Until recently, 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) was the only known modification of DNA for epigenetic regulation. In 2009, however, a second methylated cytosine, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) was discovered. This new modified base (also called the Sixth base) is generated by enzymatic conversion of 5-mC into 5-hmC by the TET family of oxygenases.
Recent results indicate that 5-hmC plays important roles distinct from 5-mC. Although its precise role has still to be shown, early evidence suggests that 5-hmC may well represent a new pathway to demethylate DNA involving a repair mechanism converting 5-hmC to cytosine. This pathway could involve further oxidation of the hydroxymethyl group to a formyl or carboxyl group followed by either deformylation or decarboxylation. The carboxyl and formyl groups of 5-Formylcytosine (5-fC) and 5-Carboxylcytosine (5-caC) could be enzymatically removed without excision of the base.
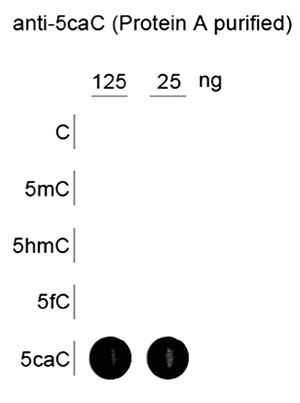
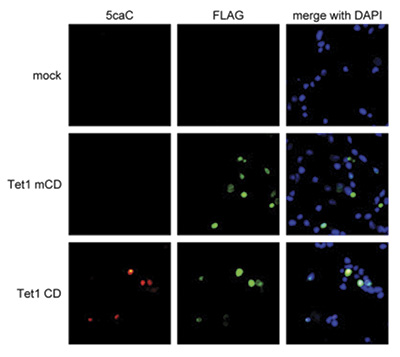
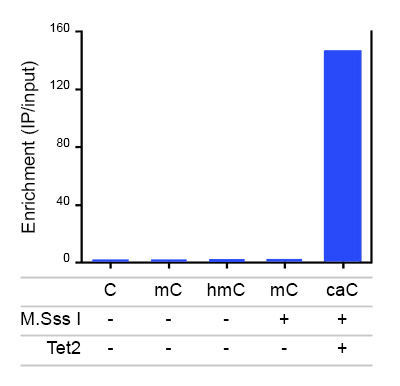
Due to their structural similarity, the different modified cytosine analogues are difficult to discriminate. The development of highly specific affinity-based reagents, such as antibodies, appears to be the most powerful way to differentially and specifically enrich 5-mC and 5-hmC sequences. We previously released highly specific antibodies directed against 5-mC and 5-hmC. Now, we also present a unique rabbit polyclonal antibody against 5-Carboxycytosine.