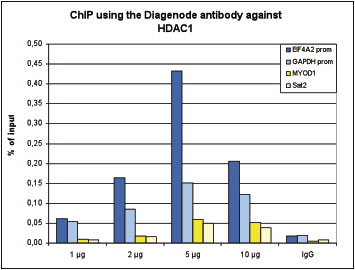
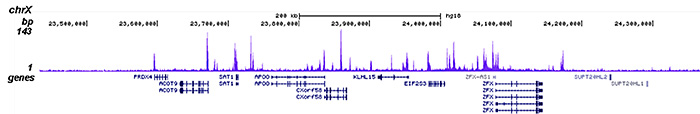
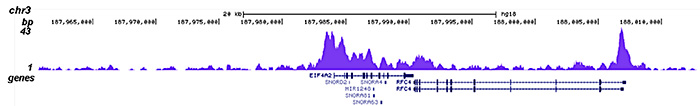
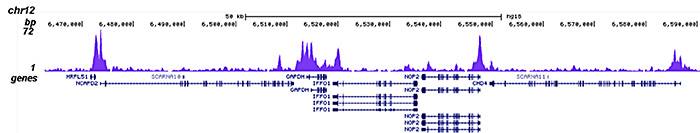
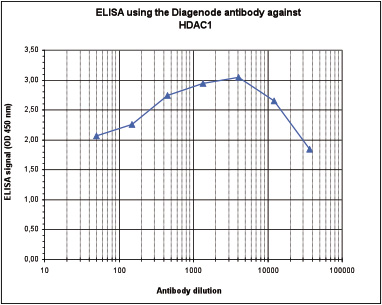
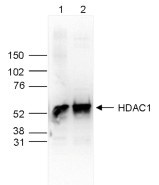
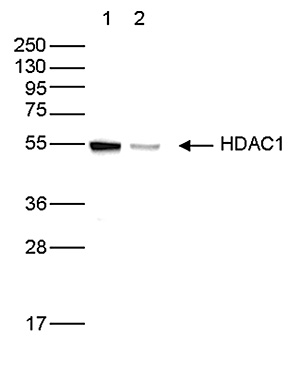
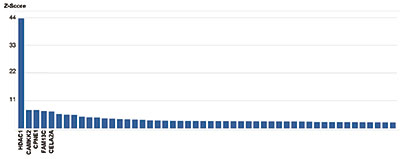
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: HDAC1 Antibody (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410325 Lot# A21-001P). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
NUP98 and RAE1 sustain progenitor function through HDAC-dependentchromatin targeting to escape from nucleolar localization.
Neely Amy E. et al.
Self-renewing somatic tissues rely on progenitors to support the continuous tissue regeneration. The gene regulatory network maintaining progenitor function remains incompletely understood. Here we show that NUP98 and RAE1 are highly expressed in epidermal progenitors, forming a separate complex in the nucleoplasm. ... |
Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 target gene regulatory networks of nephronprogenitors to control nephrogenesis.
Liu Hongbing et al.
Our studies demonstrated the critical role of Histone deacetylases (HDACs) in the regulation of nephrogenesis. To better understand the key pathways regulated by HDAC1/2 in early nephrogenesis, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-Seq) of Hdac1/2 on isolated nephron progenitor cells (NPCs) fro... |
Threonine phosphorylation of IκBζ mediates inhibition of selective proinflammatory target genes.
Grondona P, Bucher P, Schmitt A, Schönfeld C, Streibl B, Müller A, Essmann F, Liberatori S, Mohammed S, Hennig A, Kramer D, Schulze-Osthoff K, Hailfinger S
Transcription factors of the NF-κB family play a crucial role for immune responses by activating the expression of chemokines, cytokines and antimicrobial peptides involved in pathogen clearance. IκBζ, an atypical nuclear IκB protein and selective coactivator of particular NF-κB target g... |
Immunity drives regulation in cancer through NF-κB.
Collignon E, Canale A, Al Wardi C, Bizet M, Calonne E, Dedeurwaerder S, Garaud S, Naveaux C, Barham W, Wilson A, Bouchat S, Hubert P, Van Lint C, Yull F, Sotiriou C, Willard-Gallo K, Noel A, Fuks F
Ten-eleven translocation enzymes (TET1, TET2, and TET3), which induce DNA demethylation and gene regulation by converting 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), are often down-regulated in cancer. We uncover, in basal-like breast cancer (BLBC), genome-wide 5hmC changes related to regulation. We fu... |
Immunity drives TET1 regulation in cancer through NF-kB
Collignon E, Canale A, Al Wardi C, Bizet M, Calonne E, Dedeurwaerder S, Garaud S, Naveaux C, Barham W, Wilson A, Bouchat S, Hubert P, Van Lint C, Yull F, Sotiriou C, Willard-Gallo K, Noel A, Fuks F
Ten-eleven translocation enzymes (TET1, TET2, and TET3), which induce DNA demethylation and gene regulation by converting 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), are often down-regulated in cancer. We uncover, in basal-like breast cancer (BLBC), genome-wide 5hmC changes related to regulation. We fu... |
Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF10 suppresses TGFβ-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via a negative feedback mechanism
Mishra V.K. et al.
TGFβ-SMAD signaling exerts a contextual effect that suppresses malignant growth early in epithelial tumorigenesis but promotes metastasis at later stages. Longstanding challenges in resolving this functional dichotomy may uncover new strategies to treat advanced carcinomas. The Krüppel-like transcription f... |
HDAC1 negatively regulates Bdnf and Pvalb required for parvalbumin interneuron maturation in an experience-dependent manner
Koh DX and Sng JC
During early postnatal development, neuronal circuits are sculpted by sensory experience provided by the external environment. This experience-dependent regulation of circuitry development consolidates the balance of excitatory-inhibitory (E/I) neurons in the brain. The cortical barrel-column that innervates a singl... |
Genome-wide hydroxymethylcytosine pattern changes in response to oxidative stress
Delatte B, Jeschke J, Defrance M, Bachman M, Creppe C, Calonne E, Bizet M, Deplus R, Marroquí L, Libin M, Ravichandran M, Mascart F, Eizirik DL, Murrell A, Jurkowski TP, Fuks F
The TET enzymes convert methylcytosine to the newly discovered base hydroxymethylcytosine. While recent reports suggest that TETs may play a role in response to oxidative stress, this role remains uncertain, and results lack in vivo models. Here we show a global decrease of hydroxymethylcytosine in cells treated w... |
SNAIL1 combines competitive displacement of ASCL2 and epigenetic mechanisms to rapidly silence the EPHB3 tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer.
Rönsch K, Jägle S, Rose K, Seidl M, Baumgartner F, Freihen V, Yousaf A, Metzger E, Lassmann S, Schüle R, Zeiser R, Michoel T, Hecht A
EPHB3 is a critical cellular guidance factor in the intestinal epithelium and an important tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer (CRC) whose expression is frequently lost at the adenoma-carcinoma transition when tumor cells become invasive. The molecular mechanisms underlying EPHB3 silencing are incompletely underst... |
Citrullination of DNMT3A by PADI4 regulates its stability and controls DNA methylation.
Deplus R, Denis H, Putmans P, Calonne E, Fourrez M, Yamamoto K, Suzuki A, Fuks F
DNA methylation is a central epigenetic modification in mammals, with essential roles in development and disease. De novo DNA methyltransferases establish DNA methylation patterns in specific regions within the genome by mechanisms that remain poorly understood. Here we show that protein citrullination by peptidylar... |
Dimethyl fumarate regulates histone deacetylase expression in astrocytes.
Kalinin S, Polak PE, Lin SX, Braun D, Guizzetti M, Zhang X, Rubinstein I, Feinstein DL
We previously showed that dimethyl fumarate (DMF) reduces inflammatory activation in astrocytes, involving activation of transcription factor Nrf2. However, the pathways causing Nrf2 activation were not examined. We now show that DMF modifies expression of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in primary rat astrocytes. Afte... |
Phosphorylation of p65(RelA) on Ser547 by ATM Represses NF-κB-Dependent Transcription of Specific Genes after Genotoxic Stress
Sabatel H, Di Valentin E, Gloire G, Dequiedt F, Piette J, Habraken Y
|
The histone demethylase Kdm3a is essential to progression through differentiation.
Herzog M, Josseaux E, Dedeurwaerder S, Calonne E, Volkmar M, Fuks F
Histone demethylation has important roles in regulating gene expression and forms part of the epigenetic memory system that regulates cell fate and identity by still poorly understood mechanisms. Here, we examined the role of histone demethylase Kdm3a during cell differentiation, showing that Kdm3a is essential for ... |
HDAC1 Regulates Fear Extinction in Mice.
Bahari-Javan S, Maddalena A, Kerimoglu C, Wittnam J, Held T, Bähr M, Burkhardt S, Delalle I, Kügler S, Fischer A, Sananbenesi F
Histone acetylation has been implicated with the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric disorders and targeting histone deacetylases (HDACs) using HDAC inhibitors was shown to be neuroprotective and to initiate neuroregenerative processes. However, little is known about the role of individual HDAC proteins during the path... |
Enhancer of Zeste 2 (EZH2) is up-regulated in malignant gliomas and in glioma stem-like cells.
Orzan F, Pellegatta S, Poliani PL, Pisati F, Caldera V, Menghi F, Kapetis D, Marras C, Schiffer D, Finocchiaro G
AIMS: Proteins of the Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) are epigenetic gene silencers and are involved in tumour development. Their oncogenic function might be associated with their role in stem cell maintenance. The histone methyltransferase Enhancer of Zeste 2 (EZH2) is a key member of PRC2 function: we have in... |
The core binding factor CBF negatively regulates skeletal muscle terminal differentiation.
Philipot O, Joliot V, Ait-Mohamed O, Pellentz C, Robin P, Fritsch L, Ait-Si-Ali S
BACKGROUND: Core Binding Factor or CBF is a transcription factor composed of two subunits, Runx1/AML-1 and CBF beta or CBFbeta. CBF was originally described as a regulator of hematopoiesis. METHODOLOGY/PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: Here we show that CBF is involved in the control of skeletal muscle terminal differentiation. I... |
Functional connection between deimination and deacetylation of histones.
Denis H, Deplus R, Putmans P, Yamada M, Métivier R, Fuks F
Histone methylation plays key roles in regulating chromatin structure and function. The recent identification of enzymes that antagonize or remove histone methylation offers new opportunities to appreciate histone methylation plasticity in the regulation of epigenetic pathways. Peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4; a... |