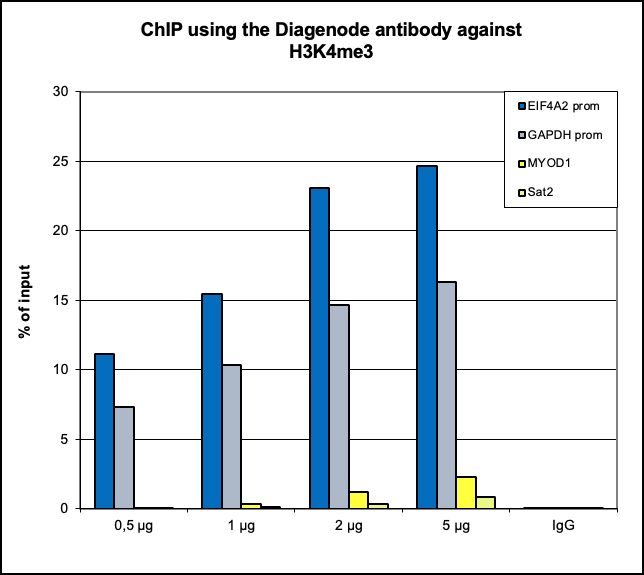
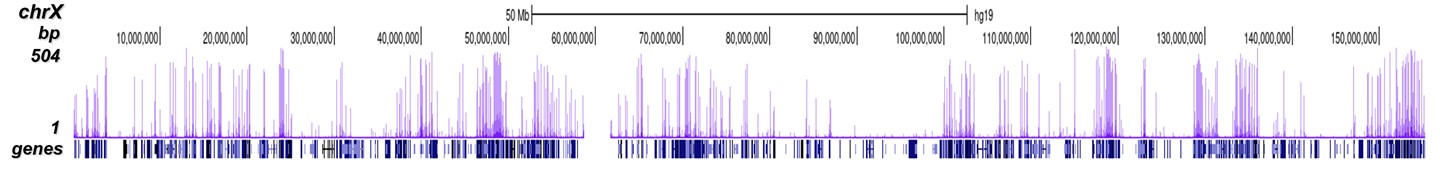
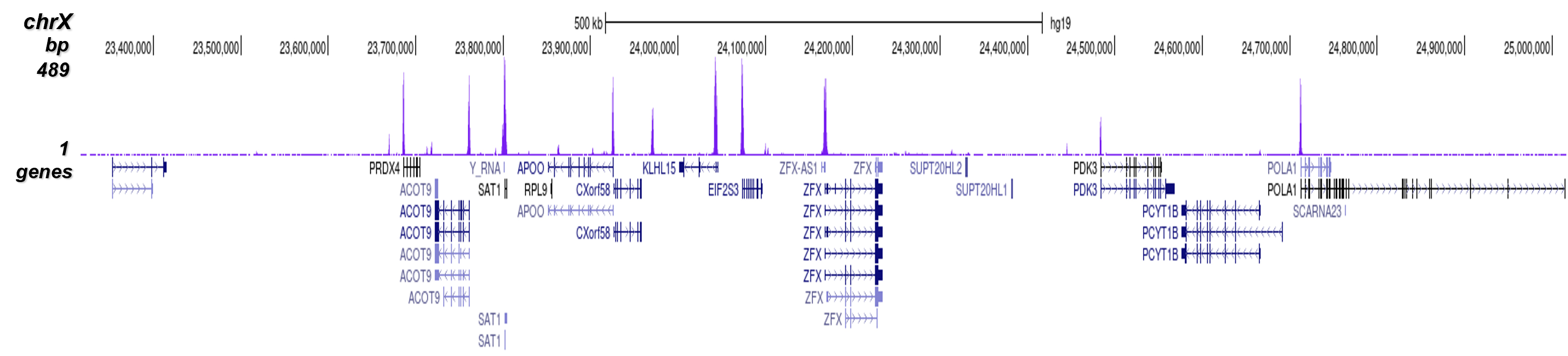
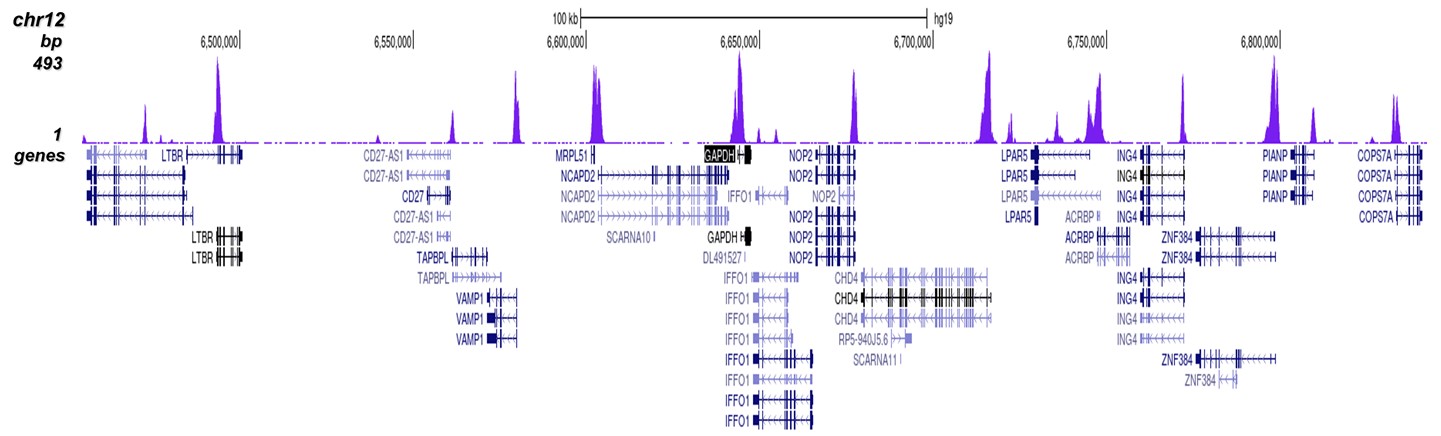
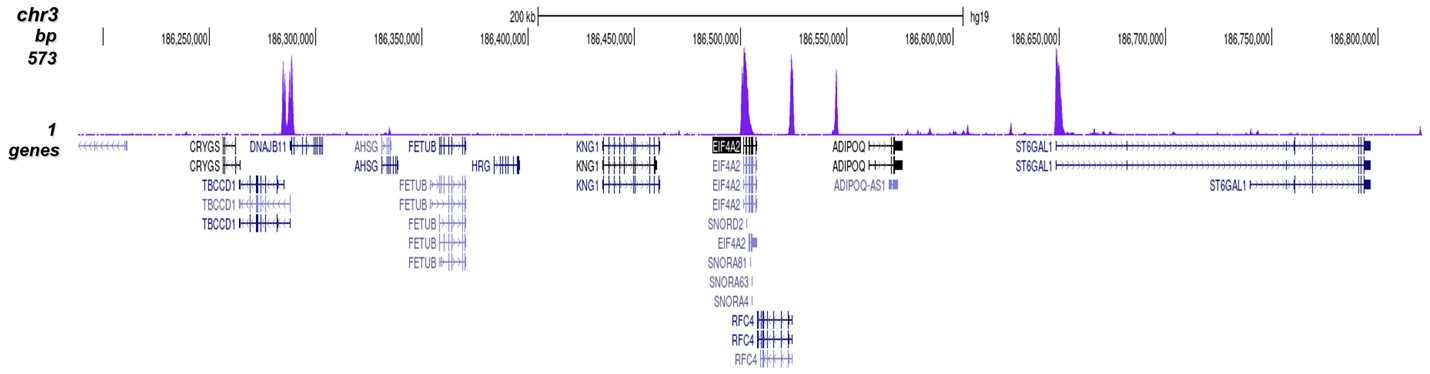
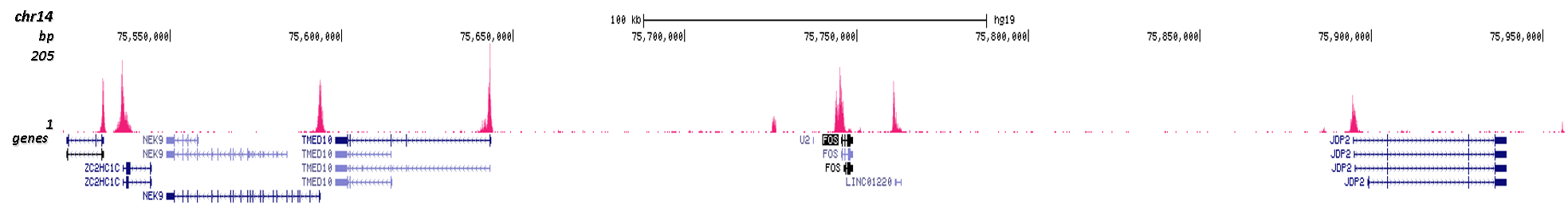
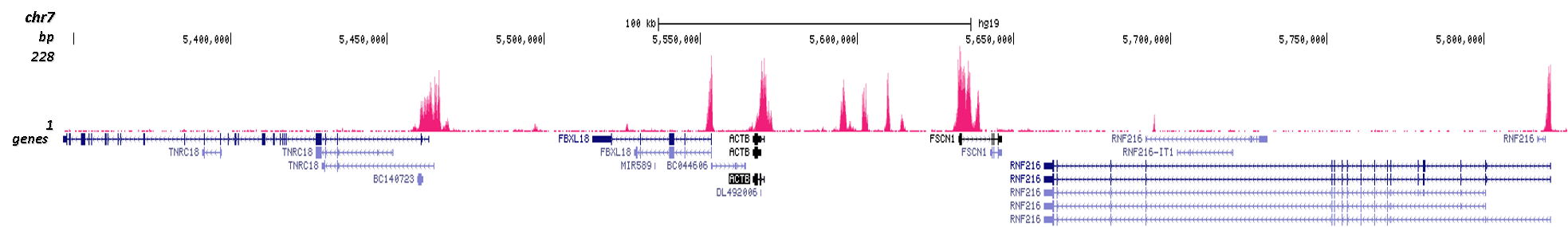
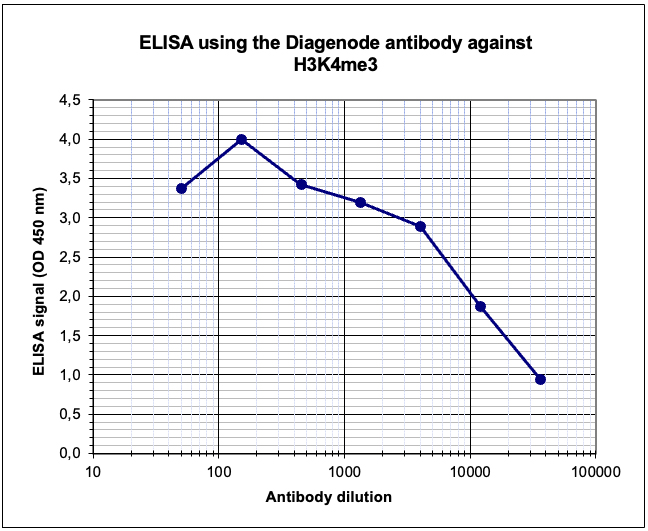
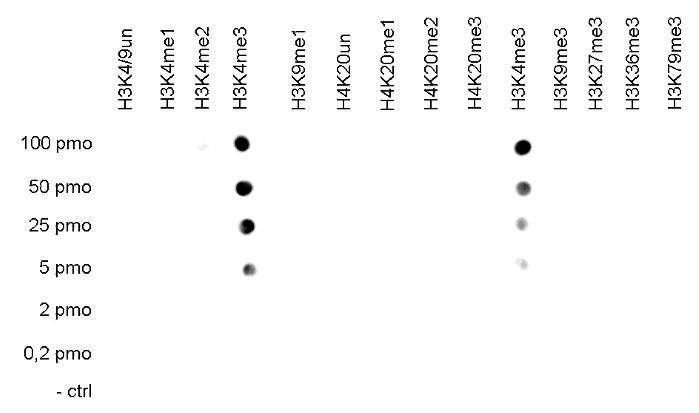
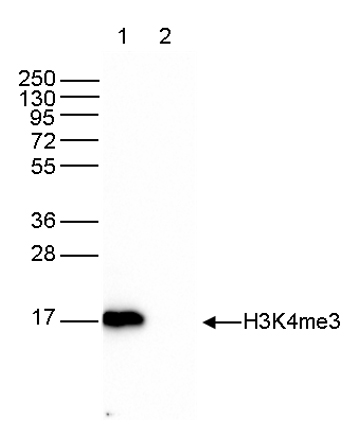
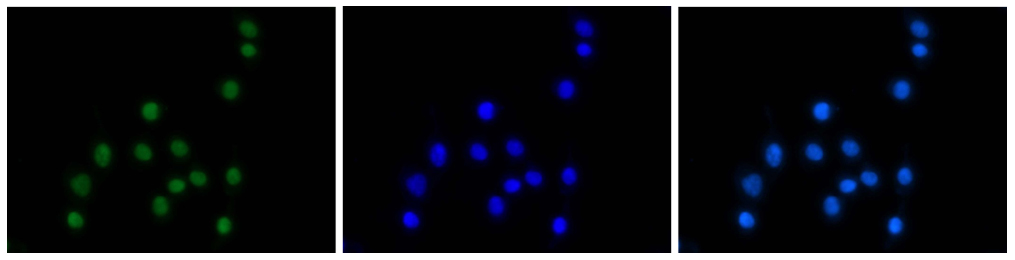
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K4me3 Antibody - ChIP-seq Grade (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410003 Lot# A8034D). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Multimodal epigenetic and enhancer network remodeling shape the transcriptional landscape of human beige adipocytes
Hazell Pickering, Sarah et al.
Epigenetic regulation is a key determinant of adipocyte fate, driving the differentiation toward white or thermogenic beige phenotypes in response to environmental cues. To dissect the mechanisms orchestrating this plasticity in human adipocytes, we conducted an integrative analysis of transcriptomic, epigenomic... |
Multimodal epigenetic and enhancer network remodeling shape the transcriptional landscape of human beige adipocytes
Hazell Pickering, Sarah et al.
Abstract
Epigenetic regulation is a key determinant of adipocyte fate, driving the differentiation toward white or thermogenic beige phenotypes in response to environmental cues. To dissect the mechanisms orchestrating this plasticity in human adipocytes, we conducted an integrative analysis of transcriptomic, epig... |
Refeeding with different levels of dietary carbohydrate modulates epigenetic stability through global DNA (de)methylation and histone modifications in juvenile and adult Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
Thongchaitriwat, Sirijanya et al.
The Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exhibits a strong metabolic response to dietary carbohydrates (CHO). Short-term refeeding after fasting with a high-carbohydrate (HC) diet has been shown to modulate CHO metabolism, but the role of epigenetic regulation in this response remains unclear. This study investiga... |
Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B-cells from a hypoxia model of the germinal center requires external unsaturated fatty acids
Havey, Larissa et al.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) drives over 200,000 cancer cases annually, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, and classic Hodgkin lymphoma-malignancies that frequently originate from germinal centers (GCs), which are physiologically hypoxic (O2 < 1%). However, conventional transformation mode... |
Epigenomics of embryogenesis in turbot
Aramburu, Oscar et al.
Embryogenesis is the foundational step of ontogeny, where a complex organism emerges from a single totipotent cell. This process is orchestrated by changes in transcriptional regulation, influenced by chromatin accessibility and epigenetic modifications, enabling transcription factor accessibility. Epigenomic re... |
Disease-specific epigenetic deregulation of enhancers, transposons, and polycomb targets in acute promyelocytic leukemia
Zhong, Xiangfu et al.
Background: Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), characterized by a fusion between the PML and RARA genes and by a block in the myeloid maturation at the promyelocytic stage.
Methods: This study investigates the epigenetic landscape of APL by integrating ChIP-se... |
Role of MNX1-mediated Histone Modifications and PBX Gene Family in MNX1-induced Leukemogenesis
Malmhäll-Bah, Eric et al.
The t(7;12)(q36;p13) AML subtype in pediatric patients is associated with the upregulation of homeodomain protein MNX1 as the initiating event for leukemogenesis. In this study, we investigated the downstream targets of MNX1 and their relationship to MNX1-induced histone modifications. Using a comprehensive appr... |
Analog epigenetic memory revealed by targeted chromatin editing
Palacios, Sebastian et al.
Cells store information by means of chromatin modifications that persist through cell divisions and can hold gene expression silenced over generations. However, how these modifications may maintain other gene expression states has remained unclear. This study shows that chromatin modifications can maintain a wide ... |
Endurance training increases a ubiquitylated form of histone H3 in the skeletal muscle, supporting Notch1 upregulation in an MDM2-dependent manner
Lam, Brian et al.
At the onset of training, each exercise session transiently shifts the distribution of histone post-transcriptional modifications (HPTMs) to activate genes that drive muscle adaptations. The resulting cyclic changes in gene expression promote the acquisition of high oxidative capacities and gains in capillaries. I... |
Active chromatin marks and up-regulation of FOXC1 in uterine epithelial cells demarcate the onset of reproductive decline in aging females
Tsolova,Aleksandra O et al.
Advanced maternal age increases the risk of pregnancy complications due, in part, to changes in the uterine environment. Here, we show that uterine aging in mice is associated with a progressive increase in transcriptional variation, accompanied by a notable accumulation of activating histone marks at multiple gen... |
Iron deficiency causes aspartate-sensitive dysfunction in CD8+ T cells
Teh, Megan R et al.
Iron is an irreplaceable co-factor for metabolism. Iron deficiency affects >1 billion people and decreased iron availability impairs immunity. Nevertheless, how iron deprivation impacts immune cell function remains poorly characterised. We interrogate how physiologically low iron availability affects CD8+&nbs... |
A spatially organized Cd24a+/ Pax9+ stem cell core governs postnatal tooth establishment
Shan, Ce et al.
Mineralized tissues are fundamental in mechanical support and protection in vertebrates. Their formation by progenitor cells during development remains elusive. Here, we show that the postnatal establishment of the molar teeth was governed by a spatially organized core of Cd24a+/Pax9+ progenitors that ... |
The chromatin reader Dido3 is a regulator of the gene network that controls B cell differentiation
Del Burgo, Fernando Gutiérrez et al.
The development of hematopoietic cell lineages is a highly complex process governed by a delicate interplay of various transcription factors. The expression of these factors is influenced, in part, by epigenetic signatures that define each stage of cell differentiation. In particular, the formation of B lymphocy... |
Epstein-Barr Virus-Driven B-Cell Transformation under Germinal Center Hypoxia Requires External Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Havey, Larissa et al.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) contributes to over 200,000 cancers annually, predominantly aggressive lymphomas originating from hypoxic germinal centers (< 1% O2). However, conventional models fail to recapitulate the physiologically relevant hypoxic microenvironment which profoundly influences B-cell metabolic remode... |
The establishment of nuclear organization in mouse embryos is orchestrated by multiple epigenetic pathways
Pal, Mrinmoy et al.
The folding of the genome in the 3D nuclear space is fundamental for regulating all DNA-related processes. The association of the genome with the nuclear lamina into lamina-associated domains (LADs) represents the earliest feature of nuclear organization during development. Here, we performed a gain-of-function sc... |
Plasma cell-free DNA chromatin immunoprecipitation profiling depicts phenotypic and clinical heterogeneity in advanced prostate cancer
Sipola, Joonatan et al.
Cell phenotype underlies prostate cancer presentation and treatment resistance and can be regulated by epigenomic features. However, the osteotropic tendency of prostate cancer limits access to metastatic tissue, meaning most prior insights into prostate cancer chromatin biology are from preclinical models that do n... |
Ectopic expression of DNMT3L in human trophoblast stem cells restores features of the placental methylome
Lea, Georgia et al.
The placental DNA methylation landscape is unique, with widespread partially methylated domains (PMDs). The placental "methylome" is conserved across mammals, a shared feature of many cancers, and extensively studied for links with pregnancy complications. Human trophoblast stem cells (hTSCs) offer exciting potent... |
Trithorax regulates long-term memory in Drosophila through epigenetic maintenance of mushroom body metabolic state and translation capacity
Nicholas Raun et al.
The role of epigenetics and chromatin in the maintenance of postmitotic neuronal cell identities is not well understood. Here, we show that the histone methyltransferase Trithorax (Trx) is required in postmitotic memory neurons of the Drosophila mushroom body (MB) to enable their capacity for long-term mem... |
The senolytic cocktail, dasatinib and quercetin, impacts the chromatin structure of both young and senescent vascular smooth muscle cells
Agnieszka Gadecka et al.
One promising strategy to alleviate aging symptoms is the treatment with senolytics that is compounds which selectively eliminate senescent cells. Some therapies aim to reduce symptoms of cellular senescence without senescent cell eradication (senomorphic activity). However, senotherapies raise many questions concer... |
EOMES establishes mesoderm and endoderm differentiation potential through SWI/SNF-mediated global enhancer remodeling
Chiara M. Schröder et al.
Highlights
Enhancer chromatin is dynamically remodeled during mesoderm/endoderm (ME) differentiation
Global ME enhancer accessibility during pluripotency exit relies on the Tbx factor EOMES
EOMES and SWI/SNF cooperate to instruct chromatin accessibility at ME gene enhancers
ME e... |
Interferon-gamma rescues FK506 dampened dendritic cell calcineurin-dependent responses to Aspergillus fumigatus via Stat3 to Stat1 switching
Amit Adlakha et al.
IScience Highlights
Calcineurin inhibitors block DC maturation in response to A. fumigatus
Lack of DC maturation impairs Th1 polarization in response to A. fumigatus
Interferon-γ restores maturation, promotes Th1 polarization and fungal killing
ChIPseq reveals in... |
Claudin-1 as a potential marker of stress-induced premature senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells
Agnieszka Gadecka et al.
Cellular senescence, a permanent state of cell cycle arrest, can result either from external stress and is then called stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS), or from the exhaustion of cell division potential giving rise to replicative senescence (RS). Despite numerous biomarkers distinguishing SIPS from RS rema... |
Trained immunity is regulated by T cell-induced CD40-TRAF6 signaling
Jacobs M.M.E. et al.
Trained immunity is characterized by histone modifications and metabolic changes in innate immune cells following exposure to inflammatory signals, leading to heightened responsiveness to secondary stimuli. Although our understanding of the molecular regulation of trained immunity has increased, the role of adaptive... |
Legionella pneumophila modulates macrophage functions through epigenetic reprogramming via the C-type lectin receptor Mincle
Stegmann F. et al.
Legionella pneumophila is a pathogen which can lead to a severe form of pneumonia in humans known as Legionnaires disease after replication in alveolar macrophages. Viable L. pneumophila actively secrete effector molecules to modulate the host’s immune response. Here, we report that L.... |
Single-cell multi-omics, spatial transcriptomics and systematic perturbation decode circuitry of neural crest fate decisions
Hu Z. et al.
Cranial neural crest (NC) cells, which can migrate, adopt multiple fates, and form most of the craniofacial skeleton, are an excellent model for studying cell fate decisions. Using time-resolved single-cell multi-omics, spatial transcriptomics, and systematic Perturb-seq, we fully deciphered zebrafish cranial NC pro... |
Systematic prioritization of functional variants and effector genes underlying colorectal cancer risk
Law P.J. et al.
Genome-wide association studies of colorectal cancer (CRC) have identified 170 autosomal risk loci. However, for most of these, the functional variants and their target genes are unknown. Here, we perform statistical fine-mapping incorporating tissue-specific epigenetic annotations and massively parallel reporter as... |
Bivalent chromatin accommodates survivin and BRG1/SWI complex to activate DNA damage response in CD4+ cells
Chandrasekaran V. et al.
Background
Bivalent regions of chromatin (BvCR) are characterized by trimethylated lysine 4 (H3K4me3) and lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3K27me3) deposition which aid gene expression control during cell differentiation. The role of BvCR in post-transcriptional DNA damage response remains unidentified. Oncoprotein ... |
RNA sequestration in P-bodies sustains myeloid leukaemia
Srikanth Kodali et al.
Post-transcriptional mechanisms are fundamental safeguards of progenitor cell identity and are often dysregulated in cancer. Here, we identified regulators of P-bodies as crucial vulnerabilities in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) through genome-wide CRISPR screens in normal and malignant haematopoietic progenitors. We... |
LL37/self-DNA complexes mediate monocyte reprogramming
Aman Damara et al.
LL37 alone and in complex with self-DNA triggers inflammatory responses in myeloid cells and plays a crucial role in the development of systemic autoimmune diseases, like psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus. We demonstrated that LL37/self-DNA complexes induce long-term metabolic and epigenetic changes in mono... |
Innate immune training restores pro-reparative myeloid functions to promote remyelination in the aged central nervous system
Tiwari V. et al.
The reduced ability of the central nervous system to regenerate with increasing age limits functional recovery following demyelinating injury. Previous work has shown that myelin debris can overwhelm the metabolic capacity of microglia, thereby impeding tissue regeneration in aging, but the underlying mechanisms are... |
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment
Perez R. F. at al.
Aging involves the deterioration of organismal function, leading to the emergence of multiple pathologies. Environmental stimuli, including lifestyle, can influence the trajectory of this process and may be used as tools in the pursuit of healthy aging. To evaluate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this context, ... |
The landscape of RNA-chromatin interaction reveals small non-coding RNAs as essential mediators of leukemia maintenance
Haiyang Yun et al.
RNA constitutes a large fraction of chromatin. Spatial distribution and functional relevance of most of RNA-chromatin interactions remain unknown. We established a landscape analysis of RNA-chromatin interactions in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In total more than 50 million interactions were captured in an AM... |
Single-cell epigenomic reconstruction of developmental trajectories from pluripotency in human neural organoid systems
Fides Zenk et al.
Cell fate progression of pluripotent progenitors is strictly regulated, resulting in high human cell diversity. Epigenetic modifications also orchestrate cell fate restriction. Unveiling the epigenetic mechanisms underlying human cell diversity has been difficult. In this study, we use human brain and retina organoi... |
SURVIVIN IN SYNERGY WITH BAF/SWI COMPLEX BINDS BIVALENT CHROMATIN REGIONS AND ACTIVATES DNA DAMAGE RESPONSE IN CD4+ T CELLS
Chandrasekaran V. et al.
This study explores a regulatory role of oncoprotein survivin on the bivalent regions of chromatin (BvCR) characterized by concomitant deposition of trimethylated lysine of histone H3 at position 4 (H3K4me3) and 27 (H3K27me3).
Intersect between BvCR and chromatin sequences bound to survivin demonstrated their co-lo... |
Multiomics uncovers the epigenomic and transcriptomic response to viral and bacterial stimulation in turbot
Aramburu O. et al.
Uncovering the epigenomic regulation of immune responses is essential for a comprehensive understanding of host defence mechanisms but remains poorly described in farmed fish. Here, we report the first annotation of the innate immune regulatory response in the genome of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus), a farmed flatfi... |
Revisiting chromatin packaging in mouse sperm
Qiangzong Yin et al.
|
Alterations in the hepatocyte epigenetic landscape in steatosis.
Maji Ranjan K. et al.
Fatty liver disease or the accumulation of fat in the liver, has been reported to affect the global population. This comes with an increased risk for the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Yet, little is known about the effects of a diet containing high fat and alcohol towards epigenet... |
Sexual differentiation in human malaria parasites is regulated bycompetition between phospholipid metabolism and histone methylation.
Harris C. T. et al.
For Plasmodium falciparum, the most widespread and virulent malaria parasite that infects humans, persistence depends on continuous asexual replication in red blood cells, while transmission to their mosquito vector requires asexual blood-stage parasites to differentiate into non-replicating gametocytes. This decisi... |
Mutant FUS induces chromatin reorganization in the hippocampus andalters memory processes.
Tzeplaeff L. et al.
Cytoplasmic mislocalization of the nuclear Fused in Sarcoma (FUS) protein is associated to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Cytoplasmic FUS accumulation is recapitulated in the frontal cortex and spinal cord of heterozygous Fus mice. Yet, the mechanisms linking FUS mislocalizati... |
The Fgf/Erf/NCoR1/2 repressive axis controls trophoblast cellfate.
Lackner A. et al.
Placental development relies on coordinated cell fate decisions governed by signalling inputs. However, little is known about how signalling cues are transformed into repressive mechanisms triggering lineage-specific transcriptional signatures. Here, we demonstrate that upon inhibition of the Fgf/Erk pathway in mous... |
Comprehensive epigenomic profiling reveals the extent of disease-specificchromatin states and informs target discovery in ankylosing spondylitis
Brown A.C. et al.
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a common, highly heritable inflammatory arthritis characterized by enthesitis of the spine and sacroiliac joints. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have revealed more than 100 genetic associations whose functional effects remain largely unresolved. Here, we present a comprehensiv... |
Chromatin profiling identifies transcriptional readthrough as a conservedmechanism for piRNA biogenesis in mosquitoes.
Qu J. et al.
The piRNA pathway in mosquitoes differs substantially from other model organisms, with an expanded PIWI gene family and functions in antiviral defense. Here, we define core piRNA clusters as genomic loci that show ubiquitous piRNA expression in both somatic and germline tissues. These core piRNA clusters are enriche... |
Epigenetic dosage identifies two major and functionally distinct beta cells ubtypes.
Dror E.et al.
The mechanisms that specify and stabilize cell subtypes remain poorly understood. Here, we identify two major subtypes of pancreatic β cells based on histone mark heterogeneity (beta HI and beta LO). Beta HI cells exhibit 4-fold higher levels of H3K27me3, distinct chromatin organization and compaction, a... |
Detailed molecular and epigenetic characterization of the Pig IPECJ2and Chicken SL-29 cell lines
de Vos J. et al.
The pig IPECJ2 and chicken SL-29 cell lines are of interest because of their untransformed nature and wide use in functional studies. Molecular characterization of these cell lines is important to gain insight into possible molecular aberrations. The aims of this paper are providing a molecular and epigenetic charac... |
Histone remodeling reflects conserved mechanisms of bovine and humanpreimplantation development.
Zhou C. et al.
How histone modifications regulate changes in gene expression during preimplantation development in any species remains poorly understood. Using CUT\&Tag to overcome limiting amounts of biological material, we profiled two activating (H3K4me3 and H3K27ac) and two repressive (H3K9me3 and H3K27me3) marks in bovine... |
Gene Regulatory Interactions at Lamina-Associated Domains
Madsen-Østerbye J. et al.
The nuclear lamina provides a repressive chromatin environment at the nuclear periphery. However, whereas most genes in lamina-associated domains (LADs) are inactive, over ten percent reside in local euchromatic contexts and are expressed. How these genes are regulated and whether they are able to interact with regu... |
Analyzing the Genome-Wide Distribution of Histone Marks byCUT\&Tag in Drosophila Embryos.
Zenk F. et al.
CUT&Tag is a method to map the genome-wide distribution of histone modifications and some chromatin-associated proteins. CUT&Tag relies on antibody-targeted chromatin tagmentation and can easily be scaled up or automatized. This protocol provides clear experimental guidelines and helpful considerations when ... |
Histone Deacetylases 1 and 2 target gene regulatory networks of nephronprogenitors to control nephrogenesis.
Liu Hongbing et al.
Our studies demonstrated the critical role of Histone deacetylases (HDACs) in the regulation of nephrogenesis. To better understand the key pathways regulated by HDAC1/2 in early nephrogenesis, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-Seq) of Hdac1/2 on isolated nephron progenitor cells (NPCs) fro... |
Balance between autophagy and cell death is maintained byPolycomb-mediated regulation during stem cell differentiation.
Puri Deepika et al.
Autophagy is a conserved cytoprotective process, aberrations in which lead to numerous degenerative disorders. While the cytoplasmic components of autophagy have been extensively studied, the epigenetic regulation of autophagy genes, especially in stem cells, is less understood. Deciphering the epigenetic regulation... |
Dietary methionine starvation impairs acute myeloid leukemia progression.
Cunningham A. et al.
Targeting altered tumor cell metabolism might provide an attractive opportunity for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). An amino acid dropout screen on primary leukemic stem cells and progenitor populations revealed a number of amino acid dependencies, of which methionine was one of the strongest. By using v... |
Trained Immunity Provides Long-Term Protection againstBacterial Infections in Channel Catfish.
Petrie-Hanson L. et al.
Beta glucan exposure induced trained immunity in channel catfish that conferred long-term protection against and infections one month post exposure. Flow cytometric analyses demonstrated that isolated macrophages and neutrophils phagocytosed higher amounts of and . Beta glucan induced changes in the distribution of ... |
bESCs from cloned embryos do not retain transcriptomic or epigenetic memory from somatic donor cells.
Navarro M. et al.
Embryonic stem cells (ESC) indefinitely maintain the pluripotent state of the blastocyst epiblast. Stem cells are invaluable for studying development and lineage commitment, and in livestock they constitute a useful tool for genomic improvement and in vitro breeding programs. Although these cells have been recently ... |
Large-scale manipulation of promoter DNA methylation revealscontext-specific transcriptional responses and stability.
de Mendoza A. et al.
BACKGROUND: Cytosine DNA methylation is widely described as a transcriptional repressive mark with the capacity to silence promoters. Epigenome engineering techniques enable direct testing of the effect of induced DNA methylation on endogenous promoters; however, the downstream effects have not yet been comprehensiv... |
HOTAIR interacts with PRC2 complex regulating the regional preadipocytetranscriptome and human fat distribution.
Kuo Feng-Chih et al.
Mechanisms governing regional human adipose tissue (AT) development remain undefined. Here, we show that the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR (HOX transcript antisense RNA) is exclusively expressed in gluteofemoral AT, where it is essential for adipocyte development. We find that HOTAIR interacts with polycomb repressive ... |
Epiblast inducers capture mouse trophectoderm stem cells in vitro andpattern blastoids for implantation in utero.
Seong Jinwoo et al.
The embryo instructs the allocation of cell states to spatially regulate functions. In the blastocyst, patterning of trophoblast (TR) cells ensures successful implantation and placental development. Here, we defined an optimal set of molecules secreted by the epiblast (inducers) that captures in vitro stable, h... |
Epigenomic analysis reveals a dynamic and context-specific macrophageenhancer landscape associated with innate immune activation and tolerance.
Zhang P. et al.
BACKGROUND: Chromatin states and enhancers associate gene expression, cell identity and disease. Here, we systematically delineate the acute innate immune response to endotoxin in terms of human macrophage enhancer activity and contrast with endotoxin tolerance, profiling the coding and non-coding transcriptome, chr... |
Epigenetic Mechanisms Mediating Cell State Transitions in Chondrocytes
Wuelling M. et al.
Epigenetic modifications play critical roles in regulating cell lineage differentiation, but the epigenetic mechanisms guiding specific differentiation steps within a cell lineage have rarely been investigated. To decipher such mechanisms, we used the defined transition from proliferating (PC) into hypertrophic chon... |
Variation in PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophil enhancersinfluences autoimmune disease susceptibility
Watt S. et al.
Neutrophils play fundamental roles in innate inflammatory response, shape adaptive immunity1, and have been identified as a potentially causal cell type underpinning genetic associations with immune system traits and diseases2,3 The majority of these variants are non-coding and the underlying mechanisms are not full... |
The CpG Island-Binding Protein SAMD1 Contributes to anUnfavorable Gene Signature in HepG2 Hepatocellular CarcinomaCells.
Simon C. et al.
The unmethylated CpG island-binding protein SAMD1 is upregulated in many human cancer types, but its cancer-related role has not yet been investigated. Here, we used the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 as a cancer model and investigated the cellular and transcriptional roles of SAMD1 using ChIP-Seq and RNA-... |
Local euchromatin enrichment in lamina-associated domains anticipatestheir repositioning in the adipogenic lineage.
Madsen-Østerbye J. et al.
BACKGROUND: Interactions of chromatin with the nuclear lamina via lamina-associated domains (LADs) confer structural stability to the genome. The dynamics of positioning of LADs during differentiation, and how LADs impinge on developmental gene expression, remains, however, elusive. RESULTS: We examined changes in t... |
ZWC complex-mediated SPT5 phosphorylation suppresses divergentantisense RNA transcription at active gene promoters.
Park K. et al.
The human genome encodes large numbers of non-coding RNAs, including divergent antisense transcripts at transcription start sites (TSSs). However, molecular mechanisms by which divergent antisense transcription is regulated have not been detailed. Here, we report a novel ZWC complex composed of ZC3H4, WDR82 and... |
Broad domains of histone marks in the highly compact macronucleargenome.
Drews F. et al.
The unicellular ciliate contains a large vegetative macronucleus with several unusual characteristics, including an extremely high coding density and high polyploidy. As macronculear chromatin is devoid of heterochromatin, our study characterizes the functional epigenomic organization necessary for gene regulation a... |
Cell-type specific transcriptional networks in root xylem adjacent celllayers
Asensi Fabado Maria Amparo et al.
Transport of water, ions and signals from roots to leaves via the xylem vessels is essential for plant life and needs to be tightly regulated. The final composition of the transpiration stream before passage into the shoots is controlled by the xylem-adjacent cell layers, namely xylem parenchyma and pericycle, in th... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple Myeloma
Elina Alaterre et al.
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have been widely used to understand themolecular processes that drive MM biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape of MM wouldadvance our un... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple
Myeloma
Alaterre, Elina and Ovejero, Sara and Herviou, Laurie and de
Boussac, Hugues and Papadopoulos, Giorgio and Kulis, Marta and
Boireau, Stéphanie and Robert, Nicolas and Requirand, Guilhem
and Bruyer, Angélique and Cartron, Guillaume and Vincent,
Laure and M
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have
been widely used to understand the molecular processes that drive MM
biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,
progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the
epigenetic landscape of MM would advance our... |
Loss of KMT2C reprograms the epigenomic landscape in hPSCsresulting in NODAL overexpression and a failure of hemogenic endotheliumspecification.
Maurya Shailendra et al.
Germline or somatic variation in the family of KMT2 lysine methyltransferases have been associated with a variety of congenital disorders and cancers. Notably, -fusions are prevalent in 70\% of infant leukaemias but fail to phenocopy short latency leukaemogenesis in mammalian models, suggesting additional factors ar... |
The long noncoding RNA H19 regulates tumor plasticity inneuroendocrine prostate cancer
Singh N. et al.
Neuroendocrine (NE) prostate cancer (NEPC) is a lethal subtype of castration-resistant prostate cancer (PCa) arising either de novo or from transdifferentiated prostate adenocarcinoma following androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). Extensive computational analysis has identified a high degree of association between th... |
Epromoters function as a hub to recruit key transcription factorsrequired for the inflammatory response
Santiago-Algarra D. et al.
Gene expression is controlled by the involvement of gene-proximal (promoters) and distal (enhancers) regulatory elements. Our previous results demonstrated that a subset of gene promoters, termed Epromoters, work as bona fide enhancers and regulate distal gene expression. Here, we hypothesized that Epromoters play a... |
Comparing the epigenetic landscape in myonuclei purified with a PCM1antibody from a fast/glycolytic and a slow/oxidative muscle.
Bengtsen Mads et al.
Muscle cells have different phenotypes adapted to different usage, and can be grossly divided into fast/glycolytic and slow/oxidative types. While most muscles contain a mixture of such fiber types, we aimed at providing a genome-wide analysis of the epigenetic landscape by ChIP-Seq in two muscle extremes, the fast/... |
Rhesus macaques self-curing from a schistosome infection can displaycomplete immunity to challenge
Amaral MS et al.
The rhesus macaque provides a unique model of acquired immunity against schistosomes, which afflict \>200 million people worldwide. By monitoring bloodstream levels of parasite-gut-derived antigen, we show that from week 10 onwards an established infection with Schistosoma mansoni is cleared in an exponential man... |
p300 suppresses the transition of myelodysplastic syndromes to acutemyeloid leukemia
Man Na et al.
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) malignancies characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis and an increased risk of leukemia transformation. Epigenetic regulators are recurrently mutated in MDS, directly implicating epigenetic dysregulation in MDS pathogenesis. Here, we... |
Differential contribution to gene expression prediction of histonemodifications at enhancers or promoters.
González-Ramírez M. et al.
The ChIP-seq signal of histone modifications at promoters is a good predictor of gene expression in different cellular contexts, but whether this is also true at enhancers is not clear. To address this issue, we develop quantitative models to characterize the relationship of gene expression with histone modification... |
DOT1L O-GlcNAcylation promotes its protein stability andMLL-fusion leukemia cell proliferation.
Song Tanjing et al.
Histone lysine methylation functions at the interface of the extracellular environment and intracellular gene expression. DOT1L is a versatile histone H3K79 methyltransferase with a prominent role in MLL-fusion leukemia, yet little is known about how DOT1L responds to extracellular stimuli. Here, we report that DOT1... |
INTS11 regulates hematopoiesis by promoting PRC2 function.
Zhang Peng et al.
INTS11, the catalytic subunit of the Integrator (INT) complex, is crucial for the biogenesis of small nuclear RNAs and enhancer RNAs. However, the role of INTS11 in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) biology is unknown. Here, we report that INTS11 is required for normal hematopoiesis and hematopoietic-spe... |
Enhanced targeted DNA methylation of the CMV and endogenous promoterswith dCas9-DNMT3A3L entails distinct subsequent histonemodification changes in CHO cells.
Marx Nicolas et al.
With the emergence of new CRISPR/dCas9 tools that enable site specific modulation of DNA methylation and histone modifications, more detailed investigations of the contribution of epigenetic regulation to the precise phenotype of cells in culture, including recombinant production subclones, is now possible. These al... |
ChIP-seq protocol for sperm cells and embryos to assess environmentalimpacts and epigenetic inheritance
Lismer, Ariane and Lambrot, Romain and Lafleur, Christine and Dumeaux,Vanessa and Kimmins, Sarah
In the field of epigenetic inheritance, delineating molecular mechanisms implicated in the transfer of paternal environmental conditions to descendants has been elusive. This protocol details how to track sperm chromatin intergenerationally. We describe mouse model design to probe chromatin states in single mouse sp... |
E2F6 initiates stable epigenetic silencing of germline genes duringembryonic development
Dahlet T. et al.
In mouse development, long-term silencing by CpG island DNA methylation is specifically targeted to germline genes; however, the molecular mechanisms of this specificity remain unclear. Here, we demonstrate that the transcription factor E2F6, a member of the polycomb repressive complex 1.6 (PRC1.6), is critical to t... |
Lasp1 regulates adherens junction dynamics and fibroblast transformationin destructive arthritis
Beckmann D. et al.
The LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (Lasp1) was originally cloned from metastatic breast cancer and characterised as an adaptor molecule associated with tumourigenesis and cancer cell invasion. However, the regulation of Lasp1 and its function in the aggressive transformation of cells is unclear. Here we use integrativ... |
Placental uptake and metabolism of 25(OH)Vitamin D determines itsactivity within the fetoplacental unit
Ashley, B. et al.
Pregnancy 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentrations are associated with maternal and fetal health outcomes, but the underlying mechanisms have not been elucidated. Using physiological human placental perfusion approaches and intact villous explants we demonstrate a role for the placenta in regulating the relation... |
Sarcomere function activates a p53-dependent DNA damage response that promotes polyploidization and limits in vivo cell engraftment.
Pettinato, Anthony M. et al.
Human cardiac regeneration is limited by low cardiomyocyte replicative rates and progressive polyploidization by unclear mechanisms. To study this process, we engineer a human cardiomyocyte model to track replication and polyploidization using fluorescently tagged cyclin B1 and cardiac troponin T. Using time-lapse i... |
The SAM domain-containing protein 1 (SAMD1) acts as a repressivechromatin regulator at unmethylated CpG islands
Stielow B. et al.
CpG islands (CGIs) are key regulatory DNA elements at most promoters, but how they influence the chromatin status and transcription remains elusive. Here, we identify and characterize SAMD1 (SAM domain-containing protein 1) as an unmethylated CGI-binding protein. SAMD1 has an atypical winged-helix domain that direct... |
Simplification of culture conditions and feeder-free expansion of bovineembryonic stem cells
Soto D. A. et al.
Bovine embryonic stem cells (bESCs) extend the lifespan of the transient pluripotent bovine inner cell mass in vitro. After years of research, derivation of stable bESCs was only recently reported. Although successful, bESC culture relies on complex culture conditions that require a custom-made base medium and mouse... |
The anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-37 is an inhibitor of trainedimmunity.
Cavalli, Giulio and Tengesdal, Isak W and Gresnigt, Mark and Nemkov, Travisand Arts, Rob J W and Domínguez-Andrés, Jorge and Molteni, Raffaella andStefanoni, Davide and Cantoni, Eleonora and Cassina, Laura and Giugliano,Silvia and Schraa, Kiki and Mill
Trained immunity (TI) is a de facto innate immune memory program induced in monocytes/macrophages by exposure to pathogens or vaccines, which evolved as protection against infections. TI is characterized by immunometabolic changes and histone post-translational modifications, which enhance production of pro-inflamma... |
Comparative analysis of histone H3K4me3 modifications between blastocystsand somatic tissues in cattle.
Ishibashi, Mao et al.
Epigenetic changes induced in the early developmental stages by the surrounding environment can have not only short-term but also long-term consequences throughout life. This concept constitutes the "Developmental Origins of Health and Disease" (DOHaD) hypothesis and encompasses the possibility of controlling livest... |
Genetic perturbation of PU.1 binding and chromatin looping at neutrophilenhancers associates with autoimmune disease.
Watt, Stephen et al.
Neutrophils play fundamental roles in innate immune response, shape adaptive immunity, and are a potentially causal cell type underpinning genetic associations with immune system traits and diseases. Here, we profile the binding of myeloid master regulator PU.1 in primary neutrophils across nearly a hundred voluntee... |
Loss of SETD1B results in the redistribution of genomic H3K4me3 in theoocyte
Hanna, C. W. et al.
Histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3) is an epigenetic mark found at gene promoters and CpG islands. H3K4me3 is essential for mammalian development, yet mechanisms underlying its genomic targeting are poorly understood. H3K4me3 methyltransferases SETD1B and MLL2 are essential for oogenesis. We investigated cha... |
Epigenomic tensor predicts disease subtypes and reveals constrained tumorevolution.
Leistico, Jacob R et al.
Understanding the epigenomic evolution and specificity of disease subtypes from complex patient data remains a major biomedical problem. We here present DeCET (decomposition and classification of epigenomic tensors), an integrative computational approach for simultaneously analyzing hierarchical heterogeneous data, ... |
Functional annotations of three domestic animal genomes provide vitalresources for comparative and agricultural research.
Kern C. et al.
Gene regulatory elements are central drivers of phenotypic variation and thus of critical importance towards understanding the genetics of complex traits. The Functional Annotation of Animal Genomes consortium was formed to collaboratively annotate the functional elements in animal genomes, starting with domesticate... |
The histone modification H3K4me3 is altered at the locus in Alzheimer'sdisease brain.
Smith, Adam et al.
Several epigenome-wide association studies of DNA methylation have highlighted altered DNA methylation in the gene in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain samples. However, no study has specifically examined histone modifications in the disease. We use chromatin immunoprecipitation-qPCR to quantify tri-methylation at hist... |
The G2-phase enriched lncRNA SNHG26 is necessary for proper cell cycleprogression and proliferation
Samdal, H. et al.
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in the regulation of cell cycle, although only a few have been functionally characterized. By combining RNA sequencing and ChIP sequencing of cell cycle synchronized HaCaT cells we have previously identified lncRNAs highly enriched for cell cycle functions. Based on a cycli... |
The epigenetic landscape in purified myonuclei from fast and slow muscles
Bengtsen, M. et al.
Muscle cells have different phenotypes adapted to different usage and can be grossly divided into fast/glycolytic and slow/oxidative types. While most muscles contain a mixture of such fiber types, we aimed at providing a genome-wide analysis of chromatin environment by ChIP-Seq in two muscle extremes, the almost co... |
WAPL maintains a cohesin loading cycle to preserve cell-type-specificdistal gene regulation.
Liu N. Q.et al.
The cohesin complex has an essential role in maintaining genome organization. However, its role in gene regulation remains largely unresolved. Here we report that the cohesin release factor WAPL creates a pool of free cohesin, in a process known as cohesin turnover, which reloads it to cell-type-specific binding sit... |
Dissecting Herpes Simplex Virus 1-Induced Host Shutoff at the RNA Level.
Friedel, Caroline C and Whisnant, Adam W and Djakovic, Lara and Rutkowski,Andrzej J and Friedl, Marie-Sophie and Kluge, Michael and Williamson, JamesC and Sai, Somesh and Vidal, Ramon Oliveira and Sauer, Sascha and Hennig,Thomas and Grothey, Arnhild an
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) induces a profound host shut-off during lytic infection. The virion host shut-off () protein plays a key role in this process by efficiently cleaving host and viral mRNAs. Furthermore, the onset of viral DNA replication is accompanied by a rapid decline in host transcriptional activity... |
Increased H3K4me3 methylation and decreased miR-7113-5p expression lead toenhanced Wnt/β-catenin signaling in immune cells from PTSD patientsleading to inflammatory phenotype.
Bam, Marpe and Yang, Xiaoming and Busbee, Brandon P and Aiello, Allison Eand Uddin, Monica and Ginsberg, Jay P and Galea, Sandro and Nagarkatti,Prakash S and Nagarkatti, Mitzi
BACKGROUND: Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a psychiatric disorder accompanied by chronic peripheral inflammation. What triggers inflammation in PTSD is currently unclear. In the present study, we identified potential defects in signaling pathways in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from individual... |
BCG Vaccination Induces Long-Term Functional Reprogramming of HumanNeutrophils.
Moorlag, Simone J C F M and Rodriguez-Rosales, Yessica Alina and Gillard,Joshua and Fanucchi, Stephanie and Theunissen, Kate and Novakovic, Borisand de Bont, Cynthia M and Negishi, Yutaka and Fok, Ezio T and Kalafati,Lydia and Verginis, Panayotis and M
The tuberculosis vaccine bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) protects against some heterologous infections, probably via induction of non-specific innate immune memory in monocytes and natural killer (NK) cells, a process known as trained immunity. Recent studies have revealed that the induction of trained immunit... |
ZNF354C is a transcriptional repressor that inhibits endothelialangiogenic sprouting.
Oo, James A and Irmer, Barnabas and Günther, Stefan and Warwick, Timothyand Pálfi, Katalin and Izquierdo Ponce, Judit and Teichmann, Tom andPflüger-Müller, Beatrice and Gilsbach, Ralf and Brandes, Ralf P andLeisegang, Matthias S
Zinc finger proteins (ZNF) are a large group of transcription factors with diverse functions. We recently discovered that endothelial cells harbour a specific mechanism to limit the action of ZNF354C, whose function in endothelial cells is unknown. Given that ZNF354C has so far only been studied in bone and tum... |
Derivation of Intermediate Pluripotent Stem Cells Amenable to PrimordialGerm Cell Specification.
Yu L. et al.
Dynamic pluripotent stem cell (PSC) states are in vitro adaptations of pluripotency continuum in vivo. Previous studies have generated a number of PSCs with distinct properties. To date, however, no known PSCs have demonstrated dual competency for chimera formation and direct responsiveness to primordial g... |
The epigenetic regulator RINF (CXXC5) maintains SMAD7 expression in human immature erythroid cells and sustains red blood cellsexpansion.
Astori A. et al.
The gene CXXC5, encoding a Retinoid-Inducible Nuclear Factor (RINF), is located within a region at 5q31.2 commonly deleted in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML). RINF may act as an epigenetic regulator and has been proposed as a tumor suppressor in hematopoietic malignancies. Howev... |
The histone H2B ubiquitin ligase RNF40 is required for HER2-drivenmammary tumorigenesis.
Wegwitz, Florian and Prokakis, Evangelos and Pejkovska, Anastasija andKosinsky, Robyn Laura and Glatzel, Markus and Pantel, Klaus and Wikman,Harriet and Johnsen, Steven A
The HER2-positive breast cancer subtype (HER2-BC) displays a particularly aggressive behavior. Anti-HER2 therapies have significantly improved the survival of patients with HER2-BC. However, a large number of patients become refractory to current targeted therapies, necessitating the development of new treatment str... |
StE(z)2, a Polycomb group methyltransferase and deposition of H3K27me3 andH3K4me3 regulate the expression of tuberization genes in potato.
Kumar, Amit and Kondhare, Kirtikumar R and Malankar, Nilam N and Banerjee,Anjan K
Polycomb Repressive Complex (PRC) group proteins regulate various developmental processes in plants by repressing the target genes via H3K27 trimethylation, whereas their function is antagonized by Trithorax group proteins-mediated H3K4 trimethylation. Tuberization in potato is widely studied, but the role of histon... |
Priming for enhanced ARGONAUTE2 activation accompanies induced resistanceto cucumber mosaic virus in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Ando, Sugihiro and Jaskiewicz, Michal and Mochizuki, Sei and Koseki, Saekoand Miyashita, Shuhei and Takahashi, Hideki and Conrath, Uwe
Systemic acquired resistance (SAR) is a broad-spectrum disease resistance response that can be induced upon infection from pathogens or by chemical treatment, such as with benzo-(1,2,3)-thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid S-methyl ester (BTH). SAR involves priming for more robust activation of defence genes upon pathogen... |
Digging Deeper into Breast Cancer Epigenetics: Insights from ChemicalInhibition of Histone Acetyltransferase TIP60 .
Idrissou, Mouhamed and Lebert, Andre and Boisnier, Tiphanie and Sanchez,Anna and Houfaf Khoufaf, Fatma Zohra and Penault-Llorca, Frédérique andBignon, Yves-Jean and Bernard-Gallon, Dominique
Breast cancer is often sporadic due to several factors. Among them, the deregulation of epigenetic proteins may be involved. TIP60 or KAT5 is an acetyltransferase that regulates gene transcription through the chromatin structure. This pleiotropic protein acts in several cellular pathways by acetylating proteins. RNA... |
NSD1-deposited H3K36me2 directs de novo methylation in the mouse malegermline and counteracts Polycomb-associated silencing.
Shirane, Kenjiro and Miura, Fumihito and Ito, Takashi and Lorincz, MatthewC
De novo DNA methylation (DNAme) in mammalian germ cells is dependent on DNMT3A and DNMT3L. However, oocytes and spermatozoa show distinct patterns of DNAme. In mouse oocytes, de novo DNAme requires the lysine methyltransferase (KMTase) SETD2, which deposits H3K36me3. We show here that SETD2 is dispensable for de nov... |
Trained Immunity-Promoting Nanobiologic Therapy Suppresses Tumor Growth andPotentiates Checkpoint Inhibition.
Priem, Bram and van Leent, Mandy M T and Teunissen, Abraham J P and Sofias,Alexandros Marios and Mourits, Vera P and Willemsen, Lisa and Klein, Emma Dand Oosterwijk, Roderick S and Meerwaldt, Anu E and Munitz, Jazz andPrévot, Geoffrey and Vera Verschuu
Trained immunity, a functional state of myeloid cells, has been proposed as a compelling immune-oncological target. Its efficient induction requires direct engagement of myeloid progenitors in the bone marrow. For this purpose, we developed a bone marrow-avid nanobiologic platform designed specifically to induce tra... |
Formation of the CenH3-Deficient Holocentromere in Lepidoptera AvoidsActive Chromatin.
Senaratne, Aruni P and Muller, Héloïse and Fryer, Kelsey A and Kawamoto,Munetaka and Katsuma, Susumu and Drinnenberg, Ines A
Despite the essentiality for faithful chromosome segregation, centromere architectures are diverse among eukaryotes and embody two main configurations: mono- and holocentromeres, referring, respectively, to localized or unrestricted distribution of centromeric activity. Of the two, some holocentromeres offer the cur... |
UTX/KDM6A suppresses AP-1 and a gliogenesis program during neuraldifferentiation of human pluripotent stem cells.
Xu, Beisi and Mulvey, Brett and Salie, Muneeb and Yang, Xiaoyang andMatsui, Yurika and Nityanandam, Anjana and Fan, Yiping and Peng, Jamy C
BACKGROUND: UTX/KDM6A is known to interact and influence multiple different chromatin modifiers to promote an open chromatin environment to facilitate gene activation, but its molecular activities in developmental gene regulation remain unclear. RESULTS: We report that in human neural stem cells, UTX binding correla... |
Epigenetic regulation of the lineage specificity of primary human dermallymphatic and blood vascular endothelial cells.
Tacconi, Carlotta and He, Yuliang and Ducoli, Luca and Detmar, Michael
Lymphatic and blood vascular endothelial cells (ECs) share several molecular and developmental features. However, these two cell types possess distinct phenotypic signatures, reflecting their different biological functions. Despite significant advances in elucidating how the specification of lymphatic and blood vasc... |
OxLDL-mediated immunologic memory in endothelial cells.
Sohrabi Y, Lagache SMM, Voges VC, Semo D, Sonntag G, Hanemann I, Kahles F, Waltenberger J, Findeisen HM
Trained innate immunity describes the metabolic reprogramming and long-term proinflammatory activation of innate immune cells in response to different pathogen or damage associated molecular patterns, such as oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL). Here, we have investigated whether the regulatory networks of trai... |
The Human Integrator Complex Facilitates Transcriptional Elongation by Endonucleolytic Cleavage of Nascent Transcripts.
Beckedorff F, Blumenthal E, daSilva LF, Aoi Y, Cingaram PR, Yue J, Zhang A, Dokaneheifard S, Valencia MG, Gaidosh G, Shilatifard A, Shiekhattar R
Transcription by RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) is pervasive in the human genome. However, the mechanisms controlling transcription at promoters and enhancers remain enigmatic. Here, we demonstrate that Integrator subunit 11 (INTS11), the catalytic subunit of the Integrator complex, regulates transcription at these loci... |
Prostate cancer reactivates developmental epigenomic programs during metastatic progression.
Pomerantz MM, Qiu X, Zhu Y, Takeda DY, Pan W, Baca SC, Gusev A, Korthauer KD, Severson TM, Ha G, Viswanathan SR, Seo JH, Nguyen HM, Zhang B, Pasaniuc B, Giambartolomei C, Alaiwi SA, Bell CA, O'Connor EP, Chabot MS, Stillman DR, Lis R, Font-Tello A, Li L,
Epigenetic processes govern prostate cancer (PCa) biology, as evidenced by the dependency of PCa cells on the androgen receptor (AR), a prostate master transcription factor. We generated 268 epigenomic datasets spanning two state transitions-from normal prostate epithelium to localized PCa to metastases-in specimens... |
The hypomethylation of imprinted genes in IVF/ICSI placenta samples is associated with concomitant changes in histone modifications.
Choux C, Petazzi P, Sanchez-Delgado M, Hernandez Mora JR, Monteagudo A, Sagot P, Monk D, Fauque P
Although more and more children are born by Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART), ART safety has not fully been demonstrated. Notably, ART could disturb the delicate step of implantation, and trigger placenta-related adverse outcomes with potential long-term effects, through disrupted epigenetic regulation. We h... |
Epigenetic priming by Dppa2 and 4 in pluripotency facilitates multi-lineage commitment.
Eckersley-Maslin MA, Parry A, Blotenburg M, Krueger C, Ito Y, Franklin VNR, Narita M, D'Santos CS, Reik W
How the epigenetic landscape is established in development is still being elucidated. Here, we uncover developmental pluripotency associated 2 and 4 (DPPA2/4) as epigenetic priming factors that establish a permissive epigenetic landscape at a subset of developmentally important bivalent promoters characterized by lo... |
Genomic deregulation of PRMT5 supports growth and stress tolerance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Schnormeier AK, Pommerenke C, Kaufmann M, Drexler HG, Koeppel M
Patients suffering from chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) display highly diverse clinical courses ranging from indolent cases to aggressive disease, with genetic and epigenetic features resembling this diversity. Here, we developed a comprehensive approach combining a variety of molecular and clinical data to pinpo... |
The hypomethylation of imprinted genes in IVF/ICSI placenta samplesis associated with concomitant changes in histone modifications.
Choux C. et al.
Although more and more children are born by Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART), ART safety has not fully been demonstrated. Notably, ART could disturb the delicate step of implantation, and trigger placenta-related adverse outcomes with potential long-term effects, through disrupted epigenetic regulation. We h... |
Measuring Histone Modifications in the Human Parasite Schistosoma mansoni
de Carvalho Augusto R, Roquis D, Al Picard M, Chaparro C, Cosseau C, Grunau C.
DNA-binding proteins play critical roles in many major processes such as development and sexual biology of Schistosoma mansoni and are important for the pathogenesis of schistosomiasis. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) are useful to characterize the association of ge... |
Histone post-translational modifications in Silene latifolia X and Y chromosomes suggest a mammal-like dosage compensation system
Luis Rodríguez Lorenzo José, Hubinský Marcel, Vyskot Boris, Hobza Roman
Silene latifolia is a model organism to study evolutionary young heteromorphic sex chromosome evolution in plants. Previous research indicates a Y-allele gene degeneration and a dosage compensation system already operating. Here, we propose an epigenetic approach based on analysis of several histone post-translation... |
TET3 controls the expression of the H3K27me3 demethylase Kdm6b during neural commitment.
Montibus B, Cercy J, Bouschet T, Charras A, Maupetit-Méhouas S, Nury D, Gonthier-Guéret C, Chauveau S, Allegre N, Chariau C, Hong CC, Vaillant I, Marques CJ, Court F, Arnaud P
The acquisition of cell identity is associated with developmentally regulated changes in the cellular histone methylation signatures. For instance, commitment to neural differentiation relies on the tightly controlled gain or loss of H3K27me3, a hallmark of polycomb-mediated transcriptional gene silencing, at specif... |
In vitro capture and characterization of embryonic rosette-stage pluripotency between naive and primed states.
Neagu A, van Genderen E, Escudero I, Verwegen L, Kurek D, Lehmann J, Stel J, Dirks RAM, van Mierlo G, Maas A, Eleveld C, Ge Y, den Dekker AT, Brouwer RWW, van IJcken WFJ, Modic M, Drukker M, Jansen JH, Rivron NC, Baart EB, Marks H, Ten Berge D
Following implantation, the naive pluripotent epiblast of the mouse blastocyst generates a rosette, undergoes lumenogenesis and forms the primed pluripotent egg cylinder, which is able to generate the embryonic tissues. How pluripotency progression and morphogenesis are linked and whether intermediate pluripotent st... |
The TGF-β profibrotic cascade targets ecto-5'-nucleotidase gene in proximal tubule epithelial cells and is a traceable marker of progressive diabetic kidney disease.
Cappelli C, Tellez A, Jara C, Alarcón S, Torres A, Mendoza P, Podestá L, Flores C, Quezada C, Oyarzún C, Martín RS
Progressive diabetic nephropathy (DN) and loss of renal function correlate with kidney fibrosis. Crosstalk between TGF-β and adenosinergic signaling contributes to the phenotypic transition of cells and to renal fibrosis in DN models. We evaluated the role of TGF-β on NT5E gene expression coding for the ec... |
LXR Activation Induces a Proinflammatory Trained Innate Immunity-Phenotype in Human Monocytes
Sohrabi Yahya, Sonntag Glenn V. H., Braun Laura C., Lagache Sina M. M., Liebmann Marie, Klotz Luisa, Godfrey Rinesh, Kahles Florian, Waltenberger Johannes, Findeisen Hannes M.
The concept of trained innate immunity describes a long-term proinflammatory memory in innate immune cells. Trained innate immunity is regulated through reprogramming of cellular metabolic pathways including cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis. Here, we have analyzed the role of Liver X Receptor (LXR), a key regula... |
A MORC-driven transcriptional switch controls Toxoplasma developmental trajectories and sexual commitment.
Farhat DC, Swale C, Dard C, Cannella D, Ortet P, Barakat M, Sindikubwabo F, Belmudes L, De Bock PJ, Couté Y, Bougdour A, Hakimi MA
Toxoplasma gondii has a complex life cycle that is typified by asexual development that takes place in vertebrates, and sexual reproduction, which occurs exclusively in felids and is therefore less studied. The developmental transitions rely on changes in the patterns of gene expression, and recent studies have assi... |
Recombination may occur in the absence of transcription in the immunoglobulin heavy chain recombination centre.
Oudinet C, Braikia FZ, Dauba A, Khamlichi AA
Developing B cells undergo V(D)J recombination to generate a vast repertoire of Ig molecules. V(D)J recombination is initiated by the RAG1/RAG2 complex in recombination centres (RCs), where gene segments become accessible to the complex. Whether transcription is the causal factor of accessibility or whether it is a ... |
Inhibition of methyltransferase activity of enhancer of zeste 2 leads to enhanced lipid accumulation and altered chromatin status in zebrafish.
den Broeder MJ, Ballangby J, Kamminga LM, Aleström P, Legler J, Lindeman LC, Kamstra JH
BACKGROUND: Recent studies indicate that exposure to environmental chemicals may increase susceptibility to developing metabolic diseases. This susceptibility may in part be caused by changes to the epigenetic landscape which consequently affect gene expression and lead to changes in lipid metabolism. The epigenetic... |
Targeting Macrophage Histone H3 Modification as a Leishmania Strategy to Dampen the NF-κB/NLRP3-Mediated Inflammatory Response.
Lecoeur H, Prina E, Rosazza T, Kokou K, N'Diaye P, Aulner N, Varet H, Bussotti G, Xing Y, Milon G, Weil R, Meng G, Späth GF
Aberrant macrophage activation during intracellular infection generates immunopathologies that can cause severe human morbidity. A better understanding of immune subversion strategies and macrophage phenotypic and functional responses is necessary to design host-directed intervention strategies. Here, we uncover a f... |
Replicational Dilution of H3K27me3 in Mammalian Cells and the Role of Poised Promoters.
Jadhav U, Manieri E, Nalapareddy K, Madha S, Chakrabarti S, Wucherpfennig K, Barefoot M, Shivdasani RA
Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) places H3K27me3 at developmental genes and is causally implicated in keeping bivalent genes silent. It is unclear if that silence requires minimum H3K27me3 levels and how the mark transmits faithfully across mammalian somatic cell generations. Mouse intestinal cells lacking EZH2 ... |
A comprehensive epigenomic analysis of phenotypically distinguishable, genetically identical female and male Daphnia pulex.
Kvist J, Athanàsio CG, Pfrender ME, Brown JB, Colbourne JK, Mirbahai L
BACKGROUND: Daphnia species reproduce by cyclic parthenogenesis involving both sexual and asexual reproduction. The sex of the offspring is environmentally determined and mediated via endocrine signalling by the mother. Interestingly, male and female Daphnia can be genetically identical, yet display large difference... |
Analysis of Histone Modifications in Rodent Pancreatic Islets by Native Chromatin Immunoprecipitation.
Sandovici I, Nicholas LM, O'Neill LP
The islets of Langerhans are clusters of cells dispersed throughout the pancreas that produce several hormones essential for controlling a variety of metabolic processes, including glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Studying the transcriptional control of pancreatic islet cells has important implications for ... |
Changes in H3K27ac at Gene Regulatory Regions in Porcine AlveolarMacrophages Following LPS or PolyIC Exposure.
Herrera-Uribe, Juber and Liu, Haibo and Byrne, Kristen A and Bond, Zahra Fand Loving, Crystal L and Tuggle, Christopher K
Changes in chromatin structure, especially in histone modifications (HMs), linked with chromatin accessibility for transcription machinery, are considered to play significant roles in transcriptional regulation. Alveolar macrophages (AM) are important immune cells for protection against pulmonary pathogens, and must... |
Functionally Annotating Regulatory Elements in the Equine Genome Using Histone Mark ChIP-Seq.
Kingsley NB, Kern C, Creppe C, Hales EN, Zhou H, Kalbfleisch TS, MacLeod JN, Petersen JL, Finno CJ, Bellone RR
One of the primary aims of the Functional Annotation of ANimal Genomes (FAANG) initiative is to characterize tissue-specific regulation within animal genomes. To this end, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-Seq) to map four histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me... |
H3K4me1 Supports Memory-like NK Cells Induced by Systemic Inflammation.
Rasid O, Chevalier C, Camarasa TM, Fitting C, Cavaillon JM, Hamon MA
Natural killer (NK) cells are unique players in innate immunity and, as such, an attractive target for immunotherapy. NK cells display immune memory properties in certain models, but the long-term status of NK cells following systemic inflammation is unknown. Here we show that following LPS-induced endotoxemia in mi... |
Trained immunity modulates inflammation-induced fibrosis.
Jeljeli M, Riccio LGC, Doridot L, Chêne C, Nicco C, Chouzenoux S, Deletang Q, Allanore Y, Kavian N, Batteux F
Chronic inflammation and fibrosis can result from inappropriately activated immune responses that are mediated by macrophages. Macrophages can acquire memory-like characteristics in response to antigen exposure. Here, we show the effect of BCG or low-dose LPS stimulation on macrophage phenotype, cytokine production,... |
MicroRNA-708 is a novel regulator of the Hoxa9 program in myeloid cells.
Schneider E, Pochert N, Ruess C, MacPhee L, Escano L, Miller C, Krowiorz K, Delsing Malmberg E, Heravi-Moussavi A, Lorzadeh A, Ashouri A, Grasedieck S, Sperb N, Kumar Kopparapu P, Iben S, Staffas A, Xiang P, Rösler R, Kanduri M, Larsson E, Fogelstrand L,
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are commonly deregulated in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), affecting critical genes not only through direct targeting, but also through modulation of downstream effectors. Homeobox (Hox) genes balance self-renewal, proliferation, cell death, and differentiation in many tissues and aberrant Hox gene... |
Epigenetic remodelling licences adult cholangiocytes for organoid formation and liver regeneration.
Aloia L, McKie MA, Vernaz G, Cordero-Espinoza L, Aleksieva N, van den Ameele J, Antonica F, Font-Cunill B, Raven A, Aiese Cigliano R, Belenguer G, Mort RL, Brand AH, Zernicka-Goetz M, Forbes SJ, Miska EA, Huch M
Following severe or chronic liver injury, adult ductal cells (cholangiocytes) contribute to regeneration by restoring both hepatocytes and cholangiocytes. We recently showed that ductal cells clonally expand as self-renewing liver organoids that retain their differentiation capacity into both hepatocytes and ductal ... |
Transcriptional alterations in glioma result primarily from DNA methylation-independent mechanisms.
Court F, Le Boiteux E, Fogli A, Müller-Barthélémy M, Vaurs-Barrière C, Chautard E, Pereira B, Biau J, Kemeny JL, Khalil T, Karayan-Tapon L, Verrelle P, Arnaud P
In cancer cells, aberrant DNA methylation is commonly associated with transcriptional alterations, including silencing of tumor suppressor genes. However, multiple epigenetic mechanisms, including polycomb repressive marks, contribute to gene deregulation in cancer. To dissect the relative contribution of DNA methyl... |
Functional analyses of a low-penetrance risk variant rs6702619/1p21.2 associating with colorectal cancer in Polish population.
Statkiewicz M, Maryan N, Kulecka M, Kuklinska U, Ostrowski J, Mikula M
Several studies employed the genome-wide association (GWA) analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to identify susceptibility regions in colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the functional studies exploring the role of associating SNPs with cancer biology are limited. Herein, using chromatin immunoprecipitat... |
β-Glucan-Induced Trained Immunity Protects against Leishmania braziliensis Infection: a Crucial Role for IL-32.
Dos Santos JC, Barroso de Figueiredo AM, Teodoro Silva MV, Cirovic B, de Bree LCJ, Damen MSMA, Moorlag SJCFM, Gomes RS, Helsen MM, Oosting M, Keating ST, Schlitzer A, Netea MG, Ribeiro-Dias F, Joosten LAB
American tegumentary leishmaniasis is a vector-borne parasitic disease caused by Leishmania protozoans. Innate immune cells undergo long-term functional reprogramming in response to infection or Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccination via a process called trained immunity, conferring non-specific protectio... |
Reactivation of super-enhancers by KLF4 in human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Tsompana M, Gluck C, Sethi I, Joshi I, Bard J, Nowak NJ, Sinha S, Buck MJ
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a disease of significant morbidity and mortality and rarely diagnosed in early stages. Despite extensive genetic and genomic characterization, targeted therapeutics and diagnostic markers of HNSCC are lacking due to the inherent heterogeneity and complexity of the dis... |
Nucleome Dynamics during Retinal Development.
Norrie JL, Lupo MS, Xu B, Al Diri I, Valentine M, Putnam D, Griffiths L, Zhang J, Johnson D, Easton J, Shao Y, Honnell V, Frase S, Miller S, Stewart V, Zhou X, Chen X, Dyer MA
More than 8,000 genes are turned on or off as progenitor cells produce the 7 classes of retinal cell types during development. Thousands of enhancers are also active in the developing retinae, many having features of cell- and developmental stage-specific activity. We studied dynamic changes in the 3D chromatin land... |
Development and epigenetic plasticity of murine Müller glia.
Dvoriantchikova G, Seemungal RJ, Ivanov D
The ability to regenerate the entire retina and restore lost sight after injury is found in some species and relies mostly on the epigenetic plasticity of Müller glia. To understand the role of mammalian Müller glia as a source of progenitors for retinal regeneration, we investigated changes in gene expres... |
The alarmin S100A9 hampers osteoclast differentiation from human circulating precursors by reducing the expression of RANK.
Di Ceglie I, Blom AB, Davar R, Logie C, Martens JHA, Habibi E, Böttcher LM, Roth J, Vogl T, Goodyear CS, van der Kraan PM, van Lent PL, van den Bosch MH
The alarmin S100A8/A9 is implicated in sterile inflammation-induced bone resorption and has been shown to increase the bone-resorptive capacity of mature osteoclasts. Here, we investigated the effects of S100A9 on osteoclast differentiation from human CD14 circulating precursors. Hereto, human CD14 monocytes were is... |
Probing the Tumor Suppressor Function of BAP1 in CRISPR-Engineered Human Liver Organoids.
Artegiani B, van Voorthuijsen L, Lindeboom RGH, Seinstra D, Heo I, Tapia P, López-Iglesias C, Postrach D, Dayton T, Oka R, Hu H, van Boxtel R, van Es JH, Offerhaus J, Peters PJ, van Rheenen J, Vermeulen M, Clevers H
The deubiquitinating enzyme BAP1 is a tumor suppressor, among others involved in cholangiocarcinoma. BAP1 has many proposed molecular targets, while its Drosophila homolog is known to deubiquitinate histone H2AK119. We introduce BAP1 loss-of-function by CRISPR/Cas9 in normal human cholangiocyte organoids. We find th... |
Complementary Activity of ETV5, RBPJ, and TCF3 Drives Formative Transition from Naive Pluripotency.
Kalkan T, Bornelöv S, Mulas C, Diamanti E, Lohoff T, Ralser M, Middelkamp S, Lombard P, Nichols J, Smith A
The gene regulatory network (GRN) of naive mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) must be reconfigured to enable lineage commitment. TCF3 sanctions rewiring by suppressing components of the ESC transcription factor circuitry. However, TCF3 depletion only delays and does not prevent transition to formative pluripotency. H... |
ChIP-seq of plasma cell-free nucleosomes identifies cell-of-origin geneexpression programs
Sadeh, Ronen and Sharkia, Israa and Fialkoff, Gavriel and Rahat, Ayelet andGutin, Jenia and Chappleboim, Alon and Nitzan, Mor and Fox-Fisher, Ilanaand Neiman, Daniel and Meler, Guy and Kamari, Zahala and Yaish, Dayana andPeretz, Tamar and Hubert, Ayala
Blood cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is derived from fragmented chromatin in dying cells. As such, it remains associated with histones that may retain the covalent modifications present in the cell of origin. Until now this rich epigenetic information carried by cell-free nucleosomes has not been explored at the genome level... |
PML modulates H3.3 targeting to telomeric and centromeric repeats in mouse fibroblasts.
Spirkoski J, Shah A, Reiner AH, Collas P, Delbarre E
Targeted deposition of histone variant H3.3 into chromatin is paramount for proper regulation of chromatin integrity, particularly in heterochromatic regions including repeats. We have recently shown that the promyelocytic leukemia (PML) protein prevents H3.3 from being deposited in large heterochromatic PML-associa... |
Long intergenic non-coding RNAs regulate human lung fibroblast function: Implications for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Hadjicharalambous MR, Roux BT, Csomor E, Feghali-Bostwick CA, Murray LA, Clarke DL, Lindsay MA
Phenotypic changes in lung fibroblasts are believed to contribute to the development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF), a progressive and fatal lung disease. Long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) have been identified as novel regulators of gene expression and protein activity. In non-stimulated cells, we o... |
Identification of ADGRE5 as discriminating MYC target between Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Kleo K, Dimitrova L, Oker E, Tomaszewski N, Berg E, Taruttis F, Engelmann JC, Schwarzfischer P, Reinders J, Spang R, Gronwald W, Oefner PJ, Hummel M
BACKGROUND: MYC is a heterogeneously expressed transcription factor that plays a multifunctional role in many biological processes such as cell proliferation and differentiation. It is also associated with many types of cancer including the malignant lymphomas. There are two types of aggressive B-cell lymphoma, name... |
Kdm6b regulates context-dependent hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and leukemogenesis.
Mallaney C, Ostrander EL, Celik H, Kramer AC, Martens A, Kothari A, Koh WK, Haussler E, Iwamori N, Gontarz P, Zhang B, Challen GA
The histone demethylase KDM6B (JMJD3) is upregulated in blood disorders, suggesting that it may have important pathogenic functions. Here we examined the function of Kdm6b in hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) to evaluate its potential as a therapeutic target. Loss of Kdm6b lead to depletion of phenotypic and functional... |
A critical regulator of Bcl2 revealed by systematic transcript discovery of lncRNAs associated with T-cell differentiation.
Saadi W, Kermezli Y, Dao LTM, Mathieu E, Santiago-Algarra D, Manosalva I, Torres M, Belhocine M, Pradel L, Loriod B, Aribi M, Puthier D, Spicuglia S
Normal T-cell differentiation requires a complex regulatory network which supports a series of maturation steps, including lineage commitment, T-cell receptor (TCR) gene rearrangement, and thymic positive and negative selection. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are difficult to assess due to limited T-ce... |
The role of TCF3 as potential master regulator in blastemal Wilms tumors.
Kehl T, Schneider L, Kattler K, Stöckel D, Wegert J, Gerstner N, Ludwig N, Distler U, Tenzer S, Gessler M, Walter J, Keller A, Graf N, Meese E, Lenhof HP
Wilms tumors are the most common type of pediatric kidney tumors. While the overall prognosis for patients is favorable, especially tumors that exhibit a blastemal subtype after preoperative chemotherapy have a poor prognosis. For an improved risk assessment and therapy stratification, it is essential to identify th... |
Extensive Recovery of Embryonic Enhancer and Gene Memory Stored in Hypomethylated Enhancer DNA.
Jadhav U, Cavazza A, Banerjee KK, Xie H, O'Neill NK, Saenz-Vash V, Herbert Z, Madha S, Orkin SH, Zhai H, Shivdasani RA
Developing and adult tissues use different cis-regulatory elements. Although DNA at some decommissioned embryonic enhancers is hypomethylated in adult cells, it is unknown whether this putative epigenetic memory is complete and recoverable. We find that, in adult mouse cells, hypomethylated CpG dinucleotides preserv... |
The epigenetic basis for the impaired ability of adult murine retinal pigment epithelium cells to regenerate retinal tissue.
Dvoriantchikova G, Seemungal RJ, Ivanov D
The epigenetic plasticity of amphibian retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) allows them to regenerate the entire retina, a trait known to be absent in mammals. In this study, we investigated the epigenetic plasticity of adult murine RPE to identify possible mechanisms that prevent mammalian RPE from regenerating retinal... |
Chromatin-Based Classification of Genetically Heterogeneous AMLs into Two Distinct Subtypes with Diverse Stemness Phenotypes.
Yi G, Wierenga ATJ, Petraglia F, Narang P, Janssen-Megens EM, Mandoli A, Merkel A, Berentsen K, Kim B, Matarese F, Singh AA, Habibi E, Prange KHM, Mulder AB, Jansen JH, Clarke L, Heath S, van der Reijden BA, Flicek P, Yaspo ML, Gut I, Bock C, Schuringa JJ
Global investigation of histone marks in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains limited. Analyses of 38 AML samples through integrated transcriptional and chromatin mark analysis exposes 2 major subtypes. One subtype is dominated by patients with NPM1 mutations or MLL-fusion genes, shows activation of the regulat... |
Comprehensive Analysis of Chromatin States in Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor Identifies Diverging Roles for SWI/SNF and Polycomb in Gene Regulation.
Erkek S, Johann PD, Finetti MA, Drosos Y, Chou HC, Zapatka M, Sturm D, Jones DTW, Korshunov A, Rhyzova M, Wolf S, Mallm JP, Beck K, Witt O, Kulozik AE, Frühwald MC, Northcott PA, Korbel JO, Lichter P, Eils R, Gajjar A, Roberts CWM, Williamson D, Hasselbla
Biallelic inactivation of SMARCB1, encoding a member of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, is the hallmark genetic aberration of atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors (ATRT). Here, we report how loss of SMARCB1 affects the epigenome in these tumors. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) on pri... |
The Wnt-Driven Mll1 Epigenome Regulates Salivary Gland and Head and Neck Cancer.
Zhu Q, Fang L, Heuberger J, Kranz A, Schipper J, Scheckenbach K, Vidal RO, Sunaga-Franze DY, Müller M, Wulf-Goldenberg A, Sauer S, Birchmeier W
We identified a regulatory system that acts downstream of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in salivary gland and head and neck carcinomas. We show in a mouse tumor model of K14-Cre-induced Wnt/β-catenin gain-of-function and Bmpr1a loss-of-function mutations that tumor-propagating cells exhibit increased Mll1 activi... |
Gamma radiation induces locus specific changes to histone modification enrichment in zebrafish and Atlantic salmon.
Lindeman LC, Kamstra JH, Ballangby J, Hurem S, Martín LM, Brede DA, Teien HC, Oughton DH, Salbu B, Lyche JL, Aleström P
Ionizing radiation is a recognized genotoxic agent, however, little is known about the role of the functional form of DNA in these processes. Post translational modifications on histone proteins control the organization of chromatin and hence control transcriptional responses that ultimately affect the phenotype. Th... |
Mutant p63 Affects Epidermal Cell Identity through Rewiring the Enhancer Landscape.
Qu J, Tanis SEJ, Smits JPH, Kouwenhoven EN, Oti M, van den Bogaard EH, Logie C, Stunnenberg HG, van Bokhoven H, Mulder KW, Zhou H
Transcription factor p63 is a key regulator of epidermal keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation. Mutations in the p63 DNA-binding domain are associated with ectrodactyly, ectodermal dysplasia, and cleft lip/palate (EEC) syndrome. However, the underlying molecular mechanism of these mutations remains unclear.... |
Promoter bivalency favors an open chromatin architecture in embryonic stem cells.
Mas G, Blanco E, Ballaré C, Sansó M, Spill YG, Hu D, Aoi Y, Le Dily F, Shilatifard A, Marti-Renom MA, Di Croce L
In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), developmental gene promoters are characterized by their bivalent chromatin state, with simultaneous modification by MLL2 and Polycomb complexes. Although essential for embryogenesis, bivalency is functionally not well understood. Here, we show that MLL2 plays a central role in ESC gen... |
PRC2 targeting is a therapeutic strategy for EZ score defined high-risk multiple myeloma patients and overcome resistance to IMiDs.
Herviou L, Kassambara A, Boireau S, Robert N, Requirand G, Müller-Tidow C, Vincent L, Seckinger A, Goldschmidt H, Cartron G, Hose D, Cavalli G, Moreaux J
BACKGROUND: Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant plasma cell disease with a poor survival, characterized by the accumulation of myeloma cells (MMCs) within the bone marrow. Epigenetic modifications in MM are associated not only with cancer development and progression, but also with drug resistance. METHODS: We ident... |
The Itaconate Pathway Is a Central Regulatory Node Linking Innate Immune Tolerance and Trained Immunity
Domínguez-Andrés Jorge, Novakovic Boris, Li Yang, Scicluna Brendon P., Gresnigt Mark S., Arts Rob J.W., Oosting Marije, Moorlag Simone J.C.F.M., Groh Laszlo A., Zwaag Jelle, Koch Rebecca M., ter Horst Rob, Joosten Leo A.B., Wijmenga Cisca, Michelucci Ales
Sepsis involves simultaneous hyperactivation of the immune system and immune paralysis, leading to both organ dysfunction and increased susceptibility to secondary infections. Acute activation of myeloid cells induced itaconate synthesis, which subsequently mediated innate immune tolerance in human monocytes. In con... |
Mapping molecular landmarks of human skeletal ontogeny and pluripotent stem cell-derived articular chondrocytes.
Ferguson GB, Van Handel B, Bay M, Fiziev P, Org T, Lee S, Shkhyan R, Banks NW, Scheinberg M, Wu L, Saitta B, Elphingstone J, Larson AN, Riester SM, Pyle AD, Bernthal NM, Mikkola HK, Ernst J, van Wijnen AJ, Bonaguidi M, Evseenko D
Tissue-specific gene expression defines cellular identity and function, but knowledge of early human development is limited, hampering application of cell-based therapies. Here we profiled 5 distinct cell types at a single fetal stage, as well as chondrocytes at 4 stages in vivo and 2 stages during in vitro differen... |
RNA Sequencing and Pathway Analysis Identify Important Pathways Involved in Hypertrichosis and Intellectual Disability in Patients with Wiedemann-Steiner Syndrome.
Mietton L, Lebrun N, Giurgea I, Goldenberg A, Saintpierre B, Hamroune J, Afenjar A, Billuart P, Bienvenu T
A growing number of histone modifiers are involved in human neurodevelopmental disorders, suggesting that proper regulation of chromatin state is essential for the development of the central nervous system. Among them, heterozygous de novo variants in KMT2A, a gene coding for histone methyltransferase, have been ass... |
Atopic asthma after rhinovirus-induced wheezing is associated with DNA methylation change in the SMAD3 gene promoter.
Lund RJ, Osmala M, Malonzo M, Lukkarinen M, Leino A, Salmi J, Vuorikoski S, Turunen R, Vuorinen T, Akdis C, Lähdesmäki H, Lahesmaa R, Jartti T
Children with rhinovirus-induced severe early wheezing have an increased risk of developing asthma later in life. The exact molecular mechanisms for this association are still mostly unknown. To identify potential changes in the transcriptional and epigenetic regulation in rhinovirus-associated atopic or nonatopic a... |
Integrative multi-omics analysis of intestinal organoid differentiation
Rik GH Lindeboom, Lisa van Voorthuijsen1, Koen C Oost, Maria J Rodríguez-Colman, Maria V Luna-Velez, Cristina Furlan, Floriane Baraille, Pascal WTC Jansen, Agnès Ribeiro, Boudewijn MT Burgering, Hugo J Snippert, & Michiel Vermeulen
Intestinal organoids accurately recapitulate epithelial homeostasis in vivo, thereby representing a powerful in vitro system to investigate lineage specification and cellular differentiation. Here, we applied a multi-omics framework on stem cell-enriched and stem cell-depleted mouse intestinal organoids to obtain a ... |
The Polycomb-Dependent Epigenome Controls β Cell Dysfunction, Dedifferentiation, and Diabetes.
Lu TT, Heyne S, Dror E, Casas E, Leonhardt L, Boenke T, Yang CH, Sagar , Arrigoni L, Dalgaard K, Teperino R, Enders L, Selvaraj M, Ruf M, Raja SJ, Xie H, Boenisch U, Orkin SH, Lynn FC, Hoffman BG, Grün D, Vavouri T, Lempradl AM, Pospisilik JA
To date, it remains largely unclear to what extent chromatin machinery contributes to the susceptibility and progression of complex diseases. Here, we combine deep epigenome mapping with single-cell transcriptomics to mine for evidence of chromatin dysregulation in type 2 diabetes. We find two chromatin-state signat... |
The reference epigenome and regulatory chromatin landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Beekman R. et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a frequent hematological neoplasm in which underlying epigenetic alterations are only partially understood. Here, we analyze the reference epigenome of seven primary CLLs and the regulatory chromatin landscape of 107 primary cases in the context of normal B cell differentiation.... |
Increased H3K9 methylation and impaired expression of Protocadherins are associated with the cognitive dysfunctions of the Kleefstra syndrome.
Iacono G, Dubos A, Méziane H, Benevento M, Habibi E, Mandoli A, Riet F, Selloum M, Feil R, Zhou H, Kleefstra T, Kasri NN, van Bokhoven H, Herault Y, Stunnenberg HG
Kleefstra syndrome, a disease with intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders and other developmental defects is caused in humans by haploinsufficiency of EHMT1. Although EHMT1 and its paralog EHMT2 were shown to be histone methyltransferases responsible for deposition of the di-methylated H3K9 (H3K9me2), th... |
Pro-inflammatory cytokines activate hypoxia-inducible factor 3α via epigenetic changes in mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.
Cuomo F, Coppola A, Botti C, Maione C, Forte A, Scisciola L, Liguori G, Caiafa I, Ursini MV, Galderisi U, Cipollaro M, Altucci L, Cobellis G
Human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (hMSCs) emerged as a promising therapeutic tool for ischemic disorders, due to their ability to regenerate damaged tissues, promote angiogenesis and reduce inflammation, leading to encouraging, but still limited results. The outcomes in clinical trials exploring hMSC therapy are ... |
Epigenetic modifiers promote mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative metabolism leading to enhanced differentiation of neuroprogenitor cells.
Martine Uittenbogaard, Christine A. Brantner, Anne Chiaramello1
During neural development, epigenetic modulation of chromatin acetylation is part of a dynamic, sequential and critical process to steer the fate of multipotent neural progenitors toward a specific lineage. Pan-HDAC inhibitors (HDCis) trigger neuronal differentiation by generating an "acetylation" signature and prom... |
Micro-ribonucleic acid-155 is a direct target of Meis1, but not a driver in acute myeloid leukemia
Schneider E. et al.
Micro-ribonucleic acid-155 (miR-155) is one of the first described oncogenic miRNAs. Although multiple direct targets of miR-155 have been identified, it is not clear how it contributes to the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. We found miR-155 to be a direct target of Meis1 in murine Hoxa9/Meis1 induced acute ... |
Metabolic Induction of Trained Immunity through the Mevalonate Pathway.
Bekkering S, Arts RJW, Novakovic B, Kourtzelis I, van der Heijden CDCC, Li Y, Popa CD, Ter Horst R, van Tuijl J, Netea-Maier RT, van de Veerdonk FL, Chavakis T, Joosten LAB, van der Meer JWM, Stunnenberg H, Riksen NP, Netea MG
Innate immune cells can develop long-term memory after stimulation by microbial products during infections or vaccinations. Here, we report that metabolic signals can induce trained immunity. Pharmacological and genetic experiments reveal that activation of the cholesterol synthesis pathway, but not the synthesis of... |
BCG Vaccination Protects against Experimental Viral Infection in Humans through the Induction of Cytokines Associated with Trained Immunity.
Arts RJW, Moorlag SJCFM, Novakovic B, Li Y, Wang SY, Oosting M, Kumar V, Xavier RJ, Wijmenga C, Joosten LAB, Reusken CBEM, Benn CS, Aaby P, Koopmans MP, Stunnenberg HG, van Crevel R, Netea MG
The tuberculosis vaccine bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) has heterologous beneficial effects against non-related infections. The basis of these effects has been poorly explored in humans. In a randomized placebo-controlled human challenge study, we found that BCG vaccination induced genome-wide epigenetic repr... |
Senescence-associated reprogramming promotes cancer stemness.
Milanovic M, Fan DNY, Belenki D, Däbritz JHM, Zhao Z, Yu Y, Dörr JR, Dimitrova L, Lenze D, Monteiro Barbosa IA, Mendoza-Parra MA, Kanashova T, Metzner M, Pardon K, Reimann M, Trumpp A, Dörken B, Zuber J, Gronemeyer H, Hummel M, Dittmar G, Lee S, Schmitt C
Cellular senescence is a stress-responsive cell-cycle arrest program that terminates the further expansion of (pre-)malignant cells. Key signalling components of the senescence machinery, such as p16, p21 and p53, as well as trimethylation of lysine 9 at histone H3 (H3K9me3), also operate as critical regulators of s... |
MLL2 conveys transcription-independent H3K4 trimethylation in oocytes
Hanna C.W. et al.
Histone 3 K4 trimethylation (depositing H3K4me3 marks) is typically associated with active promoters yet paradoxically occurs at untranscribed domains. Research to delineate the mechanisms of targeting H3K4 methyltransferases is ongoing. The oocyte provides an attractive system to investigate these mechanisms, becau... |
The histone code reader Spin1 controls skeletal muscle development
Greschik H. et al.
While several studies correlated increased expression of the histone code reader Spin1 with tumor formation or growth, little is known about physiological functions of the protein. We generated Spin1M5 mice with ablation of Spin1 in myoblast precursors using the Myf5-Cre deleter strain. Most Spin1M5 mice die shortly... |
In Situ Fixation Redefines Quiescence and Early Activation of Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells
Machado L. et al.
Summary
State of the art techniques have been developed to isolate and analyze cells from various tissues, aiming to capture their in vivo state. However, the majority of cell isolation protocols involve lengthy mechanical and enzymatic dissociation steps followed by flow cytometry, exposing cells to stres... |
GATA2/3-TFAP2A/C transcription factor network couples human pluripotent stem cell differentiation to trophectoderm with repression of pluripotency
Krendl C. et al.
To elucidate the molecular basis of BMP4-induced differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) toward progeny with trophectoderm characteristics, we produced transcriptome, epigenome H3K4me3, H3K27me3, and CpG methylation maps of trophoblast progenitors, purified using the surface marker APA. We combined th... |
The mixed lineage leukemia 4 (MLL4) methyltransferase complex is involved in transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)-activated gene transcription.
Baas R. et al.
Sma and Mad related (SMAD)-mediated Transforming Growth Factor β (TGF-β) and Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling is required for various cellular processes. The activated heterotrimeric SMAD protein complexes associate with nuclear proteins such as the histone acetyltransferases p300, PCAF and the M... |
Predicting stimulation-dependent enhancer-promoter interactions from ChIP-Seq time course data
Dzida T. et al.
We have developed a machine learning approach to predict stimulation-dependent enhancer-promoter interactions using evidence from changes in genomic protein occupancy over time. The occupancy of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), RNA polymerase (Pol II) and histone marks H2AZ and H3K4me3 were measured over time us... |
Genetic Predisposition to Multiple Myeloma at 5q15 Is Mediated by an ELL2 Enhancer Polymorphism
Li N. et al.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignancy of plasma cells. Genome-wide association studies have shown that variation at 5q15 influences MM risk. Here, we have sought to decipher the causal variant at 5q15 and the mechanism by which it influences tumorigenesis. We show that rs6877329 G > C resides in a predicted ... |
Chromosome contacts in activated T cells identify autoimmune disease candidate genes
Burren OS et al.
BACKGROUND:
Autoimmune disease-associated variants are preferentially found in regulatory regions in immune cells, particularly CD4+ T cells. Linking such regulatory regions to gene promoters in disease-relevant cell contexts facilitates identification of candidate disease genes.
RESULTS:
Within 4 h, act... |
A lncRNA fine tunes the dynamics of a cell state transition involving Lin28, let-7 and de novo DNA methylation
Li M.A. et al.
Execution of pluripotency requires progression from the naïve status represented by mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs) to a state capacitated for lineage specification. This transition is coordinated at multiple levels. Non-coding RNAs may contribute to this regulatory orchestra. We identified a rodent-specific ... |
Multivalent binding of PWWP2A to H2A.Z regulates mitosis and neural crest differentiation
Pünzeler S. et al.
Replacement of canonical histones with specialized histone variants promotes altering of chromatin structure and function. The essential histone variant H2A.Z affects various DNA-based processes via poorly understood mechanisms. Here, we determine the comprehensive interactome of H2A.Z and identify PWWP2A as a novel... |
Mouse models of 17q21.31 microdeletion and microduplication syndromes highlight the importance of Kansl1 for cognition
Arbogast T. et al.
Koolen-de Vries syndrome (KdVS) is a multi-system disorder characterized by intellectual disability, friendly behavior, and congenital malformations. The syndrome is caused either by microdeletions in the 17q21.31 chromosomal region or by variants in the KANSL1 gene. The reciprocal 17q21.31 microduplication syndrome... |
Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Petersen R. et al.
Linking non-coding genetic variants associated with the risk of diseases or disease-relevant traits to target genes is a crucial step to realize GWAS potential in the introduction of precision medicine. Here we set out to determine the mechanisms underpinning variant association with platelet quantitative traits usi... |
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) in Mouse T-cell Lines
Giaimo B.D. et al.
Signaling pathways regulate gene expression programs via the modulation of the chromatin structure at different levels, such as by post-translational modifications (PTMs) of histone tails, the exchange of canonical histones with histone variants, and nucleosome eviction. Such regulation requires the binding of signa... |
DNMT and HDAC inhibitors induce cryptic transcription start sites encoded in long terminal repeats
Brocks D. et al.
Several mechanisms of action have been proposed for DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors (DNMTi and HDACi), primarily based on candidate-gene approaches. However, less is known about their genome-wide transcriptional and epigenomic consequences. By mapping global transcription start site (TSS) an... |
Evolutionary re-wiring of p63 and the epigenomic regulatory landscape in keratinocytes and its potential implications on species-specific gene expression and phenotypes
Sethi I. et al.
Although epidermal keratinocyte development and differentiation proceeds in similar fashion between humans and mice, evolutionary pressures have also wrought significant species-specific physiological differences. These differences between species could arise in part, by the rewiring of regulatory network due to cha... |
RNA Polymerase III Subunit POLR3G Regulates Specific Subsets of PolyA(+) and SmallRNA Transcriptomes and Splicing in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells.
Lund R.J. et al.
POLR3G is expressed at high levels in human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) and is required for maintenance of stem cell state through mechanisms not known in detail. To explore how POLR3G regulates stem cell state, we carried out deep-sequencing analysis of polyA+ and smallRNA transcriptomes present in hPSCs an... |
The Dynamic Epigenetic Landscape of the Retina During Development, Reprogramming, and Tumorigenesis.
Aldiri I. et al.
In the developing retina, multipotent neural progenitors undergo unidirectional differentiation in a precise spatiotemporal order. Here we profile the epigenetic and transcriptional changes that occur during retinogenesis in mice and humans. Although some progenitor genes and cell cycle genes were epigenetically sil... |
Epigenetically-driven anatomical diversity of synovial fibroblasts guides joint-specific fibroblast functions
Frank-Bertoncelj M, Trenkmann M, Klein K, Karouzakis E, Rehrauer H, Bratus A, Kolling C, Armaka M, Filer A, Michel BA, Gay RE, Buckley CD, Kollias G, Gay S, Ospelt C
A number of human diseases, such as arthritis and atherosclerosis, include characteristic pathology in specific anatomical locations. Here we show transcriptomic differences in synovial fibroblasts from different joint locations and that HOX gene signatures reflect the joint-specific origins of mouse and human synov... |
Potent and Selective KDM5 Inhibitor Stops Cellular Demethylation of H3K4me3 at Transcription Start Sites and Proliferation of MM1S Myeloma Cells
Tumber A. et al.
Methylation of lysine residues on histone tail is a dynamic epigenetic modification that plays a key role in chromatin structure and gene regulation. Members of the KDM5 (also known as JARID1) sub-family are 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) and Fe2+-dependent oxygenases acting as histone 3 lysine 4 trimethyl (H3K4me3) demethyl... |
Decoupling of DNA methylation and activity of intergenic LINE-1 promoters in colorectal cancer
Vafadar-Isfahani N. et al.
Hypomethylation of LINE-1 repeats in cancer has been proposed as the main mechanism behind their activation; this assumption, however, was based on findings from early studies that were biased toward young and transpositionally active elements. Here, we investigate the relationship between methylation of 2 intergeni... |
Assessing histone demethylase inhibitors in cells: lessons learned
Hatch S.B. et al.
Background
Histone lysine demethylases (KDMs) are of interest as drug targets due to their regulatory roles in chromatin organization and their tight associations with diseases including cancer and mental disorders. The first KDM inhibitors for KDM1 have entered clinical trials, and efforts are ongoing to develop... |
RNF40 regulates gene expression in an epigenetic context-dependent manner
Xie W. et al.
BACKGROUND:
Monoubiquitination of H2B (H2Bub1) is a largely enigmatic histone modification that has been linked to transcriptional elongation. Because of this association, it has been commonly assumed that H2Bub1 is an exclusively positively acting histone modification and that increased H2Bub1 occupancy correlat... |
Menin regulates Inhbb expression through an Akt/Ezh2-mediated H3K27 histone modification
Gherardi S. et al.
Although Men1 is a well-known tumour suppressor gene, little is known about the functions of Menin, the protein it encodes for. Since few years, numerous publications support a major role of Menin in the control of epigenetics gene regulation. While Menin interaction with MLL complex favours transcriptional activati... |
A novel DLX3-PKC integrated signaling network drives keratinocyte differentiation
Palazzo E. et al.
Epidermal homeostasis relies on a well-defined transcriptional control of keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation, which is critical to prevent skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis or cancer. We have recently shown that the homeobox transcription factor DLX3 and the tumor suppressor p53 co-regul... |
Muscle catabolic capacities and global hepatic epigenome are modified in juvenile rainbow trout fed different vitamin levels at first feeding
Panserat S. et al.
Based on the concept of nutritional programming in mammals, we tested whether a short term hyper or hypo vitamin stimulus during first-feeding could induce long-lasting changes in nutrient metabolism in rainbow trout. Trout alevins received during the 4 first weeks of exogenous feeding a diet either without suppleme... |
DNA methylation heterogeneity defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma
Sheffield N.C. et al.
Developmental tumors in children and young adults carry few genetic alterations, yet they have diverse clinical presentation. Focusing on Ewing sarcoma, we sought to establish the prevalence and characteristics of epigenetic heterogeneity in genetically homogeneous cancers. We performed genome-scale DNA methylation ... |
MLL-AF9 and MLL-AF4 oncofusion proteins bind a distinct enhancer repertoire and target the RUNX1 program in 11q23 acute myeloid leukemia.
Prange KH et al.
In 11q23 leukemias, the N-terminal part of the mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) gene is fused to >60 different partner genes. In order to define a core set of MLL rearranged targets, we investigated the genome-wide binding of the MLL-AF9 and MLL-AF4 fusion proteins and associated epigenetic signatures in acute myeloi... |
Arabidopsis SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex binds both promoters and terminators to regulate gene expression
Archacki R. et al.
ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes are important regulators of gene expression in Eukaryotes. In plants, SWI/SNF-type complexes have been shown critical for transcriptional control of key developmental processes, growth and stress responses. To gain insight into mechanisms underlying these roles, we perfor... |
Epigenetic stress responses induce muscle stem-cell ageing by Hoxa9 developmental signals
Schwörer S. et al.
The functionality of stem cells declines during ageing, and this decline contributes to ageing-associated impairments in tissue regeneration and function. Alterations in developmental pathways have been associated with declines in stem-cell function during ageing, but the nature of this process remains poorly unders... |
Glutaminolysis and Fumarate Accumulation Integrate Immunometabolic and Epigenetic Programs in Trained Immunity
Arts R.J. et al.
Induction of trained immunity (innate immune memory) is mediated by activation of immune and metabolic pathways that result in epigenetic rewiring of cellular functional programs. Through network-level integration of transcriptomics and metabolomics data, we identify glycolysis, glutaminolysis, and the cholesterol s... |
Immunometabolic Pathways in BCG-Induced Trained Immunity
Arts R.J. et al.
The protective effects of the tuberculosis vaccine Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) on unrelated infections are thought to be mediated by long-term metabolic changes and chromatin remodeling through histone modifications in innate immune cells such as monocytes, a process termed trained immunity. Here, we show that BC... |
TET-dependent regulation of retrotransposable elements in mouse embryonic stem cells
de la Rica L. et al.
BACKGROUND:
Ten-eleven translocation (TET) enzymes oxidise DNA methylation as part of an active demethylation pathway. Despite extensive research into the role of TETs in genome regulation, little is known about their effect on transposable elements (TEs), which make up nearly half of the mouse and human genomes.... |
β-Glucan Reverses the Epigenetic State of LPS-Induced Immunological Tolerance
Novakovic B. et al.
Innate immune memory is the phenomenon whereby innate immune cells such as monocytes or macrophages undergo functional reprogramming after exposure to microbial components such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We apply an integrated epigenomic approach to characterize the molecular events involved in LPS-induced to... |
EPOP Functionally Links Elongin and Polycomb in Pluripotent Stem Cells
Beringer M. et al.
The cellular plasticity of pluripotent stem cells is thought to be sustained by genomic regions that display both active and repressive chromatin properties. These regions exhibit low levels of gene expression, yet the mechanisms controlling these levels remain unknown. Here, we describe Elongin BC as a binding fact... |
The Hematopoietic Transcription Factors RUNX1 and ERG Prevent AML1-ETO Oncogene Overexpression and Onset of the Apoptosis Program in t(8;21) AMLs
Mandoli A. et al.
The t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-associated oncoprotein AML1-ETO disrupts normal hematopoietic differentiation. Here, we have investigated its effects on the transcriptome and epigenome in t(8,21) patient cells. AML1-ETO binding was found at promoter regions of active genes with high levels of histone acetyl... |
Iterative Fragmentation Improves the Detection of ChIP-seq Peaks for Inactive Histone Marks
Laczik M. et al.
As chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) sequencing is becoming the dominant technique for studying chromatin modifications, new protocols surface to improve the method. Bioinformatics is also essential to analyze and understand the results, and precise analysis helps us to identify the effects of protocol optimizati... |
Fumarate is an epigenetic modifier that elicits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Sciacovelli M et al.
Mutations of the tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme fumarate hydratase cause hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer1. Fumarate hydratase-deficient renal cancers are highly aggressive and metastasize even when small, leading to a very poor clinical outcome2. Fumarate, a small molecule metabolite that accumulate... |
reChIP-seq reveals widespread bivalency of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in CD4(+) memory T cells
Kinkley S et al.
The combinatorial action of co-localizing chromatin modifications and regulators determines chromatin structure and function. However, identifying co-localizing chromatin features in a high-throughput manner remains a technical challenge. Here we describe a novel reChIP-seq approach and tailored bioinformatic analys... |
Phenotypic Plasticity through Transcriptional Regulation of the Evolutionary Hotspot Gene tan in Drosophila melanogaster
Gibert JM et al.
Phenotypic plasticity is the ability of a given genotype to produce different phenotypes in response to distinct environmental conditions. Phenotypic plasticity can be adaptive. Furthermore, it is thought to facilitate evolution. Although phenotypic plasticity is a widespread phenomenon, its molecular mechanisms are... |
MEF2C protects bone marrow B-lymphoid progenitors during stress haematopoiesis
Wang W et al.
DNA double strand break (DSB) repair is critical for generation of B-cell receptors, which are pre-requisite for B-cell progenitor survival. However, the transcription factors that promote DSB repair in B cells are not known. Here we show that MEF2C enhances the expression of DNA repair and recombination factors in ... |
Toxoplasma gondii TgIST co-opts host chromatin repressors dampening STAT1-dependent gene regulation and IFN-γ-mediated host defenses
Gay G et al.
An early hallmark of Toxoplasma gondii infection is the rapid control of the parasite population by a potent multifaceted innate immune response that engages resident and homing immune cells along with pro- and counter-inflammatory cytokines. In this context, IFN-γ activates a variety of T. gondii-targeting ac... |
Epigenetic dynamics of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation
Wallner S et al.
BACKGROUND:
Monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation involves major biochemical and structural changes. In order to elucidate the role of gene regulatory changes during this process, we used high-throughput sequencing to analyze the complete transcriptome and epigenome of human monocytes that were differentiated in... |
Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b Associate with Enhancers to Regulate Human Epidermal Stem Cell Homeostasis
Rinaldi L et al.
The genome-wide localization and function of endogenous Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b in adult stem cells are unknown. Here, we show that in human epidermal stem cells, the two proteins bind in a histone H3K36me3-dependent manner to the most active enhancers and are required to produce their associated enhancer RNAs. Both prote... |
PAFAH1B1 and the lncRNA NONHSAT073641 maintain an angiogenic phenotype in human endothelial cells
Josipovic I at al.
AIM:
Platelet-activating factor acetyl hydrolase 1B1 (PAFAH1B1, also known as Lis1) is a protein essentially involved in neurogenesis and mostly studied in the nervous system. As we observed a significant expression of PAFAH1B1 in the vascular system, we hypothesized that PAFAH1B1 is important during angiogenesis o... |
Chromatin immunoprecipitation from fixed clinical tissues reveals tumor-specific enhancer profiles.
Cejas P et al.
Extensive cross-linking introduced during routine tissue fixation of clinical pathology specimens severely hampers chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next-generation sequencing (ChIP-seq) analysis from archived tissue samples. This limits the ability to study the epigenomes of valuable, clinically annotated t... |
Comprehensive genome and epigenome characterization of CHO cells in response to evolutionary pressures and over time
Feichtinger J, Hernández I, Fischer C, Hanscho M, Auer N, Hackl M, Jadhav V, Baumann M, Krempl PM, Schmidl C, Farlik M, Schuster M, Merkel A, Sommer A, Heath S, Rico D, Bock C, Thallinger GG, Borth N
The most striking characteristic of CHO cells is their adaptability, which enables efficient production of proteins as well as growth under a variety of culture conditions, but also results in genomic and phenotypic instability. To investigate the relative contribution of genomic and epigenetic modifications towards... |
GATA-1 Inhibits PU.1 Gene via DNA and Histone H3K9 Methylation of Its Distal Enhancer in Erythroleukemia
Burda P, Vargova J, Curik N, Salek C, Papadopoulos GL, Strouboulis J, Stopka T
GATA-1 and PU.1 are two important hematopoietic transcription factors that mutually inhibit each other in progenitor cells to guide entrance into the erythroid or myeloid lineage, respectively. PU.1 controls its own expression during myelopoiesis by binding to the distal URE enhancer, whose deletion leads to acute m... |
Role of Annexin gene and its regulation during zebrafish caudal fin regeneration
Saxena S, Purushothaman S, Meghah V, Bhatti B, Poruri A, Meena Lakshmi MG, Sarath Babu N, Murthy CL, Mandal KK, Kumar A, Idris MM
The molecular mechanism of epimorphic regeneration is elusive due to its complexity and limitation in mammals. Epigenetic regulatory mechanisms play a crucial role in development and regeneration. This investigation attempted to reveal the role of epigenetic regulatory mechanisms, such as histone H3 and H4 lysine ac... |
Epigenetic regulation of diacylglycerol kinase alpha promotes radiation-induced fibrosis
Weigel C. et al.
Radiotherapy is a fundamental part of cancer treatment but its use is limited by the onset of late adverse effects in the normal tissue, especially radiation-induced fibrosis. Since the molecular causes for fibrosis are largely unknown, we analyse if epigenetic regulation might explain inter-individual differences i... |
Sperm-borne miRNAs and endo-siRNAs are important for fertilization and preimplantation embryonic development.
Yuan S et al.
Although it is believed that mammalian sperm carry small noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs) into oocytes during fertilization, it remains unknown whether these sperm-borne sncRNAs truly have any function during fertilization and preimplantation embryonic development. Germline-specific Dicer and Drosha conditional knockout (cK... |
MLL-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemias Activate BCL-2 through H3K79 Methylation and Are Sensitive to the BCL-2-Specific Antagonist ABT-199
Benito JM et al.
Targeted therapies designed to exploit specific molecular pathways in aggressive cancers are an exciting area of current research. Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL) mutations such as the t(4;11) translocation cause aggressive leukemias that are refractory to conventional treatment. The t(4;11) translocation produces an M... |
Standardizing chromatin research: a simple and universal method for ChIP-seq
Laura Arrigoni, Andreas S. Richter, Emily Betancourt, Kerstin Bruder, Sarah Diehl, Thomas Manke and Ulrike Bönisch
Here we demonstrate that harmonization of ChIP-seq workflows across cell types and conditions is possible when obtaining chromatin from properly isolated nuclei. We established an ultrasound-based nuclei extraction method (Nuclei Extraction by Sonication) that is highly effective across various organisms, cell ... |
Dynamic changes in histone modifications precede de novo DNA methylation in oocytes
Stewart KR et al.
Erasure and subsequent reinstatement of DNA methylation in the germline, especially at imprinted CpG islands (CGIs), is crucial to embryogenesis in mammals. The mechanisms underlying DNA methylation establishment remain poorly understood, but a number of post-translational modifications of histones are implicated in... |
Brg1 coordinates multiple processes during retinogenesis and is a tumor suppressor in retinoblastoma
Aldiri I et al.
Retinal development requires precise temporal and spatial coordination of cell cycle exit, cell fate specification, cell migration and differentiation. When this process is disrupted, retinoblastoma, a developmental tumor of the retina, can form. Epigenetic modulators are central to precisely coordinating developmen... |
Glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor kappa-b affect three-dimensional chromatin organization
Kuznetsova T et al.
BACKGROUND:
The impact of signal-dependent transcription factors, such as glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor kappa-b, on the three-dimensional organization of chromatin remains a topic of discussion. The possible scenarios range from remodeling of higher order chromatin architecture by activated transcrip... |
The homeoprotein DLX3 and tumor suppressor p53 co-regulate cell cycle progression and squamous tumor growth
Palazzo E et al.
Epidermal homeostasis depends on the coordinated control of keratinocyte cell cycle. Differentiation and the alteration of this balance can result in neoplastic development. Here we report on a novel DLX3-dependent network that constrains epidermal hyperplasia and squamous tumorigenesis. By integrating genetic and t... |
VEGF-mediated cell survival in non-small-cell lung cancer: implications for epigenetic targeting of VEGF receptors as a therapeutic approach
Barr MP et al.
AIMS:
To evaluate the potential therapeutic utility of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) in targeting VEGF receptors in non-small-cell lung cancer.
MATERIALS & METHODS:
Non-small-cell lung cancer cells were screened for the VEGF receptors at the mRNA and protein levels, while cellular responses to vari... |
Chromatin assembly factor CAF-1 represses priming of plant defence response genes
Mozgova I et al.
Plants have evolved efficient defence systems against pathogens that often rely on specific transcriptional responses. Priming is part of the defence syndrome, by establishing a hypersensitive state of defence genes such as after a first encounter with a pathogen. Because activation of defence responses has a fitnes... |
Spatiotemporal control of estrogen-responsive transcription in ERα-positive breast cancer cells.
P-Y Hsu, H-K Hsu, T-H Hsiao, Z Ye, E Wang, A L Profit, I Jatoi, Y Chen, N B Kirma, V X Jin, Z D Sharp and T H-M Huang
Recruitment of transcription machinery to target promoters for aberrant gene expression has been well studied, but underlying control directed by distant-acting enhancers remains unclear in cancer development. Our previous study demonstrated that distant estrogen response elements (DEREs) located on chromosome 20q13... |
Non-coding recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
Xose S. Puente, Silvia Beà, Rafael Valdés-Mas, Neus Villamor, Jesús Gutiérrez-Abril et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) is a frequent disease in which the genetic alterations determining the clinicobiological behaviour are not fully understood. Here we describe a comprehensive evaluation of the genomic landscape of 452 CLL cases and 54 patients with monoclonal B-lymphocytosis, a precursor disorder.... |
Allele-specific binding of ZFP57 in the epigenetic regulation of imprinted and non-imprinted monoallelic expression
Strogantsev R, Krueger F, Yamazawa K, Shi H, Gould P, Goldman-Roberts M, McEwen K, Sun B, Pedersen R, Ferguson-Smith AC
BACKGROUND:
Selective maintenance of genomic epigenetic imprints during pre-implantation development is required for parental origin-specific expression of imprinted genes. The Kruppel-like zinc finger protein ZFP57 acts as a factor necessary for maintaining the DNA methylation memory at multiple imprinting contr... |
Reinforcement of STAT3 activity reprogrammes human embryonic stem cells to naive-like pluripotency.
Chen H, Aksoy I, Gonnot F, Osteil P, Aubry M, Hamela C, Rognard C, Hochard A, Voisin S, Fontaine E, Mure M, Afanassieff M, Cleroux E, Guibert S, Chen J, Vallot C, Acloque H, Genthon C, Donnadieu C, De Vos J, Sanlaville D, Guérin JF, Weber M, Stanton LW, R
Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)/STAT3 signalling is a hallmark of naive pluripotency in rodent pluripotent stem cells (PSCs), whereas fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 and activin/nodal signalling is required to sustain self-renewal of human PSCs in a condition referred to as the primed state. It is unknown why LIF/... |
Opposite expression of CYP51A1 and its natural antisense transcript AluCYP51A1 in adenovirus type 37 infected retinal pigmented epithelial cells.
Pickl JM, Kamel W, Ciftci S, Punga T, Akusjärvi G
Cytochrome P450 family member CYP51A1 is a key enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis whose deregulation is implicated in numerous diseases, including retinal degeneration. Here we describe that HAdV-37 infection leads to downregulation of CYP51A1 expression and overexpression of its antisense non-coding Alu element (Al... |
A cohesin-OCT4 complex mediates Sox enhancers to prime an early embryonic lineage.
Abboud N, Moore-Morris T, Hiriart E, Yang H, Bezerra H, Gualazzi MG, Stefanovic S, Guénantin AC, Evans SM, Pucéat M
Short- and long-scales intra- and inter-chromosomal interactions are linked to gene transcription, but the molecular events underlying these structures and how they affect cell fate decision during embryonic development are poorly understood. One of the first embryonic cell fate decisions (that is, mesendoderm deter... |
Epigenome mapping reveals distinct modes of gene regulation and widespread enhancer reprogramming by the oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1.
Tomazou EM, Sheffield NC, Schmidl C, Schuster M, Schönegger A, Datlinger P, Kubicek S, Bock C, Kovar H
Transcription factor fusion proteins can transform cells by inducing global changes of the transcriptome, often creating a state of oncogene addiction. Here, we investigate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this process, focusing on Ewing sarcoma cells that are dependent on the EWS-FLI1 fusion protein. We establi... |
Embryonic stem cell differentiation requires full length Chd1.
Piatti P, Lim CY, Nat R, Villunger A, Geley S, Shue YT, Soratroi C, Moser M, Lusser A
The modulation of chromatin dynamics by ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling factors has been recognized as an important mechanism to regulate the balancing of self-renewal and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells (ESCs). Here we have studied the effects of a partial deletion of the gene encoding the chromatin remodel... |
A vlincRNA participates in senescence maintenance by relieving H2AZ-mediated repression at the INK4 locus.
Lazorthes S, Vallot C, Briois S, Aguirrebengoa M, Thuret JY, Laurent GS, Rougeulle C, Kapranov P, Mann C, Trouche D, Nicolas E
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) play major roles in proper chromatin organization and function. Senescence, a strong anti-proliferative process and a major anticancer barrier, is associated with dramatic chromatin reorganization in heterochromatin foci. Here we analyze strand-specific transcriptome changes during oncogene-... |
Cryosectioning the intestinal crypt-villus axis: an ex vivo method to study the dynamics of epigenetic modifications from stem cells to differentiated cells
Vincent A, Kazmierczak C, Duchêne B, Jonckheere N, Leteurtre E, Van Seuningen I
The intestinal epithelium is a particularly attractive biological adult model to study epigenetic mechanisms driving adult stem cell renewal and cell differentiation. Since epigenetic modifications are dynamic, we have developed an original ex vivo approach to study the expression and epigenetic profiles of key gene... |
Allelic expression mapping across cellular lineages to establish impact of non-coding SNPs.
Adoue V, Schiavi A, Light N, Almlöf JC, Lundmark P, Ge B, Kwan T, Caron M, Rönnblom L, Wang C, Chen SH, Goodall AH, Cambien F, Deloukas P, Ouwehand WH, Syvänen AC, Pastinen T
Most complex disease-associated genetic variants are located in non-coding regions and are therefore thought to be regulatory in nature. Association mapping of differential allelic expression (AE) is a powerful method to identify SNPs with direct cis-regulatory impact (cis-rSNPs). We used AE mapping to identify cis-... |
Obesity increases histone H3 lysine 9 and 18 acetylation at Tnfa and Ccl2 genes in mouse liver
Mikula M, Majewska A, Ledwon JK, Dzwonek A, Ostrowski J
Obesity contributes to the development of non‑alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is characterized by the upregulated expression of two key inflammatory mediators: tumor necrosis factor (Tnfa) and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (Mcp1; also known as Ccl2). However, the chromatin make-up at these genes in the... |
The specific alteration of histone methylation profiles by DZNep during early zebrafish development.
Ostrup O, Reiner AH, Aleström P, Collas P
Early embryo development constitutes a unique opportunity to study acquisition of epigenetic marks, including histone methylation. This study investigates the in vivo function and specificity of 3-deazaneplanocin A (DZNep), a promising anti-cancer drug that targets polycomb complex genes. One- to two-cell stage embr... |
Interrogation of allelic chromatin states in human cells by high-density ChIP-genotyping.
Light N, Adoue V, Ge B, Chen SH, Kwan T, Pastinen T
Allele-specific (AS) assessment of chromatin has the potential to elucidate specific cis-regulatory mechanisms, which are predicted to underlie the majority of the known genetic associations to complex disease. However, development of chromatin landscapes at allelic resolution has been challenging since sites of var... |
Differences among brain tumor stem cell types and fetal neural stem cells in focal regions of histone modifications and DNA methylation, broad regions of modifications, and bivalent promoters.
Yoo S, Bieda MC
BACKGROUND: Aberrational epigenetic marks are believed to play a major role in establishing the abnormal features of cancer cells. Rational use and development of drugs aimed at epigenetic processes requires an understanding of the range, extent, and roles of epigenetic reprogramming in cancer cells. Using ChIP-chip... |
Long Noncoding RNA TARID Directs Demethylation and Activation of the Tumor Suppressor TCF21 via GADD45A.
Arab K, Park YJ, Lindroth AM, Schäfer A, Oakes C, Weichenhan D, Lukanova A, Lundin E, Risch A, Meister M, Dienemann H, Dyckhoff G, Herold-Mende C, Grummt I, Niehrs C, Plass C
DNA methylation is a dynamic and reversible process that governs gene expression during development and disease. Several examples of active DNA demethylation have been documented, involving genome-wide and gene-specific DNA demethylation. How demethylating enzymes are targeted to specific genomic loci remains largel... |
Identification of a large protein network involved in epigenetic transmission in replicating DNA of embryonic stem cells.
Aranda S, Rutishauser D, Ernfors P
Pluripotency of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) is maintained by transcriptional activities and chromatin modifying complexes highly organized within the chromatin. Although much effort has been focused on identifying genome-binding sites, little is known on their dynamic association with chromatin across cell divisions... |
Seminoma and embryonal carcinoma footprints identified by analysis of integrated genome-wide epigenetic and expression profiles of germ cell cancer cell lines.
van der Zwan YG, Rijlaarsdam MA, Rossello FJ, Notini AJ, de Boer S, Watkins DN, Gillis AJ, Dorssers LC, White SJ, Looijenga LH
BACKGROUND: Originating from Primordial Germ Cells/gonocytes and developing via a precursor lesion called Carcinoma In Situ (CIS), Germ Cell Cancers (GCC) are the most common cancer in young men, subdivided in seminoma (SE) and non-seminoma (NS). During physiological germ cell formation/maturation, epigenetic proces... |
Nuclear ARRB1 induces pseudohypoxia and cellular metabolism reprogramming in prostate cancer
Zecchini V, Madhu B, Russell R, Pértega-Gomes N, Warren A, Gaude E, Borlido J, Stark R, Ireland-Zecchini H, Rao R, Scott H, Boren J, Massie C, Asim M, Brindle K, Griffiths J, Frezza C, Neal DE, Mills IG
Tumour cells sustain their high proliferation rate through metabolic reprogramming, whereby cellular metabolism shifts from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis, even under normal oxygen levels. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1A (HIF1A) is a major regulator of this process, but its activation under normoxic con... |
Stage-specific control of early B cell development by the transcription factor Ikaros.
Schwickert TA, Tagoh H, Gültekin S, Dakic A, Axelsson E, Minnich M, Ebert A, Werner B, Roth M, Cimmino L, Dickins RA, Zuber J, Jaritz M, Busslinger M
The transcription factor Ikaros is an essential regulator of lymphopoiesis. Here we studied its B cell-specific function by conditional inactivation of the gene encoding Ikaros (Ikzf1) in pro-B cells. B cell development was arrested at an aberrant 'pro-B cell' stage characterized by increased cell adhesion and loss ... |
A novel microscopy-based high-throughput screening method to identify proteins that regulate global histone modification levels.
Baas R, Lelieveld D, van Teeffelen H, Lijnzaad P, Castelijns B, van Schaik FM, Vermeulen M, Egan DA, Timmers HT, de Graaf P
Posttranslational modifications of histones play an important role in the regulation of gene expression and chromatin structure in eukaryotes. The balance between chromatin factors depositing (writers) and removing (erasers) histone marks regulates the steady-state levels of chromatin modifications. Here we describe... |
Pan-histone demethylase inhibitors simultaneously targeting Jumonji C and lysine-specific demethylases display high anticancer activities.
Rotili D, Tomassi S, Conte M, Benedetti R, Tortorici M, Ciossani G, Valente S, Marrocco B, Labella D, Novellino E, Mattevi A, Altucci L, Tumber A, Yapp C, King ON, Hopkinson RJ, Kawamura A, Schofield CJ, Mai A
In prostate cancer, two different types of histone lysine demethylases (KDM), LSD1/KDM1 and JMJD2/KDM4, are coexpressed and colocalize with the androgen receptor. We designed and synthesized hybrid LSD1/JmjC or "pan-KDM" inhibitors 1-6 by coupling the skeleton of tranylcypromine 7, a known LSD1 inhibitor, with 4-car... |
Interplay between active chromatin marks and RNA-directed DNA methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Greenberg MV, Deleris A, Hale CJ, Liu A, Feng S, Jacobsen SE
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mark that is associated with transcriptional repression of transposable elements and protein-coding genes. Conversely, transcriptionally active regulatory regions are strongly correlated with histone 3 lysine 4 di- and trimethylation (H3K4m2/m3). We previously showed that Arabidopsis... |
A Kinase-Independent Function of CDK6 Links the Cell Cycle to Tumor Angiogenesis.
Kollmann K, Heller G, Schneckenleithner C, Warsch W, Scheicher R, Ott RG, Schäfer M, Fajmann S, Schlederer M, Schiefer AI, Reichart U, Mayerhofer M, Hoeller C, Zöchbauer-Müller S, Kerjaschki D, Bock C, Kenner L, Hoefler G, Freissmuth M, Green AR, Moriggl
In contrast to its close homolog CDK4, the cell cycle kinase CDK6 is expressed at high levels in lymphoid malignancies. In a model for p185(BCR-ABL+) B-acute lymphoid leukemia, we show that CDK6 is part of a transcription complex that induces the expression of the tumor suppressor p16(INK4a) and the pro-angiogenic f... |
Disease-Related Growth Factor and Embryonic Signaling Pathways Modulate an Enhancer of TCF21 Expression at the 6q23.2 Coronary Heart Disease Locus.
Miller CL, Anderson DR, Kundu RK, Raiesdana A, Nürnberg ST, Diaz R, Cheng K, Leeper NJ, Chen CH, Chang IS, Schadt EE, Hsiung CA, Assimes TL, Quertermous T
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of mortality in both developed and developing countries worldwide. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have now identified 46 independent susceptibility loci for CHD, however, the biological and disease-relevant mechanisms for these associations remain elusive. Th... |
Bivalent chromatin marks developmental regulatory genes in the mouse embryonic germline in vivo.
Sachs M, Onodera C, Blaschke K, Ebata KT, Song JS, Ramalho-Santos M
Developmental regulatory genes have both activating (H3K4me3) and repressive (H3K27me3) histone modifications in embryonic stem cells (ESCs). This bivalent configuration is thought to maintain lineage commitment programs in a poised state. However, establishing physiological relevance has been complicated by the hig... |
Integrative analysis of deep sequencing data identifies estrogen receptor early response genes and links ATAD3B to poor survival in breast cancer.
Ovaska K, Matarese F, Grote K, Charapitsa I, Cervera A, Liu C, Reid G, Seifert M, Stunnenberg HG, Hautaniemi S
Identification of responsive genes to an extra-cellular cue enables characterization of pathophysiologically crucial biological processes. Deep sequencing technologies provide a powerful means to identify responsive genes, which creates a need for computational methods able to analyze dynamic and multi-level deep se... |
Expression of a large LINE-1-driven antisense RNA is linked to epigenetic silencing of the metastasis suppressor gene TFPI-2 in cancer.
Cruickshanks HA, Vafadar-Isfahani N, Dunican DS, Lee A, Sproul D, Lund JN, Meehan RR, Tufarelli C
LINE-1 retrotransposons are abundant repetitive elements of viral origin, which in normal cells are kept quiescent through epigenetic mechanisms. Activation of LINE-1 occurs frequently in cancer and can enable LINE-1 mobilization but also has retrotransposition-independent consequences. We previously reported that i... |
The developmental epigenomics toolbox: ChIP-seq and MethylCap-seq profiling of early zebrafish embryos.
Bogdanović O, Fernández-Miñán A, Tena JJ, de la Calle-Mustienes E, Gómez-Skarmeta JL
Genome-wide profiling of DNA methylation and histone modifications answered many questions as to how the genes are regulated on a global scale and what their epigenetic makeup is. Yet, little is known about the function of these marks during early vertebrate embryogenesis. Here we provide detailed protocols for ChIP... |
Genome-wide analysis of LXRα activation reveals new transcriptional networks in human atherosclerotic foam cells.
Feldmann R, Fischer C, Kodelja V, Behrens S, Haas S, Vingron M, Timmermann B, Geikowski A, Sauer S
Increased physiological levels of oxysterols are major risk factors for developing atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Lipid-loaded macrophages, termed foam cells, are important during the early development of atherosclerotic plaques. To pursue the hypothesis that ligand-based modulation of the nuclear recep... |
Regulation of transcription through acetylation of H3K122 on the lateral surface of the histone octamer.
Tropberger P, Pott S, Keller C, Kamieniarz-Gdula K, Caron M, Richter F, Li G, Mittler G, Liu ET, Bühler M, Margueron R, Schneider R
Histone modifications are key regulators of chromatin function. However, little is known to what extent histone modifications can directly impact on chromatin. Here, we address how a modification within the globular domain of histones regulates chromatin function. We demonstrate that H3K122ac can be sufficient to st... |
Histone lysine trimethylation or acetylation can be modulated by phytoestrogen, estrogen or anti-HDAC in breast cancer cell lines.
Dagdemir A, Durif J, Ngollo M, Bignon YJ, Bernard-Gallon D
AIM: The isoflavones genistein, daidzein and equol (daidzein metabolite) have been reported to interact with epigenetic modifications, specifically hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes. The objective of this study was to analyze and understand the mechanisms by which phytoestrogens act on chromatin in breast c... |
Chromatin signatures and retrotransposon profiling in mouse embryos reveal regulation of LINE-1 by RNA.
Fadloun A, Le Gras S, Jost B, Ziegler-Birling C, Takahashi H, Gorab E, Carninci P, Torres-Padilla ME
How a more plastic chromatin state is maintained and reversed during development is unknown. Heterochromatin-mediated silencing of repetitive elements occurs in differentiated cells. Here, we used repetitive elements, including retrotransposons, as model loci to address how and when heterochromatin forms during deve... |
Ezh2 maintains a key phase of muscle satellite cell expansion but does not regulate terminal differentiation.
Woodhouse S, Pugazhendhi D, Brien P, Pell JM.
Tissue generation and repair requires a stepwise process of cell fate restriction to ensure adult stem cells differentiate in a timely and appropriate manner. A crucial role has been implicated for Polycomb-group (PcG) proteins and the H3K27me3 repressive histone mark, in coordinating the transcriptional programmes ... |
Limitations and possibilities of low cell number ChIP-seq.
Gilfillan GD, Hughes T, Sheng Y, Hjorthaug HS, Straub T, Gervin K, Harris JR, Undlien DE, Lyle R
ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with high-throughput DNA sequencing (ChIP-seq) offers high resolution, genome-wide analysis of DNA-protein interactions. However, current standard methods require abundant starting material in the range of 1--20 million cells per immunoprecipitation, and re... |
Protein Group Modification and Synergy in the SUMO Pathway as Exemplified in DNA Repair.
Psakhye I, Jentsch S
Protein modification by SUMO affects a wide range of protein substrates. Surprisingly, although SUMO pathway mutants display strong phenotypes, the function of individual SUMO modifications is often enigmatic, and SUMOylation-defective mutants commonly lack notable phenotypes. Here, we use DNA double-strand break re... |
IL-23 is pro-proliferative, epigenetically regulated and modulated by chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer.
Baird AM, Leonard J, Naicker KM, Kilmartin L, O'Byrne KJ, Gray SG
BACKGROUND: IL-23 is a member of the IL-6 super-family and plays key roles in cancer. Very little is currently known about the role of IL-23 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). METHODS: RT-PCR and chromatin immunopreciptiation (ChIP) were used to examine the levels, epigenetic regulation and effects of various dr... |
New partners in regulation of gene expression: the enhancer of trithorax and polycomb corto interacts with methylated ribosomal protein l12 via its chromodomain.
Coléno-Costes A, Jang SM, de Vanssay A, Rougeot J, Bouceba T, Randsholt NB, Gibert JM, Le Crom S, Mouchel-Vielh E, Bloyer S, Peronnet F
Chromodomains are found in many regulators of chromatin structure, and most of them recognize methylated lysines on histones. Here, we investigate the role of the Drosophila melanogaster protein Corto's chromodomain. The Enhancer of Trithorax and Polycomb Corto is involved in both silencing and activation of gene ex... |
Extensive promoter hypermethylation and hypomethylation is associated with aberrant microRNA expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Baer C, Claus R, Frenzel LP, Zucknick M, Park YJ, Gu L, Weichenhan D, Fischer M, Pallasch CP, Herpel E, Rehli M, Byrd JC, Wendtner CM, Plass C
Dysregulated microRNA (miRNA) expression contributes to the pathogenesis of hematopoietic malignancies, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). However, an understanding of the mechanisms that cause aberrant miRNA transcriptional control is lacking. In this study, we comprehensively investigated the role and e... |
The histone H2B monoubiquitination regulatory pathway is required for differentiation of multipotent stem cells.
Karpiuk O, Najafova Z, Kramer F, Hennion M, Galonska C, König A, Snaidero N, Vogel T, Shchebet A, Begus-Nahrmann Y, Kassem M, Simons M, Shcherbata H, Beissbarth T, Johnsen SA
Extensive changes in posttranslational histone modifications accompany the rewiring of the transcriptional program during stem cell differentiation. However, the mechanisms controlling the changes in specific chromatin modifications and their function during differentiation remain only poorly understood. We show tha... |
Intronic RNAs mediate EZH2 regulation of epigenetic targets.
Guil S, Soler M, Portela A, Carrère J, Fonalleras E, Gómez A, Villanueva A, Esteller M
Epigenetic deregulation at a number of genomic loci is one of the hallmarks of cancer. A role for some RNA molecules in guiding repressive polycomb complex PRC2 to specific chromatin regions has been proposed. Here we use an in vivo cross-linking method to detect and identify direct PRC2-RNA interactions in human ca... |
The transcriptional and epigenomic foundations of ground state pluripotency.
Marks H, Kalkan T, Menafra R, Denissov S, Jones K, Hofemeister H, Nichols J, Kranz A, Francis Stewart A, Smith A, Stunnenberg HG
Mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells grown in serum exhibit greater heterogeneity in morphology and expression of pluripotency factors than ES cells cultured in defined medium with inhibitors of two kinases (Mek and GSK3), a condition known as "2i" postulated to establish a naive ground state. We show that the transcript... |
Control of ground-state pluripotency by allelic regulation of Nanog.
Miyanari Y, Torres-Padilla ME
Pluripotency is established through genome-wide reprogramming during mammalian pre-implantation development, resulting in the formation of the naive epiblast. Reprogramming involves both the resetting of epigenetic marks and the activation of pluripotent-cell-specific genes such as Nanog and Oct4 (also known as Pou5... |
Prepatterning of developmental gene expression by modified histones before zygotic genome activation.
Lindeman LC, Andersen IS, Reiner AH, Li N, Aanes H, Østrup O, Winata C, Mathavan S, Müller F, Aleström P, Collas P
A hallmark of anamniote vertebrate development is a window of embryonic transcription-independent cell divisions before onset of zygotic genome activation (ZGA). Chromatin determinants of ZGA are unexplored; however, marking of developmental genes by modified histones in sperm suggests a predictive role of histone m... |
IL-20 is epigenetically regulated in NSCLC and down regulates the expression of VEGF.
Baird AM, Gray SG, O'Byrne KJ
BACKGROUND: IL-20 is a pleiotrophic member of the IL-10 family and plays a role in skin biology and the development of haematopoietic cells. Recently, IL-20 has been demonstrated to have potential anti-angiogenic effects in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by down regulating COX-2. METHODS: The expression of IL-20... |
H3.5 is a novel hominid-specific histone H3 variant that is specifically expressed in the seminiferous tubules of human testes.
Schenk R, Jenke A, Zilbauer M, Wirth S, Postberg J
The incorporation of histone variants into chromatin plays an important role for the establishment of particular chromatin states. Six human histone H3 variants are known to date, not counting CenH3 variants: H3.1, H3.2, H3.3 and the testis-specific H3.1t as well as the recently described variants H3.X and H3.Y. We ... |
Epigenetic Regulation of Glucose Transporters in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
O'Byrne KJ, Baird AM, Kilmartin L, Leonard J, Sacevich C, Gray SG.
Due to their inherently hypoxic environment, cancer cells often resort to glycolysis, or the anaerobic breakdown of glucose to form ATP to provide for their energy needs, known as the Warburg effect. At the same time, overexpression of the insulin receptor in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is associated with an ... |
Characterisation of genome-wide PLZF/RARA target genes.
Spicuglia S, Vincent-Fabert C, Benoukraf T, Tibéri G, Saurin AJ, Zacarias-Cabeza J, Grimwade D, Mills K, Calmels B, Bertucci F, Sieweke M, Ferrier P, Duprez E
The PLZF/RARA fusion protein generated by the t(11;17)(q23;q21) translocation in acute promyelocytic leukaemia (APL) is believed to act as an oncogenic transcriptional regulator recruiting epigenetic factors to genes important for its transforming potential. However, molecular mechanisms associated with PLZF/RARA-de... |
Tiling histone H3 lysine 4 and 27 methylation in zebrafish using high-density microarrays.
Lindeman LC, Reiner AH, Mathavan S, Aleström P, Collas P
BACKGROUND: Uncovering epigenetic states by chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarray hybridization (ChIP-chip) has significantly contributed to the understanding of gene regulation at the genome-scale level. Many studies have been carried out in mice and humans; however limited high-resolution information exists... |
Autonomous silencing of the imprinted Cdkn1c gene in stem cells
Wood MD, Hiura H, Tunster S, Arima T, Shin J-H, Higgins M, John1 RM
Parent-of-origin specific expression of imprinted genes relies on the differential DNA methylation of specific genomic regions. Differentially methylated regions (DMRs) acquire DNA methylation either during gametogenesis (primary DMR) or after fertilization when allele-specific expression is established (secondary D... |
The histone variant macroH2A is an epigenetic regulator of key developmental genes.
Buschbeck M, Uribesalgo I, Wibowo I, Rué P, Martin D, Gutierrez A, Morey L, Guigó R, López-Schier H, Di Croce L
The histone variants macroH2A1 and macroH2A2 are associated with X chromosome inactivation in female mammals. However, the physiological function of macroH2A proteins on autosomes is poorly understood. Microarray-based analysis in human male pluripotent cells uncovered occupancy of both macroH2A variants at many gen... |
High-resolution analysis of epigenetic changes associated with X inactivation.
Marks H, Chow JC, Denissov S, Françoijs KJ, Brockdorff N, Heard E, Stunnenberg HG
Differentiation of female murine ES cells triggers silencing of one X chromosome through X-chromosome inactivation (XCI). Immunofluorescence studies showed that soon after Xist RNA coating the inactive X (Xi) undergoes many heterochromatic changes, including the acquisition of H3K27me3. However, the mechanisms that ... |
H3K64 trimethylation marks heterochromatin and is dynamically remodeled during developmental reprogramming.
Daujat S, Weiss T, Mohn F, Lange UC, Ziegler-Birling C, Zeissler U, Lappe M, Schübeler D, Torres-Padilla ME, Schneider R
Histone modifications are central to the regulation of all DNA-dependent processes. Lys64 of histone H3 (H3K64) lies within the globular domain at a structurally important position. We identify trimethylation of H3K64 (H3K64me3) as a modification that is enriched at pericentric heterochromatin and associated with re... |
Epigenetic-Mediated Downregulation of μ-Protocadherin in Colorectal Tumours
Bujko M, Kober P, Statkiewicz M, Mikula M, Ligaj M, Zwierzchowski L, Ostrowski J, Siedlecki JA
Carcinogenesis involves altered cellular interaction and tissue morphology that partly arise from aberrant expression of cadherins. Mucin-like protocadherin is implicated in intercellular adhesion and its expression was found decreased in colorectal cancer (CRC). This study has compared MUPCDH (CDHR5) expression in ... |
Analysis of active chromatin modifications in early mammalian embryos reveals uncoupling of H2A.Z acetylation and H3K36 trimethylation from embryonic genome activation
Bošković A, Bender A, Gall L, Ziegler-Birling C, Beaujean N, Torres-Padilla ME
Early embryonic development is characterized by dramatic changes in cell potency and chromatin organization. The role of histone variants in the context of chromatin remodeling during embryogenesis remains under investigated. In particular, the nuclear distribution of the histone variant H2A.Z and its modifications ... |