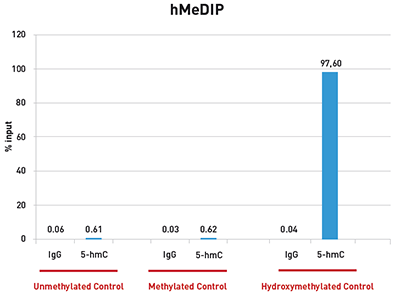
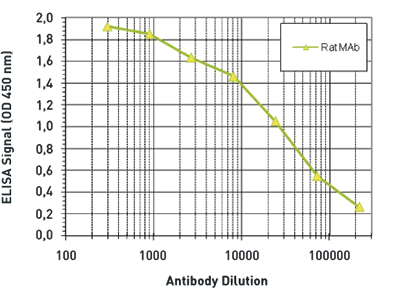
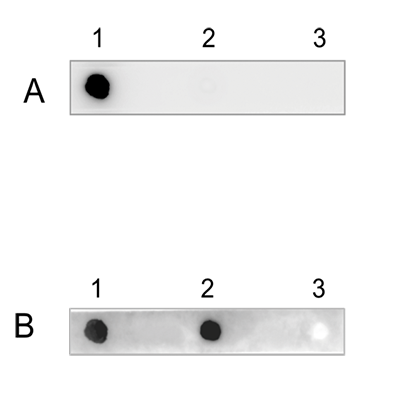
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) Antibody (rat) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15220001-100 Lot# 002). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Anticancer Activity of Jania rubens in HCT-116 Cells via EMT Suppression, TET Downregulation, and ROS-Mediated Cytotoxicity
Radwan, Zeina et al.
The red seaweed Jania rubens (J. rubens) is prevalent along the Lebanese coast and has drawn attention for its notable antineoplastic properties. Our previous data showed that its dichloromethane–methanol (DM) extract possesses antioxidant, cytotoxic, and anti-migratory effects on colon cancer cell... |
DNMT1 regulates the timing of DNA methylation by DNMT3 in anenzymatic activity-dependent manner in mouse embryonic stem cells.
Ito Takamasa et al.
DNA methylation (DNAme; 5-methylcytosine, 5mC) plays an essential role in mammalian development, and the 5mC profile is regulated by a balance of opposing enzymatic activities: DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and Ten-eleven translocation dioxygenases (TETs). In mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs), de novo DNAme by DNMT... |
Functional role of Tet-mediated RNA hydroxymethylcytosine in mouse ES
cells and during differentiation.
Lan, Jie and Rajan, Nicholas and Bizet, Martin and Penning, Audrey and
Singh, Nitesh K and Guallar, Diana and Calonne, Emilie and Li Greci, Andrea
and Bonvin, Elise and Deplus, Rachel and Hsu, Phillip J and Nachtergaele,
Sigrid and Ma, Chengjie and Song,
Tet-enzyme-mediated 5-hydroxymethylation of cytosines in DNA plays a
crucial role in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs). In RNA also,
5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) has recently been evidenced, but its
physiological roles are still largely unknown. Here we show the
contribution and function of this mark in mouse ESCs... |
Global distribution of DNA hydroxymethylation and DNA methylation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Wernig-Zorc S, Yadav MP, Kopparapu PK, Bemark M, Kristjansdottir HL, Andersson PO, Kanduri C, Kanduri M
BACKGROUND: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has been a good model system to understand the functional role of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) in cancer progression. More recently, an oxidized form of 5-mC, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has gained lot of attention as a regulatory epigenetic modification with prognostic ... |
Regulation of the DNA Methylation Landscape in Human Somatic Cell Reprogramming by the miR-29 Family
Hysolli E et al.
Reprogramming to pluripotency after overexpression of OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and MYC is accompanied by global genomic and epigenomic changes. Histone modification and DNA methylation states in induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) have been shown to be highly similar to embryonic stem cells (ESCs). However, epigenetic d... |
Transcriptome-wide distribution and function of RNA hydroxymethylcytosine
Delatte B, Wang F, Ngoc LV, Collignon E, Bonvin E, Deplus R, Calonne E, Hassabi B, Putmans P, Awe S, Wetzel C, Kreher J, Soin R, Creppe C, Limbach PA, Gueydan C, Kruys V, Brehm A, Minakhina S, Defrance M, Steward R, Fuks F.
Hydroxymethylcytosine, well described in DNA, occurs also in RNA. Here, we show that hydroxymethylcytosine preferentially marks polyadenylated RNAs and is deposited by Tet in Drosophila. We map the transcriptome-wide hydroxymethylation landscape, revealing hydroxymethylcytosine in the transcripts of many genes, nota... |
RNA biochemistry. Transcriptome-wide distribution and function of RNA hydroxymethylcytosine.
Delatte B, Wang F, Ngoc LV, Collignon E, Bonvin E, Deplus R, Calonne E, Hassabi B, Putmans P, Awe S, Wetzel C, Kreher J, Soin R, Creppe C, Limbach PA, Gueydan C, Kruys V, Brehm A, Minakhina S, Defrance M, Steward R, Fuks F
Hydroxymethylcytosine, well described in DNA, occurs also in RNA. Here, we show that hydroxymethylcytosine preferentially marks polyadenylated RNAs and is deposited by Tet in Drosophila. We map the transcriptome-wide hydroxymethylation landscape, revealing hydroxymethylcytosine in the transcripts of many genes, nota... |
CpG signalling, H2A.Z/H3 acetylation and microRNA-mediated deferred self-attenuation orchestrate foetal NOS3 expression.
Postberg J, Kanders M, Forcob S, Willems R, Orth V, Hensel KO, Weil PP, Wirth S, Jenke AC
BACKGROUND: An adverse intrauterine environment leads to permanent physiological changes including vascular tone regulation, potentially influencing the risk for adult vascular diseases. We therefore aimed to monitor responsive NOS3 expression in human umbilical artery endothelial cells (HUAEC) and to study the unde... |
White matter tract and glial-associated changes in 5-hydroxymethylcytosine following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
Tsenkina Y, Ruzov A, Gliddon C, Horsburgh K, De Sousa PA
White matter abnormalities due to age-related cerebrovascular alterations is a common pathological hallmark associated with functional impairment in the elderly which has been modeled in chronically hypoperfused mice. 5-Methylcytosine (5mC) and its oxidized derivative 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) are DNA modificat... |
Tet2 Facilitates the Derepression of Myeloid Target Genes during CEBPα-Induced Transdifferentiation of Pre-B Cells.
Kallin EM, Rodríguez-Ubreva J, Christensen J, Cimmino L, Aifantis I, Helin K, Ballestar E, Graf T
The methylcytosine hydroxylase Tet2 has been implicated in hematopoietic differentiation and the formation of myeloid malignancies when mutated. An ideal system to study the role of Tet2 in myelopoeisis is CEBPα-induced transdifferentiation of pre-B cells into macrophages. Here we found that CEBPα binds to upstream ... |
Lineage-specific distribution of high levels of genomic 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian development.
Ruzov A, Tsenkina Y, Serio A, Dudnakova T, Fletcher J, Bai Y, Chebotareva T, Pells S, Hannoun Z, Sullivan G, Chandran S, Hay DC, Bradley M, Wilmut I, De Sousa P
Methylation of cytosine is a DNA modification associated with gene repression. Recently, a novel cytosine modification, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has been discovered. Here we examine 5-hmC distribution during mammalian development and in cellular systems, and show that the developmental dynamics of 5-hmC are d... |
Genome-wide analysis of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine distribution reveals its dual function in transcriptional regulation in mouse embryonic stem cells.
Wu H, D'Alessio AC, Ito S, Wang Z, Cui K, Zhao K, Sun YE, Zhang Y
Recent studies have demonstrated that the Ten-eleven translocation (Tet) family proteins can enzymatically convert 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC). While 5mC has been studied extensively, little is known about the distribution and function of 5hmC. Here we present a genome-wide profile of 5h... |