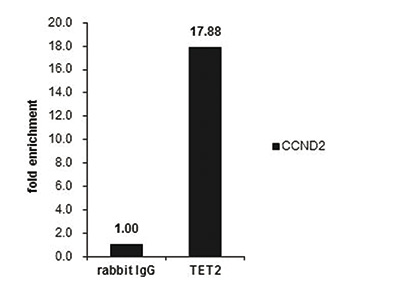
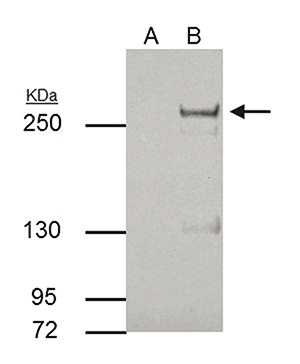
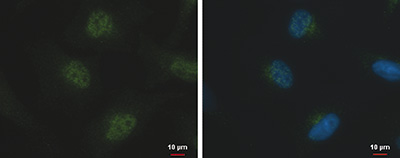
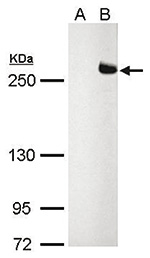
TET2 (UniProt/Swiss-Prot entry Q6N021) is a methylcytosine dioxygenase that catalyzes the conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC). 5-hmC has been recently discovered in mammalian DNA and is abundant in Purkinje neurons, granule cells, embryonic stem cells, and brain tissue, especially in areas that are associated with higher cognitive function. Although its precise role has still to be shown, recent studies indicate that 5-hmC plays important roles distinct from 5-mC. Early evidence suggests that 5-hmC may represent a new pathway to demethylate DNA involving a repair mechanism converting 5-hmC to cytosine. Mutations in TET2 have been associated with myeloproliferative diseases such as essential thrombocythemia, polycythemia vera and primary myelofibrosis.
-
产品
剪切技术
Tagmentation
Chromatin studies
DNA methylation
- Bisulfite conversion
- Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation
- Methylbinding domain protein
- Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation
Genome editing (CRISPR/Cas9)
Antibodies
- All antibodies
- Sample size antibodies
- ChIP-seq grade antibodies
- ChIP-grade antibodies
- Western Blot Antibodies
- DNA modifications
- RNA modifications
- CRISPR/Cas9 antibodies
- CUT&Tag Antibodies
NGS Library preparation
- Library preparation for ChIP-seq
- Library preparation for RNA sequencing
- Library preparation for DNA sequencing
Automation
Reagents
- 服务
- 研究领域
- 资源
- 公司
-
联系人