a vast repertoire of Ig molecules. V(D)J recombination is initiated by the RAG1/RAG2 complex in recombination centres (RCs), where gene segments become accessible to the complex. Whether transcription is the causal factor of accessibility or whether it is a ... |
Recurrent SMARCB1 Mutations Reveal a Nucleosome Acidic Patch Interaction Site That Potentiates mSWI/SNF Complex Chromatin Remodeling.
Valencia AM, Collings CK, Dao HT, St Pierre R, Cheng YC, Huang J, Sun ZY, Seo HS, Mashtalir N, Comstock DE, Bolonduro O, Vangos NE, Yeoh ZC, Dornon MK, Hermawan C, Barrett L, Dhe-Paganon S, Woolf CJ, Muir TW, Kadoch C
Mammalian switch/sucrose non-fermentable (mSWI/SNF) complexes are multi-component machines that remodel chromatin architecture. Dissection of the subunit- and domain-specific contributions to complex activities is needed to advance mechanistic understanding. Here, we examine the molecular, structural, and genome-wid... |
The SS18-SSX Fusion Oncoprotein Hijacks BAF Complex Targeting and Function to Drive Synovial Sarcoma.
McBride MJ, Pulice JL, Beird HC, Ingram DR, D'Avino AR, Shern JF, Charville GW, Hornick JL, Nakayama RT, Garcia-Rivera EM, Araujo DM, Wang WL, Tsai JW, Yeagley M, Wagner AJ, Futreal PA, Khan J, Lazar AJ, Kadoch C
Synovial sarcoma (SS) is defined by the hallmark SS18-SSX fusion oncoprotein, which renders BAF complexes aberrant in two manners: gain of SSX to the SS18 subunit and concomitant loss of BAF47 subunit assembly. Here we demonstrate that SS18-SSX globally hijacks BAF complexes on chromatin to activate an SS transcript... |
The Polycomb-Dependent Epigenome Controls β Cell Dysfunction, Dedifferentiation, and Diabetes.
Lu TT, Heyne S, Dror E, Casas E, Leonhardt L, Boenke T, Yang CH, Sagar , Arrigoni L, Dalgaard K, Teperino R, Enders L, Selvaraj M, Ruf M, Raja SJ, Xie H, Boenisch U, Orkin SH, Lynn FC, Hoffman BG, Grün D, Vavouri T, Lempradl AM, Pospisilik JA
To date, it remains largely unclear to what extent chromatin machinery contributes to the susceptibility and progression of complex diseases. Here, we combine deep epigenome mapping with single-cell transcriptomics to mine for evidence of chromatin dysregulation in type 2 diabetes. We find two chromatin-state signat... |
Epigenetic regulation of vascular NADPH oxidase expression and reactive oxygen species production by histone deacetylase-dependent mechanisms in experimental diabetes.
Manea SA, Antonescu ML, Fenyo IM, Raicu M, Simionescu M, Manea A
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by up-regulated NADPH oxidase (Nox) contribute to structural-functional alterations of the vascular wall in diabetes. Epigenetic mechanisms, such as histone acetylation, emerged as important regulators of gene expression in cardiovascular disorders. Since their role in diabete... |
CDK8/19 Mediator kinases potentiate induction of transcription by NFκB
Chen M. et al.
The nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) family of transcription factors has been implicated in inflammatory disorders, viral infections, and cancer. Most of the drugs that inhibit NFκB show significant side effects, possibly due to sustained NFκB suppression. Drugs affecting induced, but not basal, NF&k... |
Functional incompatibility between the generic NF-κB motif and a subtype-specific Sp1III element drives the formation of HIV-1 subtype C viral promoter
Verma A et al.
Of the various genetic subtypes of HIV-1, HIV-2 and SIV, only in subtype C of HIV-1, a genetically variant NF-κB binding site is found at the core of the viral promoter in association with a subtype-specific Sp1III motif. How the subtype-associated variations in the core transcription factor binding sites (TFB... |
Embryonic transcription is controlled by maternally defined chromatin state
Hontelez S et al.
Histone-modifying enzymes are required for cell identity and lineage commitment, however little is known about the regulatory origins of the epigenome during embryonic development. Here we generate a comprehensive set of epigenome reference maps, which we use to determine the extent to which maternal factors shape c... |
iRNA-seq: computational method for genome-wide assessment of acute transcriptional regulation from total RNA-seq data.
Madsen JG, Schmidt SF, Larsen BD, Loft A, Nielsen R, Mandrup S
RNA-seq is a sensitive and accurate technique to compare steady-state levels of RNA between different cellular states. However, as it does not provide an account of transcriptional activity per se, other technologies are needed to more precisely determine acute transcriptional responses. Here, we have developed an e... |
PRAME induces genomic instability in uveal melanoma
Harbour J. W. et al.
PRAME is a CUL2 ubiquitin ligase subunit that is normally expressed in the testis but becomes aberrantly overexpressed in many cancer types in association with aneuploidy and metastasis. Here, we show that PRAME is expressed predominantly in spermatogonia around the time of meiotic crossing-over in coordination with... |