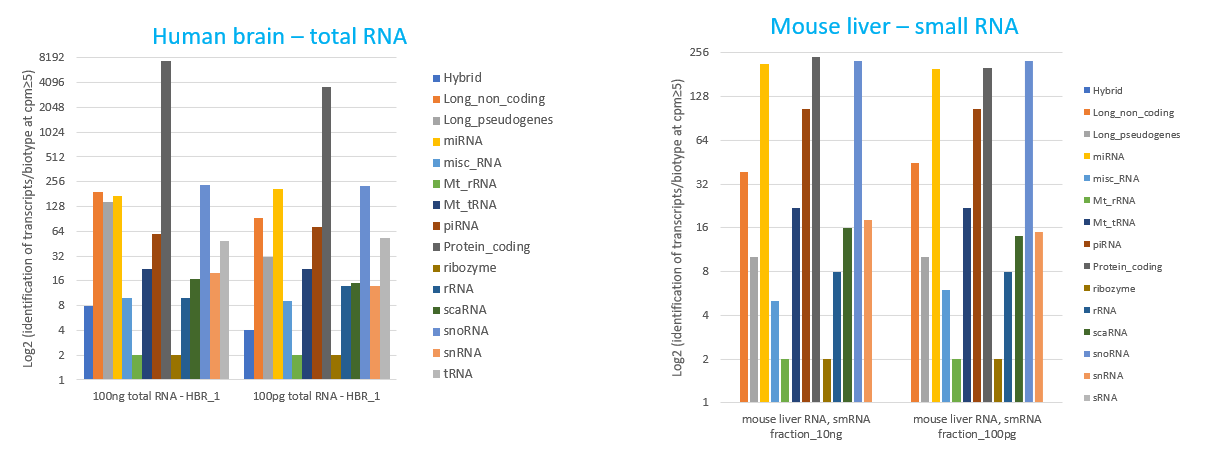
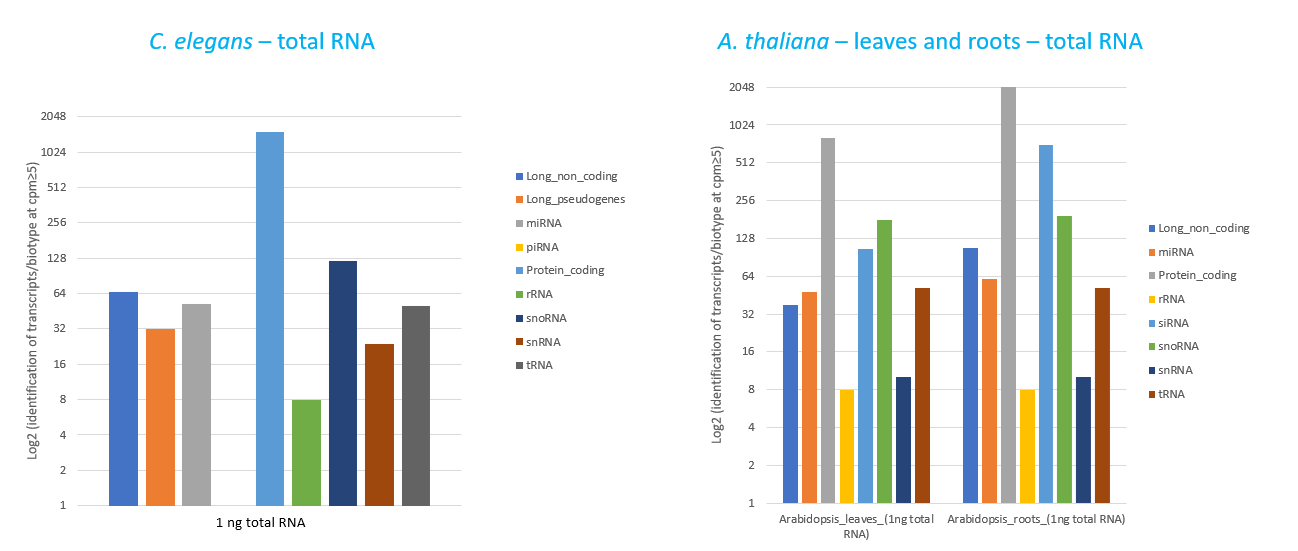
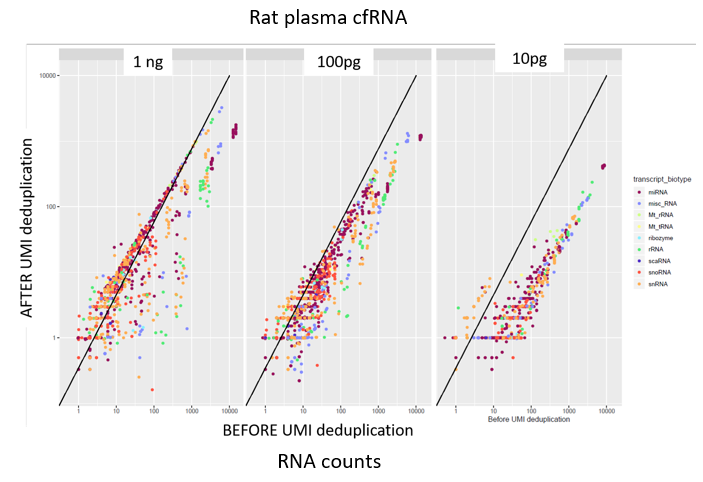
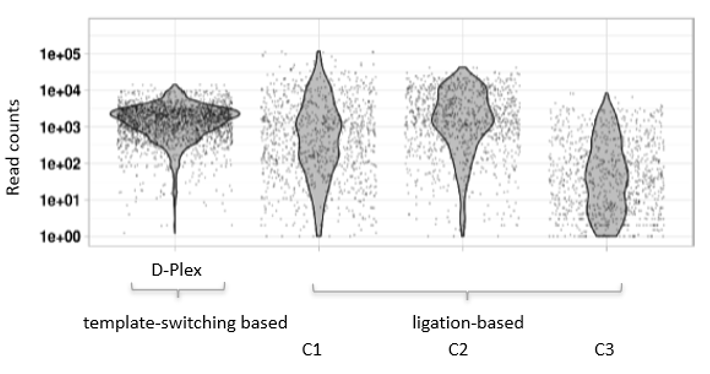
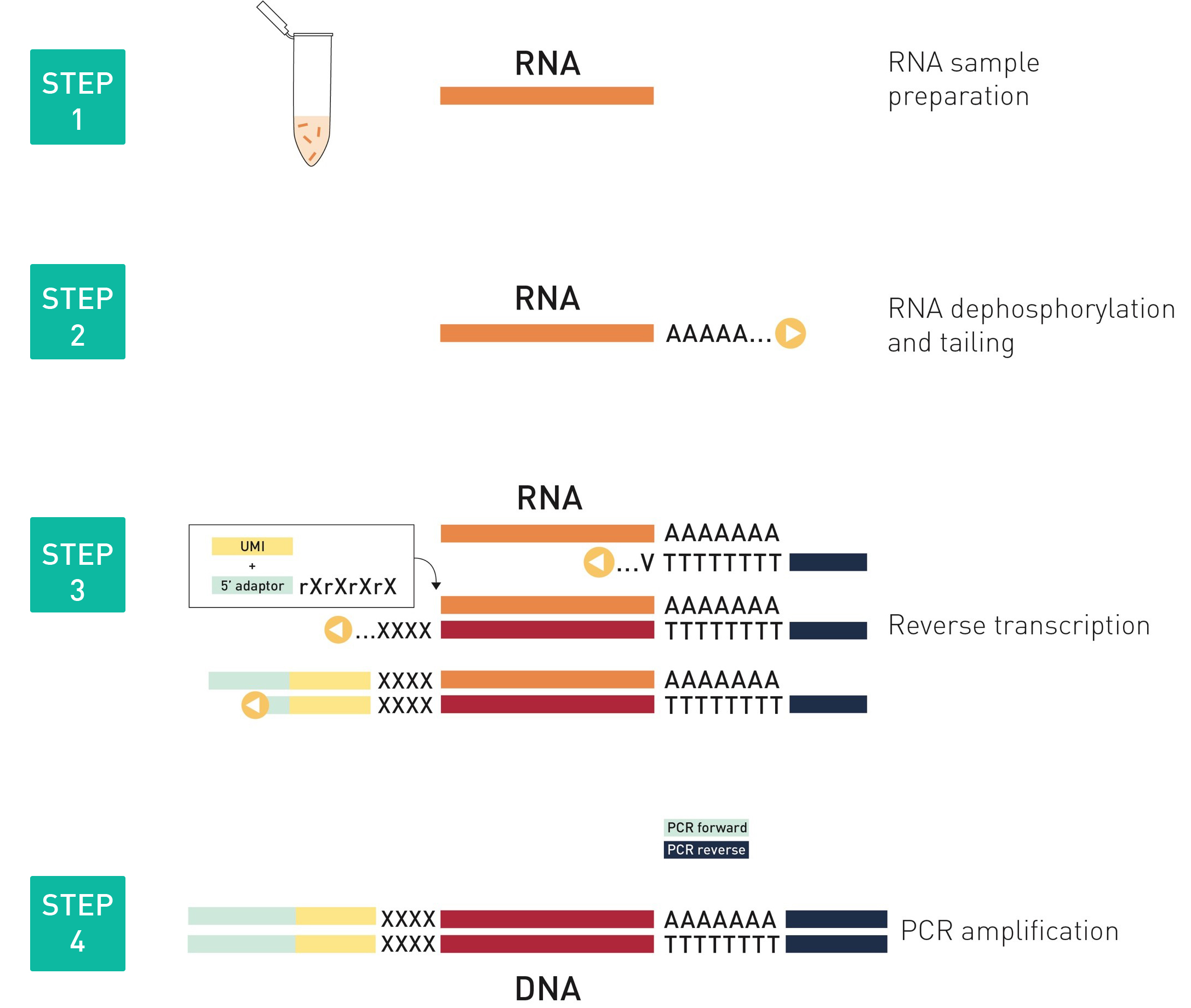
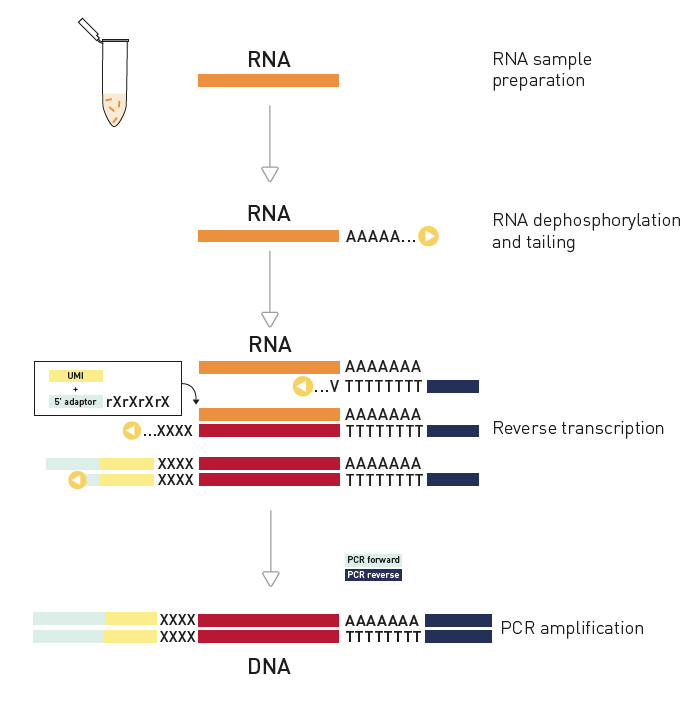
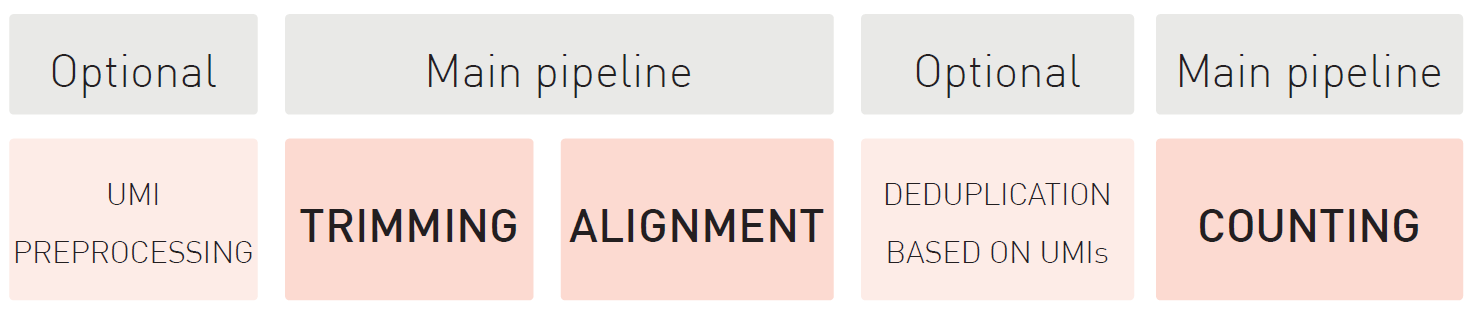
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: D-Plex Small RNA-seq Kit for Illumina (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C05030001). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
EZHIP restricts noncanonical PRC2 binding and regulates H3K27me3 intergenerational inheritance and reprogramming
Zeng, Yitian et al.
In mice, the repressive histone mark H3K27me3 undergoes both region-specific inheritance and erasure during the parental-to-embryonic transition, with the underlying mechanisms poorly understood. Here, we show that PRC2, which catalyzes H3K27me3, binds both classic Polycomb targets and noncanonical H3K27me3 domain... |
OGFOD1 enables AML chemo- and nutrient stress resistance by regulating protein synthesis
Mayerhofer C, et al.
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) commonly relapses after initial chemotherapy response. We assessed metabolic adaptations in chemoresistant cells in vivo before overt relapse, identifying altered branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) levels in patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) and immunophenotypically identified leukemia s... |
A programmed decline in ribosome levels governs human early neurodevelopment
Ni, Chunyang et al.
Many neurodevelopmental defects are linked to genes involved in housekeeping functions, such as those encoding ribosome biogenesis factors. How reductions in ribosome biogenesis can result in tissue- and developmental-specific defects remains unclear. Here we describe variants in the ribosome biogenesis factor A... |
Landscape and regulation of mRNA translation in the early C. elegans embryo
Shukla, Yash et al.
Animal embryos rely on regulated translation of maternally deposited mRNAs to drive early development. Using low-input ribosome profiling combined with RNA sequencing on precisely staged embryos, we measure mRNA translation during the first four cell cycles of C. elegans development. We uncover stage-specific patt... |
RNA G-quadruplex removal promotes a translational switch after meiosis resumption
Lu, Qiong-Wen et al.
Oocyte maturation-coupled mRNA post-transcriptional regulation is essential for the establishment of developmental potential. Previously, oocyte mRNA translation efficiencies focused on the trans-regulation of key RNA-binding protein (RBPs), rarely related to RNA structure. RNA G-quadruplexes (rG4s) are four-strande... |
Extracellular Vesicles From Follicular Fluid in Infertile Women: Size, Morphology and miRNA Content Analysis
Solène Ducarre et al.
The declining birth rates and fertility challenges in Europe have intensified global concerns over rising infertility, particularly among women. This study decisively investigates follicular fluid‐related extracellular vesicles (FF‐EVs) from infertile patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or diminished ovar... |
The assembly factor Reh1 is released from the ribosome during its initial round of translation
Sharmishtha Musalgaonkar et al.
Assembly of functional ribosomal subunits and successfully delivering them to the translating pool is a prerequisite for protein synthesis and cell growth. In S. cerevisiae, the ribosome assembly factor Reh1 binds to pre-60S subunits at a late stage during their cytoplasmic maturation. Previous work shows that ... |
Cell type-specific eQTL detection from single-cell RNA-seq reveals post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms in human islets
Twan J.J. de Winter et al.
Gene regulatory networks (GRN) must be robust to maintain cellular identity across individuals yet flexible to accommodate population genetic variants. Therefore, comparing expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) in health and disease can reveal hidden players in GRN and post-transcriptional regulation. Here, we d... |
MARTRE family proteins negatively regulate CCR4-NOT activity to protect poly(A) tail length and promote translation of maternal mRNA
Jing Yang et al.
The mammalian early embryo development requires translation of maternal mRNA inherited from the oocyte. While poly(A) tail length influences mRNA translation efficiency during the oocyte-to-embryo transition (OET), molecular mechanisms regulating maternal RNA poly(A) tail length are not fully understood. In this stu... |
Optimization of ribosome profiling in plants including structural analysis of rRNA fragments
Ting M.K.Y. et al.
Background
Ribosome profiling (or Ribo-seq) is a technique that provides genome-wide information on the translational landscape (translatome). Across different plant studies, variable methodological setups have been described which raises questions about the general comparability of data that were generated from di... |
Maternal prenatal stress induces sex-dependent changes in tRNA fragment families and cholinergic pathways in newborns
Shani Vaknine Treidel et al.
Maternal perceived prenatal stress (PPS) is a known risk factor for diverse developmental impairments in newborns, but the underlying molecular processes are incompletely understood. Here, we report that maternal PPS altered the birth profiles of blood transfer RNA fragments (tRFs), 16-50nt long non-random cleavage ... |
Inherited defects of piRNA biogenesis cause transposon de-repression, impaired spermatogenesis, and human male infertility
Stallmeyer B. et al.
piRNAs are crucial for transposon silencing, germ cell maturation, and fertility in male mice. Here, we report on the genetic landscape of piRNA dysfunction in humans and present 39 infertile men carrying biallelic variants in 14 different piRNA pathway genes, including PIWIL1, GTSF1, GPAT2, MAEL, TDR... |
Pervasive translation of Xrn1-sensitive unstable long non-coding RNAs in yeast
Andjus S. et al.
Despite being predicted to lack coding potential, cytoplasmic long non-coding (lnc)RNAs can associate with ribosomes. However, the landscape and biological relevance of lncRNAs translation remains poorly studied. In yeast, cytoplasmic Xrn1-sensitive lncRNAs (XUTs) are targeted by the Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay (NM... |
Aseptic loosening around total joint replacement in humans is regulated by miR-1246 and miR-6089 via the Wnt signalling pathway
Yi Deng at al.
Background: Total joint replacement for osteoarthritis is one of the most successful surgical procedures in modern medicine. However, aseptic loosening continues to be a leading cause of revision arthroplasty. The diagnosis of aseptic loosening remains a challenge as patients are often asymptomatic until the la... |
An inappropriate decline in ribosome levels drives a diverse set of neurodevelopmental disorders
Ni C. et al.
Many neurodevelopmental defects are linked to perturbations in genes involved in housekeeping functions, such as those encoding ribosome biogenesis factors. However, how reductions in ribosome biogenesis can result in tissue and developmental specific defects remains a mystery. Here we describe new allelic variants ... |
Challenges in characterization of transcriptomes of extracellular vesicles and non-vesicular extracellular RNA carriers
Makarova J. et al.
Since its original discovery over a decade ago, extracellular RNA (exRNA) has been found in all biological fluids. Furthermore, extracellular microRNA has been shown to be involved in communication between various cell types. Importantly, the exRNA is protected from RNases degradation by certain carriers including m... |
Guidelines for Performing Ribosome Profiling in Plants Including Structural Analysis of rRNA Fragments
Ting M.K.Y. et al.
Ribosome profiling (or Ribo-seq) is a technique that provides genome-wide information on the translational landscape (translatome). Across different plant studies, variable methodological setups have been described which raises questions about the general comparability of data that were generated from diverging meth... |
Integrated multiplexed assays of variant effect reveal cis-regulatory determinants of catechol-O-methyltransferase gene expression
Hoskins I. et al.
Multiplexed assays of variant effect are powerful methods to profile the consequences of rare variants on gene expression and organismal fitness. Yet, few studies have integrated several multiplexed assays to map variant effects on gene expression in coding sequences. Here, we pioneered a multiplexed assay based on ... |
The Ribosome Assembly Factor Reh1 is Released from the Polypeptide Exit Tunnel in the Pioneer Round of Translation
Musalgaonkar S. et al.
Assembly of functional ribosomal subunits and successfully delivering them to the translating pool is a prerequisite for protein synthesis and cell growth. In S. cerevisiae, the ribosome assembly factor Reh1 binds to pre-60S subunits at a late stage during their cytoplasmic maturation. Previous work shows ... |
Knockout of the longevity gene Klotho perturbs aging- and Alzheimer’s disease-linked brain microRNAs and tRNA fragments
Dubnov S. et al.
Overexpression of the longevity gene Klotho prolongs, while its knockout shortens lifespan and impairs cognition via altered fibroblast growth factor signaling that perturbs myelination and synapse formation; however, comprehensive analysis of Klotho’s knockout consequences on mammalian brain transcriptomics i... |
Single-cell quantification of ribosome occupancy in early mouse development
Ozadam H. et al.
Translation regulation is critical for early mammalian embryonic development1. However, previous studies had been restricted to bulk measurements2, precluding precise determination of translation regulation including allele-specific analyses. Here, to address this challenge, we developed a novel microfluidic isotach... |
DIS3 ribonuclease prevents the cytoplasmic accumulation of lncRNAs carrying non-canonical ORFs, which represent a source of cancer immunopeptides.
Foretek D. et al.
Around 12% of multiple myeloma (MM) cases harbour mutations in DIS3, which encodes an RNA decay enzyme that controls the turnover of some long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). Although lncRNAs, by definition, do not encode proteins, some can be a source of (poly)peptides with biological importance, such as antigens. T... |
Pyruvate Kinase M (PKM) binds ribosomes in a poly-ADPribosylation dependent manner to induce translational stalling.
Kejiou N. S. et al.
In light of the numerous studies identifying post-transcriptional regulators on the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), we asked whether there are factors that regulate compartment specific mRNA translation in human cells. Using a proteomic survey of spatially regulated polysome interacting proteins, we ident... |
Towards a human brain EV atlas: Characteristics of EVs from different brain regions, including small RNA and protein profiles.
Huang Y. et al.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are released from different cell types in the central nervous system (CNS) and play roles in regulating physiological and pathological functions. Although brain-derived EVs (bdEVs) have been successfully collected from brain tissue, there is not yet a "bdEV atlas" of EVs from different b... |
RNA landscapes of brain tissue and brain tissue-derived extracellularvesicles in simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection andSIV-related central nervous system pathology.
Huang Yiyao and Abdelmagid Abdelgawad Ahmed Gamal andTurchinovich Andrey and Queen Suzanne and Abreu CelinaMonteiro and Zhu Xianming and Batish Mona and Zheng Leiand Witwer Kenneth W
Antiretroviral treatment regimens can effectively control HIV replication and some aspects of disease progression. However, molecular events in end-organ diseases such as central nervous system (CNS) disease are not yet fully understood, and routine eradication of latent reservoirs is not yet in reach. Extracellular... |
Immunoregulatory Biomarkers of the Remission Phase in Type 1 Diabetes: miR-30d-5p Modulates PD-1 Expression and Regulatory T Cell Expansion
Gomez-Munoz L. et al.
The partial remission (PR) phase of type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an underexplored period characterized by endogenous insulin production and downmodulated autoimmunity. To comprehend the mechanisms behind this transitory phase and develop precision medicine strategies, biomarker discovery and patient stratification are u... |
Ageing-associated small RNA cargo of extracellular vesicles.
Kern F. et al.
Previous work on murine models and humans demonstrated global as well as tissue-specific molecular ageing trajectories of RNAs. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane vesicles mediating the horizontal transfer of genetic information between different tissues. We sequenced small regulatory RNAs (sncRNAs) in two mo... |
The piRNA-pathway factor FKBP6 is essential for spermatogenesis butdispensable for control of meiotic LINE-1 expression in humans.
Wyrwoll M.J. et al.
Infertility affects around 7\% of the male population and can be due to severe spermatogenic failure (SPGF), resulting in no or very few sperm in the ejaculate. We initially identified a homozygous frameshift variant in FKBP6 in a man with extreme oligozoospermia. Subsequently, we screened a total of 2,699 men with ... |
The seminal plasma microbiome of men with testicular germ cell tumours described by small RNA sequencing
Mørup N. et al.
Background: It has been estimated that microorganisms are involved in the pathogenesis of approximately 20% of all cancers. Testicular germ cell tumours (TGCTs) are the most common type of malignancy in young men and arise from the precursor cell, Germ Cell Neoplasia in Situ (GCNIS). The microbiome of seminal p... |
Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 inhibition attenuates extracellular vesiclerelease and improves neurobehavioral deficits in murine HIV.
Zhu X. et al.
People living with HIV (PLH) have significantly higher rates of cognitive impairment (CI) and major depressive disorder (MDD) versus the general population. The enzyme neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2) is involved in the biogenesis of ceramide and extracellular vesicles (EVs), both of which are dysregulated in PL... |
A novel, essential trans-splicing protein connects the nematode SL1snRNP to the CBC-ARS2 complex.
Fasimoye R.Y. et al.
Spliced leader trans-splicing is essential for gene expression in many eukaryotes. To elucidate the molecular mechanism of this process, we characterise the molecules associated with the Caenorhabditis elegans major spliced leader snRNP (SL1 snRNP), which donates the spliced leader that replaces the 5' untranslated ... |
Interspecies effectors of a transgenerational memory of bacterial infection in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Legüe M. et al.
The inheritance of memory is an adaptive trait. Microbes challenge the immunity of organisms and trigger behavioral adaptations that can be inherited, but how bacteria produce inheritance of a trait is unknown. We use and its bacteria to study the transgenerational RNA dynamics of interspecies crosstalk leading to a... |
Diverse Monogenic Subforms of Human Spermatogenic Failure
Nagirnaja L. et al.
Non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA) is the most severe form of male infertility and typically incurable with current medicine. Due to the biological complexity of sperm production, defining the genetic basis of NOA has proven challenging, and to date, the most advanced classification of NOA subforms is based on simple... |
Ultrasensitive Ribo-seq reveals translational landscapes during mammalian oocyte-to-embryo transition and pre-implantation development.
Xiong Z. et al.
In mammals, translational control plays critical roles during oocyte-to-embryo transition (OET) when transcription ceases. However, the underlying regulatory mechanisms remain challenging to study. Here, using low-input Ribo-seq (Ribo-lite), we investigated translational landscapes during OET using 30-150 mouse oocy... |
Translation is a key determinant controlling the fate of cytoplasmic long non-coding RNAs
Andjus Sara et al.
Despite predicted to lack coding potential, cytoplasmic long non-coding (lnc)RNAs can associate with ribosomes, resulting in some cases into the production of functional peptides. However, the biological and mechanistic relevance of this pervasive lncRNAs translation remains poorly studied. In yeast, cytoplasmic Xrn... |
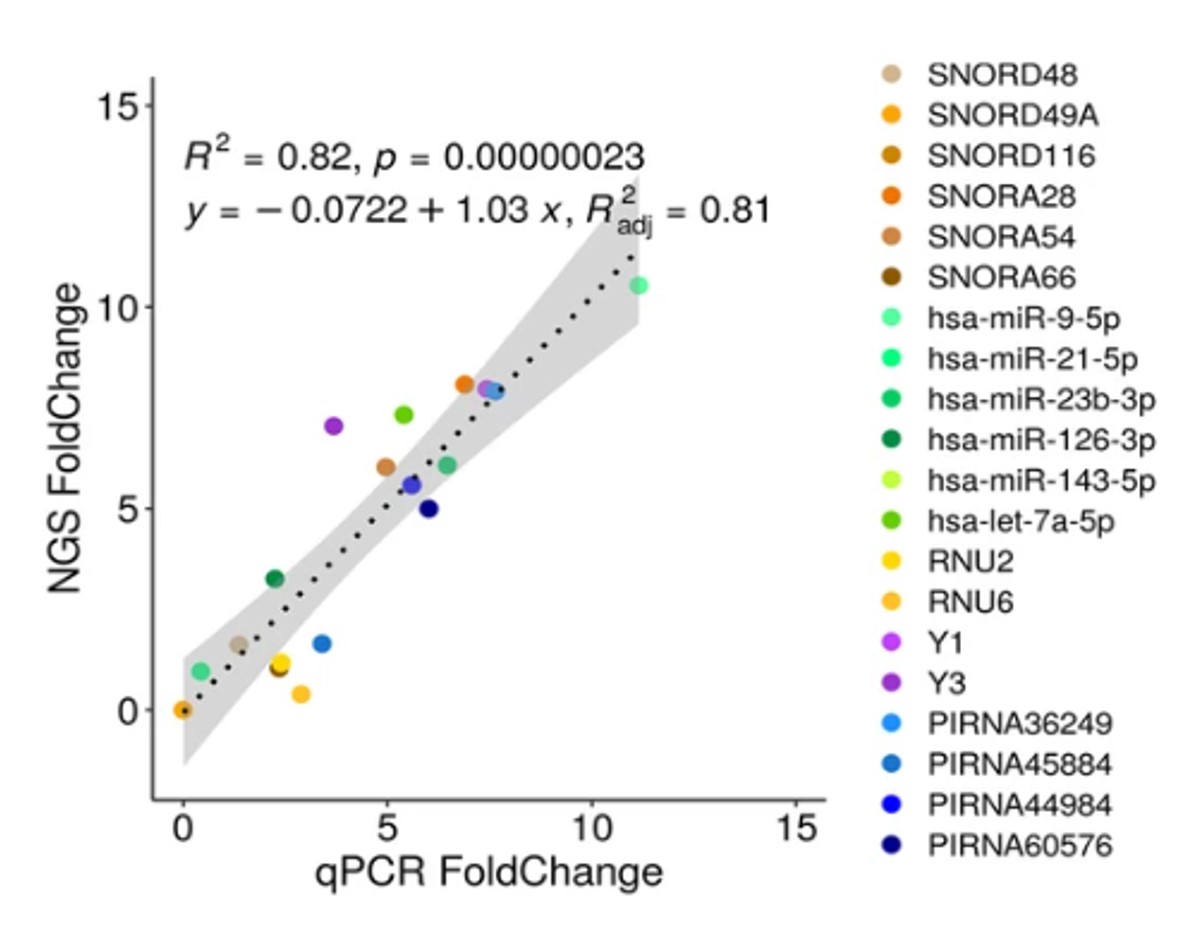
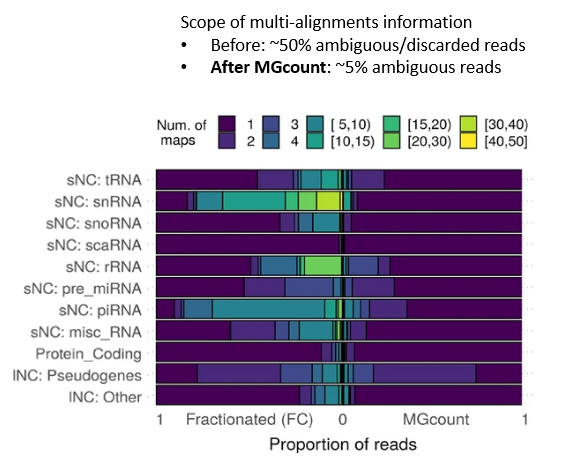
MGcount: a total RNA-seq quantification tool to address multi-mappingand multi-overlapping alignments ambiguity in non-coding transcripts
Hita Andrea, Brocart Gilles, Fernandez Ana, Rehmsmeier Marc, Alemany Anna, Schvartzman Sol
Background Total-RNA sequencing (total-RNA-seq) allows the simultaneous study of both the coding and the non-coding transcriptome. Yet, computational pipelines have traditionally focused on particular biotypes, making assumptions that are not fullfilled by total-RNA-seq datasets. Transcripts from distinct RNA biotyp... |
Single cell quantification of ribosome occupancy in early mouse development
Tori Tonn et al.
Technological limitations precluded transcriptome-wide analyses of translation at single cell resolution. To solve this challenge, we developed a novel microfluidic isotachophoresis approach, named RIBOsome profiling via IsoTachoPhoresis (Ribo-ITP), and characterized translation in single oocytes and embryos during ... |
Functional microRNA targetome undergoes degeneration-induced shift inthe retina.
Chu-Tan Joshua A et al.
BACKGROUND: MicroRNA (miRNA) play a significant role in the pathogenesis of complex neurodegenerative diseases including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), acting as post-transcriptional gene suppressors through their association with argonaute 2 (AGO2) - a key member of the RNA Induced Silencing Complex (RISC)... |
Single-cell microRNA sequencing method comparison and application tocell lines and circulating lung tumor cells
Hücker S. et al.
Molecular single cell analyses provide insights into physiological and pathological processes. Here, in a stepwise approach, we first evaluate 19 protocols for single cell small RNA sequencing on MCF7 cells spiked with 1 pg of 1,006 miRNAs. Second, we analyze MCF7 single cell equivalents of the eight best pro... |
Small RNAs in Seminal Plasma as Novel Biomarkers for Germ Cell Tumors
Mørup N. et al.
Circulating miRNAs secreted by testicular germ cell tumors (TGCT) show great potential as novel non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis of TGCT. Seminal plasma (SP) represents a biofluid closer to the primary site. Here, we investigate whether small RNAs in SP can be used to diagnose men with TGCTs or the precursor le... |
Vesicle-bound regulatory RNAs are associated with tissue aging
F. Kern, T. Kuhn, N. Ludwig, M. Simon, L. Gröger, N. Fabis, A. Salhab, T. Fehlmann, O. Hahn, A. Engel, M. Koch, J. Koehler, K. Winek, H. Soreq, G. Fuhrmann, T. Wyss-Coray, E. Meese, M. W. Laschke and A. Keller
Previous work on murine models and human demonstrated global as well as tissue-specific molecular aging trajectories in solid tissues and body fluids1–8. Extracellular vesicles like exosomes play a crucial role in communication and information exchange in between such systemic factors and solid tissues9,10. We... |
Small RNAs in Seminal Plasma as Novel Biomarkers for GermCell Tumors.
Mørup Nina et al.
Circulating miRNAs secreted by testicular germ cell tumors (TGCT) show great potential as novel non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis of TGCT. Seminal plasma (SP) represents a biofluid closer to the primary site. Here, we investigate whether small RNAs in SP can be used to diagnose men with TGCTs or the precursor le... |
miRMaster 2.0: multi-species non-coding RNA sequencing analyses at scale
Tobias Fehlmann, Fabian Kern, Omar Laham, Christina Backes, Jeffrey Solomon, Pascal Hirsch, Carsten Volz, Rolf Müller, Andreas Keller
Analyzing all features of small non-coding RNA sequencing data can be demanding and challenging. To facilitate this process, we developed miRMaster. After the analysis of over 125 000 human samples and 1.5 trillion human small RNA reads over 4 years, we present miRMaster 2 with a wide range of updates and new featur... |
Bacterial small RNAs and host epigenetic effectors of atransgenerational memory of pathogens in C. elegans
Legüe M. et al.
The inheritance of memories is adaptive for survival. Microbes interact with all organisms challenging their immunity and triggering behavioral adaptations. Some of these behaviors induced by bacteria can be inherited although the mechanisms of action are largely unexplored. In this work, we use C. elegans and its b... |
Interspecies RNA Interactome of Pathogen and Host in a Heritable Defensive Strategy.
Legüe M. et al.
Communication with bacteria deeply impacts the life history traits of their hosts. Through specific molecules and metabolites, bacteria can promote short- and long-term phenotypic and behavioral changes in the nematode . The chronic exposure of to pathogens promotes the adaptive behavior in the host's progeny called... |
Distinct Extracellular RNA Profiles in Different PlasmaComponents.
Jia Jing et al.
Circulating extracellular RNAs (exRNAs) have great potential to serve as biomarkers for a wide range of diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic applications. So far, knowledge of the difference among different sources of exRNAs is limited. To address this issue, we performed a sequential physical and biochemical pre... |
Genes with 5′ terminal oligopyrimidine tracts preferentially escape global suppression of translation by the SARS-CoV-2 NSP1 protein
Shilpa R. et al.
Viruses rely on the host translation machinery to synthesize their own proteins. Consequently, they have evolved varied mechanisms to co-opt host translation for their survival. SARS-CoV-2 relies on a non-structural protein, NSP1, for shutting down host translation. Despite this, it is currently unknown how viral pr... |
Repeat RNAs associate with replication forks and post-replicative DNA.
Gylling HM, Gonzalez-Aguilera C, Smith MA, Kaczorowski DC, Groth A, Lund AH
Non-coding RNA has a proven ability to direct and regulate chromatin modifications by acting as scaffolds between DNA and histone-modifying complexes. However, it is unknown if ncRNA plays any role in DNA replication and epigenome maintenance, including histone eviction and re-instalment of histone-modifications aft... |
The ribosomal protein S1-dependent standby site in tisB mRNA consists of a single-stranded region and a 5′ structure element
Romilly C. et al.
In bacteria, stable RNA structures that sequester ribosome-binding sites (RBS) impair translation initiation, and thus protein output. In some cases, ribosome standby can overcome inhibition by structure: 30S subunits bind sequence-nonspecifically to a single-stranded region and, on breathing of the inhibitory struc... |
The sncRNA Zoo: a repository for circulating small noncoding RNAs in animals.
Fehlmann T, Backes C, Pirritano M, Laufer T, Galata V, Kern F, Kahraman M, Gasparoni G, Ludwig N, Lenhof HP, Gregersen HA, Francke R, Meese E, Simon M, Keller A
The repertoire of small noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs), particularly miRNAs, in animals is considered to be evolutionarily conserved. Studies on sncRNAs are often largely based on homology-based information, relying on genomic sequence similarity and excluding actual expression data. To obtain information on sncRNA expres... |
NGS analysis of total small non coding RNAs from low input RNA from dried blood sampling
Marcello Pirritano, Tobias Fehlmann, Thomas Laufer, Nicole Ludwig, Gilles Gasparoni, Yongping Li, Eckart Meese, Andreas Keller, and Martin Simon
Circulating miRNAs are favored for biomarker candidates as they can reflect tissue specific miRNA dysregulation in disease contexts. Moreover, they have additional advantages that they can be monitored in a minimal invasive manner. Blood-borne miRNAs are therefore currently characterized to identify, describe and va... |
Web-based NGS data analysis using miRMaster: a large-scale meta-analysis of human miRNAs
Tobias Fehlmann, Christina Backes, Mustafa Kahraman, Jan Haas, Nicole Ludwig, Andreas E. Posch, Maximilian L. Würstle, Matthias Hübenthal, Andre Franke, Benjamin Meder, Eckart Meese, Andreas Keller
The analysis of small RNA NGS data together with the discovery of new small RNAs is among the foremost challenges in life science. For the analysis of raw high-throughput sequencing data we implemented the fast, accurate and comprehensive web-based tool miRMaster. Our toolbox provides a wide range of modules for qua... |