5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) has been recently discovered in mammalian DNA. This results from the enzymatic conversion of 5-methylcytosine into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine by the TET family of oxygenases. So far, the 5-hmC bases have been identified in Purkinje neurons, in granule cells and embryonic stem cells where they are present at high levels (up to 0,6% of total nucleotides in Purkinje cells).
Preliminary results indicate that 5-hmC may have important roles distinct from 5-mC. Although its precise role has still to be shown, early evidence suggests a few putative mechanisms that could have big implications in epigenetics : 5-hydroxymethylcytosine may well represent a new pathway to demethylate DNA involving a repair mechanism converting 5-hmC to cytosine and, as such open up entirely new perspectives in epigenetic studies.
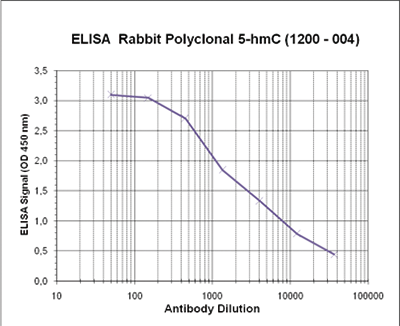
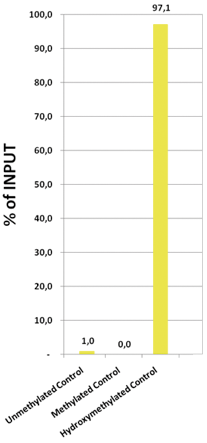
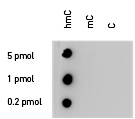
Due to the structural similarity between 5-mC and 5-hmC, these bases are experimentally almost indistinguishable. Recent articles demonstrated that the most common approaches (e.g. enzymatic approaches, bisulfite sequencing) do not account for 5-hmC. The development of the affinity-based technologies appears to be the most powerful way to differentially and specifically enrich 5-mC and 5-hmC sequences. The results shown here illustrate the use of this unique monoclonal antibody against 5-hydroxymethylcytosine that has been fully validated in various technologies.