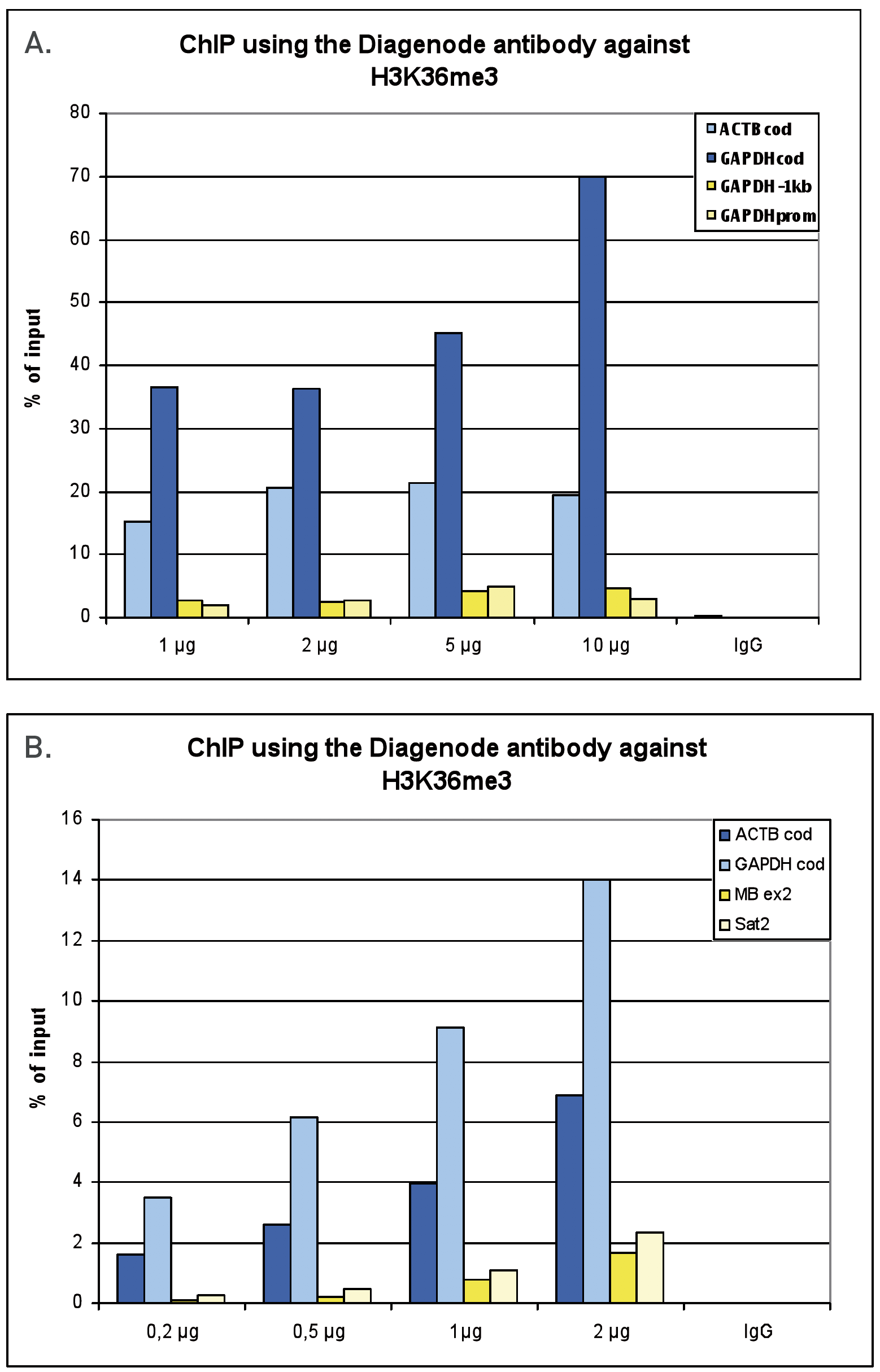
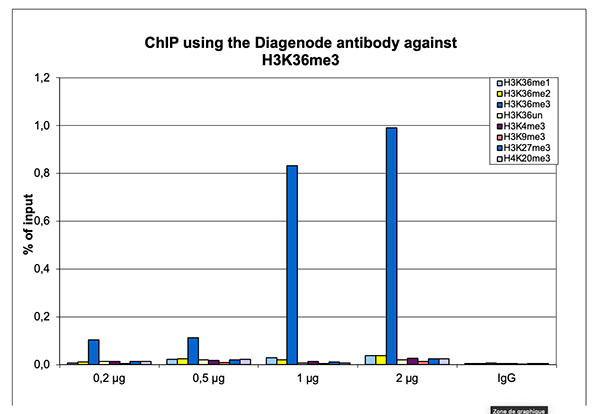
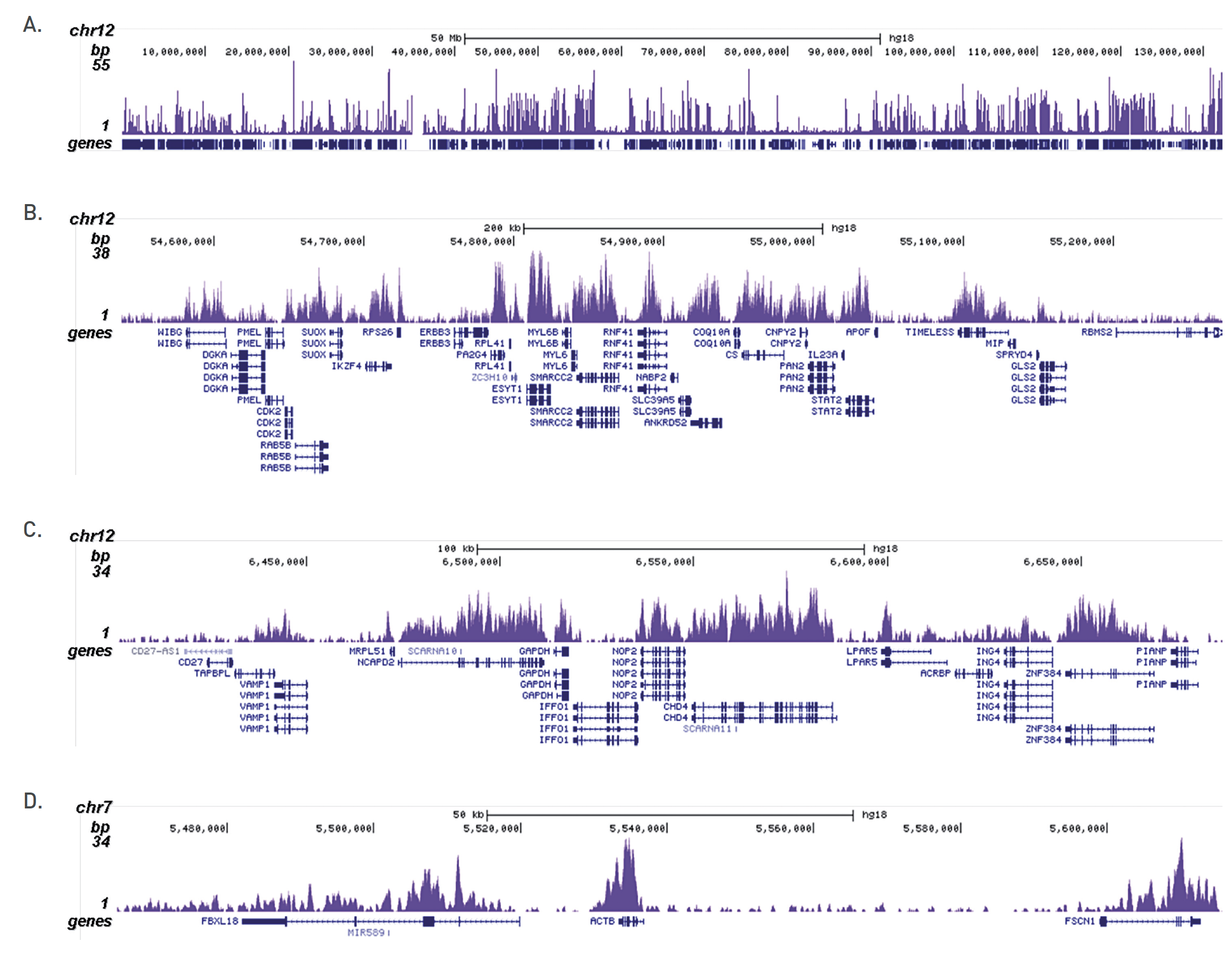
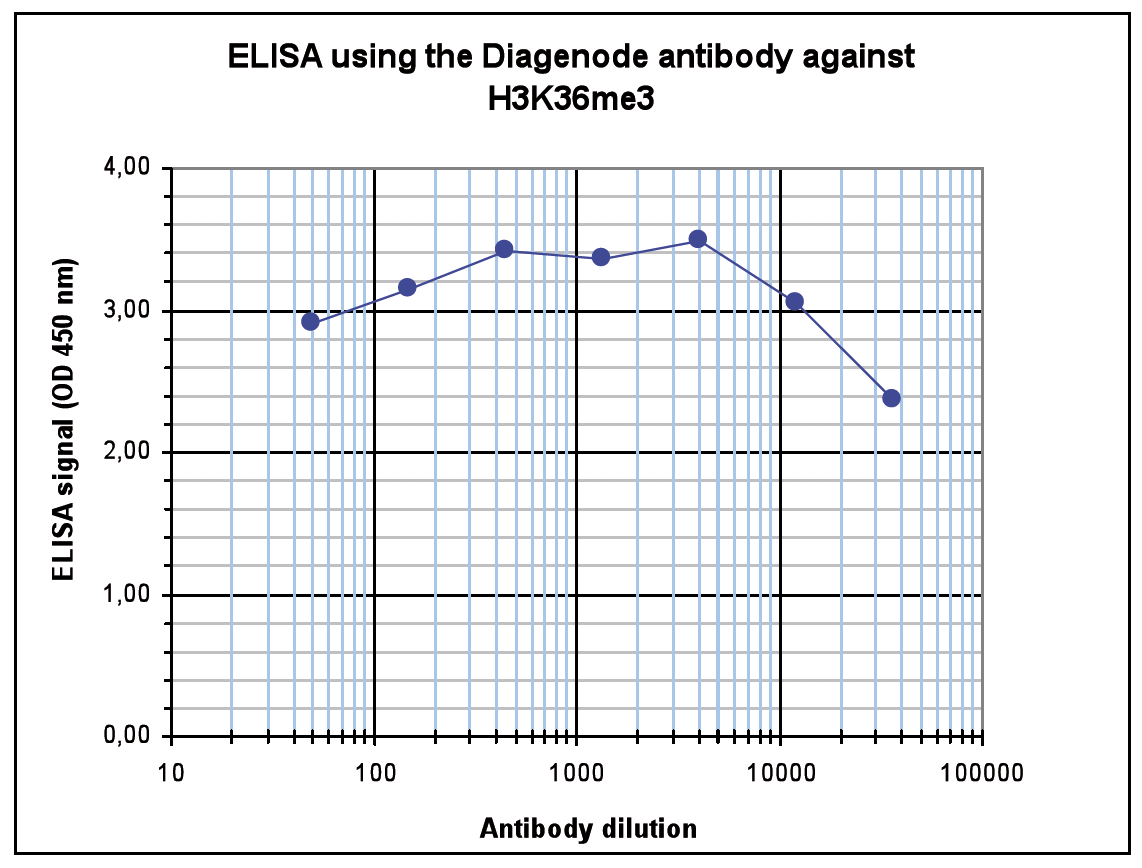
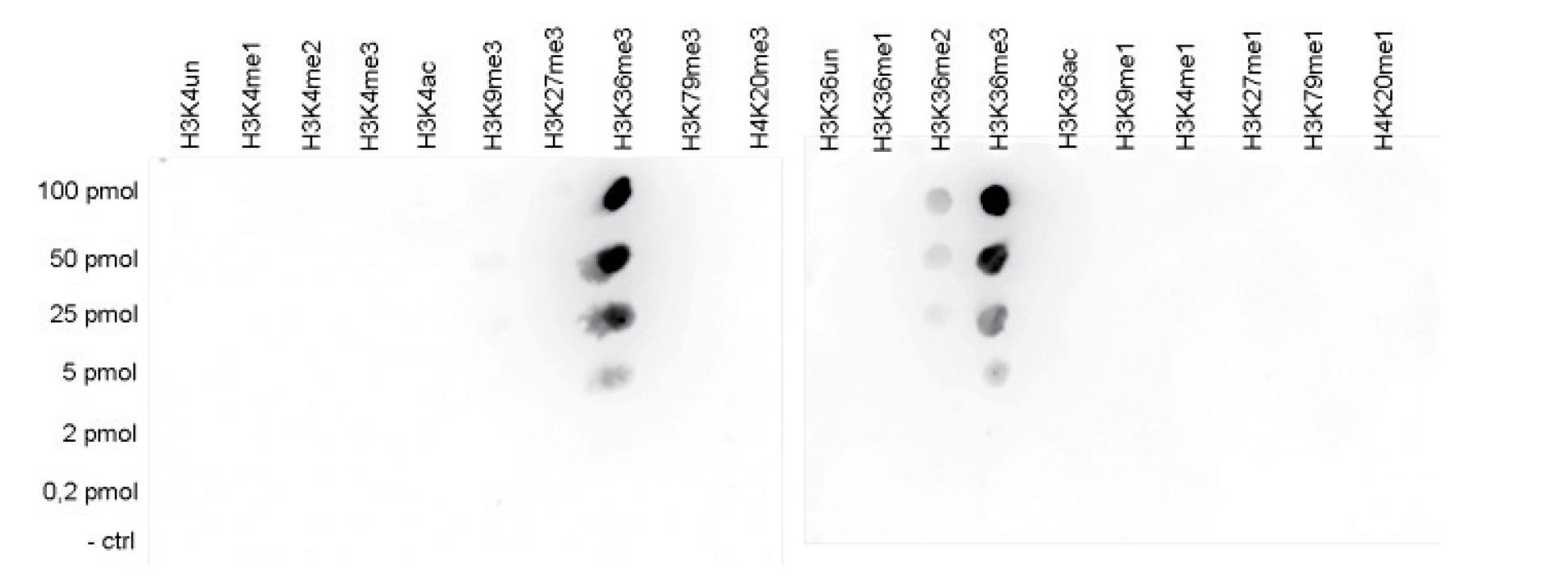
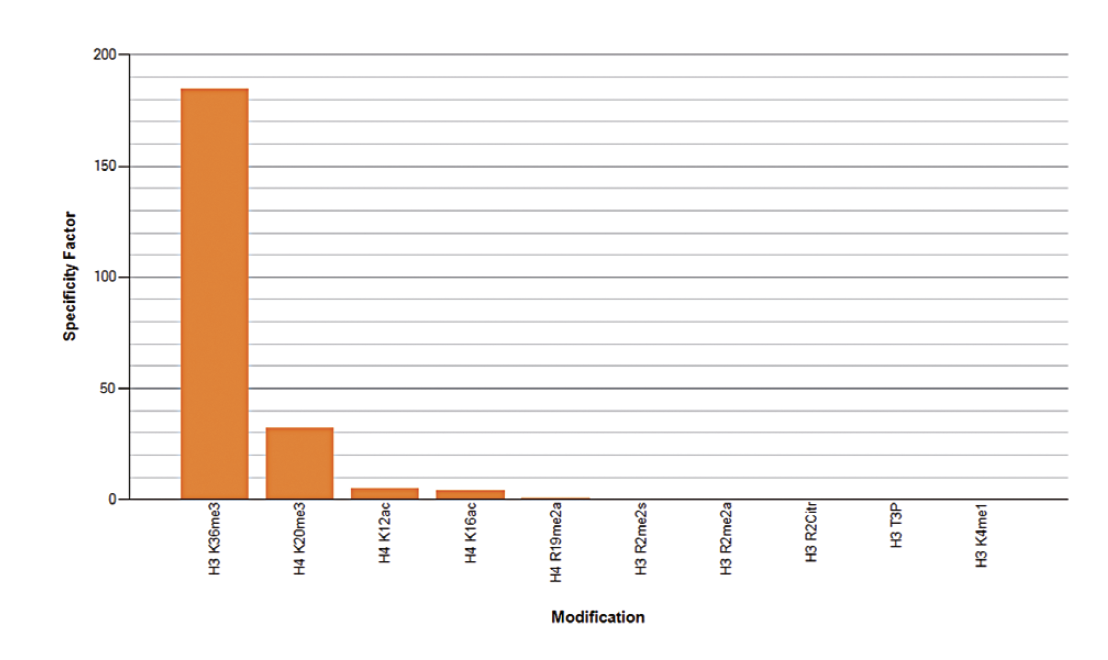
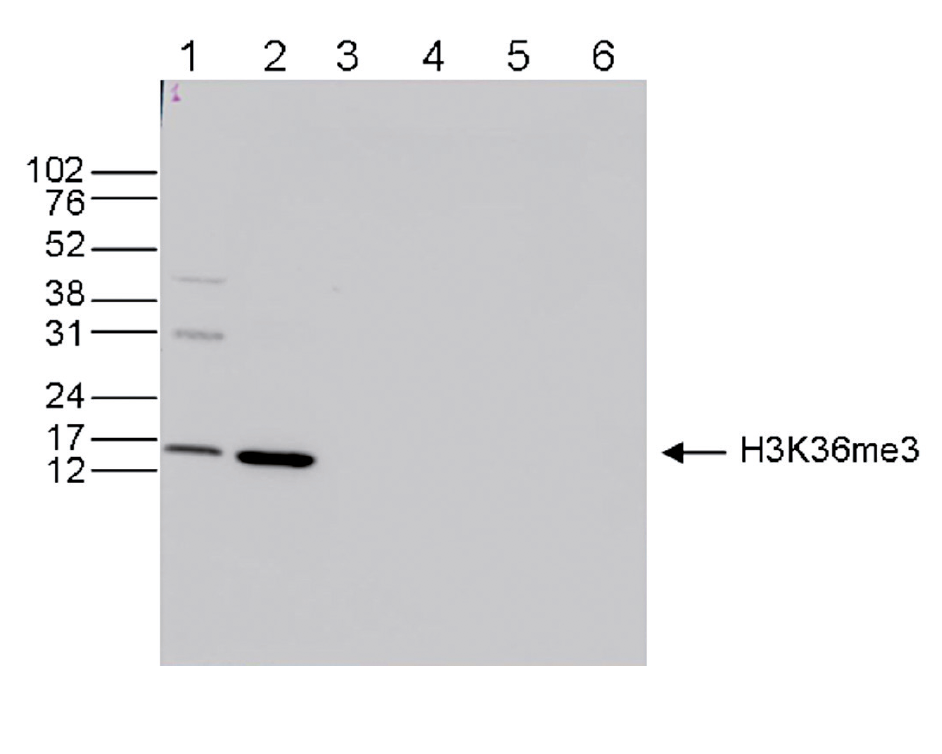
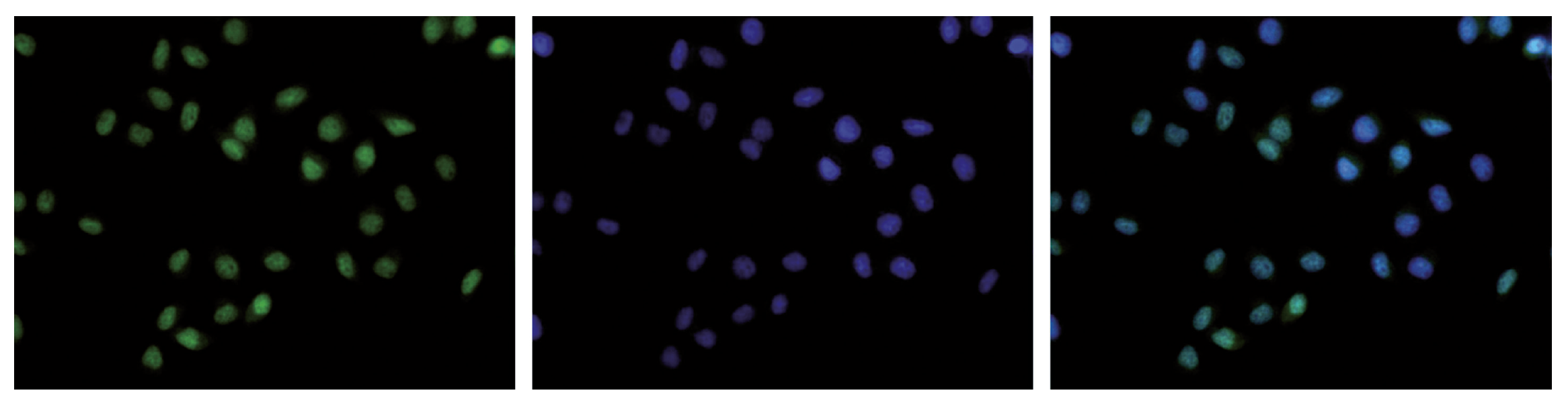
How to properly cite our product/service in your work We strongly recommend using this: H3K36me3 Antibody (sample size) (Hologic Diagenode Cat# C15410192-10 Lot# A1845P). Click here to copy to clipboard. Using our products or services in your publication? Let us know! |
Plasma cell-free DNA chromatin immunoprecipitation profiling depicts phenotypic and clinical heterogeneity in advanced prostate cancer
Sipola, Joonatan et al.
Cell phenotype underlies prostate cancer presentation and treatment resistance and can be regulated by epigenomic features. However, the osteotropic tendency of prostate cancer limits access to metastatic tissue, meaning most prior insights into prostate cancer chromatin biology are from preclinical models that do n... |
Ectopic expression of DNMT3L in human trophoblast stem cells restores features of the placental methylome
Lea, Georgia et al.
The placental DNA methylation landscape is unique, with widespread partially methylated domains (PMDs). The placental "methylome" is conserved across mammals, a shared feature of many cancers, and extensively studied for links with pregnancy complications. Human trophoblast stem cells (hTSCs) offer exciting potent... |
Motif distribution and DNA methylation underlie distinct Cdx2 binding during development and homeostasis
Alireza Lorzadeh et al.
Transcription factors guide tissue development by binding to developmental stage-specific targets and establishing an appropriate enhancer landscape. In turn, DNA and chromatin modifications direct the genomic binding of transcription factors. However, how transcription factors navigate chromatin features to selecti... |
Systematic prioritization of functional variants and effector genes underlying colorectal cancer risk
Law P.J. et al.
Genome-wide association studies of colorectal cancer (CRC) have identified 170 autosomal risk loci. However, for most of these, the functional variants and their target genes are unknown. Here, we perform statistical fine-mapping incorporating tissue-specific epigenetic annotations and massively parallel reporter as... |
A multiomic atlas of the aging hippocampus reveals molecular changes in response to environmental enrichment
Perez R. F. at al.
Aging involves the deterioration of organismal function, leading to the emergence of multiple pathologies. Environmental stimuli, including lifestyle, can influence the trajectory of this process and may be used as tools in the pursuit of healthy aging. To evaluate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this context, ... |
Alterations in the hepatocyte epigenetic landscape in steatosis.
Maji Ranjan K. et al.
Fatty liver disease or the accumulation of fat in the liver, has been reported to affect the global population. This comes with an increased risk for the development of fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Yet, little is known about the effects of a diet containing high fat and alcohol towards epigenet... |
RUNX1 colludes with NOTCH1 to reprogram chromatin in T-cell acutelymphoblastic leukemia
Islam R. et al.
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) is oncogenic in diverse types of leukemia and epithelial cancers where its expression is associated with poor prognosis. Current models suggest that RUNX1 cooperates with other oncogenic factors (e.g., NOTCH1, TAL1) to drive the expression of proto-oncogenes in T cell... |
Epigenetic dosage identifies two major and functionally distinct beta cells ubtypes.
Dror E.et al.
The mechanisms that specify and stabilize cell subtypes remain poorly understood. Here, we identify two major subtypes of pancreatic β cells based on histone mark heterogeneity (beta HI and beta LO). Beta HI cells exhibit 4-fold higher levels of H3K27me3, distinct chromatin organization and compaction, a... |
Temporal modification of H3K9/14ac and H3K4me3 histone marksmediates mechano-responsive gene expression during the accommodationprocess in poplar
Ghosh R. et al.
Plants can attenuate their molecular response to repetitive mechanical stimulation as a function of their mechanical history. For instance, a single bending of stem is sufficient to attenuate the gene expression in poplar plants to the subsequent mechanical stimulation, and the state of desensitization can last for ... |
Dietary methionine starvation impairs acute myeloid leukemia progression.
Cunningham A. et al.
Targeting altered tumor cell metabolism might provide an attractive opportunity for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). An amino acid dropout screen on primary leukemic stem cells and progenitor populations revealed a number of amino acid dependencies, of which methionine was one of the strongest. By using v... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple Myeloma
Elina Alaterre et al.
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have been widely used to understand themolecular processes that drive MM biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape of MM wouldadvance our un... |
Comprehensive characterization of the epigenetic landscape in Multiple
Myeloma
Alaterre, Elina and Ovejero, Sara and Herviou, Laurie and de
Boussac, Hugues and Papadopoulos, Giorgio and Kulis, Marta and
Boireau, Stéphanie and Robert, Nicolas and Requirand, Guilhem
and Bruyer, Angélique and Cartron, Guillaume and Vincent,
Laure and M
Background: Human multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines (HMCLs) have
been widely used to understand the molecular processes that drive MM
biology. Epigenetic modifications are involved in MM development,
progression, and drug resistance. A comprehensive characterization of the
epigenetic landscape of MM would advance our... |
Lasp1 regulates adherens junction dynamics and fibroblast transformationin destructive arthritis
Beckmann D. et al.
The LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 (Lasp1) was originally cloned from metastatic breast cancer and characterised as an adaptor molecule associated with tumourigenesis and cancer cell invasion. However, the regulation of Lasp1 and its function in the aggressive transformation of cells is unclear. Here we use integrativ... |
Sarcomere function activates a p53-dependent DNA damage response that promotes polyploidization and limits in vivo cell engraftment.
Pettinato, Anthony M. et al.
Human cardiac regeneration is limited by low cardiomyocyte replicative rates and progressive polyploidization by unclear mechanisms. To study this process, we engineer a human cardiomyocyte model to track replication and polyploidization using fluorescently tagged cyclin B1 and cardiac troponin T. Using time-lapse i... |
Dynamic association of the H3K64 trimethylation mark with genes encodingexported proteins in Plasmodium falciparum.
Jabeena, C A et al.
Epigenetic modifications have emerged as critical regulators of virulence genes and stage-specific gene expression in Plasmodium falciparum. However, the specific roles of histone core epigenetic modifications in regulating the stage-specific gene expression are not well understood. In this study, we report an uncon... |
Epigenomic landscape of human colorectal cancer unveils an aberrant core ofpan-cancer enhancers orchestrated by YAP/TAZ.
Della Chiara, Giulia et al.
Cancer is characterized by pervasive epigenetic alterations with enhancer dysfunction orchestrating the aberrant cancer transcriptional programs and transcriptional dependencies. Here, we epigenetically characterize human colorectal cancer (CRC) using de novo chromatin state discovery on a library of different patie... |
Environmental enrichment induces epigenomic and genome organization changesrelevant for cognitive function
Espeso-Gil, S. et al.
In early development, the environment triggers mnemonic epigenomic programs resulting in memory and learning experiences to confer cognitive phenotypes into adulthood. To uncover how environmental stimulation impacts the epigenome and genome organization, we used the paradigm of environmental enrichment (EE) in youn... |
Reactivation of super-enhancers by KLF4 in human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Tsompana M, Gluck C, Sethi I, Joshi I, Bard J, Nowak NJ, Sinha S, Buck MJ
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a disease of significant morbidity and mortality and rarely diagnosed in early stages. Despite extensive genetic and genomic characterization, targeted therapeutics and diagnostic markers of HNSCC are lacking due to the inherent heterogeneity and complexity of the dis... |
ChIP-seq of plasma cell-free nucleosomes identifies cell-of-origin geneexpression programs
Sadeh, Ronen and Sharkia, Israa and Fialkoff, Gavriel and Rahat, Ayelet andGutin, Jenia and Chappleboim, Alon and Nitzan, Mor and Fox-Fisher, Ilanaand Neiman, Daniel and Meler, Guy and Kamari, Zahala and Yaish, Dayana andPeretz, Tamar and Hubert, Ayala
Blood cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is derived from fragmented chromatin in dying cells. As such, it remains associated with histones that may retain the covalent modifications present in the cell of origin. Until now this rich epigenetic information carried by cell-free nucleosomes has not been explored at the genome level... |
Chromatin-Based Classification of Genetically Heterogeneous AMLs into Two Distinct Subtypes with Diverse Stemness Phenotypes.
Yi G, Wierenga ATJ, Petraglia F, Narang P, Janssen-Megens EM, Mandoli A, Merkel A, Berentsen K, Kim B, Matarese F, Singh AA, Habibi E, Prange KHM, Mulder AB, Jansen JH, Clarke L, Heath S, van der Reijden BA, Flicek P, Yaspo ML, Gut I, Bock C, Schuringa JJ
Global investigation of histone marks in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains limited. Analyses of 38 AML samples through integrated transcriptional and chromatin mark analysis exposes 2 major subtypes. One subtype is dominated by patients with NPM1 mutations or MLL-fusion genes, shows activation of the regulat... |
Integrative Proteomic Profiling Reveals PRC2-Dependent Epigenetic Crosstalk Maintains Ground-State Pluripotency.
van Mierlo G, Dirks RAM, De Clerck L, Brinkman AB, Huth M, Kloet SL, Saksouk N, Kroeze LI, Willems S, Farlik M, Bock C, Jansen JH, Deforce D, Vermeulen M, Déjardin J, Dhaenens M, Marks H
The pluripotent ground state is defined as a basal state free of epigenetic restrictions, which influence lineage specification. While naive embryonic stem cells (ESCs) can be maintained in a hypomethylated state with open chromatin when grown using two small-molecule inhibitors (2i)/leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)... |
The Itaconate Pathway Is a Central Regulatory Node Linking Innate Immune Tolerance and Trained Immunity
Domínguez-Andrés Jorge, Novakovic Boris, Li Yang, Scicluna Brendon P., Gresnigt Mark S., Arts Rob J.W., Oosting Marije, Moorlag Simone J.C.F.M., Groh Laszlo A., Zwaag Jelle, Koch Rebecca M., ter Horst Rob, Joosten Leo A.B., Wijmenga Cisca, Michelucci Ales
Sepsis involves simultaneous hyperactivation of the immune system and immune paralysis, leading to both organ dysfunction and increased susceptibility to secondary infections. Acute activation of myeloid cells induced itaconate synthesis, which subsequently mediated innate immune tolerance in human monocytes. In con... |
The Polycomb-Dependent Epigenome Controls β Cell Dysfunction, Dedifferentiation, and Diabetes.
Lu TT, Heyne S, Dror E, Casas E, Leonhardt L, Boenke T, Yang CH, Sagar , Arrigoni L, Dalgaard K, Teperino R, Enders L, Selvaraj M, Ruf M, Raja SJ, Xie H, Boenisch U, Orkin SH, Lynn FC, Hoffman BG, Grün D, Vavouri T, Lempradl AM, Pospisilik JA
To date, it remains largely unclear to what extent chromatin machinery contributes to the susceptibility and progression of complex diseases. Here, we combine deep epigenome mapping with single-cell transcriptomics to mine for evidence of chromatin dysregulation in type 2 diabetes. We find two chromatin-state signat... |
The reference epigenome and regulatory chromatin landscape of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Beekman R. et al.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a frequent hematological neoplasm in which underlying epigenetic alterations are only partially understood. Here, we analyze the reference epigenome of seven primary CLLs and the regulatory chromatin landscape of 107 primary cases in the context of normal B cell differentiation.... |
Increased H3K9 methylation and impaired expression of Protocadherins are associated with the cognitive dysfunctions of the Kleefstra syndrome.
Iacono G, Dubos A, Méziane H, Benevento M, Habibi E, Mandoli A, Riet F, Selloum M, Feil R, Zhou H, Kleefstra T, Kasri NN, van Bokhoven H, Herault Y, Stunnenberg HG
Kleefstra syndrome, a disease with intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders and other developmental defects is caused in humans by haploinsufficiency of EHMT1. Although EHMT1 and its paralog EHMT2 were shown to be histone methyltransferases responsible for deposition of the di-methylated H3K9 (H3K9me2), th... |
PRDM9 Methyltransferase Activity Is Essential for Meiotic DNA Double-Strand Break Formation at Its Binding Sites.
Diagouraga B, Clément JAJ, Duret L, Kadlec J, de Massy B, Baudat F
The programmed formation of hundreds of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) is essential for proper meiosis and fertility. In mice and humans, the location of these breaks is determined by the meiosis-specific protein PRDM9, through the DNA-binding specificity of its zinc-finger domain. PRDM9 also has methyltransferase ... |
Chromosome contacts in activated T cells identify autoimmune disease candidate genes
Burren OS et al.
BACKGROUND:
Autoimmune disease-associated variants are preferentially found in regulatory regions in immune cells, particularly CD4+ T cells. Linking such regulatory regions to gene promoters in disease-relevant cell contexts facilitates identification of candidate disease genes.
RESULTS:
Within 4 h, act... |
Platelet function is modified by common sequence variation in megakaryocyte super enhancers
Petersen R. et al.
Linking non-coding genetic variants associated with the risk of diseases or disease-relevant traits to target genes is a crucial step to realize GWAS potential in the introduction of precision medicine. Here we set out to determine the mechanisms underpinning variant association with platelet quantitative traits usi... |
DNA methylation heterogeneity defines a disease spectrum in Ewing sarcoma
Sheffield N.C. et al.
Developmental tumors in children and young adults carry few genetic alterations, yet they have diverse clinical presentation. Focusing on Ewing sarcoma, we sought to establish the prevalence and characteristics of epigenetic heterogeneity in genetically homogeneous cancers. We performed genome-scale DNA methylation ... |
β-Glucan Reverses the Epigenetic State of LPS-Induced Immunological Tolerance
Novakovic B. et al.
Innate immune memory is the phenomenon whereby innate immune cells such as monocytes or macrophages undergo functional reprogramming after exposure to microbial components such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We apply an integrated epigenomic approach to characterize the molecular events involved in LPS-induced to... |
The Hematopoietic Transcription Factors RUNX1 and ERG Prevent AML1-ETO Oncogene Overexpression and Onset of the Apoptosis Program in t(8;21) AMLs
Mandoli A. et al.
The t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-associated oncoprotein AML1-ETO disrupts normal hematopoietic differentiation. Here, we have investigated its effects on the transcriptome and epigenome in t(8,21) patient cells. AML1-ETO binding was found at promoter regions of active genes with high levels of histone acetyl... |
Neonatal monocytes exhibit a unique histone modification landscape
Bermick JR et al.
Background
Neonates have dampened expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and difficulty clearing pathogens. This makes them uniquely susceptible to infections, but the factors regulating neonatal-specific immune responses are poorly understood. Epigenetics, including histone modifications, can activate or silen... |
Epigenetic dynamics of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation
Wallner S et al.
BACKGROUND:
Monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation involves major biochemical and structural changes. In order to elucidate the role of gene regulatory changes during this process, we used high-throughput sequencing to analyze the complete transcriptome and epigenome of human monocytes that were differentiated in... |
Comprehensive genome and epigenome characterization of CHO cells in response to evolutionary pressures and over time
Feichtinger J, Hernández I, Fischer C, Hanscho M, Auer N, Hackl M, Jadhav V, Baumann M, Krempl PM, Schmidl C, Farlik M, Schuster M, Merkel A, Sommer A, Heath S, Rico D, Bock C, Thallinger GG, Borth N
The most striking characteristic of CHO cells is their adaptability, which enables efficient production of proteins as well as growth under a variety of culture conditions, but also results in genomic and phenotypic instability. To investigate the relative contribution of genomic and epigenetic modifications towards... |
Epigenome mapping reveals distinct modes of gene regulation and widespread enhancer reprogramming by the oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1.
Tomazou EM, Sheffield NC, Schmidl C, Schuster M, Schönegger A, Datlinger P, Kubicek S, Bock C, Kovar H
Transcription factor fusion proteins can transform cells by inducing global changes of the transcriptome, often creating a state of oncogene addiction. Here, we investigate the role of epigenetic mechanisms in this process, focusing on Ewing sarcoma cells that are dependent on the EWS-FLI1 fusion protein. We establi... |